Neutrophil- and Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Microvesicles Are Promising Putative Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Population, Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Cohort
2.2. Blood Collections
2.3. Immunophenotypic Analysis of MVs by Flow Cytometry
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Development and Training of BC Classifier Algorithms
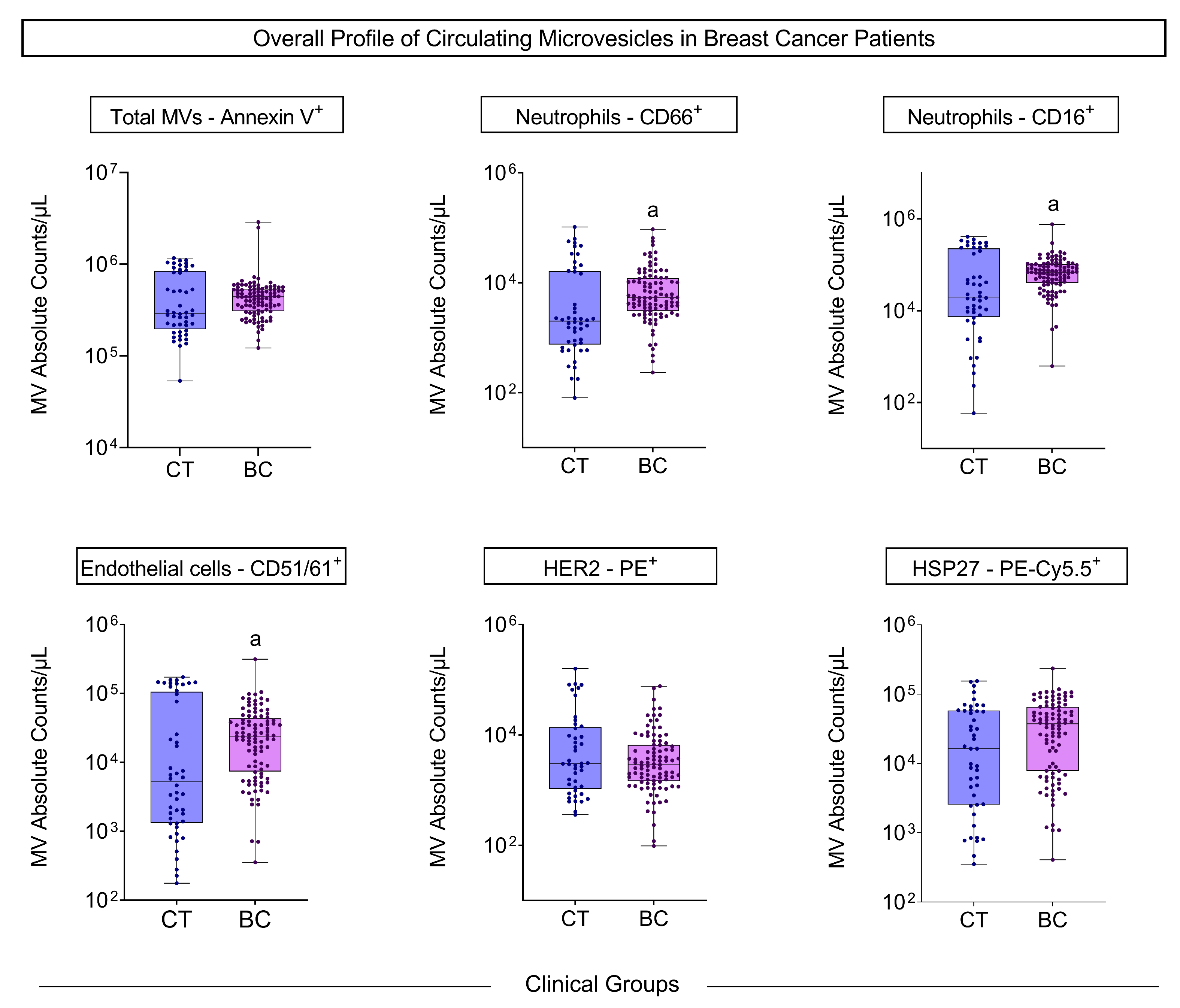
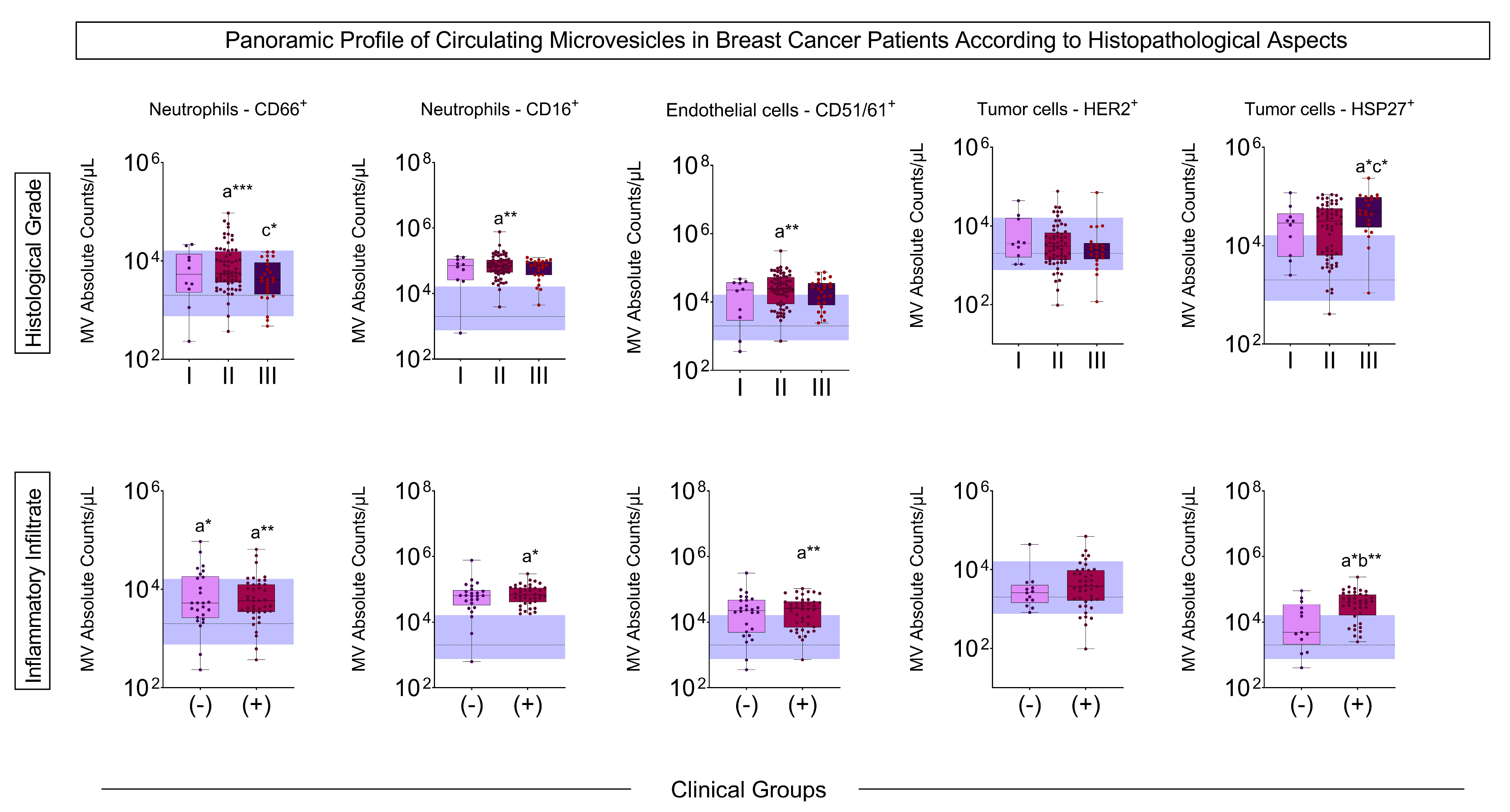
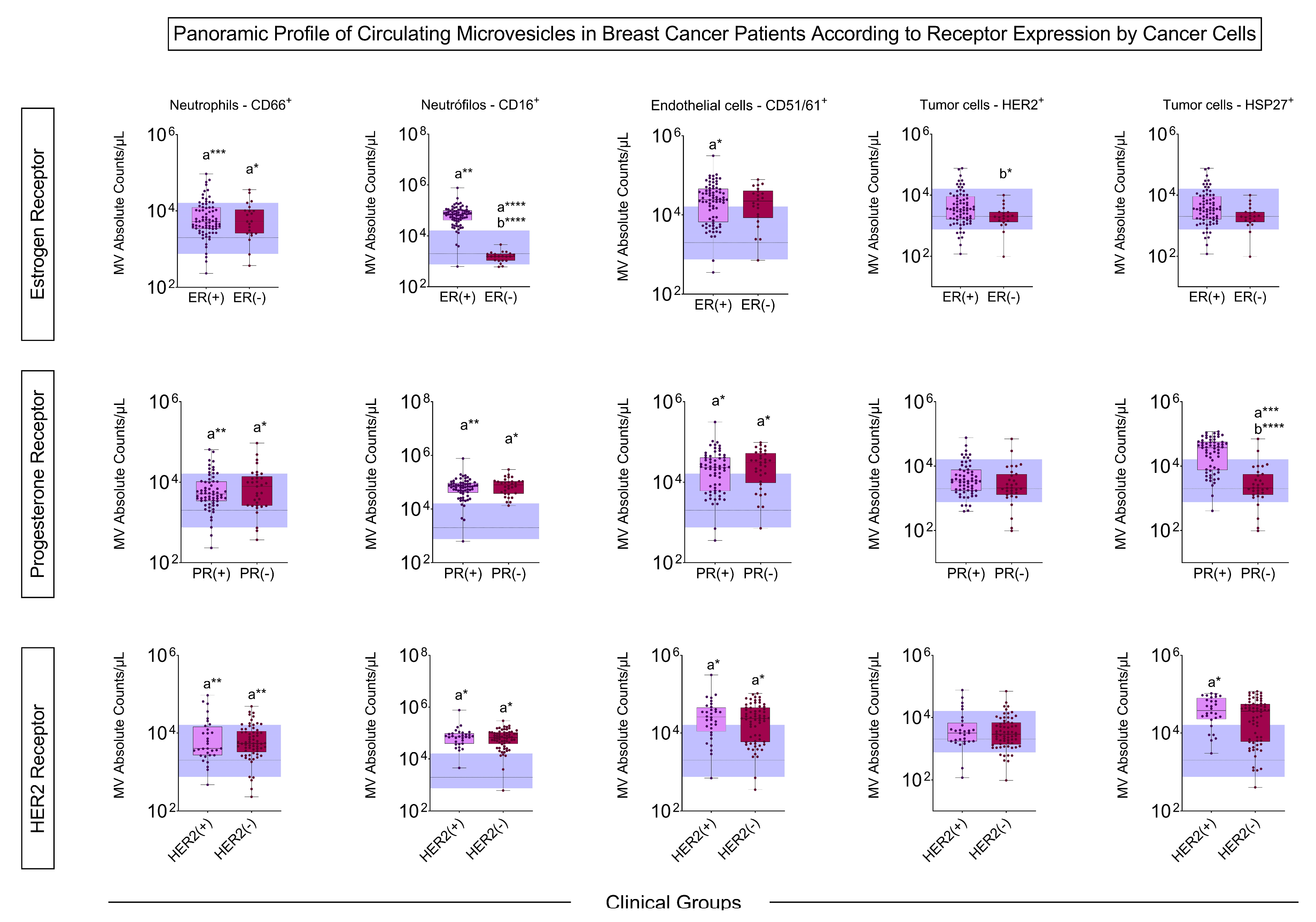
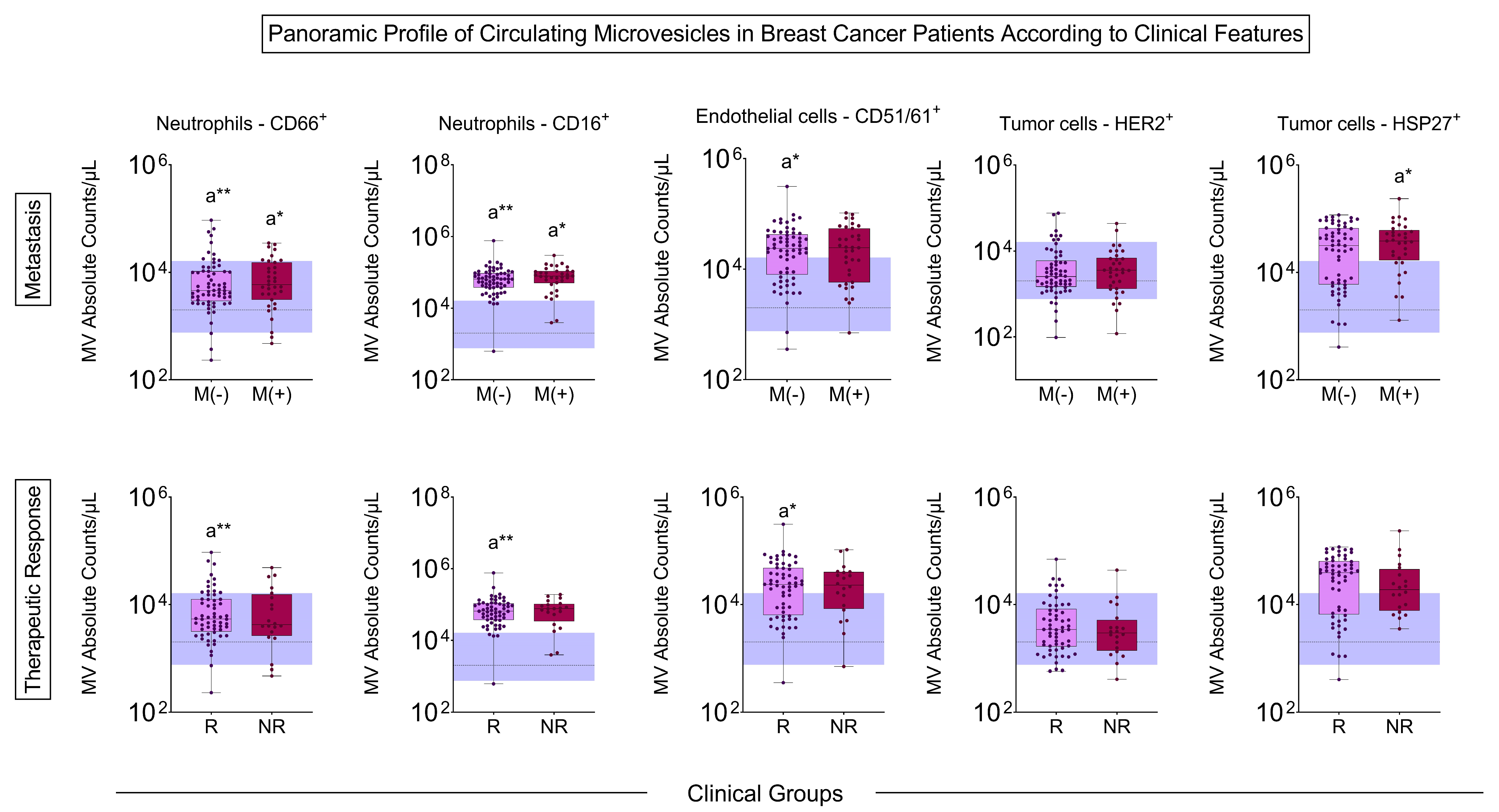
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Cohort
3.2. Microvesicle Profile Before Treatment
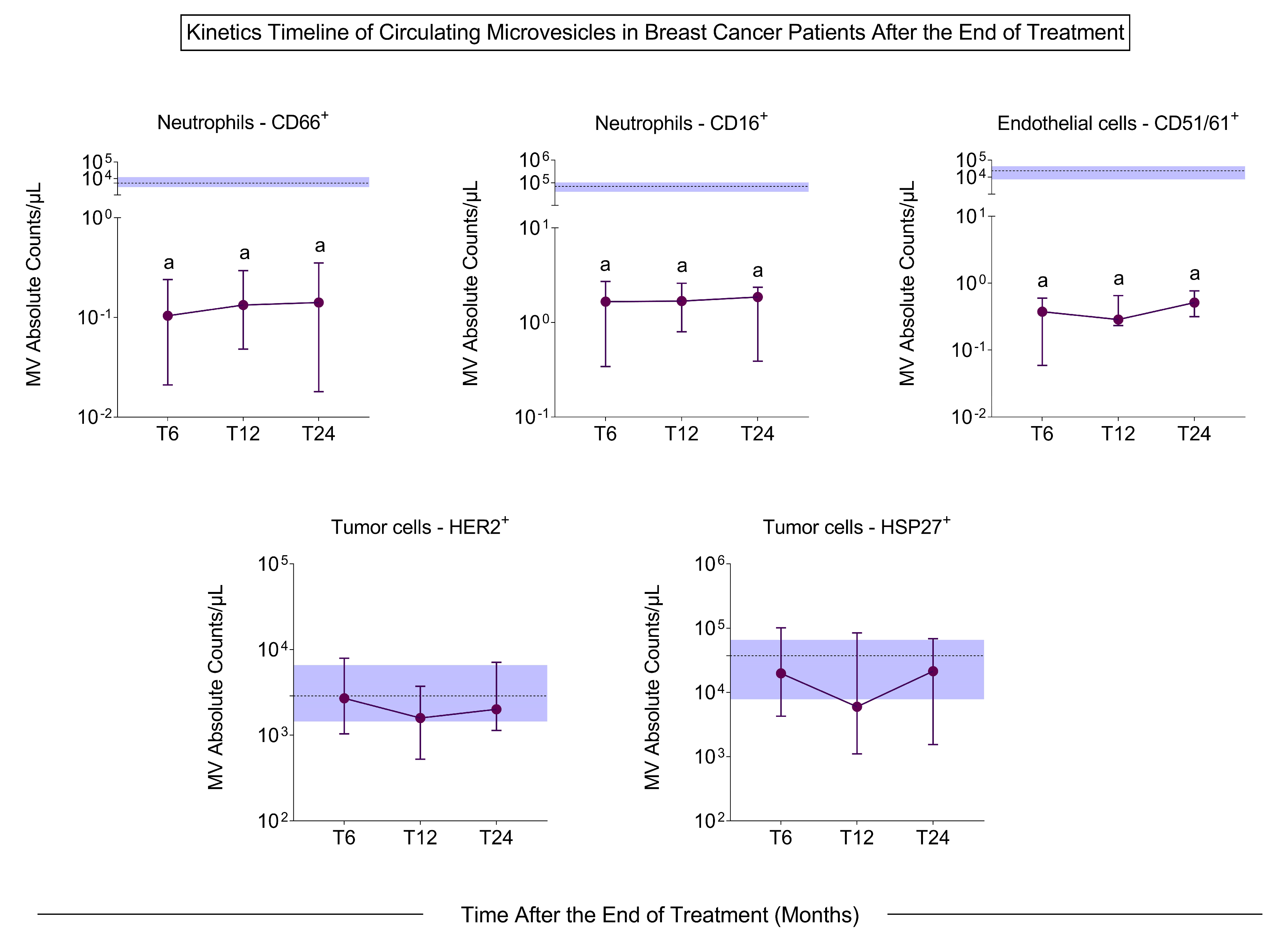
3.3. Microvesicle Profile After Treatment
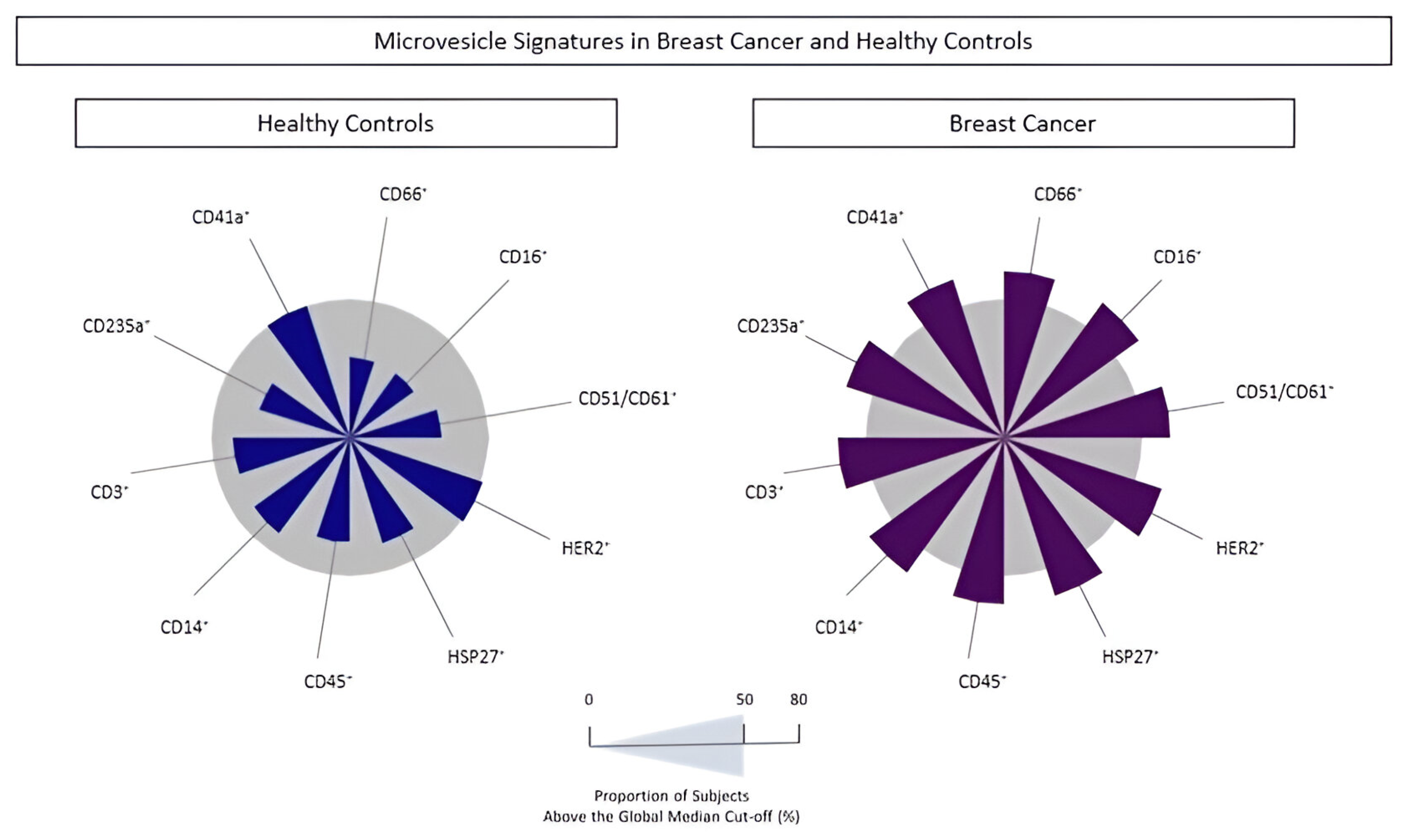
3.4. Signature Profile of Circulating MVs in BC Patients
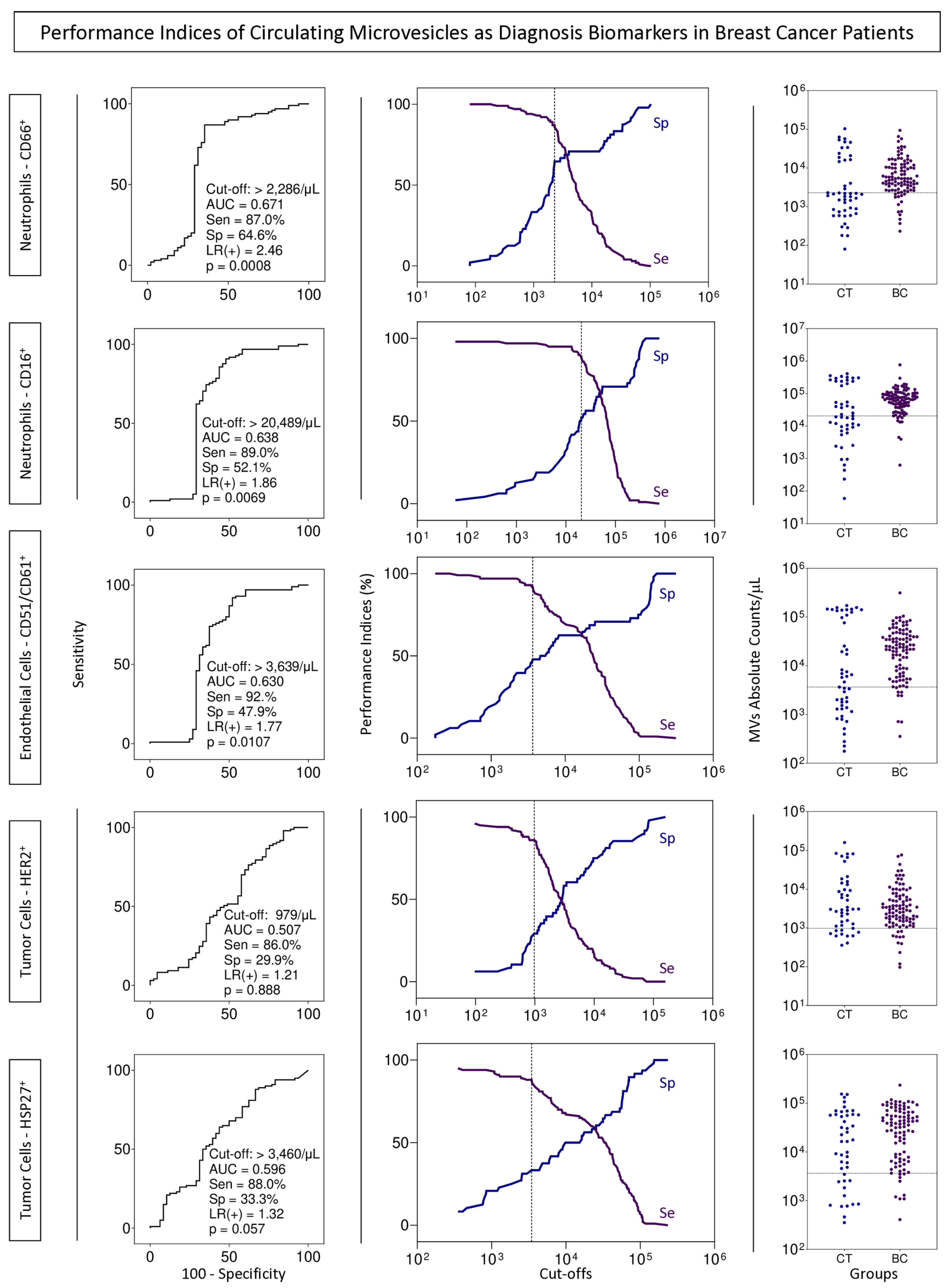
3.5. BC Biomarkers Performance Index to Identify Subgroups of Patients with Cancer
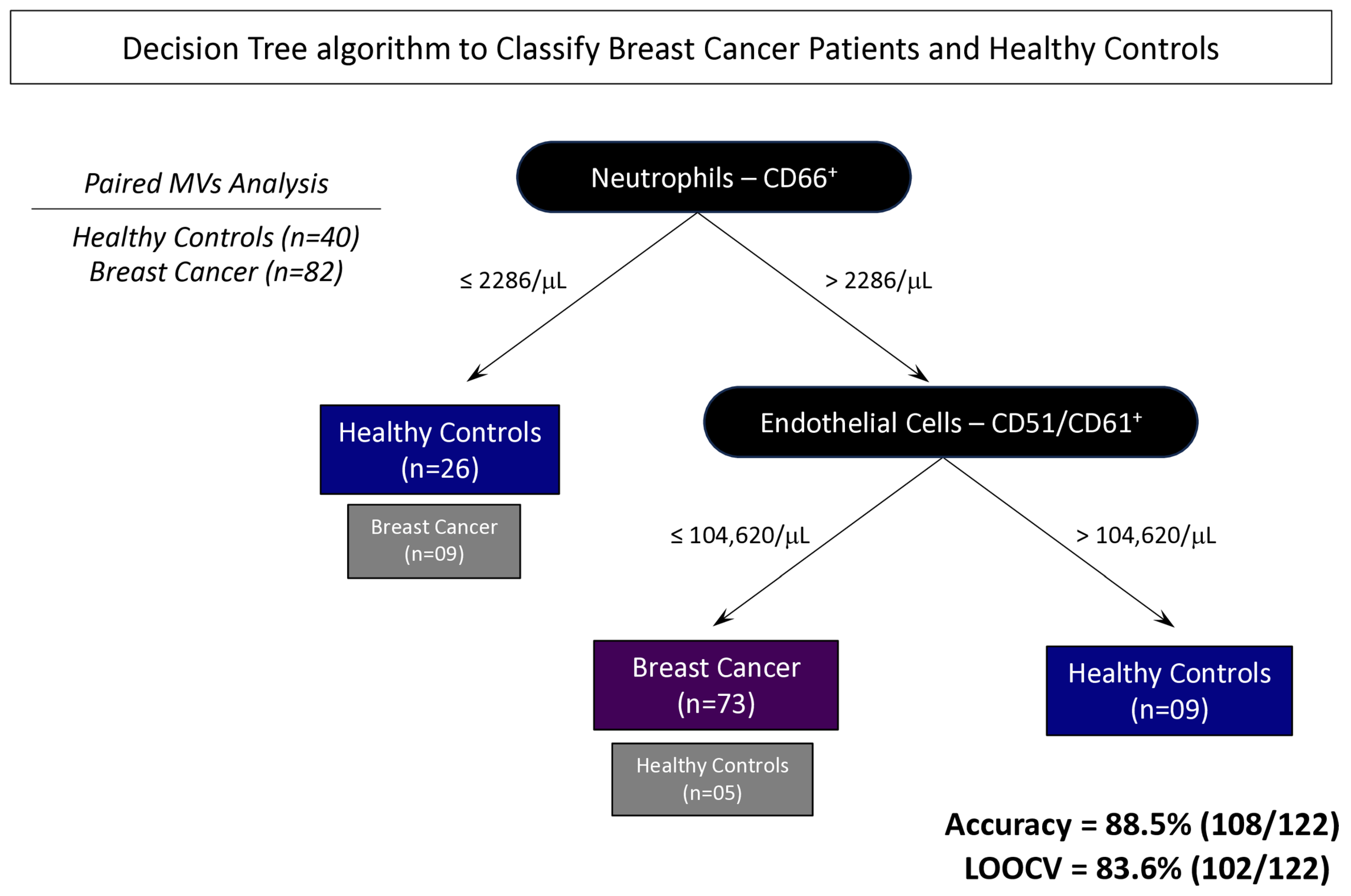
3.6. Proposal of Decision Tree Algorithm to Classify Patients with BC
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estatísticas de Cancer|INCA—Instituto Nacional de Câncer. Available online: https://www.inca.gov.br/numeros-de-cancer (accessed on 14 September 2024).
- Harbeck, N.; Penault-Llorca, F.; Cortes, J.; Gnant, M.; Houssami, N.; Poortmans, P.; Ruddy, K.; Tsang, J.; Cardoso, F. Breast cancer. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2019, 5, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maughan, K.L.; Lutterbie, M.A.; Ham, P.S. Treatment of breast cancer. Am. Fam. Physician 2010, 81, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nikanjam, M.; Kato, S.; Kurzrock, R. Liquid biopsy: Current technology and clinical applications. