Vitamin D, C-Reactive Protein, and Cardiometabolic Risk Clustering in Middle-Aged Adults: Results from the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Data Source
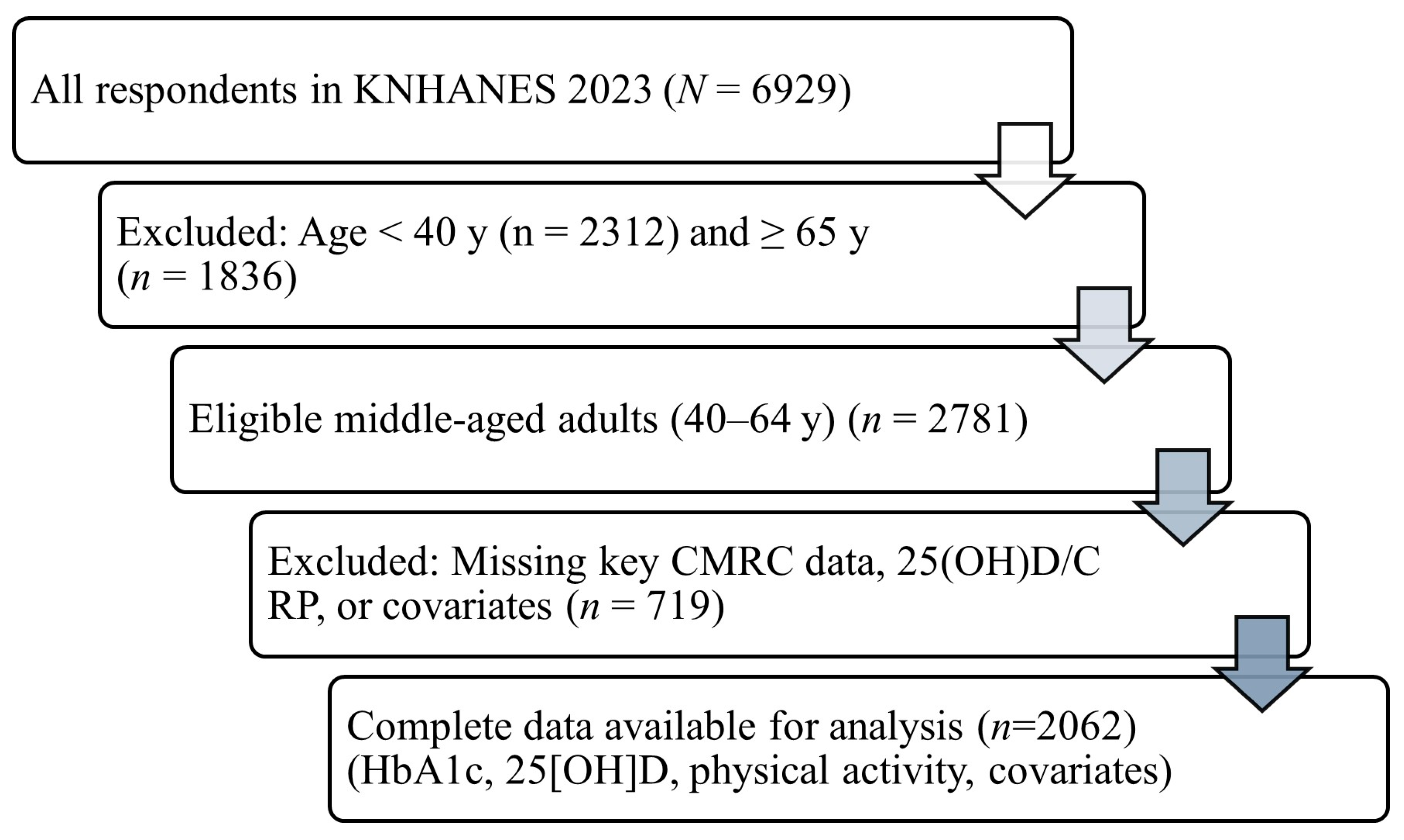
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Measures
2.3.1. Outcome Variable
2.3.2. Independent Variables
2.3.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
2.5. Ethical Considerations
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Sociodemographic, Lifestyle, and Clinical Differences Between CMRC Groups
3.3. Factors Independently Associated with CMRC
4. Discussion
4.1. Comparison with Previous Studies
4.2. Possible Mechanisms
4.3. Public Health and Clinical Implications
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CMRC | Cardiometabolic Risk Clustering |
| CRP | C-Reactive Protein |
| WHO | World Health Organization |
| KNHANES | Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey |
| KDCA | Korea Disease Control and Prevention Agency |
| IRB | Institutional Review Board |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| HDL | High-Density Lipoprotein |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| OR | Odds Ratio |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| 25(OH)D | 25-Hydroxy Vitamin D |
References
- Brauer, M.; Roth, G.A.; Aravkin, A.Y.; Zheng, P.; Abate, K.H.; Abate, Y.H.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasgholizadeh, R.; Abbasi, M.A.; Abbasian, M.; et al. Global burden and strength of evidence for 88 risk factors in 204 countries and 811 subnational locations, 1990–2021: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. Lancet 2024, 403, 2162–2203, Erratum in Lancet 2024, 404, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B. Metabolic health and cardiometabolic risk clusters: Implications for prediction, prevention, and treatment. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, C.; Chen, L.; Zhou, H.; Cai, J.; Hu, Z.; Tian, Y.; et al. Cardiovascular disease and all-cause mortality associated with individual and combined cardiometabolic risk factors. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-J.; Kang, D.R.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, W.; Jeong, Y.W.; Chun, K.-H.; Han, S.H.; Koh, K.K. Metabolic syndrome fact sheet 2024: Executive report. CardioMetabolic Syndr. J. 2024, 4, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, Z.C.-M.; Tao, A.; Chan, H.Y.-L. Effects of health coaching on cardiometabolic health in middle-aged adults: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Am. J. Health Promot. 2023, 37, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piché, M.-E.; Tchernof, A.; Després, J.-P. Obesity phenotypes, diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1477–1500, Erratum in Circ. Res. 2020, 127, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, L.; Gao, C.; Weng, R.; Fan, Y.; Xu, S.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, W. Vitamin D status and its associations with bone mineral density, bone turnover markers, and parathyroid hormone in Chinese postmenopausal women with osteopenia and osteoporosis. Front. Nutr. 2023, 10, 1307896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaseminejad-Raeini, A.; Ghaderi, A.; Sharafi, A.; Nematollahi-Sani, B.; Moossavi, M.; Derakhshani, A.; Sarab, G.A. Immunomodulatory actions of vitamin D in various immune-related disorders: A comprehensive review. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 950465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.Y.; Shin, S.; Han, S.N. Multifaceted roles of vitamin D for diabetes: From immunomodulatory functions to metabolic regulations. Nutrients 2024, 16, 3185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Argano, C.; Mirarchi, L.; Amodeo, S.; Orlando, V.; Torres, A.; Corrao, S. The role of vitamin D and its molecular bases in insulin resistance, diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease: State of the art. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajhashemy, Z.; Shahdadian, F.; Moslemi, E.; Mirenayat, F.S.; Saneei, P. Serum vitamin D levels in relation to metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and dose–response meta-analysis of epidemiologic studies. Obes. Rev. 2021, 22, e13223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammed, J.A.; Basil, B.; Mba, I.N.; Abubakar, N.D.; Lawal, A.O.; Momoh, J.A.; Yahaya, I.A. Elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein and dyslipidaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: Implications for cardiovascular risk prediction in Nigerian patients. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2025, 25, 100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amezcua-Castillo, E.; González-Pacheco, H.; Sáenz-San Martín, A.; Méndez-Ocampo, P.; Gutierrez-Moctezuma, I.; Massó, F.; Sierra-Lara, D.; Springall, R.; Rodríguez, E.; Arias-Mendoza, A.; et al. C-reactive protein: The quintessential marker of systemic inflammation in coronary artery disease—Advancing toward precision medicine. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verswijveren, S.J.; Dingle, S.; Donnelly, A.E.; Dowd, K.P.; Ridgers, N.D.; Carson, B.P.; Kearney, P.M.; Harrington, J.M.; Chappel, S.E.; Powell, C. How are different clusters of physical activity, sedentary, sleep, smoking, alcohol, and dietary behaviors associated with cardiometabolic health in older adults? A cross-sectional latent class analysis. J. Act. Sedentary Sleep Behav. 2023, 2, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saldana, G.; Liu, L.; German, C.A. Physical activity, steps, and cardiovascular disease: A literature review. Heart Mind 2025, 9, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pienaar, P.R.; Roden, L.C.; Boot, C.R.; van Mechelen, W.; Suter, J.A.; Lambert, E.V.; Rae, D.E. Associations between habitual sleep characteristics and cardiometabolic disease risk in corporate executives. Sleep Health 2024, 10, 550–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, K.; Kim, Y.; Kweon, S.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.-K.; Kim, Y.-T.; Park, O.; Jeong, E.K. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: Accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol. Health 2021, 43, e2021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mezhal, F.; Oulhaj, A.; Abdulle, A.; AlJunaibi, A.; Alnaeemi, A.; Ahmad, A.; Leinberger-Jabari, A.; Al Dhaheri, A.S.; Tuzcu, E.M.; AlZaabi, E.; et al. The interrelationship and accumulation of cardiometabolic risk factors amongst young adults in the United Arab Emirates: The UAE Healthy Future Study. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2021, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Lu, C.; Song, B.; Chen, D.; Teng, D.; Shan, Z.; Teng, W. The prevalence and clustering of metabolic syndrome risk components in Chinese population: A cross-sectional study. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1290855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, S. Association between nut consumption and metabolic syndrome in Korean adults. J. Lipid Atheroscler. 2025, 14, 219–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejabat, A.; Emamat, H.; Afrashteh, S.; Jamshidi, A.; Jamali, Z.; Farhadi, A.; Talkhabi, Z.; Nabipour, I.; Larijani, B.; Spitz, J. Association of serum 25-hydroxy vitamin D status with cardiometabolic risk factors and total and regional obesity in southern Iran: Evidence from the PoCOsteo study. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strange, R.C.; E Shipman, K.; Ramachandran, S. Metabolic syndrome: A review of the role of vitamin D in mediating susceptibility and outcome. World J. Diabetes 2015, 6, 896–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Małkowska, P. Positive effects of physical activity on insulin signaling. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2024, 46, 5467–5487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashi, Y. Smoking cessation and vascular endothelial function. Hypertens. Res. 2023, 46, 2670–2678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Strack, C.; Behrens, G.; Sag, S.; Mohr, M.; Zeller, J.; Lahmann, C.; Hubauer, U.; Loew, T.; Maier, L.; Fischer, M.; et al. Gender differences in cardiometabolic health and disease in a cross-sectional observational obesity study. Biol. Sex Differ. 2022, 13, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, R.; Masouri, M.M.; Khozani, A.A.S.A.; Soltani, S.M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A. Effects of vitamin D supplementation on blood pressure in patients With type 1 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of clinical trials. Health Sci. Rep. 2025, 8, e70524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Engwert, W.; Michałów, J.; Marciniak, J.; Birger, R.; Serwin, N.; Heryć, R.; Polikowska, A.; Goszka, M.; Wojciuk, B.; et al. Oxidative stress markers and inflammation in type 1 and 2 diabetes are affected by BMI, treatment type, and complications. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 23605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, Q.; Yang, X.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, D.; Wang, Y.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Y.; Yang, C.-X.; Pan, J.; et al. Association between baseline and changes in high-sensitive C-reactive protein and metabolic syndrome: A nationwide cohort study and meta-analysis. Nutr. Metab. 2022, 19, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, J.J.; Deo, S.V.; Welsh, P.; MacKay, D.F.; Ho, F.K.; Ferguson, L.D.; Celis-Morales, C.; Gill, J.M.R.; Pell, J.P.; Sattar, N. In which common chronic conditions can (or cannot) obesity and lifestyle factors explain higher concentrations of C-reactive protein? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 5786–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryczkowska, K.; Adach, W.; Janikowski, K.; Banach, M.; Bielecka-Dabrowa, A. Menopause and women’s cardiovascular health: Is it really an obvious relationship? Arch. Med. Sci. 2023, 19, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Liu, L.; Hu, F. Efficacy of vitamin D supplementation on glycaemic control in type 2 diabetes: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 5713–5726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gowdaiah, P.; R, M.; Nirgude, D.; Hosamani, P. High sensitivity C-reactive protein in metabolic syndrome. Int. J. Adv. Med. 2016, 3, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
| Variable | Category | n (%) or M (SD) |
|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | — | 53.04 (7.34), range 40–64 |
| Sex | Male | 896 (43.5) |
| Education | ≥College | 957 (46.4) |
| Household income | ≥Middle–high | 1402 (68.0) |
| Alcohol use (past year) | Yes | 1587 (77.0) |
| Current smoking (cigarette) | Yes | 393 (19.1) |
| WHO PA guideline met | Yes | 957 (46.4) |
| Sleep duration | ≥7 h/day | 1148 (55.7) |
| Obesity | ≥BMI 25 kg/m2 | 824 (40.0) |
| CRP (mg/L) | — | 1.29 (3.09), range 0.2–53.0 |
| Vitamin D (25(OH)D, ng/mL) | — | 24.35 (10.82), range 3.71–102.05 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | — | 24.54 (3.62), range 15.5–40.6 |
| CMRC score (0–5) | — | 1.25 (1.22) |
