PEDF and Its Role in Metabolic Disease, Angiogenesis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. PEDF and Physiological Angiogenesis
3. Using Exogenous PEDF to Curb Angiogenesis in the Eye
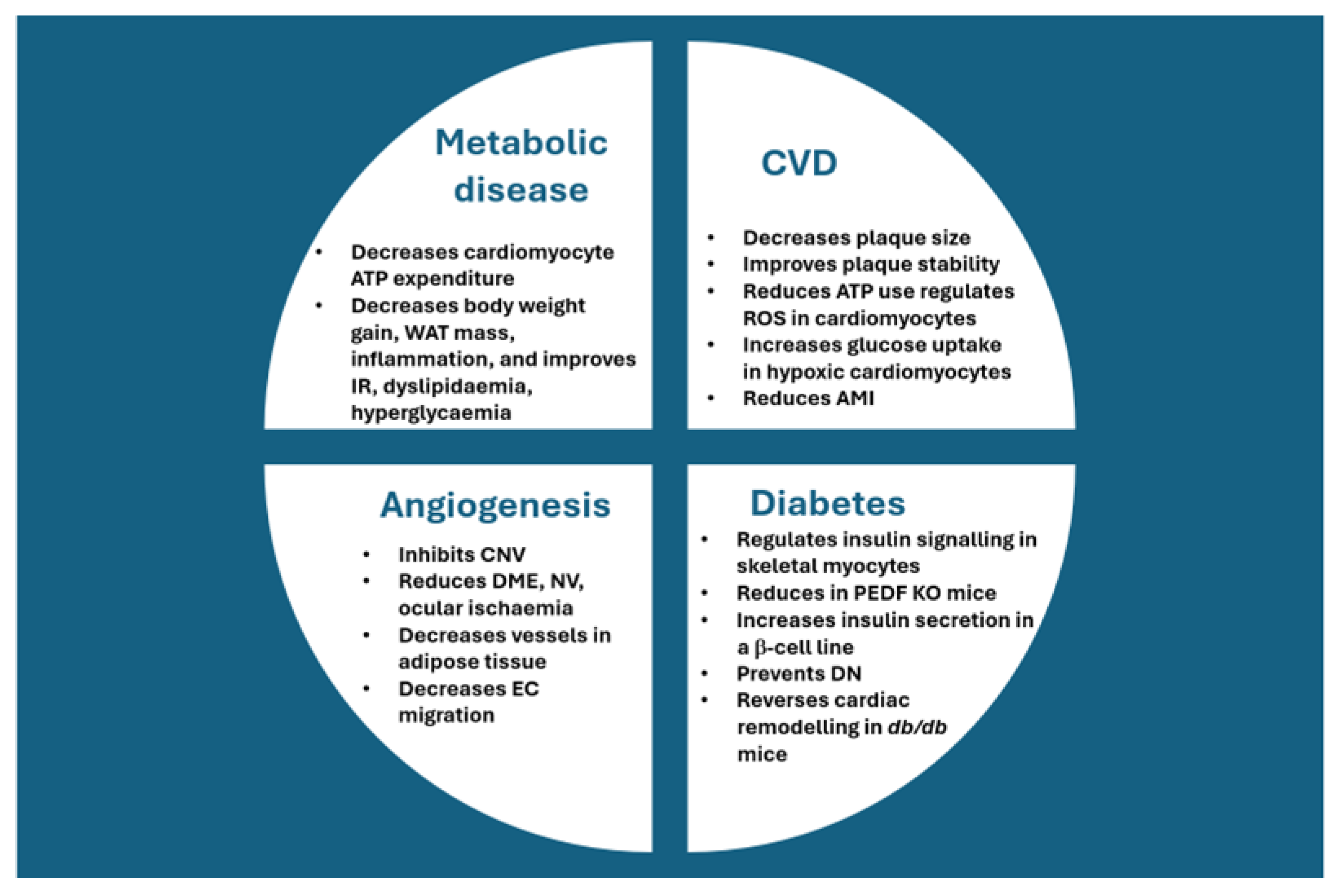
4. Administration of PEDF for Dampening of Angiogenesis in Other Conditions
5. PEDF and Diabetes
6. PEDF and Metabolism
7. PEDF and Cardiovascular Disease/Disorders (CVDs)
8. Future Directions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADAMTS5 | A disintegrin and metalloproteinase with thrombospondin motifs 5 |
| PKB | Protein kinase B |
| AMI | Acute myocardial infarction |
| AMPK | Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase |
| ATGL | Adipose triglyceride lipase |
| CKD | Chronic kidney disease |
| CVD | Cardiovascular disease |
| DN | Diabetic nephropathy |
| DR | Diabetic retinopathy |
| EC | Endothelial cell |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| EGFR | Epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ERK | Extracellular signal-regulated kinase |
| GLUT | Glucose transporter |
| Hcg | Human chorionic gonadotropin |
| HUVEC | Human umbilical vein EC |
| Inos | Inducible nitric oxide synthase |
| IRS | Insulin receptor substrate |
| JNK | c-Jun N-terminal kinase |
| KO | Knockout |
| MAPK | Mitogen-activated protein kinase |
| MVD | Microvessel density |
| MGC | Müller glial cell |
| MSC | Mesenchymal stem cell |
| OGD | Oxygen-glucose deprivation |
| OHSS | Ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome |
| OIR | Oxygen-induced retinopathy |
| OxLDL | Oxidised low-density lipoprotein |
| P13K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PEDF | Pigment epithelium-derived factor |
| PPAR-γ | Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma |
| RES | Resveratrol |
| ROS | Reactive oxygen species |
| RPE | Retinal pigment epithelium |
| SERPIN | Serine protease inhibitor |
| Sev | Small extracellular vesicle |
| SSc | Systemic sclerosis |
| TGF-β | Transforming growth factor β |
| VCAM-1 | Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 |
| VEGF | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor |
| Wnt | Wingless-related integration site |
References
- Xu, X.; Zhang, S.S.-M.; Barnstable, C.J.; Tombran-Tink, J. Molecular phylogeny of the antiangiogenic and neurotrophic serpin, pigment epithelium derived factor in vertebrates. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lucas, A.; Yaron, J.R.; Zhang, L.; Ambadapadi, S. Overview of serpins and their roles in biological systems. Methods Mol. Biol. 2018, 1826, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, J.; Wang, S.; Chen, J.; Yang, X.; Gao, G.; Zhou, T. The comparison of pathogenic role and mechanism of Kallistatin and PEDF in tumors. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Rev. Cancer 2025, 1880, 189273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanrattana, W.; Maas, C.; de Maat, S. SERPINs—From Trap to Treatment. Front. Med. 2019, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombran-Tink, J. The neuroprotective and angiogenesis inhibitory serpin, PEDF: New insights into phylogeny, function, and signaling. Front. Biosci. 2005, 10, 2131–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmi, M.; Dass, J.H.; Dass, C.R. The Various Roles of PEDF in Cancer. Cancers 2024, 16, 510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Wang, Z.; Wang, S.; Lyu, J.; Fang, Z.; Qi, W.; Yang, X.; Gao, G.; Zhou, T. Probing the familial ties between serpin members Kallistatin and PEDF: A comparative analysis review. Life Sci. 2024, 362, 123333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, E.K.; Francis, M.K.; Knepper, J.E. Recombinant pigment epithelium-derived factor PEDF binds vascular endothelial growth factor receptors 1 and 2. Vir. Cell. Dev. Biol.-Anim. 2015, 51, 730–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, E.S.; Sorenson, C.M.; Sheibani, N. PEDF expression regulates the proangiogenic and proinflammatory phenotype of the lung endothelium. Am. J. Physiol. Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L620–L634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gorman, E.A.; O’kAne, C.M.; McAuley, D.F. Acute respiratory distress syndrome in adults: Diagnosis, outcomes, long-term sequelae, and management. Lancet 2022, 400, 1157–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Q.; Shen, N.; Liang, J.; Qin, X.; Feng, S.; Chen, Y.; Xu, L. Relationship between VEGF to PEDF ratio and in-hospital mortality in acute respiratory distress syndrome patients. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falero-Perez, J.; Park, S.; Sorenson, C.M.; Sheibani, N. PEDF expression affects retinal endothelial cell proangiogenic properties through alterations in cell adhesive mechanisms. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2017, 313, C405–C420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, N.; Bano, A.; Rahman, M.A.; Guo, J.; Kang, Z.; Babar, M.A. Comparative physiological and metabolic analysis reveals a complex mechanism involved in drought tolerance in Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) induced by PGPR and PGRs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głodkowska-Mrówka, E.; Górska, E.; Ciurzyński, M.; Stelmaszczyk-Emmel, A.; Bienias, P.; Irzyk, K.; Siwicka, M.; Lipińska, A.; Ciepiela, O.; Pruszczyk, P.; et al. Pro- and antiangiogenic markers in patients with pulmonary complications of systemic scleroderma. Respir. Physiol. Neurobiol. 2015, 209, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawson, D.W.; Volpert, O.V.; Gillis, P.; Crawford, S.E.; Xu, H.-J.; Benedict, W.; Bouck, N.P. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor: A Potent Inhibitor of Angiogenesis. Science 1999, 285, 245–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, J.A.; Stellmach, V.M.; Bouck, N.P.; Bergh, A.R.; Lee, C.; Abramson, L.P.; Cornwell, M.L.; Pins, M.R.; Borensztajn, J.; Crawford, S.E. Pigment epithelium–derived factor regulates the vasculature and mass of the prostate and pancreas. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 774–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cosgrove, G.P.; Brown, K.K.; Schiemann, W.P.; Serls, A.E.; Parr, J.E.; Geraci, M.W.; Schwarz, M.I.; Cool, C.D.; Worthen, G.S. Pigment epithelium-derived factor in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A role in aberrant angiogenesis. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2004, 170, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liakouli, V.; Elies, J.; El-Sherbiny, Y.M.; Scarcia, M.; Grant, G.; Abignano, G.; Derrett-Smith, E.C.; Esteves, F.; Cipriani, P.; Emery, P.; et al. Scleroderma fibroblasts suppress angiogenesis via TGF-β/caveolin-1 dependent secretion of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2018, 77, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, M.; McLaughlin, B.; Weiss, J.; Griffiths, C. Levels of endothelial cell stimulating angiogenesis factor and vascular endothelial growth factor are elevated in psoriasis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1999, 141, 1054–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, M.; Mei, L.; Xiao, M.; Li, J.; Fang, F. Calcipotriol inhibits psoriasis-like angiogenic features in K14-VEGF transgenic mice. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2022, 32, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, Z.; Tan, J.; Xu, J.; Chen, Q.; Gu, P.; Dai, X.; Kuang, X.; Ji, S.; Liu, T.; Li, C. ADAMTS5 promotes neovascularization via autophagic degradation of PEDF in proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2023, 234, 109597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grigsby, J.G.; Parvathaneni, K.; Almanza, M.A.; Botello, A.M.; Mondragon, A.A.; Allen, D.M.; Tsin, A.T. Effects of Tamoxifen Versus Raloxifene on Retinal Capillary Endothelial Cell Proliferation. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 27, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parvathaneni, K.; Grigsby, J.G.; Betts, B.S.; Tsin, A.T. Estrogen-Induced Retinal Endothelial Cell Proliferation: Possible Involvement of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor and Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase/Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase Pathways. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 29, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ninio-Many, L.; Grossman, H.; Shomron, N.; Chuderland, D.; Shalgi, R. microRNA-125a-3p reduces cells proliferation and migration by targeting Fyn. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 2867–2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuderland, D.; Hasky, N.; Ben-Ami, I.; Kaplan-Kraicer, R.; Grossman, H.; Shalgi, R. A physiological approach for treating endometriosis by recombinant pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF). Hum. Reprod. 2013, 28, 1626–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bar-Joseph, H.; Ben-Ami, I.; Ron-El, R.; Shalgi, R.; Chuderland, D. Pigment epithelium-derived factor regulation by human chorionic gonadotropin in granulosa cells. Reproduction 2016, 151, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loegl, J.; Nussbaumer, E.; Hiden, U.; Majali-Martinez, A.; Ghaffari-Tabrizi-Wizy, N.; Cvitic, S.; Lang, I.; Desoye, G.; Huppertz, B. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF): A novel trophoblast-derived factor limiting feto-placental angiogenesis in late pregnancy. Angiogenesis 2016, 19, 373–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youssef, M.A.; Van der Veen, F.; Al-Inany, H.G.; Mochtar, M.H.; Griesinger, G.; Mohesen, M.N.; Aboulfoutouh, I.; van Wely, M. Cochrane Gynaecology and Fertility Group Gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist versus HCG for oocyte triggering in antagonist-assisted reproductive technology. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD008046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kol, S.; Huamidan, P. GnRH agonist triggering: Recent developments. Reprod. Biomed. Online 2013, 26, 226–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, I.; Chuderland, D.; Ron-El, R.; Shalgi, R.; Ben-Ami, I. GnRH Agonist Triggering Modulates PEDF to VEGF Ratio Inversely to hCG in Granulosa Cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, E1428–E1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zielińska, J.; Darmochwał-Kolarz, D. A Review of the Diagnosis, Risk Factors, and Role of Angiogenetic Factors in Hypertensive Disorders of Pregnancy. Med. Sci. Monit. 2025, 31, e945628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Montero, C.; Lima-Gómez, V.; Anguiano-Robledo, L.; Hernández-Campos, M.E.; López-Sánchez, P. Preeclampsia as predisposing factor for hypertensive retinopathy: Participation by the RAAS and angiogenic factors. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 193, 107981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wietecha, M.S.; Król, M.J.; Michalczyk, E.R.; Chen, L.; Gettins, P.G.; DiPietro, L.A. Pigment epithelium-derived factor as a multifunctional regulator of wound healing. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2015, 309, H812–H826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Yao, L.; Wang, Y. Resveratrol alleviates preeclampsia-like symptoms in rats through a mechanism involving the miR-363-3p/PEDF/VEGF axis. Microvasc. Res. 2022, 146, 104451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.M.; Yafai, Y.; Wiedemann, P.; Kuhrt, H.; Wang, Y.; Reichenbach, A.; Eichler, W. Hypoxia-induced upregulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor by retinal glial (Müller) cells. J. Neurosci. Res. 2011, 90, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Subirada, P.V.; Vaglienti, M.V.; Joray, M.B.; Paz, M.C.; Barcelona, P.F.; Sánchez, M.C. Rapamycin and Resveratrol Modulate the Gliotic and Pro-Angiogenic Response in Müller Glial Cells Under Hypoxia. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 855178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ek, E.T.H.; Dass, C.R.; Contreras, K.G.; Choong, P.F.M. Inhibition of orthotopic osteosarcoma growth and metastasis by multitargeted antitumor activities of pigment epithelium-derived factor. Clin. Exp. Metastasis 2007, 24, 93–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ek, E.T.H.; Dass, C.R.; Contreras, K.G.; Choong, P.F.M. Pigment epithelium-derived factor overexpression inhibits orthotopic osteosarcoma growth, angiogenesis and metastasis. Cancer Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ek, E.T.H.; Dass, C.R.; Contreras, K.G.; Choong, P.F.M. PEDF-derived synthetic peptides exhibit antitumor activity in an orthotopic model of human osteosarcoma. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chai, M.; Jiang, M.; Gu, C.; Lu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Tan, W. Osteogenically differentiated mesenchymal stem cells promote the apoptosis of human umbilical vein endothelial cells in vitro. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2021, 69, 2138–2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Yu, Z.; Lei, L.; Song, Y.; Liu, S.; Cui, J.; Dong, C.; Ding, J.; Cheng, X.; Su, Y.; et al. Secreted PEDF modulates fibroblast collagen synthesis through M1 macrophage polarization under expanded condition. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 142, 111951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.-J.; Huang, L.-Z.; Zhou, A.-Y.; Zhao, M.; Yu, W.-Z.; Li, X.-X. Antiangiogenesis Effects of Endostatin in Retinal Neovascularization. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2013, 29, 619–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, C.-N.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, S.-N.; Yang, L.-C.; Lai, L.-J.; Lai, C.-H.; Chen, M.-F.; Hung, C.-H.; Chen, C.-H. Inhibition of Corneal Neovascularization with the Combination of Bevacizumab and Plasmid Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor-Synthetic Amphiphile INTeraction-18 (p-PEDF-SAINT-18) Vector in a Rat Corneal Experimental Angiogenesis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 8291–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farnoodian, M.; Kinter, J.B.; Aghdam, S.Y.; Zaitoun, I.; Sorenson, C.M.; Sheibani, N. Expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor and thrombospondin-1 regulate proliferation and migration of retinal pigment epithelial cells. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araújo, R.S.; Silva, G.A. PlGF silencing combined with PEDF overexpression: Modeling RPE secretion as potential therapy for retinal neovascularization. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2020, 47, 4413–4425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coleman, D.J.; Silverman, R.H.; Rondeau, M.J.; Lloyd, H.O.; Khanifar, A.A.; Chan, R.V. Age-related macular degeneration: Choroidal ischaemia? Brit. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 1020–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, L. Combination of pigment epithelium derived factor with anti-vascular endothelial growth factor therapy protects the neuroretina from ischemic damage. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 151, 113113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xi, L.; Tikhonovich, M.; Biesemeier, A.; Julien-Schraermeyer, S.; Schraermeyer, U.; Tschulakow, A.V.; Romero, F.J. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Protects Retinal Neural Cells and Prevents Pathological Angiogenesis in an Ex Vivo Ischemia Model. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Federici, T.J. The non-antibiotic properties of tetracyclines: Clinical potential in ophthalmic disease. Pharmacol. Res. 2011, 64, 614–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, S.; Bressler, N.M. Aflibercept, bevacizumab or ranibizumab for diabetic macular oedema: Recent clinically relevant findings from DRCR.net protocol T. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamis, A.P.; Miller, J.W.; Bernal, M.-T.; D’AMico, D.J.; Folkman, J.; Yeo, T.-K.; Yeo, K.-T. Increased Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Levels in the Vitreous of Eyes With Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1994, 118, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahn, S.J.; Park, K.H.; Woo, S.J. SUBRETINAL FIBROSIS AFTER ANTIVASCULAR ENDOTHELIAL GROWTH FACTOR THERAPY IN EYES WITH MYOPIC CHOROIDAL NEOVASCULARIZATION. Retina 2016, 36, 2140–2149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Q.; Park, K.; Zhou, K.; Wassel, D.; Farjo, R.; Criswell, T.; Ma, J.-X.; Zhang, Y. Sustained therapeutic effect of an anti-inflammatory peptide encapsulated in nanoparticles on ocular vascular leakage in diabetic retinopathy. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 1049678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheibani, N.; Wang, S.; Darjatmoko, S.R.; Fisk, D.L.; Shahi, P.K.; Pattnaik, B.R.; Sorenson, C.M.; Bhowmick, R.; Volpert, O.V.; Albert, D.M.; et al. Novel anti-angiogenic PEDF-derived small peptides mitigate choroidal neovascularization. Exp. Eye Res. 2019, 188, 107798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stark, A.; Dammann, C.; Nielsen, H.C.; Volpe, M.V. A Pathogenic Relationship of Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia and Retinopathy of Prematurity? A Review of Angiogenic Mediators in Both Diseases. Front. Pediatr. 2018, 6, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clayton, J.A.; Chalothorn, D.; Faber, J.E. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A Specifies Formation of Native Collaterals and Regulates Collateral Growth in Ischemia. Circ. Res. 2008, 103, 1027–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheibani, N.; Zaitoun, I.S.; Wang, S.; Darjatmoko, S.R.; Suscha, A.; Song, Y.-S.; Sorenson, C.M.; Shifrin, V.; Albert, D.M.; Melgar-Asensio, I.; et al. Inhibition of retinal neovascularization by a PEDF-derived nonapeptide in newborn mice subjected to oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy. Exp. Eye Res. 2020, 195, 108030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eslani, M.; Putra, I.; Shen, X.; Hamouie, J.; Afsharkhamseh, N.; Besharat, S.; Rosenblatt, M.I.; Dana, R.; Hematti, P.; Djalilian, A.R. Corneal Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Are Directly Antiangiogenic via PEDF and sFLT-1. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2017, 58, 5507–5517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broadhead, M.L.; Choong, P.F.M.; Dass, C.R. Efficacy of Continuously Administered PEDF-Derived Synthetic Peptides against Osteosarcoma Growth and Metastasis. J. Biomed. Biotechnol. 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Elahy, M.; Friedhuber, A.M.; Wong, J.Y.; Hughes, J.D.; Doschak, M.R.; Dass, C.R. Triple-threat activity of PEDF in bone tumors: Tumor inhibition, tissue preservation and cardioprotection against doxorubicin. Bone 2019, 124, 103–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xiu, P.; Wang, F.; Zhong, J.; Wei, H.; Xu, Z.; Liu, F.; Li, J. P18 peptide, a functional fragment of pigment epithelial-derived factor, inhibits angiogenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma via modulating VEGF/VEGFR2 signalling pathway. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ho, T.-C.; Yeh, S.-I.; Chen, S.-L.; Chu, T.-W.; Tsao, Y.-P. A short peptide derived from pigment epithelial-derived factor exhibits an angioinhibitory effect. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, W.; Li, J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Y.; Lin, H.; Qian, H.; Fan, W. Exploration of novel anti-angiogenic PEDF-derived peptides with improved activitives by inhibiting proliferation, suppressing migration, and inducing 67LR internalization. Bioorganic Chem. 2021, 116, 105323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ju, W.; Lu, W.; Ding, L.; Bao, Y.; Hong, F.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Xu, X.; Wang, G.; Wang, W.; et al. PEDF promotes the repair of bone marrow endothelial cell injury and accelerates hematopoietic reconstruction after bone marrow transplantation. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Li, T.; Wang, J. p53 mediates PEDF-induced autophagy in human umbilical vein endothelial cells through sestrin2 signaling. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 1443–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, W.-W.; Yao, Y.-C.; Fang, S.-H.; Dai, Z.-Y.; Hong, H.-H.; Yang, X.; Shuai, X.-T.; Gao, G.-Q. Pigment epithelium-derived factor gene loaded in cRGD–PEG–PEI suppresses colorectal cancer growth by targeting endothelial cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2012, 438, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konson, A.; Pradeep, S.; D’acunto, C.W.; Seger, R. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor and its Phosphomimetic Mutant Induce JNK-Dependent Apoptosis and P38-Mediated Migration Arrest. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 49, 512–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chuderland, D.; Ben-Ami, I.; Friedler, S.; Hasky, N.; Ninio-Many, L.; Goldberg, K.; Bar-Joseph, H.; Grossman, H.; Shalgi, R. Hormonal regulation of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) expression in the endometrium. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2014, 390, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daubriac, J.; Pandya, U.; Huang, K.-T.; Pavlides, S.C.; Gama, P.; Blank, S.V.; Shukla, P.; Crawford, S.E.; Gold, L.I. Hormonal and Growth Regulation of Epithelial and Stromal Cells From the Normal and Malignant Endometrium by Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor. Endocrinology 2017, 158, 2754–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, F.; Fei, W.; Li, Z.; Yu, H.; Xi, L.; Sugawara, A. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor-Loaded PEGylated Nanoparticles as a New Antiangiogenic Therapy for Neovascularization. J. Diabetes Res. 2022, 2022, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, T.; Hu, J.; Yan, G.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, B.; Huang, Y. Pigment epithelium-derived factor regulates microvascular permeability through adipose triglyceride lipase in sepsis. Clin. Sci. 2015, 129, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Zhang, S.X.; Rowley, K.G.; Karschimkus, C.S.; Nelson, C.L.; Chung, J.S.; O’Neal, D.N.; Januszewski, A.S.; Croft, K.D.; Mori, T.A.; et al. Increased serum pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with microvascular complications, vascular stiffness and inflammation in Type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2007, 24, 1345–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katakami, N.; Kaneto, H.; Yamasaki, Y.; Matsuhisa, M. Increased serum pigment epithelium-derived factor levels in type 1 diabetic patients with diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pr. 2008, 81, e4–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, A.Y.L.; Pek, S.; Low, S.; Moh, A.; Ang, K.; Tang, W.E.; Lim, Z.; Subramaniam, T.; Sum, C.F.; Lim, S.C. Association of overhydration and serum pigment epithelium-derived factor with CKD progression in diabetic kidney disease: A prospective cohort study. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 174, 108754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujikawa, T.; Ohara, M.; Kohata, Y.; Nagaike, H.; Fukase, A.; Osaka, N.; Yashima, H.; Sato, N.; Kushima, H.; Shinmura, K.; et al. Glucose Variability is Independently Correlated with Serum Level of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes Ther. 2021, 12, 827–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hui, E.; Yeung, C.-Y.; Lee, P.C.; Woo, Y.-C.; Fong, C.H.; Chow, W.-S.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S. Elevated Circulating Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Predicts the Progression of Diabetic Nephropathy in Patients With Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E2169–E2177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.-H.; Lui, D.T.-W.; Cheung, C.Y.-Y.; Fong, C.H.-Y.; Yuen, M.M.-A.; Woo, Y.-C.; Chow, W.-S.; Wong, I.Y.-H.; Xu, A.; Lam, K.S.