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2022, 15, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Yu, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Fu, M.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Ji, R.; Gu, J.; Zhang, X. The new advance of exosome-based liquid biopsy for cancer diagnosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 22, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulet, G.; Massias, J.; Taly, V. Liquid Biopsy: General Concepts. Acta Cytol. 2019, 63, 449–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Silva, S.; Peinado, H. Mechanisms of lymph node metastasis: An extracellular vesicle perspective. Eur. J. Cell Biol. 2024, 103, 151447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonçalves, M.O.; Di Iorio, J.F.; Marin, G.V.; Meneghetti, P.; Negreiros, N.G.S.; Torrecilhas, A.C. Extracellular vesicles. Curr. Top. Membr. 2024, 94, 1–31. [Google Scholar]
- Koumangoye, R.B.; Sakwe, A.M.; Goodwin, J.S.; Patel, T.; Ochieng, J. Detachment of breast tumor cells induces rapid secretion of exosomes which subsequently mediate cellular adhesion and spreading. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e24234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.; Jaiswal, R.; Dalla, P.; Luk, F.; Bebawy, M. Microparticles in cancer: A review of recent developments and the potential for clinical application. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horne III, M.K.; Cullinane, A.M.; Merryman, P.K.; Hoddeson, E.K. The effect of red blood cells on thrombin generation. Br. J. Haematol. 