Serum γ-Glutamyltransferase Concentration Predicts Endothelial Dysfunction in Naïve Hypertensive Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Vascular Function Evaluation
2.2. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Correlational Analysis
3.2. Multivariate Analysis
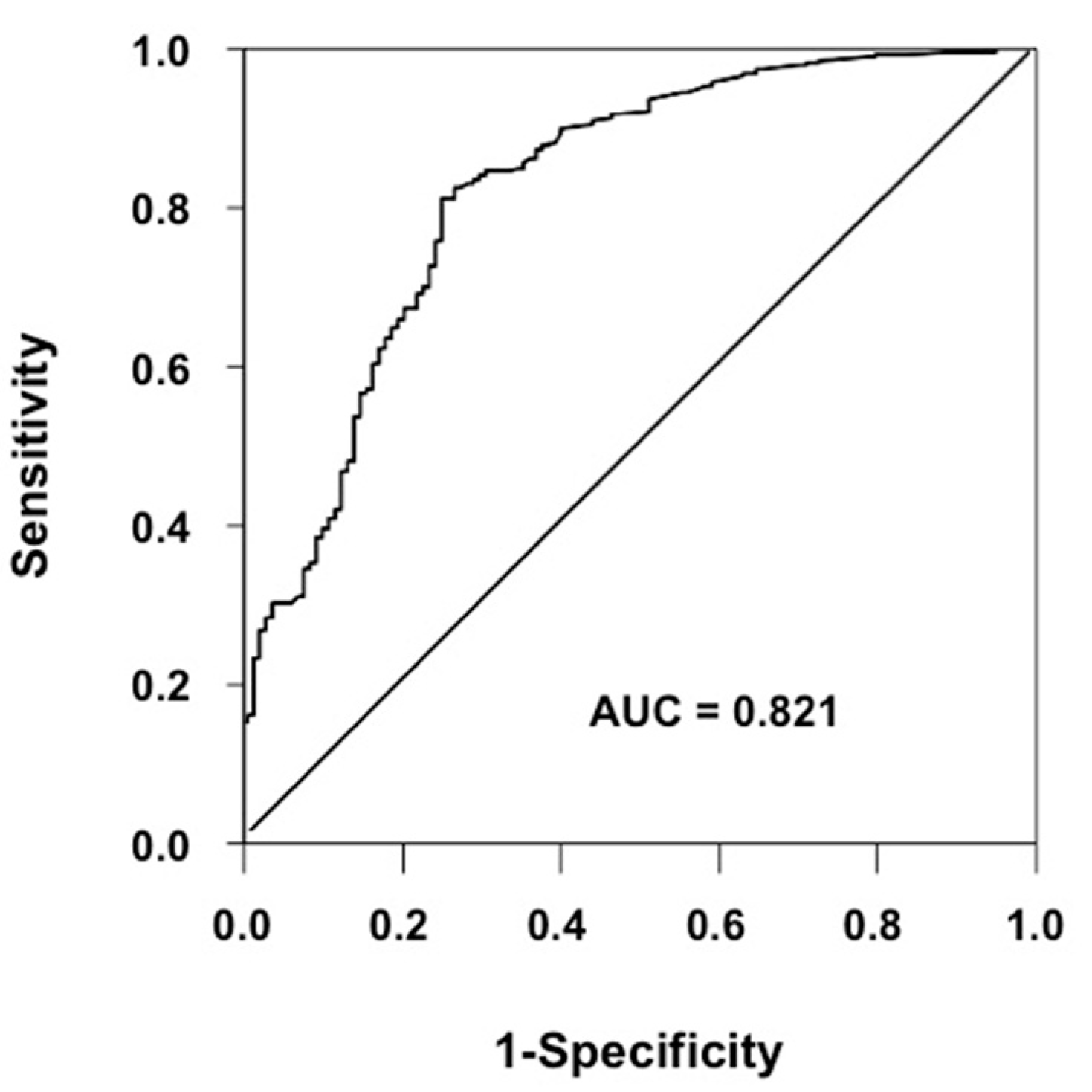
3.3. Cross-Validation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kunutsor, S.K. Gamma-glutamyltransferase-friend or foe within? Liv. Int. 2016, 36, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Silventoinen, K.; Jacobs, D.R.; Jousilahti, P.; Tuomileto, J. Glutamyltransferase, Obesity, and the Risk of Type 2 Diabetes: Observational Cohort Study among 20,158 Middle-Aged Men and Women. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2004, 89, 5410–5414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ko, S.H.; Baeg, M.K.; Han, K.D.; Ko, S.Y.; Shin, S.B.; Ko, S.H.; Ahn, Y.B. Association between gamma-glutamyltransferase and albuminuria in non diabetic adults with normal renal function. Clin. Exp. Nephrol. 2017, 21, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, J.E.; Starke, R.D.; Van Kirk, J.E. Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase: A Novel Cardiovascular Risk BioMarker. Prev. Cardiol. 2010, 13, 36–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turgut, O.; Tandogan, I.; Tandoǧan, I. Gamma-glutamyltransferase to Determine Cardiovascular Risk: Shifting the Paradigm Forward. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2011, 18, 177–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Aksakal, E.; Tanboga, I.H.; Kurt, M.; Kaygın, M.A.; Kaya, A.; Isik, T.; Ekinci, M.; Sevimli, S.; Acikel, M. The relation of serum gamma-glutamyl transferase levels with coronary lesion complexity and long-term outcome in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis 2012, 221, 596–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.D.; Xu, T.; Cheng, X.Q.; Wu, W.; Ye, Y.C.; Guo, X.Z.; Cheng, Q.; Liu, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhu, G.J.; et al. Serum Gamma-Glutamyltransferase Levels are Associated with Cardiovascular Risk Factors in China: A Nationwide Population-Based Study. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paolicchi, A.; Minotti, G.; Tonarelli, P.; Tongiani, R.; De Cesare, D.; Mezzetti, A.; Dominici, S.; Comporti, M.; Pompella, A. Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase-dependent iron reduction and LDL oxidation—A potential mechanism in atherosclerosis. J. Investig. Med. 1999, 47, 151–160. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, D.; Blomhoff, R.; Jacobs, D.R. ReviewIs Serum Gamma Glutamyltransferase a Marker of Oxidative Stress? Free. Radic. Res. 2004, 38, 535–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, R. Atherosclerosis—An inflammatory disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 115–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vane, J.R.; Anggard, E.E.; Botting, R.M. Regulatory functions on the vascular endothelium. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 27–36. [Google Scholar]
