Abstract
Background: Urological cancers (UCs) greatly impact global public health. While immunity plays an important role, the contribution of specific immune cell traits to the development of UCs remains unclear. In our study, we employed Mendelian randomization (MR) to elucidate the causal relationship between 731 immune cell traits and three common UCs, namely kidney cancer (KC), bladder cancer (BC), and prostate cancer (PC). Methods: In our research, we adopted and preprocessed the statistics of 731 immune cell types from the GWAS Catalog. The data of three common UCs were acquired from two databases, FinnGen and IEU. Five MR analysis models, including random-effect inverse-variance weighted, weighted median, MR Egger, weighted mode, and simple mode, were used to assess the association between 731 immune cell traits and UCs. Subsequently, a meta-analysis of the IVW method was performed, and the significant results were analyzed using the reverse MR method. Sensitivity analyses, including leave-one-out analysis, were also performed. Results: When analyzing the two datasets separately, 25, 41, and 23 immune phenotypes were found to be significantly associated with BC, PC, and KC, respectively. When applying meta-analysis, the combined results showed that a total of 18 immune cell types manifested the significant association, including 4 and 14 immune cell traits regarding BC and PC, respectively. Utilizing reverse MR analysis on the combined results, we found that two immune cell traits, namely lymphocyte absolute cell counts and CX3CR1 on CD14+ CD16- monocytes, showed a reverse causal relationship with PC. Conclusions: Our research depicts the immune landscape for these three common UCs, highlighting their strong genetic associations with immune cells. It provides valuable insights for identifying the systemic immunological context of cancer susceptibility and the development of blood-based immunological biomarkers and therapeutic targets.
1. Introduction
Urological cancers (UCs) account for nearly 13% of all cancers, substantially impacting global public health, especially in an aging society [1,2,3]. UC encompasses three principal malignancies: prostate cancer (PC), bladder cancer (BC), and kidney cancer (KC). According to reports, PC is the second leading malignancy in men, with an estimated 1.4 million newly diagnosed cases each year [4]. BC and KC ranked as the 10th and 14th most common cancers, respectively, with roughly 573,000 and 430,000 new cases annually, according to the estimated data [5].
Immune system disorders affect the development of UCs, while the immune system of patients with UC also changes, influencing the progression and prognosis of cancer. Researchers have highlighted the complex relationship between UCs and the immune system, mainly focusing on the alteration of the immune system in patients with UCs. In muscle-invasive BC (MIBC), the quantification of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes located in the tumor-adjacent stroma was reported to predict immune phenotype, molecular subtype, and patient outcome [6]. In non-muscle-invasive BC (NMIBC), studies suggested that PDL1+ Treg cells were induced after Bacillus Calmette–Guerin instillation [7]. For PC, it was reported that the initiation, progression, and development of castration-resistance involved the interaction of the host immune system and tumor cells [8]. Specifically, neuroendocrine differentiation (NED), induced by sustained androgen receptor inhibition, was facilitated by immune cells, resulting in the evasiveness of tumor cells under drug exposure [9,10]. For KC, research revealed that T cells made up the predominant type of immune cell in the microenvironment of clear-cell renal-cell carcinoma (ccRCC), accounting for an average of 51% [11]. The infiltrating T cells displayed an immunosuppressed phenotype, which partially explains the continued progression of ccRCC despite substantial T cell infiltration [12]. However, studies investigating the relationship between immune imbalance and tumor development remain limited, and conventional studies may introduce bias owing to selection bias, reverse causation, and the influence of multiple confounding factors.
Mendelian randomization (MR) utilizes genetic variants (single-nucleotide polymorphisms, SNPs) as instrumental variables (IVs) of the exposure, which examine the cause-and-effect relationship with the outcome while reducing bias introduced by confounding factors; it is being increasingly used for inferring the causal relationships between traits. Several studies have adopted MR to infer the causality between immune cell traits and cancers, including breast cancer and malignant neoplasm of the ovary [13,14]. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential causal relationships between 3 common urological cancers and 731 immune cell traits using MR analysis. The results of our study can contribute to the development of blood-based biomarkers for early risk assessment, guide patient stratification, and inform future directions in immunotherapy research for kidney, bladder, and prostate cancers.
2. Method
2.1. Study Design
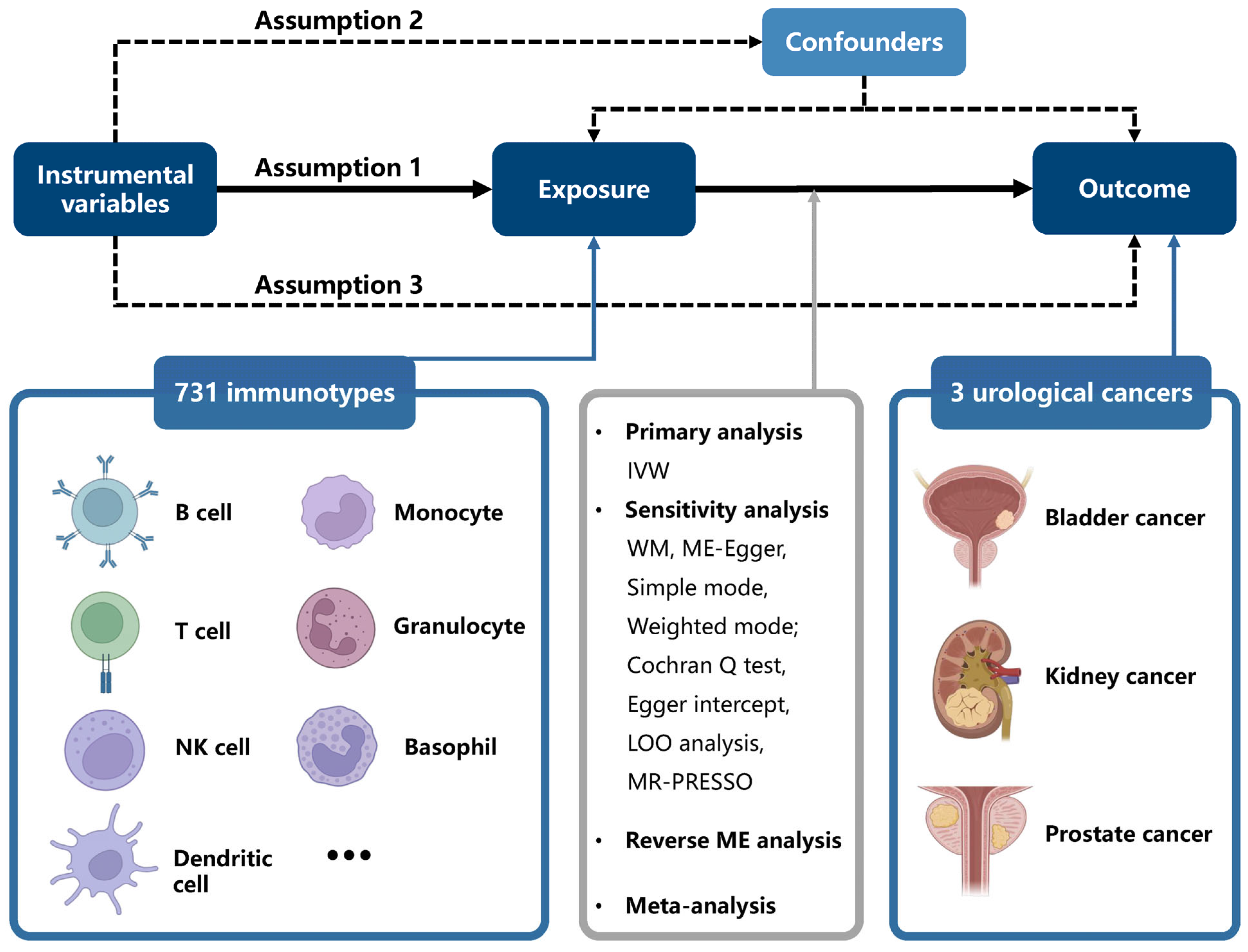
By using SNPs, which are randomly allocated in offspring, as IVs, instrumental-variable analysis mimics a randomized controlled trial (RCT) to examine causal association while remaining unaffected by confounding factors such as age and region. Additionally, this MR analysis is based on three assumptions: [1] SNPs are strongly associated with exposure; [2] SNPs are not associated with any confounders of the exposure–outcome relationship; [3] SNPs influence the outcome exclusively through exposure. In this study, we used public datasets to infer causality, and no additional ethical approval was needed owing to prior received approval. A brief overview of the study is displayed in Figure 1, and our research adhered to STROBE-MR guidelines (Supplementary Table S24).
