Integrative Neoepitope Discovery in Glioblastoma via HLA Class I Profiling and AlphaFold2-Multimer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. TCGA Glioblastoma Cohort and Clinical Stratification
2.2. Identification of Missense Neoantigens and MHC Class I Binding Affinity Prediction
2.3. Structural Prediction of Peptide–HLA Class I Complexes
- −
- pLDDT: A per-residue score that estimates the local distance difference test (lDDT-Cα) for each amino acid [36],
- −
- Predicted TM score (pTM): Assesses global folding confidence [21],
- −
- Interface predicted TM score (ipTM): Evaluates the quality and spatial positioning of interacting chains within the complex.
2.4. Statistical Analysis of Quantitative Variables
3. Results
3.1. Identification of Immunogenic Somatic Variants in Glioblastoma Through Integrated Genomic Filtering and Neoepitope Prediction
3.2. HLA-A*68:01-Mediated Neoantigen Presentation and Its Immunogenic Potential in Glioblastoma
3.3. Prioritization of Strong-Binding Peptides Based on HLA Allele Affinity Profiles
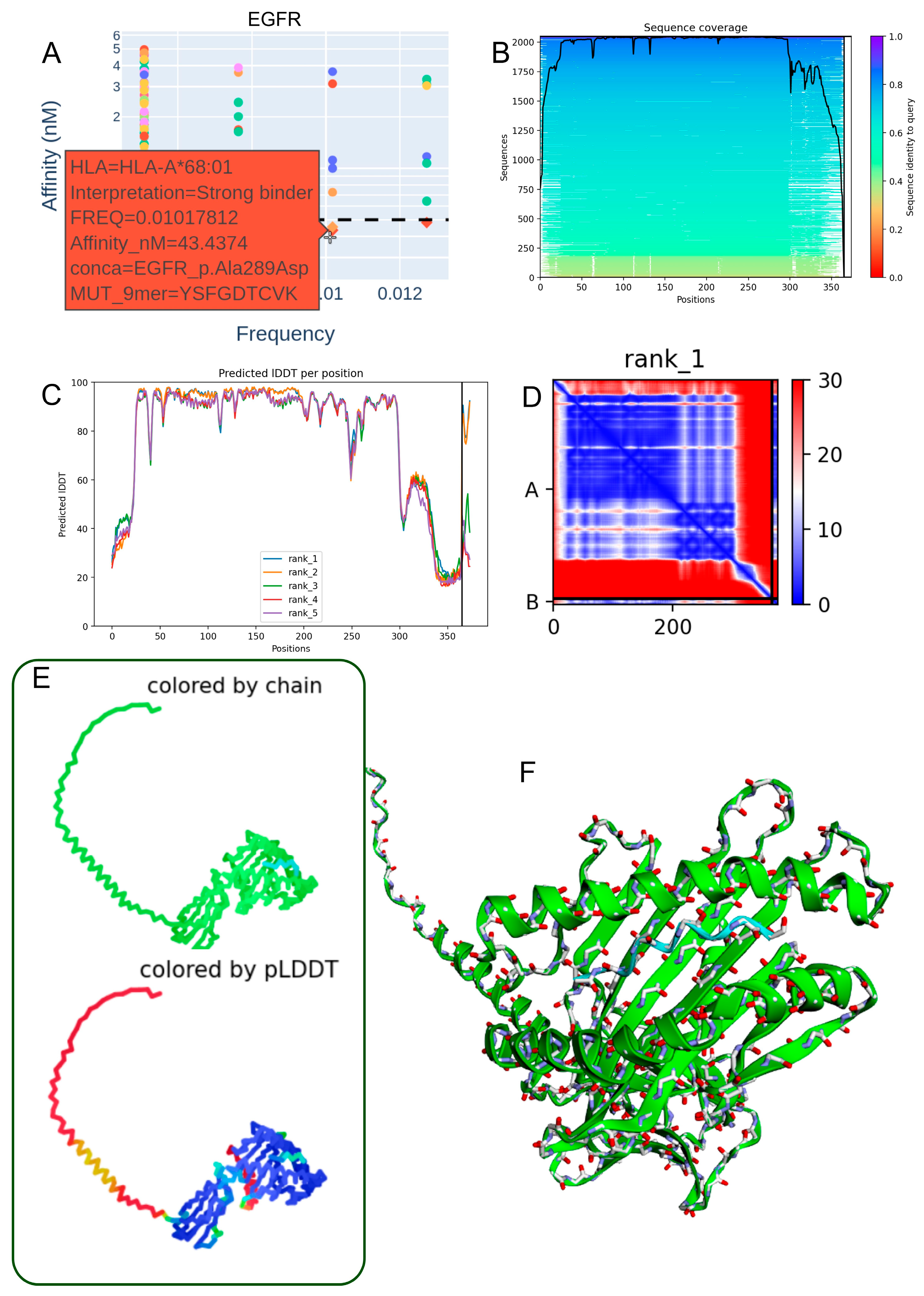
3.4. Structural Modeling of the EGFR p.Ala289Asp-Derived Peptide in Complex with HLA-A*68:01
3.5. Structural Characterization of the PIK3R1 p.Gly376Arg Mutant Peptide–HLA-A*68:01 Complex
3.6. Structural Characterization of the TP53 p.His179Arg Mutant Peptide–HLA-A*68:01 Complex
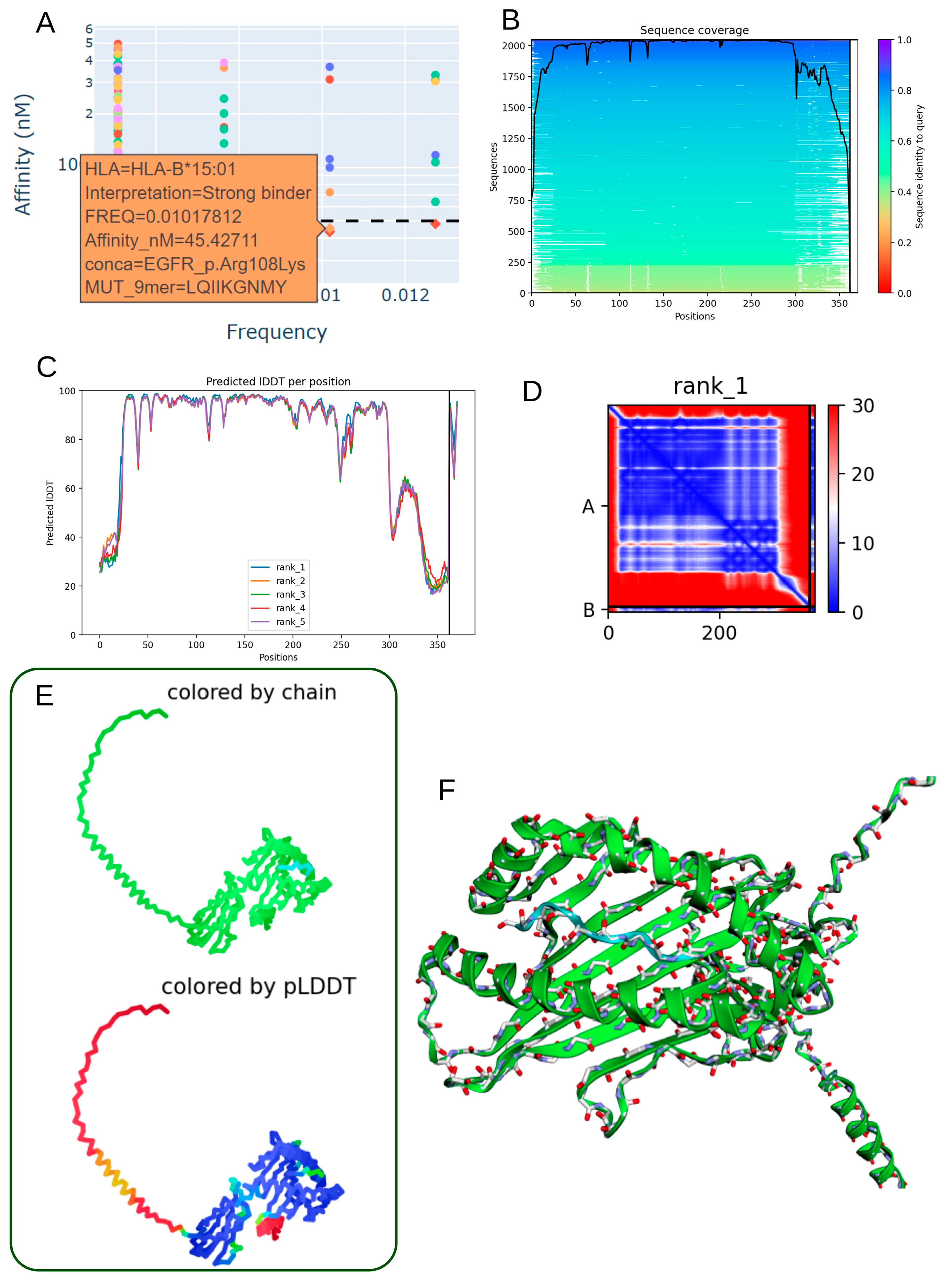
3.7. Structural Characterization of the EGFR p.Arg108Lys Mutant Peptide–HLA-B*15:01 Complex
4. Discussion
Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Koshy, M.; Villano, J.L.; Dolecek, T.A.; Howard, A.; Mahmood, U.; Chmura, S.J.; Weichselbaum, R.R.; McCarthy, B.J. Improved Survival Time Trends for Glioblastoma Using the SEER 17 Population-Based Registries. J. Neurooncol. 2012, 107, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; Van Den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: A summary. Neuro-Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, T.A.; Karajannis, M.A.; Harter, D.H. Glioblastoma Multiforme: State of the Art and Future Therapeutics. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2014, 5, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, M. Glioblastoma: Overview of Disease and Treatment. Clin. J. Oncol. Nurs. 2016, 20, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.W.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H.; et al. The Somatic Genomic Landscape of Glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, D.W.; Jones, S.; Zhang, X.; Lin, J.C.-H.; Leary, R.J.; Angenendt, P.; Mankoo, P.; Carter, H.; Siu, I.-M.; Gallia, G.L.; et al. An Integrated Genomic Analysis of Human Glioblastoma Multiforme. Science 2008, 321, 1807–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Malviya, R. Modifying the electrical, optical, and magnetic properties of cancer cells: A comprehensive approach for cancer management. Med. Adv. 2024, 2, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Chepurna, O.; Sun, T. Drug resistance in glioblastoma: From chemo- to immunotherapy. Cancer Drug Resist. 