Impact of Long-Term Statin Therapy on Incidence and Severity of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Real-World Data Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
2.2. Participants and Exposure Assessment
2.3. Outcomes
2.4. Baseline Covariates
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Recruitment
3.2. Outcomes According the Use of Statins
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential Lung-Protective Effect of Statins
4.2. Real World Data
4.3. Characteristics and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ATC | Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical |
| CAP | Community-acquired pneumonia |
| CI | Confidence interval |
| HER | Electronic health records |
| ICU | Intensive care unit |
| SIDIAP | Information System for Research in Primary Care |
References
- World Health Statistics 2024: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024.
- Torres, A.; Peetermans, W.E.; Viegi, G.; Blasi, F. Risk factors for community-acquired pneumonia in adults in Europe: A literature review. Thorax 2013, 68, 1057–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoumani, E.; Carter, J.A.; Salomonsson, S.; Stephens, J.M.; Bencina, G. Clinical, economic, and humanistic burden of community acquired pneumonia in Europe: A systematic literature review. Expert Rev. Vaccines 2023, 22, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldman, C.; Anderson, R. Community-acquired pneumonia: Still a major burden of disease. Curr. Opin. Crit. Care 2016, 22, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garcia-Gil, M.; Comas-Cufí, M.; Blanch, J.; Martí, R.; Ponjoan, A.; Alves-Cabratosa, L.; Petersen, I.; Marrugat, J.; Elosua, R.; Grau, M.; et al. Effectiveness of statins as primary prevention in people with different cardiovascular risk: A population-based cohort study. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 104, 719–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oesterle, A.; Laufs, U.; Liao, J.K. Pleiotropic effects of statins on the cardiovascular system. Circ. Res. 2017, 120, 229–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tleyjeh, I.M.; Kashour, T.; Hakim, F.A.; Zimmerman, V.A.; Erwin, P.J.; Sutton, A.J.; Ibrahim, T. Statins for the prevention and treatment of infections: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2009, 169, 1658–1667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauerova, S.; Bartuskova, H.; Muffova, B.; Janousek, L.; Fronek, J.; Petras, M.; Poledne, R.; Kralova Lesna, I. Statins directly influence the polarization of adipose tissue macrophages: A role in chronic inflammation. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parihar, S.P.; Guler, R.; Brombacher, F. Statins: A viable candidate for host-directed therapy against infectious diseases. