A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Diabetic Kidney Disease in the FinnGen Cohort
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. DKD GWAS Data Source
2.3. eQTL Files Source
2.4. Cross-Tissue TWAS Analysis Using sCCA
2.5. Single-Tissue TWAS Analysis Using FUSION
2.6. Conditional and Joint Analysis
2.7. Gene-Based Association Analysis
2.8. Single-Tissue TWAS Analysis Using Batch SMR
2.9. Single-Tissue TWAS Analysis Using FOCUS
2.10. Two-Sample MR
2.11. Over-Representation Analysis
2.12. GeneMANIA Analysis
2.13. Druggability Assessment and Tissue-Specific Expression Analysis
2.14. Ethic Approval
3. Results
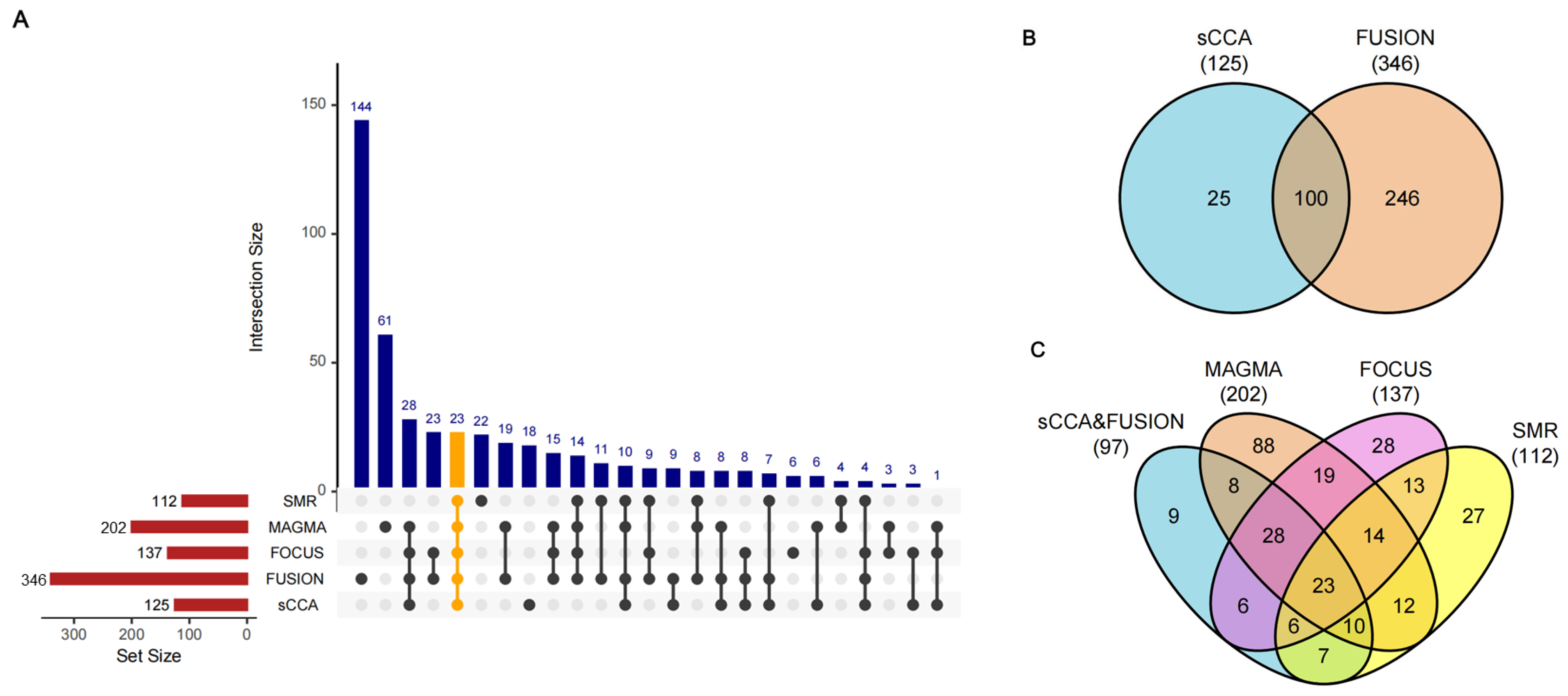
3.1. Discovery of DKD Causal Genes Through Integrative TWAS Analysis
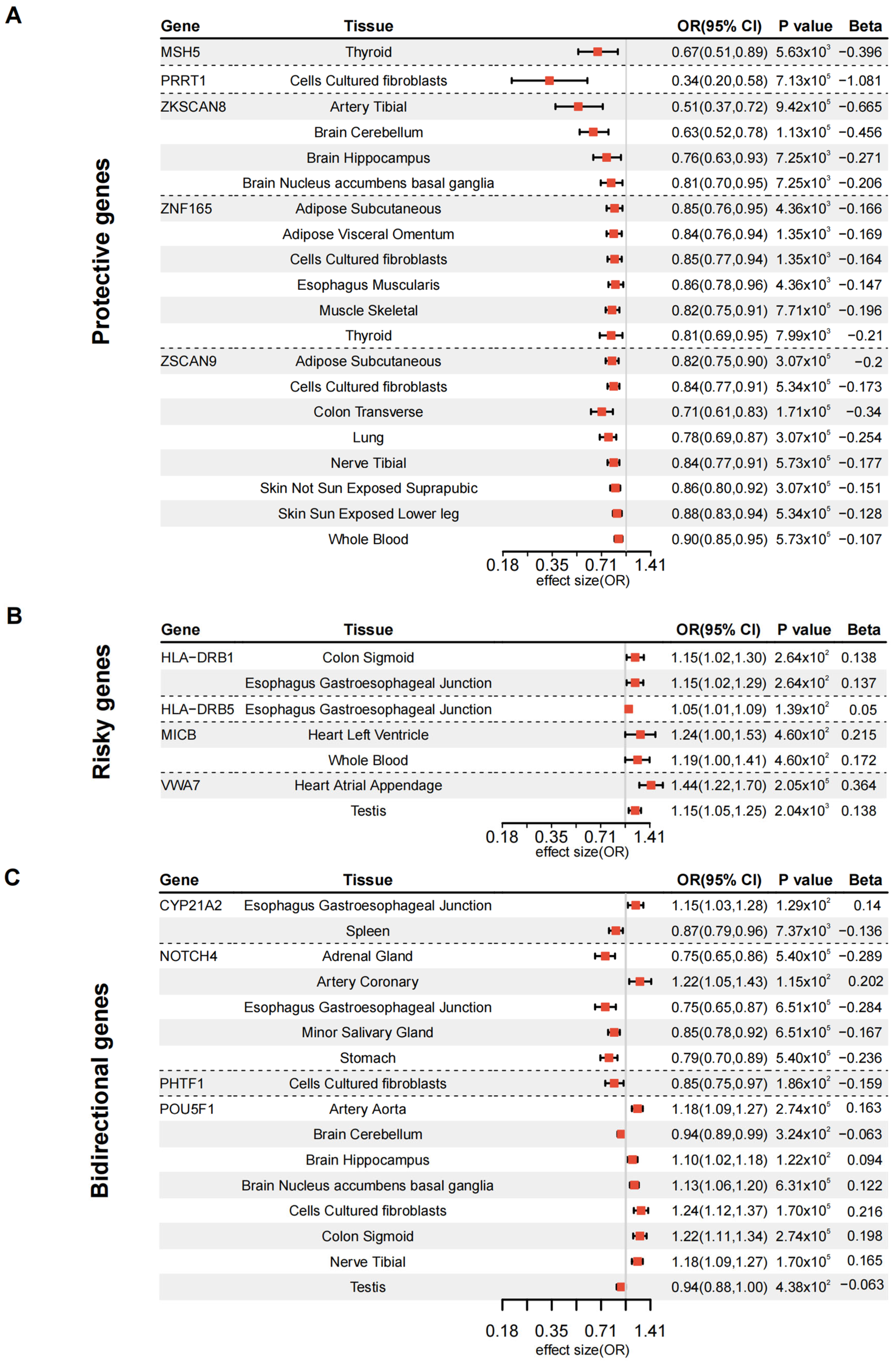
3.2. Validation of DKD Susceptibility Genes Through Tissue-Specific MR
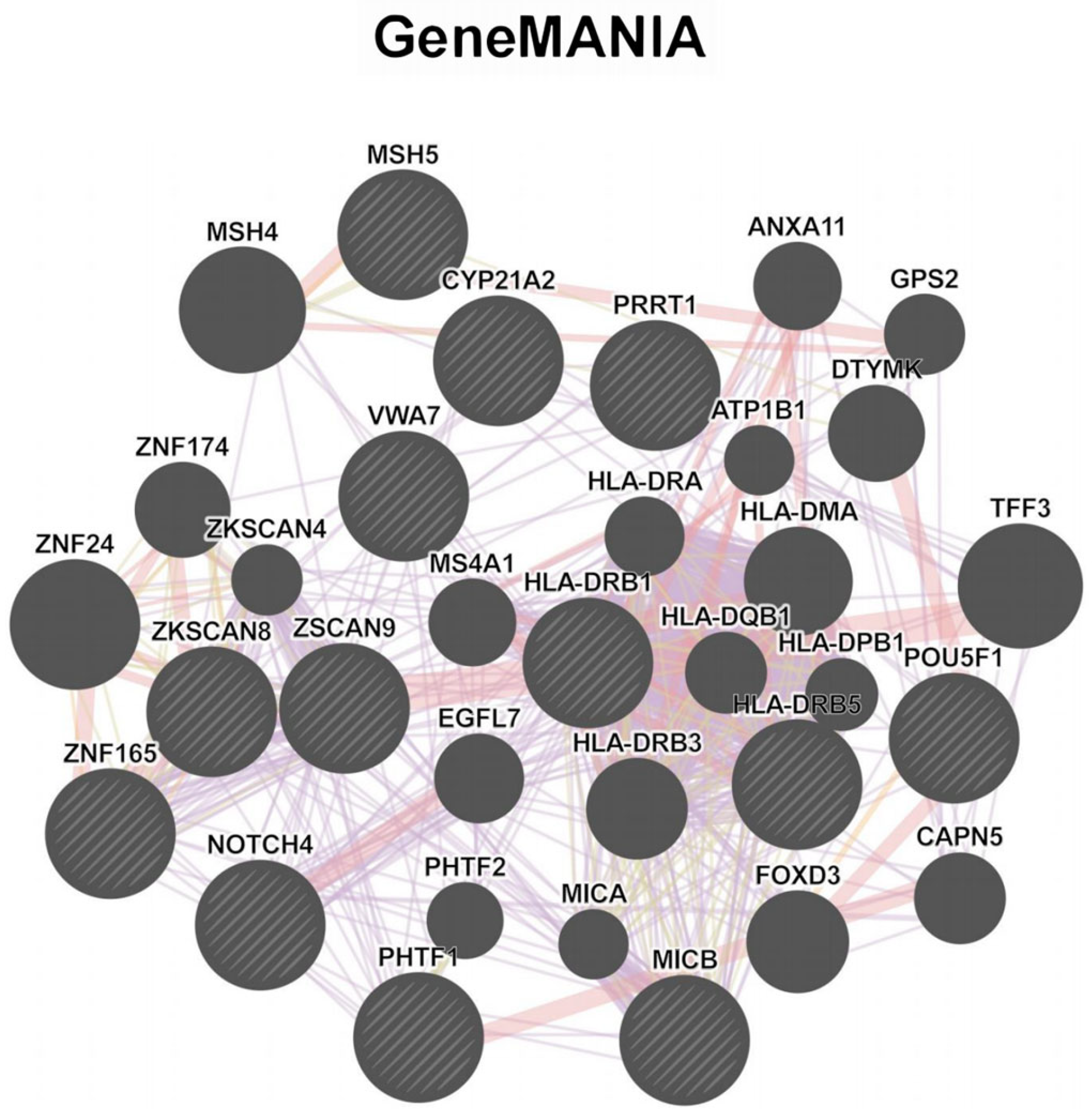
3.3. Enrichment and Network Analysis Reveal Functional Gene Clusters in DKD Pathogenesis
3.4. MR-Validated Genes as Drug Targets
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Esposito, P.; Picciotto, D.; Cappadona, F.; Costigliolo, F.; Russo, E.; Macciò, L.; Viazzi, F. Multifaceted Relationship between Diabetes and Kidney Diseases: Beyond Diabetes. World J. Diabetes 2023, 14, 1450–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costacou, T.; Orchard, T.J. Cumulative Kidney Complication Risk by 50 Years of Type 1 Diabetes: The Effects of Sex, Age, and Calendar Year at Onset. Diabetes Care 2018, 41, 426–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casey, C.; Buckley, C.M.; Kearney, P.M.; Griffin, M.D.; Dinneen, S.F.; Griffin, T.P. Social Deprivation and Diabetic Kidney Disease: A European View. J. Diabetes Investig. 2024, 15, 541–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Claessen, H.; Narres, M.; Kvitkina, T.; Wilk, A.; Friedel, H.; Günster, C.; Hoffmann, F.; Koch, M.; Jandeleit-Dahm, K.; Icks, A. Renal Replacement Therapy in People with and Without Diabetes in Germany, 2010–2016: An Analysis of More Than 25 Million Inhabitants. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuttle, K.R.; Agarwal, R.; Alpers, C.E.; Bakris, G.L.; Brosius, F.C.; Kolkhof, P.; Uribarri, J. Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets for Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2022, 102, 248–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancin, S.; Zarrella, A.; Petrelli, F.; Cosmai, S.; Cattani, D.; Lopane, D.; Scollo, S.; Morales Palomares, S.; Sguanci, M.; Amendola, A.; et al. Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Disease, and Vascular Ulcers: Prevention Strategies and Clinical Implications. Diabetology 2025, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandholm, N.; Dahlström, E.H.; Groop, P.