2006, 133, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Dean, D.C.; Hornicek, F.J.; Shi, H.; Duan, Z. Exosomes promote pre-metastatic niche formation in ovarian cancer. Mol. Cancer 2019, 18, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harada, Y.; Suzuki, T.; Fukushige, T.; Kizuka, Y.; Yagi, H.; Yamamoto, M.; Kondo, K.; Inoue, H.; Kato, K.; Taniguchi, N.; et al. Generation of the heterogeneity of extracellular vesicles by membrane organization and sorting machineries. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, E.C.P.; Agudelo, J.S.H.; da Silva, R.A.F.; Viração, T.A.; da Costa Fernandes, C.J. The role of extracellular vesicles in cancer. Curr. Top. Membr. 2024, 94, 247–285. [Google Scholar]
- Kok, V.C.; Yu, C.-C. Cancer-Derived Exosomes: Their Role in Cancer Biology and Biomarker Development. Int. J. Nanomed. 2020, 15, 8019–8036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Villasana, V.; Rashed, M.H.; Gonzalez-Cantú, Y.; Bayraktar, R.; Menchaca-Arredondo, J.L.; Vazquez-Guillen, J.M.; Rodriguez-Padilla, C.; Lopez-Berestein, G.; Resendez-Perez, D. Presence of Circulating miR-145, miR-155, and miR-382 in Exosomes Isolated from Serum of Breast Cancer Patients and Healthy Donors. Dis. Markers 2019, 2019, 6852917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haghbin, M.; Tayer, A.H.; Kamravan, M.; Jahromi, A.S. Platelet-Derived Procoagulant Microparticles as Blood-based Biomarker of Breast Cancer. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2021, 22, 1573–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bern, M.M. Extracellular vesicles: How they interact with endothelium, potentially contributing to metastatic cancer cell implants. Clin. Transl. Med. 2017, 6, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonald, E.S.; Clark, A.S.; Tchou, J.; Zhang, P.; Freedman, G.M. Clinical Diagnosis and Management of Breast Cancer. J. Nucl. Med. 2016, 57, 9S–16S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, C.