Abstract
Cardiovascular disease remains the leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide, especially in regions like Eastern Europe, South Asia, and Latin America. A significant portion of these cases (80%) is linked to atherosclerosis, which can lead to severe conditions like ischemic heart disease and stroke, with atherosclerosis (ATS) responsible for the majority of cases. This review explores the multifaceted relationship between insulin resistance (IR) and ATS, highlighting their roles as both independent and interrelated contributors to cardiovascular risk. ATS is characterized by lipid accumulation and chronic inflammation within arterial walls, driven by factors such as hypertension, dyslipidemia, and genetic predisposition, with endothelial dysfunction as a key early event. The early detection of subclinical ATS is critical and can be achieved through a combination of non-invasive imaging techniques—such as coronary artery calcium scoring and carotid ultrasound—and comprehensive risk profiling. IR, marked by impaired glucose uptake in liver, muscle, and adipose tissue, often precedes early diabetes and is associated with metabolic disturbances, including dyslipidemia and chronic inflammation. The diagnosis of IR relies on surrogate indices such as HOMA-IR, the QUICKI, and the TyG index, which facilitate screening in clinical practice. Compelling evidence indicates that IR independently predicts the progression of atherosclerotic plaques, even in non-diabetic individuals, and operates through both traditional risk factors and direct vascular effects. Understanding and targeting the IR–ATS axis is essential for the effective prevention and management of cardiovascular disease.
1. Introduction
Cardiovascular disease remains the predominant cause of morbidity and mortality globally, with a particularly high prevalence in regions such as Eastern Europe, South Asia, and Latin America [1,2]. A significant proportion of these cases (80%) are attributed to atherosclerosis (ATS), which can progress to ischemic heart disease, stroke, or peripheral arterial disease [3]. In developed nations, the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease is on the decline, primarily due to the enhanced management of risk factors, including smoking, hypertension, and dyslipidemia and the implementation of primary prevention programs [4,5].
Insulin facilitates the uptake of glucose into cells, where it serves as an energy source. However, in certain conditions, cells may develop resistance to insulin, necessitating increased insulin secretion by the pancreas. Numerous studies have established a correlation between insulin resistance and ATS [6,7,8,9,10].
The following questions arise: How can subclinical ATS be diagnosed? What are the diagnostic criteria for insulin resistance? Is there a definitive link between insulin resistance and ATS? What interventions can be implemented to ameliorate insulin resistance? Is it possible to treat insulin resistance effectively? Could routine screening for insulin resistance become standard practice? Would the early detection of insulin resistance play a crucial role in the primary prevention of cardiovascular disease? (Figure 1)
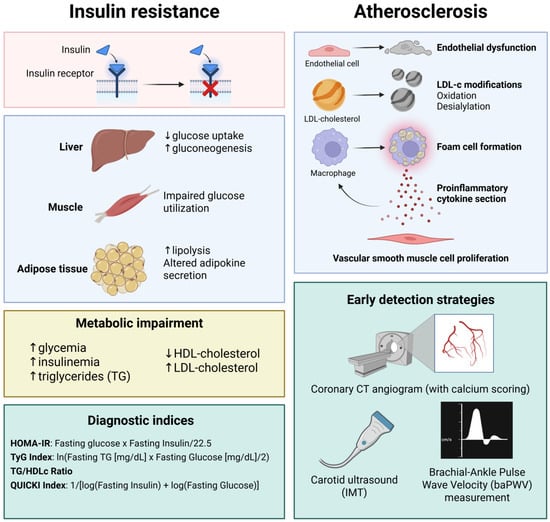
Figure 1.
The connection between insulin resistance and atherosclerosis development and progression. Insulin resistance triggers gluconeogenesis since glucose uptake mediated by GLUT-3 is impaired. At the muscle level, due to impaired GLUT-2/4-mediated glucose uptake, glucose utilization is impaired. At the adipose tissue level, lipolysis is increased and adipokine secretion is altered, leading to a metabolic impairment characterized by hyperglycemia, initial hyperinsulinemia, increased LDL-cholesterol and trigyliceride levels, and reduced serum high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol. In clinical practice, the TyG index is widely used as a screening method for insulin resistance. Alongside the TyG index, other indices such as the homeostasis model assessment of insulin resistace (HOMA-IR), the triglyceride/HDL-cholesterol ratio (TG/HDLc), and the quantitative insulin sensitivity check index (QUICKI) have also proved their utility in insulin resistance screening. Increased low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholestrol levels, in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors, leads to endothelial dysfunction and subsequent modifications of LDL-cholesterol particles, such as oxidation and desialylation, triggering a macrophage-mediated immune response. The most widely used paraclinical test for diagnosing subclinical atherosclerosis is coronary computed tomography (CT) angiogram (with calcium scoring), also suggested by the actual guidelines for improved risk stratification in coronary artery disease (CAD). Created in BioRender. Tirziu, A. (2025) https://BioRender.com/2wkbiot (accessed on 20 May 2025).
In the following sections, we will review existing data and endeavor to address these questions to the furthest extent possible.
2. Atherosclerosis: General Considerations
Atherosclerosis is characterized by the accumulation of lipids within the arterial wall. It is a chronic inflammatory condition with focal manifestations that commences in childhood and progresses through a prolonged asymptomatic phase [11]. Recognizing that an intact endothelium is the most significant factor in preventing atherosclerosis is crucial. Various “keys” to disrupt the endothelial barrier represent risk factors, including hypertension, insulin resistance, diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, smoking, genetic predispositions, and pollution, which compromise the endothelial layer and facilitate intravascular lipid accumulation in the intima. However, the precise mechanism by which this accumulation triggers inflammation remains unclear [11,12]. In the initial stages of the atherosclerotic process, following the formation of lipid striations due to the infiltration of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol particles into the arterial wall, a potentially reversible stage occurs with the formation of foam cells (macrophages that phagocytize LDL particles) and the initiation of the inflammatory response [13].
Recent research indicates that not all low-density lipoprotein (LDL) particles exhibit atherogenic properties. Specifically, the desialylation of LDL-cholesterol (LDLc) particles, has been shown to enhance their atherogenic potential [14,15]. These desialylated LDLc particles are smaller, denser, more electronegative, and exhibit an increased susceptibility to oxidation [15,16,17]. Similarly, the desialylation of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLc) molecules impairs their ability to extract lipids from peripheral tissues and transfer to the liver [18]. Furthermore, the role of inflammation in the ATS process has been increasingly recognized, providing a partial explanation for the occurrence of 50% of initial cardiovascular events in patients with normal LDLc levels [19,20,21]. Recent studies have proposed several mechanisms involved in the ATS process, highlighting the significance of genetic interactions, such as polygenic risk scores for coronary artery disease (CAD), which correlate well with plaque burden and can be utilized to assess cardiovascular risk in young patients [22,23,24,25]. These genetic factors interact with exogenous risk factors in the organs and the arterial wall [26]. However, the influence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and chronic kidney disease on ATS progression remains unclear, as does the beneficial role of exercise and the factors that confer protection in women [11].
3. Early Detection of Asymptomatic Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerotic lesions develop progressively and are frequently irreversible; however, some research suggests that lipid-rich soft plaques may be reversible. Consequently, early diagnosis and prevention are essential for effective ATS management. In alignment with this perspective, an article in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) [27] advocated for a paradigm shift from addressing the late manifestations of ATS to prioritizing early detection and prevention, as identifying the disease in its subclinical stages may offer curative potential in some instances [28]. Insulin resistance generally manifests a decade or more before the clinical diagnosis of type 2 diabetes, and this period of hyperinsulinemia may contribute to atherogenesis by fostering the formation of fatty streaks and early atheromatous lesions. The early detection of ATS should encompass a comprehensive evaluation of risk factors, including the early identification of insulin resistance before the onset of diabetes mellitus, paraclinical analyses [complete lipid profile: low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDLc), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLc), triglycerides (TG), lipoprotein a (Lp(a)), high-sensitive C-reactive protein (hsCRP), glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c), creatinine clearance (Clcreatinine), von Willebrand factor (vWF), metalloproteinases, particularly the matrix metalloproteinase type 9 (MMP-9), and various cytokines], and non-invasive imaging techniques [29,30,31] such as coronary artery calcium scoring, carotid artery ultrasound with IMT measurement, femoral artery ultrasound, and ankle–brachial index measurement.
The calcium score, as determined by computed tomography (CT) using the Agatston method, is a diagnostic tool for identifying calcifications in the coronary arteries. Typically, calcifications emerge following the prolonged progression of the ATS process within the coronary arteries, which can be detected via CT imaging. Numerous studies have demonstrated a positive correlation between the calcium score, coronary artery stenosis, and ATS [32,33,34]. Caution is advised when interpreting scores in young patients or women, as an Agatston score of 0 does not entirely exclude the presence of atherosclerosis. Nonetheless, the likelihood of myocardial infarction or mortality remains low (less than 1%) in individuals with a calcium score of 0 [35]. This scoring method has been effectively integrated into the 10-year cardiovascular risk assessment model. The Heinz Nixdorf Recall Study and the Dallas Heart Study validated the MESA risk score [36,37,38]. Carotid IMT is a widely utilized marker for detecting subclinical ATS [39,40]. The absence of atherosclerosis in the carotid arteries does not preclude its presence in the coronary arteries, as evidenced by a recent meta-analysis that found no positive correlation between IMT and cardiovascular risk in the general population [41]. Some researchers have proposed that the carotid plaque score (CPs), rather than IMT, may better correlate with the risk of future events in patients with existing cardiovascular disease [42]. Another meta-analysis suggested that combined intima-media thickness (cIMT), which includes measurements from multiple carotid segments, correlates more effectively with future cardiovascular events than measurements limited to a single carotid segment [43].
Arterial stiffness can be assessed using brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) [44]. Some studies have indicated that baPWV does not possess a strong capacity to detect subclinical ATS [45,46], although its efficacy is enhanced when combined with other tests [47].
The integration of the coronary artery calcium score, the carotid plaque score (CPs), and brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) proves more effective in detecting subclinical ATS and predicting future cardiovascular events [48].
4. Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance is defined by the impaired ability of insulin to regulate glucose metabolism in specific tissues, notably the liver, skeletal muscle, and adipose tissue, which fail to absorb glucose from the bloodstream, resulting in hyperglycemia. Insulin resistance can be either acquired, due to factors such as the accumulation of perivisceral and subcutaneous adipose tissue, physical inactivity with advancing age, and the use of certain medications, or congenital, as seen in conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome, Alstom syndrome, Rabson–Mendenhall syndrome, and Werner syndrome [49,50]. A sex difference is observed in insulin resistance, with a lower incidence in premenopausal women compared to men [51]. The primary consequences of insulin resistance include the inhibition of lipolysis in adipose tissue, reduced glucose utilization by muscles, and the inhibition of gluconeogenesis in the liver, leading to disturbances in lipid metabolism, such as increased triglycerides, decreased HDLc with modest disturbances in LDLc [52], impaired glucose tolerance, and hyperinsulinism [53]. Insulin resistance occurs significantly before it manifests as prediabetes or type 2 diabetes mellitus [54], and the patient remains asymptomatic for an extended period of time.
Insulin resistance is typically diagnosed using the hyperinsulinemic–euglycemic glucose clamp technique, as outlined by DeFronzo [55]. While precise, this method is labor-intensive and primarily utilized in specific clinical trials, posing challenges for routine clinical practice [56,57]. Consequently, in clinical settings, surrogate indices are generally employed (Table 1). Among these, the homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) is frequently used. This involves determining fasting blood glucose and insulin values, with HOMA-IR calculated as fasting blood glucose (mmol/L) × fasting insulin (mIU/L)/22.5. A HOMA-IR value exceeding 2–2.5 typically indicates insulin resistance, although this threshold may vary based on the population and clinical context. For instance, a study examining the prevalence of insulin resistance in a French population utilized a HOMA-IR cut-off value of 3.8 [58]. Conversely, the Bruneck study, which investigated insulin resistance prevalence in individuals with metabolic disorders, employed a HOMA-IR cut-off value of 2.77 [59].