2023, 6, 688–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Gu, A.; Tang, N.; Zengin, G.; Li, M.-Y.; Liu, Y. Patient-derived xenograft models in pan-cancer: From bench to clinic. Interdiscip. Med. 2025, 3, e20250016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scaringi, C.; De Sanctis, V.; Minniti, G.; Enrici, R.M. Temozolomide-Related Hematologic Toxicity. Oncol. Res. Treat. 2013, 36, 444–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schirrmacher, V. Cancer Vaccines and Oncolytic Viruses Exert Profoundly Lower Side Effects in Cancer Patients than Other Systemic Therapies: A Comparative Analysis. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilf, N.; Kuttruff-Coqui, S.; Frenzel, K.; Bukur, V.; Stevanović, S.; Gouttefangeas, C.; Platten, M.; Tabatabai, G.; Dutoit, V.; Van Der Burg, S.H.; et al. Actively Personalized Vaccination Trial for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. Nature 2019, 565, 240–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Farah, P.; Ondracek, A.; Chen, Y.; Wolinsky, Y.; Stroup, N.E.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2006–2010. Neuro-Oncol. 2013, 15, ii1–ii56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinkernagel, R.M.; Doherty, P.C. Restriction of in Vitro T Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Lymphocytic Choriomeningitis within a Syngeneic or Semiallogeneic System. Nature 1974, 248, 701–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leone, P.; Shin, E.-C.; Perosa, F.; Vacca, A.; Dammacco, F.; Racanelli, V. MHC Class I Antigen Processing and Presenting Machinery: Organization, Function, and Defects in Tumor Cells. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2013, 105, 1172–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reits, E.; Griekspoor, A.; Neijssen, J.; Groothuis, T.; Jalink, K.; Van Veelen, P.; Janssen, H.; Calafat, J.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Neefjes, J. Peptide Diffusion, Protection, and Degradation in Nuclear and Cytoplasmic Compartments before Antigen Presentation by MHC Class I. Immunity 2003, 18, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossjohn, J.; Gras, S.; Miles, J.J.; Turner, S.J.; Godfrey, D.I.; McCluskey, J. T Cell Antigen Receptor Recognition of Antigen-Presenting Molecules. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2015, 33, 169–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.N.; Schreiber, R.D. Neoantigens in Cancer Immunotherapy. Science 2015, 348, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, T.J.; Rubinsteyn, A.; Laserson, U. MHCflurry 2.0: Improved Pan-Allele Prediction of MHC Class I-Presented Peptides by Incorporating Antigen Processing. Cell Syst. 2020, 11, 418–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkizova, S.; Klaeger, S.; Le, P.M.; Li, L.W.; Oliveira, G.; Keshishian, H.; Hartigan, C.R.; Zhang, W.; Braun, D.A.; Ligon, K.L.; et al. A Large Peptidome Dataset Improves HLA Class I Epitope Prediction across Most of the Human Population. Nat. Biotechnol. 