Upregulation of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Celecoxib to Reduce Pain After Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery (POPCORN Trial): A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
1. Introduction
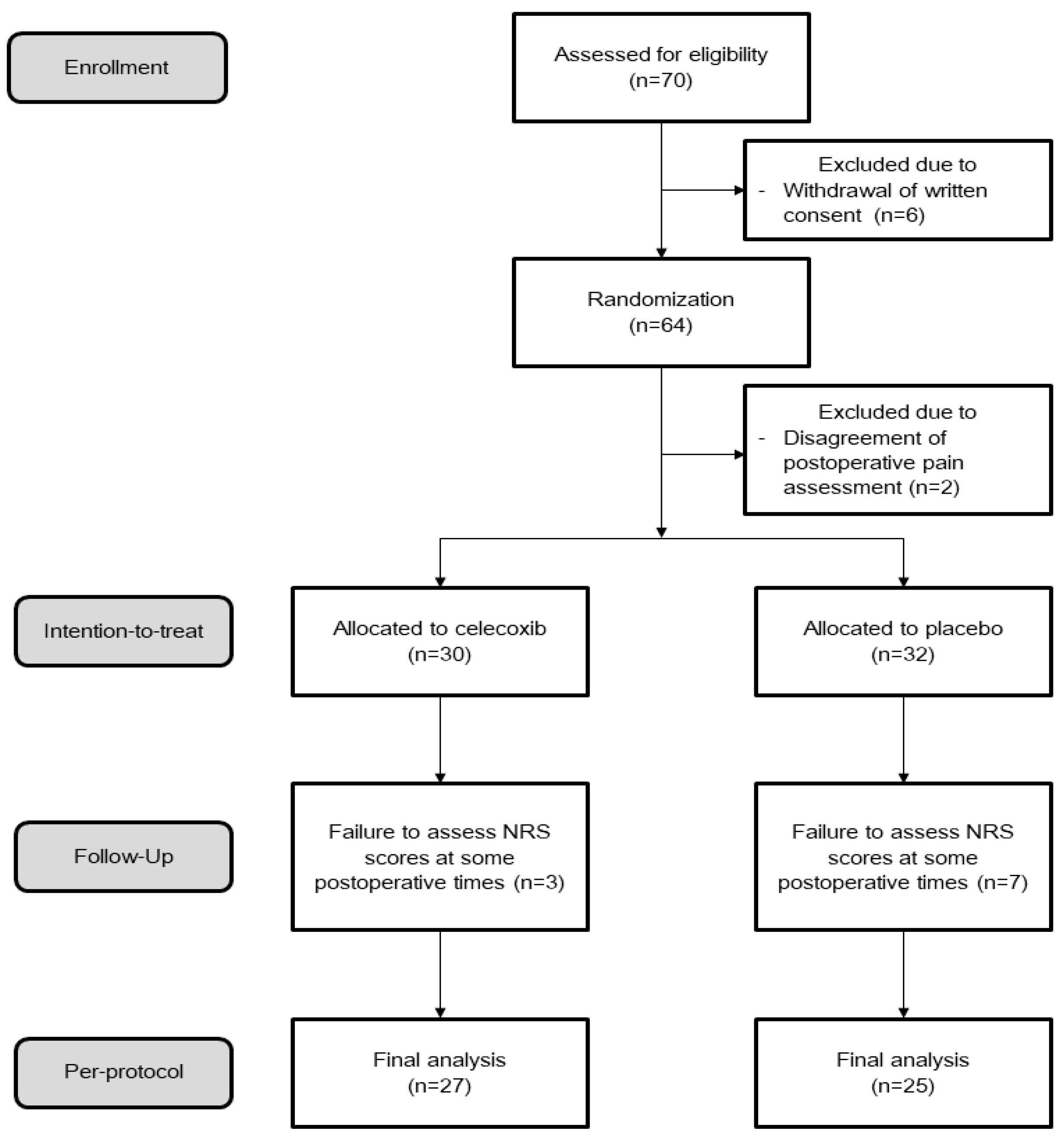
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Sample Size
2.4. Randomization
2.5. Surgical Procedures
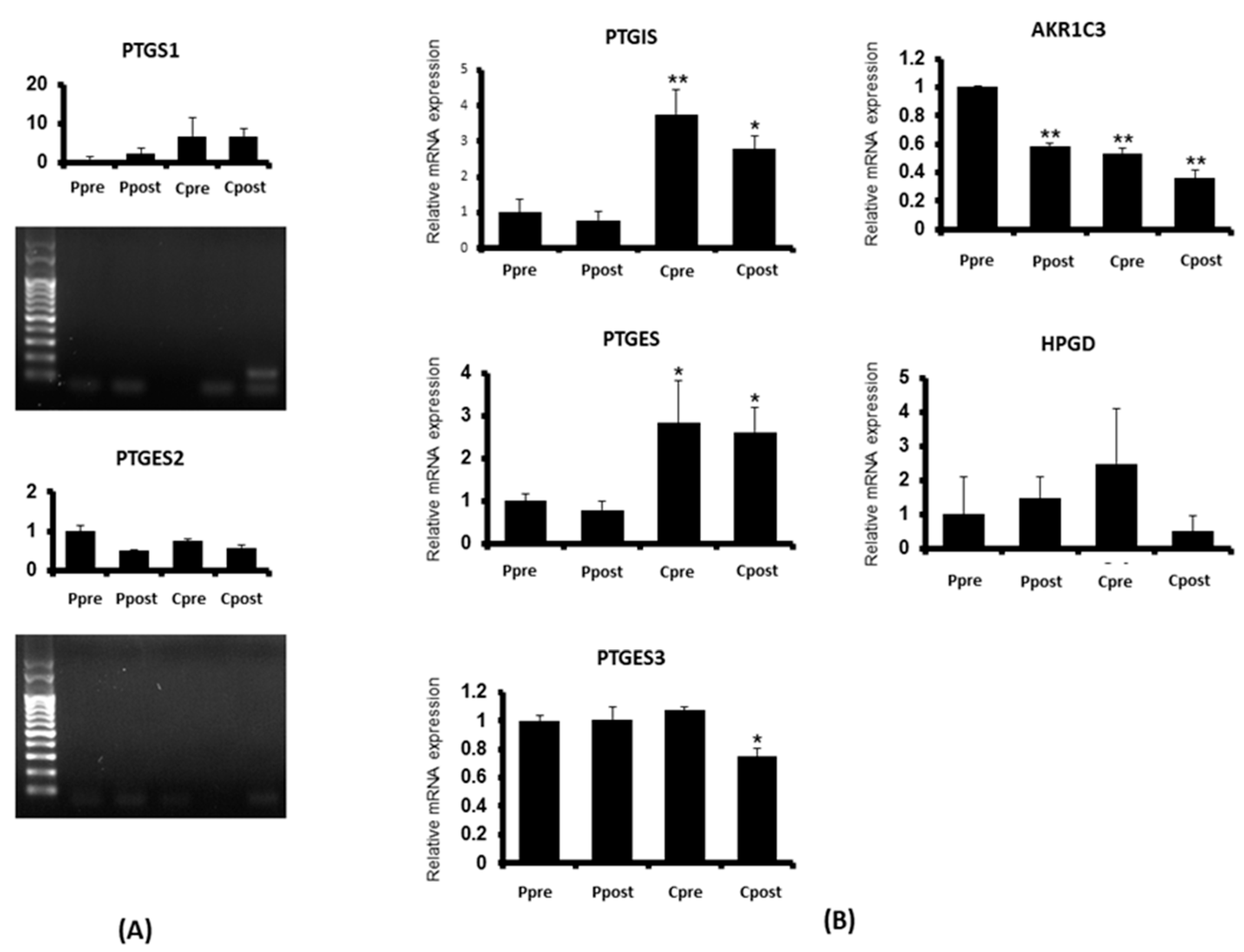
2.6. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
2.7. Immunohistochemistry
2.8. In Situ Hybridization
2.9. Endpoints
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinicopathologic Characteristics
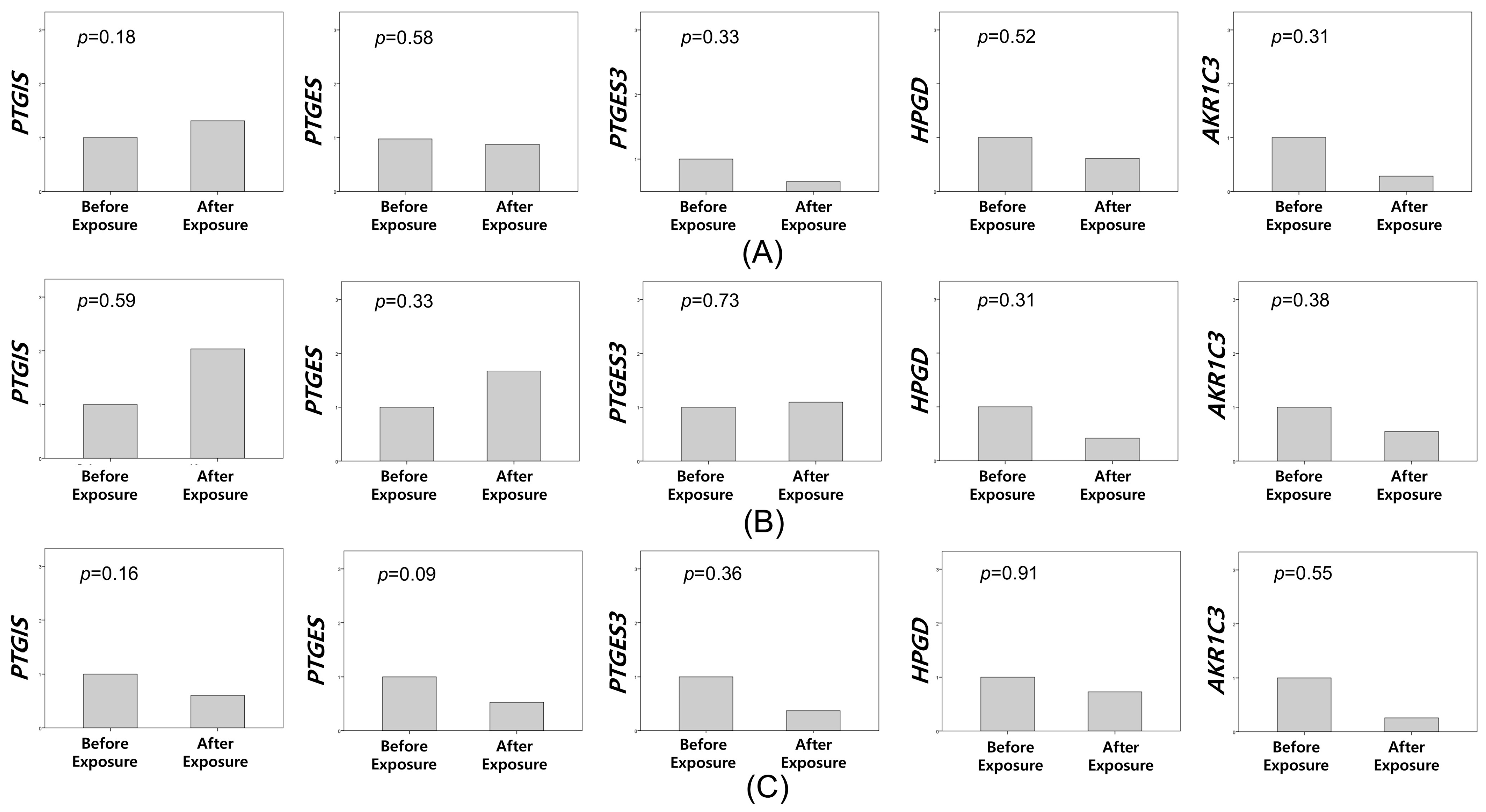
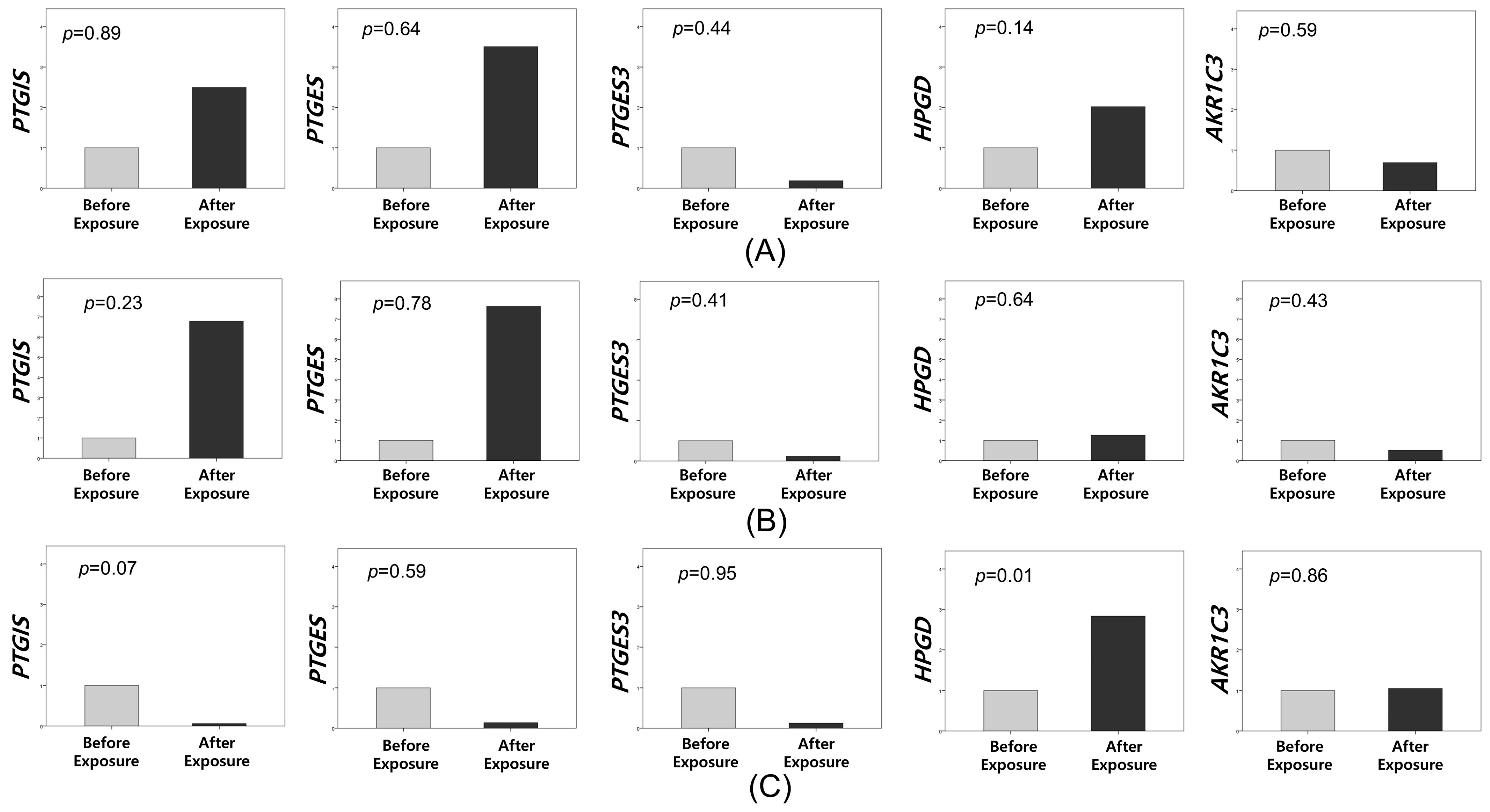
3.2. Quantitative Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction
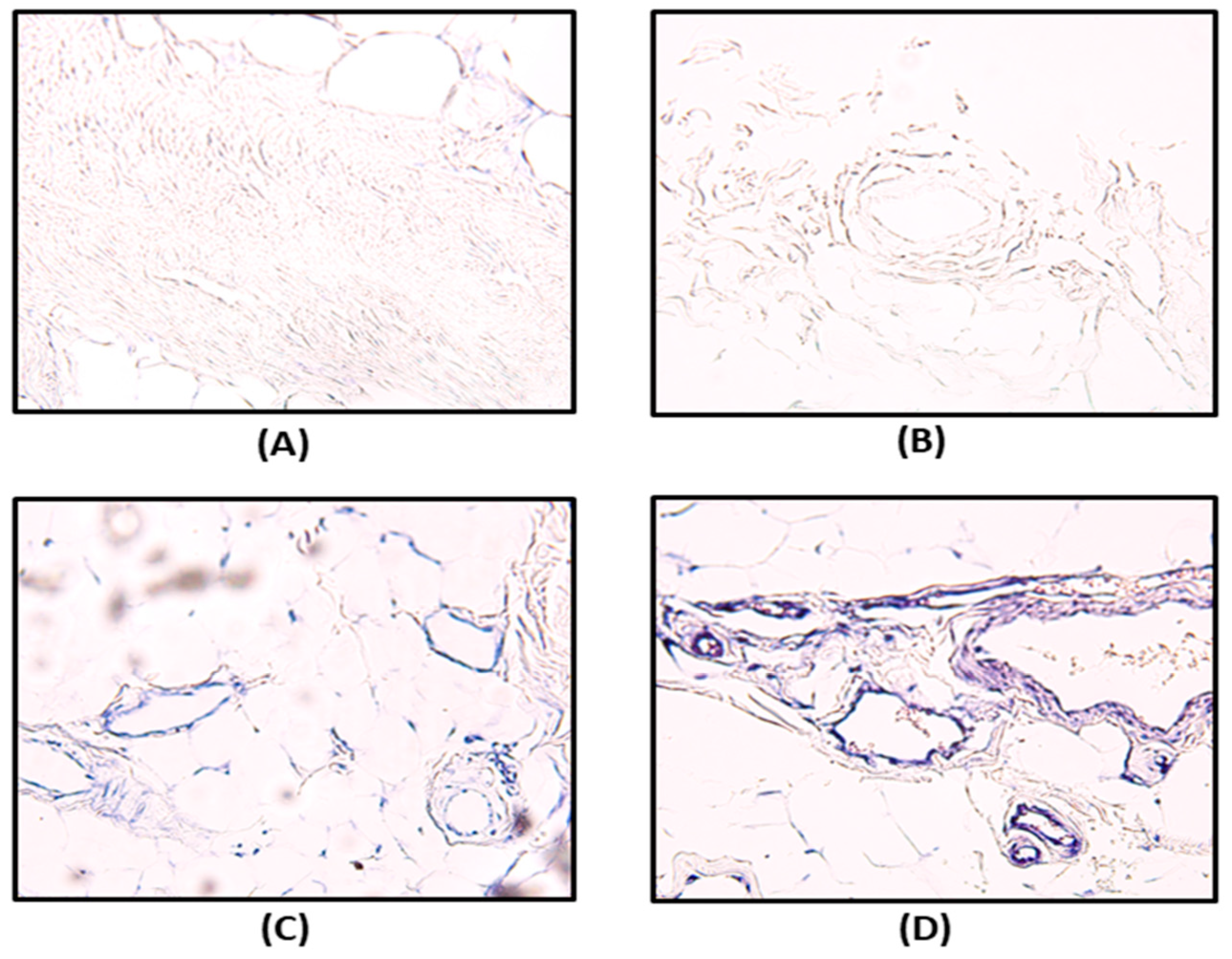
3.3. Immunohistochemistry and In Situ Hybridization
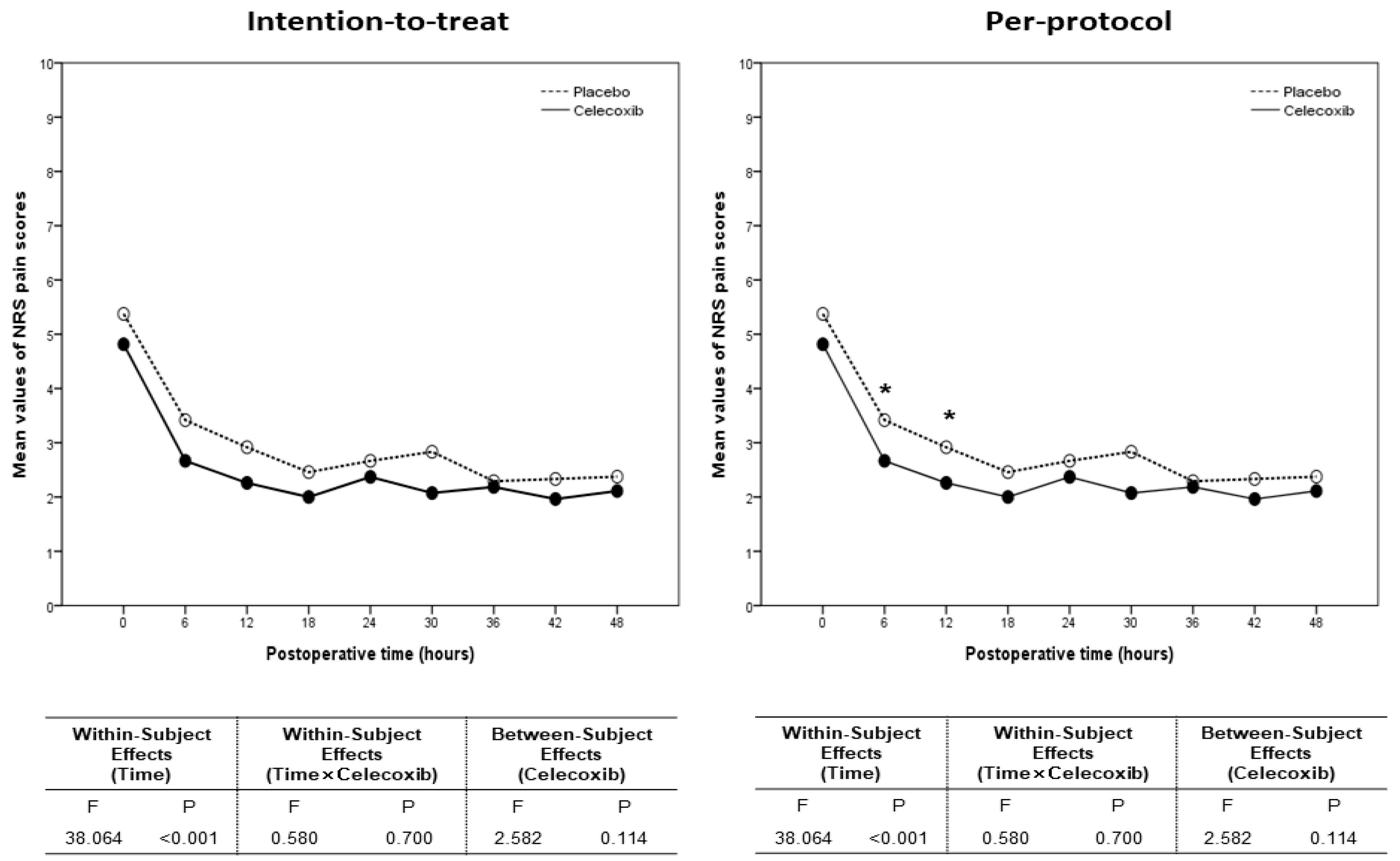
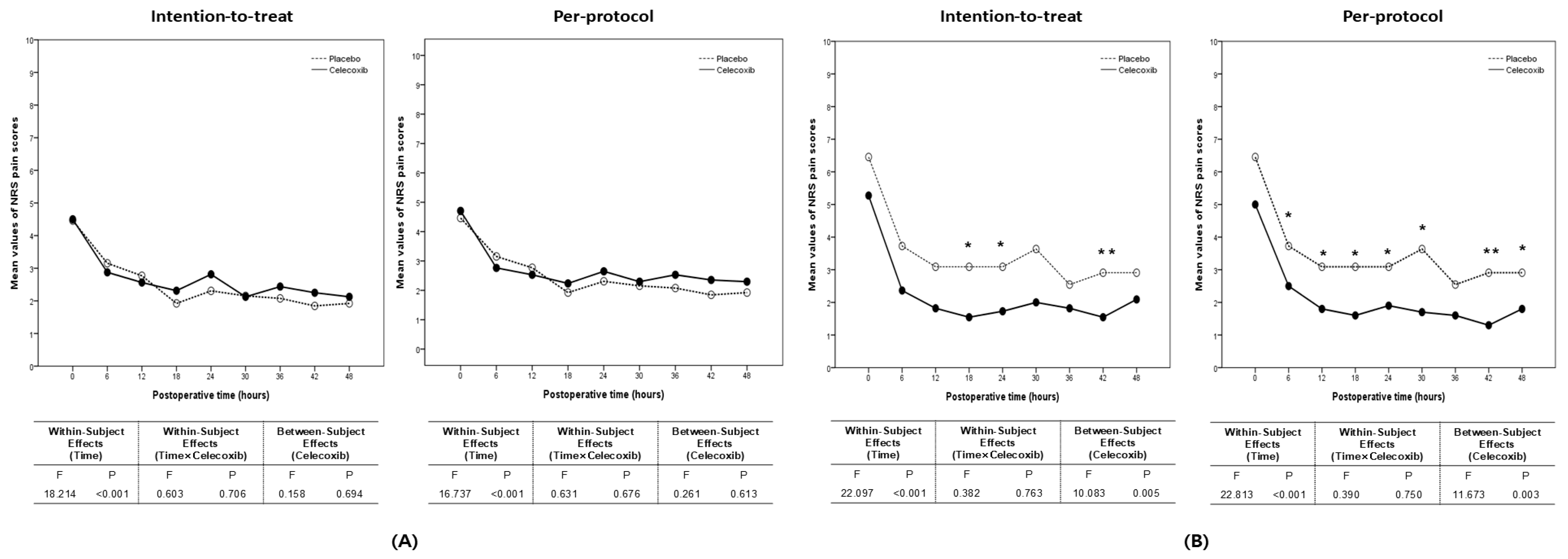
3.4. Numeric Rating Scale Pain Scores and Postoperative Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PCA | patient-controlled analgesia |
| PONV | postoperative nausea and vomiting |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| COX-2 | cyclooxygenase-2 |
| LESS | laparoendoscopic single-site |
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologists |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction |
| IHC | immunohistochemistry |
| ISH | in situ hybridization |
| NRS | numeric rating scale |
| EBL | estimated blood loss |
| ITT | intention-to-treat |
| PP | per-protocol |
| ANOVA | analysis of variance |
| PLA2G4A | phospholipase A2 group IVA |
| PTGS1 | prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 1 |
| PTGES | prostaglandin E synthase |
| PTGIS | prostaglandin I2 synthase |
| AKR1C1 | aldo-keto reductase family 1 member C1 |
| TBAS | thromboxane A synthase |
| HPGD | 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenas |
