Electroacupuncture Relieves Fibromyalgia Pain in a Female Mouse Model by Augmenting Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Suppressing Astrocyte and Microglial Activation in Nociceptive Pathways
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
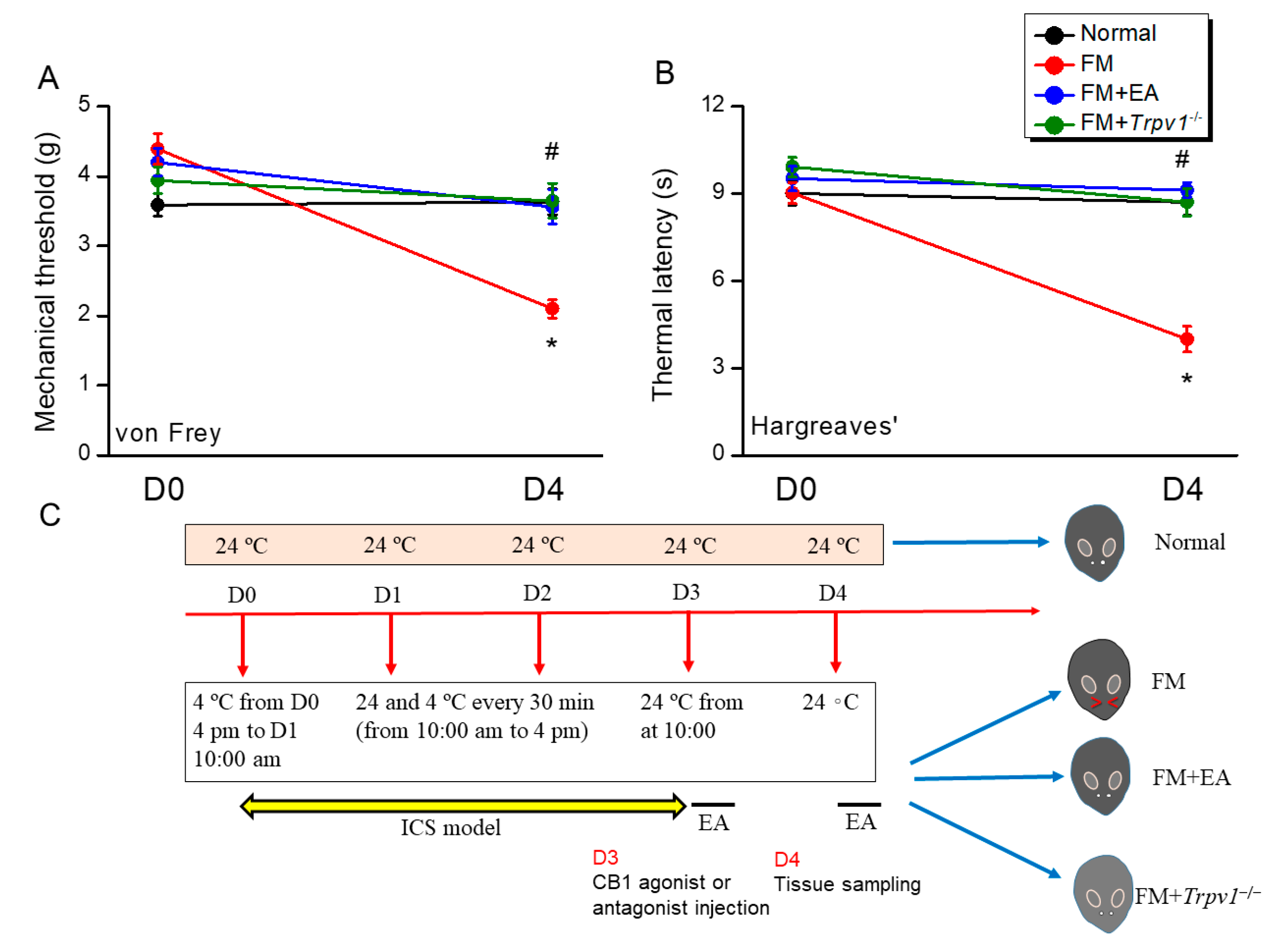
2.1. Mice and Fibromyalgia Pain Model
2.2. Nociceptive Behavior Examinations
2.3. Electroacupuncture
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. CB1 Receptor Agonist and Antagonist Administration
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Electroacupuncture (2 Hz) and Trpv1 Gene Knockout Diminished Mechanical and Thermal Hyperalgesia in Intermittent Cold Stress (ICS)-Induced Fibromyalgia Model Mice
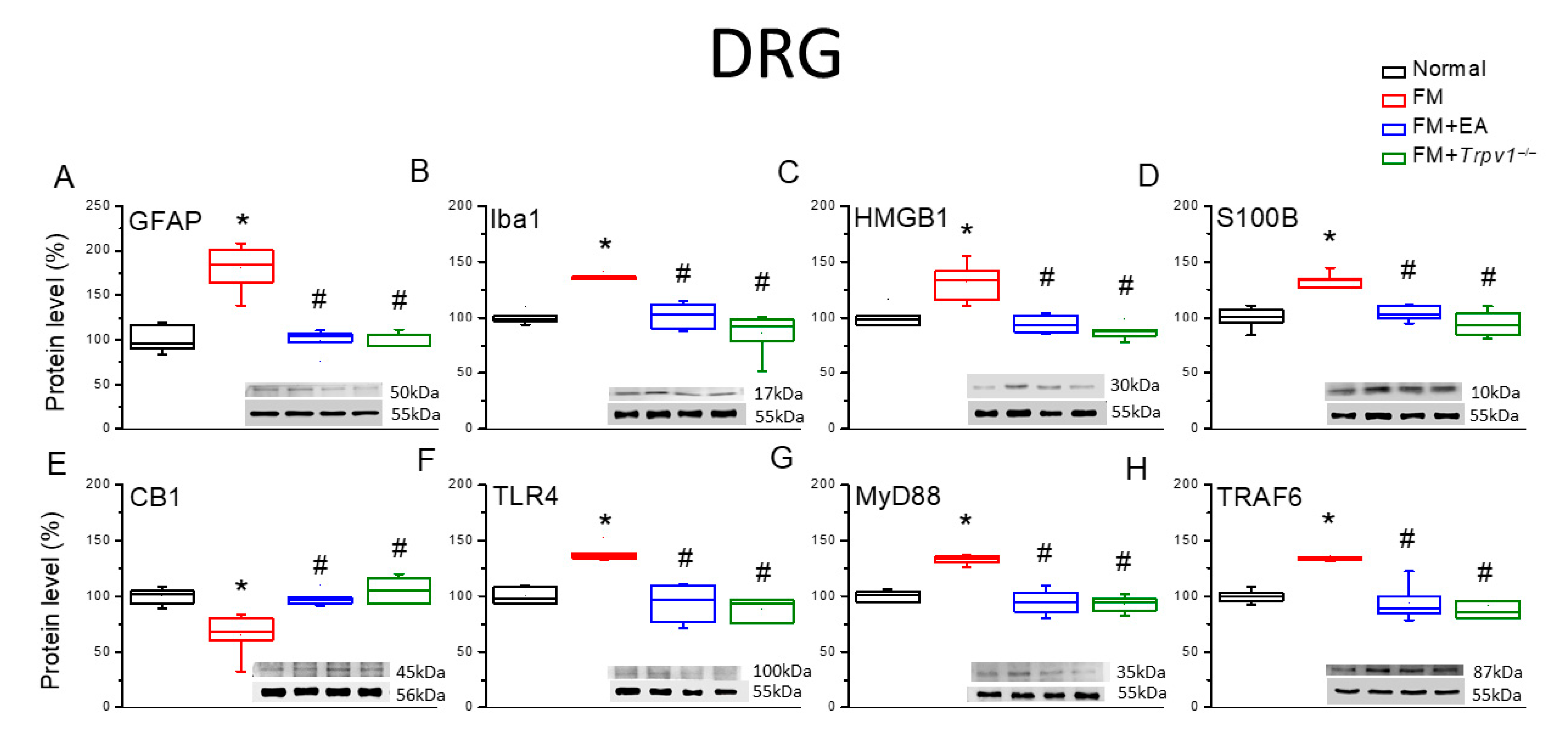
3.2. Both EA and Trpv1 Knockout Reduced Fibromyalgia-like Pain in ICS Model Mice by Suppressing Microglial and Astrocytic Activation and Promoting CB1 Pathway Activity
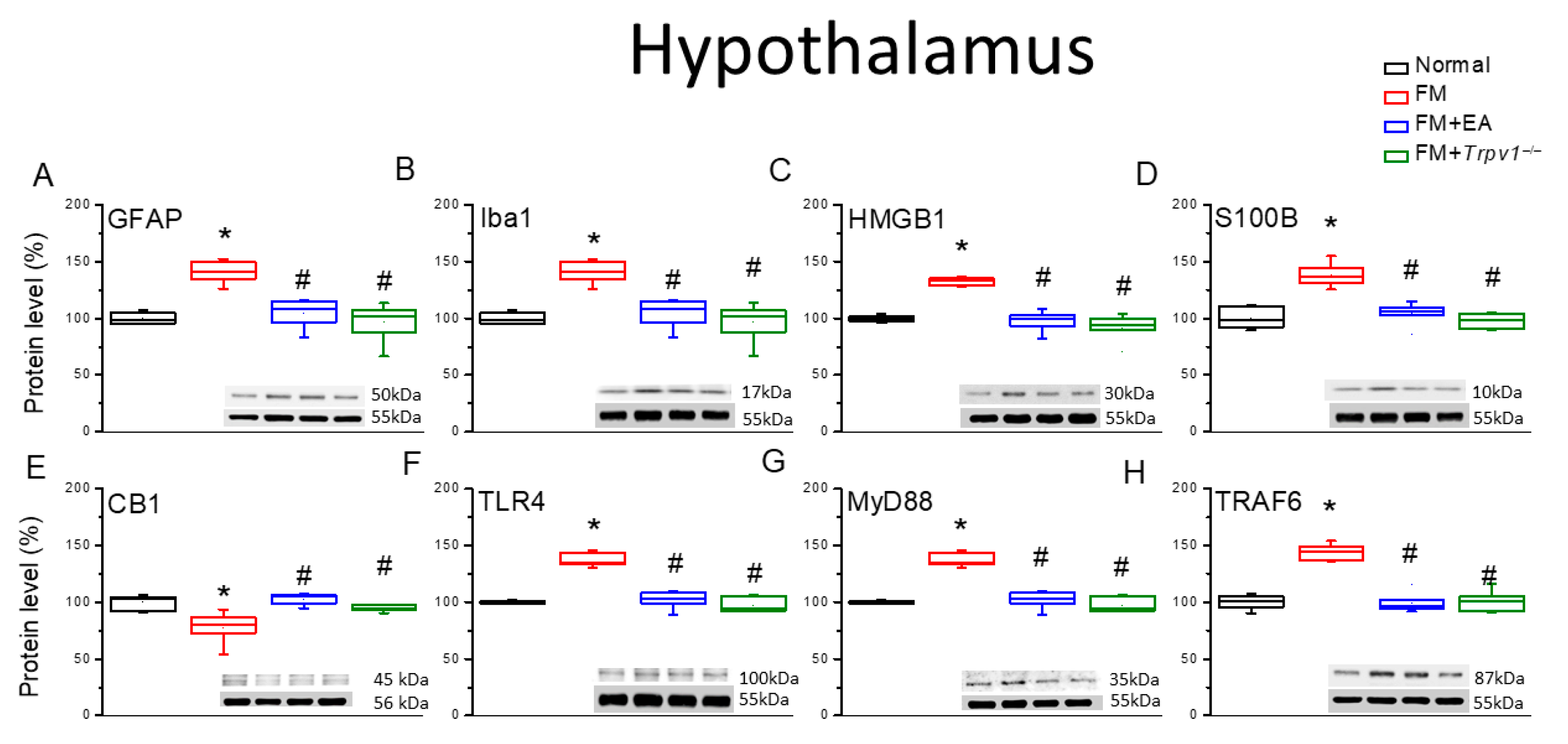
3.3. EA and Trpv1 Knockout Suppressed Fibromyalgia-like Hyperalgesia Through the Modulation of Glial Signaling at the Spinal Cord and Hypothalamic and PAG Levels
3.4. EA Significantly Reduced Fibromyalgia-like Hyperalgesia Through CB1 Receptor Activation
3.5. Distinct Downstream Mechanisms for EA-Induced CB1-Mediated Suppression of Fibromyalgia-like Hyperalgesia in the Peripheral and Central Nervous Systems
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Iannuccelli, C.; Favretti, M.; Dolcini, G.; Di Carlo, M.; Pellegrino, G.; Bazzichi, L.; Atzeni, F.; Lucini, D.; Varassi, G.; Leoni, M.L.G.; et al. Fibromyalgia: One year in review 2025. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2025, 43, 957–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Dominguez, A.J.; Rebollo-Salas, M.; Chillon-Martinez, R.; Rosales-Tristancho, A.; Villa-Del-Pino, I.; Jimenez-Rejano, J.J. The most effective therapeutic exercises for pain intensity in women with fibromyalgia: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Braz. J. Phys. Ther. 2025, 29, 101226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, S.; Zaid, M.; Imran, S.; Hai, A.; Patel, M.J. Increased frequency of fibromyalgia among patients with chronic pain presenting to internal medicine clinics of a tertiary care hospital: A cross sectional study. J. Pak. Med. Assoc. 