The triglyceride-to-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDLc) ratio (TG/HDLc ratio), with a threshold greater than 3.5 in men and 2.5 in women, is a strong indicator for diagnosing insulin resistance [60,61]. However, some researchers have noted its applicability primarily in diagnosing insulin resistance among overweight Caucasians but not in African Americans [60,62]. An alternative index utilized in clinical practice is the QUICKI, calculated as 1/[log fasting insulin (μU/mL) + log fasting glucose (mg/dL)], which provides a more accurate characterization of insulin resistance compared to the HOMA index [63,64].
Another index, the Matsuda index, incorporates insulin and fasting glucose levels along with glucose tolerance test results in its calculation formula (10,000/√(fasting G × fasting I) (mean G × mean I)), serving as an indicator of insulin sensitivity [65]. A study conducted in a non-diabetic Finnish population demonstrated that the Matsuda index exhibited superior sensitivity to the HOMA index for diagnosing insulin resistance in this cohort [66].
Recently, a novel marker, the triglyceride glucose index (TyG), was proposed, calculated as TyG index = ln (fasting triglycerides [mg/dL] × fasting glucose [mg/dL]/2) [67,68]. The development of this index was motivated by the high cost and impracticality of large-scale insulinemia determination. The TyG index was introduced as an alternative for diagnosing insulin resistance, with various cut-off values proposed: >ln 4.68 (sensitivity of 96.5%, specificity of 85%) [69]; >ln 4.66 (sensitivity of 86.2%, specificity of 44.1%) [70]; >ln 4.49 (specificity of 82%, sensitivity of 82.6%) [71]. This index has also shown a strong correlation with 10-year cardiovascular risk [72,73], atrial fibrillation risk, particularly in women [74,75], coronary calcium score [76], subclinical atherosclerosis and arterial stiffness [77], the prevalence and severity of coronary heart disease [78,79], metabolic syndrome in obese Caucasian patients [80,81], metabolic syndrome in Asian patients [82], the general population with or without metabolic syndrome [81], and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [83,84,85]. Consequently, the TyG index is a marker for screening and diagnosing various pathologies primarily associated with insulin resistance and metabolic syndrome [86]. Some studies have indicated that the TyG index predicts the development of atherosclerosis more effectively than HOMA-IR, as evidenced by the intima-media thickness (IMT) index and coronary artery calcium score [87,88]. It is important to note that the HOMA-IR index is not applicable to patients with diabetes mellitus who are undergoing insulin treatment. The TyG index is employed in these cases [89].
The lipid accumulation product (LAP) index has been proposed as an alternative measure for assessing insulin resistance. This index was developed to describe the accumulation of subcutaneous adipose tissue more accurately and is considered to provide a more precise assessment of obesity risk compared to the body mass index (BMI). The LAP index is calculated using waist circumference and fasting triglyceride levels, with the formula LAP = (WC-65) × TG for men and (WC-58) × TG for women [90]. Subsequent studies have demonstrated that the LAP index offers superior estimates of 10-year cardiovascular risk compared to BMI, waist circumference, the waist-to-hip ratio, and the waist-to-height ratio [91]. Although the LAP index is not traditionally used as a measure of insulin resistance, it may offer a more effective assessment of insulin resistance risk than HOMA-IR or the QUICKI, as evidenced by a study conducted on a non-obese (BMI < 21 kg/m2) normoglycemic male population in Asia [92]. Furthermore, recent research has indicated that the LAP index serves as a reliable indicator for diagnosing metabolic syndrome in the obese adult population, outperforming the body adiposity index (BAI) [93], which is calculated as
The indices used to evaluate insulin resistance are summarized in Table 1.

Table 1.
Surrogate indices for measuring insulin resistance.
Table 1.
Surrogate indices for measuring insulin resistance.
| Index | HOMA-IR | QUICKI | Matsuda Index | TyG Index | TG/HDLc Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fasting glucose | X | X | - | X | |
| Fasting insulin | X | X | |||
| Fasting triglycerides | - | - | - | X | X |
| Glucose tolerance test | - | - | X | - | |
| HDLc | - | - | - | - | X |
| Calculation formula | [glucose] (mmol/L) × [insulin] (µU/mL)/22.5 [94] | 1/[log (lµU/mL) + log (log (G(mg/dL)))] [95] | 10,000/√[(fasting G × fasting I) (mean G × mean I)] [65] | [ln (fasting triglycerides) (mg/dL) × fasting glucose (mg/dL)/2] [69] | TG/HDLc level |
| Insulin resistance | NV < 2.0–2.5 | 0.382 ± 0.007 for non-obese, 0.331 ± 0.01 for obese, and 0.304 ± 0.007 for diabetic individuals | <4.3 predicts IR | NV < 4 >9 [72,96] | Ideal: less than 2 Moderate risk: between 2 and 4 High risk: 4 or higher |
| Cost | Medium | Medium | High | Low | Low |
HOMA—homeostasis model assessment; QUICKI—quantitative insulin sensitivity check index; TyG index—triglyceride and glucose index; TG/HDLc ratio—triglyceride to HDL-cholesterol ratio; NV—normal value; G—glucose.
The interrelationship between insulin resistance and atherosclerosis in humans is a critical area of study due to its significant implications for cardiovascular health [97]. Insulin resistance, a defining feature of type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome, is characterized by the body’s reduced ability to utilize insulin effectively, resulting in hyperinsulinemia and a series of metabolic disturbances. Conversely, atherosclerosis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the arterial walls, driven by the accumulation of lipids, immune cells, and fibrous tissue, leading to plaque formation and arterial stiffening. The interplay between these two conditions is intricate, involving multiple biochemical pathways and genetic factors that contribute to the progression of the disease [98].
5. Biochemical Pathways Linking Insulin Resistance to Atherosclerosis
Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis are two closely intertwined conditions that contribute significantly to cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. The relationship between these two conditions is complex and bidirectional, with insulin resistance exacerbating atherosclerosis and vice versa [99]. The molecular mechanisms underlying the insulin resistance-and-atherosclerosis relationship involve complex interactions between metabolic, inflammatory, and vascular pathways [100,101,102,103]. Insulin resistance creates a pro-atherogenic environment by altering lipid metabolism, promoting inflammation, and impairing vascular function. Understanding these mechanisms provides a foundation for developing targeted therapies to mitigate the burden of cardiovascular disease in insulin-resistant states.
5.1. Endothelial Dysfunction
5.1.1. NO Pathway
Insulin resistance is intricately linked to endothelial dysfunction, a pivotal early event in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. The endothelium, a monolayer of cells lining the vasculature, plays a crucial role in maintaining vascular homeostasis by regulating vascular tone and inhibiting leukocyte adhesion and platelet aggregation. Insulin resistance compromises endothelial function by diminishing the bioavailability of nitric oxide, a potent vasodilator, while simultaneously augmenting the production of reactive oxygen species [104,105]. Insulin stimulates typically endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) activity via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, promoting NO production and vasodilation. Insulin resistance disrupts this pathway, leading to endothelial dysfunction and increased vascular tone [106,107].
This imbalance fosters oxidative stress, which subsequently activates pro-inflammatory pathways, including the nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) pathway, resulting in the upregulation of adhesion molecules such as intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM-1) and vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) [108].
Nitric oxide (NO) is produced by endothelial cells and plays a key role in vasodilation, facilitating insulin delivery to skeletal muscles and other insulin-sensitive tissues. Reduced NO bioavailability impairs vasodilation, decreases insulin-mediated glucose uptake, and contributes to insulin resistance. Studies in healthy humans have demonstrated a positive correlation between endothelial NO production and insulin sensitivity, suggesting that NO deficiency directly impairs insulin action in the vasculature [109,110]. NO promotes insulin signaling by enhancing endothelial cell insulin uptake and trans-endothelial transport, partly through protein S-nitrosylation and the inhibition of protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B), which negatively regulates insulin signaling pathways. NO donors can restore insulin uptake and signaling impaired by inflammatory cytokines or high-fat diets, illustrating the protective role of NO against insulin resistance at the cellular level [111]. Insulin resistance, especially in type 2 diabetes, is associated with decreased nitric oxide synthase activity. This impairment contributes to vascular insulin resistance and metabolic dysfunction [112]. Some evidence suggests that reduced NO bioavailability in obesity and diabetes negatively affects insulin secretion, whereas other studies indicate that NO can inhibit glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. Restoring NO levels has shown beneficial metabolic effects in type 2 diabetes [113]. Nitric oxide deficiency contributes to insulin resistance primarily by impairing endothelial function, reducing insulin delivery to tissues, and disrupting insulin signaling pathways. This deficiency is common in obesity, type 2 diabetes, and related metabolic disorders. Strategies that increase NO bioavailability have potential therapeutic benefits for improving insulin sensitivity and preventing vascular complications associated with insulin resistance. This relationship highlights NO as a critical mediator linking vascular health and metabolic control in insulin-resistant states.
5.1.2. Activity of Mitogen-Activated Protein Kinase (MAPK) Pathway
While PI3K pathways are blunted, insulin’s mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)-dependent pathways remain intact, increasing endothelin-1 (ET-1) secretion, a potent vasoconstrictor. Compensatory hyperinsulinemia in insulin-resistant states further activates MAPK pathways, amplifying ET-1 release and upregulating adhesion molecules (e.g., VCAM-1, E-selectin), promoting monocyte adhesion and atherosclerosis [114,115].
MAPKs play a central role in endothelial dysfunction by mediating inflammatory and stress responses that disrupt endothelial cell function and vascular integrity [116]. MAPKs, including ERK1/2, JNK, and p38, regulate endothelial activation in response to pro-inflammatory stimuli. While ERK1/2 generally supports growth and cytoprotection, JNK and p38 are more involved in inflammatory and stress signaling. The balance and crosstalk among MAPKs influence the inflammatory status of endothelial cells, contributing to leukocyte migration and atherosclerosis progression [117]. The activation of p38 MAPK leads to the phosphorylation of microtubule-associated protein 4 (MAP4), which causes microtubule disassembly and endothelial barrier dysfunction [118]. The chronic activation of endothelial MAPK pathways results in increased vascular permeability, endothelial network disruption, and heightened inflammatory mediator production (e.g., sICAM, VCAM, IL-1β). This leads to vascular leakiness and inflammation-associated endothelial dysfunction, which can impair hematopoietic stem cell niches and promote myeloid-biased differentiation under stress conditions [119]. Altered MAPK signaling is implicated in the worsening of endothelial dysfunction in diseases such as insulin resistance, where vascular MAPK dysregulation exacerbates endothelial deterioration [120]. Their interaction with other inflammatory pathways like NF-κB further exacerbates endothelial injury, contributing to vascular diseases and impaired tissue homeostasis. This understanding positions MAPK pathways as potential therapeutic targets to restore endothelial function and vascular integrity in inflammatory and chronic vascular conditions [116,119,120,121].
5.2. Insulin Resistance and Inflammation
Insulin resistance and inflammation are closely interconnected, often creating a vicious cycle that exacerbates metabolic dysfunction and increases the risk of diseases like type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular conditions. Chronic inflammation, especially obesity-induced inflammation, is a key driver of insulin resistance. Inflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), produced by adipose tissue and immune cells like macrophages, interfere with insulin signaling pathways in tissues including fat, muscle, and liver. This inhibition leads to reduced insulin sensitivity and impaired glucose metabolism [122,123]. When insulin signaling is impaired, it can increase the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines, creating a feedback loop where inflammation and insulin resistance worsen each other [124].
