Beyond Chemotherapy: Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders
Abstract
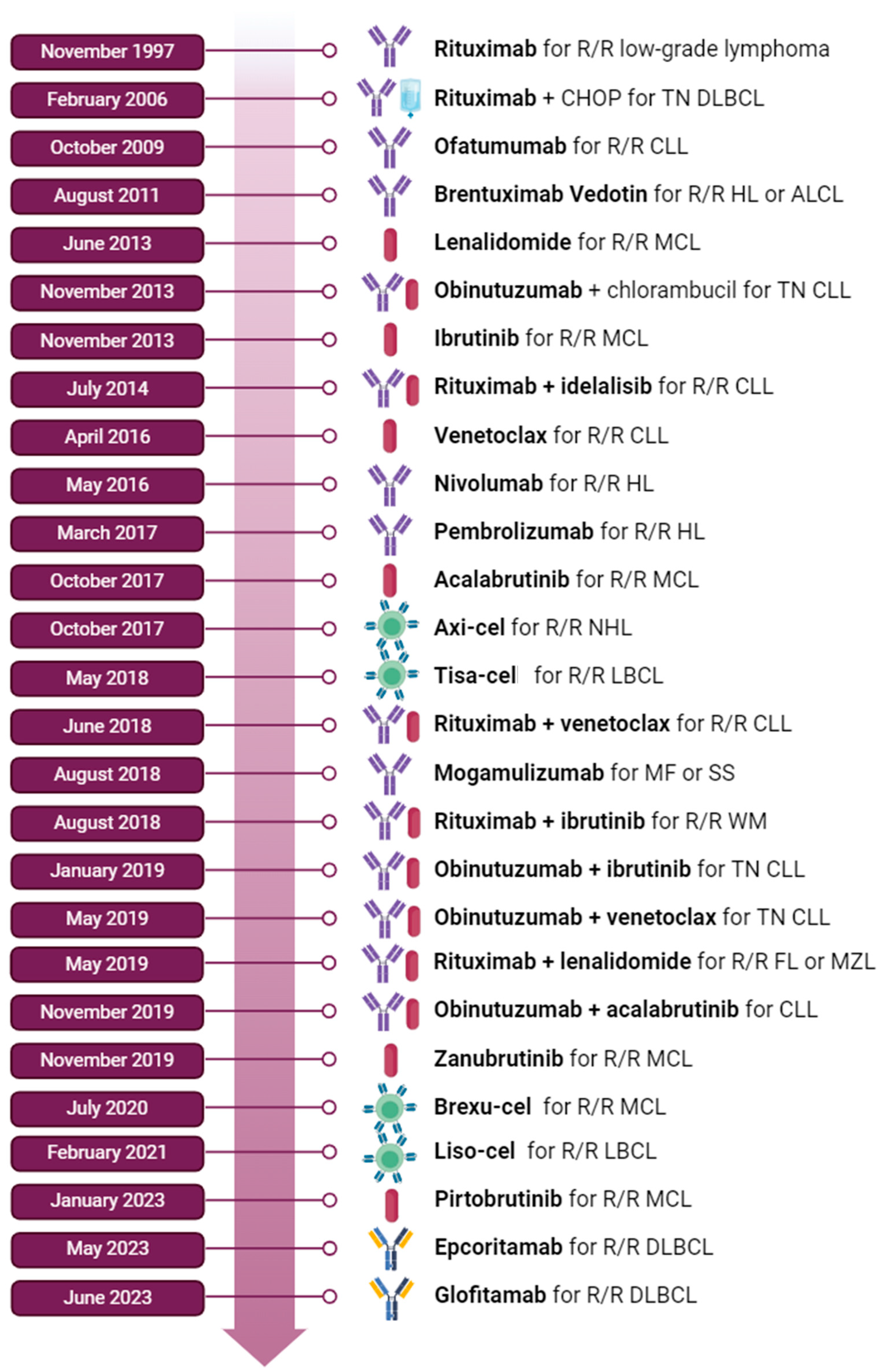
1. Introduction
2. Early-Phase/Basket Trials
3. Indolent NHL
3.1. Follicular Lymphoma (FL)
3.2. Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL)
4. Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL)
5. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) and Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma (PMBCL)
6. Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma (PCNSL)
7. Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL)
8. Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma, Not Otherwise Specified (PTCL-NOS)
9. Cellular Therapy in Lymphoproliferative Disorders
9.1. Indolent Lymphomas
9.2. CLL
9.3. DLBCL
9.4. PMBCL
9.5. PCNSL
9.6. HL
9.7. T-Cell Malignancies
10. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/nhl.html (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Hodgkin Lymphoma—Cancer Stat Facts. Available online: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/hodg.html (accessed on 13 March 2024).
