Beyond the Biological Effect of a Chemically Characterized Poplar Propolis: Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity and Comparison with Flurbiprofen in Cytokines Release by LPS-Stimulated Human Mononuclear Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Propolis Sample
2.2. Total Flavonoids Determination
2.3. HPLC-DAD Analysis
2.4. In Vitro Anti-Inflammatory Activity
2.5. Propolis Antibacterial Activity
2.6. Propolis Anti-Influenza Activity
2.6.1. Antiviral Activity (Pre-Infection)
2.6.2. Antiviral Activity (Post-Cell Absorption)
2.6.3. Cytotoxic Activity of PP on MDCK Cells
2.6.4. In Vitro Anti-Neuraminidase Activity
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Chemical Analysis of European Poplar Type Propolis
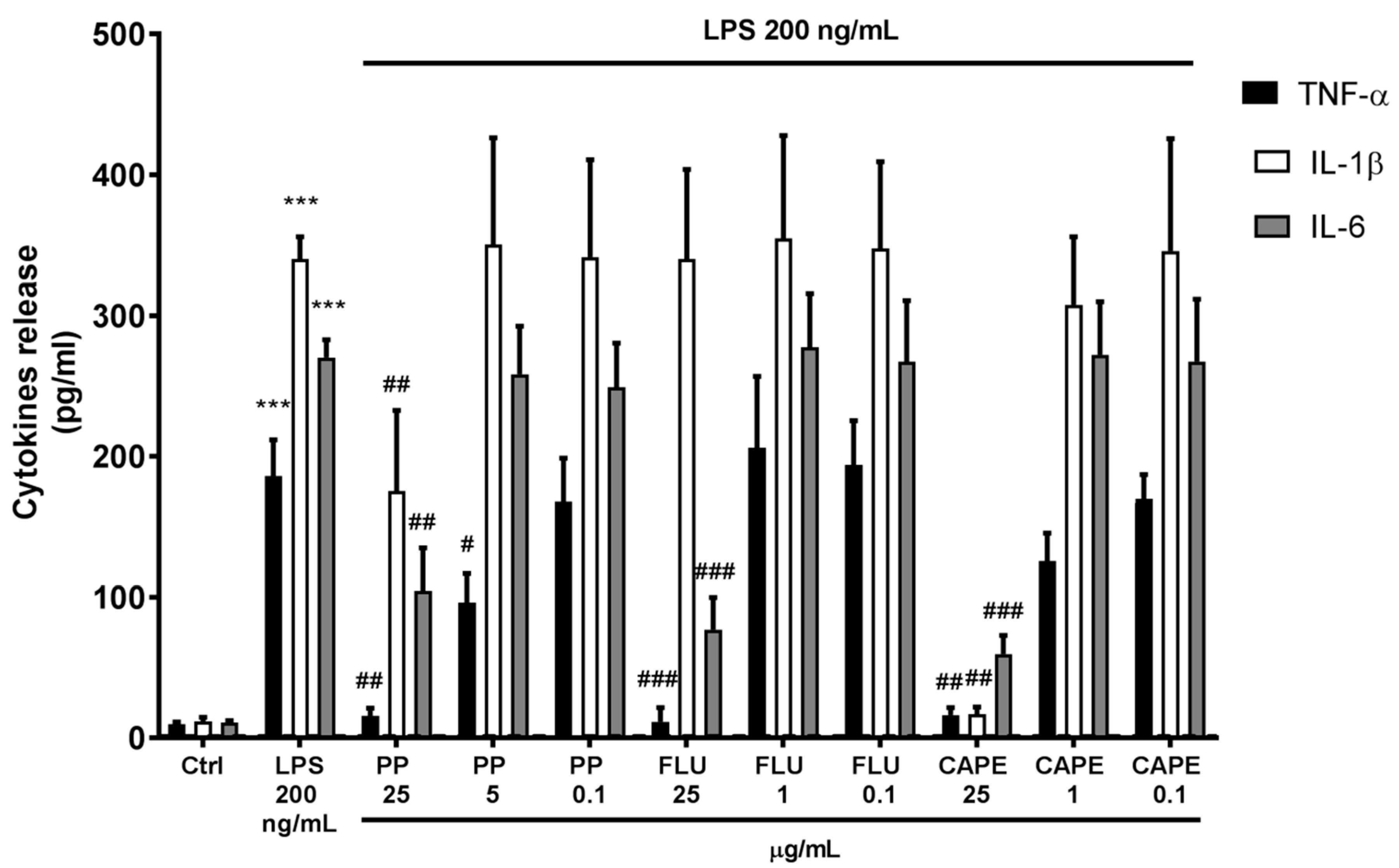
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Effectiveness of Propolis Compared to CAPE and Flurbiprofen
3.3. Antibacterial Activity of Propolis Against Gram+ and Gram− Strains
3.4. Antiviral Activity of Propolis Against A/PR/8 H1N1 Influenza Virus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, C.; Wu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H. Effect of ethanol/water solvents on phenolic profiles and antioxidant properties of beijing propolis extracts. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2015, 2015, 595393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuropatnicki, A.K.; Szliszka, E.; Krol, W. Historical aspects of propolis research in modern times. Evid Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2013, 2013, 964149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Zhang, C.P.; Wang, K.; Li, G.Q.; Hu, F.L. Recent advances in the chemical composition of propolis. Molecules 2014, 19, 19610–19632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omene, C.; Kalac, M.; Wu, J.; Marchi, E.; Frenkel, K.; O’Connor, O.A. Propolis and its active component, Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester (CAPE), modulate breast cancer therapeutic targets via an epigenetically mediated mechanism of action. J. Cancer Sci. 2013, 5, 334–342. [Google Scholar]
- Búfalo, M.C.; Sforcin, J.M. The modulatory effects of caffeic acid on human monocytes and its involvement in propolis action. J. Pharm. 2015, 67, 740–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miranda, M.M.; Panis, C.; Cataneo, A.H.; da Silva, S.S.; Kawakami, N.Y.; Lopes, L.G.; Morey, A.T.; Yamauchi, L.M.; Andrade, C.G.; Cecchini, R.; et al. Nitric oxide and Brazilian propolis combined accelerates tissue repair by modulating cell migration, cytokine production and collagen deposition in experimental leishmaniasis. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornara, L.; Biagi, M.; Xiao, J.; Burlando, B. Therapeutic Properties of Bioactive Compounds from Different Honeybee Products. Front. Pharm. 