Macrophages are central to the pathophysiology of atherosclerosis, and insulin resistance markedly alters their function. Insulin-resistant macrophages demonstrate increased uptake of modified lipids, heightened production of inflammatory cytokines, and impaired efferocytosis (the clearance of apoptotic cells) [125,126]. This leads to the accumulation of apoptotic debris, necrotic core formation, and plaque instability. Furthermore, insulin resistance activates the unfolded protein response in macrophages, inducing apoptosis and further plaque necrosis [127,128].
In both conditions (atherosclerosis and insulin resistance) there is a switch in macrophage populations from an anti-inflammatory type (M2) to a pro-inflammatory type (M1), a switch that causes a vicious circle [129]. M1 macrophages ingest lipoproteins, which leads to the formation of foam cells. These cells are a key component of atherosclerotic plaques, which are deposits that form in the walls of arteries. These macrophages secrete pro-inflammatory cytokines like interleukin-6 (IL-6) and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), thereby amplifying the inflammatory response. In the context of insulin resistance, M1 macrophages increase tissue-based inflammation through the secretion of inflammatory markers. This inflammation can interfere with insulin signaling, worsening insulin resistance and contributing to the development of type 2 diabetes [130].
Insulin resistance associated with fibrous cap thinning was reported in various clinical studies, in which the necrotic core volume assessed both by coronary CT angiography and optical coherence tomography was positively correlated with HOMA-IR [131,132].
The mechanism of insulin resistance-mediated thin-cap fibroatheromata (TCFA) production involves the impairment of the PI3K/Akt pathway in macrophages, reducing cell survival and increasing endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. PI3K/ Akt pathway suppression leads to heightened vulnerability to ER stress-induced apoptosis. The accumulation of unfolded proteins (unfolded protein response) induced by free cholesterol loading or oxidized LDL triggers the CHOP (GADD153) pathway, augmenting macrophage death [133,134]. Insulin-resistant macrophages upregulate the scavenger receptor A, leading to more cholesterol uptake, generating a positive feedback loop that augments macrophage apoptosis. An impaired MEK-ERK pathway triggers defective SERCA signaling. Increased intracellular calcium concentration triggers the formation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP), allowing cytochrome c to be released into the cytoplasm which, in turn, triggers caspase-mediated apoptosis. The accumulation of dead cells increases the necrotic core volume, exacerbating inflammation and plaque instability 5. Furthermore, foam cell apoptosis releases free cholesterol in the plaque microenvironment, leading to cholesterol crystal accumulation [135]. Cholesterol crystals are phagocytosed by macrophages and disrupt phagolysosomal integrity, leading to cytoplasmic cathepsin leakage. Cathepsin leakage augments the NLRP3 inflammasome assembly, leading to increased IL-1β and IL-18 release [136]. Both IL-1β and IL-18 activate monocytes and T cells to secrete additional inflammatory mediators, such as IL-6 and interferon-γ, perpetuating local vascular inflammation [137,138].
Adaptive immunity also influences plaque stability by the T cell and B cell receptor-mediated recognition of epitopes from oxidized LDL particles and heat shock proteins. IL-18 promotes Th1 cell differentiation with further interferon-γ production and macrophage activation [139]. Furthermore, IL-1β production activates Th17 lymphocytes, enhancing the recruitment and activation of inflammatory cells, including neutrophils and monocytes. This, in turn, augments vascular inflammation and accelerates atherosclerotic plaque development. Regulatory T cells (Tregs), CD4+, CD25+, and Foxp3+ play a crucial role in suppressing inflammation and atherosclerosis by inhibiting pro-inflammatory immune cells and releasing anti-inflammatory cytokines like TGF-β and IL-10. They help maintain plaque stability by promoting collagen production and reducing plaque inflammation, while their depletion accelerates lesion formation. The balance between Tregs and pro-inflammatory T cells, especially Th1 cells, determines atherosclerosis progression, with Tregs counteracting lesion growth and promoting plaque regression through inflammation resolution and tissue repair. Additionally, Tregs encourage macrophage polarization toward the anti-inflammatory M2 phenotype, enhancing the clearance of dead cells and further supporting plaque stabilization and regression. Supporting these mechanisms, a study by Liuzzo et al. showed that patients with acute coronary syndromes expressed a higher proportion of Th1 lymphocytes, while the Treg population was poorly represented [140]. The explanation for the altered Th1/Treg ratio in atherosclerotic conditions might be attributed to the downregulation of Foxp3 and CD25, leading to an impaired anti-inflammatory response. Meanwhile, Th1 cells expand and secrete IFN-γ and TNF-α, which drive macrophage activation, endothelial dysfunction, and plaque instability. This shift toward a dominant pro-inflammatory Th1 response and diminished anti-inflammatory Treg activity exacerbates vascular inflammation, lesion progression, and plaque vulnerability [141,142,143].
Additionally, insulin resistance augments reactive oxygen species production, leading to an imbalance between matrix metalloproteinases (particularly MMP-9) and their inhibitors (TIMPs). This imbalance, despite facilitating smooth muscle cell migration and plaque expansion, makes atherosclerotic plaque more prone to rupture, leading to acute cardiovascular events [144,145] (Figure 2).
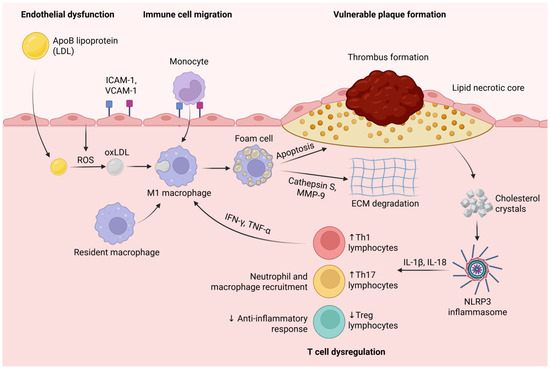
Figure 2.
Endothelial dysfunction promotes the infiltration of ApoB-containing lipoproteins (LDLs) into the arterial wall, where they undergo oxidative modification (oxLDL) via reactive oxygen species (ROS). OxLDL triggers the recruitment of monocytes through the upregulation of adhesion molecules (ICAM-1, VCAM-1). Monocytes differentiate into resident and M1 macrophages, which engulf oxidized LDL (oxLDL) to form foam cells. Pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFN-γ, TNF-α) secreted by Th1 lymphocytes further activate M1 macrophages, amplifying inflammation. Foam cell apoptosis and the secretion of proteases such as cathepsin S and MMP-9 contribute to extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, the thinning of the fibrous cap, and the expansion of the lipid necrotic core. Cholesterol crystals released from dying foam cells activate the NLRP3 inflammasome, leading to increased secretion of IL-1β and IL-18, which further recruit inflammatory cells and perpetuate vascular inflammation. The dysregulation of T cell subsets-characterized by increased Th1 and Th17 lymphocytes and decreased regulatory T cells (Tregs) exacerbates inflammation, disrupts anti-inflammatory responses, and promotes plaque instability and thrombus formation. Created in BioRender. Tirziu, A. (2025) https://BioRender.com/lcalh3v (accessed on 20 May 2025).
5.3. Dyslipidemia and Lipid Metabolism
Insulin resistance is frequently associated with dyslipidemia, characterized by elevated triglycerides, LDL-C, and small, dense LDL particles. These lipid abnormalities facilitate the infiltration of LDL into the arterial wall, where it undergoes oxidation (oxLDL) and is subsequently internalized by macrophages via scavenger receptors, culminating in foam cell formation and the initiation of atherosclerotic plaques [146,147]. Insulin resistance impairs the regulation of lipid metabolism, leading to increased free fatty acid flux from adipose tissue to the liver. This results in the overproduction of very-low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) and the accumulation of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins in the bloodstream. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins are not just markers but are likely causal risk factors for inflammation, atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, and even all-cause mortality. Extensive population studies have shown that higher levels of triglycerides and remnant cholesterol are linked with significantly increased risks of myocardial infarction, ischemic heart disease, ischemic stroke, and overall mortality [148,149].
5.4. Hepatic Insulin Resistance and Inflammation
Hepatic insulin resistance is a critical contributor to systemic inflammation and atherosclerosis. In response to insulin resistance, the liver synthesizes pro-inflammatory cytokines and acute-phase reactants such as CRP. These factors exacerbate endothelial dysfunction, enhance the expression of adhesion molecules, and increase the uptake of oxidized LDL by macrophages, all of which contribute to the formation and progression of atherosclerotic plaques [150,151].
5.5. The Role of Estrogen Deficiency
Before menopause, women typically experience a lower incidence of cardiovascular disease (CVD) compared to men; however, this gap narrows significantly after menopause. This dysfunction tends to worsen following menopause. Estrogen plays a vital role in maintaining endothelial health by promoting the production of nitric oxide (NO), a key vasodilator that helps relax blood vessels and sustain vascular tone. Additionally, it reduces levels of endothelin-1, a potent vasoconstrictor and pro-inflammatory peptide produced by the endothelium [152].
The decline in estrogen levels during menopause reduces the availability of NO and increases oxidative stress, contributing to endothelial dysfunction [153]. Experimental and clinical studies show that estrogen deficiency increases vascular free radical production and enhances vasoconstriction mediated by angiotensin II, further contributing to endothelial dysfunction [154,155]. Clinical evidence indicates that estrogen replacement therapy can improve endothelial function in postmenopausal women by restoring NO-mediated vasodilation and reducing oxidative stress. However, the efficacy of such treatment may depend on timing and receptor status [153,156].
5.6. Role of Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells (VSMCs)
VSMCs play a significant role in the relationship between insulin resistance and vascular disease, particularly atherosclerosis and remodeling. Under normal conditions, insulin maintains VSMC quiescence (a non-proliferative state) and modestly stimulates migration. Insulin promotes VSMC differentiation by increasing alpha-smooth muscle actin (alpha-SMA) expression, a marker of the contractile phenotype. However, insulin can also enhance VSMC migration through the MAP kinase pathway [157]. Insulin resistance in VSMCs disrupts normal insulin signaling pathways, particularly those involving insulin receptor substrate-1 (IRS-1) and downstream PI3K-Akt signaling. Angiotensin II (ANG II) induces the phosphorylation and degradation of IRS-1 in VSMCs, impairing insulin signaling and reducing glucose uptake [158]. The loss of normal insulin receptor signaling in VSMCs leads to increased proliferation and migration, key processes in atherosclerosis progression. VSMCs lacking insulin receptors show resistance to mTOR inhibition, suppressing typical proliferation and migration, thus exacerbating vascular disease [159]. Insulin resistance in VSMCs involves selective impairment of the PI3K-Akt pathway (responsible for metabolic actions like glucose uptake).
In contrast, the MAPK pathway (linked to mitogenic and inflammatory responses) remains active or is upregulated. This imbalance promotes VSMC proliferation, migration, and inflammation, contributing to vascular pathology. Therapeutic agents that improve insulin sensitivity, such as PPAR-γ agonists (e.g., pioglitazone), can help restore insulin signaling balance in VSMCs, reducing pathological proliferation and migration and potentially slowing atherosclerosis progression [160].
5.7. The Role of Maladaptive Responses to the Disruption of Cellular Homeostasis
Maladaptive responses to cellular stress are central to the progression from temporary dysfunction to chronic disease. They represent a breakdown in the cell’s capacity to restore homeostasis, often resulting in tissue injury, inflammation, and organ dysfunction [161].