2020, 38, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; et al. Highly Accurate Protein Structure Prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, R.; O’Neill, M.; Pritzel, A.; Antropova, N.; Senior, A.; Green, T.; Žídek, A.; Bates, R.; Blackwell, S.; Yim, J.; et al. Protein Complex Prediction with AlphaFold-Multimer. BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, J.; Lee, J. Can AlphaFold2 Predict Protein-Peptide Complex Structures Accurately? BioRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinegger, M.; Söding, J. MMseqs2 Enables Sensitive Protein Sequence Searching for the Analysis of Massive Data Sets. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 1026–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pak, M.A.; Markhieva, K.A.; Novikova, M.S.; Petrov, D.S.; Vorobyev, I.S.; Maksimova, E.S.; Kondrashov, F.A.; Ivankov, D.N. Using AlphaFold to Predict the Impact of Single Mutations on Protein Stability and Function. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0282689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karolchik, D.; Hinrichs, A.S.; Furey, T.S.; Roskin, K.M.; Sugnet, C.W.; Haussler, D.; Kent, W.J. The UCSC Table Browser Data Retrieval Tool. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, D493–D496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cingolani, P.; Platts, A.; Wang, L.L.; Coon, M.; Nguyen, T.; Wang, L.; Land, S.J.; Lu, X.; Ruden, D.M. A Program for Annotating and Predicting the Effects of Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms, SnpEff: SNPs in the Genome of Drosophila Melanogaster Strain W1118; Iso-2; Iso-3. Fly 2012, 6, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, J.; Pujar, S.; Loveland, J.E.; Astashyn, A.; Bennett, R.; Berry, A.; Cox, E.; Davidson, C.; Ermolaeva, O.; Farrell, C.M.; et al. A Joint NCBI and EMBL-EBI Transcript Set for Clinical Genomics and Research. Nature 2022, 604, 310–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidney, J.; Peters, B.; Frahm, N.; Brander, C.; Sette, A. HLA Class I Supertypes: A Revised and Updated Classification. BMC Immunol. 2008, 9, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrieta-Bolaños, E.; Hernández-Zaragoza, D.I.; Barquera, R. An HLA Map of the World: A Comparison of HLA Frequencies in 200 Worldwide Populations Reveals Diverse Patterns for Class I and Class II. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 866407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barker, D.J.; Maccari, G.; Georgiou, X.; Cooper, M.A.; Flicek, P.; Robinson, J.; Marsh, S.G.E. The IPD-IMGT/HLA Database. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D1053–D1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, G.; Lee, S.; Levy Karin, E.; Kim, H.; Moriwaki, Y.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M.; Mirdita, M. Easy and Accurate Protein Structure Prediction Using ColabFold. Nat. Protoc. 