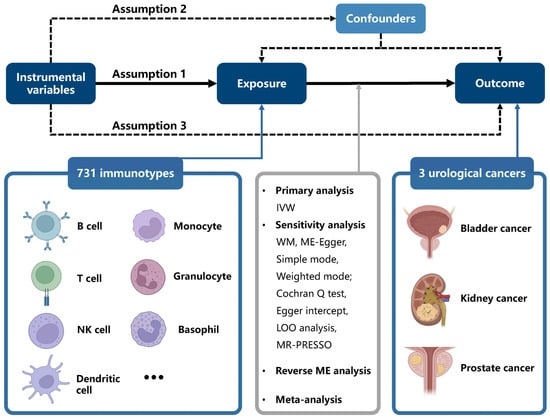
Figure 1.
Study design of Mendelian randomization analysis of immune cell signatures in UCs. All figures were produced with BioRender (https://app.biorender.com/)(accessed on 16 February 2025).
2.2. GWAS Data Sources
The immune cell data were acquired from the publicly accessible GWAS Catalog (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/ (accessed on 16 February 2025)) [15,16], covering registration codes from GCST90001391 to GCST90002121, which were originally derived from Dr. Valeria Orrù et al. [17]. The study used 731 immune cell traits, including 389 median fluorescence intensities (MFIs), which reflected surface antigen levels, 32 morphological parameters (MPs), 118 absolute cell counts (AC), and 192 relative cell counts (RCs). In detail, MFI, AC, and RC features encompassed immune cell panels including TBNK (T cells, B cells, natural killer cells), mature-stage T cells, Treg cells, B cells, myeloid cells, monocytes, and cDCs, while MP features mainly included TBNK and cDCs.
The genetic data regarding the three common UCs—BC, PC, and KC—were sourced from two databases, including the FinnGen database and the Open GWAS database. Informed consent was acquired from European individuals included in the study cohort. The GWAS IDs for data from the Open GWAS database were ieu-b-4874, ieu-b-85, and ukb-b-1316 for BC, PC, and KC, respectively. More details can be found in the Supplementary Materials. Notably, there was no overlap between the two cohorts mentioned above, indicating the feasibility of implementing a two-sample MR study.
2.3. Selection Criteria for Instrumental Variables
To satisfy the relevance assumption between SNPs and the exposure, a significance threshold of 1 × 10−5 was applied. Additionally, SNPs with strong linkage disequilibrium were then filtered (r2 < 0.001), at a window size of 10,000 kb. In addition, to address potential estimation bias generated by weak IVs, we estimated the F-statistic. Weak IVs with F-statistics < 10 were subsequently eliminated. Moreover, the minor allele frequency was used to prune exposures related to rare variants, with a threshold of 0.01. Lastly, palindromic SNPs were also removed, and filtered SNPs were harmonized to guarantee consistency in the estimation of causal effects for the same effect allele.
2.4. Mendelian Randomization Analysis
Five MR methods, namely random-effect inverse-variance weighted (IVW), MR Egger, weighted median, weighted mode, and simple mode, were used to assess the association between exposure and outcome. The IVW method was used as the primary approach to estimate the causal effects. For each IV, the effect size was estimated using the Wald ratio (WR). Weighted median (WM) and MR Egger were utilized to generate unbiased estimates with invalid IVs, which can improve the robustness of IVW estimates, in spite of their inefficiency (wider CIs). MR Egger allows for pleiotropic effects that are uncorrelated with the variant–exposure relationships, while WM assumes that over 50% of the IVs are valid to yield unbiased estimates. To guarantee the robustness of our findings, the leave-one-out analysis was performed.
To evaluate pleiotropy, MR Egger intercept analysis was performed. Heterogeneity was tested using Cochran’s Q statistic, and I2 statistics were computed for evaluation. Heterogeneity was considered absent (I2 < 25%) or mild (I2 < 50%), according to I2 statistics. To enhance the robustness of our results, we selected the significant results from one database and conducted a meta-analysis of the IVW-MR estimates across the two data sources. Moreover, reverse MR analysis was conducted to infer bidirectional causality regarding the significant immune traits identified by meta-analysis.