-L. Circulating AFABP, FGF21, and PEDF Levels as Prognostic Biomarkers of Sight-threatening Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, e799–e806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.; Cheng, R.; Park, K.; Benyajati, S.; Moiseyev, G.; Sun, C.; Olson, L.E.; Yang, Y.; Eby, B.K.; Lau, K.; et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor, a noninhibitory serine protease inhibitor, is renoprotective by inhibiting the Wnt pathway. Kidney Int. 2016, 91, 642–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.S.; Gao, T.; Gvritishvili, A.; You, H.; Liu, Y.; Cooper, T.K.; Reeves, W.B.; Tombran-Tink, J.; Morris, S.M.; Vacher, J. Protective role of small pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) peptide in diabetic renal injury. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2013, 305, F891–F900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Boyle, J.P.; Thompson, T.J.; Gregg, E.W.; Barker, L.E.; Williamson, D.F. Projection of the year 2050 burden of diabetes in the US adult population: Dynamic modeling of incidence, mortality, and prediabetes prevalence. Popul. Health Metr. 2010, 8, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, A.S.; You, H.; Gao, T.; Gvritishvili, A.; Cooper, T.K.; Tombran-Tink, J.; Long, D. Delayed Treatment with a Small Pigment Epithelium Derived Factor (PEDF) Peptide Prevents the Progression of Diabetic Renal Injury. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0133777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhang, L.; Chen, D.; Yu, K.; Gan, H.; Yang, G. PEDF relieves kidney injury in type 2 diabetic nephropathy mice by reducing macrophage infiltration. Endokrynol. Polska 2021, 72, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishibashi, Y.; Matsui, T.; Ohta, K.; Tanoue, R.; Takeuchi, M.; Asanuma, K.; Fukami, K.; Okuda, S.; Nakamura, K.-I.; Yamagishi, S.-I. PEDF inhibits AGE-induced podocyte apoptosis via PPAR-gamma activation. Microvasc. Res. 2013, 85, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.; Zhang, S.X.; Gosmanova, A.; Aston, C.; Dashti, A.; Baker, M.Z.; Lyons, T.; Ma, J.-X. Increased serum pigment epithelium derived factor levels in Type 2 diabetes patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2008, 82, e5–e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, A.J.; Fu, D.; Azar, M.; Stoner, J.A.; Kaufman, D.G.; Zhang, S.; Klein, R.L.; Lopes-Virella, M.F.; Ma, J.-X.; Lyons, T.J. Clinical correlates of serum pigment epithelium-derived factor in type 2 diabetes patients. J. Diabetes its Complicat. 2014, 28, 353–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okonkwo, U.A.; Chen, L.; Ma, D.; Haywood, V.A.; Barakat, M.; Urao, N.; DiPietro, L.A.; Kirchmair, R. Compromised angiogenesis and vascular Integrity in impaired diabetic wound healing. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0231962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özdemir, G.; Ergün, Y.; Bakariş, S.; Kılınç, M.; Durdu, H.; Ganiyusufoğlu, E. Melatonin prevents retinal oxidative stress and vascular changes in diabetic rats. Eye 2014, 28, 1020–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gattu, A.K.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Iwakiri, Y.; Jay, S.; Saltzman, M.; Doll, J.; Protiva, P.; Samuel, V.T.; Crawford, S.E.; Chung, C. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Suppresses IL-1β-Mediated c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase (JNK) Activation to Improve Hepatocyte Insulin Signaling. Endocrinology 2014, 155, 1373–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnagarin, R.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Dass, C.R. PEDF attenuates insulin-dependent molecular pathways of glucose homeostasis in skeletal myocytes. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 422, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crowe, S.; Wu, L.E.; Economou, C.; Turpin, S.M.; Matzaris, M.; Hoehn, K.L.; Hevener, A.L.; James, D.E.; Duh, E.J.; Watt, M.J. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Contributes to Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Cell Metab. 2009, 10, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, I.C.; Carnagarin, R.; Armstrong, J.; Lin, D.P.L.; Baxter-Holland, M.; Elahy, M.; Dass, C.R. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor: Inhibition of Phosphorylation of Insulin Receptor (IR)/IR Substrate (IRS), Osteogeneration from Adipocytes, and Increased Levels Due to Doxorubicin Exposure. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Carlessi, R.; Walz, N.; Cruzat, V.F.; Keane, K.; John, A.N.; Jiang, F.-X.; Carnagarin, R.; Dass, C.R.; Newsholme, P. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) regulates metabolism and insulin secretion from a clonal rat pancreatic beta cell line BRIN-BD11 and mouse islets. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2016, 426, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carnagarin, R.; Elahy, M.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Dass, C.R. Insulin antagonises pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF)-induced modulation of lineage commitment of myocytes and heterotrophic ossification. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2018, 472, 159–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dillmann, W.H. Diabetic Cardiomyopathy. Circ. Res. 2019, 124, 1160–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, T.; Wang, Y. PEDF Overexpression Ameliorates Cardiac Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Cardiomyopathy via Regulation of Energy Metabolism. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obesity Targets Ther. 2025, 18, 217–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Smit, E.; Brouwers, M.C.G.J.; Goossens, G.H.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; van Greevenbroek, M.M.J.; Mariman, E.C.M. Plasma pigment epithelium-derived factor is positively associated with obesity in Caucasian subjects, in particular with the visceral fat depot. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 159, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sabater, M.; Moreno-Navarrete, J.M.; Ortega, F.J.; Pardo, G.; Salvador, J.; Ricart, W.; FrühBeck, G.; FernánDez-Real, J.M. Circulating Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Levels Are Associated with Insulin Resistance and Decrease after Weight Loss. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 4720–4728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Famulla, S.; Lamers, D.; Hartwig, S.; Passlack, W.; Horrighs, A.; Cramer, A.; Lehr, S.; Sell, H.; Eckel, J. Pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) is one of the most abundant proteins secreted by human adipocytes and induces insulin resistance and inflammatory signaling in muscle and fat cells. Int. J. Obes. 2011, 35, 762–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chavan, S.S.; Hudson, L.K.; Li, J.H.; Ochani, M.; Harris, Y.; Patel, N.B.; Katz, D.; Scheinerman, J.A.; Pavlov, V.A.; Tracey, K.J. Identification of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor as an Adipocyte-Derived Inflammatory Factor. Mol. Med. 2012, 18, 1161–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sylvetsky, A.C.; Issa, N.T.; Chandran, A.; Brown, R.J.; Alamri, H.J.; Aitcheson, G.; Walter, M.; Rother, K.I. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor Declines in Response to an Oral Glucose Load and Is Correlated with Vitamin D and BMI but Not Diabetes Status in Children and Young Adults. Horm. Res. Paediatr. 2017, 87, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tryggestad, J.B.; Wang, J.J.; Zhang, S.X.; Thompson, D.M.; Short, K.R. Elevated plasma pigment epithelium-derived factor in children with type 2 diabetes mellitus is attributable to obesity. Pediatr. Diabetes 2014, 16, 600–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tolusso, B.; Gigante, M.R.; Alivernini, S.; Petricca, L.; Fedele, A.L.; Di Mario, C.; Aquilanti, B.; Magurano, M.R.; Ferraccioli, G.; Gremese, E. Chemerin and PEDF Are Metaflammation-Related Biomarkers of Disease Activity and Obesity in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Xu, M.; Zhang, X.; Barnstable, C.J.; Li, X.; Tombran-Tink, J. Deletion of the Pedf gene leads to inflammation, photoreceptor loss and vascular disturbances in the retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2022, 222, 109171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, R.; Luo, X.-Q.; Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.-L.; Qiao, H.; Wang, N.; Yan, J.-Q. Cold Exposure Differentially Stimulates Angiogenesis in BAT and WAT of Mice: Implication in Adrenergic Activation. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 42, 974–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feld, J.; Chandran, V.; Haroon, N.; Inman, R.; Gladman, D. Axial disease in psoriatic arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis: A critical comparison. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 14, 363–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Yang, F.; He, S.; Yu, H.; Wang, Q.; Li, M.; Zeng, X.; Leng, X. Serum proteome analysis identifies a potential biomarker for axial psoriatic arthritis. Eur. J. Med Res. 2024, 29, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Huang, Z.; Zhu, L.; Yu, X.; Gao, T.; Feng, J.; Hong, H.; Yin, H.; Zhou, T.; Qi, W.; et al. The contrary intracellular and extracellular functions of PEDF in HCC development. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, F.; Fitchev, P.; Franco, O.E.; Ivanisevic, J.; Scheibler, A.; Hayward, S.W.; Brendler, C.B.; Welte, M.A.; Crawford, S.E. PEDF regulates plasticity of a novel lipid–MTOC axis in prostate cancer-associated fibroblasts. J. Cell Sci. 2018, 131, jcs.213579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagishi, S.-I.; Adachi, H.; Abe, A.; Yashiro, T.; Enomoto, M.; Furuki, K.; Hino, A.; Jinnouchi, Y.; Takenaka, K.; Matsui, T.; et al. Elevated Serum Levels of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in the Metabolic Syndrome. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 91, 2447–2450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogata, N.; Matsuoka, M.; Matsuyama, K.; Shima, C.; Tajika, A.; Nishiyama, T.; Wada, M.; Jo, N.; Higuchi, A.; Minamino, K.; et al. Plasma Concentration of Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor in Patients with Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 92, 1176–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franck, N.; Gummesson, A.; Jernås, M.; Glad, C.; Svensson, P.-A.; Guillot, G.; Rudemo, M.; Nyström, F.H.; Carlsson, L.M.S.; Olsson, B. Identification of Adipocyte Genes Regulated by Caloric Intake. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2011, 96, E413–E418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-T.; Hsu, L.-W.; Chen, K.-D.; Kung, C.-P.; Goto, S.; Chen, C.-L. Decreased PEDF Expression Promotes Adipogenic Differentiation through the Up-Regulation of CD36. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalasani, N.; Younossi, Z.; LaVine, J.E.; Charlton, M.; Cusi, K.; Rinella, M.; Harrison, S.A.; Brunt, E.M.; Sanyal, A.J. The diagnosis and management of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Practice guidance from the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology 2018, 67, 328–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, K.-T.; Chen, K.-D.; Hsu, L.-W.; Kung, C.-P.; Li, S.-R.; Chen, C.-C.; Chiu, K.-W.; Goto, S.; Chen, C.-L. Decreased PEDF Promotes Hepatic Fatty Acid Uptake and Lipid Droplet Formation in the Pathogenesis of NAFLD. Nutrients 2020, 12, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daemen, S.; Van Zandvoort, M.; Parekh, S.H.; Hesselink, M.K.C. Microscopy tools for the investigation of intracellular lipid storage and dynamics. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 153–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi, F.; Fitchev, P.; Brooks, K.M.; Franco, O.E.; Cheng, K.; Hayward, S.W.; Welte, M.A.; Crawford, S.E. Lipid droplet velocity is a microenvironmental sensor of aggressive tumors regulated by V-ATPase and PEDF. Mod. Pathol. 2019, 99, 1822–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, F.; Zhang, H.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Z.; Huang, B.; Miao, H.