2021, 71, 2740–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.H. Fibromyalgia Symptoms Reduced by Osteopathic Manipulative Medicine and Gabapentin. J. Am. Osteopath. Assoc. 2018, 118, 349–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Schmid, C.H.; Fielding, R.A.; Harvey, W.F.; Reid, K.F.; Price, L.L.; Driban, J.B.; Kalish, R.; Rones, R.; McAlindon, T. Effect of tai chi versus aerobic exercise for fibromyalgia: Comparative effectiveness randomized controlled trial. BMJ 2018, 360, k851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, A.A.; Liu, Y.; Nguyen, J.; Spraggins, R.; Reed, D.S.; Lee, C.; Hasoon, J.; Kaye, A.D. Efficacy of acupuncture in the treatment of fibromyalgia. Orthop. Rev. 2021, 13, 25085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cordon, B.; Orduna, E.; Vilades, E.; Garcia-Martin, E.; Garcia-Campayo, J.; Puebla-Guedea, M.; Polo, V.; Larrosa, J.M.; Pablo, L.E.; Vicente, M.J.; et al. Analysis of Retinal Layers in Fibromyalgia Patients with Premium Protocol in Optical Tomography Coherence and Quality of Life. Curr. Eye Res. 2022, 47, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Elsayed, A.; Gilligan, C. Cannabis for treating fibromyalgia. Pain Pract. 2023, 23, 566–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.S.; Mahajan, U.B.; Agrawal, Y.O.; Patil, K.R.; Patil, C.R.; Ojha, S.; Sharma, C.; Goyal, S.N. Plant-derived natural therapeutics targeting cannabinoid receptors in metabolic syndrome and its complications: A review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 132, 110889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svizenska, I.; Dubovy, P.; Sulcova, A. Cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 (CB1 and CB2), their distribution, ligands and functional involvement in nervous system structures--a short review. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2008, 90, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anthony, A.T.; Rahmat, S.; Sangle, P.; Sandhu, O.; Khan, S. Cannabinoid Receptors and Their Relationship with Chronic Pain: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2020, 12, e10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benamar, K. IUPHAR review- Preclinical models of neuropathic pain: Evaluating multifunctional properties of natural cannabinoid receptors ligands. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 199, 107013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biswas, K. Microglia mediated neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative diseases: A review on the cell signaling pathways involved in microglial activation. J. Neuroimmunol. 2023, 383, 578180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Tong, F.; Li, H.; Bin, Y.; Ding, P.; Peng, L.; Liu, Z.; Dong, X. Maturation, Morphology, and Function: The Decisive Role of Intestinal Flora on Microglia: A Review. J. Integr. Neurosci. 2023, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roshanipour, N.; Shahriyari, E.; Ghaffari Laleh, M.; Vahedi, L.; Mirjand Gerami, S.; Khamaneh, A. Associations of TLR4 and IL-8 genes polymorphisms with age-related macular degeneration (AMD): A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmic Genet. 2021, 42, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetab Boushehri, M.A.; Lamprecht, A. TLR4-Based Immunotherapeutics in Cancer: A Review of the Achievements and Shortcomings. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4777–4800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Deng, Q.; Guo, M.; Li, X.; Xian, D.; Zhong, J. Proanthocyanidins: A novel approach to Henoch-Schonlein purpura through balancing immunity and arresting oxidative stress via TLR4/MyD88/NF-kappaB signaling pathway (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2023, 25, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhang, X. Efficacy of Acupuncture in Postoperative Pain-Relieving: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pain. Manag. Nurs. 2025, 26, 319–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardelli, J.D.C.; Gubitoso, B.; Botelho, A.L.; Valente, M.; Reis, A.C.D. Efficacy of acupuncture on craniomandibular myofascial pain in temporomandibular disorder patients: A systematic review. Heliyon 2024, 10, e32075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Satyanarayanan, S.K.; Lin, Y.W.; Su, K.P. Clinical efficacy and immune effects of acupuncture in patients with comorbid chronic pain and major depression disorder: A double-blinded, randomized controlled crossover study. Brain Behav. Immun. 2023, 110, 339–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates CFA-induced Inflammatory Pain by suppressing Nav1.8 through S100B, TRPV1, Opioid, and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, H.Y.; Hsieh, C.L.; Huang, C.P.