- Panza, J.A.; Quyyumi, A.A.; Brush, J.E.; Epstein, S.E. Abnormal Endothelium-Dependent Vascular Relaxation in Patients with Essential Hypertension. New. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 323, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perticone, F.; Ceravolo, R.; Candigliota, M.; Ventura, G.; Iacopino, S.; Sinopoli, F.; Mattioli, P.L. Obesity and body fat distribution induce endothelial dysfunction by oxidative stress: Protective effect of vitamin C. Diabetes 2001, 50, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perticone, F.; Ceravolo, R.; Pujia, A.; Ventura, G.; Iacopino, S.; Scozzafava, A.; Ferraro, A.; Chello, M.; Mastroroberto, P.; Verdecchia, P.; et al. Prognostic significance of endothelial dysfunction in hypertensive patients. Circulation 2001, 104, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quyyumi, A.A. Endothelial function in health and disease: New insights into the genesis of cardiovascular disease. Am. J. Med. 1998, 105, 32S–39S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonetti, O.; Lerman, P.; Lerman, L.O. Endothelial dysfunction: A marker of atherosclerotic risk. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Boil. 2003, 23, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perticone, F.; Maio, R.; Perticone, M.; Sciacqua, A.; Shehaj, E.; Naccarato, P.; Sesti, G. Endothelial Dysfunction and Subsequent Decline in Glomerular Filtration Rate in Hypertensive Patients. Circulation 2010, 122, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perticone, F.; Maio, R.; Perticone, M.; Miceli, S.; Sciacqua, A.; Tassone, E.J.; Shehaj, E.; Tripepi, G.; Sesti, G. Endothelial dysfunction predicts regression of hypertensive cardiac mass. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 167, 1188–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halcox, J.; Donald, A.E.; Ellins, E.; Witte, D.; Shipley, M.; Brunner, E.J.; Marmot, M.; Deanfield, J. Endothelial Function Predicts Progression of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness. Circulation 2009, 119, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, R.; Schoneveld, O.J.; Pappa, A.; Panayiotidis, M.I. The central role of glutathione in the pathophysiology of human diseases. Arch. Physiol. Biochem. 2007, 113, 234–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, J.; Tomiyama, H.; Yambe, M.; Koji, Y.; Motobe, K.; Shiina, K.; Yamamoto, Y.; Yamashina, A. Elevated serum levels of alanine aminotransferase and gamma glutamyltransferase are markers of inflammation and oxidative stress independent of the metabolic syndrome. Atherosclerosis 2006, 189, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.