2.5. Evaluation of Ancestry-Specific Causal Associations
To explore potential differences in causal relationships across ancestries, we performed an MR analysis using data from a non-European population. Specifically, we searched the IEU Open GWAS catalog and only identified a PC GWAS conducted in the Biobank Japan (BBJ) cohort (GWAS ID: bbj-a-148). This dataset included 109,347 participants, among whom 5408 were diagnosed with PC. A p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were conducted using R version 4.2.1 (The R Project for Statistical Computing; https://www.r-project.org/ (accessed on 16 February 2025)). “ldscr” and “TwoSampleMR” packages were used. To control for multiple comparisons, Bonferroni correction was applied based on the number of primary hypotheses tested. Specifically, our study investigated the potential causal associations between 3 distinct urological cancers and 731 immune cell traits using MR analysis. Since the primary interest was the three cancer types—each considered an independent outcome—the significance threshold was adjusted by dividing 0.05 by 3 (i.e., p < 0.0167) to account for testing across the three cancer types [13]. When evaluating the meta-analysis, reverse MR analysis, heterogeneity, and horizontal pleiotropy, a p-value of less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Causal Relationship Between Immune Cell Traits and BC
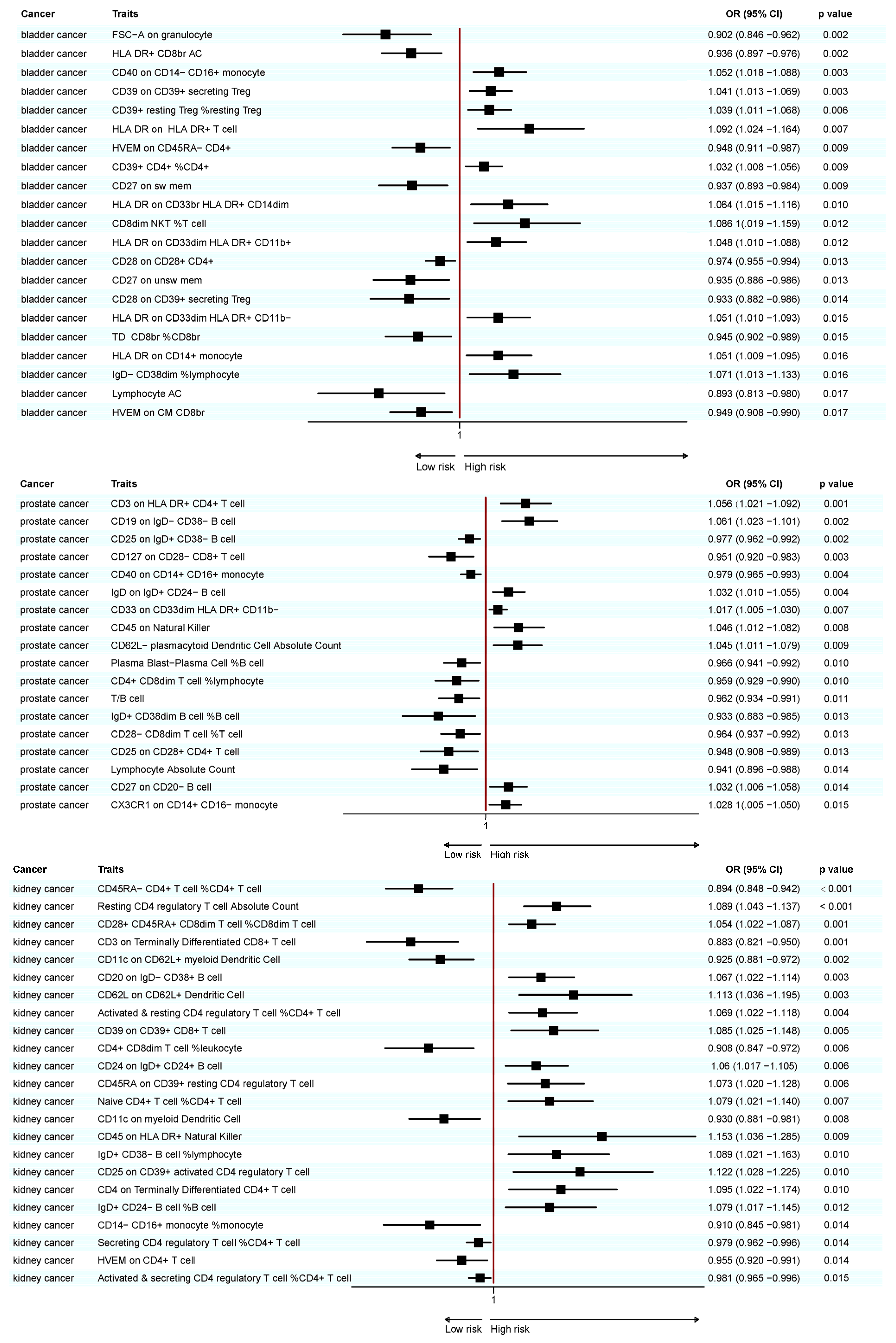
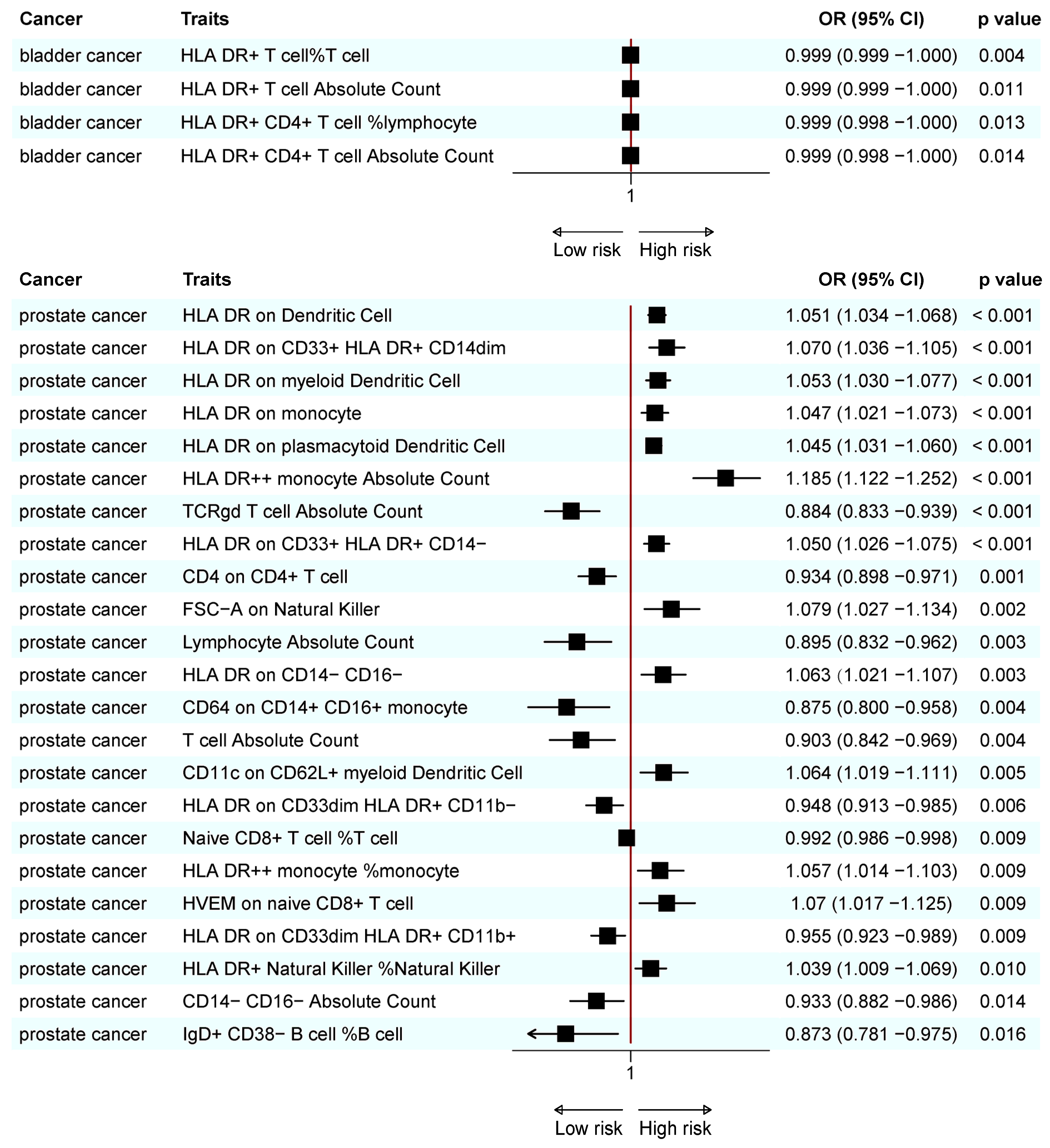
A total of 25 immunotypes were significantly associated with BC based on the IVW method. Specifically, two immune cell traits from the TBNK panel, three from the Treg panel, one from the B cell panel, three from the myeloid panel, and two from the monocyte panel showed a positive association with BC risk. In contrast, six immune cell traits from the TBNK panel, three from the T cell maturation stages panel, two from the Treg panel, two from the B cell panel, and one from the cDCs panel demonstrated a negative association (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4; Supplementary Tables S3 and S13).