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Induction of Inflammatory Pain by Regulating Opioid and Adenosine Pathways in Mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 15679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeh, Y.A.; Hsu, H.C.; Lin, M.C.; Chen, T.S.; Lin, W.C.; Huang, H.M.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Regulates Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression in a Mouse Fibromyalgia Model: Pharmacological and Chemogenetic Modulation. Life 2024, 14, 1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, H.C.; Park, H.J.; Liao, H.Y.; Chuang, K.T.; Lin, Y.W. Accurate Chemogenetics Determines Electroacupuncture Analgesia Through Increased CB1 to Suppress the TRPV1 Pathway in a Mouse Model of Fibromyalgia. Life 2025, 15, 819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, P.C.; Yen, C.M.; Lin, M.C.; Chen, Y.H.; Liao, H.Y.; Huang, Y.W.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Attenuates Fibromyalgia Pain via Toll-like Receptor 4 in the Mouse Brain. Life 2023, 13, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anh, D.T.N.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture Mitigates TRPV1 Overexpression in the Central Nervous System Associated with Fibromyalgia in Mice. Life 2024, 14, 1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.W.; Chou, A.I.W.; Su, H.; Su, K.P. Transient receptor potential V1 (TRPV1) modulates the therapeutic effects for comorbidity of pain and depression: The common molecular implication for electroacupuncture and omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids. Brain Behav. Immun. 2020, 89, 604–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd-Ellatief, R.B.; Mohamed, H.K.; Kotb, H.I. Reactive Astrogliosis in an Experimental Model of Fibromyalgia: Effect of Dexmedetomidine. Cells Tissues Organs 2018, 205, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Hartung, J.E.; Bortsov, A.V.; Kim, S.; O’Buckley, S.C.; Kozlowski, J.; Nackley, A.G. Sustained stimulation of beta(2)-and beta(3)-adrenergic receptors leads to persistent functional pain and neuroinflammation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2018, 73, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, I.H.; Hsu, H.C.; Lin, I.Y.; Chuang, K.T.; Lin, Y.W. Eicosapentaenoic acid alleviates fibromyalgia-like pain by modulating microglia, astrocytes, and toll-Like receptor 4 signaling in the mice cerebellum. Nutr. Neurosci. 