-W. Extracellular Vesicles of Neutrophils. Immune Netw. 2018, 18, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarreal-García, V.; Estupiñan-Jiménez, J.R.; Vivas-Mejía, P.E.; Gonzalez-Villasana, V.; Vázquez-Guillén, J.M.; Reséndez-Pérez, D. A vicious circle in breast cancer: The interplay between inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and microRNAs. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 980694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubenich, D.S.; Omizzollo, N.; Szczepański, M.J.; Reichert, T.E.; Whiteside, T.L.; Ludwig, N.; Braganhol, E. Small extracellular vesicle-mediated bidirectional crosstalk between neutrophils and tumor cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2021, 61, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Ji, C.; Zhang, H.; Shi, H.; Mao, F.; Qian, H.; Xu, W.; Wang, D.; Pan, J.; Fang, X.; et al. Engineered neutrophil-derived exosome-like vesicles for targeted cancer therapy. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabj8207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshamsan, B.; Elshenawy, M.A.; Aseafan, M.; Fahmy, N.; Badran, A.; Elhassan, T.; Alsayed, A.; Suleman, K.; Al-Tweigeri, T. Prognostic significance of the neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio in locally advanced breast cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Distel, L.; Erber, R.; Büttner-Herold, M.; Rosahl, M.-C.; Ott, O.J.; Strnad, V.; Hack, C.C.; Hartmann, A.; Hecht, M.; et al. Tumor-Associated Neutrophils Are a Negative Prognostic Factor in Early Luminal Breast Cancers Lacking Immunosuppressive Macrophage Recruitment. Cancers 2024, 16, 3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zhang, X.; Jiang, L.; Li, Y.; Zheng, Q. Tumor endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicles contribute to tumor microenvironment remodeling. Cell Commun. Signal. 