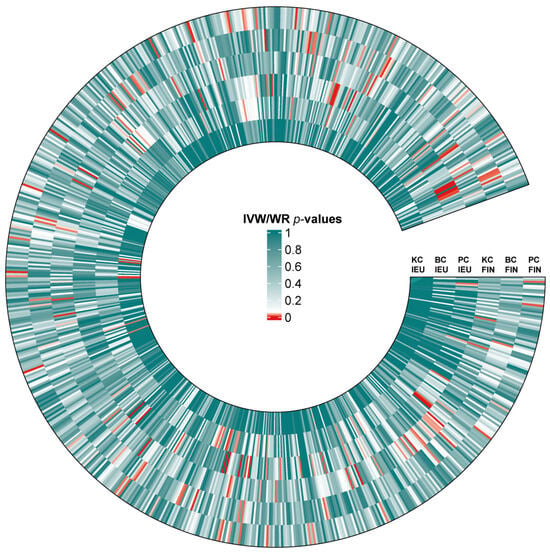
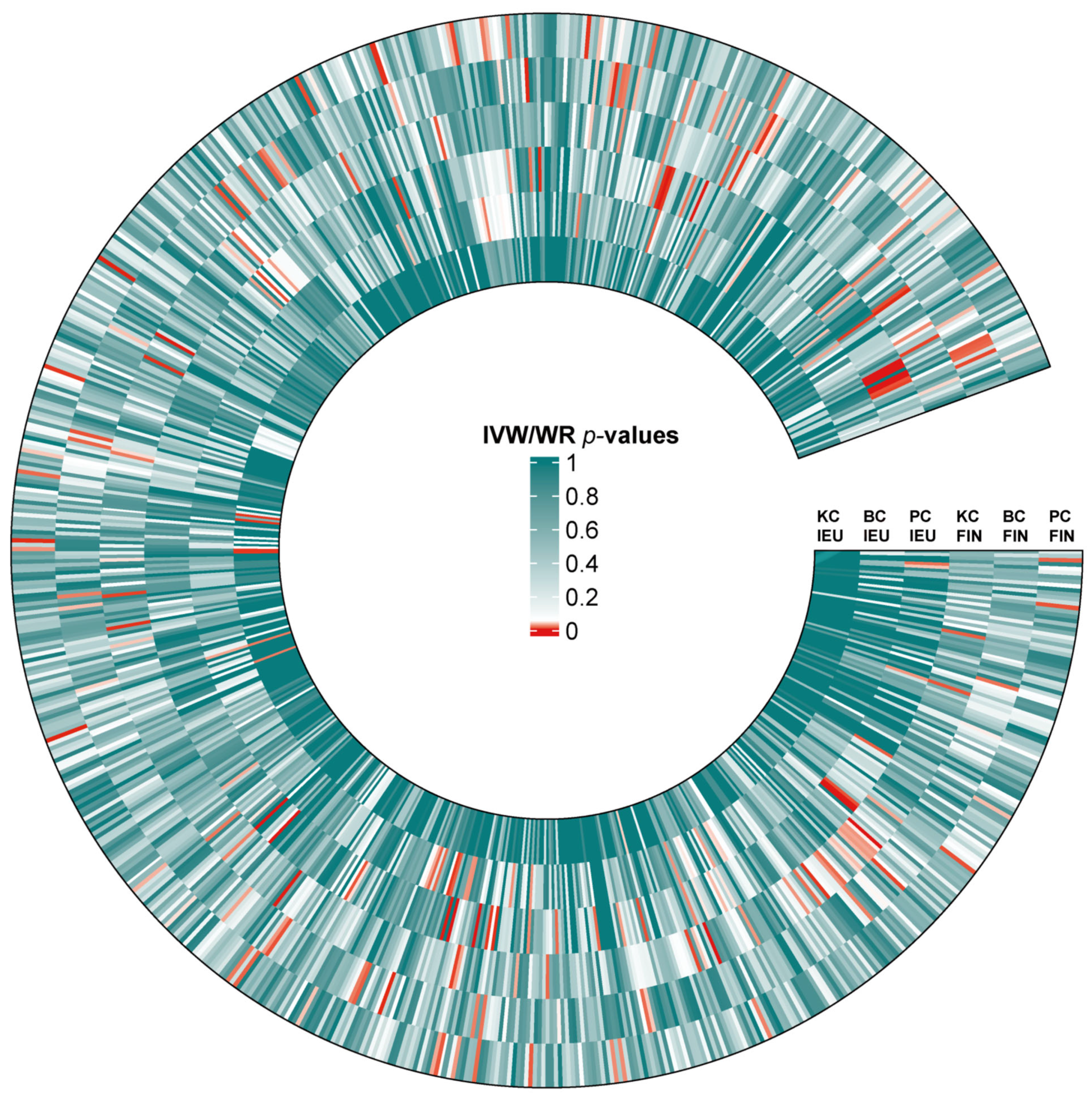
Figure 2.
Heat map of IVW/WR estimates for three urological cancers from two databases. Standardized beta values of the inverse-variance weighted or Wald ratio (IVW/WR) are shown for associations between blood immune traits and kidney cancer (KC), bladder cancer (BC), and prostate cancer (PC) across two GWAS sources: IEU and FinnGen (FIN). The color of each cell represents the p-value of IVW/WR methods.
