Intestinal Dysbiosis and Immune Activation in Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Comparative Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Role of the Gut Microbiome in Health and Disease
3. KD
3.1. Epidemiology
3.2. Pathogenesis
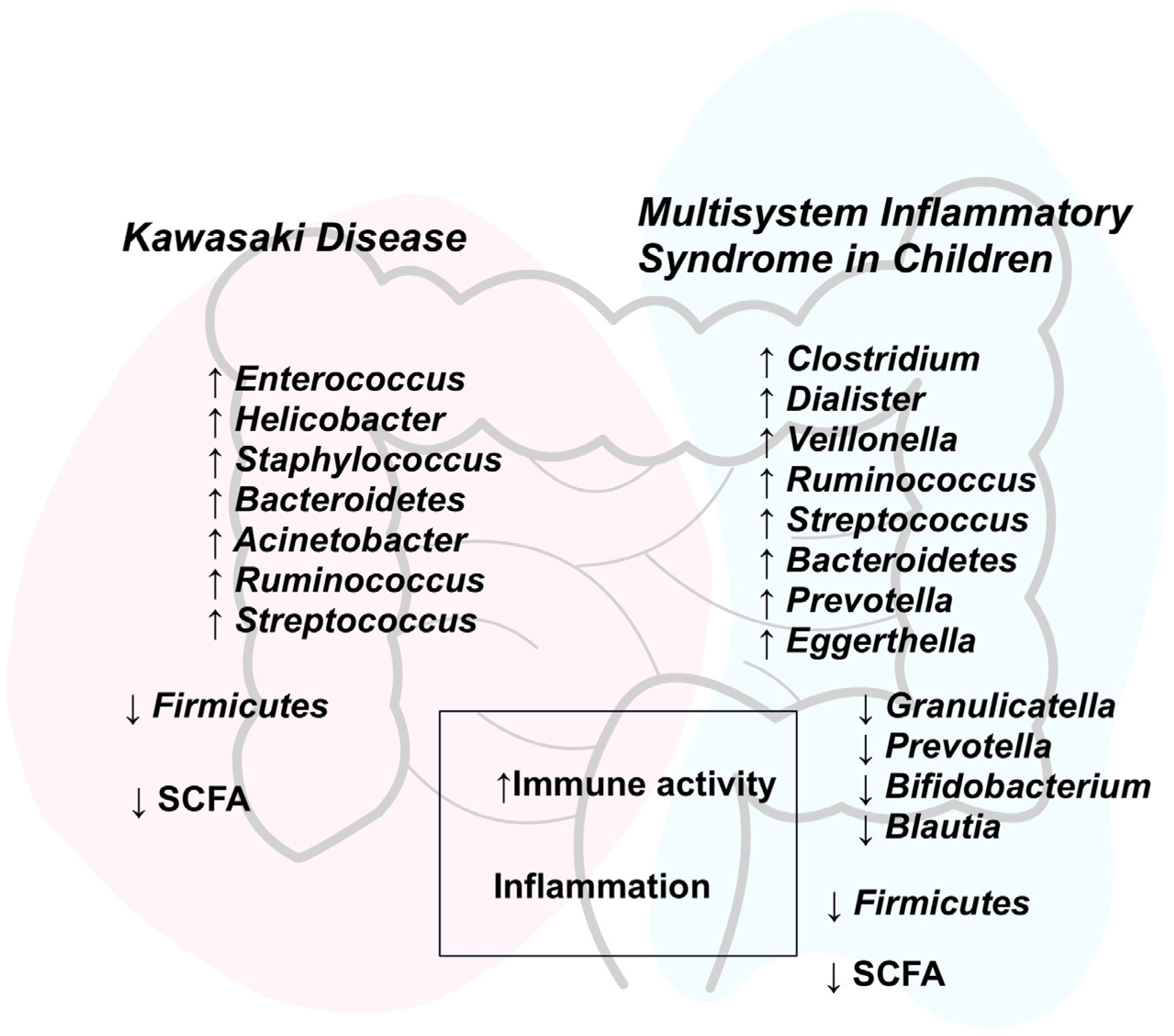
3.3. Intestinal Dysbiosis
3.4. Clinical Manifestation
4. MIS-C
4.1. Epidemiology
4.2. Pathogenesis
4.3. Intestinal Dysbiosis
4.4. Clinical Manifestation
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
- Recent years have seen advances in the understanding of gut dysbiosis in MIS-C and KD.