Maladaptive stress responses in insulin resistance involve the following: 1. Cellular Stresses (factors such as nutrient overload, physical inactivity, hypoxia, and environmental toxins induce cellular stresses, including oxidative, nitrosative, carbonyl, genotoxic, and endoplasmic reticulum stress). 2. Stress Response Pathways. (Cells initiate adaptive responses like the unfolded protein response, DNA damage response, and autophagy to restore homeostasis. However, chronic or excessive activation leads to maladaptive outcomes-persistent inflammation, apoptosis, and impaired insulin signaling.) 3. Beta Cell Dysfunction (in pancreatic beta cells, maladaptive responses to chronic stress result in impaired insulin secretion, dedifferentiation, and apoptosis, contributing to the progression from compensation to decompensation in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes). 4. Trained Immunity (insulin resistance alters immune cell metabolism, particularly in macrophages, promoting a state of “trained immunity” that sustains maladaptive inflammatory responses and further disrupts metabolic homeostasis) [162].
Maladaptive stress responses in atherosclerosis involve the following: 1. Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. (Chronic ER stress in vascular cells triggers the UPR. If unresolved, this leads to apoptosis, inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and oxidative stress—all key drivers of atherosclerotic plaque formation and instability). 2. Mechanical Forces and Vascular Homeostasis. (Normally, endothelial and vascular smooth muscle cells adapt to mechanical forces like shear stress to maintain vascular health. Chronic disturbed flow or other risk factors can make these adaptive responses maladaptive, resulting in the sustained production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), activating pro-inflammatory pathways (MAPK, NF-κB) and promoting a pro-atherogenic state). 3. Unresolved Inflammation (atherosclerosis is now understood as a chronic inflammatory disease, in which maladaptive cellular responses fail to resolve inflammation, perpetuating vascular injury and plaque progression) [163].
Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis involve maladaptive cellular responses to metabolic and environmental stressors, particularly chronic inflammation, oxidative stress, and impaired autophagy [162]. While insulin resistance and atherosclerosis can develop independently, maladaptive stress responses in one can exacerbate the other. For example, insulin resistance promotes vascular inflammation and endothelial dysfunction, accelerating atherosclerosis [164]. Maladaptive cellular responses to disrupted homeostasis are central to developing and progressing insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. These maladaptive processes, originally evolved as adaptive mechanisms to restore balance, become detrimental when chronically activated, leading to persistent inflammation, cellular dysfunction, and ultimately, disease [163,165].
6. Genetic Factors in Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis
6.1. Genetic Predisposition to Metabolic Syndrome
Family history and genetic predisposition significantly contribute to the development of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. Numerous genetic markers associated with insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease have been identified, including variants in the IRS1, CHI3L1, and CD36 genes [166,167]. These genetic factors influence lipid metabolism, inflammatory responses, and insulin signaling pathways, thereby creating a predisposition to both conditions.
6.2. Haplotypes and Protective Genetic Variants
Specific haplotypes upstream of the insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS1) gene are linked to insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, and atherosclerosis. For instance, one haplotype has been found to confer protection against insulin resistance, adverse lipid profiles, and asymptomatic atherosclerosis, indicating a genetic connection between these conditions [168]. These findings underscore the potential of genetic screening and personalized therapies in managing insulin resistance and atherosclerosis.
6.3. Epigenetic and Environmental Interactions
Epigenetic modifications, such as DNA methylation and histone acetylation, also contribute to the development of insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. These changes are influenced by environmental factors, including diet and lifestyle, and may regulate the expression of genes involved in insulin signaling and lipid metabolism. Understanding these interactions is essential for developing targeted interventions to mitigate the risk of atherosclerosis in insulin-resistant individuals [169].
7. Is There a Link Between Insulin Resistance and ATS?
Numerous studies have identified a correlation between insulin resistance and cardiovascular risk [170,171]. Insulin resistance results in elevated insulin levels and hyperglycemia, even prior to the onset of diabetes mellitus [172]. A recent meta-analysis demonstrated that increased insulin levels and hyperglycemia, even in individuals without diabetes, are associated with heightened cardiovascular risk [173]. Insulin resistance may contribute to atherosclerotic disease through mechanisms such as dyslipidemia, endothelial dysfunction, hypertension, and inflammation, although these mechanisms are not yet fully elucidated [133,171,174].
In the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA), insulin resistance, as measured by HOMA-IR, was correlated with subclinical ATS, as indicated by IMT or the coronary calcium score, but only in the presence of metabolic syndrome [175]. Conversely, in a cohort of 3741 patients with HbA1c < 6% and no known cardiovascular disease, insulin resistance measured by HOMA-IR > 3 was correlated with subclinical ATS, as evidenced by carotid IMT or the coronary calcium score [176]. A recent study identified a correlation between insulin resistance (defined as HOMA-IR > 2.5) and subclinical ATS (measured by carotid IMT or ankle–brachial index), independent of other risk factors [177].
Another recent study evaluated the correlation between insulin resistance (characterized by the HOMA-IR index, TyG index, and triglyceride levels) and subclinical ATS (detected by the calcium score and IMT in the carotid arteries), as well as arterial stiffness (measured by brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV)). Upon reviewing several studies, it was concluded that the TyG index positively correlated with the calcium score, and both the TyG index and triglyceride levels correlated with baPWV. However, carotid artery IMT indices did not exhibit a positive correlation with any measure of insulin resistance. It was concluded that, among the measurements used to detect insulin resistance, the TyG index correlated most effectively with subclinical ATS, and its introduction into clinical practice was proposed [178]. The integration of the TyG index into current practice could enhance cardiovascular risk assessment, although this requires confirmation in future studies, both as a marker and therapeutic target [89,178].
8. Therapeutic Strategies for Insulin Resistance
Insulin resistance generates a high burden of cardiovascular diseases, as a 10-year history of type 2 diabetes is associated with a 20% risk of experiencing a myocardial infarction and a 40% likelihood of MI recurrence [179]. Currently, there is no specific pharmacological treatment for insulin resistance; however, it can be modulated through lifestyle modifications, increased physical activity, or certain medications [180,181,182]. Various drug classes have been identified that enhance insulin sensitivity in patients with prediabetes or diabetes mellitus, including biguanides, thiazolidinediones, GLP-1 receptor agonists, and SGLT2 inhibitors. Metformin is one such drug with evidence supporting its ability to improve insulin sensitivity through multiple mechanisms [183]. It has been shown to enhance insulin sensitivity in individuals with prediabetes, type 2 diabetes mellitus, obesity, polycystic ovary syndrome, and non-alcoholic hepatic steatosis by increasing peripheral glucose utilization, augmenting insulin receptor tyrosine kinase activity, promoting glycogen synthesis, and enhancing the recruitment and activity of GLUT4 [184]. Some studies have concluded that SGLT2 inhibitors, when administered to patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus, ameliorate insulin resistance (as measured by HOMA-IR) primarily by increasing glucose uptake in skeletal muscle and promoting lipolysis in adipose tissue. GLP-1 receptor agonists (liraglutide, semaglutide, and exenatide) have been found to inhibit macrophage inflammatory responses, thereby reducing insulin resistance [185]. Additionally, these agents facilitate weight loss and are recommended for obesity treatment, with improvements in insulin sensitivity observed prior to significant weight reduction [186,187].
Tirzepatide, a dual GIP and GLP-1 receptor agonist approved by the FDA in 2022, has shown significant improvements in glycemic control and weight reduction without increasing hypoglycemia risk, further improving insulin resistance in T2D patients [188].
Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitors (DPP-4i) (sitagliptin, vildagliptin, and linagliptin) have been shown to enhance insulin resistance in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus by mitigating macrophage-induced inflammation without affecting insulin secretion [189,190,191]. Pioglitazone improves insulin sensitivity by reducing muscle lipids and reorganizing lipids in adipose tissue [192], thereby decreasing the risk of major cardiovascular events (myocardial infarction and nonfatal stroke) in patients with prediabetes and diabetes, although it is associated with an increased risk of heart failure, bone fractures, and weight gain [193]. A pertinent question is whether insulin administration is advantageous for patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus and insulin resistance. This question was addressed in a study where, in patients with high insulin resistance (measured by HOMA-IR, with the cut-off point for high insulin resistance being the median = 4.55; interquartile range = [2.39–7.91]), exogenous insulin administration was associated with an elevated risk of mortality or major cardiovascular events, as well as a deterioration in renal function [194].
A groundbreaking new treatment called ReCET (Re-Cellularization via Electroporation Therapy) was presented in 2024. This procedure, performed under deep sedation, aims to improve the body’s sensitivity to its own insulin, addressing the root cause of insulin resistance. When combined with semaglutide, a GLP-1 receptor agonist, this approach eliminated the need for insulin therapy in 86% of patients in a small first-in-human study. Larger trials are underway to validate these promising results [195]. PATAS is an emerging medication in development that targets insulin resistance by correcting abnormalities in fat cells. It works by separating two proteins that block insulin’s action, thereby allowing fat cells to absorb glucose without needing insulin. This treatment could prevent T2D and other insulin resistance-related conditions like fatty liver and metabolic syndrome. Human trials are expected to begin in 2025, and it may be administered via injection or patch [196].
9. Conclusions
The intricate relationship between insulin resistance and atherosclerosis is increasingly recognized as a pivotal factor in the development and progression of cardiovascular disease. Insulin resistance independently predicts the progression of atherosclerotic plaques, even in individuals without diabetes, and acts through both traditional cardiovascular risk factors and direct vascular effects. The early detection of both subclinical ATS and IR is essential, as these conditions often precede overt clinical disease by years, providing a critical window for intervention.
The diagnosis of IR in clinical practice relies on surrogate indices such as HOMA-IR, the QUICKI, and the TyG index, which are helpful for screening and risk assessment. The early detection of ATS can be achieved through a combination of non-invasive imaging techniques (such as coronary artery calcium scoring and carotid ultrasound) and comprehensive risk profiling, which should include the identification of insulin resistance. However, the heterogeneity in diagnostic thresholds and the influence of population-specific factors highlight the need for standardized approaches and further research. Understanding and targeting the IR–ATS axis is essential for the effective prevention and management of cardiovascular disease, as interventions aimed at ameliorating insulin resistance may have a significant impact on reducing cardiovascular risk. Genetic factors and changes that affect gene expression play a role in both insulin resistance and atherosclerosis, suggesting that personalized medicine may become increasingly important in managing cardiovascular risk. This integrated approach would help clinicians identify high-risk individuals earlier and personalize treatment strategies accordingly. Future research should focus on refining diagnostic criteria, elucidating underlying mechanisms, and evaluating the impact of early, routine screening for IR in diverse populations.
