Efficacy of Early Postoperative Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy in Preventing Persistent Macular Oedema in Patients After Epiretinal Membrane Surgery
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Group
2.2. Ophthalmological Questionnaire
2.3. Ophthalmic Examinations
2.4. Multifocal Electroretinography (RetiScan System, Roland Consult, Germany)
2.5. Microperimetry (Macular Integrity Assessment, MAIA; CenterVue, Italy)
2.6. Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy
2.7. Statistical Analysis
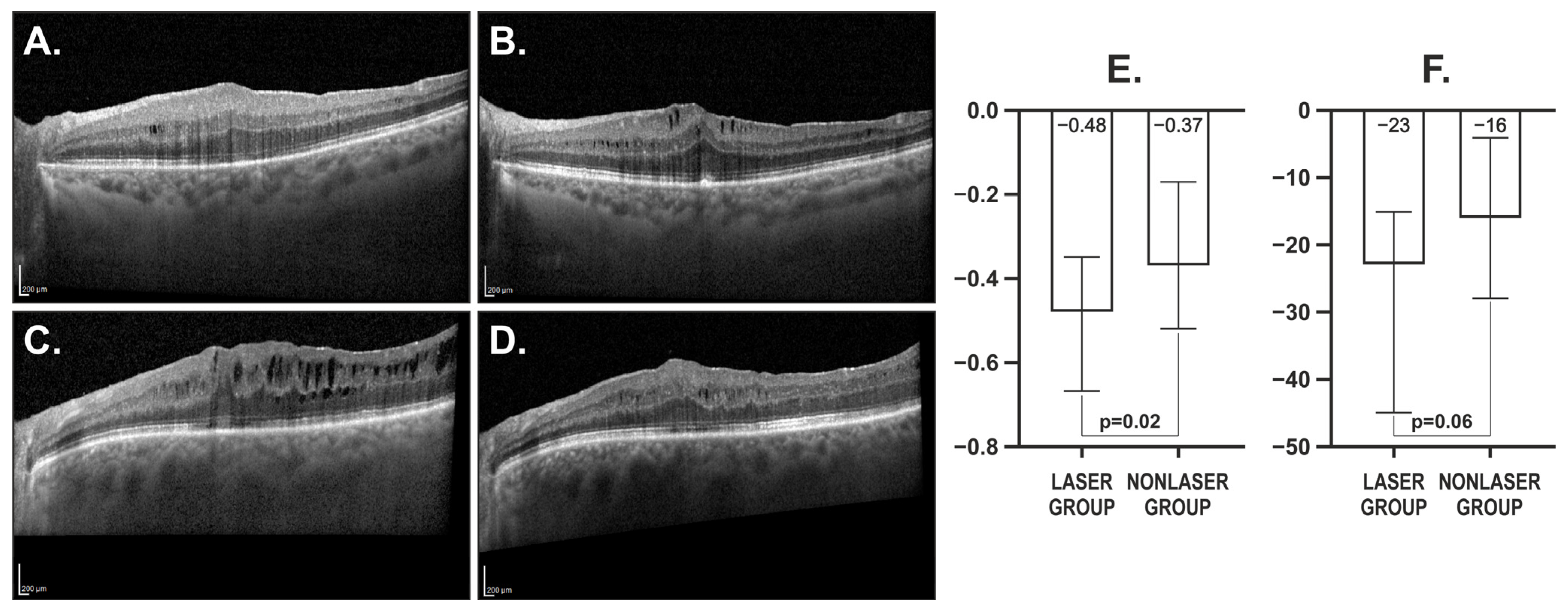
3. Results
3.1. Preoperative Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Postoperative Changes in Morphological and Functional Characteristics
3.3. The Relationships Between the Analysed Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fung, A.T.; Galvin, J.; Tran, T. Epiretinal membrane: A review. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2021, 49, 289–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luttrull, J.K. Subthreshold Diode Micropulse Laser (SDM) for Persistent Macular Thickening and Limited Visual Acuity After Epiretinal Membrane Peeling. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2020, 14, 1177–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.J.; Jo, Y.J.; Kwon, H.J.; Lee, S.M.; Park, S.W.; Byon, I.S.; Lee, J.E. Perioperative intraretinal fluid observed using optical coherence tomography in the epiretinal membrane. BMC Ophthalmol. 2020, 20, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matoba, R.; Morizane, Y. Surgical Treatment of Epiretinal Membrane. Acta Med. Okayama 2021, 75, 403–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliano, L.; Fogliato, G.; Gorgoni, F.; Corbelli, E.; Bandello, F.; Codenotti, M. Idiopathic epiretinal membrane surgery: Safety, efficacy and patient-related outcomes. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2019, 13, 1253–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Rhee, K.M.; Woo, S.J.; Yu, Y.S.; Chung, H.; Park, K.H. Long-Term Temporal Changes of Macular Thickness and Visual Outcome after Vitrectomy for Idiopathic Epiretinal Membrane. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 150, 701–709.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, E.; Colorado-Zavala, M.F.; Almuhtaseb, H.; Venkatesh, R.; Parolini, B.; Chhablani, J. Anatomical and functional changes after internal limiting membrane peeling. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2025, 70, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kohli, P.; Tripathy, K.; Patel, B.C. Macular Edema. In StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK576396/ (accessed on 25 August 2025).
