Acute Myeloid Leukemia Genome Characterization Study and Subtype Classification Employing Feature Selection and Bayesian Networks
Abstract
1. Introduction
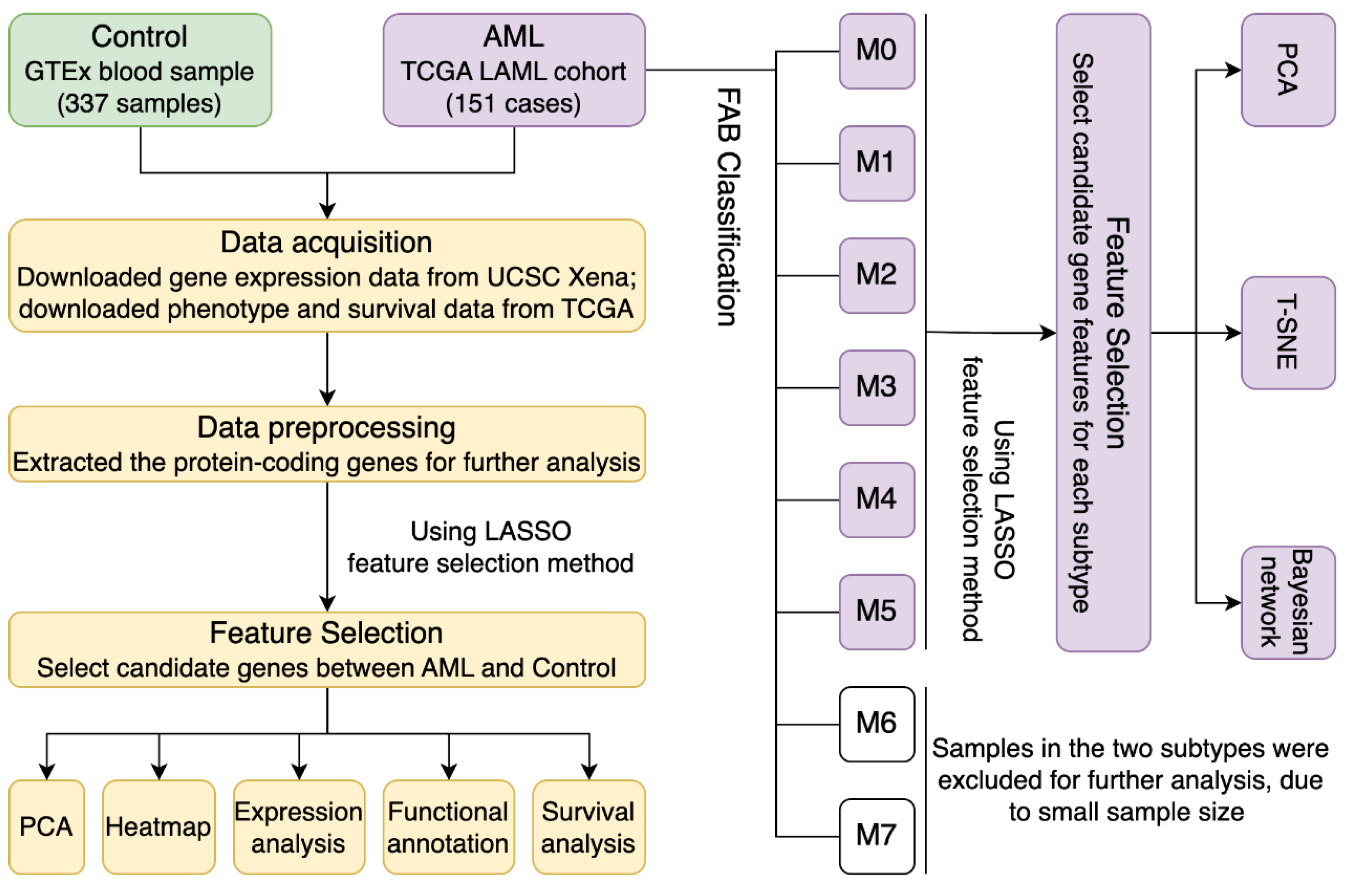
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
2.2. Using LASSO for Gene Feature Selection Between Different Groups
2.3. Gene Functional Annotation
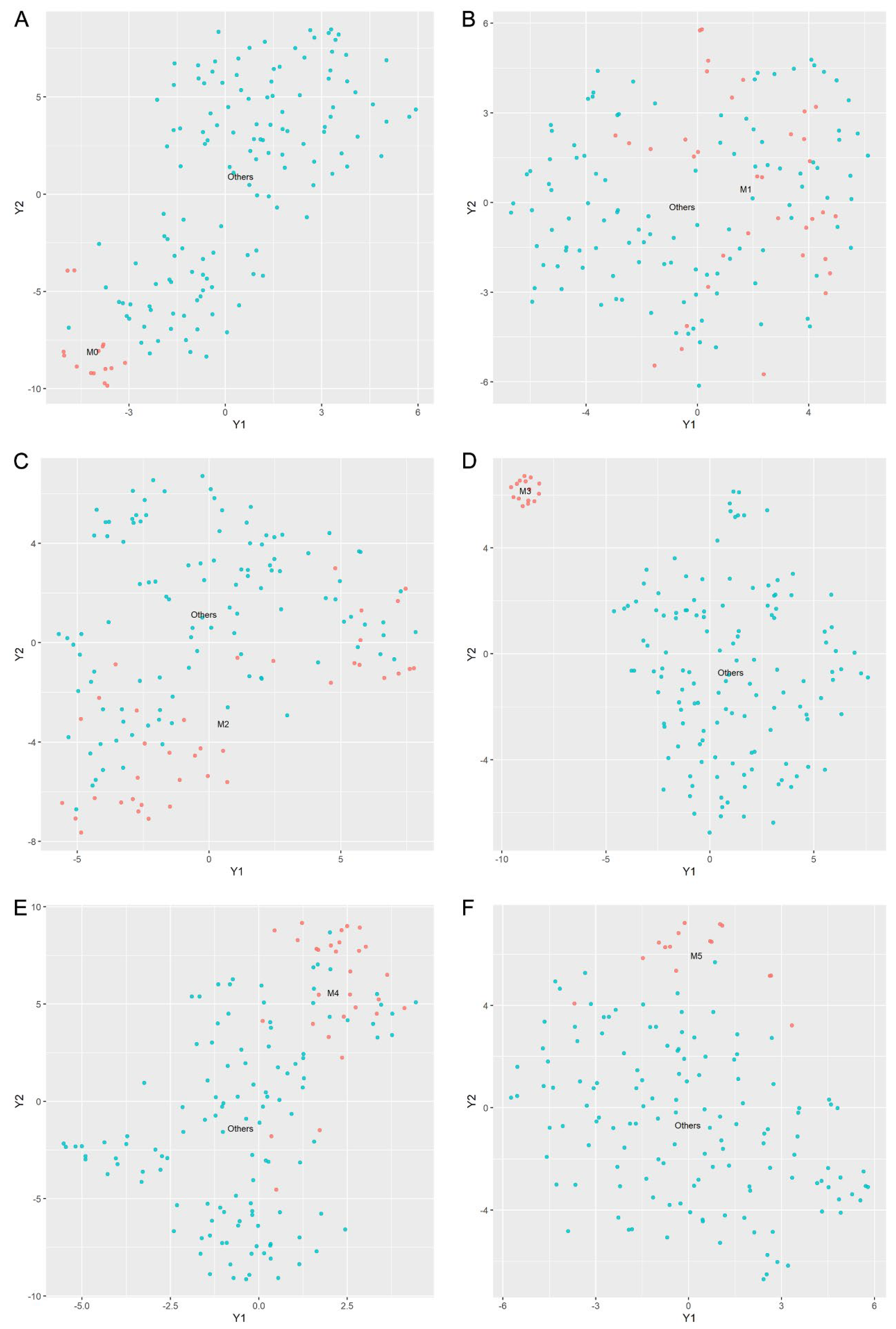
2.4. Classification Visualization
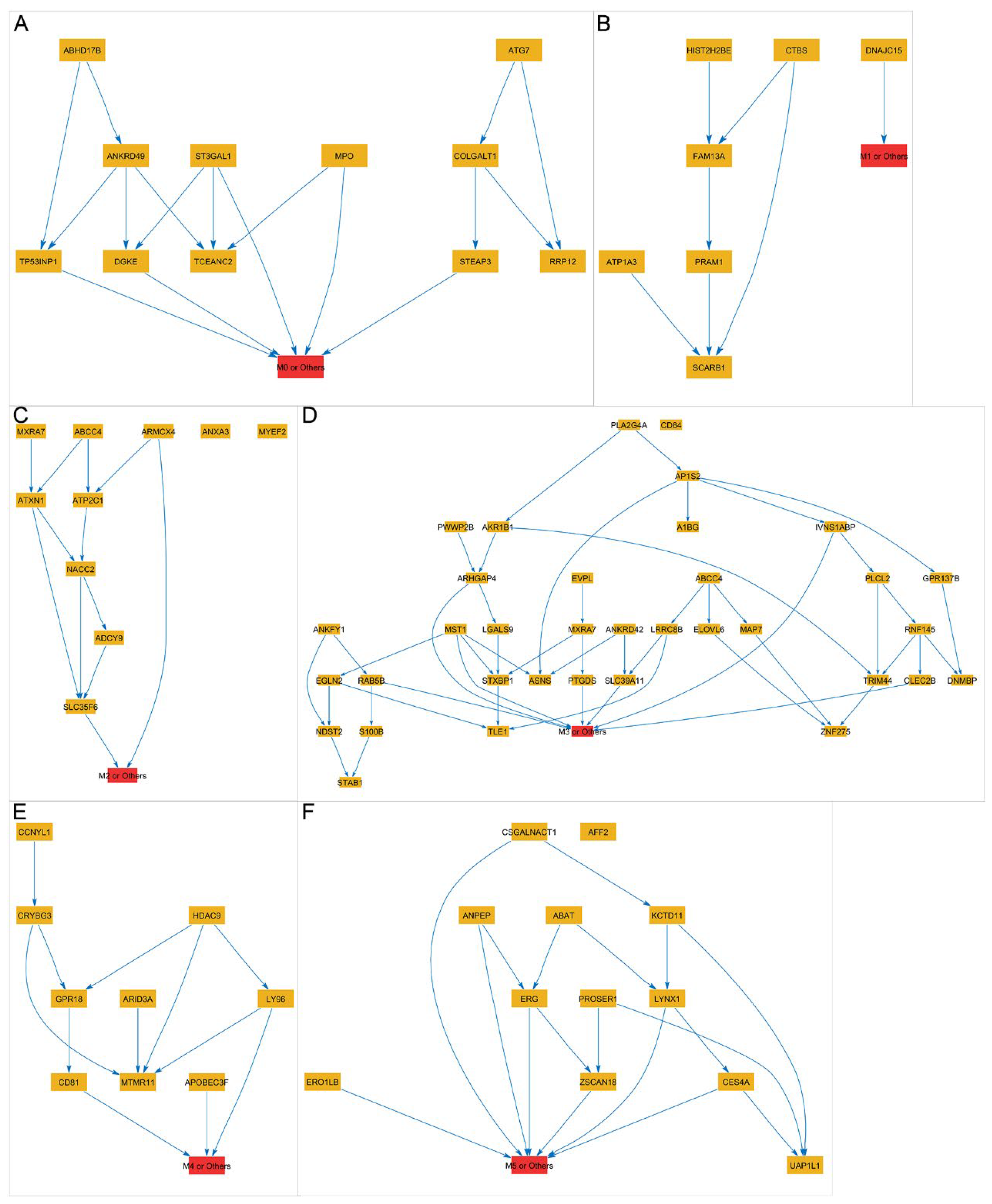
2.5. Construct Bayesian Network Using PC-Stable Algorithm
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
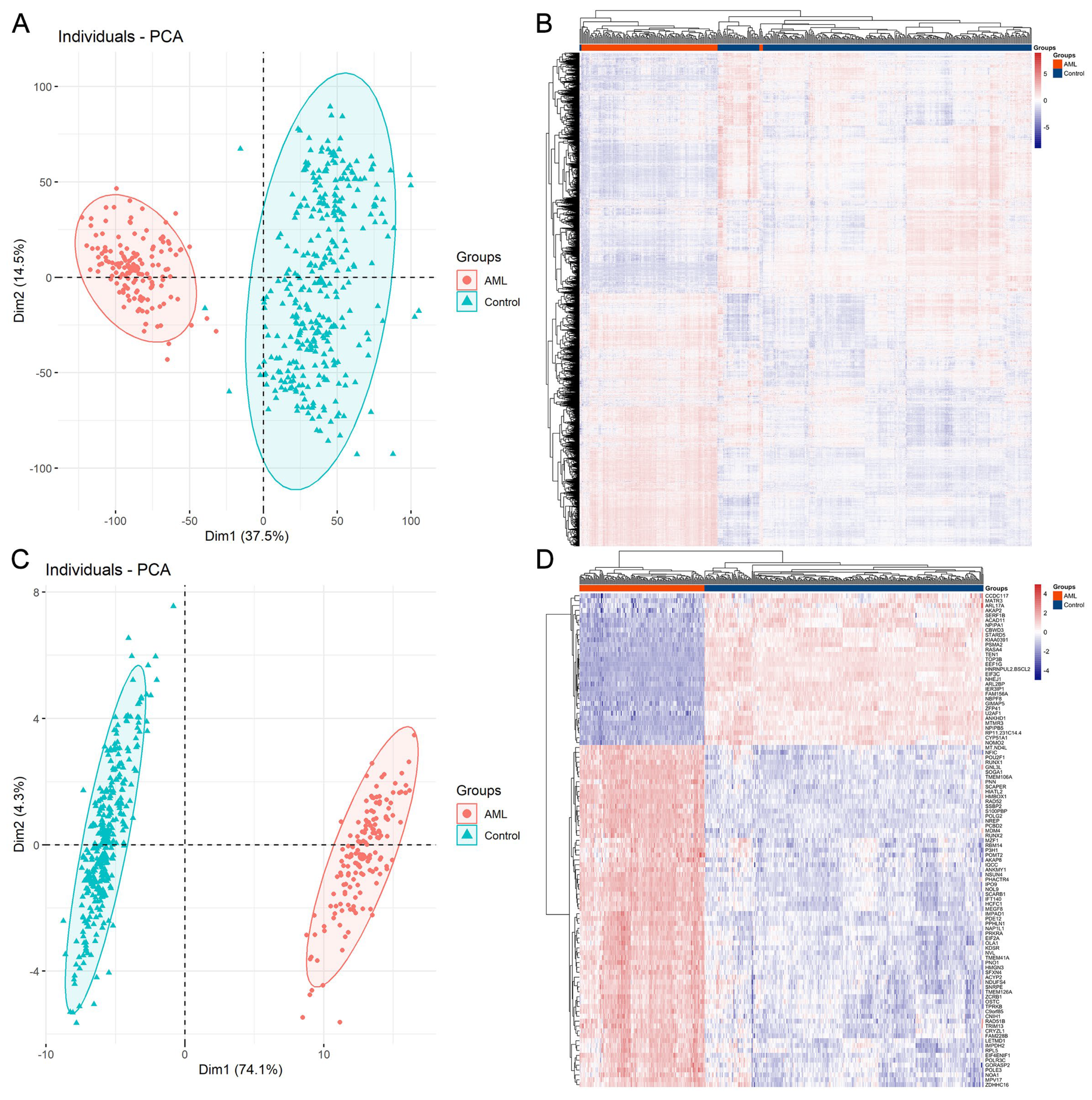
3.1. Protein-Coding Gene Profiling Analysis of AML and Control Samples
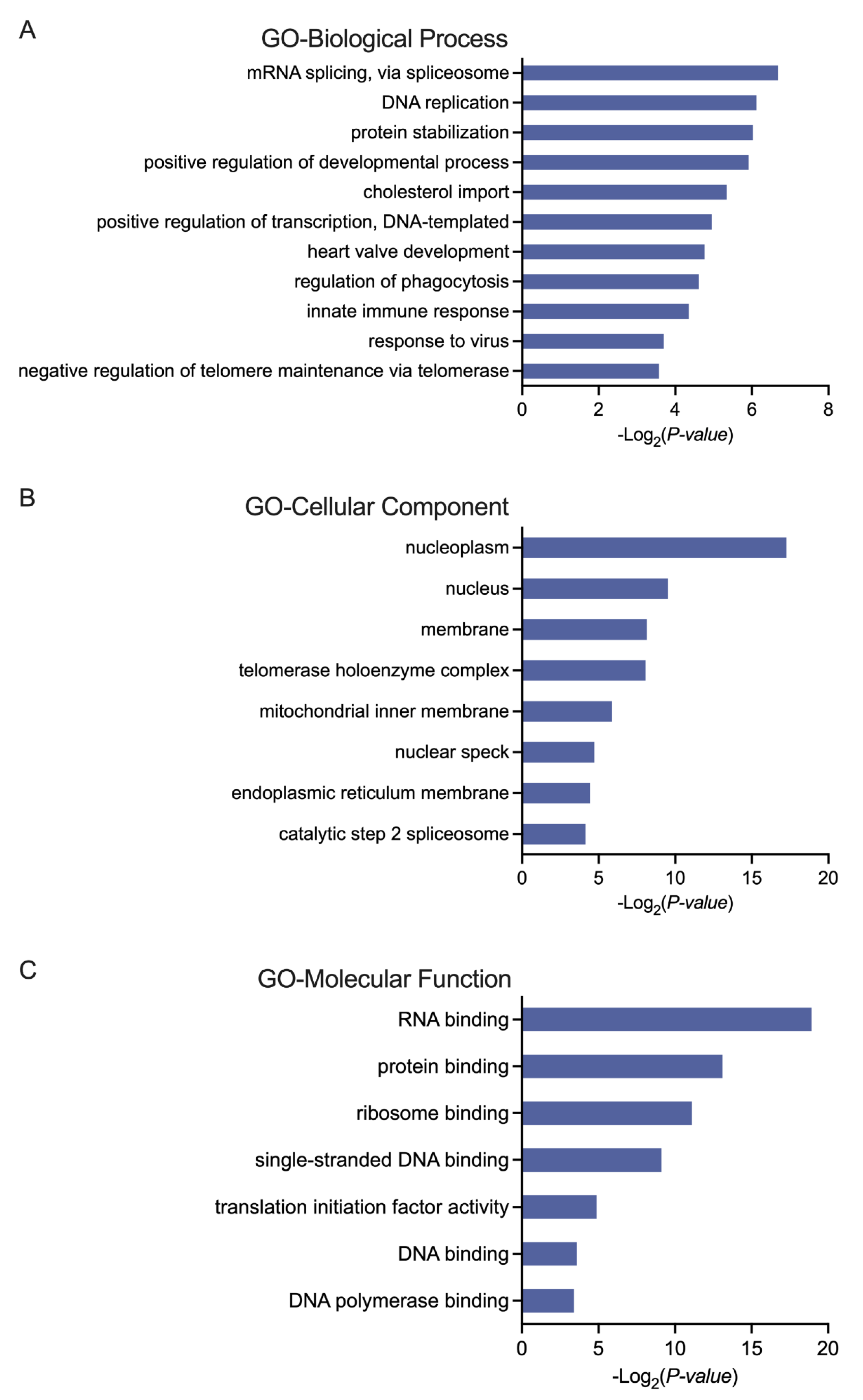
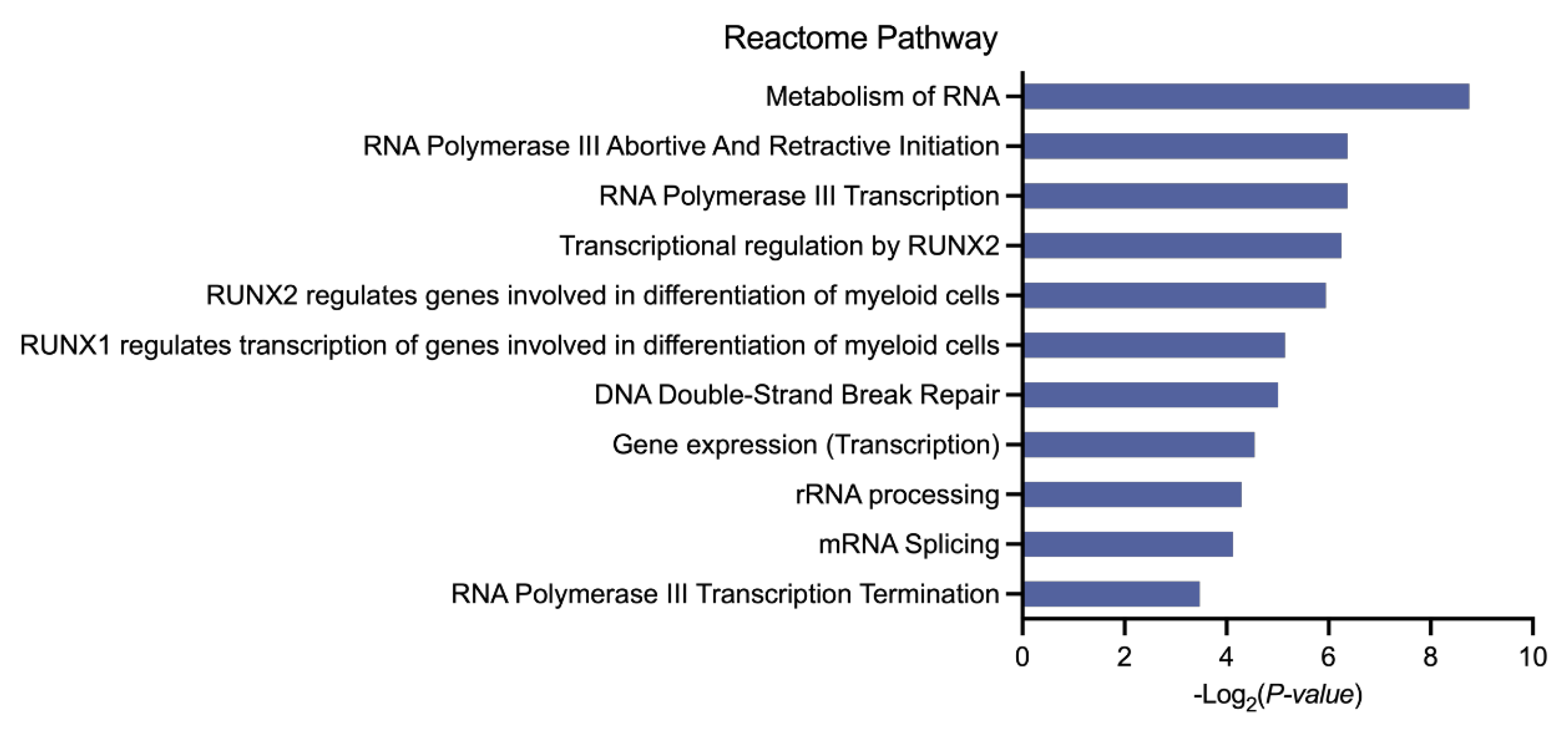
3.2. Biological Analysis of the Selected Genes in AML
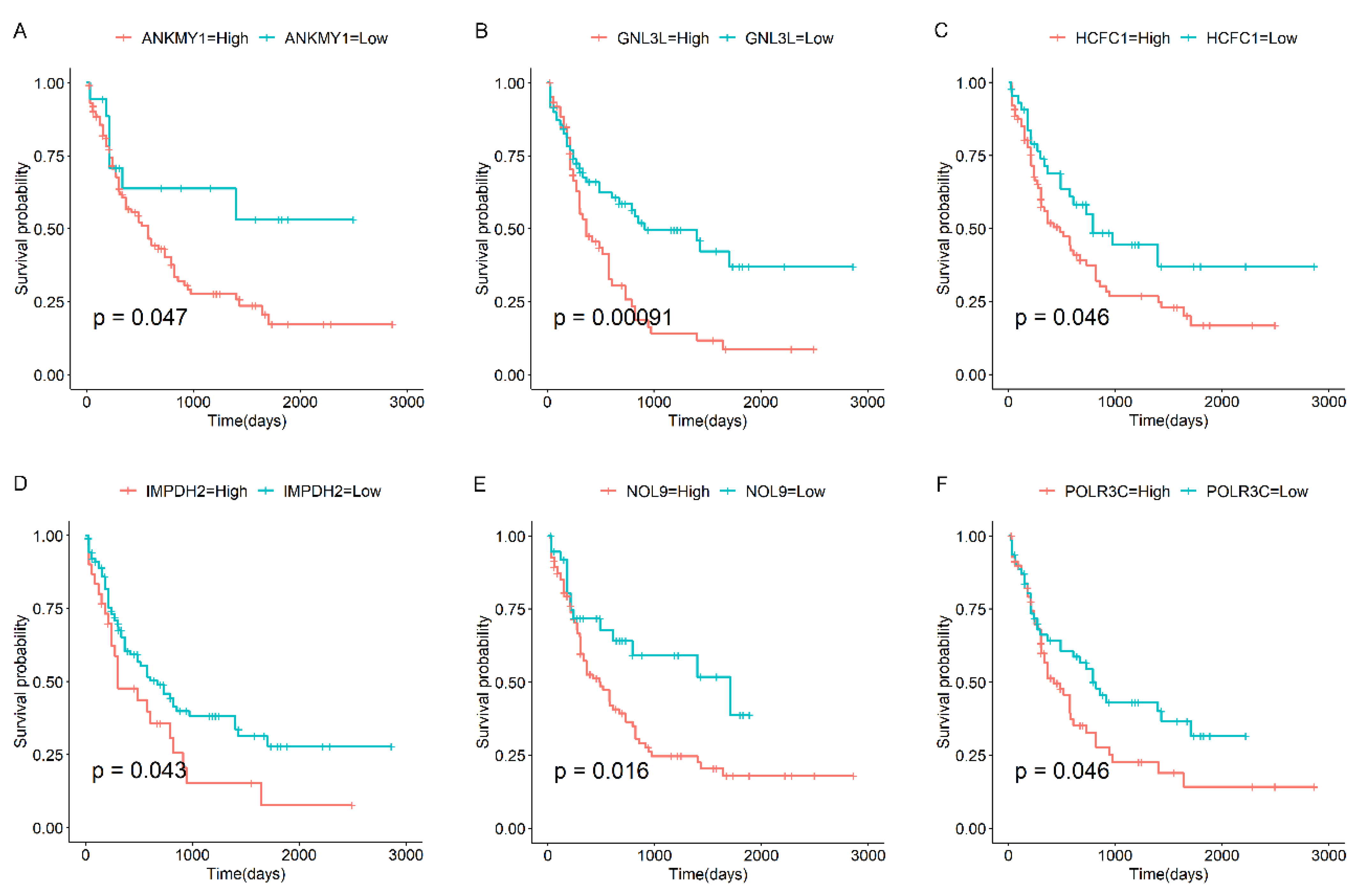
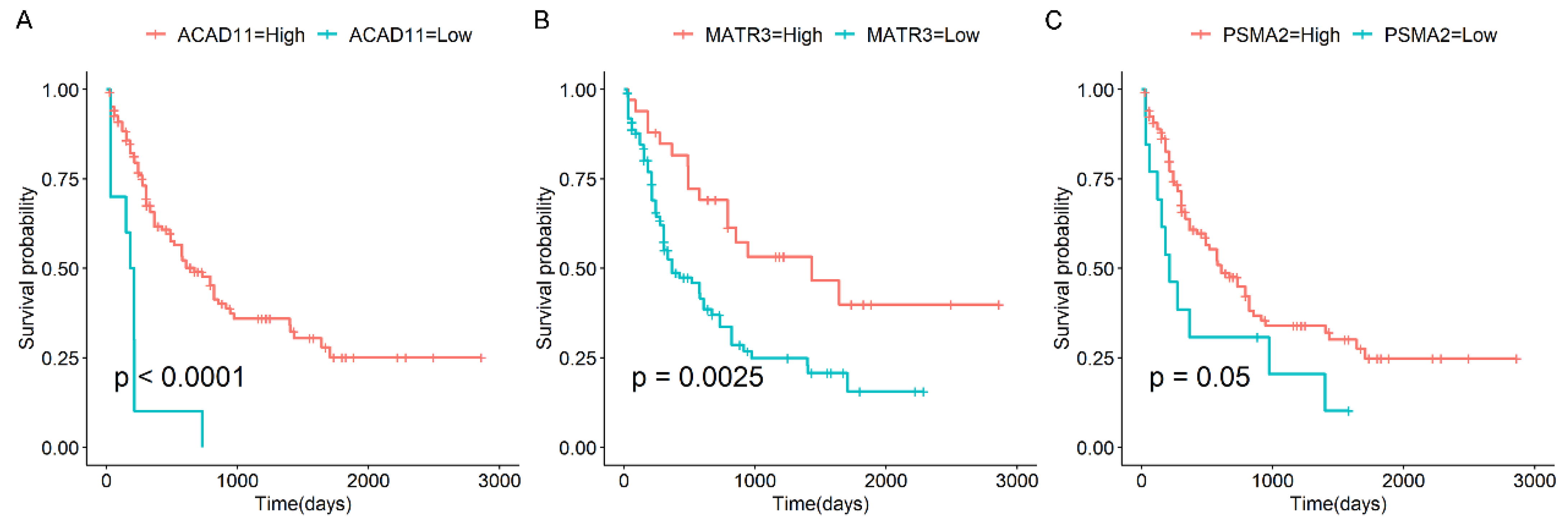
3.3. Survival Analysis of Candidate Genes in AML
3.4. Using the LASSO Method to Select Gene Subsets for Classifying AML Subtypes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AML | Acute myeloid leukemia |
| LASSO | Least Absolute Shrinkage and Selection Operator |
| HSCs | Hematopoietic stem cells |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| FAB | French–American–British |
| SVM | Support vector machines |
| RF | Random forests |
| GTEx | Genotype-Tissue Expression |
| TCGA | The Cancer Genome Atlas |
| DAVID | Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| t-SNE | t-distributed stochastic neighbor embedding |
| PCA | Principal component analysis |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| BP | Biological processes |
| CC | Cellular component |
| MF | Molecular function |
| Pol III | RNA polymerase III |
References
- Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network; Ley, T.J.; Miller, C.; Ding, L.; Raphael, B.J.; Mungall, A.J.; Robertson, A.; Hoadley, K.; Triche, T.J., Jr.; Laird, P.W.; et al. Genomic and epigenomic landscapes of adult de novo acute myeloid leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 2059–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohner, H.; Weisdorf, D.J.; Bloomfield, C.D. Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1136–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khoury, J.D.; Solary, E.; Abla, O.; Akkari, Y.; Alaggio, R.; Apperley, J.F.; Bejar, R.; Berti, E.; Busque, L.; Chan, J.K.C.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Myeloid and Histiocytic/Dendritic Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1703–1719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Q.; Yun, S.; Sallman, D.A.; Vincelette, N.D.; Peng, G.; Zhang, L.; Lancet, J.E.; Padron, E. Integrative molecular subtypes of acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, P.Y.; Wang, R.W.; Jing, R.; Li, X.; Ma, J.H.; Li, K.M.; Wang, H. Research progress on molecular biomarkers of acute myeloid leukemia. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1078556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prada-Arismendy, J.; Arroyave, J.C.; Röthlisberger, S. Molecular biomarkers in acute myeloid leukemia. Blood Rev. 2017, 31, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wong, M.P.M.; Ng, R.K. Aberrant DNA Methylation in Acute Myeloid Leukemia and Its Clinical Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, I.R.; Auerbach, J.; Gola, D.; Held, E.; Holzinger, E.R.; Legault, M.A.; Sun, R.; Tintle, N.; Yang, H.C. Machine learning and data mining in complex genomic data—A review on the lessons learned in Genetic Analysis Workshop 19. BMC Genet. 2016, 17 (Suppl. 2), 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, G.D.; Ching, W.H.; Cornejo-Páramo, P.; Wong, E.S. Decoding enhancer complexity with machine learning and high-throughput discovery. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pudjihartono, N.; Fadason, T.; Kempa-Liehr, A.W.; O’Sullivan, J.M. A Review of Feature Selection Methods for Machine Learning-Based Disease Risk Prediction. Front. Bioinform. 