2017, 8, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pierro, F.; Zanvit, A.; Colombo, M. Role of a proprietary propolis-based product on the wait-and-see approach in acute otitis media and in preventing evolution to tracheitis, bronchitis, or rhinosinusitis from nonstreptococcal pharyngitis. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2016, 9, 409–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zannoni, G.; Russo, E. Comparison between bee propolis and flurbiprofen in pharyngitis. Piante Medicinali 2017, 16, 21. [Google Scholar]
- Biagi, M.; Manca, D.; Barlozzini, B.; Miraldi, E.; Giachetti, D. Optimization of extraction of drugs containing polyphenols using an innovative technique. Agro Food Ind. Hi Tech 2014, 25, 60–65. [Google Scholar]
- Biagi, M.; Collodel, G.; Corsini, M.; Pascarelli, N.A.; Moretti, E. Protective effect of Propolfenol® on induced oxidative stress in human spermatozoa. Andrologia 2018, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Governa, P.; Marchi, M.; Cocetta, V.; De Leo, B.; Saunders, P.T.K.; Catanzaro, D.; Miraldi, E.; Montopoli, M.; Biagi, M. Effects of Boswellia Serrata Roxb. and Curcuma longa L. in an In Vitro Intestinal Inflammation Model Using Immune Cells and Caco-2. Pharmaceuticals (Basel) 2018, 11, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, M.; Giachetti, D.; Miraldi, E.; Figura, N. New non-alcoholic formulation for hand disinfection. J. Chemother. 2014, 26, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maróstica Junior, M.R.; Daugsch, A.; Moraes, C.S.; Queiroga, C.L.; Pastore, G.M.; Parki, Y.K. Comparison of volatile and polyphenolic compounds in Brazilian green propolis and its botanical origin Baccharis dracunculifolia. Food Sci. Technol. 2008, 28, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardana, C.; Scaglianti, M.; Pietta, P.; Simonetti, P. Analysis of the polyphenolic fraction of propolis from different sources by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2007, 45, 390–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quosdorf, S.; Schuetz, A.; Kolodziej, H. Different Inhibitory Potencies of Oseltamivir Carboxylate, Zanamivir, and Several Tannins on Bacterial and Viral Neuraminidases as Assessed in a Cell-Free Fluorescence-Based Enzyme Inhibition Assay. Molecules 2017, 22, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankova, V. Chemical diversity of propolis and the problem of standardization. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 100, 114–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biagi, M.; Miraldi, E.; Figura, N.; Magnano, A.R.; Ierardi, G.; Manca, D.; Corsini, M.; Barlozzini, B.; Mannari, C.; Stiaccini, G.; et al. Gastroprotective and anti Helicobacter pylori activities of propolis. Planta Medica 2011, 77, 1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, D.B. Pharyngitis. Prim. Care 1996, 23, 