2022, 20, 97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezentsev, A.; Merks, R.M.; O’Riordan, E.; Chen, J.; Mendelev, N.; Goligorsky, M.S.; Brodsky, S.V. Endothelial microparticles affect angiogenesis in vitro: Role of oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1106–H1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mostefai, H.; Andriantsitohaina, R.; Martínez, M. Plasma membrane microparticles in angiogenesis: Role in ischemic diseases and in cancer. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lombardo, G.; Gili, M.; Grange, C.; Cavallari, C.; Dentelli, P.; Togliatto, G.; Taverna, D.; Camussi, G.; Brizzi, M.F. IL-3R-alpha blockade inhibits tumor endothelial cell-derived extracellular vesicle (EV)-mediated vessel formation by targeting the β-catenin pathway. Oncogene 2017, 37, 1175–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-C.; Tseng, C.-C.; Hsiao, C.-C.; Chang, H.-C.; Chang, L.-T.; Fang, W.-F.; Leu, S.; Wang, Y.-H.; Tsai, T.-H.; Yang, C.-T.; et al. Circulating endothelial-derived activated microparticle: A useful biomarker for predicting one-year mortality in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 173401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, L.G.; Ham, S.; Shin, H.; Chai, E.P.Z.; Lek, E.S.H.; Lobb, R.J.; Müller, A.F.; Mathivanan, S.; Yeo, B.; Choi, Y.; et al. Tumor microenvironmental cytokines bound to cancer exosomes determine uptake by cytokine receptor-expressing cells and biodistribution. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grzegrzółka, J.; Kurnol, K.; Piotrów, P.; Puła, B.; Kobierzycki, C.; Piotrowska, A.; Jabłońska, K.; Wojnar, A.; Ryś, J.; Dzięgiel, P.; et al. Hsp-27 expression in invasive ductal breast carcinoma. Folia Histochem. Cytobiol. 