2022, 2, 927312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Ru, X.; Sun, P.; Wang, J. Using feature selection and Bayesian network identify cancer subtypes based on proteomic data. J. Proteom. 2023, 280, 104895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, P.; Huang, H.; Liu, C. Feature selection revisited in the single-cell era. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Wang, J. Functional Proteomic Profiling Analysis in Four Major Types of Gastrointestinal Cancers. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Cai, N.; Pacheco, P.P.; Narrandes, S.; Wang, Y.; Xu, W. Applications of Support Vector Machine (SVM) Learning in Cancer Genomics. Cancer Genom. Proteom. 2018, 15, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Feng, Y.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Shi, J.; Chang, W.; Wang, J. ForestSubtype: A cancer subtype identifying approach based on high-dimensional genomic data and a parallel random forest. BMC Bioinform. 2023, 24, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, E.; Lindsay, J.; Lee, C.; Măndoiu, I.I.; Nelson, C.E. Feature selection and classifier performance on diverse bio- logical datasets. BMC Bioinform. 2014, 15 (Suppl. 13), S4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lonsdale, J.; Thomas, J.; Salvatore, M.; Phillips, R.; Lo, E.; Shad, S.; Hasz, R.; Walters, G.; Garcia, F.; Young, N.; et al. The Genotype-Tissue Expression (GTEx) project. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Jensen, M.A.; Zenklusen, J.C. A Practical Guide to The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA). In Statistical Genomics. Methods in Molecular Biology; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2016; Volume 1418, pp. 111–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutter, C.; Zenklusen, J.C. The Cancer Genome Atlas: Creating Lasting Value beyond Its Data. Cell 2018, 173, 283–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Choi, Y.J.; Kim, I.K.; Lee, H.S.; Kim, H.; Baik, S.H.; Kim, N.K.; Lee, K.Y. LASSO-Based Machine Learning Algorithm for Prediction of Lymph Node Metastasis in T1 Colorectal Cancer. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 53, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Dai, L.; Shen, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, M.; Yang, X.; Qiu, Y.; Wang, W. Comprehensive Molecular Analyses of a Macrophage-Related Gene Signature with Regard to Prognosis, Immune Features, and Biomarkers for Immunotherapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma Based on WGCNA and the LASSO Algorithm. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 843408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, G., Jr.; Sherman, B.T.; Hosack, D.A.; Yang, J.; Gao, W.; Lane, H.C.; Lempicki, R.A. DAVID: Database for Annotation, Visualization, and Integrated Discovery. Genome Biol. 2003, 4, P3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. Mining causal relationships among clinical variables for cancer diagnosis based on Bayesian analysis. BioData Min. 2015, 8, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Chen, X.; Wang, J.; Meydan, C.; Glass, J.L.; Shih, A.H.; Delwel, R.; Levine, R.L.; Mason, C.E.; Melnick, A.M. Somatic Mutations Drive Specific, but Reversible, Epigenetic Heterogeneity States in AML. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 1934–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueda, K.; Steidl, U. Epigenetic Achilles’ heel of AML. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 481–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodrigues, C.P.; Shvedunova, M.; Akhtar, A. Epigenetic Regulators as the Gatekeepers of Hematopoiesis. Trends Genet. 2020, 37, P125–P142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, P.; Mencia-Trinchant, N.; Savenkov, O.; Simon, M.S.; Cheang, G.; Lee, S.; Samuel, M.; Ritchie, E.K.; Guzman, M.L.; Ballman, K.V.; et al. Somatic mutations precede acute myeloid leukemia years before diagnosis. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1015–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mill, C.P.; Fiskus, W.; DiNardo, C.D.; Birdwell, C.; Davis, J.A.; Kadia, T.M.; Takahashi, K.; Short, N.; Daver, N.; Ohanian, M.; et al. Effective therapy for AML with RUNX1 mutation by cotreatment with inhibitors of protein translation and BCL2. Blood 2022, 139, 907–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadugu, B.A.; Nonavinkere Srivatsan, S.; Heard, A.; Alberti, M.O.; Ndonwi, M.; Liu, J.; Grieb, S.; Bradley, J.; Shao, J.; Ahmed, T.; et al. U2af1 is a haplo-essential gene required for hematopoietic cancer cell survival in mice. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 131, e141401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Manero, G.; Pemmaraju, N.; Alvarado, Y.; Naqvi, K.; Ravandi, F.; Jabbour, E.; De Lumpa, R.; Kantarjian, H.; Advani, A.; Mukherjee, S.; et al. Results of a Phase 1/2a dose-escalation study of FF-10501-01, an IMPDH inhibitor, in patients with acute myeloid leukemia or myelodysplastic syndromes. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 1943–1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Sato, N.; Yabushita, T.; Li, J.; Jia, Y.; Tamura, M.; Asada, S.; Fujino, T.; Fukushima, T.; Yonezawa, T.; et al. IMPDH inhibition activates TLR-VCAM1 pathway and suppresses the development of MLL-fusion leukemia. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e15631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Z.; Pan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chu, J.; Cong, Y.; Fang, Q. GNL3L exhibits pro-tumor activities via NF-κB pathway as a poor prognostic factor in acute myeloid leukemia. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 4072–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Y.; Hu, A.; Qu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Wang, H.; Feng, Y.; Hu, Y.; He, L.; Wu, H.; Wang, X. Covalent targeting the LAS1-NOL9 axis for selective treatment in NPM1 mutant acute myeloid leukemia. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 189, 106700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.W.; Park, M. Comparison of cancer subtype identification methods combined with feature selection methods in omics data analysis. BioData Min. 2023, 16, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papaemmanuil, E.; Gerstung, M.; Bullinger, L.; Gaidzik, V.I.; Paschka, P.; Roberts, N.D.; Potter, N.E.; Heuser, M.; Thol, F.; Bolli, N.; et al. Genomic Classification and Prognosis in Acute Myeloid Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 374, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, K.A.; Bell, C.C.; Dawson, M.A. Epigenetic therapies in acute myeloid leukemia: Where to from here? Blood 2019, 134, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeganeh, M.; Hernandez, N. RNA polymerase III transcription as a disease factor. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 865–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhargava, P. Epigenetic regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1829, 1015–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiNardo, C.D.; Erba, H.P.; Freeman, S.D.; Wei, A.H. Acute myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2023, 401, 2073–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Döhner, H.; Wei, A.H.; Appelbaum, F.R.; Craddock, C.; DiNardo, C.D.; Dombret, H.; Ebert, B.L.; Fenaux, P.; Godley, L.A.; Hasserjian, R.P.; et al. Diagnosis and management of AML in adults: 2022 recommendations from an international expert panel on behalf of the ELN. Blood 2022, 140, 1345–1377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marjanovic, I.; Karan-Djurasevic, T.; Kostic, T.; Virijevic, M.; Vukovic, N.S.; Pavlovic, S.; Tosic, N. Prognostic significance of combined BAALC and MN1 gene expression level in acute myeloid leukemia with normal karyotype. Int. J. Lab. Hematol. 