-H. Genetic and Epigenetic Background of Diabetic Kidney Disease. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1163001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uffelmann, E.; Huang, Q.Q.; Munung, N.S.; de Vries, J.; Okada, Y.; Martin, A.R.; Martin, H.C.; Lappalainen, T.; Posthuma, D. Genome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Rev. Methods Primers 2021, 1, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Li, M.; Lu, Q.; Weng, H.; Wang, J.; Zekavat, S.M.; Yu, Z.; Li, B.; Gu, J.; Muchnik, S.; et al. A Statistical Framework for Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Analysis. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 568–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Wen, W.; Beeghly-Fadiel, A.; Shu, X.-O.; Díez-Obrero, V.; Long, J.; Bao, J.; Wang, J.; Liu, Q.; Cai, Q.; et al. Identifying Putative Susceptibility Genes and Evaluating Their Associations with Somatic Mutations in Human Cancers. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 105, 477–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusev, A.; Ko, A.; Shi, H.; Bhatia, G.; Chung, W.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Jansen, R.; de Geus, E.J.C.; Boomsma, D.I.; Wright, F.A.; et al. Integrative Approaches for Large-Scale Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 245–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mancuso, N.; Freund, M.K.; Johnson, R.; Shi, H.; Kichaev, G.; Gusev, A.; Pasaniuc, B. Probabilistic Fine-Mapping of Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 675–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbeira, A.N.; Pividori, M.; Zheng, J.; Wheeler, H.E.; Nicolae, D.L.; Im, H.K. Integrating Predicted Transcriptome from Multiple Tissues Improves Association Detection. PLoS Genet. 2019, 15, e1007889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, Y.; Zeng, J.; Zhang, F.; Zhu, Z.; Qi, T.; Zheng, Z.; Lloyd-Jones, L.R.; Marioni, R.E.; Martin, N.G.; Montgomery, G.W.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Omics Summary Data Reveals Putative Mechanisms Underlying Complex Traits. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Mancuso, N.; Gusev, A.; Majumdar, A.; Major, M.; Pasaniuc, B.; Kraft, P. Leveraging Expression from Multiple Tissues Using Sparse Canonical Correlation Analysis and Aggregate Tests Improves the Power of Transcriptome-Wide Association Studies. PLoS Genet. 