| 0 | 716 (34.7) | |
| 1 | 581 (28.2) | |
| 2 | 424 (20.6) | |
| 3 | 231 (11.2) | |
| 4 | 93 (4.5) | |
| 5 | 17 (0.8) |
| Variable | CMRC Absent (n = 1721) n (%) or M (SD) | CMRC Present (n = 341) n (%) or M (SD) | χ2/t | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic characteristics | ||||
| Age (years) | 52.81 (7.36) | 54.20 (7.14) | −3.20 | 0.001 |
| Male | 672 (39.1) | 220 (64.5) | 39.90 | <0.001 |
| Education ≥ college | 823 (47.8) | 134 (39.3) | 8.32 | 0.004 |
| Household income (middle–high) | 1180 (68.6) | 222 (65.1) | 1.57 | 0.211 |
| Lifestyle factors | ||||
| Alcohol use (past year, yes) | 1329 (77.2) | 258 (75.7) | 0.39 | 0.531 |
| Current smoker (cigarette) | 294 (17.1) | 99 (29.0) | 26.34 | <0.001 |
| WHO PA guideline met (yes) | 825 (48.0) | 132 (38.7) | 9.74 | 0.002 |
| Average sleep duration (h/day) | 6.86 (1.14) | 6.71 (1.19) | 2.37 | 0.018 |
| Sleep ≥ 7 h/day | 968 (56.2) | 180 (52.8) | 1.38 | 0.240 |
| Anthropometric measures | ||||
| Obese (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2) | 551 (32.0) | 273 (80.1) | 273.80 | <0.001 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 23.90 (3.35) | 27.79 (3.59) | −19.76 | <0.001 |
| Waist circumference (cm) | 83.11 (9.4) | 90.52 (8.6) | −14.29 | <0.001 |
| Clinical and biochemical markers | ||||
| Systolic BP (mmHg) | 117.52 (14.6) | 123.18 (12.9) | −7.24 | <0.001 |
| Diastolic BP (mmHg) | 75.69 (9.5) | 77.82 (8.9) | −4.40 | <0.001 |
| Fasting glucose (mg/dL) | 98.84 (20.9) | 117.97 (35.6) | −15.20 | <0.001 |
| HDL-cholesterol (mg/dL) | 50.59 (14.7) | 42.75 (13.5) | 9.92 | <0.001 |
| Triglycerides (mg/dL) | 118.97 (83.5) | 231.77 (158.3) | −12.30 | <0.001 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 1.22 (3.05) | 1.62 (3.28) | −2.07 | 0.030 |
| Vitamin D (25(OH)D, ng/mL) | 24.08 (7.37) | 22.61 (7.13) | 3.63 | <0.001 |
| Predictor | B | p | aOR | 95% CI for OR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 0.034 | <0.001 | 1.035 | 1.015–1.055 |
| Male sex | −0.505 | <0.001 | 0.603 | 0.449–0.810 |
| Education (≥middle school) | −0.202 | 0.166 | 0.817 | 0.617–1.084 |
| Household income (middle-high) | −0.025 | 0.860 | 0.975 | 0.734–1.296 |
| Current smoking | 0.562 | 0.001 | 1.755 | 1.255–2.453 |
| Alcohol use (past year) | −0.227 | 0.158 | 0.797 | 0.582–1.091 |
| WHO PA guideline met (yes) | −0.344 | 0.010 | 0.709 | 0.545–0.923 |
| Sleep ≥ 7 h/day | −0.033 | 0.801 | 0.967 | 0.748–1.251 |
| CRP 1–3 mg/L | 0.334 | 0.026 | 1.396 | 1.041–1.873 |
| CRP ≥ 3 mg/L | 0.490 | 0.033 | 1.633 | 1.003–2.658 |
| Vitamin D ≥ 20 ng/mL | −0.278 | 0.039 | 0.757 | 0.581–0.987 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 25 kg/m2) | 2.115 | <0.001 | 8.286 | 6.123–11.212 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, C.; Jang, K. Vitamin D, C-Reactive Protein, and Cardiometabolic Risk Clustering in Middle-Aged Adults: Results from the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112762
Lee C, Jang K. Vitamin D, C-Reactive Protein, and Cardiometabolic Risk Clustering in Middle-Aged Adults: Results from the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112762
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Changhee, and Kyeongmin Jang. 2025. "Vitamin D, C-Reactive Protein, and Cardiometabolic Risk Clustering in Middle-Aged Adults: Results from the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES)" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112762
APA StyleLee, C., & Jang, K. (2025). Vitamin D, C-Reactive Protein, and Cardiometabolic Risk Clustering in Middle-Aged Adults: Results from the 2023 Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Biomedicines, 13(11), 2762. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112762