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Dong, H.; et al. A decrease of ATP production steered by PEDF in cardiomyocytes with oxygen-glucose deprivation is associated with an AMPK-dependent degradation pathway. Int. J. Cardiol. 2018, 257, 262–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-C.; Lee, T.-Y.; Leu, Y.-L.; Wang, S.-H. Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Transl. Res. 2019, 210, 26–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Akiba, J.; Matsui, T.; Nakamura, K.; Hisamoto, T.; Abe, M.; Ikezono, Y.; Wada, F.; Iwamoto, H.; Nakamura, T.; et al. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Prevents Hepatic Fat Storage, Inflammation, and Fibrosis in Dietary Steatohepatitis of Mice. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2017, 62, 1527–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Li, X.; Tan, J.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, B.; Deng, S.; et al. Pigment Epithelial-Derived Factor Deficiency Accelerates Atherosclerosis Development via Promoting Endothelial Fatty Acid Uptake in Mice With Hyperlipidemia. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e013028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Liu, M.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Liu, X.; Ni, M.; Dong, M.; Luan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Xu, X.; et al. PEDF improves atherosclerotic plaque stability by inhibiting macrophage inflammation response. Int. J. Cardiol. 2017, 235, 37–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nozue, T.; Yamagishi, S.-I.; Hirano, T.; Yamamoto, S.; Tohyama, S.; Fukui, K.; Umezawa, S.; Onishi, Y.; Kunishima, T.; Hibi, K.; et al. Pigment epithelium-derived factor is associated with necrotic core progression during statin therapy. Coron. Artery Dis. 2015, 26, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Wang, S.; Li, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, P. The effects of pigment epithelium-derived factor on atherosclerosis: Putative mechanisms of the process. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2018, 17, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Yao, S.; Tian, H.; Jiao, P.; Yang, N.; Zhu, P.; Qin, S. Pigment epithelium-derived factor alleviates endothelial injury by inhibiting Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2017, 16, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z. PEDF attenuates hypoxia-induced apoptosis and necrosis in H9c2 cells by inhibiting p53 mitochondrial translocation via PEDF-R. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2015, 465, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Yu, H.; Wang, M.; Dong, H.; et al. PEDF regulates lipid metabolism and reduces apoptosis in hypoxic H9c2 cells by inducing autophagy related 5-mediated autophagy via PEDF-R. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 7170–7176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-K.; Liang, H.-L.; Li, Z.; Gu, C.-H.; Yi, D.-H.; Pei, J.-M. Pigment epithelium-derived factor promotes Fas-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis via its receptor phospholipase A2. Life Sci. 2014, 99, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhuang, W.; Yuan, G.; Sun, T.; Jiang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, Z.; Dong, H. PEDF and PEDF-derived peptide 44mer protect cardiomyocytes against hypoxia-induced apoptosis and necroptosis via anti-oxidative effect. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 5637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Wang, X.; Lu, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z. PEDF protects cardiomyocytes by promoting FUNDC1-mediated mitophagy via PEDF-R under hypoxic condition. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3394–3404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, W.; Zhang, H.; Pan, J.; Li, Z.; Wei, T.; Cui, H.; Liu, Z.; Guan, Q.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z. PEDF and PEDF-derived peptide 44mer inhibit oxygen–glucose deprivation-induced oxidative stress through upregulating PPARγ via PEDF-R in H9c2 cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 472, 482–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Guan, Q.; Qiu, F.; Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z. PEDF Inhibits the Activation of NLRP3 Inflammasome in Hypoxia Cardiomyocytes through PEDF Receptor/Phospholipase A2. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, Z.; Huang, B.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Miao, H.; et al. PEDF improves cardiac function in rats subjected to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by inhibiting ROS generation via PEDF-R. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3243–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Liu, X.; Miao, H.; Huang, B.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Quan, X.; Zhu, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z. PEDF increases GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake in rat ischemic myocardium via PI3K/AKT pathway in a PEDFR-dependent manner. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 283, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Luo, Q.; Shen, N.; Qin, X.; Jia, C.; Chao, Z.; Zhang, L.; Qin, H.; Liu, X.; Quan, X.; et al. PEDF Protects Endothelial Barrier Integrity during Acute Myocardial Infarction via 67LR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X.; Chao, Z.; Qin, X.; Quan, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Jia, C.; Qin, H.; Zhang, H. Pigment epithelium-derived factor maintains tight junction stability after myocardial infarction in rats through inhibition of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 417, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, Z.; Feng, S.-J.; Xu, L.; Shi, H.-X.; Chen, L.-L.; Yuan, G.-D.; Yan, W.; Zhuang, W.; Zhang, Y.