Extracellular Vesicles and PD-L1—A Review of Complex Immunoregulatory Properties and Clinical Importance
Abstract
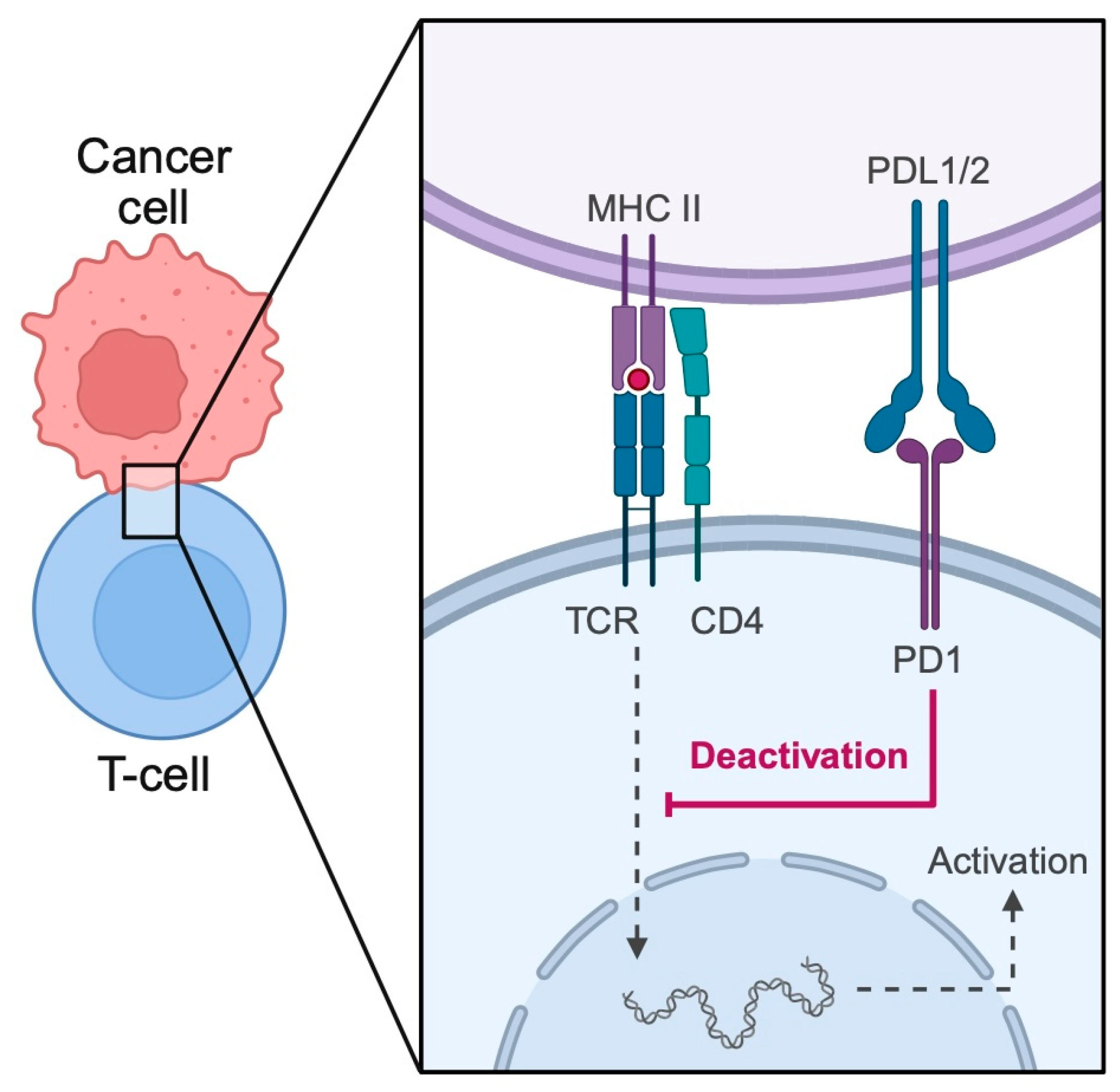
1. Introduction
2. Extracellular Vesicles and PD-1—The Relationship with Pathological Conditions
2.1. Cancer
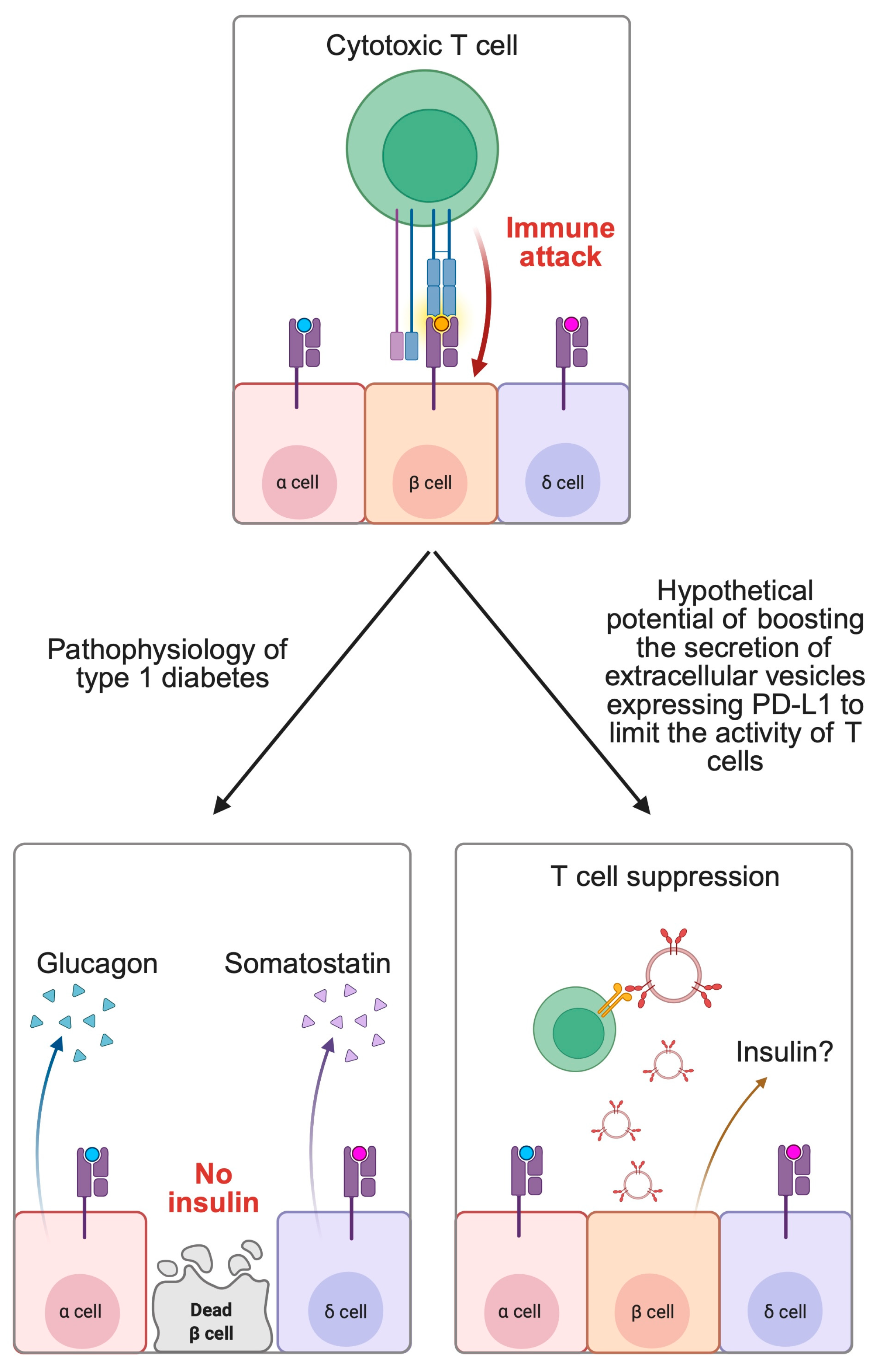
2.2. Autoimmune Diseases
3. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| EVs | Extracellular vesicles |
| MVBs | Multi-vesicular bodies |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| DCs | Dendritic cells |
| PD-1 | Programmed cell death protein 1 |
| PD-L1 | Programmed cell death protein ligand 1 |
| ITIM | Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based inhibitor motif |
| ITSM | Immunoreceptor tyrosine-based switch motif |
| TCR | T cell receptor |
| BCR | B cell receptor |
| RA | Rheumatoid arthritis |
| SLE | Systemic lupus erythematosus |
| TAMs | Tumor associated macrophages |
| MDSCs | Myeloid-derived suppressor cells |
| CTLA-4 | Cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 |
| TIM-3 | T cell immunoglobulin-3 |
| TDEs | Tumor-derived exosomes |
| CPS | Combined positive score |
| ORR | Objective response rate |
| ICI | Immune checkpoint inhibitor |
| CTC | Circulating tumor cell |
| DLBCL | Diffuse large B cell lymphoma |
| NSCLC | Non-small cell lung carcinoma |
| MSCs | Mesenchymal stromal cells |
| T1DM | Type 1 diabetes melitus |
References
- Iraci, N.; Leonardi, T.; Gessler, F.; Vega, B.; Pluchino, S. Focus on Extracellular Vesicles: Physiological Role and Signalling Properties of Extracellular Membrane Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meldolesi, J. Extracellular vesicles, news about their role in immune cells: Physiology, pathology and diseases. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2019, 196, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bazzan, E.; Tinè, M.; Casara, A.; Biondini, D.; Semenzato, U.; Cocconcelli, E.; Balestro, E.; Damin, M.; Radu, C.M.; Turato, G.; et al. Critical Review of the Evolution of Extracellular Vesicles’ Knowledge: From 1946 to Today. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Ou, M.; Yang, P.; Ning, M. The role of extracellular vesicle immune checkpoints in cancer. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2024, 216, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammadipoor, A.; Hershfield, M.R.; Linsenbardt, H.R.; Smith, J.; Mack, J.; Natesan, S.; Averitt, D.L.; Stark, T.R.; Sosanya, N.M. Biological function of Extracellular Vesicles (EVs): A review of the field. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 8639–8651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallal, S.; Tűzesi, Á.; Grau, G.E.; Buckland, M.E.; Alexander, K.L. Understanding the extracellular vesicle surface for clinical molecular biology. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, e12260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vagner, T.; Spinelli, C.; Minciacchi, V.R.; Balaj, L.; Zandian, M.; Conley, A.; Zijlstra, A.; Freeman, M.R.; Demichelis, F.; De, S.; et al. Large extracellular vesicles carry most of the tumour DNA circulating in prostate cancer patient plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1505403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Li, Y.; Peng, J.; Wu, D.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L.; Yan, X.; Du, Y.; Yu, L. Discovery of the migrasome, an organelle mediating release of cytoplasmic contents during cell migration. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 24–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buzás, E.I.; Tóth, E.; Sódar, B.W.; Szabó-Taylor, K. Molecular interactions at the surface of extracellular vesicles. Semin. Immunopathol. 2018, 40, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aloi, N.; Drago, G.; Ruggieri, S.; Cibella, F.; Colombo, P.; Longo, V. Extracellular Vesicles and Immunity: At the Crossroads of Cell Communication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ventimiglia, L.N.; Alonso, M.A. Biogenesis and Function of T Cell-Derived Exosomes. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2016, 4, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Lee, M.J.; Park, S.J.; Lee, M.S. Lipopolysaccharide-Preconditioned Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells Induce M1 Polarization of Macrophages through Extracellular Vesicles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reed, T.; Schorey, J.; D’Souza-Schorey, C. Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Means of Co-opting Macrophage Polarization in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 746432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robbins, P.D.; Morelli, A.E. Regulation of immune responses by extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 195–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.Y.; Zhu, Y.; Shen, Y.Y.; Xu, Q.Y.; Tang, H.Y.; Cui, N.X.; Jiang, L.; Dai, X.M.; Chen, W.Q.; Lin, Q.; et al. The role of PD-1 signaling in health and immune-related diseases. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1163633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, X.; Xiong, F.; Ge, J.; Xiang, B.; Wu, X.; Ma, J.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; et al. Role of the tumor microenvironment in PD-L1/PD-1-mediated tumor immune escape. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wang, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, F.; Zeng, X. The PD-1/PD-L pathway in rheumatic diseases. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2021, 120, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, R.; Feizisani, F.; Shomali, N.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Hemmatzadeh, M.; Gholizadeh Navashenaq, J.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F.; Bokov, D.O.; Janebifam, M.; Mohammadi, H. PD-1/PD-L1 blockade: Prospectives for immunotherapy in cancer and autoimmunity. IUBMB Life 2021, 73, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Qiao, G.; Hassan, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Kong, H.; Zeng, W.; Yin, F.; Zhang, J. Program Death-1 Suppresses Autoimmune Arthritis by Inhibiting Th17 Response. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2016, 64, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Liao, W.; Chen, M.; Shan, S.; Song, Y.; Zhang, S.; Song, H.; Yuan, Z. Expression of programmed death-1 (PD-1) on CD4+ and CD8+ T cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation 2014, 37, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Q.; Ye, J.; Zeng, L.; Luo, Z.; Deng, Z.; Li, X.; Guo, Y.; Huang, Z.; Li, J. Elevated expression of PD-1 on T cells correlates with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.; La Cava, A.; Hahn, B.H. Blockade of programmed death-1 in young (New Zealand Black x New Zealand White)F1 mice promotes the suppressive capacity of CD4+ regulatory T cells protecting from lupus-like disease. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 5402–5410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristjansdottir, H.; Steinsson, K.; Gunnarsson, I.; Gröndal, G.; Erlendsson, K.; Alarcón-Riquelme, M.E. Lower expression levels of the programmed death 1 receptor on CD4+CD25+ T cells and correlation with the PD-1.3A genotype in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 1702–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: The next generation. Cell 2011, 144, 646–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, M.; Ustoyev, Y. Cancer and the Immune System: The History and Background of Immunotherapy. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2019, 35, 150923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Itahashi, K.; Irie, T.; Nishikawa, H. Regulatory T-cell development in the tumor microenvironment. Eur. J. Immunol. 2022, 52, 1216–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommen, D.S.; Schumacher, T.N. T Cell Dysfunction in Cancer. Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 547–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricci, J.E. Tumor-induced metabolic immunosuppression: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets. Cell Rep. 2025, 44, 115206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Q.H.; Zheng, J.Q.; Ding, J.Y.; Wu, Y.F.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.L.; Chen, G. Exosome-Mediated Immunosuppression in Tumor Microenvironments. Cells 2022, 11, 1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteran, L.; Erez, N. The Dark Side of Fibroblasts: Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts as Mediators of Immunosuppression in the Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Liu, D.; Li, L. PD-1/PD-L1 pathway: Current researches in cancer. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2020, 10, 727–742. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Liu, B.; Cao, Y.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Jin, G.; Qin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Cui, K.; Zhou, L.; et al. Colorectal Cancer-Derived Small Extracellular Vesicles Promote Tumor Immune Evasion by Upregulating PD-L1 Expression in Tumor-Associated Macrophages. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2102620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.K.; Mohamed, A.H.; Amer Alsaiari, A.; Olegovich Bokov, D.; Ali Patel, A.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Shafie, A.; Adnan Ashour, A.; Azhar Kamal, M.; Ahmad, F.; et al. The role of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment and pathogenesis of psoriasis. Cytokine 2024, 182, 156699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crespo, J.; Sun, H.; Welling, T.H.; Tian, Z.; Zou, W. T cell anergy, exhaustion, senescence, and stemness in the tumor microenvironment. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2013, 25, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jiang, P.; Wei, S.; Xu, X.; Wang, J. Regulatory T cells in tumor microenvironment: New mechanisms, potential therapeutic strategies and future prospects. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Speiser, D.E.; Chijioke, O.; Schaeuble, K.; Münz, C. CD4. Nat. Cancer 2023, 4, 317–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebhardt, T.; Park, S.L.; Parish, I.A. Stem-like exhausted and memory CD8. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2023, 23, 780–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brudno, J.N.; Maus, M.V.; Hinrichs, C.S. CAR T Cells and T-Cell Therapies for Cancer: A Translational Science Review. JAMA 2024, 332, 1924–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribas, A.; Shin, D.S.; Zaretsky, J.; Frederiksen, J.; Cornish, A.; Avramis, E.; Seja, E.; Kivork, C.; Siebert, J.; Kaplan-Lefko, P.; et al. PD-1 Blockade Expands Intratumoral Memory T Cells. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2016, 4, 194–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. BAVENCIO—Avelumab Injection, Solution, Concentrate. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/1e71a605-bd71-478c-8e10-aa6895676e32/1e71a605-bd71-478c-8e10-aa6895676e32.xml (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. IMFINZI—Durvalumab Injection, Solution. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/46c42e77-0dc8-4f43-a22c-1e7a70b232f6/46c42e77-0dc8-4f43-a22c-1e7a70b232f6.xml#ID_8002BACE-4843-4450-AEDE-4A94C0DCCB0E (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. TECENTRIQ—Atezolizumab Injection, Solution. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/f4fe4626-4d6c-4c50-9d52-51aae17f27d6/f4fe4626-4d6c-4c50-9d52-51aae17f27d6.xml (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. OPDIVO—Nivolumab Injection. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/93e7652b-4aac-498e-8fd0-5746918d0c67/93e7652b-4aac-498e-8fd0-5746918d0c67.xml (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. KEYTRUDA—Pembrolizumab Injection, Powder, Lyophilized, for Solution. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/2076cef2-520c-466d-a2cd-ecf4ec221126/2076cef2-520c-466d-a2cd-ecf4ec221126.xml (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. JEMPERLI—Dostarlimab Injection. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/cffa5af8-7472-4775-a6f7-5bdf1e4fecaa/cffa5af8-7472-4775-a6f7-5bdf1e4fecaa.xml (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. ZYNYZ—Retifanlimab-dlwr Injection. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/584c49ff-644e-49e0-a1bd-3573d00656c2/584c49ff-644e-49e0-a1bd-3573d00656c2.xml (accessed on 29 May 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. LOQTORZI—Toripalimab-tpzi Injection. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/eb8f028a-5e93-498e-bfdd-85530ddfe3b0/eb8f028a-5e93-498e-bfdd-85530ddfe3b0.xml (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. LIBTAYO—Cemiplimab-rwlc Injection. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/36e9f5d9-378e-4c8c-82bb-0908cb5cd65f/36e9f5d9-378e-4c8c-82bb-0908cb5cd65f.xml (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- FDA. Highlights of Prescribing Information. TEVIMBRA—Tislelizumab-jsgr Injection, Solution, Concentrate. Available online: https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/spl/data/647bb29e-a6de-4d8d-9261-bec01673ca77/647bb29e-a6de-4d8d-9261-bec01673ca77.xml (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Chen, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, X.; Tao, H.; Zhang, S.; Ma, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, J.; Qian, Y.; Cui, P.; et al. Response Efficacy of PD-1 and PD-L1 Inhibitors in Clinical Trials: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 562315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariam, A.; Kamath, S.; Schveder, K.; McLeod, H.L.; Rotroff, D.M. Biomarkers for Response to Anti-PD-1/Anti-PD-L1 Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Large Meta-Analysis. Oncology 2023, 37, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casagrande, S.; Sopetto, G.B.; Bertalot, G.; Bortolotti, R.; Racanelli, V.; Caffo, O.; Giometto, B.; Berti, A.; Veccia, A. Immune-Related Adverse Events Due to Cancer Immunotherapy: Immune Mechanisms and Clinical Manifestations. Cancers 2024, 16, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Zheng, S.; Han, B.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Lu, Y.; Sun, Q.; Hu, X.; Wu, J. The expansion of MDSCs induced by exosomal PD-L1 promotes the progression of gastric cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.C.; Pierpont, T.M.; Argueta-Zamora, D.; Wilson, K.; August, A.; Cerione, R.A. PTEN loss in glioma cell lines leads to increased extracellular vesicle biogenesis and PD-L1 cargo in a PI3K-dependent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2025, 301, 108143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.M.; Yu, Z.L.; Xia, H.F.; Zhang, L.Z.; Fu, Q.Y.; Wang, Y.; Gong, H.Y.; Chen, G. EGFR Mutation and TKI Treatment Promote Secretion of Small Extracellular Vesicle PD-L1 and Contribute to Immunosuppression in NSCLC. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, L.; Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, C.; Bu, J.; Sun, T.; Wei, J. Liquid biopsy in cancer current: Status, challenges and future prospects. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alix-Panabières, C.; Pantel, K. Advances in liquid biopsy: From exploration to practical application. Cancer Cell 2025, 43, 161–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.W.; Shi, D.; Wan, X.C.; Hu, J.; Su, Y.F.; Zeng, Y.P.; Hu, Z.J.; Yu, B.H.