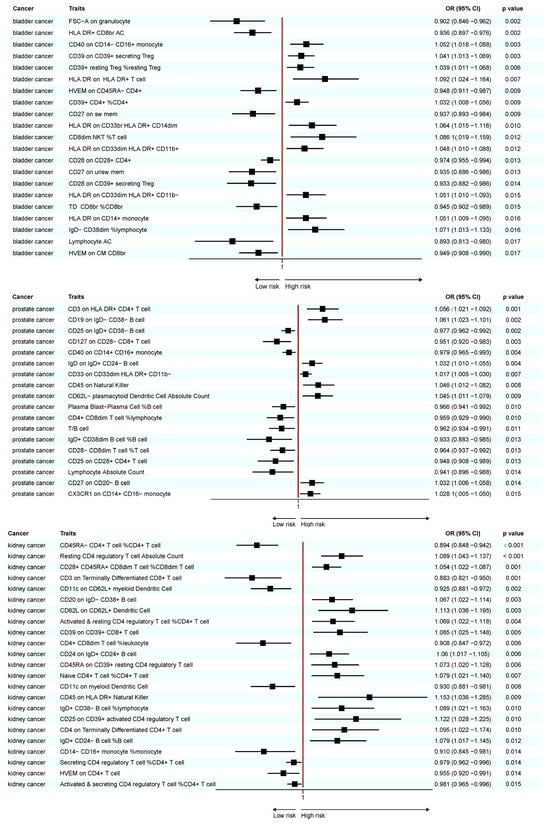
Figure 3.
Forest plot of significant MR results in the FinnGen database.
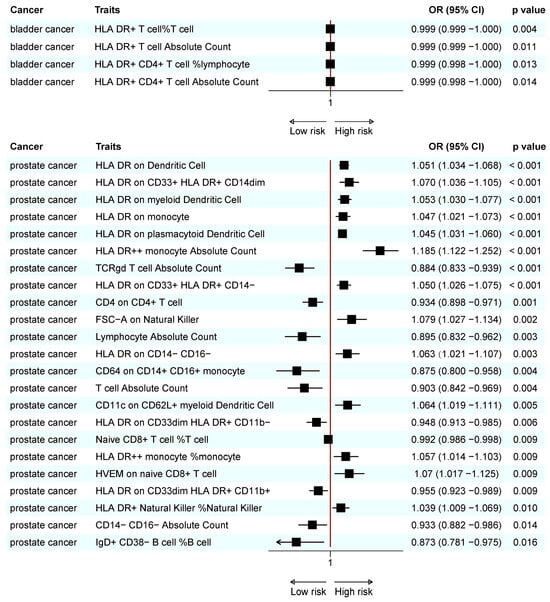
Figure 4.
Forest plot of significant MR results in the IEU database.
In general, only three immunotypes, including HLA DR on CD33br HLA DR+ CD14dim, HLA DR on CD33dim HLA DR+ CD11b+, and HLA DR on CD14+ monocytes, showed mild heterogeneity, and none of the immune traits showed pleiotropy (Table 1; Supplementary Tables S4, S5, S13 and S14).

Table 1.
Heterogeneity and horizontal pleiotropy of positive MR analysis results with immune cells as exposure and UCs as outcome.
3.2. Causal Relationships Between Immune Cell Traits and PC
A total of 41 immune cell traits were significantly associated with PC. Specifically, immune cell traits of TBNK (n = 6) and the maturation stages of T cells (n = 1), B cells (n = 3), myeloid cells (n = 3), monocytes (n = 3), and cDCs (n = 5) were positively associated with PC risk. Conversely, immune cell traits of TBNK (n = 6) and the maturation stage of T cells (n = 2), Tregs (n = 3), B cells (n = 4), myeloid cells (n = 2), and monocytes (n = 3) showed a negative association (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4; Supplementary Tables S6 and S15).
Generally, for PC, four immunotypes exhibited heterogeneity, including CD3 on HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells, the proportion of CD4+ CD8dim T cells within lymphocytes, HLA DR on CD14- CD16-, and HLA DR on CD33dim HLA DR+ CD11b-. The proportion of CD4+ CD8dim T cells within lymphocytes and HLA DR on myeloid dendritic cells were the only two immune traits that demonstrated pleiotropy (Table 1; Supplementary Tables S7, S8, S16 and S17).
3.3. Causal Relationship Between Immune Cell Traits and KC
A total of 23 immune cell traits were significantly associated with KC (Figure 2, Figure 3 and Figure 4; Supplementary Tables S9 and S18). To elaborate, one TBNK trait, two maturation stages of T cell traits, six Treg traits, four B cell traits, and one cDC trait demonstrated a positive association with an elevated risk of KC. On the contrary, one TBNK trait, three maturation stages of T cell traits, two Treg traits, one monocyte trait, and two cDC traits were negatively associated with KC risk.
In total, as for KC, only one immunotype named CD11c on myeloid dendritic cells showed mild heterogeneity. CD39 on CD39+ CD8+ T cells and CD24 on IgD+ CD24+ B cells were the only two immunotypes that exhibited pleiotropy (Table 1; Supplementary Tables S10, S11, S19 and S20).
3.4. Combined Results for Urological Cancers from Meta-Analysis and Reverse MR Analysis
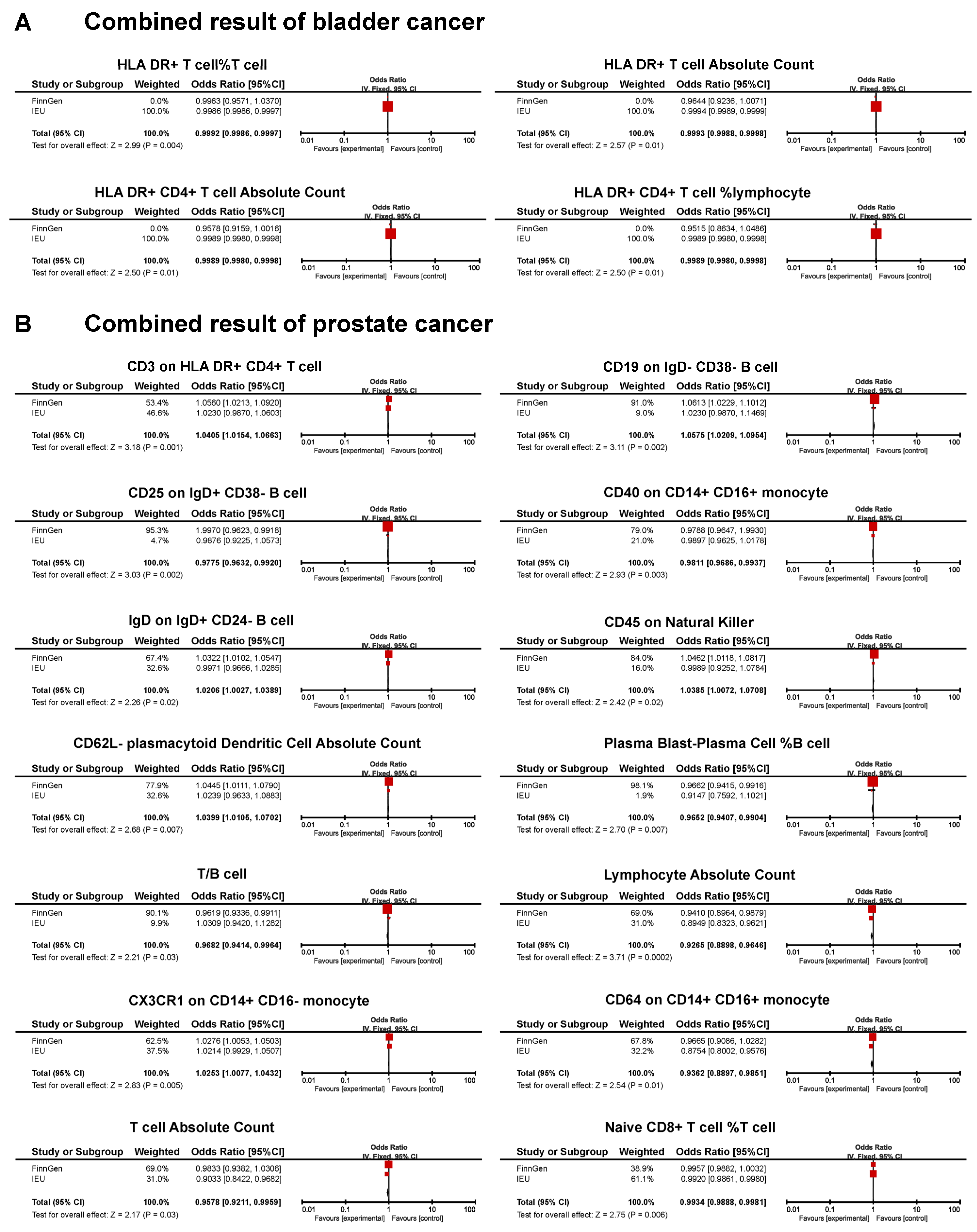
A meta-analysis found that 18 immunotypes exhibited a significant association with UCs (Figure 5).