The evidence supports a direct and clinically significant link between insulin resistance and atherosclerosis and highlights the importance of early detection and intervention in individuals at risk. Integrating the early detection and management of insulin resistance into cardiovascular prevention frameworks is crucial to mitigating the morbidity and mortality associated with atherosclerosis. Further research is required to investigate the interplay between metabolic and vascular health, which will be vital for developing more effective, individualized strategies for cardiovascular risk reduction.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, D.M.B. and R.M.C.; methodology, A.D.B. and R.P., D.M.B.; investigation, D.M.B., R.M.C., O.A. and A.T.; writing—original draft preparation, A.D.B., D.M.B., O.A. and R.M.C.; writing—review and editing, A.T., R.M.C. and D.M.B.; visualization, A.T.; supervision, D.M.B., R.M.C. and O.A.; project administration, A.D.B. and R.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
We would like to acknowledge “Victor Babes” University of Medicine and Pharmacy Timisoara, for their support in covering the costs of publication for this research paper.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript:
| Abbreviation | Full Term |
| ATS | Atherosclerosis |
| GLUT | Glucose Transporter (e.g., GLUT-2, GLUT-3, GLUT-4) |
| LDL | Low-Density Lipoprotein |
| LDLc | Low-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| HDLc | High-Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol |
| TG | Triglyceride |
| TyG | Triglyceride Glucose Index |
| CAD | Coronary Artery Disease |
| CT | Computed Tomography |
| JACC | Journal of the American College of Cardiology |
| Lp(a) | Lipoprotein(a) |
| MMP-9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase-9 |
| IMT | Intima-Media Thickness |
| CPs | Carotid Plaque Score |
| cIMT | Combined Intima-Media Thickness |
| baPWV | Brachial–Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity |
| HOMA-IR | Homeostatic Model Assessment for Insulin Resistance |
| QUICKI | Quantitative Insulin Sensitivity Check Index |
| G | Glucose (in the Context of the Matsuda Index Formula) |
| I | Insulin (in the Context of the Matsuda Index Formula) |
| ln | Natural Logarithm |
| log | Base 10 logarithm |
References
- Vos, T.; Lim, S.S.; Abbafati, C.; Abbas, K.M.; Abbasi, M.; Abbasifard, M.; Abbasi-Kangevari, M.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global burden of 369 diseases and injuries in 204 countries and territories, 1990–2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. Lancet 2020, 396, 1204–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Cao, G.; Jing, W.; Liu, J.; Liu, M. Global trends and regional differences in incidence and mortality of cardiovascular disease, 1990−2019: Findings from 2019 global burden of disease study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2023, 30, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedkoff, L.; Briffa, T.; Zemedikun, D.; Herrington, S.; Wright, F.L. Global Trends in Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Clin. Ther. 2023, 45, 1087–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahn, R.; Robertson, R.M.; Smith, R.; Eddy, D. The Impact of Prevention on Reducing the Burden of Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, 1686–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrzadeh, H.; Sharifi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Arzaghi, S.M.; Tajallizade-Khoob, Y.; Tootee, A.; Benetos, A.; Biffi, A.; Boavida, J.-M.; Capodanno, D.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines on cardiovascular disease prevention in clinical practice. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3227–3337. [Google Scholar]
- Fakhrzadeh, H.; Sharifi, F.; Alizadeh, M.; Arzaghi, S.M.; Tajallizade-Khoob, Y.; Tootee, A.; Alatab, S.; Mirarefin, M.; Badamchizade, Z.; Kazemi, H. Relationship between insulin resistance and subclinical atherosclerosis in individuals with and without type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2015, 15, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanley, A.J.G.; Williams, K.; Stern, M.P.; Haffner, S.M. Homeostasis Model Assessment of Insulin Resistance in Relation to the Incidence of Cardiovascular Disease. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1177–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fragoso, A.; Mendes, F.; Silva, A.P.; Neves, P.L. Insulin resistance as a predictor of cardiovascular morbidity and end-stage renal disease. J. Diabetes Complicat. 2015, 29, 1098–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Z.; Huang, R.; Xu, X.; Liu, W.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.; Guo, Y.; Zhuang, X.; Zhen, L. Long-Term High Level of Insulin Resistance Is Associated with an Increased Prevalence of Coronary Artery Calcification: The CARDIA Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e028985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, E.; Formentini, G.; Calcaterra, F.; Lombardi, S.; Marini, F.; Zenari, L.; Saggiani, F.; Poli, M.; Perbellini, S.; Raffaelli, A.; et al. HOMA-Estimated Insulin Resistance Is an Independent Predictor of Cardiovascular Disease in Type 2 Diabetic Subjects. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björkegren, J.L.M.; Lusis, A.J. Atherosclerosis: Recent developments. Cell 2022, 185, 1630–1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pepin, M.E.; Gupta, R.M. The Role of Endothelial Cells in Atherosclerosis. Am. J. Pathol. 2024, 194, 499–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebari-Benslaiman, S.; Galicia-García, U.; Larrea-Sebal, A.; Olaetxea, J.R.; Alloza, I.; Vandenbroeck, K.; Benito-Vicente, A.; Benito-Vicente, A. Pathophysiology of Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alipov, V.I.; Sukhorukov, V.N.; Karagodin, V.P.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Chemical composition of circulating native and desialylated low density lipoprotein: What is the difference? Vessel Plus 2017, 1, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orekhov, A.N.; Ivanova, E.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Sobenin, I.A. Circulating desialylated low density lipoprotein. Cor Vasa 2017, 59, e149–e156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashirskikh, D.; Chicherina, N.; Sobenin, I.; Orekhov, A. Effect of LDL desialylation on the development of atherosclerosis in mice. Atherosclerosis 2023, 379, S73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glanz, V.; Bezsonov, E.E.; Soldatov, V.; Orekhov, A.N. Thirty-Five-Year History of Desialylated Lipoproteins Discovered by Vladimir Tertov. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezentsev, A.; Bezsonov, E.; Kashirskikh, D.; Baig, M.S.; Eid, A.H.; Orekhov, A. Proatherogenic Sialidases and Desialylated Lipoproteins: 35 Years of Research and Current State from Bench to Bedside. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libby, P.; Okamoto, Y.; Rocha, V.Z.; Folco, E. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: Transition From Theory to Practice. Circ. J. 2010, 74, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Packard, R.R.; Libby, P. Inflammation in Atherosclerosis: From Vascular Biology to Biomarker Discovery and Risk Prediction. Clin. Chem. 2008, 54, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajoolabady, A.; Pratico, D.; Lin, L.; Mantzoros, C.S.; Bahijri, S.; Tuomilehto, J.; Ren, J. Inflammation in atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology and mechanisms. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cornelissen, A.; Gadhoke, N.V.; Ryan, K.; Hodonsky, C.J.; Mitchell, R.; Bihlmeyer, N.A.; Duong, T.; Chen, Z.; Dikongue, A.; Sakamoto, A.; et al. Polygenic Risk Score Associates with Atherosclerotic Plaque Characteristics at Autopsy. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 300–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragam, K.G.; Natarajan, P. Polygenic Scores to Assess Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klarin, D.; Natarajan, P. Clinical utility of polygenic risk scores for coronary artery disease. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2022, 19, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agbaedeng, T.A.; Noubiap, J.J.; Mato, E.P.M.; Chew, D.P.; Figtree, G.A.; Said, M.A.; van der Harst, P. Polygenic risk score and coronary artery disease: A meta-analysis of 979,286 participant data. Atherosclerosis 2021, 333, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koplev, S.; Seldin, M.; Sukhavasi, K.; Ermel, R.; Pang, S.; Zeng, L.; Bankier, S.; Di Narzo, A.; Cheng, H.; Meda, V.; et al. A mechanistic framework for cardiometabolic and coronary artery diseases. Nat. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 1, 85–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, R.V.; Fuster, V.; Bundgaard, H.; Fuster, J.J.; Johri, A.M.; Kofoed, K.F.; Douglas, P.S.; Diederichsen, A.; Shapiro, M.D.; Nicholls, S.J.; et al. Personalized Intervention Based on Early Detection of Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2024, 83, 2112–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinberg, D.; Grundy, S.M. The Case for Treating Hypercholesterolemia at an Earlier Age. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2012, 60, 2640–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Serés-Noriega, T.; Perea, V.; Amor, A.J. Screening for Subclinical Atherosclerosis and the Prediction of Cardiovascular Events in People with Type 1 Diabetes. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.K.; Bhatia, H.S.; Allen, T.S.; Grainger, T.; Pouncey, A.L.; Dichek, D.; Virmani, R.; Golledge, J.; Allison, M.A.; Powell, J.T. Assessment of Subclinical Atherosclerosis in Asymptomatic People In Vivo: Measurements Suitable for Biomarker and Mendelian Randomization Studies. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2024, 44, 24–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frías Vargas, M.; Jarauta, E. Detección de aterosclerosis subclínica mediante ecografía vascular como método de evaluación de riesgo vascular. Protoc. Simpl. Clínica E Investig. En Arterioscler. 2024, 36, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, J.; Cai, Q.; Chen, R.; Wu, W.; Wang, P.; Zhang, G.; Zhen, J. Relationship between Coronary Artery Calcium Score and Coronary Stenosis. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2023, 2023, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenland, P.; Blaha, M.J.; Budoff, M.J.; Erbel, R.; Watson, K.E. Coronary Calcium Score and Cardiovascular Risk. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 434–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Bera, K.; Kikano, E.; Pierce, J.D.; Gan, J.; Rajdev, M.; Ciancibello, L.M.; Gupta, A.; Rajagopalan, S.; Gilkeson, R.C. Coronary Artery Calcium Scoring: Current Status and Future Directions. RadioGraphics 2022, 42, 947–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortensen, M.B.; Gaur, S.; Frimmer, A.; Bøtker, H.E.; Sørensen, H.T.; Kragholm, K.H.; Peter, S.R.N.; Steffensen, F.H.; Jensen, R.V.; Mæng, M.; et al. Association of Age With the Diagnostic Value of Coronary Artery Calcium Score for Ruling Out Coronary Stenosis in Symptomatic Patients. JAMA Cardiol. 2022, 7, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, R.L.; Jorgensen, N.W.; Budoff, M.; Blaha, M.J.; Post, W.S.; Kronmal, R.A.; Bild, D.E.; Shea, S.; Liu, K.; Watson, K.E.; et al. 10-Year Coronary Heart Disease Risk Prediction Using Coronary Artery Calcium and Traditional Risk Factors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2015, 66, 1643–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paixao, A.R.; Berry, J.D.; Neeland, I.J.; Ayers, C.R.; Rohatgi, A.; de Lemos, J.A.; Khera, A. Coronary Artery Calcification and Family History of Myocardial Infarction in the Dallas Heart Study. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 7, 679–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erbel, R.; Möhlenkamp, S.; Moebus, S.; Schmermund, A.; Lehmann, N.; Stang, A.; Dragano, N.; Grönemeyer, D.; Seibel, R.; Kälsch, H.; et al. Coronary Risk Stratification, Discrimination, and Reclassification Improvement Based on Quantification of Subclinical Coronary Atherosclerosis. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1397–1406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezu, T.; Hosomi, N.; Aoki, S.; Matsumoto, M. Carotid Intima-Media Thickness for Atherosclerosis. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 18–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, S.; Koga, M.; Toyoda, K.; Minematsu, K.; Yasaka, M.; Nagai, Y.; Aoki, S.; Nezu, T.; Hosomi, N.; Kagimura, T.; et al. Factors Associated with Intima-Media Complex Thickness of the Common Carotid Artery in Japanese Noncardioembolic Stroke Patients with Hyperlipidemia: The J-STARS Echo Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2018, 25, 359–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, M.W.; Polak, J.F.; Kavousi, M.; Mathiesen, E.B.; Völzke, H.; Tuomainen, T.-P.; Sander, D.; Plichart, M.; Catapano, A.L.; Robertson, C.M.; et al. Carotid intima-media thickness progression to predict cardiovascular events in the general population (the PROG-IMT collaborative project): A meta-analysis of individual participant data. Lancet 2012, 379, 2053–2062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, H.; Nakagawa, T.; Okada, H.; Nakahashi, T.; Mori, M.; Sakata, K.; Nohara, A.; Takamura, M.; Kawashiri, M.-A. Clinical Impact of Carotid Plaque Score rather than Carotid Intima-Media Thickness on Recurrence of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Events. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2020, 27, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.; Wan, Y.; Barinas-Mitchell, E.; Fujiyoshi, A.; Cui, H.; Maimaiti, A.; Xu, R.; Li, J.; Suo, C.; Zaid, M. Varying Definitions of Carotid Intima-Media Thickness and Future Cardiovascular Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e031217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamashina, A.; Tomiyama, H.; Takeda, K.; Tsuda, H.; Arai, T.; Hirose, K.; Koji, Y.; Hori, S.; Yamamoto, Y. Validity, Reproducibility, and Clinical Significance of Noninvasive Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity Measurement. Hypertens. Res. 2002, 25, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, T.; Ohishi, M.; Onishi, M.; Ito, N.; Takeya, Y.; Maekawa, Y.; Rakugi, H. Cut-Off Value of Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity to Predict Cardiovascular Disease in Hypertensive Patients: A Cohort Study. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2013, 20, 391–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, H.J.; Cho, S.-A.; Cho, J.-Y.; Lee, S.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, S.H.; Hong, S.J.; Yu, C.W.; Lim, D.-S. Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity is Associated with Composite Carotid and Coronary Atherosclerosis in a Middle-Aged Asymptomatic Population. J. Atheroscler. Thromb. 2016, 23, 1033–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.-J.M.; Liu, C.-C.; Hsu, P.-J.M.; Hu, K.-C.; Hung, C.-L.; Yu, L.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C.M.; Shih, S.-C. Risk assessment indicators and brachial-ankle pulse wave velocity to predict atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. Medicine 2022, 101, e29609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iino, R.; Yokoyama, N.; Konno, K.; Naito, K.; Isshiki, T. Impact of Combined Assessment of Coronary Artery Calcium Score, Carotid Artery Plaque Score, and Brachial-Ankle Pulse Wave Velocity for Early Coronary Revascularization in Patients with Suspected Coronary Artery Disease. Int. Heart J. 2012, 53, 154–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Samuel, V.T.; Shulman, G.I. The pathogenesis of insulin resistance: Integrating signaling pathways and substrate flux. J. Clin. Investig. 2016, 126, 12–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, W.; Araki, E.; Ishigaki, Y.; Hirota, Y.; Maegawa, H.; Yamauchi, T.; Yorifuji, T.; Katagiri, H. New classification and diagnostic criteria for insulin resistance syndrome. Endocr. J. 2022, 69, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenhill, C. Sex differences in insulin resistance. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjornstad, P.; Eckel, R.H. Pathogenesis of Lipid Disorders in Insulin Resistance: A Brief Review. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2018, 18, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, G. Insulin and insulin resistance. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2005, 26, 19–39. [Google Scholar]
- Lawal, Y.; Bello, F.; Kaoje, Y.S. Prediabetes Deserves More Attention: A Review. Clin. Diabetes 2020, 38, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeFronzo, R.A.; Tobin, J.D.; Andres, R. Glucose clamp technique: A method for quantifying insulin secretion and resistance. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 1979, 237, E214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K. Hyperinsulinemic–Euglycemic Clamp to Assess Insulin Sensitivity In Vivo; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 221–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ayala, J.E.; Bracy, D.P.; Malabanan, C.; James, F.D.; Ansari, T.; Fueger, P.T.; McGuinness, O.P.; Wasserman, D.H. Hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic Clamps in Conscious, Unrestrained Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2011, 57, 2188. [Google Scholar]
- Marques-Vidal, P.; Mazoyer, E.; Bongard, V.; Gourdy, P.; Ruidavets, J.-B.; Drouet, L.; Ferrières, J. Prevalence of Insulin Resistance Syndrome in Southwestern France and Its Relationship with Inflammatory and Hemostatic Markers. Diabetes Care 2002, 25, 1371–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, E.; Kiechl, S.; Willeit, J.; Oberhollenzer, F.; Egger, G.; Targher, G.; Alberiche, M.; Bonadonna, R.C.; Muggeo, M. Prevalence of insulin resistance in metabolic disorders: The Bruneck Study. Diabetes 1998, 47, 1643–1649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumner, A.E.; Finley, K.B.; Genovese, D.J.; Criqui, M.H.; Boston, R.C. Fasting Triglyceride and the Triglyceride–HDL Cholesterol Ratio Are Not Markers of Insulin Resistance in African Americans. Arch. Intern. Med. 2005, 165, 1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuna-Puente, B.; Disse, E.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Laville, M.; Capeau, J.; Bastard, J.P. How can we measure insulin sensitivity/resistance? Diabetes Metab. 2011, 37, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim-Dorner, S.J.; Deuster, P.A.; Zeno, S.A.; Remaley, A.T.; Poth, M. Should triglycerides and the triglycerides to high-density lipoprotein cholesterol ratio be used as surrogates for insulin resistance? Metabolism 2010, 59, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antuna-Puente, B.; Faraj, M.; Karelis, A.D.; Garrel, D.; Prud’homme, D.; Rabasa-Lhoret, R.; Bastard, J.-P. HOMA or QUICKI: Is it useful to test the reproducibility of formulas? Diabetes Metab. 2008, 34, 294–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Sullivan, G.; Quon, M.J. Assessing the Predictive Accuracy of QUICKI as a Surrogate Index for Insulin Sensitivity Using a Calibration Model. Diabetes 2005, 54, 1914–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, M.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin sensitivity indices obtained from oral glucose tolerance testing: Comparison with the euglycemic insulin clamp. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenzo, C.; Haffner, S.M.; Stančáková, A.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. Fasting and OGTT-derived Measures of Insulin Resistance as Compared With the Euglycemic-Hyperinsulinemic Clamp in Nondiabetic Finnish Offspring of Type 2 Diabetic Individuals. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2015, 100, 544–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simental-Mendía, L.E.; Rodríguez-Morán, M.; Guerrero-Romero, F. The Product of Fasting Glucose and Triglycerides As Surrogate for Identifying Insulin Resistance in Apparently Healthy Subjects. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2008, 6, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurniawan, L.B. Triglyceride-Glucose Index as a Biomarker of Insulin Resistance, Diabetes Mellitus, Metabolic Syndrome, And Cardiovascular Disease: A Review. EJIFCC 2024, 35, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero-Romero, F.; Simental-Mendía, L.E.; González-Ortiz, M.; Martínez-Abundis, E.; Ramos-Zavala, M.G.; Hernández-González, S.O.; Jacques-Camarena, O.; Rodri, M. The Product of Triglycerides and Glucose, a Simple Measure of Insulin Sensitivity. Comparison with the Euglycemic-Hyperinsulinemic Clamp. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 95, 3347–3351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aman, M.; Resnawita, D.; Rasyid, H.; Kasim, H.; Bakri, S.; Umar, H.; Daud, N.A.; Seweng, A. The concordance of triglyceride glucose index (TyG index) and homeostatic model assessment for insulin resistance (Homa-IR) in non-diabetic subjects of adult Indonesian males. Clin. Epidemiol. Glob. Health 2021, 9, 227–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salazar, J.; Bermúdez, V.; Calvo, M.; Olivar, L.C.; Luzardo, E.; Navarro, C.; Mencia, H.; Martínez, M.; Rivas-Ríos, J.; Wilches-Durán, S.; et al. Optimal cutoff for the evaluation of insulin resistance through triglyceride-glucose index: A cross-sectional study in a Venezuelan population. F1000Research 2018, 6, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avagimyan, A.; Pogosova, N.; Fogacci, F.; Aghajanova, E.; Djndoyan, Z.; Patoulias, D.; Sasso, L.L.; Bernardi, M.; Faggiano, A.; Mohammadifard, N.; et al. Triglyceride-glucose index (TyG) as a novel biomarker in the era of cardiometabolic medicine. Int. J. Cardiol. 2025, 418, 132663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rafiee, H.; Mohammadifard, N.; Nouri, F.; Tabatabaei, G.A.; Najafian, J.; Sadeghi, M.; Boshtam, M.; Roohafza, H.; Haghighatdoost, F.; Hassannejad, R.; et al. Association of triglyceride glucose index with cardiovascular events: Insights from the Isfahan Cohort Study (ICS). Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Abudukeremu, A.; Jiang, Y.; Cao, Z.; Wu, M.; Ma, J.; Sun, R.; He, W.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; et al. U-shaped association between the triglyceride–glucose index and atrial fibrillation incidence in a general population without known cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azarboo, A.; Behnoush, A.H.; Vaziri, Z.; Daneshvar, M.S.; Taghvaei, A.; Jalali, A.; Cannavo, A.; Khalaji, A. Assessing the association between triglyceride-glucose index and atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurbuz, D.C.; Varis, E. Correlation Between Coronary Artery Calcium Score and Triglyceride-Glucose Index in Post-menopausal Women. Cureus 2023, 15, e39034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajdeya, O.; Beran, A.; Mhanna, M.; Alharbi, A.; Burmeister, C.; Abuhelwa, Z.; Malhas, S.-E.; Khader, Y.; Sayeh, W.; Assaly, R.; et al. Triglyceride Glucose Index for the Prediction of Subclinical Atherosclerosis and Arterial Stiffness: A Meta-analysis of 37,780 Individuals. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2022, 47, 101390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, K.-B.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, B.K.; Heo, R.; Han, D.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, S.-E.; Sung, J.M.; Cho, I.; Park, H.-B.; et al. The relationship of insulin resistance estimated by triglyceride glucose index and coronary plaque characteristics. Medicine 2018, 97, e10726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Wang, X.; Wu, J.; Zhang, M.; Cui, M. Triglyceride–glucose index and the incidence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases: A meta-analysis of cohort studies. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2021, 20, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primo, D.; Izaola, O.; de Luis, D.A. Triglyceride-Glucose Index Cutoff Point Is an Accurate Marker for Predicting the Prevalence of Metabolic Syndrome in Obese Caucasian Subjects. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2023, 79, 238–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipoorashrafi, S.A.; Seyedi, S.A.; Rabizadeh, S.; Ebrahimi, M.; Ranjbar, S.A.; Reyhan, S.K.; Meysamie, A.; Nakhjavani, M.; Esteghamati, A. The accuracy of triglyceride-glucose (TyG) index for the screening of metabolic syndrome in adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2022, 32, 2677–2688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Li, X.; Wu, H.; Su, F.; Cao, L.; Ren, X.; Hu, J.; Tatenda, G.; Cheng, M.; Wen, Y. Triglyceride-Glucose Index for the Diagnosis of Metabolic Syndrome: A Cross-Sectional Study of 298,652 Individuals Receiving a Health Check-Up in China. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2022, 2022, 3583603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Ma, J.; Yu, P.; Zheng, K.; Liu, F.; Luo, J. The triglyceride and glucose index and risk of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A dose–response meta-analysis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 13, 1043169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khamseh, M.E.; Malek, M.; Jahangiri, S.; Nobarani, S.; Hekmatdoost, A.; Salavatizadeh, M.; Soltanieh, S.; Chehrehgosha, H.; Taheri, H.; Montazeri, Z.; et al. Insulin Resistance/Sensitivity Measures as Screening Indicators of Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease and Liver Fibrosis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2024, 69, 1430–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beran, A.; Ayesh, H.; Mhanna, M.; Wahood, W.; Ghazaleh, S.; Abuhelwa, Z.; Sayeh, W.; Aladamat, N.; Musallam, R.; Matar, R.; et al. Triglyceride-Glucose Index for Early Prediction of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis of 121,975 Individuals. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, S.S.; Kuriyakose, D.; Polisetty, L.D.; Patil, A.A.; Ameen, D.; Bonu, R.; Shetty, S.P.; Biswas, P.; Ulrich, M.T.; Letafatkar, N.; et al. Diagnostic and prognostic value of triglyceride glucose index: A comprehensive evaluation of meta-analysis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2024, 23, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, Y.K.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, E.H.; Lee, M.J.; Yang, D.H.; Kang, J.-W.; Jung, C.H.; Park, J.-Y.; Kim, H.-K.; et al. Triglyceride Glucose-Waist Circumference Better Predicts Coronary Calcium Progression Compared with Other Indices of Insulin Resistance: A Longitudinal Observational Study. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 10, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irace, C.; Carallo, C.; Scavelli, F.B.; De Franceschi, M.S.; Esposito, T.; Tripolino, C.; Gnasso, A. Markers of insulin resistance and carotid atherosclerosis. A comparison of the homeostasis model assessment and triglyceride glucose index. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2013, 67, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, L.