2025, 20, 620–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidi, A.; Møller, M.H.; Malhis, N.; Bui, J.M.; Gsponer, J. AlphaFold-Multimer Accurately Captures Interactions and Dynamics of Intrinsically Disordered Protein Regions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2406407121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariani, V.; Biasini, M.; Barbato, A.; Schwede, T. lDDT: A Local Superposition-Free Score for Comparing Protein Structures and Models Using Distance Difference Tests. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2722–2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Guan, P.; Flower, D.R. Quantitative Structure–Activity Relationships and the Prediction of MHC Supermotifs. Methods 2004, 34, 444–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro, M.; Sipos, B.; Pieper, N.; Biskup, S. Major Histocompatibility Complex Class 1 (MHC1) Loss among Patients with Glioblastoma (GBM). J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, e14523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butt, N.S.; Kurdi, M.; Fadul, M.M.; Hakamy, S.; Addas, B.M.J.; Faizo, E.; Alkhayyat, S.; Bamaga, A.K.; Alsinani, T.; Katib, Y.; et al. Major Histocompatibility Class-I (MHC-I) Downregulation in Glioblastoma Is a Poor Prognostic Factor but Not a Predictive Indicator for Treatment Failure. Pathol.—Res. Pract. 2023, 250, 154816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Middleton, D.; Menchaca, L.; Rood, H.; Komerofsky, R. New Allele Frequency Database: Http://Www.Allelefrequencies.Net. Tissue Antigens 2003, 61, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Xu, J.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2009–2013. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 18, v1–v75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Liao, P.; Vecchione-Koval, T.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2010–2014. Neuro-Oncol. 2017, 19, v1–v88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz-Robles, D.; Reyes, P.A.; Monteón-Padilla, V.M.; Ortiz-Muñiz, A.R.; Vargas-Alarcón, G. MHC Class I and Class II Genes in Mexican Patients with Chagas Disease. Hum. Immunol. 2004, 65, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukushima, T.; Favereaux, A.; Huang, H.; Shimizu, T.; Yonekawa, Y.; Nakazato, Y.; Ohagki, H. Genetic Alterations in Primary Glioblastomas in Japan. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2006, 65, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Ohgaki, H.; Dessen, P.; Jourde, B.; Horstmann, S.; Nishikawa, T.; Di Patre, P.-L.; Burkhard, C.; Schüler, D.; Probst-Hensch, N.M.; Maiorka, P.C.; et al. Genetic Pathways to Glioblastoma. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 6892–6899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Ross, J.L.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Brat, D.J. Immunopathology of Glioblastoma. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2025, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemeny, H.R.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Farber, S.H.; Champion, C.D.; Lorrey, S.J.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Woroniecka, K.I.; Cui, X.; Shen, S.H.; Rhodin, K.E.; et al. Targeting PD-L1 Initiates Effective Antitumor Immunity in a Murine Model of Cushing Disease. Clin. Cancer Res. Off. J. Am. Assoc. Cancer Res. 2020, 26, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Variable | Level | Male (n = 183) | Female (n = 104) | Total (n = 290) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumor shortest_dimension | mean (sd) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.5 (0.2) | 0.8311346 |