-H.; Jacobs, D.R. Association between serum gamma-glutamyltransferase and C-reactive protein. Atherosclerosis 2005, 178, 327–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andreozzi, F.; Laratta, E.; Procopio, C.; Hribal, M.L.; Sciacqua, A.; Perticone, M.; Miele, C.; Perticone, F.; Sesti, G. Interleukin-6 Impairs the Insulin Signaling Pathway, Promoting Production of Nitric Oxide in Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells. Mol. Cell. Boil. 2007, 27, 2372–2383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.; Lim, J.-S.; Yang, J.-H.; Ha, M.-H.; Jacobs, D.R. Serum gamma-glutamyltransferase within its normal range predicts a chronic elevation of alanine aminotransferase: A four year follow-up study. Free Radic. Res. 2005, 39, 589–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sciacqua, A.; Perticone, M.; Miceli, S.; Laino, I.; Tassone, E.; Grembiale, R.D.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G.; Perticone, F. Endothelial dysfunction and non-alcoholic liver steatosis in hypertensive patients. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2011, 21, 485–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | All n = 500 | hs-CRP Group n = 400 | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 47 ± 11 | 47 ± 11 | 0.998 |
| Gender, M (%) | 256 (51) | 183 (46) | 0.0001 |
| Body mass index, kg/m2 | 27.3 ± 3.6 | 27.3 ± 3.6 | 0.997 |
| SBP, mm Hg | 149 ± 17 | 149 ± 17 | 0.999 |
| DBP, mm Hg | 91 + 12 | 91±12 | 0.998 |
| Heart rate, bpm | 72 ± 9 | 73 ± 9 | 0.098 |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 205 ± 31 | 205 ± 31 | 0.997 |
| Smokers, No (%) | 78 (16) | 75 (19) | 0.246 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | 95 ± 11 | 95 ± 11 | 0.998 |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 130 ± 31 | 129 ± 31 | 0.631 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 52 ± 12 | 52 ± 12 | 0.997 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 116 ± 40 | 116 ± 41 | 0.999 |
| e-GFR, ml/min/1.73/m2 | 85 ± 20 | 88 ± 18 | 0.020 |
| ALT, UI/L | 21±11 | 21 ± 11 | 0.999 |
| AST, UI/L | 22 ± 9 | 22 ± 9 | 0.998 |
| γ-GT, UI/L | 33 ± 14 | 32 ± 14 | 0.287 |
| hs-CRP, mg/L | 4.1 ± 2.2 | ||
| FBF baseline, mL·0.100 tissue−1·min−1 | 3.4 ± 0.7 | 3.3 ± 0.6 | 0.024 |
| FBF maximal response to acetylcholine, % of increase | 303 ± 180 | 318 ± 183 | 0.218 |
| Response to sodium nitroprusside, % of increase | 317 ± 110 | 315 ± 107 | 0.784 |
| Vascular resistance, U | 34 + 8 | 34 + 7 | 0.998 |
| R | p | |
|---|---|---|
| γ-GT, UI/L | −0.587 | 0.0001 |
| ALT, UI/L | −0.559 | 0.0001 |
| AST, UI/L | −0.464 | 0.0001 |
| e-GFR, mL/min/1.73/m2 | 0257 | 0.0001 |
| Gender, male vs. female | 0.191 | 0.0001 |
| Age, years | −0.171 | 0.0001 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | −0.152 | 0.0001 |
| Fasting glucose, mg/dL | −0.101 | 0.012 |
| Systolic blood pressure, mmHg | −0.055 | 0.0108 |
| Diastolic blood pressure, mmHg | −0.031 | 0.248 |