2025, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, D.S.; Forsberg, A.; Sandstrom, A.; Bergan, C.; Kadetoff, D.; Protsenko, E.; Lampa, J.; Lee, Y.C.; Hoglund, C.O.; Catana, C.; et al. Brain glial activation in fibromyalgia—A multi-site positron emission tomography investigation. Brain Behav. Immun. 2019, 75, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, B.; Hunyady, A.; Bencze, N.; Kormos, V.; Szentes, N.; Denes, A.; Lenart, N.; Borbely, E.; Helyes, Z. IL-1 Mediates Chronic Stress-Induced Hyperalgesia Accompanied by Microglia and Astroglia Morphological Changes in Pain-Related Brain Regions in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wakatsuki, K.; Kiryu-Seo, S.; Yasui, M.; Yokota, H.; Kida, H.; Konishi, H.; Kiyama, H. Repeated cold stress, an animal model for fibromyalgia, elicits proprioceptor-induced chronic pain with microglial activation in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2024, 21, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boehnke, K.F.; Gagnier, J.J.; Matallana, L.; Williams, D.A. Cannabidiol Use for Fibromyalgia: Prevalence of Use and Perceptions of Effectiveness in a Large Online Survey. J. Pain. 2021, 22, 556–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yassin, M.; Oron, A.; Robinson, D. Effect of adding medical cannabis to analgesic treatment in patients with low back pain related to fibromyalgia: An observational cross-over single centre study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2019, 37 (Suppl. S116), 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, C.; Bittencourt, P.C.T.; Pelegrini, A. Ingestion of a THC-Rich Cannabis Oil in People with Fibromyalgia: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trial. Pain. Med. 2020, 21, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, C.M.; Hsieh, C.L.; Lin, Y.W. Electroacupuncture reduces chronic fibromyalgia pain through attenuation of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 signaling pathway in mouse brains. Iran. J. Basic. Med. Sci. 2020, 23, 894–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, C.; Parkitny, L.; Strath, L.; Wagener, B.M.; Barker, A.; Younger, J. Altered response to Toll-like receptor 4 activation in fibromyalgia: A low-dose, human experimental endotoxemia pilot study. Brain Behav. Immun. Health 2023, 34, 100707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, S.; Singh, A.; Kant, R.; Surolia, A. TLR4 activation by lysozyme induces pain without inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1065226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, W.; Li, X.; Jing, B.; Chang, S.