- Haydinger, C.D.; Ferreira, L.B.; Williams, K.A.; Smith, J.R. Mechanisms of macular edema. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1128811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massin, P.; Allouch, C.; Haouchine, B.; Metge, F.; Paques, M.; Tangui, L.; Erginay, A.; Gaudric, A. Optical coherence tomography of idiopathic macular epiretinal membranes before and after surgery. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2000, 130, 732–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Huang, Z.; Huang, D.; Zheng, D.; Lin, P.; Lin, Y.; Chen, W. Subthreshold micropulse laser therapy for early postoperative macular thickening following surgical removal of epiretinal membrane. BMC Ophthalmol. 2024, 24, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawęcki, M. Micropulse Laser Treatment of Retinal Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; He, W.; Qi, S. Evaluating the efficacy of subthreshold micropulse laser combined with anti-VEGF drugs in the treatment of diabetic macular edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2025, 16, 1553311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sorrentino, T.; Allegrini, D.; De Rosa, G.; Santoru, F.; Crepaldi, L.; Feo, A.; Zanellati, G.; Marconi, S.; Auricchio, F.; Romano, M.R. Settings and Clinical Applications of Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy: A Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Long, H.; Hu, Q. Efficacy of subthreshold micropulse laser for chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: A meta-analysis. Photodiagn. Photodyn. Ther. 2022, 39, 102931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eng, V.A.; Wood, E.H.; Boddu, S.; Karth, P.A.; Leng, T. Preventing progression in nonexudative age-related macular degeneration with subthreshold laser therapy: A systematic review. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retina 2019, 50, e61–e70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdina, T.; D’Aloisio, R.; Lazzerini, A.; Ferrari, C.; Valerio, E.; Mastropasqua, R.; Cavallini, G.M. The Role of Subthreshold Micropulse Yellow Laser as an Alternative Option for the Treatment of Refractory Postoperative Cystoid Macular Edema. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfiglio, V.; Rejdak, R.; Nowomiejska, K.; Zweifel, S.A.; Wiest, M.R.J.; Romano, G.L.; Bucolo, C.; Gozzo, L.; Castellino, N.; Patane, C.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Subthreshold Micropulse Yellow Laser for Persistent Diabetic Macular Edema After Vitrectomy: A Pilot Study. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 832448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, G.; Liu, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, M.; Xie, J.; Wang, Q.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y. Safety and efficacy of subthreshold micropulse yellow laser for persistent subretinal fluid after scleral bucking: A randomized clinical trial. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 20874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Govetto, A.; Lalane, R.A., III; Sarraf, D.; Figueroa, M.S.; Hubschman, J.P. Insights into epiretinal membranes: Presence of ectopic inner foveal layers and a new optical coherence tomography staging scheme. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 175, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.B.; Bach, M.; Kondo, M.; Li, S.; Walker, S.; Holopigian, K.; Viswanathan, S.; Robson, A.G. ISCEV standard for clinical multifocal electroretinography (mfERG) (2021 update). Doc. Ophthalmol. 2021, 142, 5–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawęcki, M.; Jaszczuk-Maciejewska, A.; Jurska-Jaśko, A.; Grzybowski, A. Functional and morphological outcome in patients with chronic central serous chorioretinopathy treated by subthreshold micropulse laser. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2017, 255, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gawęcki, M.; Jaszczuk-Maciejewska, A.; Jurska-Jaśko, A.; Kneba, M.; Grzybowski, A. Transfoveal micropulse laser treatment of central serous chorioretinopathy within six months of disease onset. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, V.; Matonti, F.; Zarranz-Ventura, J.; Stewart, M.W. Impact of fluid compartments on functional outcomes for patients with neovascular age-related macular degeneration: A systematic literature review. Retina 2022, 42, 589–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viggiano, P.; Scotti, G.; Termite, A.C.; Savastano, A.; Boscia, G.; Clemente, A.; Salvelli, A.; Giancipoli, E.; Pignatelli, F.; Evangelista, F.; et al. Choroidal remodeling after subthreshold micropulse laser in chronic central serous chorioretinopathy: Short-term outcomes. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vujosevic, S.; Gatti, V.; Muraca, A.; Brambilla, M.; Villani, E.; Nucci, P.; Rossetti, L.; De Cilla, S. Optical coherence tomography angiography changes after subthreshold micropulse yellow laser in diabetic macular edema. Retina 2020, 40, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iuliano, L.; Cisa di Gresy, G.; Fogliato, G.; Corbelli, E.; Bandello, F.; Codenotti, M. Increased risk of postsurgical macular edema in high stage idiopathic epiretinal membranes. Eye Vis. 2021, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Evaluated Parameters | SMLT Group | Control Non-Laser Group | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 35 | 33 | |
| Gender (F/M) | 21/14 | 20/13 | |
| Age Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 72 (9) 70.86 ± 6.03 | 72 (6) 71.97 ± 5.07 | 0.64 |
| Govetto stage: 1—n (%) 2—n (%) 3—n (%) 4—n (%) | 2 (6%) 10 (29%) 16 (46%) 7 (20%) | 4 (12%) 10 (30%) 12 (36%) 7 (21%) | 0.76 |
| BCVA [Snellen charts] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 0.4 (0.3) 0.44 ± 0.21 | 0.5 (0.2) 0.46 ± 0.2 | 0.75 |
| BCVA [ETDRS charts] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 22 (20) 19.29 ± 10.76 | 22 (8) 19.7 ± 9.39 | 0.91 |
| Presence of metamorphopsia at the time of evaluation 1—Yes n (%) 0—No n (%) | 26 (76%) 8 (24%) | 22 (69%) 10 (31%) | 0.58 |
| Duration of metamorphopsia 1—<6 months n (%) 2—6–12 months n (%) 3—>12 months n (%) | 9 (33%) 7 (26%) 11 (41%) | 7 (30%) 8 (35%) 8 (35%) | 0.79 |
| Central ETDRS retinal thickness [μm] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 497 (103) 502.11 ± 75.85 | 505 (121) 502.12 ± 91.12 | 0.93 |
| Total retinal volume [mm3] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 10.85 (1.35) 10.95 ± 1.15 | 11.12 (1.77) 10.97 ± 1.59 | 0.89 |
| Choroidal area [mm2] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 1.56 (1.9) 1.56 ± 0.42 | 1.54 (0.6) 1.6 ± 0.44 | 0.74 |
| Subfoveal choroidal thickness [μm] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 210 (117) 230.57 ± 79.04 | 245 (108) 247.97 ± 83.25 | 0.38 |
| FAZ area in SVC [mm2] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 0.13 (0.12) 0.16 ± 0.14 | 0.16 (0.18) 0.2 ± 0.18 | 0.3 |
| FAZ area in DVC [mm2] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 0.25 (0.29) 0.3 ± 0.24 | 0.24 (0.45) 0.39 ± 0.33 | 0.48 |
| P1 wave amplitude in R1 [nV/degree2] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 72.05 (47.27) 73.48 ± 26.05 | 63.43 (35.72) 67.43 ± 27.8 | 0.25 |
| P1 wave implicit time in R1 [ms] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 48 (4.9) 47.15 ± 4.07 | 45.1 (6.9) 46.61 ± 4.98 | 0.39 |
| Average threshold [dB] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 24.1 (3.7) 23.19 ± 3.36 | 24.5 (2.9) 24.37 ± 2.13 | 0.25 |
| Fixation Stability P1 [%] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 96 (13) 91.09 ± 11.71 | 98 (7) 94.12 ± 7.74 | 0.28 |
| Fixation Stability P2 [%] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 100 (2) 97.66 ± 5.38 | 100 (1) 98.42 ± 2.89 | 0.42 |