-Q.; et al. PEDF Improves Cardiac Function in Rats with Acute Myocardial Infarction via Inhibiting Vascular Permeability and Cardiomyocyte Apoptosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 5618–5634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, H.; Quan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Miao, H.; Huang, B.; Dong, H.; et al. Pigment Epithelium–Derived Factor Increases Native Collateral Blood Flow to Improve Cardiac Function and Induce Ventricular Remodeling After Acute Myocardial Infarction. J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2019, 8, e013323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Hou, H.; Yi, W.; Yang, G.; Gu, C.; Lau, W.B.; Gao, E.; Ma, X.; Lu, Z.; Wei, X.; et al. Increased expression of pigment epithelium-derived factor in aged mesenchymal stem cells impairs their therapeutic efficacy for attenuating myocardial infarction injury‡. Eur. Hear. J. 2011, 34, 1681–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Quan, X.; Liu, X.; Sun, T.; Wei, T.; Pan, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, M.; Dong, H.; et al. Strategies to Attenuate Myocardial Infarction and No-Reflow Through Preservation of Vascular Integrity by Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor. Hum. Gene Ther. 2022, 33, 330–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Gao, E.; MacDonnell, S.M.; Wang, W.; Kolpakov, M.; Nakayama, H.; Zhang, X.; Jaleel, N.; Harris, D.M.; et al. Increasing Cardiac Contractility After Myocardial Infarction Exacerbates Cardiac Injury and Pump Dysfunction. Circ. Res. 2010, 107, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, P.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Xu, H.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Dong, H.; Zhang, Z.; et al. Pigment Epithelium-Derived Factor (PEDF) Improves Ischemic Cardiac Functional Reserve Through Decreasing Hypoxic Cardiomyocyte Contractility Through PEDF Receptor (PEDF-R). J. Am. Hear. Assoc. 2016, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bullock, J.; Polato, F.; Lulli, D.C.; Sagar, V.; Abaandou, L.; Shiloach, J.; Becerra, S.P. Expression and production of pigment epithelium-derived factor (PEDF) and PEDF receptor variants from mammalian and bacterial cells. Protein Expr. Purif. 2022, 194, 106072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, H.; Rebustini, I.T.; Becerra, S.P.; Wang, Y. Pigment epithelium-derived factor engineered to increase glycosaminoglycan affinity while maintaining bioactivity. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 605, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, P.X.; Martinez, J.; Dass, C.R. Stimulation of bone regeneration with pigment epithelium-derived factor microparticles: Evidence in silico, in vitro and in vivo. Pharmazie 2016, 71, 382–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, C.R.; Contreras, K.G.; Dunstan, D.E.; Choong, P.F. Chitosan microparticles encapsulating PEDF plasmid demonstrate efficacy in an orthotopic metastatic model of osteosarcoma. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3026–3033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antoniazzi, F. Type VI Osteogenesis imperfecta: Effect of plasma transfusion on bone metabolism. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents 2022, 36, 389–395. [Google Scholar]
- Ta, H.; Dass, C.R.; Larson, I.; Choong, P.F.; Dunstan, D.E. A chitosan hydrogel delivery system for osteosarcoma gene therapy with pigment epithelium-derived factor combined with chemotherapy. Biomaterials 2009, 30, 4815–4823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elahy, M.; Doschak, M.R.; Hughes, J.D.; Baindur-Hudson, S.; Dass, C.R. Alginate Bead-Encapsulated PEDF Induces Ectopic Bone Formation In Vivo in the Absence of Co-Administered Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Curr. Drug Targets 2018, 19, 467–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, H.; Xu, C.; Shi, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, M.; Jiang, L. Biomimetic exosome harnessing exosomal lipidomics and functional proteins for PEDF-pDNA delivery in high altitude pulmonary edema intervention. J. Control. Release 2025, 379, 652–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahbazi, B.; Arab, S.S.; Mafakher, L.; Azadmansh, K.; Teimoori-Toolabi, L. Computational assessment of pigment epithelium-derived factor as an anti-cancer protein during its interaction with the receptors. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 41, 4575–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bani-Ahmad, E.; Dass, J.; Dass, C.R. Anticancer potential of PEDF peptides. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Tschulakow, A.V.; Karthikeyan, S.S.; Wang, K.; Kochanek, S.; Schraermeyer, U.; Julien-Schraermeyer, S. Reduction of pathological retinal neovascularization, vessel obliteration, and artery tortuosity by PEDF protein in an oxygen-induced ischemic retinopathy rat model. Faseb. Bioadv. 2024, 6, 311–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Thangavel, C.; Djuric, N.; Raveendran, M.; Soundararajan, D.C.R.; Nayagam, S.M.; Matchado, M.S.; Anand, K.S.S.V.; Venkateshwaran, K. Profiling extra cellular matrix associated proteome of human fetal nucleus pulposus in search for regenerative targets. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rörby, E.; Billing, M.; Dahl, M.; Warsi, S.; Andradottir, S.; Miharada, K.; Siva, K.; Jönsson, J.-I.; Blank, U.; Karlsson, G.; et al. The stem cell regulator PEDF is dispensable for maintenance and function of hematopoietic stem cells. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dass, C.R. PEDF and Its Role in Metabolic Disease, Angiogenesis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071780
Dass CR. PEDF and Its Role in Metabolic Disease, Angiogenesis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071780
Chicago/Turabian StyleDass, Crispin R. 2025. "PEDF and Its Role in Metabolic Disease, Angiogenesis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071780
APA StyleDass, C. R. (2025). PEDF and Its Role in Metabolic Disease, Angiogenesis, Cardiovascular Disease, and Diabetes. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1780. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071780