References
- Mouton, W.G.; Bessell, J.R.; Otten, K.T.; Maddern, G.J. Pain after laparoscopy. Surg. Endosc. 1999, 13, 445–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cao, L.; Yang, Z.; Qi, L.; Chen, M. Robot-assisted and laparoscopic vs open radical prostatectomy in clinically localized prostate cancer: Perioperative, functional, and oncological outcomes: A Systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2019, 98, e15770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhave Chittawar, P.; Franik, S.; Pouwer, A.W.; Farquhar, C. Minimally invasive surgical techniques versus open myomectomy for uterine fibroids. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, CD004638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sinha, S.; Munikrishnan, V.; Montgomery, J.; Mitchell, S.J. The impact of patient-controlled analgesia on laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Ann. R. Coll. Surg. Engl. 2007, 89, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serralta Serra, A.; Bueno Lledo, J.; Sanhauja Santafe, A.; Garcia Espinosa, R.; Arnal Bertomeu, C.; Martinez Casan, P.; Planells Roig, M. Course of postoperative pain in laparoscopic cholecystectomy under multimodal anesthesia-analgesia in ambulatory care. Rev. Esp. Anestesiol. Reanim. 2002, 49, 461–467. [Google Scholar]
- Talbot, K.; Madden, V.J.; Jones, S.L.; Moseley, G.L. The sensory and affective components of pain: Are they differentially modifiable dimensions or inseparable aspects of a unitary experience? A systematic review. Br. J. Anaesth. 2019, 123, e263–e272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donatsky, A.M.; Bjerrum, F.; Gogenur, I. Intraperitoneal instillation of saline and local anesthesia for prevention of shoulder pain after laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A systematic review. Surg. Endosc. 