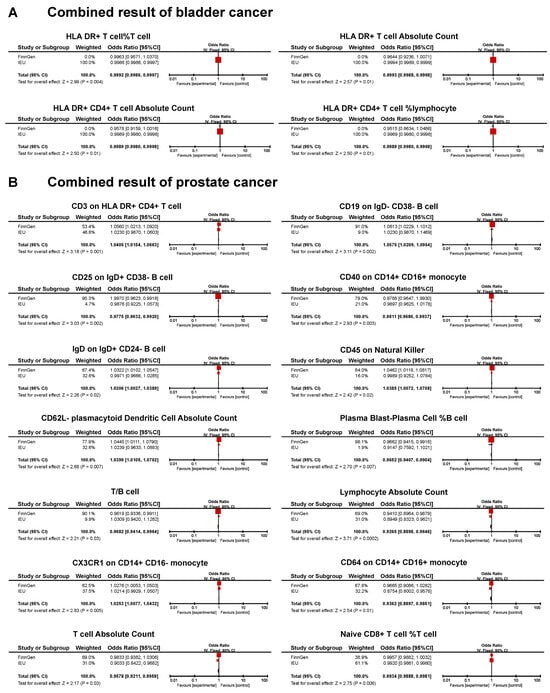
Figure 5.
Forest plot of the significant combined result of MR analysis. (A) Significant combined result of BC; (B) significant combined result of PC.
The combined results confirm the negative causal risk of the proportion of HLA DR+ T cells within T cells, HLA DR+ T cell AC, HLA DR+ CD4+ T cell AC, and the proportion of HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells within lymphocytes in BC. In PC, the results of the meta-analysis confirmed the positive relationship of CD3 in HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells, CD19 on IgD- CD38- B cells, IgD on IgD+ CD24- B cells, CD45 on natural killer cells, CD62L- plasmacytoid dendritic cell AC, and CX3CR1 in CD14+ CD16- monocytes. In addition, a negative association was found for CD25 on IgD+ CD38- B cells, CD40 on CD14+ CD16+ monocytes, the proportion of plasma blast-plasma cells within B cells, T/B cells, lymphocyte AC, CD64 on CD14+ CD16+ monocytes, T cell AC, and the proportion of naive CD8+ T cells within T cells. In KC, none of the immunophenotypes was found to be significantly associated with the risk (Figure 5).
Reverse MR analysis was applied to the significant results obtained from meta-analysis. We found that PC was associated with lower levels of lymphocyte AC and CX3CR1 on the CD14+ CD16- monocyte. The remaining sixteen immunotypes did not show significant results (Table 2; Supplementary Table S21).

Table 2.
Result of the reverse MR analysis carried out on immunophenotypes and UC with direct causality.
3.5. Differences in Causal Relationship Across Ethnic Groups
In total, 30 immune cell traits were found to be causally associated with the risk of PC in the BBJ dataset. Among these, 12 immune cell traits showed positive association, while 18 immune cell traits manifested the opposite results (Supplementary Table S25). Notably, none of these associations were directionally consistent with those identified in the meta-analysis of the European cohort.
4. Discussion
Harnessing a wide range of GWAS data, we investigated the causal connections between 731 immune cell traits and 3 common UCs: BC, PC, and KC. Our study employed meta-analysis to guarantee the robustness of the results. When applying only MR analysis, we identified 89 immune cell traits associated with UCs. As for meta-analysis, 18 immune cell traits only in BC and PC were identified as causally associated, 2 of which were found to be significantly associated in the reverse MR analysis.
BC can be mainly divided into two categories according to its T stage, which are MIBC and NMIBC. MIBC accounts for about 50–60% of overall cases and is the primary cause of death in BC patients owing to its invasiveness. For MIBC patients at cT2-4aN0M0, cisplatin-based combinatory neoadjuvant chemotherapy is advocated. In recent years, with research investigating the effectiveness of anti-PD-1/PD-L1 drugs, chemoimmunotherapy has aroused the public’s attention for its capability of improving patients’ survival. Regarding adjuvant therapy, immunotherapy also served as a possible option. For patients at an elevated risk of recurrence following surgery, the FDA approved the administration of nivolumab, which is a classic agent targeting PD-1. Therefore, it is important to describe the immune landscape of BC for the purpose of more efficient utilization of immunotherapy [18].
Previously, Li et al. reported 16 immune cell traits associated with BC using the MR method [19]. However, in our study, only four immune cell signatures were identified as causally associated through meta-analysis, all of which showed negative association with the risk of BC. HLA DR+ CD4+ T cell was identified as a vital cell type decreasing the risk of BC. HLA DR belongs to class II major histocompatibility complex molecules in the human leukocyte antigen system, which are predominantly expressed on certain immune cells’ surfaces, such as antigen-presenting cells, including dendritic cells, B cells, and macrophages. During immune responses, antigen-presenting cells express the complex of HLA-DR molecules and exogenous or endogenous antigenic peptide fragments and interact with the T cell receptors on CD4+ T cells, thereby activating the T cells. When expressed on T cells, they were identified as a late-stage activation marker [20]. It is acknowledged that CD4+ T cells could differentiate into immune-stimulating and immunosuppressive cells, the balance of which plays a pivotal role in the tumor environment [21]. Drawing from our result, HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells, whose immune-activated subtype outnumbered the immunosuppressive subtype, were assumed to show a pivotally protective role against the onset of BC. Furthermore, HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells were significantly enriched in the peripheral blood of patients responding to immunotherapy in a pan-cancer study, demonstrating their potential for predicting immunotherapy responses [22]. However, another study showed the opposite result when analyzing patients with lung cancer, which may be explained by the heterogeneous function of HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells in different cancers. Future studies are needed to explicitly explain the crucial effect of HLA DR+ CD4+ T cells on BC.