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wei, P.; et al. Universal extracellular vesicles and PD-L1+ extracellular vesicles detected by single molecule array technology as circulating biomarkers for diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Oncoimmunology 2021, 10, 1995166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Du, Z.; Huang, M.; Wang, D.; Fong, W.P.; Liang, J.; Fan, L.; Wang, Y.; Yang, H.; Chen, Z.; et al. Circulating PD-L1 is associated with T cell infiltration and predicts prognosis in patients with CRLM following hepatic resection. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Che, X.; Qu, J.; Hou, K.; Wen, T.; Li, Z.; Li, C.; Wang, S.; Xu, L.; Liu, Y.; et al. Exosomal PD-L1 Retains Immunosuppressive Activity and is Associated with Gastric Cancer Prognosis. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 26, 3745–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslami, S.Z.; Cortés-Hernández, L.E.; Sinoquet, L.; Gauthier, L.; Vautrot, V.; Cayrefourcq, L.; Avoscan, L.; Jacot, W.; Pouderoux, S.; Viala, M.; et al. Circulating tumour cells and PD-L1-positive small extracellular vesicles: The liquid biopsy combination for prognostic information in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 130, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Jin, W.; Xu, K.; Zheng, X.; Zhou, Y.; Luo, M.; Yan, C.; Jin, E. Blood exosome PD-L1 is associated with PD-L1 expression measured by immunohistochemistry, and lymph node metastasis in lung cancer. Tissue Cell 2022, 79, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sholl, L.M.; Awad, M.; Basu Roy, U.; Beasley, M.B.; Cartun, R.W.; Hwang, D.M.; Kalemkerian, G.; Lopez-Rios, F.; Mino-Kenudson, M.; Paintal, A.; et al. Programmed Death Ligand-1 and Tumor Mutation Burden Testing of Patients With Lung Cancer for Selection of Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapies: Guideline From the College of American Pathologists, Association for Molecular Pathology, International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer, Pulmonary Pathology Society, and LUNGevity Foundation. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2024, 148, 757–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, F.; Gu, Y.; Kang, B.; Heskia, F.; Pachot, A.; Bonneville, M.; Wei, P.; Liang, J. PD-L1 detection on circulating tumor-derived extracellular vesicles (T-EVs) from patients with lung cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2021, 10, 2441–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöne, N.; Kemper, M.; Menck, K.; Evers, G.; Krekeler, C.; Schulze, A.B.; Lenz, G.; Wardelmann, E.; Binder, C.; Bleckmann, A. PD-L1 on large extracellular vesicles is a predictive biomarker for therapy response in tissue PD-L1-low and -negative patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Miguel-Perez, D.; Russo, A.; Arrieta, O.; Ak, M.; Barron, F.; Gunasekaran, M.; Mamindla, P.; Lara-Mejia, L.; Peterson, C.B.; Er, M.E.; et al. Extracellular vesicle PD-L1 dynamics predict durable response to immune-checkpoint inhibitors and survival in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Peng, X.; Yang, S.; Li, X.; Huang, M.; Wei, S.; Zhang, S.; He, G.; Zheng, H.; Fan, Q.; et al. Extracellular vesicle PD-L1 in reshaping tumor immune microenvironment: Biological function and potential therapy strategies. Cell Commun. Signal 2022, 20, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ricklefs, F.L.; Alayo, Q.; Krenzlin, H.; Mahmoud, A.B.; Speranza, M.C.; Nakashima, H.; Hayes, J.L.; Lee, K.; Balaj, L.; Passaro, C.; et al. Immune evasion mediated by PD-L1 on glioblastoma-derived extracellular vesicles. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar2766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Huang, X.; Shi, X.; Jiang, M.; Liu, H.; Zhao, L. LAMTOR1 decreased exosomal PD-L1 to enhance immunotherapy efficacy in non-small cell lung cancer. Mol. Cancer 2024, 23, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, L.; Wu, B.; Li, T.; Beer, L.A.; Sharma, G.; Li, M.; Lee, C.N.; Liu, S.; Yang, C.; Huang, L.; et al. HRS phosphorylation drives immunosuppressive exosome secretion and restricts CD8. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 4078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Raposo, G.; Théry, C. Biogenesis, secretion, and intercellular interactions of exosomes and other extracellular vesicles. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2014, 30, 255–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Sun, X.; Yang, J.; Yu, P.; Hu, G.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, S.; et al. MFGE8 induces anti-PD-1 therapy resistance by promoting extracellular vesicle sorting of PD-L1. Cell Rep. Med. 2025, 6, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shin, J.M.; Lee, C.H.; Son, S.; Kim, C.H.; Lee, J.A.; Ko, H.; Shin, S.; Song, S.H.; Park, S.S.; Bae, J.H.; et al. Sulfisoxazole Elicits Robust Antitumour Immune Response Along with Immune Checkpoint Therapy by Inhibiting Exosomal PD-L1. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, e2103245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Im, E.J.; Lee, C.H.; Moon, P.G.; Rangaswamy, G.G.; Lee, B.; Lee, J.M.; Lee, J.C.; Jee, J.G.; Bae, J.S.; Kwon, T.K.; et al. Sulfisoxazole inhibits the secretion of small extracellular vesicles by targeting the endothelin receptor A. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.G.; Gao, Y.; Gao, Y.S.; Dai, X.J.; Chen, P. Identification of the exosomal PD-L1 inhibitor to promote the PD-1 targeting therapy of gastric cancer. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2024, 268, 116182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Li, T.; Wang, Q.; Yan, K.; Ma, S.; Lin, Y.; Zeng, G.; Liu, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, D. Dual-Synergistic Nanomodulator Alleviates Exosomal PD-L1 Expression Enabling Exhausted Cytotoxic T Lymphocytes Rejuvenation for Potentiated iRFA-Treated Hepatocellular Carcinoma Immunotherapy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 32818–32833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yao, H.; Wang, H.; Fang, J.Y.; Xu, J. Repurposing screen identifies Amlodipine as an inducer of PD-L1 degradation and antitumor immunity. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1128–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Lee, C.H.; Baek, M.C. Dissecting exosome inhibitors: Therapeutic insights into small-molecule chemicals against cancer. Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 1833–1843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Wang, H.; Zhao, W.; Ge, X.; Huang, W.; Lin, F.; Tang, W.; Li, A.; Liu, S.; Li, R.K.; et al. Targeting type Iγ phosphatidylinositol phosphate kinase overcomes oxaliplatin resistance in colorectal cancer. Theranostics 2022, 12, 4386–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.K.; Zheng, S.; Long, Y.; Wang, K.M.; Xiao, B.L.; Li, J.B.; Zhang, W.; Song, H.; Chen, G. High-throughput screening identifies ibuprofen as an sEV PD-L1 inhibitor for synergistic cancer immunotherapy. Mol. Ther. 2024, 32, 3580–3596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Liao, M.; Yu, S.; Yuan, B.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, L.; Tang, Y. Exosomes-delivered PD-L1 siRNA and CTLA-4 siRNA protect against growth and tumor immune escape in colorectal cancer. Genomics 2023, 115, 110646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.M.; Bahal, R.; Rasmussen, T.P.; Manautou, J.E.; Zhong, X.B. The growth of siRNA-based therapeutics: Updated clinical studies. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 189, 114432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yang, R.; Liu, C.; Hsu, J.M.; Jiang, Z.; Sun, L.; Wei, Y.; Li, C.W.; Yu, D.; et al. Activated T cell-derived exosomal PD-1 attenuates PD-L1-induced immune dysfunction in triple-negative breast cancer. Oncogene 2021, 40, 4992–5001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradowska-Gorycka, A.; Wajda, A.; Romanowska-Prochnicka, K.; Walczuk, E.; Kuca-Warnawin, E.; Kmiolek, T.; Stypinska, B.; Rzeszotarska, E.; Majewski, D.; Jagodzinski, P.P.; et al. Th17/Treg-Related Transcriptional Factor Expression and Cytokine Profile in Patients With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 572858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Yu, L.; Zhuang, L.G.; Pei, X.Y.; Wang, Q.; Jin, G.X. The changes in peripheral blood Th17 and Treg ratios in Hashimoto’s thyroiditis are accompanied by differential PD-1/PD-L1 expression. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 959477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostergaard, M.; van Vollenhoven, R.F.; Rudin, A.; Hetland, M.L.; Heiberg, M.S.; Nordstrom, D.C.; Nurmohamed, M.T.; Gudbjornsson, B.; Ornbjerg, L.M.; Boyesen, P.; et al. Certolizumab pegol, abatacept, tocilizumab or active conventional treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis: 48-week clinical and radiographic results of the investigator-initiated randomised controlled NORD-STAR trial. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2023, 82, 1286–1295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, A.P.; Jasenecova, M.; Vasconcelos, J.C.; Filer, A.; Raza, K.; Qureshi, S.; D’Agostino, M.A.; McInnes, I.B.; Isaacs, J.D.; Pratt, A.G.; et al. Abatacept in individuals at high risk of rheumatoid arthritis (APIPPRA): A randomised, double-blind, multicentre, parallel, placebo-controlled, phase 2b clinical trial. Lancet 2024, 403, 838–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnerbauer, M.; Beyer, T.; Nirschl, L.; Farrenkopf, D.; Losslein, L.; Vandrey, O.; Peter, A.; Tsaktanis, T.; Kebir, H.; Laplaud, D.; et al. PD-L1 positive astrocytes attenuate inflammatory functions of PD-1 positive microglia in models of autoimmune neuroinflammation. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 5555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, D.; Okazaki, I.M.; Maeda, T.K.; Maruhashi, T.; Shimizu, K.; Arakaki, R.; Takemoto, T.; Ishimaru, N.; Okazaki, T. PD-1 agonism by anti-CD80 inhibits T cell activation and alleviates autoimmunity. Nat. Immunol. 2022, 23, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curnock, A.P.; Bossi, G.; Kumaran, J.; Bawden, L.J.; Figueiredo, R.; Tawar, R.; Wiseman, K.; Henderson, E.; Hoong, S.J.; Gonzalez, V.; et al. Cell-targeted PD-1 agonists that mimic PD-L1 are potent T cell inhibitors. JCI Insight 2021, 6, e152468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Chen, Q.; Wang, F. Mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of ulcerative colitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of experimental and clinical studies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Sun, Y.; Xu, W.; Chang, F.; Wang, Y.; Ding, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Involved Strategies for Rheumatoid Arthritis Therapy. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, e2305116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, B.X.; Fang, S.B.; Xie, Y.C.; Lou, D.X.; Wu, Z.C.; Li, C.G.; Liu, X.Q.; Zhou, Z.R.; Huang, L.X.; Tian, T.; et al. Small extracellular vesicles derived from human mesenchymal stem cells prevent Th17-dominant neutrophilic airway inflammation via immunoregulation on Th17 cells. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 133, 112126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, F.; Fei, Z.; Dai, H.; Xu, J.; Fan, Q.; Shen, S.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, Q.; Chu, J.; Peng, F.; et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles with High PD-L1 Expression for Autoimmune Diseases Treatment. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2106265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, X.; Kugeratski, F.G.; Dowlatshahi, D.P.; Sugimoto, H.; Arian, K.A.; Fan, Y.; Huang, L.; Wills, D.; Lilla, S.; Hodge, K.; et al. Engineered Immunomodulatory Extracellular Vesicles from Epithelial Cells with the Capacity for Stimulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity in Cancer and Autoimmunity. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 5193–5216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yan, J.; Chen, Q.; Cheng, H.; Huang, P.; Gu, Z. Engineered PD-L1-Expressing Platelets Reverse New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, e1907692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Li, L.; Jing, Z.; Ma, Y.; Lan, T.; Li, Y.; Lin, Z.; Fang, W.; Zhang, J.; et al. Bioengineered Artificial Extracellular Vesicles Presenting PD-L1 and Gal-9 Ameliorate New-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes 2024, 73, 1325–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Qi, C.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X.; Qiu, L.; Wang, H.; Xu, L.; Wu, Z.; Liu, J.; et al. Engineered Cytokine-Primed Extracellular Vesicles with High PD-L1 Expression Ameliorate Type 1 Diabetes. Small 2023, 19, e2301019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Drug Name | Mechanism of Action | Cancer Types | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Avelumab | anti-PD-L1 | Merkel cell carcinoma, Urothelial carcinoma, Renal cell carcinoma | [40] |
| Durvalumab | anti-PD-L1 | Lung cancer (NSCLC and SCLC), Biliary tract cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Endometrial cancer, bladder cancer | [41] |
| Atezolizumab | anti-PD-L1 | Lung cancer (NSCLC and SCLC), Hepatocellular carcinoma, Melanoma, Alveolar soft part sarcoma | [42] |
| Nivolumab | anti-PD-1 | Melanoma, NSCLC, Malignant pleural mesothelioma, Renal cell carcinoma, Classical Hodgkin lymphoma, HNSCC, Urothelial carcinoma, Colorectal cancer, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Esophageal carcinoma, Gastric cancer | [43] |
| Pembrolizumab | anti-PD-1 | Melanoma, NSCLC, Malignant pleural mesothelioma, HNSCC, Classical Hodgkin lymphoma, Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma, Urothelial Cancer, Microsatellite Instability-High or Mismatch Repair Deficient Cancer, Microsatellite Instability-High or Mismatch Repair Deficient Colorectal Cancer, Gastric Cancer, Esophageal Cancer, Cervical Cancer, Hepatocellular Carcinoma, Biliary Tract Cancer, MCC, RCC, Endometrial carcinoma, Tumor Mutational Burden-High (TMB-H) Cancer, Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma, Triple-Negative Breast Cancer | [44] |
| Dostarlimab | anti-PD-1 | Endometrial Cancer, Mismatch Repair Deficient Recurrent or Advanced Solid Tumors | [45] |
| Retifanlimab | anti-PD-1 | Merkel cell carcinoma | [46] |
| Toripalimab-tpzi | anti-PD-1 | Nasopharyngeal carcinoma | [47] |
| Cemiplimab | anti-PD-1 | Cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma, Basal cel cancer, NSCLC | [48] |
| Tislelizumab | anti-PD-1 | Esophageal cancer, Gastric cancer | [49] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiełbowski, K.; Plewa, P.; Szulc, J.; Ćmil, M.; Bakinowska, E.; Pawlik, A. Extracellular Vesicles and PD-L1—A Review of Complex Immunoregulatory Properties and Clinical Importance. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061356
Kiełbowski K, Plewa P, Szulc J, Ćmil M, Bakinowska E, Pawlik A. Extracellular Vesicles and PD-L1—A Review of Complex Immunoregulatory Properties and Clinical Importance. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(6):1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061356
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiełbowski, Kajetan, Paulina Plewa, Jacek Szulc, Maciej Ćmil, Estera Bakinowska, and Andrzej Pawlik. 2025. "Extracellular Vesicles and PD-L1—A Review of Complex Immunoregulatory Properties and Clinical Importance" Biomedicines 13, no. 6: 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061356
APA StyleKiełbowski, K., Plewa, P., Szulc, J., Ćmil, M., Bakinowska, E., & Pawlik, A. (2025). Extracellular Vesicles and PD-L1—A Review of Complex Immunoregulatory Properties and Clinical Importance. Biomedicines, 13(6), 1356. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13061356