2013, 27, 2283–2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, H.S.; Yim, G.W. Comparison of Vaginal Natural Orifice Transluminal Endoscopic Surgery (vNOTES) and Laparoendoscopic Single-Site (LESS) Hysterectomy on Postoperative Pain Reduction: A Randomized Pilot Study. Pain Ther. 2021, 10, 1401–1411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunyavejchevin, S.; Prayoonwech, C.; Sriprajittichai, P. Preemptive analgesic efficacy of parecoxib vs placebo in infertile women undergoing diagnostic laparoscopy: Randomized controlled trial. J. Minim. Invasive Gynecol. 2012, 19, 585–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.M.; Lv, Z.T.; Zhang, Y.N.; Jiang, W.X.; Li, H.N.; Nie, M.B. Efficacy and Safety of Postoperative Pain Relief by Parecoxib Injection after Laparoscopic Surgeries: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pain Pract. 2018, 18, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, K.K. Evaluation of intravenous parecoxib for the relief of acute post-surgical pain. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs. 2000, 9, 2717–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toloczko-Iwaniuk, N.; Dziemianczyk-Pakiela, D.; Nowaszewska, B.K.; Celinska-Janowicz, K.; Miltyk, W. Celecoxib in Cancer Therapy and Prevention—Review. Curr. Drug Targets 2019, 20, 302–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derry, S.; Moore, R.A. Single dose oral celecoxib for acute postoperative pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 2013, CD004233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Recard, A.; Issioui, T.; White, P.F.; Klein, K.; Watcha, M.F.; Stool, L.; Shah, M. The efficacy of celecoxib premedication on postoperative pain and recovery times after ambulatory surgery: A dose-ranging study. Anesth. Analg. 2003, 96, 1631–1635. [Google Scholar]