719–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Groote, D.; Zangerle, P.F.; Gevaert, Y.; Fassotte, M.F.; Beguin, Y.; Noizat-Pirenne, F.; Pirenne, J.; Gathy, R.; Lopez, M.; Dehart, L.; et al. Direct stimulation of cytokines (IL-1β, TNF-α, IL-6, IL-2, IFN-γ and GM-CSF) in whole blood. I. Comparison with isolated PBMC stimulation. Cytokine 1992, 4, 239–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armutcu, F.; Akyol, S.; Ustunsoy, S.; Turan, F.F. Therapeutic potential of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and its anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2015, 9, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowie, A.; O’Neill, L.A. Oxidative stress and nuclear factor-kappaB activation: A reassessment of the evidence in the light of recent discoveries. Biochem. Pharm. 2000, 59, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sforcin, J.M. Propolis and the immune system: A review. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 113, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsi, R.O.; Funari, S.R.C.; Soares, A.M.V.C.; Calvi, S.A.; Oliveira, S.L.; Sforcin, J.M.; Bankova, V. Immunomodulatory action of propolis on macrophage activation. J. Venom. Anim. Toxins Incl. Trop. Dis. 2000, 6, 205–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shtyrya, Y.A.; Mochalova, L.V.; Bovin, N.V. Influenza Virus Neuraminidase: Structure and Function. Acta Nat. 2009, 1, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, Y.K.; Meenu, M.; Mohan, P. The Tamiflu fiasco and lessons learnt. Indian J. Pharmacol. 2015, 47, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costi, R.; Santo, R.D.; Artico, M.; Massa, S.; Ragno, R.; Loddo, R.; La Colla, M.; Tramontano, E.; La Colla, P.; Pani, A. 2,6-Bis(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzylydene) derivatives of cyclohexanone: Novel potent HIV-1 integrase inhibitors that prevent HIV-1 multiplication in cell-based assays. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2004, 12, 199–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stepanovic, S.; Antic, N.; Dakic, I.; Svabic-Vlahovic, M. In vitro antimicrobial activity of propolis and synergism between propolis and antimicrobial drugs. Microbiol. Res. 2003, 158, 353–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cos, P.; Vlietinck, A.J.; Berghe, D.V.; Maes, L. Anti-infective potential of natural products: How to develop a stronger in vitro ‘proof-of-concept’. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2006, 106, 290–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, H.; Ulrich-Merzenich, G. Synergy research: Approaching a new generation of phytopharmaceuticals. Phytomedicine 2009, 16, 97–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
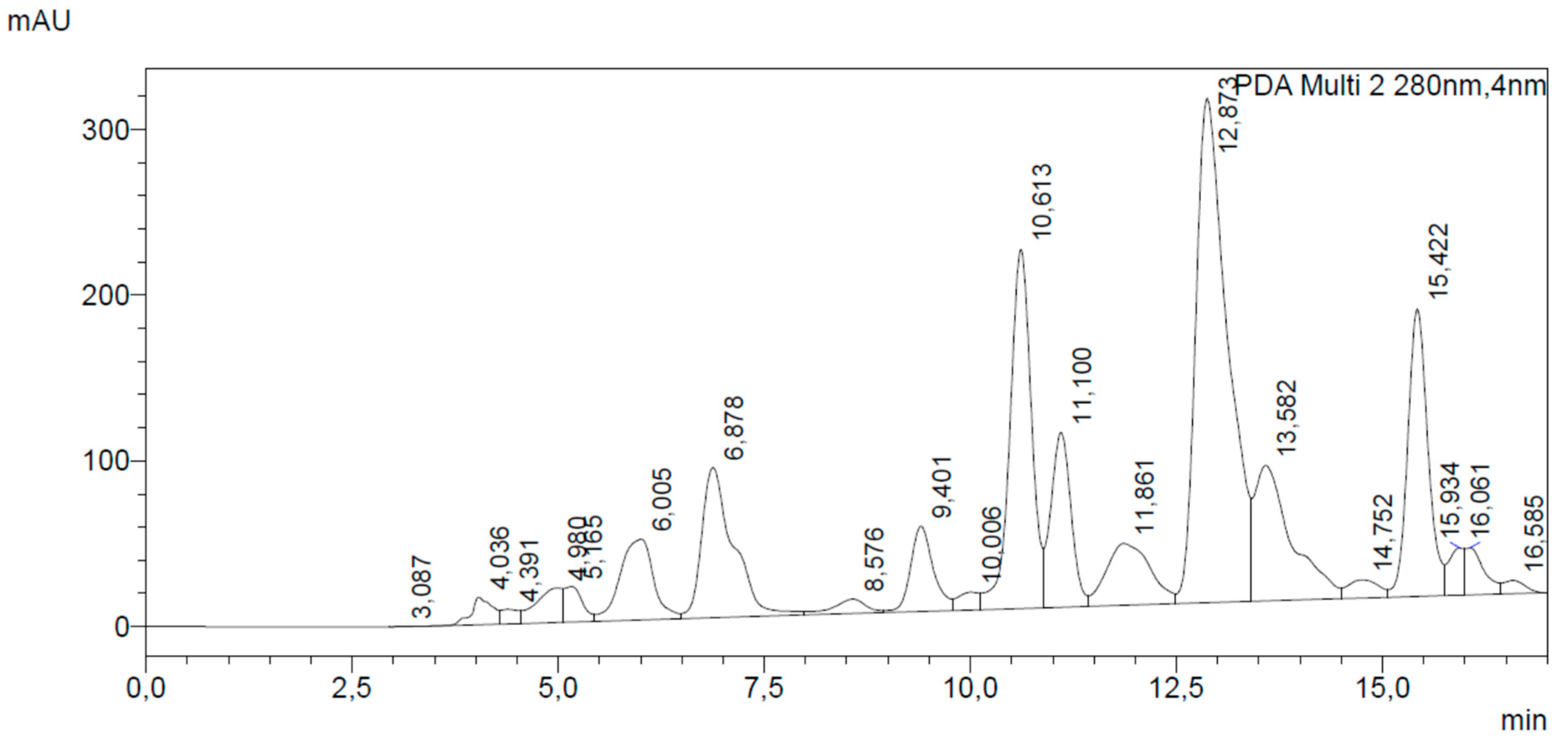
| Constituent | Content [mg/g Dry Propolis] |
|---|---|
| galangin | 42.25 ± 0.51 |
