Novel Nargenicin A1 Analog Inhibits Angiogenesis by Downregulating the Endothelial VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling and Tumoral HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture and Hypoxic Conditions
2.3. Cell Viability Assay
2.4. Cell Proliferation Assay
2.5. Chemoinvasion Assay
2.6. Capillary Tube Formation Assay
2.7. Adhesion Assay
2.8. Chorioallantoic Membrane (CAM) Assay
2.9. Western Blot Analysis
2.10. Tumor Cell-Induced Chemoinvasion Assay
2.11. Tumor Cell-Induced Capillary Tube Formation Assay
2.12. Measurement of VEGF by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
2.13. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of Compound 9 on In Vitro Angiogenesis of HUVECs
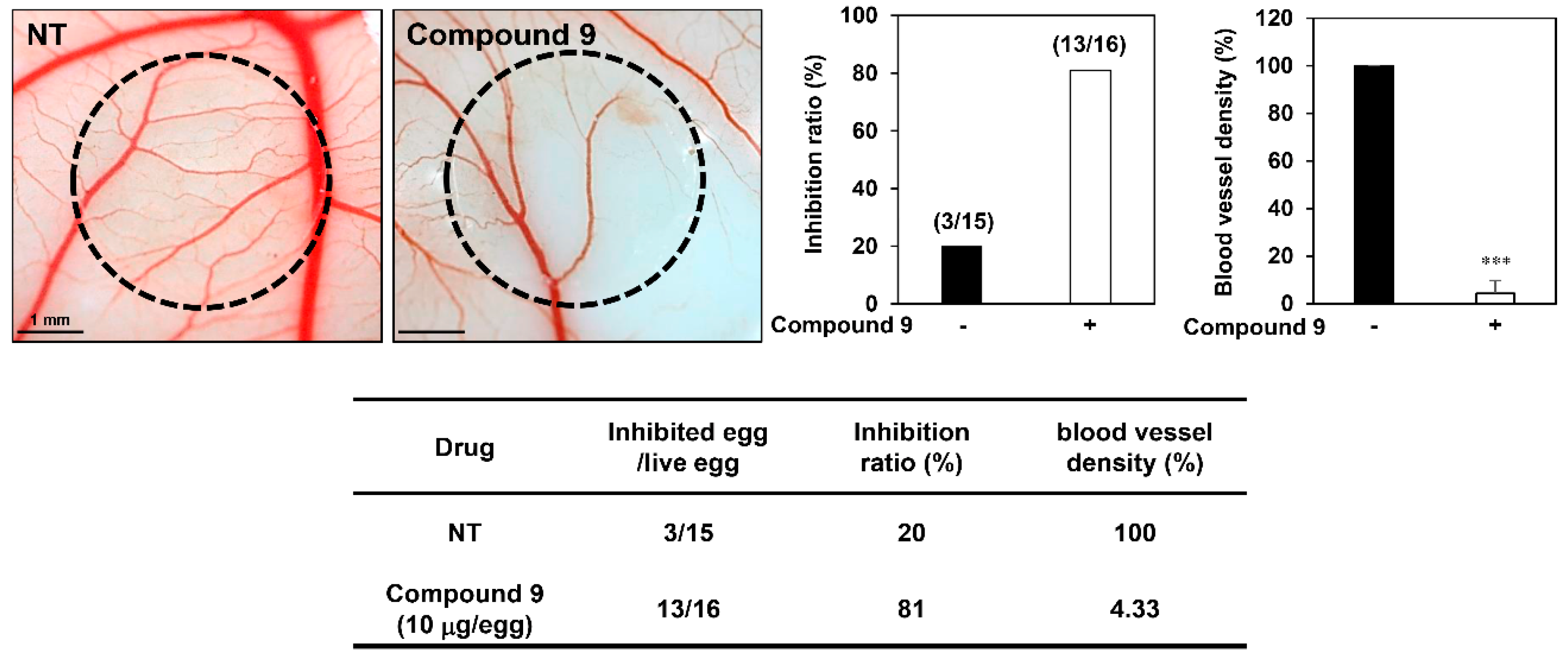
3.2. Effect of Compound 9 on In Vivo Angiogenesis
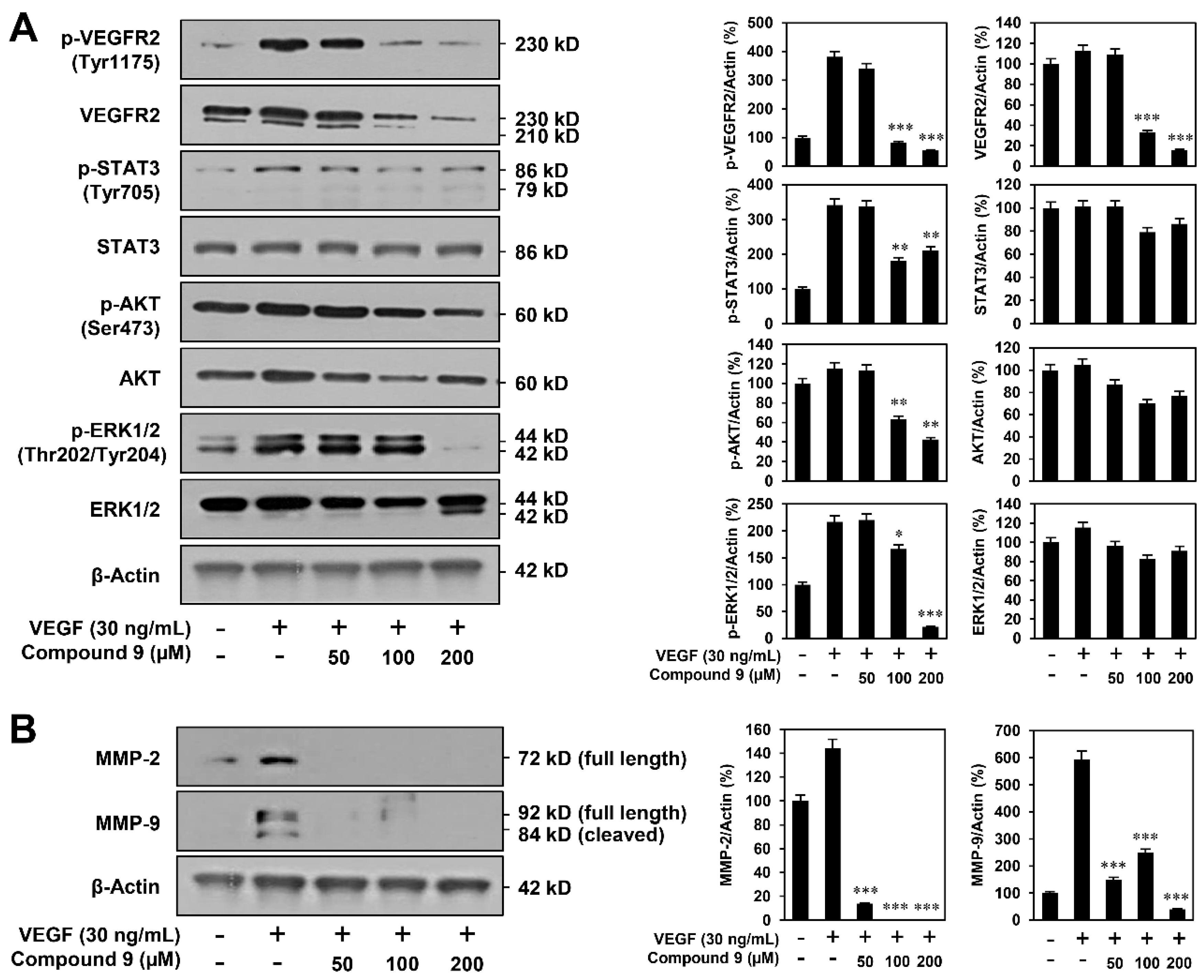
3.3. Effect of Compound 9 on VEGFR2-Mediated Downstream Signaling Pathways
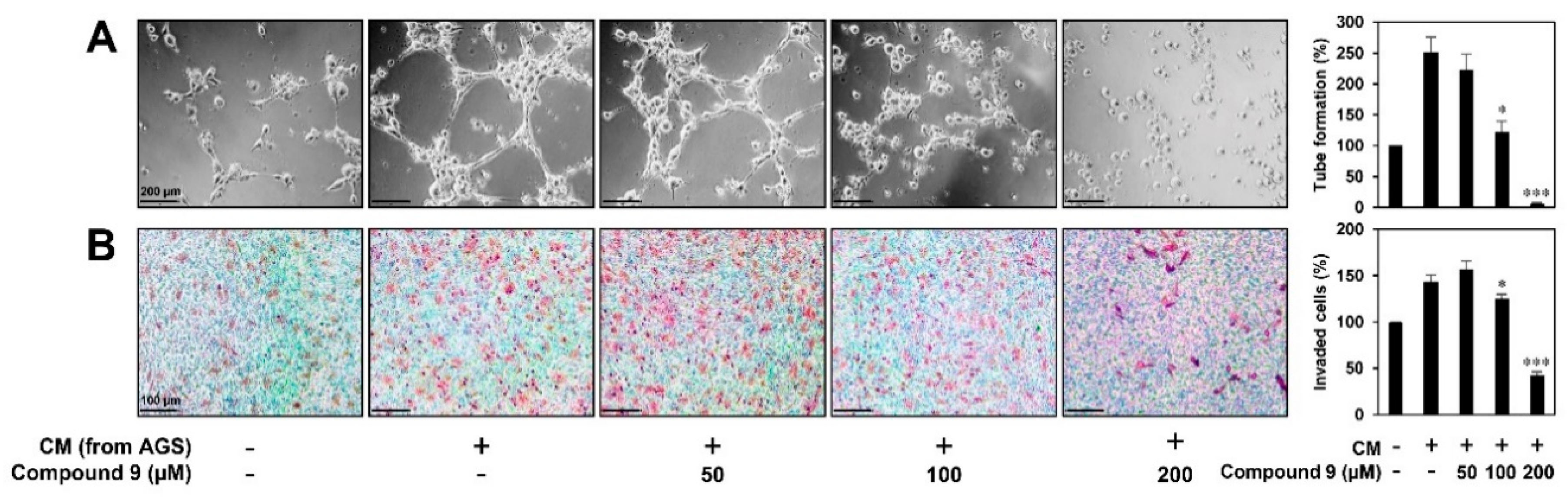
3.4. Effect of Compound 9 on Tumor Cell-Induced Angiogenesis in Vitro
3.5. Effect of Compound 9 on HIF-1α and VEGF Expression in Tumor Cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Folkman, J. Seminars in Medicine of the Beth Israel Hospital, Boston. Clin. Appl. Res. Angiogenesis N. Engl. J. Med. 1995, 333, 1757–1763. [Google Scholar]
- Andre, T.; Chastre, E.; Kotelevets, L.; Vaillant, J.C.; Louvet, C.; Balosso, J.; Le Gall, E.; Prévot, S.; Gespach, C. Tumoral angiogenesis: Physiopathology, prognostic value and therapeutic perspectives. Rev. Med. Interne 1998, 19, 904–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granci, V.; Dupertuis, Y.M.; Pichard, C. Angiogenesis as a potential target of pharmaconutrients in cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2010, 13, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risau, W. Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Nature 1997, 386, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, H.N.; Jang, J.P.; Han, J.M.; Jang, J.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Jung, H.J. Antiangiogenic potential of microbial metabolite elaiophylin for targeting tumor angiogenesis. Molecules 2018, 23, 563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shanmugam, M.K.; Warrier, S.; Kumar, A.P.; Sethi, G.; Arfuso, F. Potential role of natural compounds as anti-angiogenic agents in cancer. Curr. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2017, 15, 503–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roskoski, R., Jr. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signaling in tumor progression. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2007, 62, 179–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrara, N.; Kerbel, R.S. Angiogenesis as a therapeutic target. Nature 2005, 438, 967–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.M.; Tsai, C.H.; Hung, W.C. Foretinib inhibits angiogenesis, lymphangiogenesis and tumor growth of pancreatic cancer in vivo by decreasing VEGFR-2/3 and TIE-2 signaling. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 14940–14952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Koch, S.; Tugues, S.; Li, X.; Gualandi, L.; Claesson-Welsh, L. Signal transduction by vascular endothelial growth factor receptors. Biochem. J. 2011, 437, 169–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karar, J.; Maity, A. PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in angiogenesis. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2011, 4, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sohng, J.K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Seong, C.N.; Baik, K.S.; Park, S.C.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, S.Y.; Simkhada, J.R.; Yoo, J.C. Production, isolation and biological activity of nargenicin from Nocardia sp. CS682. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2008, 31, 1339–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, D.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Yi, J.S.; Pokhrel, A.R.; Shrestha, B.; Parajuli, P.; Shrestha, A.; Yamaguchi, T.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, S.Y.; et al. Enhanced production of nargenicin A1 and creation of a novel derivative using a synthetic biology platform. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 9917–9931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal, D.; Le, T.T.; Pandey, R.P.; Jha, A.K.; Gurung, R.; Parajuli, P.; Pokhrel, A.R.; Yoo, J.C.; Sohng, J.K. Enhanced production of nargenicin A(1) and generation of novel glycosylated derivatives. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 2934–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal, D.; Han, J.M.; Mishra, R.; Pandey, R.P.; Kim, T.S.; Rayamajhi, V.; Jung, H.J.; Yamaguchi, T.; Sohng, J.K. Characterization of tailoring steps of nargenicin A1 biosynthesis reveals a novel analogue with anticancer activities. ACS Chem. Biol. 2020, 15, 1370–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, K.; Roberts, O.L.; Thomas, A.M.; Cross, M.J. Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2: Structure, function, intracellular signalling and therapeutic inhibition. Cell. Signal. 