- Crofford, L.J. COX-1 and COX-2 tissue expression: Implications and predictions. J. Rheumatol. Suppl. 1997, 49, 15–19. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ershov, P.V.; Yablokov, E.O.; Kaluzhskiy, L.A.; Mezentsev, Y.V.; Ivanov, A.S. Prostanoid Signaling in Cancers: Expression and Regulation Patterns of Enzymes and Receptors. Biology 2022, 11, 590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muzii, L.; Marana, R.; Brunetti, L.; Orlando, G.; Michelotto, B.; Benedetti Panici, P. Atypical endometriosis revisited: Clinical and biochemical evaluation of the different forms of superficial implants. Fertil. Steril. 2000, 74, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omori, T.; Yamamoto, K.; Hara, H.; Shinno, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Sugimura, K.; Wada, H.; Takahashi, H.; Yasui, M.; Miyata, H.; et al. A randomized controlled trial of single-port versus multi-port laparoscopic distal gastrectomy for gastric cancer. Surg. Endosc. 2021, 35, 4485–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuhaus, S.J.; Watson, D.I. Pneumoperitoneum and peritoneal surface changes: A review. Surg. Endosc. 2004, 18, 1316–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umano, G.R.; Delehaye, G.; Noviello, C.; Papparella, A. The "Dark Side" of Pneumoperitoneum and Laparoscopy. Minim. Invasive Surg. 2021, 2021, 5564745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lousse, J.C.; Defrere, S.; Colette, S.; Van Langendonckt, A.; Donnez, J. Expression of eicosanoid biosynthetic and catabolic enzymes in peritoneal endometriosis. Hum. Reprod. 2010, 25, 734–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Ma, X.; Li, Z.; Gao, X.; Wang, F.; Liu, L.; Shen, G.; Sang, Y.; Li, M.; Li, Y.; et al. Celecoxib enhances the efficacy of 15-hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase gene therapy in treating murine breast cancer. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 139, 797–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, M.; Myung, S.J.; Fink, S.P.; Lawrence, E.; Lutterbaugh, J.; Yang, P.; Zhou, X.; Liu, D.; Rerko, R.M.; Willis, J.; et al. 