2021, 17, e1008973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, J.; Yang, X.; Tan, C.; Wang, L.; Meng, L.; Han, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, L. A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Migraine. J. Headache Pain. 2024, 25, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Q.; Liu, R.; Chen, H.; Yang, X.; Dong, J.; Bai, M.; Lu, Y.; Leng, Y. Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Coronary Atherosclerosis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1149113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, S.; Sun, C.; Zhai, W.; Wei, W.; Liu, J. Gaining New Insights into the Etiology of Ulcerative Colitis through a Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1425370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doke, T.; Huang, S.; Qiu, C.; Liu, H.; Guan, Y.; Hu, H.; Ma, Z.; Wu, J.; Miao, Z.; Sheng, X.; et al. Transcriptome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies DACH1 as a Kidney Disease Risk Gene That Contributes to Fibrosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, 141801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, L.; Qiu, M.; Tan, L.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Zhu, H.; Jiang, S.; Su, X.; Li, A. Renal and Cerebral RAS Interaction Contributes to Diabetic Kidney Disease. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2019, 11, 2925–2939. [Google Scholar]
- Miura, T.; Kuno, A.; Tanaka, M. Diabetes Modulation of the Myocardial Infarction-Acute Kidney Injury Axis. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2022, 322, H394–H405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Folestad, E.; Mehlem, A.; Ning, F.C.; Oosterveld, T.; Palombo, I.; Singh, J.; Olauson, H.; Witasp, A.; Thorell, A.; Stenvinkel, P.; et al. Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor B-Mediated Fatty Acid Flux in the Adipose-Kidney Axis Contributes to Lipotoxicity in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Kidney Int. 2025, 107, 492–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, I.-W.; Tsai, T.-H.; Lo, C.-J.; Chou, Y.-J.; Yeh, C.-H.; Cheng, M.-L.; Lai, C.-C.; Sytwu, H.-K.; Tsai, T.-F. Discovery of a Biomarker Signature That Reveals a Molecular Mechanism Underlying Diabetic Kidney Disease via Organ Cross Talk. Diabetes Care 2022, 45, e102–e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.-J.; Shi, J.-J.; Mao, C.-Y.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Y.-F.; Fan, Y.; Hu, Z.-W.; Yu, W.-K.; Hao, X.-Y.; Li, M.-J.; et al. Identifying Causal Genes for Migraine by Integrating the Proteome and Transcriptome. J. Headache Pain. 2023, 24, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, C.; Laporte, A.D.; Spiegelman, D.; Akçimen, F.; Joober, R.; Dion, P.A.; Rouleau, G.A. Transcriptome-Wide Association Study of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder Identifies Associated Genes and Phenotypes. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Leeuw, C.A.; Mooij, J.M.; Heskes, T.; Posthuma, D. MAGMA: Generalized Gene-Set Analysis of GWAS Data. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2015, 11, e1004219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Hu, H.; Bakshi, A.; Robinson, M.R.; Powell, J.E.; Montgomery, G.W.; Goddard, M.E.; Wray, N.R.; Visscher, P.M.; et al. Integration of Summary Data from GWAS and eQTL Studies Predicts Complex Trait Gene Targets. Nat. Genet. 2016, 48, 481–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Huang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Zheng, C.; Shao, W.; Wang, G.; Zhang, W. Using a Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis to Explore the Relationship between Physical Activity and Alzheimer’s Disease. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; He, Q.-Y. ReactomePA: An R/Bioconductor Package for Reactome Pathway Analysis and Visualization. Mol. Biosyst. 2016, 12, 477–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finan, C.; Gaulton, A.; Kruger, F.A.; Lumbers, R.T.; Shah, T.; Engmann, J.; Galver, L.; Kelley, R.; Karlsson, A.; Santos, R.; et al. The Druggable Genome and Support for Target Identification and Validation in Drug Development. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaag1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sollis, E.; Mosaku, A.; Abid, A.; Buniello, A.; Cerezo, M.; Gil, L.; Groza, T.; Güneş, O.; Hall, P.; Hayhurst, J.; et al. The NHGRI-EBI GWAS Catalog: Knowledgebase and Deposition Resource. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D977–D985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buniello, A.; Suveges, D.; Cruz-Castillo, C.; Llinares, M.B.; Cornu, H.; Lopez, I.; Tsukanov, K.; Roldán-Romero, J.M.; Mehta, C.; Fumis, L.; et al. Open Targets Platform: Facilitating Therapeutic Hypotheses Building in Drug Discovery. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, D1467–D1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Landrum, M.J.; Lee, J.M.; Benson, M.; Brown, G.R.; Chao, C.; Chitipiralla, S.; Gu, B.; Hart, J.; Hoffman, D.; Jang, W.; et al. ClinVar: Improving Access to Variant Interpretations and Supporting Evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018, 46, D1062–D1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.; Liang, K.; Zhen, J.; Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, Z.; et al. Sirt6 Deficiency Exacerbates Podocyte Injury and Proteinuria through Targeting Notch Signaling. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Q.; Ying, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liao, C.; Li, A. HLA-DRB5 Promotes Immune Thrombocytopenia via Activating CD8+ T Cells. Open Med. 2024, 19, 20240955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, H.; Sun, C.; Wei, S.; Tao, J.; Jia, Z.; Chen, X.; Lv, W.; Lv, H.; Tang, G.; et al. Epigenome-Wide Methylation Haplotype Association Analysis Identified HLA-DRB1, HLA-DRB5 and HLA-DQB1 as Risk Factors for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Int. J. Immunogenet. 2023, 50, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Ying, Q.; Chen, Y.; Liao, C.; Li, A.; Ye, Q. HLA-DRB5 Overexpression Promotes Platelet Reduction in Immune Thrombocytopenia Mice Model by Facilitating MHC-II-Mediated Antigen Presentation. Acta Haematol. 2025, 148, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobi, T.; Massier, L.; Klöting, N.; Horn, K.; Schuch, A.; Ahnert, P.; Engel, C.; Löffler, M.; Burkhardt, R.; Thiery, J.; et al. HLA Class II Allele Analyses Implicate Common Genetic Components in Type 1 and Non-Insulin-Treated Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, dgaa027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, M.; Wang, L.; Li, Q.; Han, Q.; Peng, X.; Xie, Y.; Wu, J.; et al. Targeting Tissue-Resident Memory CD8+ T Cells in the Kidney Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy to Ameliorate Podocyte Injury and Glomerulosclerosis. Mol. Ther. 2022, 30, 2746–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackermann, D.; Vogt, B.; Bochud, M.; Burnier, M.; Martin, P.-Y.; Paccaud, F.; Ehret, G.; Guessous, I.; Ponte, B.; Pruijm, M.; et al. Increased Glucocorticoid Metabolism in Diabetic Kidney Disease. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0269920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Deng, X.; Zhou, J.; Qiu, K.; Deng, M.; Lin, Z.; Mosha, S.S.; Li, W. The Association Of Serum Cortisol Level with Microalbuminuria in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes and Prediabetes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 2998–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, S.; Wang, Y. Relationship between Cortisol and Diabetic Microvascular Complications: A Retrospective Study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asao, T.; Oki, K.; Yoneda, M.; Tanaka, J.; Kohno, N. Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Activity Is Associated with the Prevalence of Chronic Kidney Disease in Diabetic Patients. Endocr. J. 2016, 63, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lao, Q.; Burkardt, D.D.; Kollender, S.; Faucz, F.R.; Merke, D.P. Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia Due to Two Rare CYP21A2 Variant Alleles, Including a Novel Attenuated CYP21A1P/CYP21A2 Chimera. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2023, 11, e2195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fracasso, P.M.; Goodner, S.A.; Wildi, J.D.; Naughton, M.J.; Linette, G.P.; Govindan, R.; Tan, B.R.; Blum, K.A.; Jones, G.J.; Pearce, T.E.; et al. A Phase I Study of Apolizumab, an Anti-HLA-DR ß-Chain Monoclonal Antibody, in Patients with Solid Tumor Malignancies. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 45, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamaliyan, Z.; Clarke, T.L. Zinc Finger Proteins: Guardians of Genome Stability. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1448789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incorvaia, L.; Bazan Russo, T.D.; Gristina, V.; Perez, A.; Brando, C.; Mujacic, C.; Di Giovanni, E.; Bono, M.; Contino, S.; Ferrante Bannera, C.; et al. The Intersection of Homologous Recombination (HR) and Mismatch Repair (MMR) Pathways in DNA Repair-Defective Tumors. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2024, 8, 190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeWitt, J.T.; Raghunathan, M.; Haricharan, S. Nonrepair Functions of DNA Mismatch Repair Proteins: New Avenues for Precision Oncology. Trends Cancer 2025, 11, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hess, D.L.; Kelly-Goss, M.R.; Cherepanova, O.A.; Nguyen, A.T.; Baylis, R.A.; Tkachenko, S.; Annex, B.H.; Peirce, S.M.; Owens, G.K. Perivascular Cell-Specific Knockout of the Stem Cell Pluripotency Gene Oct4 Inhibits Angiogenesis. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mou, Y.; Yue, Z.; Wang, X.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Y.; Li, R.; Sun, X. OCT4 Remodels the Phenotype and Promotes Angiogenesis of HUVECs by Changing the Gene Expression Profile. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2016, 13, 386–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Geng, S.; Weng, J.; Lu, Z.; Zeng, L.; Li, M.; Deng, C.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Du, X. Analysis of the Expression of PHTF1 and Related Genes in Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia. Cancer Cell Int. 2015, 15, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, J.; Liang, G.; Liu, Z.; Cai, H. Associations of GWAS-Supported Non-MHC Genes with Autoimmune Thyroiditis in Patients with Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2021, 14, 3017–3026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hebbar, P.; Abu-Farha, M.; Alkayal, F.; Nizam, R.; Elkum, N.; Melhem, M.; John, S.E.; Channanath, A.; Abubaker, J.; Bennakhi, A.