| 63% BCEA: area [deg2] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 0.6 (1.5) 1.44 ± 2.45 | 0.4 (0.7) 2.7 ± 10.44 | 0.61 |
| 95% BCEA: area [deg2] Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | 1.8 (4.5) 4.33 ± 7.32 | 1.3 (2.1) 8.11 ± 31.28 | 0.65 |
| Evaluated Parameters 1 Month After PPV | SMLT Group Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | Control Non-Laser Group Median (IQR) Mean ± SD | p * |
|---|---|---|---|
| BCVA [Snellen charts] | 0.7 (0.4) 0.63 ± 0.21 | 0.6 (0.2) 0.61 ± 0.18 | 0.61 |
| BCVA [ETDRS charts] | 28 (14) 24.8 ± 9.83 | 28 (12) 26 ± 8.4 | 0.81 |
| Central ETDRS retinal thickness [μm] | 430 (57) 438.17 ± 39.64 | 443 (65) 448.1 ± 71.37 | 0.67 |
| Total retinal volume [mm3] | 9.78 (0.9) 9.83 ± 0.62 | 9.92 (1.03) 9.83 ± 0.93 | 0.65 |
| Choroidal area [mm2] | 1.51 (0.78) 1.55 ± 0.42 | 1.46 (0.47) 1.54 ± 0.36 | 0.95 |
| Subfoveal choroidal thickness [μm] | 228 (107) 234.46 ± 78.32 | 238 (89) 234.21 ± 68.49 | 0.9 |
| FAZ area in SVC [mm2] | 0.1 (0.08) 0.13 ± 0.11 | 0.1 (0.11) 0.14 ± 0.11 | 0.67 |
| FAZ area in DVC [mm2] | 0.17 (0.11) 0.18 ± 0.08 | 0.23 (0.17) 0.3 ± 0.29 | 0.07 |
| P1 wave amplitude in R1 [nV/degree2] | 75.45 (30.43) 73.86 ± 23.61 | 69.43 (20.15) 71.84 ± 24.28 | 0.59 |
| P1 wave implicit time in R1 [ms] | 50 (5.8) 49.57 ± 3.98 | 50 (5.9) 49.44 ± 4.67 | 0.88 |
| Average threshold [dB] | 24.3 (2.7) 23.62 ± 2.97 | 24.6 (3) 24.46 ± 2.17 | 0.43 |
| Fixation Stability P1 [%] | 98 (8) 94.22 ± 9.23 | 98 (4) 96.39 ± 6.66 | 0.32 |
| Fixation Stability P2 [%] | 100 (1) 98.44 ± 4.13 | 100 (0) 99.48 ± 1.55 | 0.35 |
| 63% BCEA: area [deg2] | 0.4 (0.8) 0.94 ± 1.65 | 0.4 (0.4) 0.57 ± 0.78 | 0.39 |
| 95% BCEA: area [deg2] | 1.2 (2.55) 2.83 ± 4.92 | 1.1 (1.2) 1.67 ± 2.33 | 0.35 |
| Evaluated Parameters | Rs Before PPV | p * |
|---|---|---|
| BCVA [Snellen chart] | +0.35 | 0.04 |
| BCVA [ETDRS charts] | +0.29 | 0.08 |
| Govetto stage [1–4] | −0.46 | 0.006 |
| Central ETDRS retinal thickness [μm] | −0.44 | 0.008 |
| Choroidal area [mm2] | −0.27 | 0.12 |
| Subfoveal choroidal thickness [μm] | −0.26 | 0.14 |
| FAZ area in SVC [mm2] | +0.14 | 0.46 |
| FAZ area in DVC [mm2] | −0.32 | 0.11 |
| P1 wave amplitude in R1 [nV/degree2] | +0.39 | 0.02 |
| P1 wave implicit time in R1 [ms] | +0.15 | 0.4 |
| Average threshold [dB] | +0.66 | <0.001 |
| Fixation Stability P1 [%] | +0.24 | 0.17 |
| Fixation Stability P2 [%] | +0.23 | 0.19 |
| 63% BCEA: vertical [°] | −0.33 | 0.051 |
| 95% BCEA: vertical [°] | −0.34 | 0.048 |
| 63% BCEA: area [deg2] | −0.29 | 0.09 |
| 95% BCEA: area [deg2] | −0.29 | 0.09 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ziontkowska-Wrzałek, A.; Dzięciołowska, M.; Safranow, K.; Machalińska, A. Efficacy of Early Postoperative Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy in Preventing Persistent Macular Oedema in Patients After Epiretinal Membrane Surgery. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092113
Ziontkowska-Wrzałek A, Dzięciołowska M, Safranow K, Machalińska A. Efficacy of Early Postoperative Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy in Preventing Persistent Macular Oedema in Patients After Epiretinal Membrane Surgery. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092113
Chicago/Turabian StyleZiontkowska-Wrzałek, Alicja, Monika Dzięciołowska, Krzysztof Safranow, and Anna Machalińska. 2025. "Efficacy of Early Postoperative Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy in Preventing Persistent Macular Oedema in Patients After Epiretinal Membrane Surgery" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092113
APA StyleZiontkowska-Wrzałek, A., Dzięciołowska, M., Safranow, K., & Machalińska, A. (2025). Efficacy of Early Postoperative Subthreshold Micropulse Laser Therapy in Preventing Persistent Macular Oedema in Patients After Epiretinal Membrane Surgery. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2113. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092113