2012, 50, 527–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibert, B.; Eckel, B.; Gonin, V.; Goldschneider, D.; Fombonne, J.; Deux, B.; Mehlen, P.; Arrigo, A.-P.; Clézardin, P.; Diaz-Latoud, C. Targeting heat shock protein 27 (HspB1) interferes with bone metastasis and tumour formation in vivo. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Banerjee, S.; Lin, C.-F.L.; Skinner, K.A.; Schiffhauer, L.M.; Peacock, J.; Hicks, D.G.; Redmond, E.M.; Morrow, D.; Huston, A.; Shayne, M.; et al. Heat shock protein 27 differentiates tolerogenic macrophages that may support human breast cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2011, 71, 318–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liebhardt, S.; Ditsch, N.; Nieuwland, R.; Rank, A.; Jeschke, U.; Von Koch, F.; Friese, K.; Toth, B. CEA-, Her2/neu-, BCRP- and Hsp27-positive microparticles in breast cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2010, 30, 1707–1712. [Google Scholar]
- Sierko, E.; Sobierska, M.; Zabrocka, E.; Myśliwiec, M.; Kruszewska, J.; Lipska, A.; Radziwon, P.; Wojtukiewicz, M.Z. Endothelial Microparticles and Blood Coagulation Activation in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Undergoing Radiotherapy or Radiochemotherapy. Vivo 2019, 33, 627–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Cui, P.; Hou, B.; Zhuang, C.; Wei, G.; Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Hu, Y. Predicting disease progression in advanced non-small cell lung cancer with circulating neutrophil-derived and platelet-derived microparticles. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ginsburg, O.; Yip, C.; Brooks, A.; Cabanes, A.; Caleffi, M.; Yataco, J.A.D.; Gyawali, B.; McCormack, V.; de Anderson, M.M.; Mehrotra, R.; et al. Breast cancer early detection: A phased approach to implementation. Cancer 2020, 126, 2379–2393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L. Early Diagnosis of Breast Cancer. Sensors 2017, 17, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Control Group | Cancer Group | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| n (%) | p-Value | n (%) | p-Value | |
| Total | 48 (100) | - | 100 (100) | - |
| Age in years, median (IQR) | 58 (51–63) | - | 53 (43–60) | - |
| Age range | ||||
| 18–49 | 10 (21) | <0.0001 | 35 (35) | 0.003 |
| 50–73 | 38 (79) | 65 (65) | ||
| Family history of breast, ovarian, prostate, and bowel cancers | ||||
| Absent | 30 (63) | 0.0833 | 59 (59) | 0.071 |
| Present | 18 (37) | 41 (41) | ||
| Treatment | ||||
| Adjuvant | N/A | - | 60 (60) | 0.045 |
| Neoadjuvant | N/A | - | 40 (40) | |
| Clinical staging based on the TNM system | ||||
| I | N/A | - | 23 (23) | <0.001 |
| II | N/A | - | 42 (42) | |
| III | N/A | - | 26 (26) | |
| IV | N/A | - | 9 (9) | |
| Histological grade | ||||
| I | N/A | - | 10 (10) | <0.001 |
| II | N/A | - | 64 (64) | |
| III | N/A | - | 25 (25) | |
| N/A | N/A | - | 1 (1) | |
| Inflammatory infiltrate in the tumor stroma | ||||
| Absent | N/A | - | 15 (15) | <0.001 |
| Present | N/A | - | 41 (41) | |
| N/A | N/A | - | 44 (44) | |
| Estrogen receptor | ||||
| Negative | N/A | - | 22 (22) | <0.001 |
| Positive | N/A | - | 76 (76) | |
| N/A | N/A | - | 2 (2) | |
| Progesterone receptor | ||||
| Negative | N/A | - | 35 (35) | 0.006 |
| Positive | N/A | - | 62 (62) | |
| N/A | N/A | - | 3 (3) | |
| HER2 | ||||
| Negative | N/A | - | 66 (66) | 0.058 |
| Positive | N/A | - | 46 (46) | |
| N/A | N/A | - | 2 (2) | |
| Metastasis before chemotherapy treatment | ||||
| Absent | N/A | - | 65 (65) | 0.012 |