- SCFAs hold promise as adjunctive therapy, particularly in KD; however, this aspect remains underexplored in the context of MIS-C.
- Greater emphasis should be placed on scientific investigations into diagnostic and monitoring biomarkers.
- The analysis of long-term alterations in gut microbiota is essential due to potential clinical implications. Research on this topic in the context of MIS-C remains significantly limited.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| KD | Kawasaki Disease |
| PIMS | Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome |
| MIS-C | Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children |
| SCFA | Short-Chain Fatty Acid |
| GALT | Gut-Associated Lymphoid Tissue |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| Treg | T Regulatory Cells |
| Ig | Immunoglobulin |
| IL | Interleukin |
| IVIG | Intravenous Immunoglobulin |
| TGF | Transforming Growth Factor |
| TNF | Tumor Necrosis Factor |
| IFN | Interferon |
| NT-proBNP | N-Terminal Pro-Brain Natriuretic Peptide |
References
- Harahsheh, A.S.; Shah, S.; Dallaire, F.; Manlhiot, C.; Khoury, M.; Lee, S.; Fabi, M.; Mauriello, D.; Tierney, E.S.S.; Sabati, A.A.; et al. Kawasaki Disease in the Time of COVID-19 and MIS-C—The International Kawasaki Disease Registry. Can. J. Cardiol. 2023, 40, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolis, A.S.; Manolis, T.A. Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporally Associated With SARS-Cov-2 Infection (PIMS-TS): Kawasaki-Like Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) During the COVID-19 Pandemic with Predominant Myocarditis: Kawasaki-Like Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Rhythmos 2020, 15, 42–46. [Google Scholar]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Arditi, M. Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Common Inflammatory Pathways of Two Distinct Diseases. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 49, 647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, E.; Lang, D. Unraveling the Gut: The Pivotal Role of Intestinal Mechanisms in Kawasaki Disease Pathogenesis. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1496293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupu, A.; Gavrilovici, C.; Mihai, C.M.; Tonco, D.C.; Nedelcu, A.H.; Pertea, L.; Chisnoiu, T.; Baciu, G.; Stoicescu, R.M.; Salaru, D.L.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Kawasaki Disease. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1554787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suskun, C.; Kilic, O.; Yilmaz Ciftdogan, D.; Guven, S.; Karbuz, A.; Ozkaya Parlakay, A.; Kara, Y.; Kacmaz, E.; Sahin, A.; Boga, A.; et al. Intestinal Microbiota Composition of Children with Infection with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome (MIS-C). Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teramoto, Y.; Akagawa, S.; Hori, S.I.; Tsuji, S.; Higasa, K.; Kaneko, K. Dysbiosis of the Gut Microbiota as a Susceptibility Factor for Kawasaki Disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1268453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kogut, M.H.; Lee, A.; Santin, E. Microbiome and Pathogen Interaction with the Immune System. Poult. Sci. 2020, 99, 1906–1913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maciel-Fiuza, M.F.; Muller, G.C.; Campos, D.M.S.; do Socorro Silva Costa, P.; Peruzzo, J.; Bonamigo, R.R.; Veit, T.; Vianna, F.S.L. Role of Gut Microbiota in Infectious and Inflammatory Diseases. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1098386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kane, A.S.; Godfrey, M.; Rivas, M.N.; Arditi, M.; Fasano, A.; Yonker, L.M. The Spectrum of Postacute Sequelae of COVID-19 in Children: From MIS-C to Long COVID. Annu. Rev. Virol. 2024, 11, 327–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Yue, Y.; Wang, L.; Deng, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Zhao, M.; Yuan, Z.; Tan, C.; Cao, Y. Altered Gut Microbiota Correlated with Systemic Inflammation in Children with Kawasaki Disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Q.; Kang, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, M.; Zhao, C. Interplay of Gut Microbiota in Kawasaki Disease: Role of Gut Microbiota and Potential Treatment Strategies. Future Microbiol. 2025, 20, 357–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Comito, D.; Romano, C. Dysbiosis in the Pathogenesis of Pediatric Inflammatory Bowel Diseases. Int. J. Inflam. 2012, 2012, 687143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torun, A.; Hupalowska, A.; Trzonkowski, P.; Kierkus, J.; Pyrzynska, B. Intestinal Microbiota in Common Chronic Inflammatory Disorders Affecting Children. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 642166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuddenham, S.; Sears, C.L. The Intestinal Microbiome and Health. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2015, 28, 464–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Ramos, P.D.L.; García-Botella, A.; García-Lledó, A.; Hernández-Sampelayo, T.; Gómez-Pavón, J.; Del Castillo, J.G.; Martín-Delgado, M.C.; Sánchez, F.J.M.; Martínez-Sellés, M.; et al. Human Intestinal Microbiome: Role in Health and Disease. Rev. Española Quimioter. 2024, 37, 438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lynch, S.V.; Pedersen, O. The Human Intestinal Microbiome in Health and Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2369–2379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, C.; Barman, D.; Tripathi, D.; Dutta, S.; Bhattacharya, C.; Alam, M.; Choudhury, P.; Devi, U.; Mahanta, J.; Rasaily, R.; et al. Influence of Maternal Breast Milk and Vaginal Microbiome on Neonatal Gut Microbiome: A Longitudinal Study during the First Year. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e04967-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suárez-Martínez, C.; Santaella-Pascual, M.; Yagüe-Guirao, G.; Martínez-Graciá, C. Infant Gut Microbiota Colonization: Influence of Prenatal and Postnatal Factors, Focusing on Diet. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1236254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, L.; Jin, B.; Xu, X.; Zuo, X.; Li, Y.; Li, Z. The Effects of Delivery Mode on the Gut Microbiota and Health: State of Art. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 724449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollister, E.B.; Riehle, K.; Luna, R.A.; Weidler, E.M.; Rubio-Gonzales, M.; Mistretta, T.A.; Raza, S.; Doddapaneni, H.V.; Metcalf, G.A.; Muzny, D.M.; et al. Structure and Function of the Healthy Pre-Adolescent Pediatric Gut Microbiome. Microbiome 2015, 3, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, B.; Salonen, A.; Ponsero, A.J.; Jokela, R.; Kolho, K.L.; de Vos, W.M.; Korpela, K. Gut Microbiota Wellbeing Index Predicts Overall Health in a Cohort of 1000 Infants. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinninella, E.; Raoul, P.; Cintoni, M.; Franceschi, F.; Miggiano, G.A.D.; Gasbarrini, A.; Mele, M.C. What Is the Healthy Gut Microbiota Composition? A Changing Ecosystem across Age, Environment, Diet, and Diseases. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adak, A.; Khan, M.R. An Insight into Gut Microbiota and Its Functionalities. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 76, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Selwi, A.G.M.; Barkat, A. Composition and Development of the Intestinal Microbiome in Children and Its Changes with Certain Pathologies (Cystic Fibrosis, Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome, Type 1 Diabetes, and Autism): Meta-Analysis. Egypt. J. Hosp. Med. 2023, 90, 636–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Yan, D.; Chen, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Qian, G. Recent Insights and Advances in Gut Microbiota’s Influence on Host Antiviral Immunity. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1536778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Bemark, M.; Spencer, J. Human Gut-associated Lymphoid Tissue: A Dynamic Hub Propagating Modulators of Inflammation. Clin. Transl. Med. 2023, 13, e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, H.; Arbab, S.; Tian, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, C.Q.; Li, Q.; Li, K. Crosstalk between Gut Microbiota and Host Immune System and Its Response to Traumatic Injury. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1413485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spragge, F.; Bakkeren, E.; Jahn, M.T.; Araujo, E.B.N.; Pearson, C.F.; Wang, X.; Pankhurst, L.; Cunrath, O.; Foster, K.R. Microbiome Diversity Protects against Pathogens by Nutrient Blocking. Science 2023, 382, eadj3502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xiao, L.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, H. The Microbiota: A Crucial Mediator in Gut Homeostasis and Colonization Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1417864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Chai, Z.; Chen, S.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhou, Y. Intestinal Mucus Components and Secretion Mechanisms: What We Do and Do Not Know. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jandhyala, S.M.; Talukdar, R.; Subramanyam, C.; Vuyyuru, H.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Role of the Normal Gut Microbiota. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 8787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan Pillai, S.; Gagnon, C.A.; Foster, C.; Ashraf, A.P. Exploring the Gut Microbiota: Key Insights Into Its Role in Obesity, Metabolic Syndrome, and Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 2709–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Ju, D.; Zeng, X. Mechanisms and Clinical Implications of Human Gut Microbiota-Drug Interactions in the Precision Medicine Era. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, M.E.; Boles, J.S.; Simon, Z.D.; Alvarez, S.D.; McFarland, N.R.; Okun, M.S.; Zimmermann, E.M.; Forsmark, C.E.; Tansey, M.G. Comparative Analysis of Parkinson’s and Inflammatory Bowel Disease Gut Microbiomes Reveals Shared Butyrate-Producing Bacteria Depletion. NPJ Park. Dis. 2025, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barone, M.; D’Amico, F.; Brigidi, P.; Turroni, S. Gut Microbiome–Micronutrient Interaction: The Key to Controlling the Bioavailability of Minerals and Vitamins? Biofactors 2022, 48, 307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Feng, X.; Hu, Y.; Su, S. The Human Gut Microbiota Is Associated with Host Lifestyle: A Comprehensive Narrative Review. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 16, 1549160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, N.; Saeed, A.; Ashfaq, A.; Haider, S.; Shah, A.; Jurrat, H.; Ansar, W.; Nazir, Z.; Musaddaq, R.; Khan, H.R.; et al. The Role of Lifestyle in Modulating the Gut Microbiome: Lifestyle and Gut Microbiome. Future Biotechnol. 2025, 5, 10–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopera-Maya, E.A.; Kurilshikov, A.; van der Graaf, A.; Hu, S.; Andreu-Sánchez, S.; Chen, L.; Vila, A.V.; Gacesa, R.; Sinha, T.; Collij, V.; et al. Effect of Host Genetics on the Gut Microbiome in 7738 Participants of the Dutch Microbiome Project. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 143–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- David, L.A.; Maurice, C.F.; Carmody, R.N.; Gootenberg, D.B.; Button, J.E.; Wolfe, B.E.; Ling, A.V.; Devlin, A.S.; Varma, Y.; Fischbach, M.A.; et al. Diet Rapidly and Reproducibly Alters the Human Gut Microbiome. Nature 2014, 505, 559–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, S.; Jung, S.C.; Kwak, K.; Kim, J.S. The Role of Prebiotics in Modulating Gut Microbiota: Implications for Human Health. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 4834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafe, A.N.; Edo, G.I.; Majeed, O.S.; Gaaz, T.S.; Akpoghelie, P.O.; Isoje, E.F.; Igbuku, U.A.; Owheruo, J.O.; Opiti, R.A.; Garba, Y.; et al. A Review on Probiotics and Dietary Bioactives: Insights on Metabolic Well-Being, Gut Microbiota, and Inflammatory Responses. Food Chem. Adv. 2025, 6, 100919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asefa, Z.; Belay, A.; Welelaw, E.; Haile, M. Postbiotics and Their Biotherapeutic Potential for Chronic Disease and Their Feature Perspective: A Review. Front. Microbiomes 2025, 4, 1489339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smolinska, S.; Popescu, F.D.; Zemelka-Wiacek, M. A Review of the Influence of Prebiotics, Probiotics, Synbiotics, and Postbiotics on the Human Gut Microbiome and Intestinal Integrity. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 3673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.P.; Bhoraniya, S.J.; Kalola, S.D.; Rukadikar, A.; Ravi, R.; Farooqui, S.; Rukadikar, C. Gut Microbiota and Its Impact on Chronic Diseases: A Comprehensive Review. J. Pharm. Bioallied Sci. 2025, 17, S1080–S1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hul, M.; Cani, P.D.; Petifils, C.; De Vos, W.M.; Tilg, H.; El Omar, E.M. What Defines a Healthy Gut Microbiome? Gut 2024, 73, 1893–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shulman, S.T.; De Inocencio, J.; Hirsch, R. Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 1995, 42, 1205–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedrich, C.M.; Schnabel, A.; Hospach, T. Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 373670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundel, R.P. Kawasaki Disease. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2015, 41, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T. Kawasaki Disease. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2014, 17, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, E.; Sundel, R. Kawasaki Disease at 50 Years. JAMA Pediatr. 2016, 170, 1093–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scuccimarri, R. Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 59, 425–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newburger, J.W.; Takahashi, M.; Burns, J.C. Kawasaki Disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1738–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnden, A.; Takahashi, M.; Burgner, D. Kawasaki Disease. BMJ 2009, 338, 1133–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dionne, A.; Newburger, J.W. Kawasaki Disease. In Nadas’ Pediatric Cardiology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 567–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rife, E.; Gedalia, A. Kawasaki Disease: An Update. Curr. Rheumatol. Rep. 2020, 22, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Manubens, J.; Bou, R.; Anton, J. Diagnosis and Classification of Kawasaki Disease. J. Autoimmun. 