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin dehydrogenase inactivation as a mechanism of resistance to celecoxib chemoprevention of colon tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 9409–9413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, N.D.; Barclay, K.; Catling, S.J.; Martin, D.G.; Morgan, R.H. Day case laparoscopy: A survey of postoperative pain and an assessment of the value of diclofenac. Anaesthesia 1991, 46, 1077–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovorka, J.; Kallela, H.; Korttila, K. Effect of intravenous diclofenac on pain and recovery profile after day-case laparoscopy. Eur. J. Anaesthesiol. 1993, 10, 105–108. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
| Characteristics | Celecoxib (n = 30) | Placebo (n = 32) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (year, mean, SD) | 49.1 ± 9.6 | 50 ± 11.6 | 0.73 |
| BMI (kg/m2, mean, SD) | 23 ± 2.9 | 22.7 ± 3.1 | 0.69 |
| Previous surgery (n, %) | 17 (53.1) | 11 (36.7) | 0.21 |
| Types of surgical procedures (n, %) | 0.80 | ||
| Unilateral salpingo-oophorectomy | 3 (10) | 1 (3.1) | |
| Bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy | 5 (16.7) | 5 (15.6) | |
| Unilateral ovarian cystectomy | 1 (3.3) | 3 (9.4) | |
| Bilateral ovarian cystectomy | 1 (3.3) | 1 (3.1) | |
| Hysterectomy | 16 (53.3) | 16 (50) | |
| Myomectomy | 4 (13.3) | 6 (18.8) | |
| The exposure time of peritoneal tissues to CO2 (minutes, mean, SD) | 60.3 ± 54.7 | 60.5 ± 50.5 | 0.59 |
| Gene | GenBank No. | Forward | Reverse |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTGIS | BC101811.1 | CATGTGCAGTGTCAAAAGTCG | TGCATCTCCTCTGACACACC |
| PTGES | BC008280.1 | GGTCTTGGGTTCCTGTATGG | AAAGACATCCAAAGCCAACG |
| PTGES3 | BC003005.1 | TGGGGCAATTTTAAGTCAGC | TTGCCTAGGACCTCAACAGC |
| HPGD | L76465.1 | GGCATAGTTGGATTCACACG | AACAAAGCCTGGACAAATGG |
| AKR1C3 | BT007286.1 | AGTACAAGCCTGTCTGCAACC | TCTCGTTGAGATCCCAGAGC |
| (A) HPGD Expression | ||||||
| Grade | Before Exposure to CO2 | p Value | After Exposure to CO2 | p Value | ||