- Frick, M.A.; Vachani, C.C.; Hampshire, M.K.; Bach, C.; Arnold-Korzeniowski, K.; Metz, J.M.; Hill-Kayser, C.E. Patient-Reported Survivorship Care Practices and Late Effects After Treatment of Hodgkin and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. JCO Clin. Cancer Inform. 2018, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.C.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Morschhauser, F.; Cartron, G.; Joergensen, J.M.; Bachy, E.; Bories, P.; Campbell, V.; Fontanet, B.; Patah, P.P.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Golcadomide, a Novel Cereblon E3 Ligase Modulator (CELMoD) Agent, Combined with Rituximab in a Phase 1/2 Open-Label Study of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 4496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, M.; Zhou, K.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.; Jin, Z.; Li, L.; Jing, H.; Peng, Z.; et al. A Novel Dual Covalent and Non-Covalent Next Generation Inhibitor of Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase LP-168 in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory B Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma: Safety and Efficacy Results from a Phase 1 Study. Blood 2023, 142, 4400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grommes, C.; Tun, H.; Rosenthal, A.C.; Lunning, M.A.; Ramchandren, R.; Regales, L.; Zhao, W.; Lane, M.; Wang, C.; von Roemeling, R.; et al. Takeaim Lymphoma: An Open-Label, Dose Escalation and Expansion Trial of Emavusertib (CA-4948) in Combination with Ibrutinib in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2023, 142, 4497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, J.; Yu, W.; Jin, Z.; Zhou, K.; Yang, H.; Li, F.; Li, L.; Hu, M.; Zhou, X.; Jin, J. A Phase I Study Evaluating the Safety, Tolerability, Pharmacokinetics, and Preliminary Antitumor Activity of Dual CK1ε/PI3Kδ Inhibitor HZ-H08905 in Adult Patients with Relapsed and/or Refractory Hematologic Malignancies. Blood 2023, 142, 4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, K.; Jing, H.; Wu, J.; Yang, H.; Bai, Y.; Fang, K.; Liu, Z.; Zhu, J.; Cheah, C.Y. First Report of Phase 1 Studies of DZD8586, a BBB Penetrant LYN/BTK Dual Inhibitor, in Patients with B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL). Blood 2023, 142, 4465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spurgeon, S.; Mei, M.; Barr, P.M.; Barrientos, J.; de Vos, S.; Furman, R.; Patel, K.; Thompson, P.; Choi, M.Y.; Kallam, A.; et al. P1200: Zilovertamab vedotin (mk-2140) in relapsed or refractory (r/r) non-hodgkin lymphoma (nhl): Updated results from the phase 1 waveline-001 study. Hemasphere 2023, 7, e54506b2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habermann, T.M.; LaPlant, B.; Micallef, I.; Finnes, H.D.; Schimke, J.; Klebig, R.; Hanley, N.; King, R.L.; Witzig, T.E.; Markovic, S. A First in Human Phase I Trial (LS1681) of Abraxane/Rituximab 160 Nm Nanoparticle (AR160) in Relapsed Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas Including Transformed Follicular Lymphoma: A Final Report. Blood 2023, 142, 4471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F.; Nastoupil, L.; Feugier, P.; Schiano de Colella, J.-M.; Tilly, H.; Palomba, M.L.; Bachy, E.; Fruchart, C.; Libby, E.N.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; et al. Six-Year Results From RELEVANCE: Lenalidomide Plus Rituximab (R2) Versus Rituximab-Chemotherapy Followed by Rituximab Maintenance in Untreated Advanced Follicular Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 3239–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strati, P.; Feng, L.; Westin, J.; Nair, R.; Fayad, L.; Rodriguez, M.A.; Chihara, D.; Malpica, L.; Henderson, J.; Gallardo, M.; et al. Addition of Acalabrutinib to Lenalidomide and Rituximab Induces High Complete Response Rates in Patients with Previously Untreated Follicular Lymphoma: Results of a Phase II Study. Blood 2023, 142, 983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Sehn, L.H.; Matasar, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Assouline, S.; Giri, P.; Kuruvilla, J.; Canales, M.; Dietrich, S.; Fay, K.