-C.; Xu, J.-N.; Wang, T.-T.; Hua, F.; Li, J.-J. Triglyceride-glucose index as a marker in cardiovascular diseases: Landscape and limitations. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2022, 21, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahn, H.S. The “lipid accumulation product” performs better than the body mass index for recognizing cardiovascular risk: A population-based comparison. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2005, 5, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyrou, I.; Panagiotakos, D.B.; Kouli, G.-M.; Georgousopoulou, E.; Chrysohoou, C.; Tsigos, C.; Tousoulis, D.; Pitsavos, C. Lipid accumulation product in relation to 10-year cardiovascular disease incidence in Caucasian adults: The ATTICA study. Atherosclerosis 2018, 279, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anoop, S.S.; Dasgupta, R.; Rebekah, G.; Jose, A.; Inbakumari, M.P.; Finney, G.; Finney, G.; Thomas, N. Lipid accumulation product (LAP) as a potential index to predict risk of insulin resistance in young, non-obese Asian Indian males from Southern India: Observations from hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp studies. BMJ Open Diabetes Res. Care 2021, 9, e002414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamini, S.; Bondesan, A.; Caroli, D.; Sartorio, A. The Lipid Accumulation Product Index (LAP) and the Cardiometabolic Index (CMI) Are Useful for Predicting the Presence and Severity of Metabolic Syndrome in Adult Patients with Obesity. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matthews, D.R.; Hosker, J.P.; Rudenski, A.S.; Naylor, B.A.; Treacher, D.F.; Turner, R.C. Homeostasis model assessment: Insulin resistance and β-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 1985, 28, 412–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mather, K.J.; Hunt, A.E.; Steinberg, H.O.; Paradisi, G.; Hook, G.; Katz, A.; Quon, M.J.; Alain, D. Baron Repeatability Characteristics of Simple Indices of Insulin Resistance: Implications for Research Applications. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 5457–5464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, S.P.; Juvanhol, L.L.; Bressan, J.; Hermsdorff, H.H.M. Triglyceride glucose index: A new biomarker in predicting cardiovascular risk. Prev. Med. Rep. 2022, 29, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizza, S.; Cardellini, M.; Martelli, E.; Porzio, O.; Pecchioli, C.; Nicolucci, A.; Marx, N.; Lauro, D.; Ippoliti, A.; Romeo, F.; et al. Occult impaired glucose regulation in patients with atherosclerosis is associated to the number of affected vascular districts and inflammation. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 316–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Consoli, C.; Martelli, E.; D’adamo, M.; Menghini, R.; Arcelli, D.; Porzio, O.; Pandolfi, A.; Pistolese, G.R.; Consoli, A.; Lauro, R.; et al. Insulin Resistance Affects Gene Expression in Endothelium. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, e7–e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.a.; Montagnani, M.; Koh, K.K.; Quon, M.J. Reciprocal Relationships Between Insulin Resistance and Endothelial Dysfunction. Circulation 2006, 113, 1888–1904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, E.A.; Reaven, P.D. Molecular and Signaling Mechanisms of Atherosclerosis in Insulin Resistance. Endocrinol. Metab. Clin. N. Am. 2006, 35, 525–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cubbon, R.M.; Kahn, M.B.; Wheatcroft, S.B. Effects of insulin resistance on endothelial progenitor cells and vascular repair. Clin. Sci. 2009, 117, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearney, M.T.; Duncan, E.R.; Kahn, M.; Wheatcroft, S.B. Insulin resistance and endothelial cell dysfunction: Studies in mammalian models. Exp. Physiol. 2008, 93, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsueh, W.A.; Lyon, C.J.; Quiñones, M.J. Insulin resistance and the endothelium. Am. J. Med. 2004, 117, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Park, K.; Li, C.; Rask-Madsen, C.; Mima, A.; Qi, W.; Mizutani, K.; Huang, P.; King, G.L. Induction of Vascular Insulin Resistance and Endothelin-1 Expression and Acceleration of Atherosclerosis by the Overexpression of Protein Kinase C-β Isoform in the Endothelium. Circ. Res. 2013, 113, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashraf, F.U.N.; Ghouri, K.; Someshwar, F.; Kumar, S.; Kumar, N.; Kumari, K.; Bano, S.; Ahmad, S.; Khawar, M.H.; Ramchandani, L.; et al. Insulin Resistance and Coronary Artery Disease: Untangling the Web of Endocrine-Cardiac Connections. Cureus 2023, 15, e51066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muniyappa, R.; Sowers, J.R. Role of insulin resistance in endothelial dysfunction. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2013, 14, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potenza, M.A.; Addabbo, F.; Montagnani, M. Vascular actions of insulin with implications for endothelial dysfunction. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2009, 297, E568–E577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, T.; Yang, T.; Chen, H.; Fu, D.; Hu, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, Q.; Yu, H.; Xu, W.; Xie, X. New insights into oxidative stress and inflammation during diabetes mellitus-accelerated atherosclerosis. Redox. Biol. 2019, 20, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.; Meininger, C.J. Nitric oxide and vascular insulin resistance. BioFactors 2009, 35, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stühlinger, M.C. Relationship Between Insulin Resistance and an Endogenous Nitric Oxide Synthase Inhibitor. JAMA 2002, 287, 1420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, A.X.; Aylor, K.; Barrett, E.J. Nitric Oxide Directly Promotes Vascular Endothelial Insulin Transport. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4030–4042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sansbury, B.E.; Hill, B.G. Regulation of obesity and insulin resistance by nitric oxide. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2014, 73, 383–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gheibi, S.; Ghasemi, A. Insulin secretion: The nitric oxide controversy. EXCLI J. 2020, 19, 1227–1245. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jansson, P.-A. Endothelial dysfunction in insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes. J. Intern. Med. 2007, 262, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muniyappa, R.; Chen, H.; Montagnani, M.; Sherman, A.; Quon, M.J. Endothelial dysfunction due to selective insulin resistance in vascular endothelium: Insights from mechanistic modeling. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab.. 2020, 319, E629–E646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akbar, N.; Forteath, C.; Hussain, M.S.; Reyskens, K.; Belch, J.J.F.; Lang, C.C.; Mordi, I.R.; Bhalraam, U.; Arthur, J.S.C.; Khan, F. Mitogen and Stress-Activated Kinases 1 and 2 Mediate Endothelial Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoefen, R.J.; Berk, B.C. The role of MAP kinases in endothelial activation. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2002, 38, 271–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Hu, J.; He, T.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, X.; Lan, X.; Zhang, D.; Mei, H.; Che, B.; Huang, Y. P38/MAPK contributes to endothelial barrier dysfunction via MAP4 phosphorylation-dependent microtubule disassembly in inflammation-induced acute lung injury. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalingam, P.; Poulos, M.G.; Lazzari, E.; Gutkin, M.C.; Lopez, D.; Kloss, C.C.; Crowley, M.J.; Katsnelson, L.; Freire, A.G.; Greenblatt, M.B.; et al. Chronic activation of endothelial MAPK disrupts hematopoiesis via NFKB dependent inflammatory stress reversible by SCGF. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, A.; Yang, Y.M.; Yan, C.; Kaley, G.; Hintze, T.H.; Sun, D. Altered MAPK Signaling in Progressive Deterioration of Endothelial Function in Diabetic Mice. Diabetes 2012, 61, 3181–3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino, D.A.; DeFronzo, R.A. Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis: Implications for Insulin-Sensitizing Agents. Endocr. Rev. 2019, 40, 1447–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Ballantyne, C.M. Metabolic Inflammation and Insulin Resistance in Obesity. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1549–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Luca, C.; Olefsky, J.M. Inflammation and insulin resistance. FEBS Lett. 2008, 582, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimobayashi, M.; Albert, V.; Woelnerhanssen, B.; Frei, I.C.; Weissenberger, D.; Meyer-Gerspach, A.C.; Clement, N.; Moes, S.; Colombi, M.; Meier, J.A.; et al. Insulin resistance causes inflammation in adipose tissue. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 1538–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, G.D.B.; Goedeke, L. Macrophage immunometabolism in diabetes-associated atherosclerosis. Immunometabolism 2023, 5, e00032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, C.P.; Han, S.; Senokuchi, T.; Tall, A.R. The Macrophage at the Crossroads of Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis. Circ. Res. 2007, 100, 1546–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Tall, A.; Accili, D. The Impact of Macrophage Insulin Resistance on Advanced Atherosclerotic Plaque Progression. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabas, I.; Seimon, T.; Arellano, J.; Li, Y.; Forcheron, F.; Cui, D.; Han, S.; Liang, C.-P.; Tall, A.; Accili, D. The Impact of Insulin Resistance on Macrophage Death Pathways in Advanced Atherosclerosis. Novartis Found. Symp. 2007, 286, 99–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kraler, S.; Mueller, C.; Libby, P.; Bhatt, D.L. Acute coronary syndromes: Mechanisms, challenges, and new opportunities. Eur. Hear. J. 2025, ehaf289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stöhr, R.; Federici, M. Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis: Convergence between metabolic pathways and inflammatory nodes. Biochem. J. 2013, 454, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, J.; Auscher, S.; Shamoun, A.; Pararajasingam, G.; Heinsen, L.J.; Andersen, T.R.; Lindholt, J.S.; Diederichsen, A.C.P.; Lambrechtsen, J.; Egstrup, K. Insulin resistance is associated with high-risk coronary artery plaque composition in asymptomatic men between 65 and 75 years and no diabetes: A DANCAVAS cross-sectional sub-study. Atherosclerosis 2023, 385, 117328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iguchi, T.; Hasegawa, T.; Otsuka, K.; Matsumoto, K.; Yamazaki, T.; Nishimura, S.; Nakata, S.; Ehara, S.; Kataoka, T.; Shimada, K.; et al. Insulin resistance is associated with coronary plaque vulnerability: Insight from optical coherence tomography analysis. Eur. Hear. J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bornfeldt, K.E.; Tabas, I. Insulin Resistance, Hyperglycemia, and Atherosclerosis. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Liang, C.-P.; DeVries-Seimon, T.; Ranalletta, M.; Welch, C.L.; Collins-Fletcher, K.; Accili, D.; Tabas, I.; Tall, A.R. Macrophage insulin receptor deficiency increases ER stress-induced apoptosis and necrotic core formation in advanced atherosclerotic lesions. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 257–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoudi, A.; Shamoun, F.E.; Kalavakunta, J.K.; Abela, G.S. Cholesterol crystal induced arterial inflammation and destabilization of atherosclerotic plaque. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 1959–1967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duewell, P.; Kono, H.; Rayner, K.J.; Sirois, C.M.; Vladimer, G.; Bauernfeind, F.G.; Abela, G.S.; Franchi, L.; Nuñez, G.; Schnurr, M.; et al. NLRP3 inflammasomes are required for atherogenesis and activated by cholesterol crystals. Nature 2010, 464, 1357–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbate, A.; Toldo, S.; Marchetti, C.; Kron, J.; Van Tassell, B.W.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-1 and the Inflammasome as Therapeutic Targets in Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1260–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bahrami, A.; Sathyapalan, T.; Sahebkar, A. The Role of Interleukin-18 in the Development and Progression of Atherosclerosis. Curr. Med. Chem. 2021, 28, 1757–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahoute, C.; Herbin, O.; Mallat, Z.; Tedgui, A. Adaptive immunity in atherosclerosis: Mechanisms and future therapeutic targets. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liuzzo, G.; Montone, R.A.; Gabriele, M.; Pedicino, D.; Giglio, A.F.; Trotta, F.; Galiffa, V.A.; Previtero, M.; Severino, A.; Biasucci, L.M.; et al. Identification of unique adaptive immune system signature in acute coronary syndromes. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 168, 564–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, C.; Kim, H.I.; Park, J.; Guo, J.; Huang, W. The role of immune cells in different stages of atherosclerosis. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 21, 1129–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butcher, M.J.; Filipowicz, A.R.; Waseem, T.C.; McGary, C.M.; Crow, K.J.; Magilnick, N.; Boldin, M.; Lundberg, P.S.; Galkina, E.V. Atherosclerosis-Driven Treg Plasticity Results in Formation of a Dysfunctional Subset of Plastic IFNγ + Th1/Tregs. Circ. Res. 2016, 119, 1190–1203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Xiang, X.; Nie, L.; Guo, X.; Zhang, F.; Wen, C.; Xia, Y.; Mao, L. The emerging role of Th1 cells in atherosclerosis and its implications for therapy. Front. Immunol. 2023, 13, 1079668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigro, J.; Osman, N.; Dart, A.M.; Little, P.J. Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis. Endocr. Rev. 2006, 27, 242–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacek, T.; Rahman, S.; Yu, S.; Neamtu, D.; Givimani, S.; Tyagi, S. Matrix metalloproteinases in atherosclerosis: Role of nitric oxide, hydrogen sulfide, homocysteine, and polymorphisms. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2015, 173, 173–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meshkani, R.; Adeli, K. Hepatic insulin resistance, metabolic syndrome and cardiovascular disease. Clin. Biochem. 2009, 42, 1331–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toledo-Corral, C.M.; Alderete, T.L.; Goran, M.I. Dyslipidemia: Relationship to Insulin Resistance, Fatty Liver, and Sub-Clinical Atherosclerosis. In Lipid Management; Springer International Publishing: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 65–79. [Google Scholar]