2021, 43, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yagi, T.; Morimoto, A.; Eguchi, M.; Hibi, S.; Sako, M.; Ishii, E.; Mizutani, S.; Imashuku, S.; Ohki, M.; Ichikawa, H. Identification of a gene expression signature associated with pediatric AML prognosis. Blood 2003, 102, 1849–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haferlach, C.; Kern, W.; Schindela, S.; Kohlmann, A.; Alpermann, T.; Schnittger, S.; Haferlach, T. Gene expression of BAALC, CDKN1B, ERG, and MN1 adds independent prognostic information to cytogenetics and molecular mutations in adult acute myeloid leukemia. Genes Chromosomes Cancer 2012, 51, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panagopoulos, I.; Gorunova, L.; Andersen, H.K.; Bergrem, A.; Dahm, A.; Andersen, K.; Micci, F.; Heim, S. PAN3-PSMA2 fusion resulting from a novel t(7;13)(p14;q12) chromosome translocation in a myelodysplastic syndrome that evolved into acute myeloid leukemia. Exp. Hematol. Oncol. 2018, 7, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N. Analysis of prognostic biomarker models and immune microenvironment in acute myeloid leukemia by integrative bioinformatics. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 149, 9609–9619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, S.; Li, F.; Wang, S.; Wang, W.; Sheng, X.; Feng, L. Comprehensively Analyzed Macrophage-Regulated Genes Indicate That PSMA2 Promotes Colorectal Cancer Progression. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 618902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attig, J.; Agostini, F.; Gooding, C.; Chakrabarti, A.M.; Singh, A.; Haberman, N.; Zagalak, J.A.; Emmett, W.; Smith, C.W.J.; Luscombe, N.M.; et al. Heteromeric RNP Assembly at LINEs Controls Lineage-Specific RNA Processing. Cell 2018, 174, 1067–1081.e17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Komatsu, K.; Sakaguchi, K.; Shimizu, D.; Yamoto, K.; Kato, F.; Miyairi, I.; Ogata, T.; Saitsu, H. Characterization of KMT2A::MATR3 fusion in a patient with acute lymphoblastic leukemia and monitoring of minimal residual disease by nanoplate digital PCR. Pediatr. Blood Cancer 2023, 70, e30120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angelescu, S.; Berbec, N.M.; Colita, A.; Barbu, D.; Lupu, A.R. Value of multifaced approach diagnosis and classification of acute leukemias. Maedica 2012, 7, 254–260. [Google Scholar]