| Celecoxib (n = 12, %) | Placebo (n = 16, %) | Celecoxib (n = 12, %) | Placebo (n = 16, %) | |||
| Grade 1 (no or weak) | 9 (75) | 10 (62.5) | 0.78 | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0.01 |
| Grade 2 (moderate) | 2 (16.7) | 4 (25) | 2 (16.7) | 10 (62.5) | ||
| Grade 3 (strong) | 1 (8.3) | 2 (12.5) | 10 (83.3) | 6 (37.5) | ||
| (B) Changes in HPGD Expression Before and After CO2 Exposure | ||||||
| Degree of Change | Celecoxib (n = 12, %) | Placebo (n = 16, %) | p Value | |||
| Level 1 increase * | 5 (41.7) | 14 (87.5) | 0.01 | |||
| Level 2 Increase † | 7 (58.3) | 2 (12.5) | ||||
| Postoperative Time | Intention-to-Treat Population | Per Protocol Population | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib (n = 30) | Placebo (n = 32) | p Value | Celecoxib (n = 27) | Placebo (n = 25) | p Value | |
| 0 h | 4.5 (1, 9) | 5 (3, 10) | 0.51 | 4 (1, 9) | 5 (3, 10) | 0.35 |
| 6 h | 2.5 (0, 5) | 3 (0, 5) | 0.18 | 2 (1, 5) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.03 |
| 12 h | 2 (1, 6) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.10 | 2 (1, 6) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.03 |
| 18 h | 2 (1, 5) | 2 (0, 6) | 0.23 | 2 (1, 4) | 2 (0, 6) | 0.27 |
| 24 h | 2 (0, 7) | 2.5 (0, 5) | 0.43 | 2 (0, 7) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.31 |
| 30 h | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 10) | 0.40 | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (1, 10) | 0.32 |
| 36 h | 2 (0 6) | 2 (0, 5) | 0.86 | 2 (0, 6) | 2 (1, 5) | 0.69 |
| 42 h | 2 (0, 5) | 2.5 (0, 5) | 0.19 | 2 (0, 5) | 3 (0, 5) | 0.24 |
| 48 h | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 5) | 0.72 | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 5) | 0.47 |
| Postoperative Time | Intention-to-Treat | Per Protocol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib (n = 19) | Placebo (n = 15) | p Value | Celecoxib (n = 17) | Placebo (n = 13) | p Value | |