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study Identifies Novel Risk Variants from RPS6KA1, CADPS, VARS, and DHX58 for Fasting Plasma Glucose in Arab Population. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Gene_id | Protein Names | Druggability Tier | Target Type | Drugs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CYP21A2 | ENSG00000231852 | Steroid 21-hydroxylase | 3B | Clinical trial | BBP-631 |
| HLA-DRB1 | ENSG00000196126 | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DRB1 beta chain | 1 | Successful | Glatiramer acetate; Apolizumab |
| HLA-DRB5 | ENSG00000198502 | HLA class II histocompatibility antigen, DR beta 5 chain | 1 | Clinical trial | Apolizumab |
| MICB | ENSG00000204516 | MHC class I polypeptide-related sequence B | / | / | / |
| MSH5 | ENSG00000204410 | MutS protein homolog 5 | / | / | / |
| NOTCH4 | ENSG00000204301 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 4 | 3A | Clinical trial | Parsatuzumab (MEGF0444A); Crenigacestat (LY3039478) |
| PHTF1 | ENSG00000116793 | Protein PHTF1 | / | / | / |
| POU5F1 | ENSG00000204531 | POU domain, class 5, transcription factor 1 | / | / | / |
| PRRT1 | ENSG00000204314 | Proline-rich transmembrane protein 1 | / | / | / |
| VWA7 | ENSG00000204396 | von Willebrand factor A domain-containing protein 7 | / | / | / |
| ZKSCAN8 | ENSG00000198315 | Zinc finger protein with KRAB and SCAN domains 8 | / | / | / |
| ZNF165 | ENSG00000197279 | Zinc finger protein 165 | / | / | / |
| ZSCAN9 | ENSG00000137185 | Zinc finger and SCAN domain-containing protein 9 | / | / | / |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, M.; Li, Z.; Lu, Y.; Sun, P.; Chen, Y.; Yang, L. A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Diabetic Kidney Disease in the FinnGen Cohort. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051231
Liu M, Li Z, Lu Y, Sun P, Chen Y, Yang L. A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Diabetic Kidney Disease in the FinnGen Cohort. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051231
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Menghan, Zehua Li, Yao Lu, Pingping Sun, Ying Chen, and Li Yang. 2025. "A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Diabetic Kidney Disease in the FinnGen Cohort" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051231
APA StyleLiu, M., Li, Z., Lu, Y., Sun, P., Chen, Y., & Yang, L. (2025). A Cross-Tissue Transcriptome-Wide Association Study Reveals Novel Susceptibility Genes for Diabetic Kidney Disease in the FinnGen Cohort. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1231. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051231