| Clinical Characteristics | AML Cohort |
|---|---|
| Age | |
| N/Range | 151/(21–88) |
| Average | 54.17 ± 16.07 |
| Gender (N) | |
| Male | 83 |
| Female | 68 |
| Race (N) | |
| Asian | 1 |
| Black | 13 |
| White | 135 |
| Not reported | 2 |
| Subtype (N) | |
| M0 | 15 |
| M1 | 35 |
| M2 | 38 |
| M3 | 15 |
| M4 | 29 |
| M5 | 15 |
| M6 | 2 |
| M7 | 1 |
| Not reported | 1 |
| OS_status (N) | |
| Alive | 52 |
| Dead | 80 |
| Not reported | 19 |
| OS_time (Days) | |
| Alive | 927.73 ± 730.63 |
| Dead | 414.50 ± 385.15 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z.; Li, J.; Li, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Genome Characterization Study and Subtype Classification Employing Feature Selection and Bayesian Networks. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051067
Li Z, Li J, Li S, Wang Y, Wang J. Acute Myeloid Leukemia Genome Characterization Study and Subtype Classification Employing Feature Selection and Bayesian Networks. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(5):1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051067
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zhenzhen, Jingwen Li, Sifan Li, Yangyang Wang, and Jihan Wang. 2025. "Acute Myeloid Leukemia Genome Characterization Study and Subtype Classification Employing Feature Selection and Bayesian Networks" Biomedicines 13, no. 5: 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051067
APA StyleLi, Z., Li, J., Li, S., Wang, Y., & Wang, J. (2025). Acute Myeloid Leukemia Genome Characterization Study and Subtype Classification Employing Feature Selection and Bayesian Networks. Biomedicines, 13(5), 1067. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13051067