| 0 h | 5 (1, 8) | 5 (3, 7) | 0.82 | 3 (1, 8) | 5 (3, 7) | 0.81 |
| 6 h | 3 (1, 8) | 3 (0, 5) | 0.71 | 3 (1, 5) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.39 |
| 12 h | 2 (1, 6) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.34 | 2 (1, 6) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.33 |
| 18 h | 2 (1, 4) | 2 (0, 4) | 0.55 | 2 (1, 4) | 2 (0, 4) | 0.47 |
| 24 h | 3 (0, 7) | 2 (0, 5) | 0.46 | 3 (0, 7) | 2 (1, 5) | 0.64 |
| 30 h | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 5) | 0.52 | 2 (0, 5) | 1 (1, 5) | 0.70 |
| 36 h | 2 (1, 6) | 1 (0, 4) | 0.27 | 2 (1, 6) | 1 (1, 4) | 0.38 |
| 42 h | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 3) | 0.47 | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 3) | 0.35 |
| 48 h | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 3) | 0.44 | 2 (0, 5) | 2 (0, 3) | 0.50 |
| Postoperative Time | Intention-to-Treat | Per Protocol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Celecoxib (n = 11) | Placebo (n = 17) | p Value | Celecoxib (n = 10) | Placebo (n = 12) | p Value | |
| 0 h | 4 (2, 9) | 6 (3, 10) | 0.36 | 4 (2, 0) | 6 (3, 10) | 0.13 |
| 6 h | 2 (0, 4) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.09 | 2 (1, 4) | 4 (2, 5) | 0.02 |
| 12 h | 2 (1, 5) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.15 | 1.5 (1. 4) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.03 |
| 18 h | 1 (1, 5) | 2 (1, 6) | 0.02 | 1 (1, 4) | 2 (1, 6) | 0.01 |
| 24 h | 2 (1, 4) | 3 (1, 5) | 0.05 | 2 (1, 3) | 3 (2, 5) | 0.02 |
| 30 h | 2 (0, 3) | 3 (1, 10) | 0.08 | 2 (0, 3) | 3 (1, 10) | 0.04 |
| 36 h | 1.5 (0, 3) | 2.5 (1, 5) | 0.11 | 1.5 (0, 3) | 2.5 (1, 5) | 0.09 |
| 42 h | 1 (0, 2) | 3 (0, 5) | <0.01 | 1 (0, 2) | 3 (1, 5) | <0.01 |
| 48 h | 2 (1, 3) | 2 (0, 5) | 0.18 | 2 (1, 3) | 2.5 (1, 5) | 0.04 |
| Outcomes | Celecoxib (n = 30) | Placebo (n = 32) | p Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Operation time (min, mean, SD) | 71.9 ± 56.6 | 80.7 ± 51.1 | 0.52 |