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2019, 19, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wildes, T.J.; Grippin, A.; Fasanya, H.; Dyson, K.A.; Brantly, M. Effect of atorvastatin on humoral immune response to 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination in healthy volunteers: The StatVax randomized clinical trial. Vaccine 2019, 37, 1313–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chalmers, J.D.; Short, P.M.; Mandal, P.; Akram, A.R.; Hill, A.T. Statins in community acquired pneumonia: Evidence from experimental and clinical studies. Respir. Med. 2010, 104, 1081–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombauts, A.; Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Cuervo, G.; Gudiol, C.; Carratalà, J. Role of the inflammatory response in community-acquired pneumonia: Clinical implications. Expert Rev. Anti. Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, S.D.; Tsai, M.C.; Lin, H.C.; Kang, J.H. Statin use and clinical outcomes among pneumonia patients. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 879–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzinska, F.S.; Dosanjh, D.P.; Parekh, D.; Dancer, R.C.; Patel, J.; Nightingale, P.; Walton, G.M.; Sapey, E.; Thickett, D.R. Statin therapy in patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeenny, R.M.; Mansour, H.; Kabbara, W.K.; Chamoun, N.; Audi, M.; Yared, Y.; Salameh, P. Effects of statins on clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 300060520938586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batais, M.A.; Khan, A.R.; Bin Abdulhak, A.A. The use of statins and risk of community-acquired pneumonia. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2017, 19, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recalde, M.; Rodríguez, C.; Burn, E.; Far, M.; García, D.; Carrere-Molina, J.; Benítez, M.; Moleras, A.; Pistillo, A.; Bolíbar, B.; et al. Data resource profile: The Information System for Research in Primary Care (SIDIAP). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, e324–e336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochoa-Gondar, O.; Torras-Vives, V.; de Diego-Cabanes, C.; Satué-Gracia, E.M.; Vila-Rovira, A.; Forcadell-Perisa, M.J.; Ribas-Seguí, D.; Rodríguez-Casado, C.; Vila-Córcoles, A. Incidence and risk factors of pneumococcal pneumonia in adults: A population-based study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2023, 23, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gil, M.; Comas-Cufí, M.; Ramos, R.; Martí, R.; Alves-Cabratosa, L.; Parramon, D.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Baena-Díez, J.M.; Salvador-González, B.; Elosua, R.; et al. Effectiveness of statins as primary prevention in people with gout: A population-based cohort study. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. Ther. 2019, 24, 542–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domínguez-Berjón, M.F.; Borrell, C.; Cano-Serral, G.; Esnaola, S.; Nolasco, A.; Pasarín, M.I.; Ramis, R.; Saurina, C.; Escolar-Pujolar, A. Constructing a deprivation index based on census data in large Spanish cities (the MEDEA project). Gac. Sanit. 2008, 22, 179–187, Spanish. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwagami, M.; Shinozaki, T. Introduction to matching in case-control and cohort studies. Ann. Clin. Epidemiol. 