- Nordestgaard, B.G. Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins and Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease. Circ. Res. 2016, 118, 547–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Soffer, G. Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk: Current status and treatments. Curr. Opin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Obes. 2021, 28, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoleri, D.; Titchenell, P.M. Resolving the Paradox of Hepatic Insulin Resistance. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 7, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bazotte, R.B.; Silva, L.G.; Schiavon, F.P. Insulin resistance in the liver: Deficiency or excess of insulin? Cell Cycle 2014, 13, 2494–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somani, Y.B.; Pawelczyk, J.A.; De Souza, M.J.; Kris-Etherton, P.M.; Proctor, D.N. Aging women and their endothelium: Probing the relative role of estrogen on vasodilator function. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2019, 317, H395–H404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taddei, S.; Virdis, A.; Ghiadoni, L.; Mattei, P.; Sudano, I.; Bernini, G.; Pinto, S.; Salvetti, A. Menopause Is Associated with Endothelial Dysfunction in Women. Hypertension 1996, 28, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, S.; Bäumer, A.T.; Strehlow, K.; van Eickels, M.; Grohé, C.; Ahlbory, K.; Rösen, R.; Böhm, M.; Nickenig, G. Endothelial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress During Estrogen Deficiency in Spontaneously Hypertensive Rats. Circulation 2001, 103, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, S.K.; Das, S.; Jaarin, K. A detailed microscopic study of the changes in the aorta of experimental model of postmenopausal rats fed with repeatedly heated palm oil. Int. J. Exp. Pathol. 2009, 90, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.J.; Lee, D.W.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, I.K. Effect of estrogen on endothelial dysfunction in postmenopausal women with diabetes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2001, 54, S81–S92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.L.; Gurevich, I.; Draznin, B. Insulin Affects Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotype and Migration Via Distinct Signaling Pathways. Diabetes 2003, 52, 2562–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, H.; Mehta, P.K.; Taniyama, Y.; Lassègue, B.; Seidel-Rogol, B.; Martin, A.S.; Griendling, K.K. Vascular smooth muscle insulin resistance, but not hypertrophic signaling, is independent of angiotensin II-induced IRS-1 phosphorylation by JNK. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2011, 301, C1415–C1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lightell, D.J.; Moss, S.C.; Woods, T.C. Loss of Canonical Insulin Signaling Accelerates Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Proliferation and Migration Through Changes in p27Kip1 Regulation. Endocrinology 2011, 152, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cersosimo, E.; Xu, X.; Musi, N. Potential role of insulin signaling on vascular smooth muscle cell migration, proliferation, and inflammation pathways. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2012, 302, C652–C657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, J.V.H. Adaptive and maladaptive roles of lipid droplets in health and disease. Am. J. Physiol. Physiol. 2022, 322, C468–C481. [Google Scholar]
- Onyango, A.N. Cellular Stresses and Stress Responses in the Pathogenesis of Insulin Resistance. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2018, 2018, 4321714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viola, J.; Soehnlein, O. Atherosclerosis–A matter of unresolved inflammation. Semin. Immunol. 2015, 27, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Semenkovich, C.F. Insulin resistance and atherosclerosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, C.; Schwartz, M.A. The Role of Cellular Adaptation to Mechanical Forces in Atherosclerosis. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2008, 28, 2101–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abou Ziki, M.D.; Mani, A. Metabolic syndrome. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2016, 27, 162–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, S.-A.; Hong, J.; Kim, Y.; Hong, G.; Baik, S.; Choi, K.; Lee, M.-K.; Lee, K.-R. Identification of genetic variants related to metabolic syndrome by next-generation sequencing. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perumalsamy, S.; Huri, H.Z.; Abdullah, B.M.; Mazlan, O.; Wan Ahmad, W.A.; Vethakkan, S.R.D.B. Genetic Markers of Insulin Resistance and Atherosclerosis in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Coronary Artery Disease. Metabolites 2023, 13, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, C. Epigenetic regulation of insulin action and secretion–role in the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 288, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ormazabal, V.; Nair, S.; Elfeky, O.; Aguayo, C.; Salomon, C.; Zuñiga, F.A. Association between insulin resistance and the development of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmas, C.E.; Bousvarou, M.D.; Kostara, C.E.; Papakonstantinou, E.J.; Salamou, E.; Guzman, E. Insulin resistance and cardiovascular disease. J. Int. Med. Res. 2023, 51, 03000605231164548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Færch, K.; Vaag, A.; Holst, J.J.; Hansen, T.; Jørgensen, T.; Borch-Johnsen, K. Natural History of Insulin Sensitivity and Insulin Secretion in the Progression From Normal Glucose Tolerance to Impaired Fasting Glycemia and Impaired Glucose Tolerance: The Inter99 Study. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 439–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarwar, N.; Sattar, N.; Gudnason, V.; Danesh, J. Circulating concentrations of insulin markers and coronary heart disease: A quantitative review of 19 Western prospective studies. Eur. Heart J. 2007, 28, 2491–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoelson, S.E. Inflammation and insulin resistance. J. Clin. Investig. 2006, 116, 1793–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoni, A.G.; Wong, N.D.; Shea, S.; Ma, S.; Liu, K.; Preethi, S.; Jacobs, D.R.; Wu, C.; Saad, M.F.; Szklo, M. Insulin Resistance, Metabolic Syndrome, and Subclinical Atherosclerosis. Diabetes Care 2007, 30, 2951–2956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iglesies-Grau, J.; Garcia-Alvarez, A.; Oliva, B.; Mendieta, G.; García-Lunar, I.; Fuster, J.J.; Devesa, A.; Pérez-Herreras, C.; Fernández-Ortiz, A.; Brugada, R.; et al. Early insulin resistance in normoglycemic low-risk individuals is associated with subclinical atherosclerosis. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2023, 22, 350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landowska, M.; Kałuża, B.; Watała, C.; Babula, E.; Żuk-Łapan, A.; Woźniak, K.; Kargul, A.; Jurek, J.; Korcz, T.; Cicha-Brzezińska, M.; et al. Is Insulin Resistance an Independent Predictor of Atherosclerosis? J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, D.A.; Ponir, C.; Shapiro, M.D.; Chevli, P.A. Associations between insulin resistance indices and subclinical atherosclerosis: A contemporary review. Am. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2024, 18, 100676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, J.; Liu, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, F.; Liu, Y. Type 2 Diabetes and Myocardial Infarction: Recent Clinical Evidence and Perspective. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 24, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snel, M.; Jonker, J.T.; Schoones, J.; Lamb, H.; de Roos, A.; Pijl, H.; Smit, J.W.A.; Meinders, A.E.; Jazet, I.M. Ectopic Fat and Insulin Resistance: Pathophysiology and Effect of Diet and Lifestyle Interventions. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 2012, 983814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hawley, J.A. Exercise as a therapeutic intervention for the prevention and treatment of insulin resistance. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2004, 20, 383–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedewa, M.V.; Gist, N.H.; Evans, E.M.; Dishman, R.K. Exercise and Insulin Resistance in Youth: A Meta-Analysis. Pediatrics. 2014, 133, e163–e174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Aa, M.P.; Elst, M.A.J.; van de Garde, E.M.W.; van Mil, E.G.A.H.; Knibbe, C.A.J.; van der Vorst, M.M.J. Long-term treatment with metformin in obese, insulin-resistant adolescents: Results of a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial. Nutr. Diabetes 2016, 6, e228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herman, R.; Kravos, N.A.; Jensterle, M.; Janež, A.; Dolžan, V. Metformin and Insulin Resistance: A Review of the Underlying Mechanisms behind Changes in GLUT4-Mediated Glucose Transport. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.S.; Jun, H.S. Anti-Inflammatory Effects of GLP-1-Based Therapies beyond Glucose Control. Mediat. Inflamm. 2016, 2016, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Ma, B.; Fan, L.; Yi, N.; Lu, B.; Wang, Q.; Liu, R. GLP-1 Improves Adipocyte Insulin Sensitivity Following Induction of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 16, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashayekhi, M.; Nian, H.; Mayfield, D.; Devin, J.K.; Gamboa, J.L.; Yu, C.; Silver, H.J.; Niswender, K.; Luther, J.M.; Brown, N.J. Weight Loss–Independent Effect of Liraglutide on Insulin Sensitivity in Individuals with Obesity and Prediabetes. Diabetes 2024, 73, 38–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrao, S.; Pollicino, C.; Maggio, D.; Torres, A.; Argano, C. Tirzepatide against obesity and insulin-resistance: Pathophysiological aspects and clinical evidence. Front. Endocrinol. 2024, 15, 1402583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okura, T.; Fujioka, Y.; Nakamura, R.; Ito, Y.; Kitao, S.; Anno, M.; Matsumoto, K.; Shoji, K.; Okura, H.; Matsuzawa, K.; et al. Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 inhibitor improves insulin resistance in Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes: A single-arm study, a brief report. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2022, 14, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, F.; Ni, Y.; Nagashimada, M.; Nagata, N.; Xu, L.; Mukaida, N.; Kaneko, S.; Ota, T. DPP-4 Inhibition by Linagliptin Attenuates Obesity-Related Inflammation and Insulin Resistance by Regulating M1/M2 Macrophage Polarization. Diabetes 2016, 65, 2966–2979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saini, K.; Sharma, S.; Khan, Y. DPP-4 inhibitors for treating T2DM-hype or hope? An analysis based on the current literature. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1130625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasouli, N.; Raue, U.; Miles, L.M.; Lu, T.; Di Gregorio, G.B.; Elbein, S.C.; Kern, P.A. Pioglitazone improves insulin sensitivity through reduction in muscle lipid and redistribution of lipid into adipose tissue. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2005, 288, E930–E934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.W.; Saver, J.L.; Wu, Y.L.; Chen, T.H.; Lee, M.; Ovbiagele, B. Pioglitazone and cardiovascular outcomes in patients with insulin resistance, pre-diabetes and type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e013927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, C.E.; Eiler, C.; Walker, R.J.; Egede, L.E. Insulin Therapy for Insulin Resistant Patients—Harm or Benefit? Diabetes 2018, 1, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Busch, C.B.E.; Meiring, S.; van Baar, A.C.G.; Holleman, F.; Nieuwdorp, M.; Bergman, J.J.G.H.M. Recellularization via electroporation therapy of the duodenum combined with glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist to replace insulin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes: 12-month results of a first-in-human study. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2024, 100, 896–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreyer, E.; Obringer, C.; Messaddeq, N.; Kieffer, B.; Zimmet, P.; Fleming, A.; Geberhiwot, T.; Marion, V. PATAS, a First-in-Class Therapeutic Peptide Biologic, Improves Whole-Body Insulin Resistance and Associated Comorbidities In Vivo. Diabetes 2022, 71, 2034–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).