2007, 19, 2003–2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stetler-Stevenson, W.G. Matrix metalloproteinases in angiogenesis: A moving target for therapeutic intervention. J. Clin. Investig. 1999, 103, 1237–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Forsythe, J.A.; Jiang, B.H.; Iyer, N.V.; Agani, F.; Leung, S.W.; Koos, R.D.; Semenza, G.L. Activation of vascular endothelial growth factor gene transcription by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1996, 16, 4604–4613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Benjamin, L.E. Tumorigenesis and the angiogenic switch. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 401–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Sun, M.Z.; Liu, S.; Yeh, D.; Yu, L.; Song, Y.; Gong, L.; Hao, L.; Hu, J.; Shao, S. Smad4 mediates malignant behaviors of human ovarian carcinoma cell through the effect on expressions of E-cadherin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and VEGF. Bmb Rep. 2010, 43, 554–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibuya, M. Differential roles of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 and receptor-2 in angiogenesis. J. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2006, 39, 469–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Schmitt, C.E.; Woolls, M.J.; Holland, M.B.; Kim, J.D.; Jin, S.W. Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling regulates the segregation of artery and vein via ERK activity during vascular development. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2013, 430, 1212–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Niu, G.; Wright, K.L.; Huang, M.; Song, L.; Haura, E.; Turkson, J.; Zhang, S.; Wang, T.; Sinibaldi, D.; Coppola, D.; et al. Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor angiogenesis. Oncogene 2002, 21, 2000–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, B.; Shen, J.; Cao, J.; Zhou, Y.; Shang, L.; Jin, S.; Cao, S.; Che, D.; Liu, F.; Yu, Y. Interleukin-17 promotes angiogenesis by stimulating VEGF production of cancer cells via the STAT3/GIV signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Painter, R.E.; Adam, G.C.; Arocho, M.; DiNunzio, E.; Donald, R.G.; Dorso, K.; Genilloud, O.; Gill, C.; Goetz, M.; Hairston, N.N.; et al. Elucidation of DnaE as the antibacterial target of the natural product, nargenicin. Chem. Biol. 2015, 22, 1362–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, S.H.; Yoo, J.C.; Kim, T.S. Nargenicin enhances 1, 25-dihydroxyvitamin D3-and all-trans retinoic acid-induced leukemia cell differentiation via PKCβI/MAPK pathways. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, J.C.; Cho, H.S.; Park, E.; Park, J.A.; Kim, S.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, C.S.; Kim, S.J.; Chun, H.S. Nargenicin attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in BV-2 cells. Neuroreport 2009, 20, 1007–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.; Kwon, D.H.; Hwang, S.J.; Han, M.H.; Jeong, J.W.; Hong, S.H.; Cha, H.J.; Hong, S.H.; Kim, G.Y.; Lee, H.J.; et al. Protective effects of nargenicin A1 against tacrolimus-induced oxidative stress in Hirame Natural Embryo cells. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2019, 16, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaupel, P.; Harrison, L. Tumor hypoxia: Causative factors, compensatory mechanisms and cellular response. Oncologist 2004, 9 (Suppl. 5), 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Semenza, G.L. HIF-1 and tumor progression: Pathophysiology and therapeutics. Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmeliet, P.; Dor, Y.; Herbert, J.M.; Fukumura, D.; Brusselmans, K.; Dewerchin, M.; Neeman, M.; Bono, F.; Abramovitch, R.; Maxwel, P.; et al. Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 1998, 394, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.M.; Choi, Y.S.; Dhakal, D.; Sohng, J.K.; Jung, H.J. Novel Nargenicin A1 Analog Inhibits Angiogenesis by Downregulating the Endothelial VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling and Tumoral HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8080252
Han JM, Choi YS, Dhakal D, Sohng JK, Jung HJ. Novel Nargenicin A1 Analog Inhibits Angiogenesis by Downregulating the Endothelial VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling and Tumoral HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(8):252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8080252
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jang Mi, Ye Seul Choi, Dipesh Dhakal, Jae Kyung Sohng, and Hye Jin Jung. 2020. "Novel Nargenicin A1 Analog Inhibits Angiogenesis by Downregulating the Endothelial VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling and Tumoral HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway" Biomedicines 8, no. 8: 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8080252
APA StyleHan, J. M., Choi, Y. S., Dhakal, D., Sohng, J. K., & Jung, H. J. (2020). Novel Nargenicin A1 Analog Inhibits Angiogenesis by Downregulating the Endothelial VEGF/VEGFR2 Signaling and Tumoral HIF-1α/VEGF Pathway. Biomedicines, 8(8), 252. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8080252