| Smoking, yes vs. no | 0.028 | 0.269 |
| LDL cholesterol, mg/dL | −0.024 | 0.300 |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | −0.007 | 0.435 |
| HDL cholesterol, mg/dL | 0.001 | 0.494 |
| Partial r2 | Total r2 | b Coefficient | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| γ-GT | 35.4 | 35.4 | −0.362 | 0.0001 |
| ALT | 12.3 | 46.7 | −0.297 | 0.0001 |
| AST | 5.4 | 52.1 | −0.217 | 0.0001 |
| e-GFR | 1.9 | 54.0 | 0.199 | 0.0001 |
| Gender | 2.1 | 56.1 | 0.166 | 0.0001 |
| Smoking | 0.4 | 56.5 | −0.061 | 0.044 |
| OR | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-GT, 10 UI/L | 1.927 | 1.548–2.399 | 0.0001 |
| ALT, 10 UI/L | 2.175 | 1.608–2.941 | 0.0001 |
| AST, 10 UI/L | 1.973 | 1.369–2.788 | 0.0001 |
| Gender, male vs. female | 2.695 | 1.413–5.141 | 0.003 |
| e-GFR, 10 mL/min/1.73/m2 | 0.699 | 0.583–0.837 | 0.0001 |
| OR | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-GT, 10 UI/L | 2.089 | 1.545–2.823 | 0.0001 |
| ALT, 10 UI/L | 1.556 | 1.045–2.316 | 0.029 |
| AST, 10 UI/L | 1.865 | 1.146–3.035 | 0.019 |
| Gender, male vs. female | 2.742 | 1.147–6.558 | 0.023 |
| e-GFR, 10 mL/min/1.73/m2 | 0.656 | 0.522–0.825 | 0.0001 |
| OR | 95% CI | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| γ-GT, 10 UI/L | 1.819 | 1.335–2.480 | 0.0001 |
| ALT, 10 UI/L | 2.733 | 1.747–4.273 | 0.0001 |
| AST, 10 UI/L | 1.831 | 1.141–2.937 | 0.012 |
| Gender, male vs. female | 2.014 | 0.827–4.904 | 0.123 |
| e-GFR, 10 mL/min/1.73/m2 | 0.710 | 0.558–0.903 | 0.005 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Perticone, M.; Maio, R.; Caroleo, B.; Sciacqua, A.; Suraci, E.; Gigliotti, S.; Martino, F.; Andreozzi, F.; Sesti, G.; Perticone, F. Serum γ-Glutamyltransferase Concentration Predicts Endothelial Dysfunction in Naïve Hypertensive Patients. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070207
Perticone M, Maio R, Caroleo B, Sciacqua A, Suraci E, Gigliotti S, Martino F, Andreozzi F, Sesti G, Perticone F. Serum γ-Glutamyltransferase Concentration Predicts Endothelial Dysfunction in Naïve Hypertensive Patients. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(7):207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070207
Chicago/Turabian StylePerticone, Maria, Raffaele Maio, Benedetto Caroleo, Angela Sciacqua, Edoardo Suraci, Simona Gigliotti, Francesco Martino, Francesco Andreozzi, Giorgio Sesti, and Francesco Perticone. 2020. "Serum γ-Glutamyltransferase Concentration Predicts Endothelial Dysfunction in Naïve Hypertensive Patients" Biomedicines 8, no. 7: 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070207
APA StylePerticone, M., Maio, R., Caroleo, B., Sciacqua, A., Suraci, E., Gigliotti, S., Martino, F., Andreozzi, F., Sesti, G., & Perticone, F. (2020). Serum γ-Glutamyltransferase Concentration Predicts Endothelial Dysfunction in Naïve Hypertensive Patients. Biomedicines, 8(7), 207. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8070207