| Tumor longest_dimension | mean (sd) | 1.1 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.4) | 1.1 (0.4) | 0.6930486 |
| mutation_count | mean (sd) | 52.7 (18.9) | 61.4 (21.1) | 55.8 (20.2) | 0.0003163 |
| tmb_nonsynonymous | mean (sd) | 1.8 (0.6) | 2 (0.7) | 1.9 (0.7) | 0.0003700 |
| fraction_genome_altered | mean (sd) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.2 (0.1) | 0.0289327 |
| karnofsky_performance score | mean (sd) | 76.2 (18) | 74.6 (17.1) | 75.7 (17.6) | 0.5465281 |
| disease_free_months | mean (sd) | 8.9 (10.4) | 9.1 (7.9) | 9 (9.6) | 0.8649928 |
| diagnosis_age | mean (sd) | 60.5 (12.9) | 61.9 (13.2) | 61 (13) | 0.3792085 |
| overall_survival_months | mean (sd) | 13.6 (12.9) | 15.7 (16.5) | 14.3 (14.3) | 0.2242429 |
| Gene | Mutation_ID | Mutation_AA | Mutation_CDS | Frequency |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EGFR | COSM191968 | p.R222C | c.664C>T | 1.53 × 102 |
| PIK3R1 | COSM1438284 | p.G376R | c.1126G>A | 1.27 × 102 |
| EGFR | COSM4970170 | p.R108K | c.323G>A | 1.02 × 102 |
| EGFR | COSM21685 | p.A289D | c.866C>A | 1.02 × 102 |
| EGFR | COSM1559807 | p.R252C | c.754C>T | 7.63 × 103 |
| EGFR | COSM6919374 | p.T263P | c.787A>C | 7.63 × 103 |
| TP53 | COSM3403255 | p.C275Y | c.824G>A | 7.63 × 103 |
| TP53 | COSM10889 | p.H179R | c.536A>G | 7.63 × 103 |
| H3F3A | COSM327929 | p.G35R | c.103G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| PIK3CA | COSM12591 | p.M1043V | c.3127A>G | 5.09 × 103 |
| PDGFRA | COSM3409357 | p.E229K | c.685G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| PDGFRA | COSM3409362 | p.L655F | c.1965G>C | 5.09 × 103 |
| PIK3R1 | COSM3410369 | p.K379N | c.1137A>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| EGFR | COSM6951164 | p.G63R | c.187G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| EGFR | COSM7484095 | p.Y270C | c.809A>G | 5.09 × 103 |
| EGFR | COSM2149971 | p.H304Y | c.910C>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| EGFR | COSM2155593 | p.T363I | c.1088C>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| GRM3 | COSM218933 | p.R183C | c.547C>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| JAK2 | COSM29104 | p.R564Q | c.1691G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| ATRX | COSM1716715 | p.R1803H | c.5408G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| DCAF12L2 | COSM385381 | p.P334L | c.1001C>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| DCAF12L2 | COSM1315186 | p.R246H | c.737G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| FLNA | COSM3406147 | p.V1240M | c.3718G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| PTEN | COSM5135 | p.G36R | c.106G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| PTEN | COSM5045 | p.S170N | c.509G>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| RABEP1 | COSM7296694 | p.T279M | c.836C>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| TP53 | COSM4781979 | p.D281A | c.842A>C | 5.09 × 103 |