| pinocembrin | 27.30 ± 0.26 |
| CAPE | 11.21 ± 0.10 |
| Parameter | Control | LPS |
|---|---|---|
| Cytokines dosage (pg/mL) | ||
| TNF-α | 9.76 ± 1.60 | 185.95 ± 25.78 *** |
| IL-1β | 11.77 ± 2.91 | 340.01 ± 15.94 *** |
| IL-2 | 4.24 ± 0.57 | 4.50 ± 1.01 |
| IL-6 | 10.84 ± 1.48 | 270.31 ± 12.64 *** |
| IL-17 | 17.10 ± 3.45 | 16.44 ± 3.65 |
| Sample | Parameter | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration (μg/mL) | TNF-α | IL-1β | IL-2 | IL-6 | IL-17 | |
| Cytokines Dosage (pg/mL) | ||||||
| PP | 25 | 10.83 ± 1.44 | 42.02 ± 8.17 * | 4.20 ± 0.34 | 16.15 ± 1.21 * | 15.05 ± 1.26 |
| FLU | 25 | 11.71 ± 1.19 | 76.39 ± 16.00 ** | 4.32 ± 0.48 | 12.47 ± 0.95 | 16.76 ± 1.58 |
| CAPE | 25 | 9.86 ± 0.98 | 12.95 ± 1.29 | 3.90 ± 0.32 | 10.95 ± 0.99 | 15.39 ± 1.44 |
| Bacterial Strain | MIC (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| S. aureus | 625 |
| MRSA | 625 |
| S. epidermidis | 2500 |
| S. pyogenes | 156 |
| S. pneumoniae | 625 |
| E. coli | 5000 |
| P. aeruginosa | 2500 |
| Sample | IC50 (μg/mL) |
|---|---|
| oseltamivir | 5.88 ± 0.89 |
| PP | 35.29 ± 4.08 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Governa, P.; Cusi, M.G.; Borgonetti, V.; Sforcin, J.M.; Terrosi, C.; Baini, G.; Miraldi, E.; Biagi, M. Beyond the Biological Effect of a Chemically Characterized Poplar Propolis: Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity and Comparison with Flurbiprofen in Cytokines Release by LPS-Stimulated Human Mononuclear Cells. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7040073
Governa P, Cusi MG, Borgonetti V, Sforcin JM, Terrosi C, Baini G, Miraldi E, Biagi M. Beyond the Biological Effect of a Chemically Characterized Poplar Propolis: Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity and Comparison with Flurbiprofen in Cytokines Release by LPS-Stimulated Human Mononuclear Cells. Biomedicines. 2019; 7(4):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7040073
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoverna, Paolo, Maria Grazia Cusi, Vittoria Borgonetti, José Mauricio Sforcin, Chiara Terrosi, Giulia Baini, Elisabetta Miraldi, and Marco Biagi. 2019. "Beyond the Biological Effect of a Chemically Characterized Poplar Propolis: Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity and Comparison with Flurbiprofen in Cytokines Release by LPS-Stimulated Human Mononuclear Cells" Biomedicines 7, no. 4: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7040073
APA StyleGoverna, P., Cusi, M. G., Borgonetti, V., Sforcin, J. M., Terrosi, C., Baini, G., Miraldi, E., & Biagi, M. (2019). Beyond the Biological Effect of a Chemically Characterized Poplar Propolis: Antibacterial and Antiviral Activity and Comparison with Flurbiprofen in Cytokines Release by LPS-Stimulated Human Mononuclear Cells. Biomedicines, 7(4), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines7040073