2022, 4, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.S.; Groenwold, R.H.; Pestman, W.R.; Belitser, S.V.; Roes, K.C.; Hoes, A.W.; de Boer, A.; Klungel, O.H. Propensity score balance measures in pharmacoepidemiology: A simulation study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2014, 23, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, D.; Imai, K.; King, G.; Stuart, E.A. MatchIt: Nonparametric preprocessing for parametric causal inference. J. Stat. Soft. 2011, 42, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arel-Bundock, V.; Greifer, N.; Heiss, A. How to interpret statistical models using marginaleffects for R and Python. J. Stat. Soft. 2024, 111, 1–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sjoberg, D.; Baillie, M.; Fruechtenicht, C.; Haesendonckx, S.; Treis, T. ggsurvfit: Flexible Time-to-Event Figures. R Package version 1.1.0. 2025. Available online: https://github.com/pharmaverse/ggsurvfit (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2025; Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 20 April 2025).
- Vinogradova, Y.; Coupland, C.; Hippisley-Cox, J. Risk of pneumonia in patients taking statins: Population-based nested case-control study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2011, 61, e742–e748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Myles, P.R.; Hubbard, R.B.; McKeever, T.M.; Pogson, Z.; Smith, C.J.; Gibson, J.E. Risk of community-acquired pneumonia and the use of statins, ace inhibitors and gastric acid suppressants: A population-based case-control study. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2009, 18, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlienger, R.G.; Fedson, D.S.; Jick, S.S.; Jick, H.; Meier, C.R. Statins and the risk of pneumonia: A population-based, nested case-control study. Pharmacotherapy 2007, 27, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dublin, S.; Jackson, M.L.; Nelson, J.C.; Weiss, N.S.; Larson, E.B.; Jackson, L.A. Statin use and risk of community acquired pneumonia in older people: Population based case-control study. BMJ 2009, 338, b2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, A.G.; Nielsen, R.B.; Riis, A.H.; Johnsen, S.P.; Sørensen, H.T.; Thomsen, R.W. The impact of statin use on pneumonia risk and outcome: A combined population-based case-control and cohort study. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novack, V.; MacFadyen, J.; Malhotra, A.; Almog, Y.; Glynn, R.J.; Ridker, P.M. The effect of rosuvastatin on incident pneumonia: Results from the JUPITER trial. CMAJ Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2012, 184, E367–E372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coston, T.D.; Wright, S.W.; Phunpang, R.; Dulsuk, A.; Thiansukhon, E.; Chaisuksant, S.; Tanwisaid, K.; Chuananont, S.; Morakot, C.; Sangsa, N.; et al. Statin use and reduced risk of pneumonia in patients with melioidosis: A lung-specific statin association. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2024, 21, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erkkilä, L.; Jauhiainen, M.; Laitinen, K.; Haasiom, K.; Tiirola, T.; Saikku, P.; Leinonen, M. Effect of simvastatin, an established lipid-lowering drug, on pulmonary Chlamydia pneumoniae infection in mice. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2005, 49, 3959–3962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statt, S.; Ruan, J.W.; Hung, L.Y.; Chang, C.Y.; Huang, C.T.; Lim, J.H.; Li, J.D.; Wu, R.; Kao, C.Y. Statin-conferred enhanced cellular resistance against bacterial pore-forming toxins in airway epithelial cells. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 53, 689–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosch, J.W.; Boyd, A.R.; Hinojosa, E.; Pestina, T.; Hu, Y.; Persons, D.A.; Orihuela, C.J.; Tuomanen, E.I. Statins protect against fulminant pneumococcal infection and cytolysin toxicity in a mouse model of sickle cell disease. J. Clin. Invest. 2010, 120, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hennessy, E.; O’Callaghan, J.; Mooij, M.J.; Legendre, C.; Camacho-Vanegas, O.; Camacho, S.C.; Adams, C.; Martignetti, J.A.; O’Gara, F. The impact of simvastatin on pulmonary effectors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection. PLoS One 2014, 9, e102200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomsen, R.W.; Riis, A.; Kornum, J.B.; Christensen, S.; Johnsen, S.P.; Sørensen, H.T. Preadmission use of statins and outcomes after hospitalization with pneumonia: Population-based cohort study of 29,900 patients. Arch. Intern. Med. 2008, 168, 2081–2087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franchi, C.; Rossio, R.; Mandelli, S.; Ardoino, I.; Nobili, A.; Peyvandi, F.; Mannucci, P.M.; REPOSI Investigators. Statins, ACE/ARBs drug use, and risk of pneumonia in hospitalized older patients: A retrospective cohort study. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2024, 19, 689–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, B.; Yang, S.T.; Wei, K.K.; Yu, A.S.; Kim, B.J.; Gould, M.K.; Sim, J.J. Statin use and mortality among patients hospitalized with sepsis: A retrospective cohort study within Southern California, 2008-2018. Crit. Care Res. Pract. 2022, 2022, 7127531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Tao, Y.; Chen, W.M.; Wu, S.Y.; Zhang, J. Optimal statin use for prevention of sepsis in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2023, 15, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, J.Y.; Eberg, M.; Ernst, P.; Filion, K.B. Statin potency and the risk of hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2017, 83, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, D.M.; Woodward, M.; Muntner, P.; Falzon, L.; Kronish, I. Predictors of nonadherence to statins: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Pharmacother. 2010, 44, 1410–1421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Statin New-Users N = 319,782 | Statin Non-Users N = 319,782 | p-Value | SMD | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) (women) | 180,405 (56.4) | 182,112 (56.9) | <0.001 | 0.011 |