| Present | N/A | - | 35 (35) | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Moreira, T.B.; Silvestrini, M.M.A.; Gomes, A.L.d.F.M.; Rangel, K.K.; Costa, Á.P.; Gomes, M.S.; do Amaral, L.R.; Martins-Filho, O.A.; Salles, P.G.d.O.; Braga, L.C.; et al. Neutrophil- and Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Microvesicles Are Promising Putative Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030587
Moreira TB, Silvestrini MMA, Gomes ALdFM, Rangel KK, Costa ÁP, Gomes MS, do Amaral LR, Martins-Filho OA, Salles PGdO, Braga LC, et al. Neutrophil- and Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Microvesicles Are Promising Putative Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(3):587. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030587
Chicago/Turabian StyleMoreira, Thayse Batista, Marina Malheiros Araújo Silvestrini, Ana Luiza de Freitas Magalhães Gomes, Kerstin Kapp Rangel, Álvaro Percínio Costa, Matheus Souza Gomes, Laurence Rodrigues do Amaral, Olindo Assis Martins-Filho, Paulo Guilherme de Oliveira Salles, Letícia Conceição Braga, and et al. 2025. "Neutrophil- and Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Microvesicles Are Promising Putative Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis" Biomedicines 13, no. 3: 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030587
APA StyleMoreira, T. B., Silvestrini, M. M. A., Gomes, A. L. d. F. M., Rangel, K. K., Costa, Á. P., Gomes, M. S., do Amaral, L. R., Martins-Filho, O. A., Salles, P. G. d. O., Braga, L. C., & Teixeira-Carvalho, A. (2025). Neutrophil- and Endothelial Cell-Derived Extracellular Microvesicles Are Promising Putative Biomarkers for Breast Cancer Diagnosis. Biomedicines, 13(3), 587. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13030587