For PC, surgery or radiation therapy is recommended for localized disease, although the recurrence rate is still difficult to control (25–35%) [23]. Regarding recurrent PC, androgen deprivation therapy targeting androgen receptors is considered the standard treatment. Yet, by inducing microenvironment changes, like NED, prostate tumor cells could adapt to androgen deprivation and evolve into a more aggressive form, which is known as castration-resistant PC. In recent years, immunotherapy has served as an alternative treatment for patients. However, since PC is a frustrating, immunogenic “cold” tumor, characterized by an immunosuppressive microenvironment like restricted CD8+ T cells, patients receive unsatisfactory results when treated with immunotherapy [24]. Hence, it is crucial to investigate the links between the immune system and PC, providing insights into potential predictors or targets for new agents.
In PC, a meta-analysis identified 14 immune cell signatures linked to risk, comprising 6 risk factors and 8 protective factors. In the former study, authors found that three immune cell traits increased the risk of PC [25]. However, in our meta-analysis, none of these results showed significance, which may be explained by the bias introduced by drawing from only one database [25]. Notably, two immune cell traits, named lymphocyte absolute count and CX3CR1 on the CD14+ CD16- monocyte, were found to be significant in reverse MR analysis. Regarding the former, lower levels were associated with a higher risk of PC, and PC, in turn, diminished the count of lymphocytes, which contributed to an unceasingly decreased level. The bidirectional relationship in the case of the latter was different. Higher levels of CX3CR1 on CD14+ CD16- monocytes elevated the risk of PC, while PC downregulated its level as a negative feedback mechanism. CX3CR1 is a chemokine receptor majorly involved in regulating monocyte chemotaxis and tumor angiogenesis. It was speculated in another Mendelian randomization study that CX3CR1 on CD14+ CD16- monocytes may promote the onset of PC through the CX3CR1/CX3CL1 signaling pathway, which is actively involved in promoting tumor angiogenesis, migration, and infiltration [25]. When PC develops, we assume that CX3CR1 may be downregulated, which is consistent with a prior study measuring the level of CX3CR1 expression in PC in contrast with adjacent normal tissue [26].
In KC, immunotherapy was recommended as the first-line standard option for patients with intermediate/poor-risk metastatic tumors. In spite of these important advancements, only minor patient cohorts achieved longstanding disease control in RCC populations. Hence, elucidating the relationship between the immune system and KC is of high significance. In KC, 23 immune cell signatures were regarded as significant factors, including 13 risk factors and 10 protective factors, through analyzing FinnGen data. However, results from the IEU dataset analyzed by IVW analysis retrieved no significant results, which was also consistent with the inefficiency of immune therapy for KC to a certain extent. Since meta-analysis was not applicable, the significant results obtained only from the FinnGen dataset, with relatively lower robustness, should be interpreted with caution.
It is important to note that the immune cell traits examined in this study were measured in peripheral blood. While these systemic immune traits may not fully represent the complex and spatially organized immune landscape within the tumor microenvironment, they nonetheless provide valuable insights into general immune status and regulation across individuals. Blood-based immune markers are widely used in clinical and epidemiological research due to their accessibility, reproducibility, and compatibility with large-scale genomic datasets. Moreover, accumulating evidence suggests that systemic immune dysregulation can influence tumorigenesis, modulate host immune surveillance, and affect responses to therapy. Therefore, although our findings should be interpreted with caution regarding direct relevance to tumor-infiltrating immune cells, they offer meaningful information about the systemic immunological context of cancer susceptibility and may contribute to the development of blood-based immunological biomarkers and therapeutic targets for future translational studies.
As acknowledged, immune phenotypes can be shaped by a wide range of factors, including genetic background, environmental exposures, lifestyle habits, and even psychological status [27]. These factors vary substantially across ethnic groups, particularly with respect to immunogenetic architecture [28]. For example, a comprehensive pan-ancestry analysis by Dr. Jian Carrot-Zhang and colleagues involving 10,638 patients from The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) revealed significant ethnic differences in genomic and immunologic profiles. Notably, increased FBXW7 mutations were observed in patients of African descent, while VHL and PBRM1 mutations were decreased in African-origin renal cancer patients. Additionally, East Asian patients with bladder cancer exhibited reduced immune activity compared to European patients [29]. These findings underscore the biological rationale for caution when extrapolating MR results across ancestries. Therefore, MR associations derived from European populations may not be directly applicable to non-European groups. However, large sample GWAS datasets for UCs in non-European ancestries remain limited, with PC in East Asians being a notable exception. To explore it further, we conducted replication MR analysis using Japanese GWAS data to reveal the causal effect between 731 immune cell traits and PC risk. We found that 30 immune cell traits were causally associated with the risk of PC, while none of these associations were directionally consistent with those observed in meta-analyses in European-ancestry cohorts. Further studies are warranted to investigate immune cell traits associated with other cancer types in diverse ancestral populations.
There exist several limitations in our research. Firstly, MR analysis simply provides evidence for unidirectional causality linking immune cell traits to three common UCs; thus, comprehensive molecular experiments are needed to discover the actual mechanisms related to specific immune cell traits and cancer. Additionally, it is widely recognized that interactions between cells in the tumor microenvironment are common, which implies that analyzing the effect of a single immune cell trait on cancer could introduce bias. Lastly, heterogeneity and pleiotropy were found in some immune cell traits when analyzing only one dataset, which could have distorted the findings. Fortunately, only mild heterogeneity existed for the significant results obtained by meta-analysis.
5. Conclusions
In our study, we uncovered the immune landscape for three common UCs—BC, PC, and KC—by analyzing two datasets separately. To emphasize some specific immune traits, we adopted a meta-analysis strategy, demonstrating causal links between 18 immune cell traits and cancers with robustness. Our study underscored the integral association between peripheral blood immune cells and the three common UCs at both the genetic and genomic levels. Although clear mechanisms cannot be elucidated through our study, it offers valuable insights for identifying the systemic immunological context of cancer susceptibility and may contribute to the development of blood-based immunological biomarkers and therapeutic targets for future translational studies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/biomedicines13061480/s1.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.W.; data curation, X.C., G.H. and R.S.; investigation, Z.C. and Y.X.; methodology, Y.X., H.L. and F.J.; project administration, S.W.; resources, S.W. and T.L.; software, Y.W., M.Z. and Y.L.; supervision, S.W. and T.L.; validation, H.W. and H.Y.; visualization, Y.X. and X.C.; writing—original draft, Z.C. and Y.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.C. and X.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable, as informed consent was obtained in the original studies from which data were drawn for this work.