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Mosunetuzumab, a Bispecific Antibody, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1055–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, L.; Okwali, M.; Ghione, P.; Owens, C.; Hamlin, P.A.; Lue, J.K.; Epstein-Peterson, Z.D.; Palomba, M.L.; Kumar, A.; Torka, P.; et al. Subcutaneous (SC) Mosunetuzumab (Mosun) As First-Line Therapy for Patients (Pts) with High Tumor-Burden Follicular Lymphoma (FL): First Results of a Multicenter Phase 2 Study. Blood 2023, 142, 604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F.; Patel, K.; Bobillo, S.; Cordoba, R.; Eyre, T.A.; Bishton, M.; Houot, R.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zou, L.; Osborne, W.; et al. Preliminary Findings of a Phase Ib/II Trial Indicate Manageable Safety and Promising Efficacy for Mosunetuzumab in Combination with Lenalidomide (M+Len) in Previously Untreated (1L) Follicular Lymphoma (FL). Blood 2023, 142, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linton, K.; Jurczak, W.; Lugtenburg, P.; Gyan, E.; Sureda Balari, A.M.; Christensen, J.H.; Hess, B.; Tilly, H.; Cordoba, R.; Lewis, D.; et al. Epcoritamab SC Monotherapy Leads to Deep and Durable Responses in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: First Data Disclosure from the Epcore NHL-1 Follicular Lymphoma Dose-Expansion Cohort. Blood 2023, 142, 1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchings, M.; Morschhauser, F.; Iacoboni, G.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Offner, F.C.; Sureda, A.; Salles, G.; Martínez-Lopez, J.; Crump, M.; Thomas, D.N.; et al. Glofitamab, a Novel, Bivalent CD20-Targeting T-Cell–Engaging Bispecific Antibody, Induces Durable Complete Remissions in Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphoma: A Phase I Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 1959–1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannerji, R.; Arnason, J.E.; Advani, R.H.; Brown, J.R.; Allan, J.N.; Ansell, S.M.; Barnes, J.A.; O’Brien, S.M.; Chávez, J.C.; Duell, J.; et al. Odronextamab, a Human CD20×CD3 Bispecific Antibody in Patients with CD20-Positive B-Cell Malignancies (ELM-1): Results from the Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Cohort in a Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 1 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2022, 9, e327–e339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falchi, L.; Vardhana, S.A.; Salles, G.A. Bispecific Antibodies for the Treatment of B-Cell Lymphoma: Promises, Unknowns, and Opportunities. Blood 2023, 141, 467–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Mayer, J.; Flowers, C.R.; Bijou, F.; Oliveira, A.C.D.; Song, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Merli, M.; Bouabdallah, K.; Ganly, P.; et al. ROSEWOOD: A Phase II Randomized Study of Zanubrutinib Plus Obinutuzumab Versus Obinutuzumab Monotherapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 5107–5117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alderuccio, J.; Alencar, A.J.; Schatz, J.H.; Kuker, R.; Pongas, G.; Reis, I.M.; Spiegel, J.Y.; Andara, L.M.; Lekakis, L.J.; Gyedu, J.S.; et al. Limited Duration Loncastuximab Tesirine with Rituximab Induces High Complete Metabolic Response Rate in High-Risk Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma—A Phase 2 Study. Blood 2023, 142, 984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eskelund, C.W.; Dahl, C.; Hansen, J.W.; Westman, M.; Kolstad, A.; Pedersen, L.B.; Montano-Almendras, C.P.; Husby, S.; Freiburghaus, C.; Ek, S.; et al. TP53 Mutations Identify Younger Mantle Cell Lymphoma Patients Who Do Not Benefit from Intensive Chemoimmunotherapy. Blood 2017, 130, 1903–1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Soumerai, J.; Abramson, J.S.; Barnes, J.A.; Caron, P.; Chabowska, M.; Devlin, M.; Dogan, A.; Falchi, L.; Garcia, R.N.; et al. A Multicenter Phase 2 Trial of Zanubrutinib, Obinutuzumab, and Venetoclax (BOVen) in Patients with Treatment-Naïve, TP53-Mutant Mantle Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visco, C.; Di Rocco, A.; Evangelista, A.; Quaglia, F.M.; Tisi, M.C.; Morello, L.; Zilioli, V.R.; Rusconi, C.; Hohaus, S.; Sciarra, R.; et al. Outcomes in First Relapsed-Refractory Younger Patients with Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Results from the MANTLE-FIRST Study. Leukemia 2021, 35, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rule, S.; Dreyling, M.; Goy, A.; Hess, G.; Auer, R.; Kahl, B.; Hernández-Rivas, J.