2014, 48–49, 113–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleftheriou, D.; Levin, M.; Shingadia, D.; Tulloh, R.; Klein, N.J.; Brogan, P.A. Management of Kawasaki Disease. Arch. Dis. Child. 2014, 99, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onouchi, Y. The Genetics of Kawasaki Disease. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 26–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rowley, A.H.; Shulman, S.T. The Epidemiology and Pathogenesis of Kawasaki Disease. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 427762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W. Kawasaki Disease. Pediatr. Rev. 2018, 39, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beckley, M.A.; Shrestha, S.; Singh, K.K.; Portman, M.A. The Role of Mitochondria in the Pathogenesis of Kawasaki Disease. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1017401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, K.; Akagawa, S.; Akagawa, Y.; Kimata, T.; Tsuji, S. Our Evolving Understanding of Kawasaki Disease Pathogenesis: Role of the Gut Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 555472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porritt, R.A.; Zemmour, D.; Abe, M.; Lee, Y.; Narayanan, M.; Carvalho, T.T.; Gomez, A.C.; Martinon, D.; Santiskulvong, C.; Fishbein, M.C.; et al. NLRP3 Inflammasome Mediates Immune-Stromal Interactions in Vasculitis. Circ. Res. 2021, 129, E183–E200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.Y.; Qi, H.R. Pyroptosis in Kawasaki Disease: From Mechanisms to Targeted Interventions. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1566985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Jia, S.; Xue, X.; Guo, C.; Dong, K. Gut Microbiota: A Novel Target for Exercise-Mediated Regulation of NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. Front. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1476908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.K.; Arditi, M.; Noval Rivas, M. Gut Microbiota Alterations in Patients with Kawasaki Disease. Arter. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2025, 45, 345–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinumaki, A.; Sekizuka, T.; Hamada, H.; Kato, K.; Yamashita, A.; Kuroda, M. Characterization of the Gut Microbiota of Kawasaki Disease Patients by Metagenomic Analysis. Front. Microbiol. 2015, 6, 141697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundel, R.P.; Petty, R.E. Kawasaki Disease. In Textbook of Pediatric Rheumatology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 505–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saguil, A.; Fargo, M.; Grogan, S.; Eisenhower, D.D. Diagnosis and Management of Kawasaki Disease. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 91, 365–371. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Jindal, A.K.; Pilania, R.K. Diagnosis of Kawasaki Disease. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 21, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burns, J.C. The Etiologies of Kawasaki Disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2024, 134, e176938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noval Rivas, M.; Arditi, M. Kawasaki Disease: Pathophysiology and Insights from Mouse Models. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 391–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harnden, A.; Tulloh, R.; Burgner, D. Kawasaki Disease. BMJ 2014, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Tang, K.; Levin, M.; Irfan, O.; Morris, S.K.; Wilson, K.; Klein, J.D.; Bhutta, Z.A. COVID-19 and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Adolescents. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e276–e288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consiglio, C.R.; Cotugno, N.; Sardh, F.; Pou, C.; Amodio, D.; Rodriguez, L.; Tan, Z.; Zicari, S.; Ruggiero, A.; Pascucci, G.R.; et al. The Immunology of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children with COVID-19. Cell 2020, 183, 968–981.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, L.; Van Paemel, R.; Haerynck, F. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Related to COVID-19: A Systematic Review. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2021, 180, 2019–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, A.D.; Zambrano, L.D.; Yousaf, A.R.; Abrams, J.Y.; Meng, L.; Wu, M.J.; Melgar, M.; Oster, M.E.; Godfred Cato, S.E.; Belay, E.D.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children—United States, February 2020–July 2021. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, 75, e1165–e1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, C.; Ganigara, M.; Galeotti, C.; Burns, J.; Berganza, F.M.; Hayes, D.A.; Singh-Grewal, D.; Bharath, S.; Sajjan, S.; Bayry, J. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Kawasaki Disease: A Critical Comparison. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2021, 17, 731–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radia, T.; Williams, N.; Agrawal, P.; Harman, K.; Weale, J.; Cook, J.; Gupta, A. Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome in Children & Adolescents (MIS-C): A Systematic Review of Clinical Features and Presentation. Paediatr. Respir. Rev. 2021, 38, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esposito, S.; Principi, N. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children Related to SARS-CoV-2. Pediatr. Drugs 2021, 23, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, L.R.; Rose, E.B.; Horwitz, S.M.; Collins, J.P.; Newhams, M.M.; Son, M.B.F.; Newburger, J.W.; Kleinman, L.C.; Heidemann, S.M.; Martin, A.A.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in U.S. Children and Adolescents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 334–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sacco, K.; Castagnoli, R.; Vakkilainen, S.; Liu, C.; Delmonte, O.M.; Oguz, C.; Kaplan, I.M.; Alehashemi, S.; Burbelo, P.D.; Bhuyan, F.; et al. Immunopathological Signatures in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children and Pediatric COVID-19. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1050–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeoh, Y.K.; Zuo, T.; Lui, G.C.Y.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Q.; Li, A.Y.L.; Chung, A.C.K.; Cheung, C.P.; Tso, E.Y.K.; Fung, K.S.C.; et al. Gut Microbiota Composition Reflects Disease Severity and Dysfunctional Immune Responses in Patients with COVID-19. Gut 2021, 70, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavounidis, A.; Alderson, J.; Quastel, M. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: Getting to the Heart of the Matter. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2020, 20, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zari, A.; Redwan, E.M.; Raszek, M.; Cowley, D.; Hromić-Jahjefendić, A.; Uversky, V.N.; Fabrowski, M.; Brogna, C.; Piscopo, M.; Rubio-Casillas, A. Interplay between Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children, Interleukin 6, Microbiome, and Gut Barrier Integrity. Immuno 2024, 4, 226–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romani, L.; Del Chierico, F.; Macari, G.; Pane, S.; Ristori, M.V.; Guarrasi, V.; Gardini, S.; Pascucci, G.R.; Cotugno, N.; Perno, C.F.; et al. The Relationship Between Pediatric Gut Microbiota and SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12, 908492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malicevic, U.; Rai, V.; Skrbic, R.; Agrawal, D.K. NLRP3 Inflammasome and Gut Dysbiosis Linking Diabetes Mellitus and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Arch. Intern. Med. Res. 2024, 7, 200–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dufort, E.M.; Koumans, E.H.; Chow, E.J.; Rosenthal, E.M.; Muse, A.; Rowlands, J.; Barranco, M.A.; Maxted, A.M.; Rosenberg, E.S.; Easton, D.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children in New York State. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.B.F.; Burns, J.C.; Newburger, J.W. A New Definition for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Pediatrics 2023, 151, e2022060302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, M.; Advani, S.; Moreira, A.; Zoretic, S.; Martinez, J.; Chorath, K.; Acosta, S.; Naqvi, R.; Burmeister-Morton, F.; Burmeister, F.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Systematic Review. eClinicalMedicine 2020, 26, 100527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, J.M. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022, 22, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaied, T.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Burns, J.C.; Saidi, A.; Dionne, A.; Lang, S.M.; Newburger, J.W.; de Ferranti, S.; Friedman, K.G. Review of Cardiac Involvement in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Circulation 2021, 143, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bautista-Rodriguez, C.; Sanchez-De-Toledo, J.; Clark, B.C.; Herberg, J.; Bajolle, F.; Randanne, P.C.; Salas-Mera, D.; Foldvari, S.; Chowdhury, D.; Munoz, R.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: An International Survey. Pediatrics 2021, 147, e2020024554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooqi, K.M.; Chan, A.; Weller, R.J.; Mi, J.; Jiang, P.; Abrahams, E.; Ferris, A.; Krishnan, U.S.; Pasumarti, N.; Suh, S.; et al. Longitudinal Outcomes for Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021051155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McArdle, A.J.; Vito, O.; Patel, H.; Seaby, E.G.; Shah, P.; Wilson, C.; Broderick, C.; Nijman, R.; Tremoulet, A.H.; Munblit, D.; et al. Treatment of Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, M.B.F.; Murray, N.; Friedman, K.; Young, C.C.; Newhams, M.M.; Feldstein, L.R.; Loftis, L.L.; Tarquinio, K.M.; Singh, A.R.; Heidemann, S.M.; et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children—Initial Therapy and Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, M.; Shariff, M.A.; Tay, E.T.; Mortel, D.; Savadkar, S.; Lee, H.; Kondamudi, N.; Liang, T. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. J. Emerg. Med. 2022, 62, 28–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capone, C.A.; Misra, N.; Ganigara, M.; Epstein, S.; Rajan, S.; Acharya, S.S.; Hayes, D.A.; Kearney, M.B.; Romano, A.; Friedman, R.A.; et al. Six Month Follow-up of Patients with Multi-System Inflammatory Syndrome in Children. Pediatrics 2021, 148, e2021050973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alfalasi, M.; Snobar, R.; Shaalan, I.; Alkhaaldi, A.; Khawaja, K.; Aldhanhani, H.; Ghatasheh, G.; Mahmood, K.; Aljaberi, N. Kawasaki Disease in the Pre- and Post-COVID-19 Era: Shifts in Patterns and Outcomes from a Multi-Center Study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2025, 184, 367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Liao, J.; Xiang, L.; Zhang, S.; Yan, Y. Current Knowledge of TNF-α Monoclonal Antibody Infliximab in Treating Kawasaki Disease: A Comprehensive Review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1237670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Ma, L.; Su, W.; Liu, Y.; Xie, N.; Liu, J. NLRP3 Inflammasome in Health and Disease (Review). Int. J. Mol. Med. 2025, 55, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchitti, E.; Bottino, P.; Sidoti, F.; Carpino, A.; Pruccoli, G.; Ramenghi, U.; Costa, C.; Ala, U.; Parodi, E.; Traversi, D. Investigating the Role of Gut Microbiota in Pediatric Patients with Severe COVID-19 or MIS-C. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, T.; Yamamura, K.; Sakai, Y. The Up-to-Date Pathophysiology of Kawasaki Disease. Clin. Transl. Immunol. 2021, 10, e1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feleszko, W.; Okarska-Napierała, M.; Buddingh, E.P.; Bloomfield, M.; Sediva, A.; Bautista-Rodriguez, C.; Brough, H.A.; Eigenmann, P.A.; Eiwegger, T.; Eljaszewicz, A.; et al. Pathogenesis, Immunology, and Immune-Targeted Management of the Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) or Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome (PIMS): EAACI Position Paper. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2023, 34, e13900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.M.; Gupta, R.; Desai, N.; Desai, S.S.; Gowri, V.; Shobhavat, L.; Gupta, M.; Bargir, U.A.; Jodhawat, N.; Surve, S.; et al. Understanding the Relevance of Immunological Markers in Severe Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children through Machine Learning. J. Lab. Physicians 2024, 16, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hufnagel, M.; Armann, J.; Jakob, A.; Doenhardt, M.; Diffloth, N.; Hospach, A.; Schneider, D.T.; Trotter, A.; Roessler, M.; Schmitt, J.; et al. A Comparison of Pediatric Inflammatory Multisystem Syndrome Temporarily-Associated with SARS-CoV-2 and Kawasaki Disease. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, C.; Wei, Z.; Li, X. Identification of Novel Metabolism-Related Biomarkers of Kawasaki Disease by Integrating Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Analysis and Machine Learning Algorithms. Front. Immunol. 2025, 16, 1541939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, H.C. Diagnosis, Progress, and Treatment Update of Kawasaki Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, A.; Kumar, N.P.; Hanna, L.E.; Putlibai, S.; Karthick, M.; Rajamanikam, A.; Sadasivam, K.; Sundaram, B.; Babu, S. Plasma Biomarker Profiling of PIMS-TS, COVID-19 and SARS-CoV2 Seropositive Children—A Cross-Sectional Observational Study from Southern India. eBioMedicine 2021, 66, 103317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaňková, L.; Bufka, J.; Křížková, V. Pathophysiological and Clinical Point of View on Kawasaki Disease and MIS-C. Pediatr. Neonatol. 2023, 64, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Zeng, R.; Ye, J. Alteration of the Oral and Gut Microbiota in Patients with Kawasaki Disease. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Luo, G.; Ji, Z.; Pan, S. No Causal Association between Gut Microbiota and Kawasaki Disease: A Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Pediatr. Res. 2025, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, L.; Liu, X.; Lan, Y.; Hua, Y.; Fan, Z.; Li, Y. Metagenomic Analysis Demonstrates Distinct Changes in the Gut Microbiome of Kawasaki Diseases Children. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1416185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Pilania, R.K.; Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Dhaliwal, M.; Rawat, A.; Singh, S. Kawasaki Disease and the Environment: An Enigmatic Interplay. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1259094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jena, P.K.; Wakita, D.; Gomez, A.C.; Carvalho, T.T.; Atici, A.E.; Narayanan, M.; Lee, Y.; Fishbein, M.C.; Cani, P.D.; de Vos, W.M.; et al. The Intestinal Microbiota Contributes to the Development of Immune-Mediated Cardiovascular Inflammation and Vasculitis in Mice. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Qian, F.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, J.; Cen, J.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, J.; Luo, M.; Jia, C.; Rong, X.; et al. The Reduced SCFA-Producing Gut Microbes Are Involved in the Inflammatory Activation in Kawasaki Disease. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1124118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martindale, R.G.; Mundi, M.S.; Hurt, R.T.; McClave, S.A. Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Clinical Practice: Where Are We? Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 2025, 28, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.Y.; Khachatryan, L.G.; Younis, N.K.; Mustafa, M.A.; Ahmad, N.; Athab, Z.H.; Polyanskaya, A.V.; Kasanave, E.V.; Mirzaei, R.; Karampoor, S. Microbiota-Derived Short Chain Fatty Acids in Pediatric Health and Diseases: From Gut Development to Neuroprotection. Front. Microbiol. 2024, 15, 1456793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, B.; Julia, B.; Małgorzata, B.; Natalia, D.; Halina Manifestations, P.-S.; Brzyska, A.; Bogucka, J.; Bojarska, M.; Domańska, N.; Piecewicz-Szczęsna, H. Manifestations of the Pediatric Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome Temporally Related with SARS-CoV-2 (PIMS) in the Gastrointestinal, Cardiovascular, Nervous and Respiratory Systems. J. Educ. Health Sport. 2022, 12, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Zhang, D.Y.; Chen, S.J.; Lv, Y.T.; Huang, S.M.; Chen, C.; Zeng, F.; Chen, R.X.; Zhang, X.D.; Xiong, J.X.; et al. Long-Term Alterations in Gut Microbiota Following Mild COVID-19 Recovery: Bacterial and Fungal Community Shifts. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2025, 15, 1565887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| KD | PIMS/MIS-C | |
|---|---|---|
| Epidemiology | 0.01% of children, mostly aged <5 y.o. [47,48,49]. | 0.002% of people, mostly aged <21 y.o. with a mean age of 8 y.o. [81]. |
| Trigger | A genetic predisposition and post-infectious influence have been suggested [48]. | Associated with SARS-CoV2 infection occurring typically 4–6 weeks after [76]. |
| Main clinical features | Fever, rash, conjunctivitis, cervical lymphadenopathy, and swelling or erythema of the hands and feet [47]. | Fever, mucocutaneous manifestations, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and shock [82]. |
| Gut dysbiosis | A decrease in SCFA-producing bacteria and an increase in proinflammatory bacterial species [7,67]. | It plays a significant role in disruption of the intestinal barrier and modulating immune responses [86]. |
| Cardiac abnormalities | Coronary artery aneurysms, mitral valve regurgitation, pericardial effusion, myocarditis, and impaired left ventricular function [57,70,71]. | Reduced ejection fraction, myocarditis, and cardiogenic shock [80,91,92]. |
| Laboratory abnormalities | Elevated CRP, thrombocytosis, anemia, hypoalbuminemia, elevated transaminase levels, neutrophilia [70,71]. | Elevated CRP, neutrophilia, lymphopenia, increased troponin T levels, elevated pro-BNP, elevated D-dimer levels, thrombocytopenia [80]. |
| Treatment | IVIG + asprin, corticosteroids, and/or biologic agents [70]. | IVIG, corticosteroids, and biologic agents [92]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soczyńska, J.; Topola, E.; Gawełczyk, W.; Viscardi, S.; Butyńska, K.; Woźniak, S. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Immune Activation in Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Comparative Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081953
Soczyńska J, Topola E, Gawełczyk W, Viscardi S, Butyńska K, Woźniak S. Intestinal Dysbiosis and Immune Activation in Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Comparative Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(8):1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081953
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoczyńska, Julia, Ewa Topola, Wiktor Gawełczyk, Szymon Viscardi, Kamila Butyńska, and Sławomir Woźniak. 2025. "Intestinal Dysbiosis and Immune Activation in Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Comparative Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations" Biomedicines 13, no. 8: 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081953
APA StyleSoczyńska, J., Topola, E., Gawełczyk, W., Viscardi, S., Butyńska, K., & Woźniak, S. (2025). Intestinal Dysbiosis and Immune Activation in Kawasaki Disease and Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children: A Comparative Review of Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations. Biomedicines, 13(8), 1953. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13081953