Data Availability Statement
Data on immune cells were sourced from the publicly accessible GWAS Catalog (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/gwas/ (accessed on 16 February 2025)), covering registration numbers from GCST90001391 to GCST90002121. The genetic data regarding three common urological cancers were sourced from the FinnGen website (https://r10.finngen.fi/ (accessed on 16 February 2025)) and the Open GWAS database (https://gwas.mrcieu.ac.uk/ (accessed on 16 February 2025)). The GWAS IDs for the Open GWAS database are ieu-b-4874, ieu-b-85, and ukb-b-1316.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors disclose no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dy, G.W.; Gore, J.L.; Forouzanfar, M.H.; Naghavi, M.; Fitzmaurice, C. Global Burden of Urologic Cancers, 1990–2013. Eur. Urol. 2017, 71, 437–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.; Ouk, S.; Clegg, N.J.; Chen, Y.; Watson, P.A.; Arora, V.; Sawyers, C.L. Development of a second-generation antiandrogen for treatment of advanced prostate cancer. Science 2009, 324, 787–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Cancer Research Fund International. Cancer Trends. Available online: https://www.wcrf.org/cancer-trends (accessed on 16 February 2025).
- Znaor, A.; Skakkebaek, N.E.; Rajpert-De Meyts, E.; Kuliš, T.; Laversanne, M.; Gurney, J.; Sarfati, D.; McGlynn, K.A.; Bray, F. Global patterns in testicular cancer incidence and mortality in 2020. Int. J. Cancer 2022, 151, 692–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfannstiel, C.; Strissel, P.L.; Chiappinelli, K.B.; Sikic, D.; Wach, S.; Wirtz, R.M.; Wullweber, A.; Taubert, H.; Breyer, J.; Otto, W.; et al. The Tumor Immune Microenvironment Drives a Prognostic Relevance That Correlates with Bladder Cancer Subtypes. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2019, 7, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevalier, M.F.; Schneider, A.K.; Cesson, V.; Dartiguenave, F.; Lucca, I.; Jichlinski, P.; Nardelli-Haefliger, D.; Derré, L. Conventional and PD-L1-expressing Regulatory T Cells are Enriched During BCG Therapy and may Limit its Efficacy. Eur. Urol. 2018, 74, 540–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, W.Q. The evolving role of immune cells in prostate cancer. Cancer Lett. 2022, 525, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carceles-Cordon, M.; Kelly, W.K.; Gomella, L.; Knudsen, K.E.; Rodriguez-Bravo, V.; Domingo-Domenech, J. Cellular rewiring in lethal prostate cancer: The architect of drug resistance. Nat. Rev. Urol. 2020, 17, 292–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker, C.; Sartor, O. Abiraterone and increased survival in metastatic prostate cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 767. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Montero, C.M.; Rini, B.I.; Finke, J.H. The immunology of renal cell carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 721–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chevrier, S.; Levine, J.H.; Zanotelli, V.R.T.; Silina, K.; Schulz, D.; Bacac, M.; Ries, C.H.; Ailles, L.; Jewett, M.A.S.; Moch, H.; et al. An Immune Atlas of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Cell 2017, 169, 736–749.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Yao, Y.; Zhai, S.; Ni, F.; Wang, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Li, H.; Hu, H.; Zhang, H.; et al. The role of immune cell signatures in the pathogenesis of ovarian-related diseases: A causal inference based on Mendelian randomization. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 110, 6541–6550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, Z.; Yang, Y. The association between immune cells and breast cancer: Insights from mendelian randomization and meta-analysis. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 111, 230–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerezo, M.; Sollis, E.; Ji, Y.; Lewis, E.; Abid, A.; Bircan, K.O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J.; John, S.; Mosaku, A.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: Standards for reusability, sustainability and diversity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D998–D1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orrù, V.; Steri, M.; Sidore, C.; Marongiu, M.; Serra, V.; Olla, S.; Sole, G.; Lai, S.; Dei, M.; Mulas, A.; et al. Complex genetic signatures in immune cells underlie autoimmunity and inform therapy. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollica, V.; Rizzo, A.; Massari, F. Adjuvant Nivolumab in Muscle-Invasive Urothelial Carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 956–957. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Lv, C.; Chen, J.; Shang, K.; He, H.; Chen, C. Complex causal association between immune cell phenotypes and bladder cancer: A mendelian randomization and mediation study. Int. J. Surg. 2024, 111, 1568–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, R.; Guo, Z.; Wei, W.; Wang, T.; Ouyang, R.; Yuan, X.; Xing, Y.; Wang, F.; Wu, S.; et al. Immunological profiling for short-term predictive analysis in PD-1/PD-L1 therapy for lung cancer. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, R.E.; Richardson, E.K.; Toh, H.C. Revisiting the role of CD4(+) T cells in cancer immunotherapy-new insights into old paradigms. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021, 28, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mispelbaum, R.; Hattenhauer, S.T.; Held, S.A.E.; Brossart, P.; Heine, A. Baseline immune signature score of Tregs × HLA-DR+CD4+ T Cells × PD1+CD8+ T Cells Predict Outcome Immunotherapy in Cancer patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1054161. [Google Scholar]
- Drake, C.G. Prostate cancer as a model for tumour immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2010, 10, 580–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; He, Z.; Gao, Y.; Feng, D.; Wei, X.; Huang, Y.; Hou, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, W. Dual-Pronged Attack: pH-Driven Membrane-Anchored NIR Dual-Type Nano-Photosensitizer Excites Immunogenic Pyroptosis and Sequester Immune Checkpoint for Enhanced Prostate Cancer Photo-Immunotherapy. Adv. Sci. 2023, 10, e2302422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, M.; Zhan, X.; Zhong, F.P. Causal role of immune cells in prostate cancer: A bidirectional Mendelian-randomization analyses. Aging 2024, 16, 10477–10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsaur, I.; Noack, A.; Makarevic, J.; Oppermann, E.; Waaga-Gasser, A.M.; Gasser, M.; Borgmann, H.; Huesch, T.; Gust, K.M.; Reiter, M.; et al. CCL2 Chemokine as a Potential Biomarker for Prostate Cancer: A Pilot Study. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 47, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swaby, A.; Atallah, A.; Varol, O.; Cristea, A.; Quail, D.F. Lifestyle and host determinants of antitumor immunity and cancer health disparities. Trends Cancer 2023, 9, 1019–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergin, A.R.T.; Salgado, R.; Loi, S. Ethnicity, Immunity, and Outcomes: Biology versus Socioeconomic Status. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2023, 11, 705–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrot-Zhang, J.; Chambwe, N.; Damrauer, J.S.; Knijnenburg, T.A.; Robertson, A.G.; Yau, C.; Zhou, W.; Berger, A.C.; Huang, K.L.; Newberg, J.Y.; et al. Comprehensive Analysis of Genetic Ancestry and Its Molecular Correlates in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 639–654.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).