-Á.; Qi, K.; Deshpande, S.; Parisi, L.; et al. Ibrutinib for the Treatment of Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Extended 3.5-Year Follow up from a Pooled Analysis. Haematologica 2019, 104, e211–e214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Jurczak, W.; Trněný, M.; Belada, D.; Wrobel, T.; Ghosh, N.; Keating, M.M.; van Meerten, T.; Alvarez, R.F.; von Keudell, G.; et al. Ibrutinib Combined with Venetoclax in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Mantle Cell Lymphoma: Primary Analysis Results from the Randomized Phase 3 Sympatico Study. Blood 2023, 142, LBA-2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, J.B.; Shah, N.N.; Jurczak, W.; Zinzani, P.L.; Cheah, C.Y.; Eyre, T.A.; Ujjani, C.S.; Koh, Y.; Kim, W.S.; Nasta, S.D.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Mantle Cell Lymphoma (MCL) Patients with Prior cBTKi: Safety and Efficacy Including High-Risk Subgroup Analyses from the Phase 1/2 BRUIN Study. Blood 2023, 142, 981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sawaf, O.; Zhang, C.; Tandon, M.; Sinha, A.; Fink, A.-M.; Robrecht, S.; Samoylova, O.; Liberati, A.M.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Opat, S.; et al. Venetoclax plus Obinutuzumab versus HLorambucil plus Obinutuzumab for Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (CLL14): Follow-up Results from a Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 1188–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichhorst, B.; Niemann, C.; Kater, A.P.; Fürstenau, M.; Von Tresckow, J.; Zhang, C.; Robrecht, S.; Gregor, M.; Juliusson, G.; Thornton, P.; et al. A Randomized Phase III Study of Venetoclax-Based Time-Limited Combination Treatments (RVe, GVe, GIVe) Vs Standard Chemoimmunotherapy (CIT: FCR/BR) in Frontline Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (CLL) of Fit Patients: First Co-Primary Endpoint Analysis of the International Intergroup GAIA (CLL13) Trial. Blood 2021, 138, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Kipps, T.J.; Jacobs, R.; Opat, S.; Barr, P.M.; Tedeschi, A.; Trentin, L.; Bannerji, R.; et al. Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib plus Venetoclax for First-Line Treatment of CLL: Primary Analysis of the CAPTIVATE FD Cohort. Blood 2022, 139, 3278–3289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Owen, C.; Moreno, C.; Follows, G.; Munir, T.; Levin, M.-D.; Benjamini, O.; Janssens, A.; Osterborg, A.; Robak, T.; et al. Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib-Venetoclax in Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and Comorbidities. NEJM Evid. 2022, 1, EVIDoa2200006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanafelt, T.D.; Wang, X.V.; Hanson, C.A.; Paietta, E.M.; O’Brien, S.; Barrientos, J.; Jelinek, D.F.; Braggio, E.; Leis, J.F.; Zhang, C.C.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes for Ibrutinib-Rituximab and Chemoimmunotherapy in CLL: Updated Results of the E1912 Trial. Blood 2022, 140, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmen, P.; Pitchford, A.; Bloor, A.; Broom, A.; Young, M.; Kennedy, B.; Walewska, R.; Furtado, M.; Preston, G.; Neilson, J.R.; et al. Ibrutinib and Rituximab versus Fludarabine, Cyclophosphamide, and Rituximab for Patients with Previously Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (FLAIR): Interim Analysis of a Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2023, 24, 