| TP53 | COSM10943 | p.D281H | c.841G>C | 5.09 × 103 |
| TP53 | COSM99626 | p.C238F | c.713G>T | 5.09 × 103 |
| TP53 | COSM11218 | p.T155N | c.464C>A | 5.09 × 103 |
| Identifier | Frequency | Mut_9mer | Position | Legacy Mutation Id | Hla | Affinity_Nm |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PIK3R1_p.Gly376Arg | 1.27 × 102 | YTLTLRKGR | 9 | COSM1438284 | HLA-A*68:01 | 48.161 |
| EGFR_p.Arg108Lys | 1.02 × 102 | LQIIKGNMY | 5 | COSM4970170 | HLA-B*15:01 | 45.427 |
| EGFR_p.Ala289Asp | 1.02 × 102 | DTCVKKCPR | 1 | COSM21685 | HLA-A*68:01 | 43.446 |
| EGFR_p.Ala289Asp | 1.02 × 102 | YSFGDTCVK | 5 | COSM21685 | HLA-A*68:01 | 43.437 |
| TP53_p.His179Arg | 7.63 × 103 | EVVRRCPHR | 9 | COSM10889 | HLA-A*68:01 | 34.725 |
| PDGFRA_p.Leu655Phe | 5.09 × 103 | GPHFNIVNL | 4 | COSM3409362 | HLA-B*07:02 | 46.540 |
| PDGFRA_p.Leu655Phe | 5.09 × 103 | HLGPHFNIV | 6 | COSM3409362 | HLA-A*02:01 | 37.647 |
| PDGFRA_p.Leu655Phe | 5.09 × 103 | IMTHLGPHF | 9 | COSM3409362 | HLA-B*15:01 | 49.837 |
| EGFR_p.Gly63Arg | 5.09 × 103 | VLRNLEITY | 3 | COSM6951164 | HLA-B*15:01 | 37.790 |
| EGFR_p.Tyr270Cys | 5.09 × 103 | LMLCNPTTY | 4 | COSM7484095 | HLA-B*15:01 | 28.328 |
| GRM3_p.Arg183Cys | 5.09 × 103 | LSDKSCYDY | 6 | COSM218933 | HLA-A*01:01 | 38.499 |
| ATRX_p.Arg1803His | 5.09 × 103 | VMKKHAHIL | 5 | COSM1716715 | HLA-B*08:01 | 35.925 |
| DCAF12L2_p.Arg246His | 5.09 × 103 | PVYAHIHPR | 7 | COSM1315186 | HLA-A*68:01 | 41.433 |
| PTEN_p.Gly36Arg | 5.09 × 103 | IAMRFPAER | 4 | COSM5135 | HLA-A*68:01 | 36.127 |
| TP53_p.Thr155Asn | 5.09 × 103 | DSTPPPGNR | 8 | COSM11218 | HLA-A*68:01 | 36.966 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Francés, R.; Bonifacio-Mundaca, J.; Casafont, Í.; Desterke, C.; Mata-Garrido, J. Integrative Neoepitope Discovery in Glioblastoma via HLA Class I Profiling and AlphaFold2-Multimer. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112715
Francés R, Bonifacio-Mundaca J, Casafont Í, Desterke C, Mata-Garrido J. Integrative Neoepitope Discovery in Glioblastoma via HLA Class I Profiling and AlphaFold2-Multimer. Biomedicines. 2025; 13(11):2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112715
Chicago/Turabian StyleFrancés, Raquel, Jenny Bonifacio-Mundaca, Íñigo Casafont, Christophe Desterke, and Jorge Mata-Garrido. 2025. "Integrative Neoepitope Discovery in Glioblastoma via HLA Class I Profiling and AlphaFold2-Multimer" Biomedicines 13, no. 11: 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112715
APA StyleFrancés, R., Bonifacio-Mundaca, J., Casafont, Í., Desterke, C., & Mata-Garrido, J. (2025). Integrative Neoepitope Discovery in Glioblastoma via HLA Class I Profiling and AlphaFold2-Multimer. Biomedicines, 13(11), 2715. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines13112715