| Age, mean (SD) | 71.09 (7.55) | 71.09 (7.55) | 0.963 | <0.001 |
| Smoking n (%) | <0.001 | 0.078 | ||
| Smoker | 33,532 (10.5) | 39,519 (12.4) | ||
| Former smoker | 47,249 (14.8) | 40,761 (12.7) | ||
| Hypertension, n (%) | 119,638 (37.4) | 94,498 (29.6) | <0.001 | 0.167 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 46,093 (14.4) | 19,932 (6.2) | <0.001 | 0.271 |
| Hypercholesterolemia, n (%) | 98,696 (30.9) | 60,454 (18.9) | <0.001 | 0.279 |
| Obesity, n (%) | 44,892 (14.0) | 30,983 (9.7) | <0.001 | 0.135 |
| Charlson index, median [IQR] | 2.00 [1.00, 3.00] | 2.00 [1.00, 2.00] | <0.001 | 0.167 |
| MEDEA deprivation index, n (%) | <0.001 | 0.072 | ||
| Rural | 21,629 (6.8) | 23,662 (7.4) | ||
| Semi-rural | 17,726 (5.5) | 18,944 (5.9) | ||
| Urban with low deprivation | 62,725 (19.6) | 68,602 (21.5) | ||
| Semi-urban | 39,256 (12.3) | 38,647 (12.1) | ||
| Urban with medium-low deprivation | 50,357 (15.7) | 51,499 (16.1) | ||
| Urban with medium-high deprivation | 68,173 (21.3) | 62,318 (19.5) | ||
| Urban with high deprivation | 59,478 (18.6) | 55,542 (17.4) | ||
| Pneumococcal vaccination, n (%) | 24,734 (7.7) | 21,021 (6.6) | <0.001 | 0.045 |
| Statin New Users | Statin Non-Users | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Events | Incidence Rate (95% CI) | Events | Incidence Rate (95% CI) | Adjusted Risk Ratio * (95% CI) | |
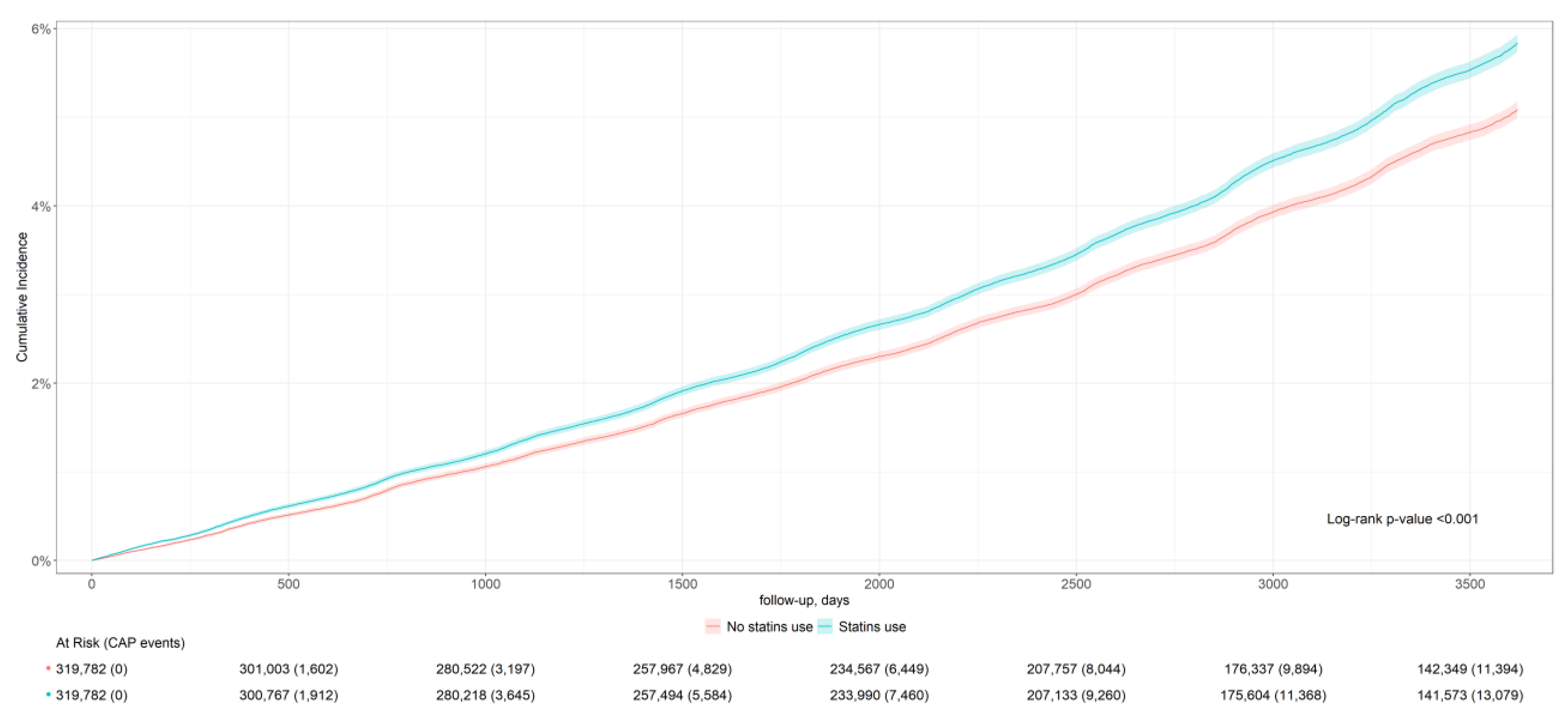
| CAP incidence | 13,453 | 42.1 (41.9; 42.2) | 11,715 | 36.6 (36.5; 36.8) | 0.94 (0.91; 0.96) |
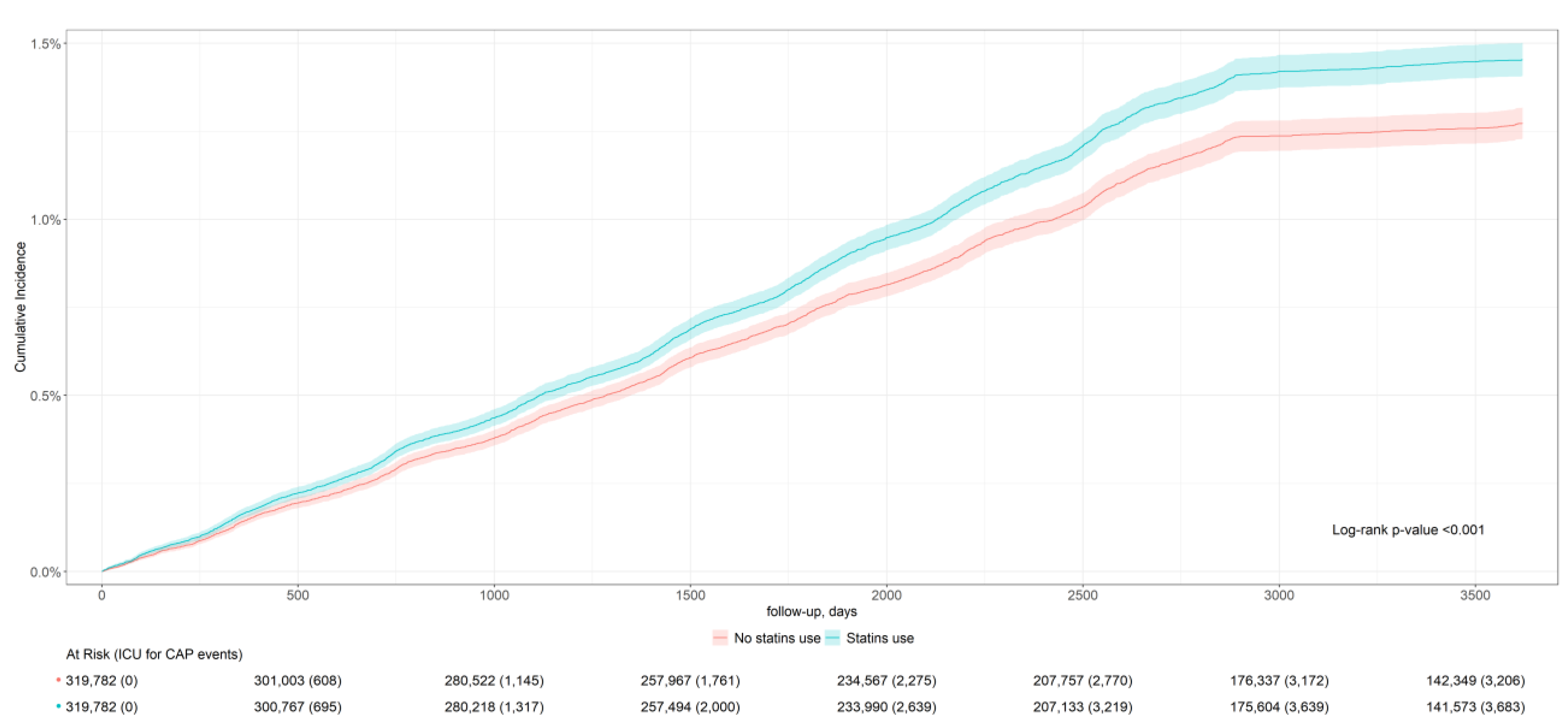
| CAP severity (ICU admission) | 3690 | 11.5 (11.5; 11.6) | 3223 | 10.1 (10.0; 10.1) | 0.93 (0.88; 0.98) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Toledo, D.; Cartanyà-Hueso, À.; Morros, R.; Giner-Soriano, M.; Domínguez, À.; Vilaplana-Carnerero, C.; Grau, M. Impact of Long-Term Statin Therapy on Incidence and Severity of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Real-World Data Analysis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061438
Toledo D, Cartanyà-Hueso À, Morros R, Giner-Soriano M, Domínguez À, Vilaplana-Carnerero C, Grau M. Impact of Long-Term Statin Therapy on Incidence and Severity of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Real-World Data Analysis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061438
Chicago/Turabian StyleToledo, Diana, Àurea Cartanyà-Hueso, Rosa Morros, Maria Giner-Soriano, Àngela Domínguez, Carles Vilaplana-Carnerero, and María Grau. 2025. "Impact of Long-Term Statin Therapy on Incidence and Severity of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Real-World Data Analysis" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061438
APA StyleToledo, D., Cartanyà-Hueso, À., Morros, R., Giner-Soriano, M., Domínguez, À., Vilaplana-Carnerero, C., & Grau, M. (2025). Impact of Long-Term Statin Therapy on Incidence and Severity of Community-Acquired Pneumonia: A Real-World Data Analysis. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061438







