Immune Dysregulation at the Maternal–Fetal Interface Exacerbates Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in an Inflammatory Arthritis Murine Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Mouse Model of IA
2.2. Mouse Model of IA Pregnancy
2.3. Mouse Dissection
2.4. Preparation of Single-Cell Suspensions from Spleen and Lymph Nodes
2.5. Digestion of Placentas and Preparation of Single-Cell Suspensions
2.6. Calculation of Embryo Resorption Rate
2.7. ELISA
2.8. CBA
2.9. Hematoxylin-Eosin Staining
2.10. Flow Cytometry
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Induction of IA in SKG Mice
3.2. APOs in the IA Group
3.3. Systemic Levels of Inflammatory Cytokines in Pregnant Mice with IA
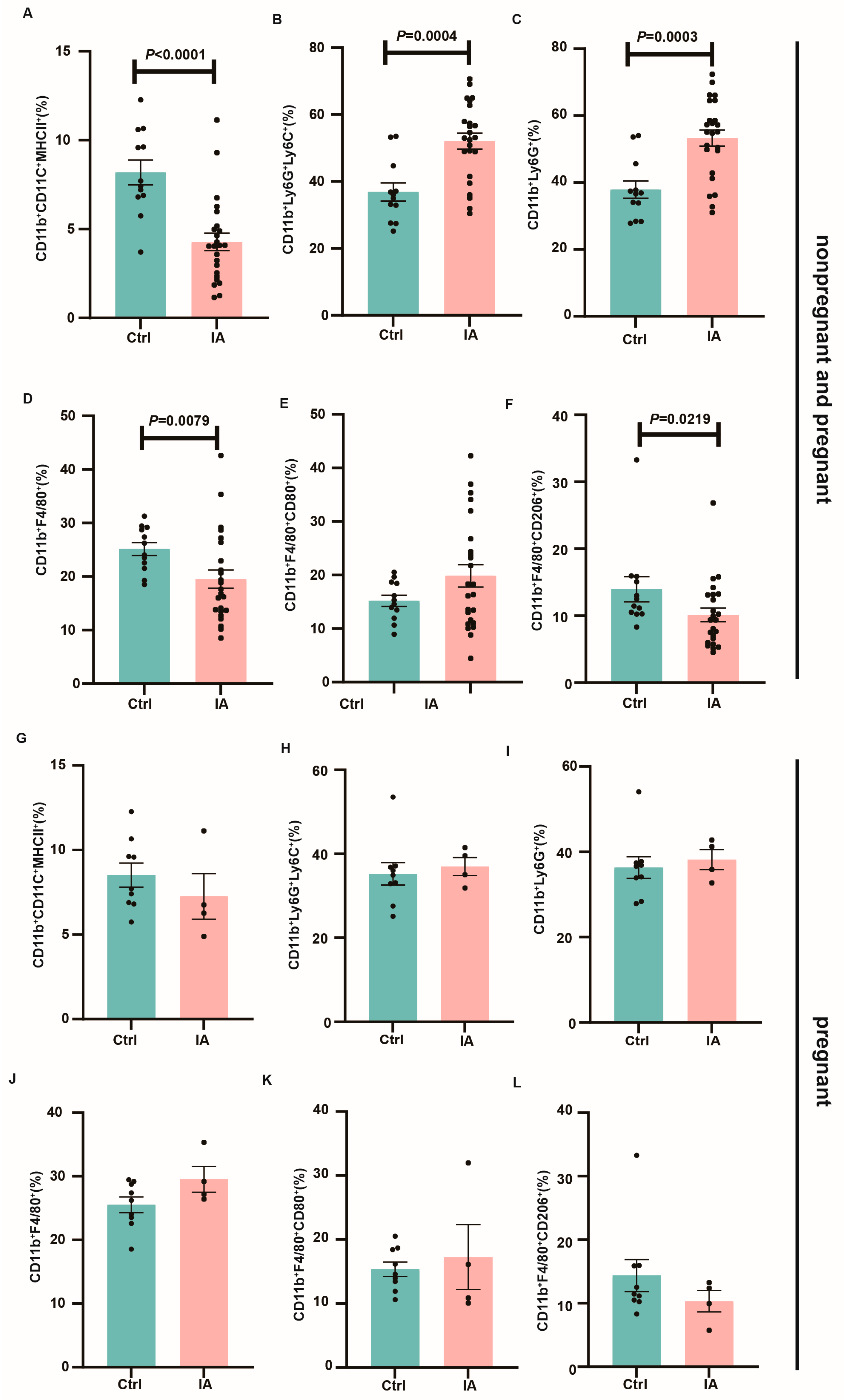
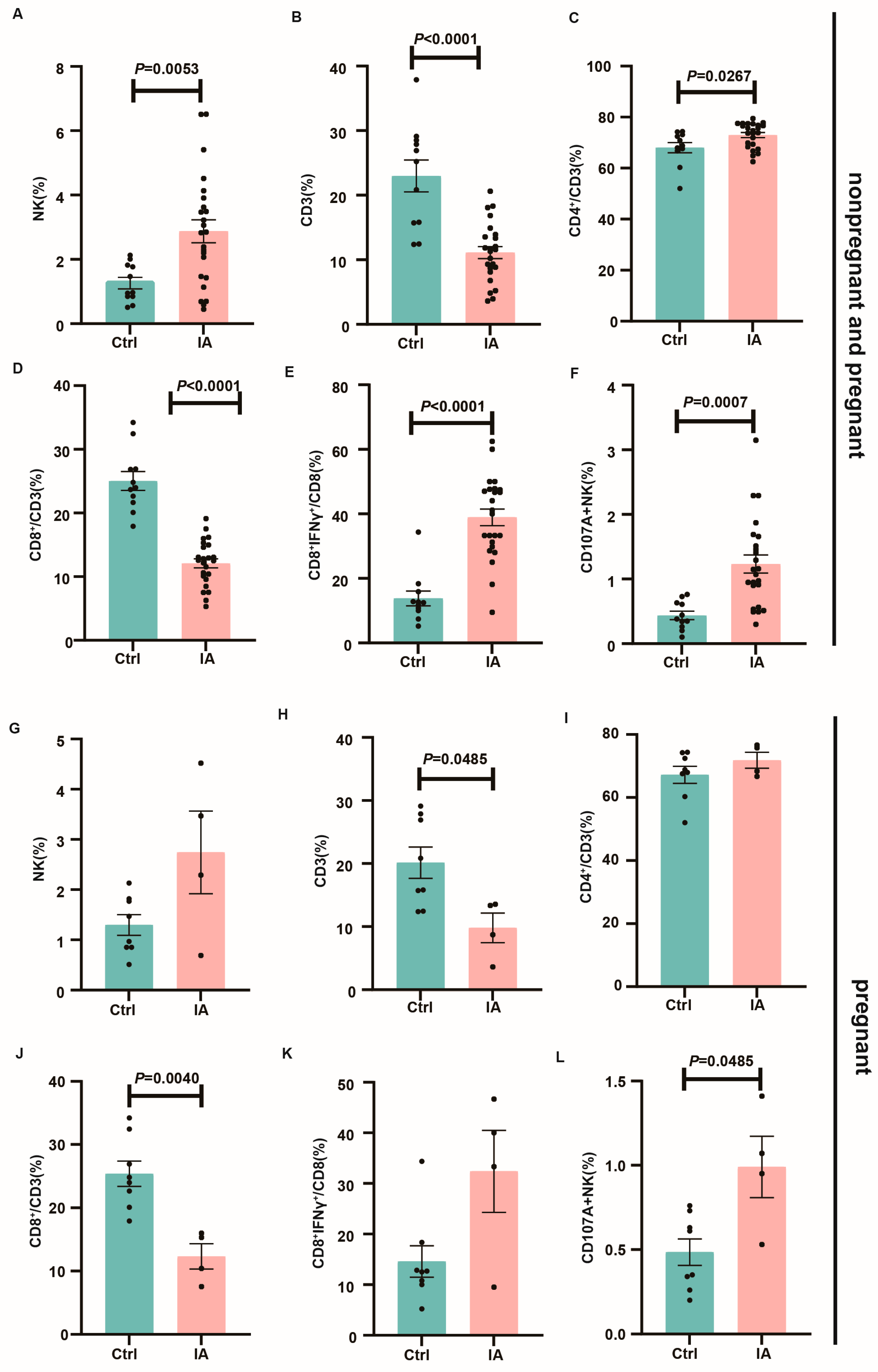
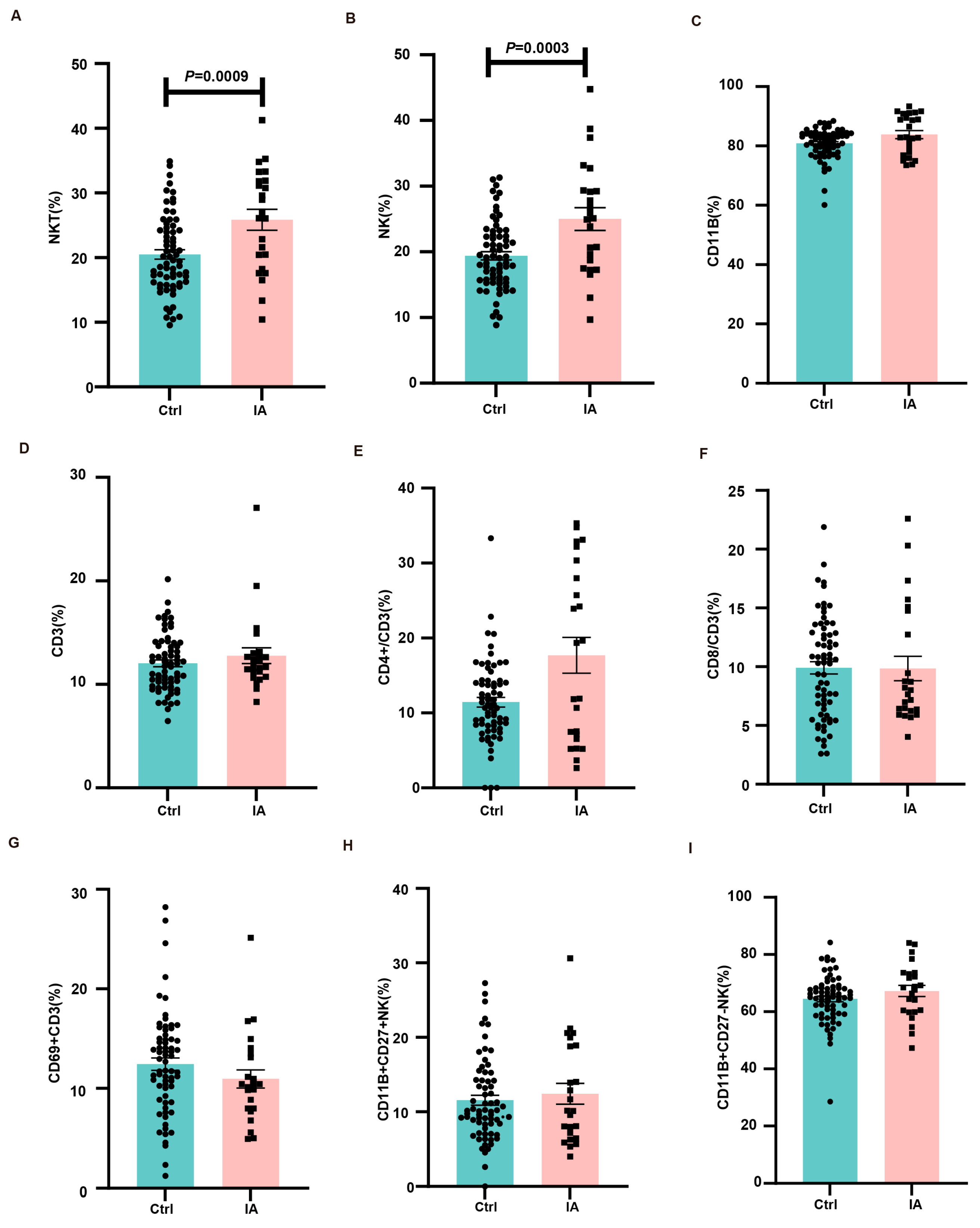
3.4. Immune Subpopulations in the Spleen and Draining Lymph Nodes of Pregnant IA Mice
3.5. Immune Microenvironment at the Maternal–Fetal Interface
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Strengths and Limitations
7. Interpretation
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Perretti, M.; Cooper, D.; Dalli, J.; Norling, L.V. Immune resolution mechanisms in inflammatory arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2017, 13, 87–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X. Innate Lymphocytes in Inflammatory Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 565275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iwaszko, M.; Biały, S.; Bogunia-Kubik, K. Significance of Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 in Inflammatory Arthritis. Cells 2021, 10, 3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badley, E.M.; Kasman, N.M. The Impact of Arthritis on Canadian Women. BMC Womens Health 2004, 4, S18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Märker-Hermann, E.; Bauer, H.; Gromnica-Ihle, E. Rheumatic diseases in pregnancy. Dtsch. Med. Wochenschr. 2008, 133, 2410–2414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, B.; Luo, Y.; Xu, J.; Sammaritano, L.; Salmon, J.; Lockshin, M.; Goodman, S.; Ibrahim, S. Trends in Maternal and Fetal Outcomes Among Pregnant Women with Systemic Lupus Erythematosus in the United States: A Cross-sectional Analysis. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smeele, H.T.W.; Dolhain, R. Current perspectives on fertility, pregnancy and childbirth in patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, S32–S35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, E.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Lee, S.M.; Jun, J.K.; Lee, E.B.; Kim, Y.G. Pregnancy outcomes in Korean women with ankylosing spondylitis. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2019, 36, 721–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.J.; Chang, J.C.; Lai, E.L.; Liao, T.L.; Chen, H.H.; Hung, W.T.; Hsieh, T.Y.; Huang, W.N.; Chen, Y.H.; Lin, C.H.; et al. Maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnancies in systemic lupus erythematosus: A nationwide population-based study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2020, 50, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakobsson, G.; Stephansson, O.; Askling, J.; Jacobsson, L. Pregnancy outcomes in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: A nationwide register study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 75, 1838–1842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unal, C.; Fadiloglu, E.; Tanacan, A.; Zaim, O.; Beksac, M. Retrospective evaluation of pregnancies with ankylosing spondylitis in a tertiary center in Turkey. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2020, 23, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kishore, S.; Mittal, V.; Majithia, V. Obstetric outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis: Results from Nationwide Inpatient Sample Database 2003–2011. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2019, 49, 236–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zbinden, A.; van den Brandt, S.; Østensen, M.; Villiger, P.; Förger, F. Risk for adverse pregnancy outcome in axial spondyloarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: Disease activity matters. Rheumatology 2018, 57, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgård, B.; Larsen, M.; Friedman, S.; Knudsen, T.; Fedder, J. Decreased chance of a live born child in women with rheumatoid arthritis after assisted reproduction treatment: A nationwide cohort study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 78, 328–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinet, E.; Labrecque, J.; Pineau, C.; Clarke, A.; St-Pierre, Y.; Platt, R.; Bernatsky, S. A population-based assessment of live births in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2012, 71, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudwaleit, M.; Landewé, R.; van der Heijde, D.; Listing, J.; Brandt, J.; Braun, J.; Burgos-Vargas, R.; Collantes-Estevez, E.; Davis, J.; Dijkmans, B.; et al. The development of Assessment of SpondyloArthritis international Society classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis (part I): Classification of paper patients by expert opinion including uncertainty appraisal. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2009, 68, 770–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavender, T.; Hofmeyr, G.J.; Neilson, J.P.; Kingdon, C.; Gyte, G.M. Caesarean section for non-medical reasons at term. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2012, 2012, CD004660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mørk, S.; Voss, A.; Möller, S.; Bliddal, M. Spondyloarthritis and Outcomes in Pregnancy and Labor: A Nationwide Register-Based Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 73, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, S.; Molto, A. Pregnancy & neonatal outcomes in spondyloarthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 37, 101868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zucchi, D.; Tani, C.; Mosca, M. Reproductive Health in RA, Lupus, and APS. J. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 30, S42–S48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakai, T.; Fukui, S.; Ozawa, H.; Kitada, A.; Okada, M.; Kishimoto, M. Management of pregnant with rheumatoid arthritis: Preconception care, pregnancy and lactation strategies, and maternal-fetal outcomes. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2024, 39, 102022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Förger, F.; Villiger, P. Immunological adaptations in pregnancy that modulate rheumatoid arthritis disease activity. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2020, 16, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pina Vegas, L.; Drouin, J.; Weill, A.; Dray-Spira, R. Pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis: An 11-year French nationwide study. RMD Open 2024, 10, e003762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, Y.; Chang, H.; Chiou, M.; Luo, S.; Kuo, C. Fetal-neonatal and maternal pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A population-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e059203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nørgaard, M.; Larsson, H.; Pedersen, L.; Granath, F.; Askling, J.; Kieler, H.; Ekbom, A.; Sørensen, H.; Stephansson, O. Rheumatoid arthritis and birth outcomes: A Danish and Swedish nationwide prevalence study. J. Intern. Med. 2010, 268, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strouse, J.; Donovan, B.; Fatima, M.; Fernandez-Ruiz, R.; Baer, R.; Nidey, N.; Forbess, C.; Bandoli, G.; Paynter, R.; Parikh, N.; et al. Impact of autoimmune rheumatic diseases on birth outcomes: A population-based study. RMD Open 2019, 5, e000878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, B.; Lee, S.; Lindsay, S.; Wingard, D.; Jones, K.; Lemus, H.; Chambers, C. Disease Severity and Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Results from the Organization of Teratology Information Specialists Autoimmune Diseases in Pregnancy Project. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 1376–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Steenwinkel, F.; Hokken-Koelega, A.; de Man, Y.; de Rijke, Y.; de Ridder, M.; Hazes, J.; Dolhain, R. Circulating maternal cytokines influence fetal growth in pregnant women with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1995–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, P.; Dolhain, R. Fertility, Pregnancy, and Lactation in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Rheum. Dis. Clin. N. Am. 2017, 43, 227–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pósfai, É.; Bánhidy, F.; Urbán, R.; Czeizel, A. Birth Outcomes of Children Born to Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cent. Eur. J. Public Health 2015, 23, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jølving, L.; Nielsen, J.; Kesmodel, U.; Nielsen, R.; Beck-Nielsen, S.; Nørgård, B. Children Born by Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Increased Susceptibility for Chronic Diseases: A Nationwide Cohort Study. Arthritis Care Res. 2018, 70, 1192–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, W.; Wu, T.; Jin, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Qi, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Z.; et al. Maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnant women with rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Rheumatol. 2023, 42, 855–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Rayes, H.; Abdulaziz, S.; Alotaibi, A.; Alaithan, M.; Attar, M.; Daghasi, H.; Melibari, R.; Althagafi, A.; Elnady, B. Adverse Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on Pregnancy Outcomes: A Saudi Arabia Prospective Multicenter Study. Open Access Rheumatol. 2021, 13, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, C.; Förger, F.; Bandoli, G.; Chambers, C. Factors Associated with Preterm Delivery Among Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Women with Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis. Arthritis Care Res. 2019, 71, 1019–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Xu, L.; Mao, S. Association between disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis and maternal and fetal outcomes in pregnant women: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2023, 23, 724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Roberts, C.; Simpson, J.; March, L. Pregnancy Outcomes in Women with Rare Autoimmune Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 3314–3323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostensen, M.; Brucato, A.; Carp, H.; Chambers, C.; Dolhain, R.; Doria, A.; Förger, F.; Gordon, C.; Hahn, S.; Khamashta, M.; et al. Pregnancy and reproduction in autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Rheumatology 2011, 50, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sammaritano, L.; Bermas, B.; Chakravarty, E.; Chambers, C.; Clowse, M.; Lockshin, M.; Marder, W.; Guyatt, G.; Branch, D.; Buyon, J.; et al. 2020 American College of Rheumatology Guideline for the Management of Reproductive Health in Rheumatic and Musculoskeletal Diseases. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 529–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakaguchi, N.; Takahashi, T.; Hata, H.; Nomura, T.; Tagami, T.; Yamazaki, S.; Sakihama, T.; Matsutani, T.; Negishi, I.; Nakatsuru, S.; et al. Altered thymic T-cell selection due to a mutation of the ZAP-70 gene causes autoimmune arthritis in mice. Nature 2003, 426, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boissier, M.C.; Bessis, N. Do we need animal models to advance research on inflammatory joint disease? Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 84, 381–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, A.; Jo, S.; Nakamura, S.; Aparnathi, M.K.; Boroojeni, S.F.; Korshko, M.; Park, Y.S.; Gupta, H.; Vijayan, S.; Rockel, J.S.; et al. HIF-1α and MIF enhance neutrophil-driven type 3 immunity and chondrogenesis in a murine spondyloarthritis model. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2024, 21, 770–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, H.; Bae, E.K.; Kim, H.; Lim, D.H.; Chung, T.Y.; Lee, J.; Jeon, C.H.; Koh, E.M.; Cha, H.S. Spondyloarthritis features in zymosan-induced SKG mice. Jt. Bone Spine 2017, 85, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruutu, M.; Thomas, G.; Steck, R.; Degli-Esposti, M.A.; Zinkernagel, M.S.; Alexander, K.; Velasco, J.; Strutton, G.; Tran, A.; Benham, H.; et al. β-glucan triggers spondylarthritis and Crohn’s disease-like ileitis in SKG mice. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2012, 64, 2211–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.A.; Thomas, R. The SKG model of spondyloarthritis. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2018, 31, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, K.; Lindgaard, L.; Wogensen, L.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Thomsen, J.; Sakaguchi, S.; Stengaard-Pedersen, K.; Hauge, E. SKG arthritis as a model for evaluating therapies in rheumatoid arthritis with special focus on bone changes. Rheumatol. Int. 2013, 33, 1127–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.W.; Liu, W.Y.; Jawad, M.; Ci, L.; Cao, Y.Y.; Xi, J.; Wu, J.Y.; Lei, Y.Y.; Hu, Y.S.; You, X.Y.; et al. Aristolochic acid IVa ameliorates arthritis in SKG Mice by regulating macrophage polarization and Th17/Treg balance. Phytomedicine 2025, 139, 156557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlebacher, A. Immunology of the maternal-fetal interface. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2013, 31, 387–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalkunte, S.S.; Mselle, T.F.; Norris, W.E.; Wira, C.R.; Sentman, C.L.; Sharma, S. Vascular endothelial growth factor C facilitates immune tolerance and endovascular activity of human uterine NK cells at the maternal-fetal interface. J. Immunol. 2009, 182, 4085–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashkar, A.; Di Santo, J.; Croy, B. Interferon gamma contributes to initiation of uterine vascular modification, decidual integrity, and uterine natural killer cell maturation during normal murine pregnancy. J. Exp. Med. 2000, 192, 259–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, J.; Hu, R.; Zou, H.; Wang, J.; Yue, Z.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Xue, B.; et al. Folic Acid Alleviates Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Oxidative Stress in Bovine Placental Trophoblast Cells by Regulating the NRF2/mTOR Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Huang, Y.; Liu, X.; Zhang, X.; Cao, Y.; Kong, X.; Yuan, X.; Xu, J.; Zhu, H. Apelin/APJ system protects placental trophoblasts from hypoxia-induced oxidative stress through activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway in preeclampsia. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2023, 208, 759–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilburn, B.; Wang, J.; Duniec-Dmuchowski, Z.; Leach, R.; Romero, R.; Armant, D. Extracellular matrix composition and hypoxia regulate the expression of HLA-G and integrins in a human trophoblast cell line. Biol. Reprod. 2000, 62, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirković, A.; Vilotić, A.; Borozan, S.; Nacka-Aleksić, M.; Bojić-Trbojević, Ž.; Krivokuća, M.; Battino, M.; Giampieri, F.; Dekanski, D. Oleuropein Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Human Trophoblast Cells. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Tian, F.; Lin, Y.; Xu, W. Oxidative Stress: Placenta Function and Dysfunction. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2016, 76, 258–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barut, A.; Barut, F.; Kandemir, N.; Aktunc, E.; Arikan, I.; Harma, M.; Harma, M.; Gun, B. Placental chorangiosis: The association with oxidative stress and angiogenesis. Gynecol. Obstet. Investig. 2012, 73, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karahoda, R.; Zaugg, J.; Fuenzalida, B.; Kallol, S.; Moser-Haessig, R.; Staud, F.; Albrecht, C. Trophoblast Differentiation Affects Crucial Nutritive Functions of Placental Membrane Transporters. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2022, 10, 820286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Ma, Z.; Zhu, P.; Guan, W.; Zhang, S.; Chen, F. Leucine supplementation during late gestation globally alters placental metabolism and nutrient transport via modulation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in sows. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 2083–2097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, J.; Laven, J.S.; Hazes, J.M.; Dolhain, R.J. Brief Report: Miscarriages in Female Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients: Associations with Serologic Findings, Disease Activity, and Antirheumatic Drug Treatment. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2015, 67, 1738–1743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eudy, A.M.; McDaniel, G.; Clowse, M.E. Pregnancy in rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective study. Clin. Rheumatol. 2017, 37, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, S.D.; Vollan, T.A.; Svec, M.A. Pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis in Washington State. Matern. Child Health J. 2006, 10, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljary, H.; Czuzoj-Shulman, N.; Spence, A.R.; Abenhaim, H.A. Pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis: A retrospective population-based cohort study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2018, 33, 618–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobsson, L.T.; Jacobsson, M.E.; Askling, J.; Knowler, W.C. Perinatal characteristics and risk of rheumatoid arthritis. Br. Med. J. 2003, 326, 1068–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Williams, A.; Grantz, K.; Seeni, I.; Robledo, C.; Li, S.; Ouidir, M.; Nobles, C.; Mendola, P. Obstetric and neonatal complications among women with autoimmune disease. J. Autoimmun. 2019, 103, 102287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallenius, M.; Salvesen, K.Å.; Daltveit, A.K.; Skomsvoll, J.F. Rheumatoid arthritis and outcomes in first and subsequent births based on data from a national birth registry. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2013, 93, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfberg, A.J.; Lee-Parritz, A.; Peller, A.J.; Lieberman, E.S. Association of rheumatologic disease with preeclampsia. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 103, 1190–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harmon, A.C.; Cornelius, D.C.; Amaral, L.M.; Faulkner, J.L.; Cunningham, M.W., Jr.; Wallace, K.; LaMarca, B. The role of inflammation in the pathology of preeclampsia. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 409–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motta, F.; Codullo, V.; Ramoni, V.; Cesari, S.; Ferrario, G.; Fiandrino, G.; Beneventi, F.; Rampello, S.; Johnsson, H.; Montecucco, C.; et al. Role of placental inflammatory mediators and growth factors in patients with rheumatic diseases with a focus on systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 2020, 60, 3307–3316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossintseva, I.; Wong, S.; Johnstone, E.; Guilbert, L.; Olson, D.M.; Mitchell, B.F. Proinflammatory cytokines inhibit human placental 11beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2 activity through Ca2+ and cAMP pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 290, E282–E288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Bozec, A.; Ramming, A.; Schett, G. Anti-inflammatory and immune-regulatory cytokines in rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2018, 15, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowden, A.L.; Valenzuela, O.A.; Vaughan, O.R.; Jellyman, J.K.; Forhead, A.J. Glucocorticoid programming of intrauterine development. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2016, 56, S121–S132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra van Nieuwenhoven, A.L.; Heineman, M.J.; Faas, M.M. The immunology of successful pregnancy. Hum. Reprod. Update 2003, 9, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faas, M.M.; de Vos, P. Uterine NK cells and macrophages in pregnancy. Placenta 2017, 56, 44–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saito, S.; Tsukaguchi, N.; Hasegawa, T.; Michimata, T.; Tsuda, H.; Narita, N. Distribution of Th1, Th2, and Th0 and the Th1/Th2 cell ratios in human peripheral and endometrial T cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 1999, 42, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santner-Nanan, B.; Peek, M.J.; Khanam, R.; Richarts, L.; Zhu, E.; Fazekas de St Groth, B.; Nanan, R. Systemic increase in the ratio between Foxp3+ and IL-17-producing CD4+ T cells in healthy pregnancy but not in preeclampsia. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7023–7030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Nakashima, A.; Shima, T.; Ito, M. Th1/Th2/Th17 and regulatory T-cell paradigm in pregnancy. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 63, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veenstra van Nieuwenhoven, A.L.; Bouman, A.; Moes, H.; Heineman, M.J.; de Leij, L.F.; Santema, J.; Faas, M.M. Endotoxin-induced cytokine production of monocytes of third-trimester pregnant women compared with women in the follicular phase of the menstrual cycle. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2003, 188, 1073–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Luppi, P.; Deloia, J.A. Monocytes of preeclamptic women spontaneously synthesize pro-inflammatory cytokines. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faas, M.M.; Kunnen, A.; Dekker, D.C.; Harmsen, H.J.; Aarnoudse, J.G.; Abbas, F.; De Vos, P.; Van Pampus, M.G. Porphyromonas Gingivalis and E-coli induce different cytokine production patterns in pregnant women. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melgert, B.N.; Spaans, F.; Borghuis, T.; Klok, P.A.; Groen, B.; Bolt, A.; de Vos, P.; van Pampus, M.G.; Wong, T.Y.; van Goor, H.; et al. Pregnancy and preeclampsia affect monocyte subsets in humans and rats. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piccinni, M.; Lombardelli, L.; Logiodice, F.; Kullolli, O.; Romagnani, S.; Le Bouteiller, P. T helper cell mediated-tolerance towards fetal allograft in successful pregnancy. Clin. Mol. Allergy 2015, 13, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurzadeh, M.; Ghalandarpoor-Attar, S.; Ghalandarpoor-Attar, S.; Rabiei, M. The Role of Interferon (IFN)-γ in Extravillous Trophoblast Cell (EVT) Invasion and Preeclampsia Progression. Reprod. Sci. 2023, 30, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atta, D.S.; Girbash, E.F.; Abdelwahab, S.M.; Abdeldayem, H.M.; Tharwat, I.; Ghonaim, R. Maternal cytokines and disease severity influence pregnancy outcomes in women with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2015, 29, 3358–3363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elderman, M.; Hugenholtz, F.; Belzer, C.; Boekschoten, M.; de Haan, B.; de Vos, P.; Faas, M. Changes in intestinal gene expression and microbiota composition during late pregnancy are mouse strain dependent. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres-Bartho, J.; Barakonyi, A.; Par, G.; Polgar, B.; Palkovics, T.; Szereday, L. Progesterone as an immunomodulatory molecule. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2001, 1, 1037–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellembakken, J.R.; Aukrust, P.; Olafsen, M.K.; Ueland, T.; Hestdal, K.; Videm, V. Activation of leukocytes during the uteroplacental passage in preeclampsia. Hypertension 2002, 39, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacks, G.P.; Clover, L.M.; Bainbridge, D.R.; Redman, C.W.; Sargent, I.L. Flow cytometric measurement of intracellular Th1 and Th2 cytokine production by human villous and extravillous cytotrophoblast. Placenta 2001, 22, 550–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göhner, C.; Plösch, T.; Faas, M.M. Immune-modulatory effects of syncytiotrophoblast extracellular vesicles in pregnancy and preeclampsia. Placenta 2017, 60, S41–S51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vacca, P.; Vitale, C.; Montaldo, E.; Conte, R.; Cantoni, C.; Fulcheri, E.; Darretta, V.; Moretta, L.; Mingari, M.C. CD34+ hematopoietic precursors are present in human decidua and differentiate into natural killer cells upon interaction with stromal cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 2402–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, X.; Sun, R.; Tong, X.; Ling, B.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Natural killer cells promote immune tolerance by regulating inflammatory TH17 cells at the human maternal-fetal interface. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 110, E231–E240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.F.; Charnock-Jones, D.S.; Zhang, E.; Hiby, S.; Malik, S.; Day, K.; Licence, D.; Bowen, J.M.; Gardner, L.; King, A.; et al. Angiogenic growth factor messenger ribonucleic acids in uterine natural killer cells. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 1823–1834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Zhou, Y.; Ni, X.; Tong, X.; Xu, X.; Dong, Z.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z.; Wei, H. Natural Killer Cells Promote Fetal Development through the Secretion of Growth-Promoting Factors. Immunity 2017, 47, 1100–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, X.; Wei, H. Reproductive immune microenvironment. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2022, 152, 103654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chazara, O.; Xiong, S.; Moffett, A. Maternal KIR and fetal HLA-C: A fine balance. J Leukoc. Biol. 2011, 90, 703–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhury, R.H.; Dunk, C.E.; Lye, S.J.; Harris, L.K.; Aplin, J.D.; Jones, R.L. Decidual leucocytes infiltrating human spiral arterioles are rich source of matrix metalloproteinases and degrade extracellular matrix in vitro and in situ. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2018, 81, e13054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagamatsu, T.; Schust, D.J. The immunomodulatory roles of macrophages at the maternal-fetal interface. Reprod. Sci. 2010, 17, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeters, P.B.; Grimble, R.F. The conditional role of inflammation in pregnancy and cancer. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 32, 460–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firestein, G.S.; McInnes, I.B. Immunopathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Immunity 2017, 46, 183–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.M.; Yang, H.; Li, M.; Yeh, C.C.; Schatz, F.; Lockwood, C.J.; Di, W.; Huang, S.J. Pro-inflammatory cytokine-stimulated first trimester decidual cells enhance macrophage-induced apoptosis of extravillous trophoblasts. Placenta 2012, 33, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alijotas-Reig, J.; Llurba, E.; Gris, J.M. Potentiating maternal immune tolerance in pregnancy: A new challenging role for regulatory T cells. Placenta 2014, 35, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vento-Tormo, R.; Efremova, M.; Botting, R.; Turco, M.; Vento-Tormo, M.; Meyer, K.; Park, J.; Stephenson, E.; Polański, K.; Goncalves, A.; et al. Single-cell reconstruction of the early maternal-fetal interface in humans. Nature 2018, 563, 347–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Diao, L.; Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Kwak-Kim, J. The role of decidual immune cells on human pregnancy. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2017, 124, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Co, E.; Gormley, M.; Kapidzic, M.; Rosen, D.; Scott, M.; Stolp, H.; McMaster, M.; Lanier, L.; Bárcena, A.; Fisher, S. Maternal decidual macrophages inhibit NK cell killing of invasive cytotrophoblasts during human pregnancy. Biol. Reprod. 2013, 88, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, S.; Dunk, C.; Aplin, J.; Harris, L.; Jones, R. Evidence for immune cell involvement in decidual spiral arteriole remodeling in early human pregnancy. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 174, 1959–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Lopez, N.; StLouis, D.; Lehr, M.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Arenas-Hernandez, M. Immune cells in term and preterm labor. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2014, 11, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nancy, P.; Erlebacher, A. T cell behavior at the maternal-fetal interface. Int. J. Dev. Biol. 2014, 58, 189–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Sung, N.; Gilman-Sachs, A.; Kwak-Kim, J. T Helper (Th) Cell Profiles in Pregnancy and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses: Th1/Th2/Th9/Th17/Th22/Tfh Cells. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Zheng, Q.; Jin, L. Dynamic Function and Composition Changes of Immune Cells During Normal and Pathological Pregnancy at the Maternal-Fetal Interface. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haseeb, A.; Haqqi, T. Immunopathogenesis of osteoarthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2013, 146, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadi-Samani, M.; Bagheri, N.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Shirzad, H. Inhibition of Th1 and Th17 Cells by Medicinal Plants and Their Derivatives: A Systematic Review. Phytother. Res. 2017, 31, 1128–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Udalova, I.; Mantovani, A.; Feldmann, M. Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2016, 12, 472–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Yuan, K.; Lu, Q.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, S.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Wang, H.; Luo, G.; Wang, T.; et al. Emodin ameliorates rheumatoid arthritis by promoting neutrophil apoptosis and inhibiting neutrophil extracellular trap formation. Mol. Immunol. 2019, 112, 188–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Hou, Y.; Zhang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, D.; Tao, S.; Ni, F. CD49a regulates the function of human decidual natural killer cells. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2019, 81, e13101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Hao, C.; Lin, Y.; Yin, G.; Bao, S.; Qiu, L.; Lin, Q. Increased prevalence of T helper 17 (Th17) cells in peripheral blood and decidua in unexplained recurrent spontaneous abortion patients. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2010, 84, 164–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Q.; Li, Q.; Fu, Y.; Ren, C.; Jiang, A.; Meng, Y. Decidual macrophages in recurrent spontaneous abortion. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 994888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
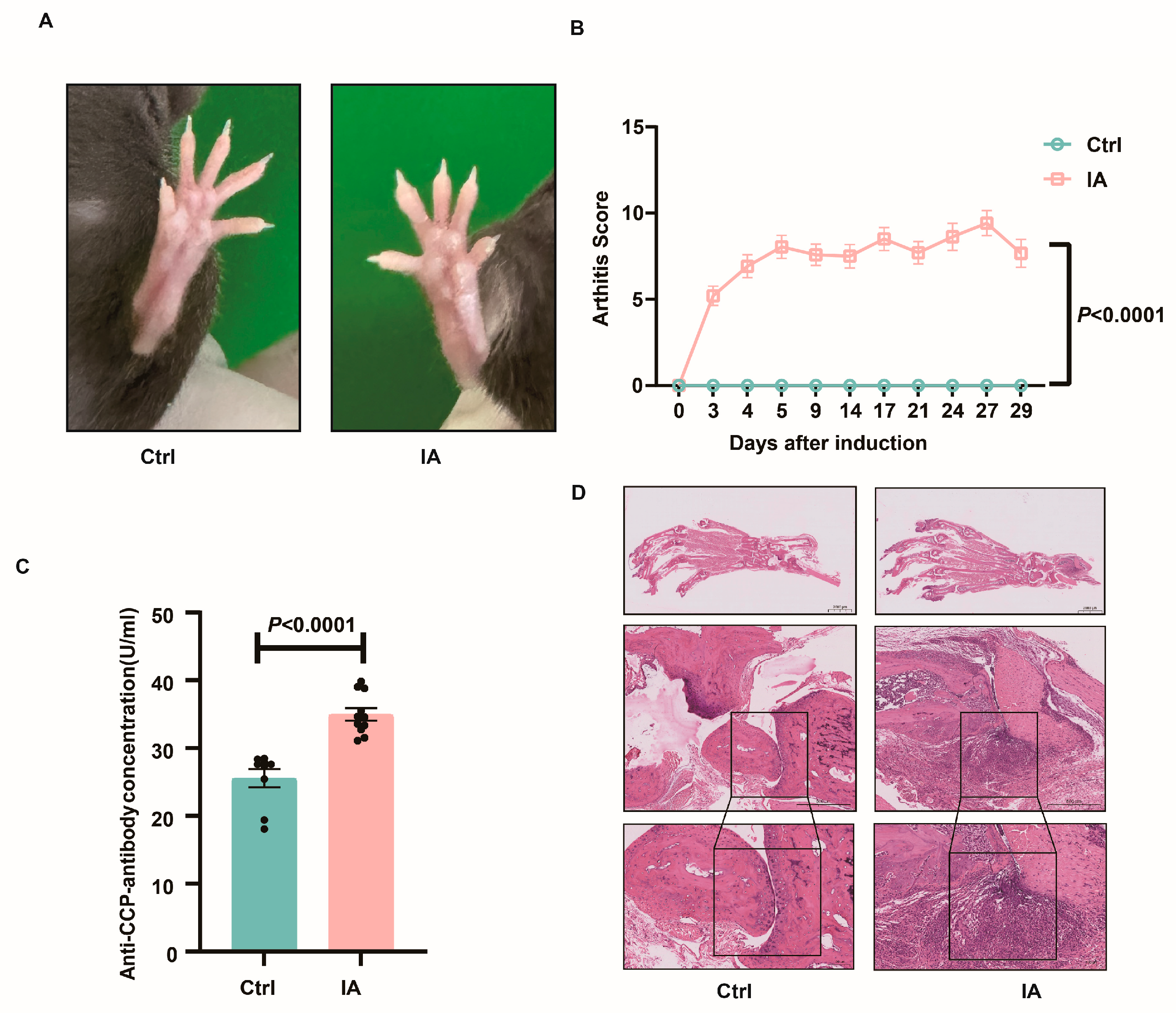
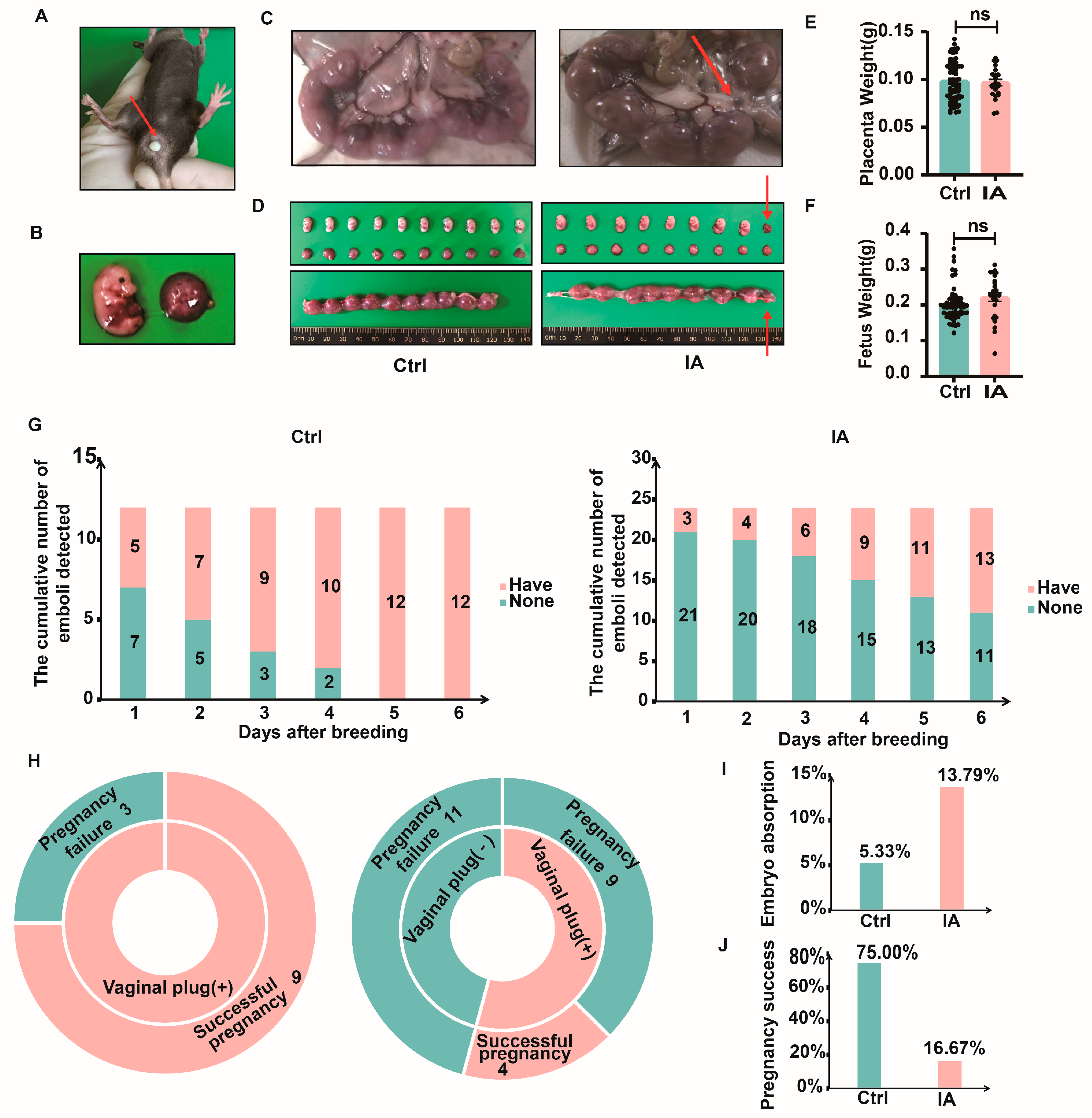
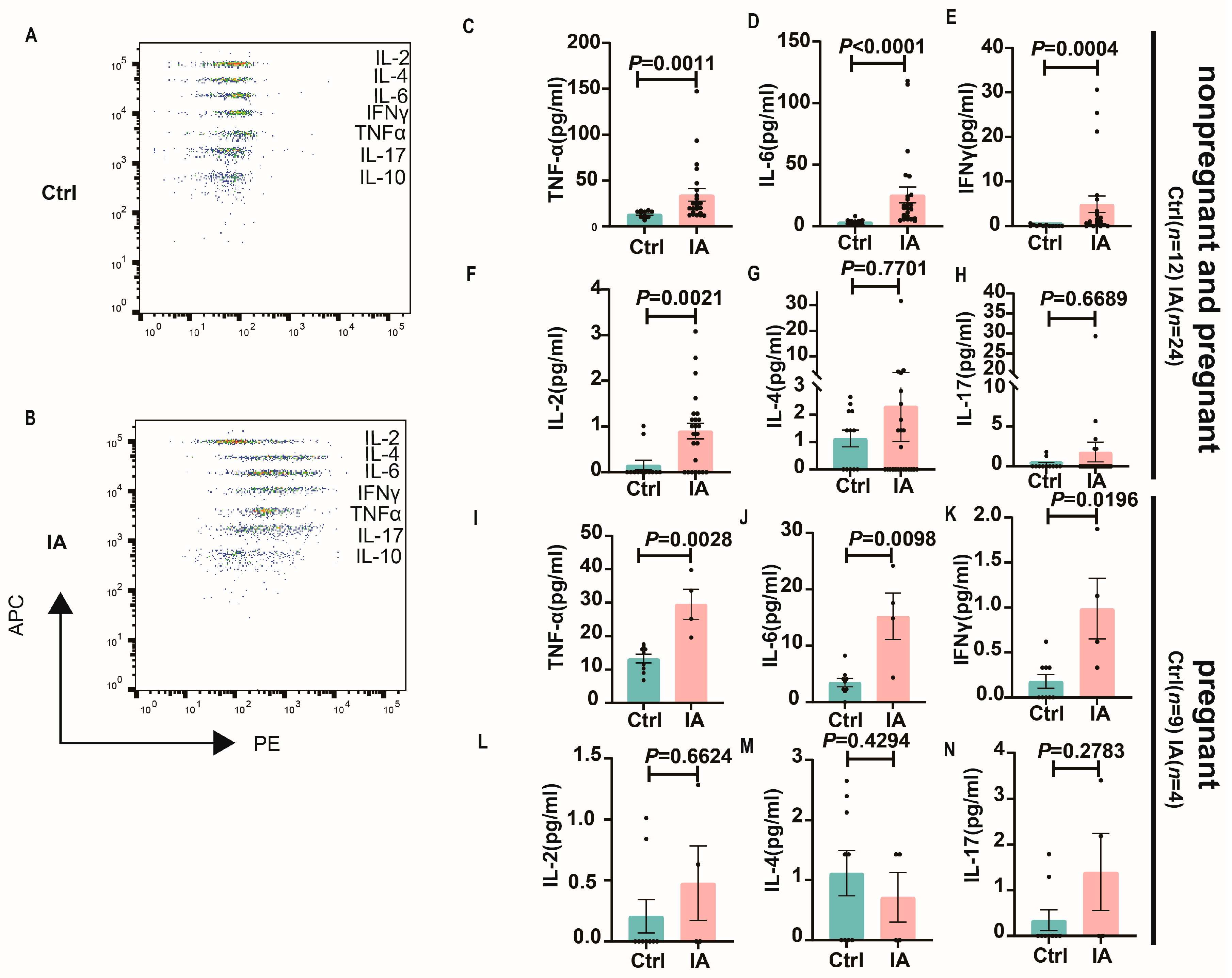
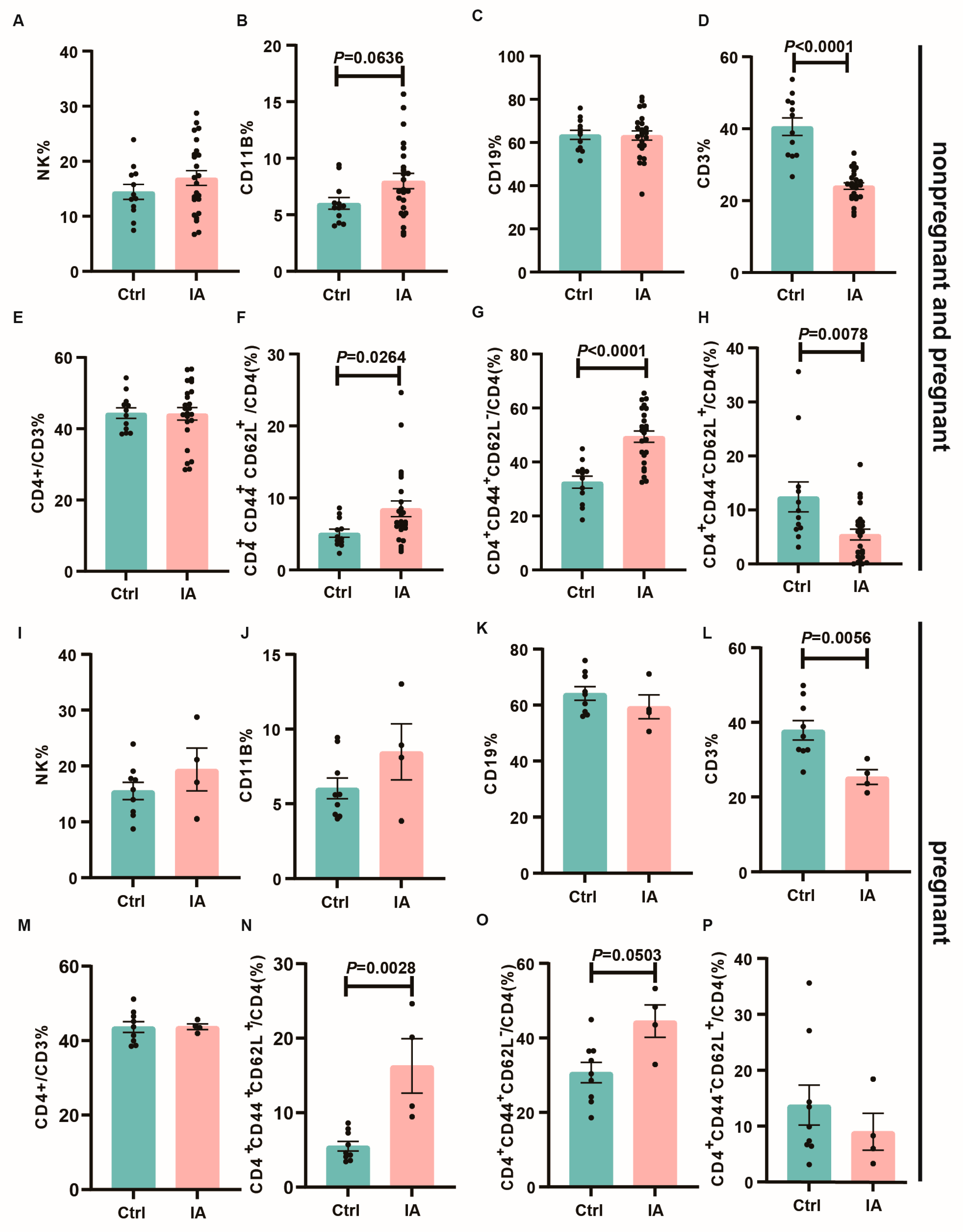
| Group | Number (n) | Total Number of Embryos (n) | Number of Absorbed Embryos (n) | Rate of Embryo Absorption (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 12 | 75 | 4 | 5.33 |
| IA | 24 | 29 | 4 | 13.79 |
| Group | Number (n) | With Vaginal Plug (n) | Without Vaginal Plug (n) | Successful Pregnancy (n) | Pregnancy Failure (n) | Pregnancy Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ctrl | 12 | 12 | 0 | 9 | 3 | 75 |
| IA | 24 | 13 | 11 | 4 | 20 | 16.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, C.; Li, W.; Liu, X.; Ma, Z.; Chen, J.; Gong, Q.; Braunstein, Z.; Rao, X.; Wei, Y.; Zhong, J. Immune Dysregulation at the Maternal–Fetal Interface Exacerbates Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in an Inflammatory Arthritis Murine Model. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061440
Yang C, Li W, Liu X, Ma Z, Chen J, Gong Q, Braunstein Z, Rao X, Wei Y, Zhong J. Immune Dysregulation at the Maternal–Fetal Interface Exacerbates Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in an Inflammatory Arthritis Murine Model. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061440
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Chenxi, Wenjuan Li, Xinxin Liu, Zijun Ma, Jun Chen, Quan Gong, Zachary Braunstein, Xiaoquan Rao, Yingying Wei, and Jixin Zhong. 2025. "Immune Dysregulation at the Maternal–Fetal Interface Exacerbates Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in an Inflammatory Arthritis Murine Model" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061440
APA StyleYang, C., Li, W., Liu, X., Ma, Z., Chen, J., Gong, Q., Braunstein, Z., Rao, X., Wei, Y., & Zhong, J. (2025). Immune Dysregulation at the Maternal–Fetal Interface Exacerbates Adverse Pregnancy Outcomes in an Inflammatory Arthritis Murine Model. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1440. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061440