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, G.; Zhang, D. Stigmasterol regulates microglial M1/M2 polarization via the TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway to alleviate neuropathic pain. Phytother. Res. 2024, 38, 265–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncalves Dos Santos, G.; Li, R.; Ng, M.P.E.; Lemes, J.B.P.; Vieira, W.F.; Nagy, I.; Tambeli, C.H.; Parada, C.A. CB(1) receptor-dependent desensitisation of TRPV1 channels contributes to the analgesic effect of dipyrone in sensitised primary sensory neurons. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 4615–4626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hsiao, I.-H.; Lin, M.-C.; Hsu, H.-C.; Chae, Y.; Lin, I.-Y.; Lin, Y.-W. Electroacupuncture Relieves Fibromyalgia Pain in a Female Mouse Model by Augmenting Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Suppressing Astrocyte and Microglial Activation in Nociceptive Pathways. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092112
Hsiao I-H, Lin M-C, Hsu H-C, Chae Y, Lin I-Y, Lin Y-W. Electroacupuncture Relieves Fibromyalgia Pain in a Female Mouse Model by Augmenting Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Suppressing Astrocyte and Microglial Activation in Nociceptive Pathways. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(9):2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092112
Chicago/Turabian StyleHsiao, I-Han, Ming-Chia Lin, Hsin-Cheng Hsu, Younbyoung Chae, I-Ying Lin, and Yi-Wen Lin. 2025. "Electroacupuncture Relieves Fibromyalgia Pain in a Female Mouse Model by Augmenting Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Suppressing Astrocyte and Microglial Activation in Nociceptive Pathways" Biomedicines 13, no. 9: 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092112
APA StyleHsiao, I.-H., Lin, M.-C., Hsu, H.-C., Chae, Y., Lin, I.-Y., & Lin, Y.-W. (2025). Electroacupuncture Relieves Fibromyalgia Pain in a Female Mouse Model by Augmenting Cannabinoid Receptor 1 Expression and Suppressing Astrocyte and Microglial Activation in Nociceptive Pathways. Biomedicines, 13(9), 2112. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13092112