| Estimated blood loss (mL, mean, SD) | 265.1 ± 226.1 | 198.6 ± 161.3 | 0.19 |
| No. of transfusion (median, range) | 0 (0, 1) | 0 (0, 2) | 0.29 |
| No. of rescue analgesics (median, range) | 0 (0, 4) | 0 (0, 3) | 0.62 |
| Discontinuation of PCA use (n, %) | 7 (23.3) | 6 (18.8) | 0.75 |
| Duration of hospitalization (d, range) | 5 (4, 9) | 5 (4, 5) | 0.86 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, K.H.; Park, S.; Lee, S.; Ham, J.; Lim, W.; Song, G.; Kim, H.S. Upregulation of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Celecoxib to Reduce Pain After Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery (POPCORN Trial): A Randomized Controlled Trial. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071784
Han KH, Park S, Lee S, Ham J, Lim W, Song G, Kim HS. Upregulation of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Celecoxib to Reduce Pain After Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery (POPCORN Trial): A Randomized Controlled Trial. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(7):1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071784
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Kyung Hee, Sunwoo Park, Seungmee Lee, Jiyeon Ham, Whasun Lim, Gwonhwa Song, and Hee Seung Kim. 2025. "Upregulation of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Celecoxib to Reduce Pain After Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery (POPCORN Trial): A Randomized Controlled Trial" Biomedicines 13, no. 7: 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071784
APA StyleHan, K. H., Park, S., Lee, S., Ham, J., Lim, W., Song, G., & Kim, H. S. (2025). Upregulation of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Celecoxib to Reduce Pain After Laparoendoscopic Single-Site Surgery (POPCORN Trial): A Randomized Controlled Trial. Biomedicines, 13(7), 1784. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13071784