535–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharman, J.P.; Egyed, M.; Jurczak, W.; Skarbnik, A.; Pagel, J.M.; Flinn, I.W.; Kamdar, M.; Munir, T.; Walewska, R.; Corbett, G.; et al. Acalabrutinib with or without Obinutuzumab versus HLorambucil and Obinutuzmab for Treatment-Naive Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia (ELEVATE TN): A Randomised, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2020, 395, 1278–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, C.; Greil, R.; Demirkan, F.; Tedeschi, A.; Anz, B.; Larratt, L.; Simkovic, M.; Novak, J.; Strugov, V.; Gill, D.; et al. First-Line Treatment of Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia with Ibrutinib plus Obinutuzumab versus Chlorambucil plus Obinutuzumab: Final Analysis of the Randomized, Phase III iLLUMINATE Trial. Haematologica 2022, 107, 2108–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, C.S.; Brown, J.R.; Kahl, B.S.; Ghia, P.; Giannopoulos, K.; Jurczak, W.; Šimkovič, M.; Shadman, M.; Österborg, A.; Laurenti, L.; et al. Zanubrutinib versus Bendamustine and Rituximab in Untreated Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (SEQUOIA): A Randomised, Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barr, P.M.; Owen, C.; Robak, T.; Tedeschi, A.; Bairey, O.; Burger, J.A.; Hillmen, P.; Coutre, S.E.; Dearden, C.; Grosicki, S.; et al. Up to 8-Year Follow-up from RESONATE-2: First-Line Ibrutinib Treatment for Patients with Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 3440–3450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.; Jones, J.A.; Coutre, S.E.; Mato, A.R.; Hillmen, P.; Tam, C.; Österborg, A.; Siddiqi, T.; Thirman, M.J.; Furman, R.R.; et al. Ibrutinib for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia with 17p Deletion (RESONATE-17): A Phase 2, Open-Label, Multicentre Study. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1409–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, J.N.; Shanafelt, T.; Wiestner, A.; Moreno, C.; O’Brien, S.M.; Li, J.; Krigsfeld, G.; Dean, J.P.; Ahn, I.E. Long-Term Efficacy of First-Line Ibrutinib Treatment for Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia in Patients with TP53 Aberrations: A Pooled Analysis from Four Clinical Trials. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürstenau, M.; Ritgen, M.; Robrecht, S.; Von Tresckow, J.; Zhang, C.; Schilhabel, A.; Gregor, M.; Thornton, P.; Staber, P.B.; Tadmor, T.; et al. First-Line Venetoclax Combinations in Fit Patients with CLL: 4-Year Follow-up and NGS-Based MRD Analysis from the Phase 3 GAIA/CLL13 Trial. Blood 2023, 142, 635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.P.; Harrup, R.; Kipps, T.J.; Eichhorst, B.; Owen, C.J.; Assouline, S.; Lamanna, N.; Robak, T.; Serna, J.d.l.; Jaeger, U.; et al. MURANO: Final 7 Year Follow up and Retreatment Analysis in Venetoclax-Rituximab (VenR)-Treated Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (R/R CLL). Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 239–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davids, M.S.; Fischer, K.; Robrecht, S.; Zhang, C.; Ahn, I.E.; Porro Lurà, M.; Sinai, W.; Chyla, B.; Sail, K.; Pesko, J.; et al. ReVenG: A Phase 2 Study of Venetoclax Plus Obinutuzumab Retreatment in Patients with Relapsed Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia. Blood 2021, 138, 2634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghia, P.; Allan, J.N.; Siddiqi, T.; Wierda, W.G.; Tam, C.S.; Moreno, C.; Tedeschi, A.; Szafer-Glusman, E.; Zhou, C.; Abbazio, C.; et al. Fixed-Duration Ibrutinib + Venetoclax in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia (Cll)/Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (Sll): 4-Y Follow-up from the Fd Cohort of the Phase 2 Captivate Study. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 238–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woyach, J.A.; Brown, J.R.; Ghia, P.; Roeker, L.E.; Patel, K.; Eyre, T.A.; Munir, T.; Lech-Maranda, E.; Lamanna, N.; Tam, C.S.; et al. Pirtobrutinib in Post-cBTKi CLL/SLL: ~30 Months Follow-up and Subgroup Analysis With/Without Prior BCL2i from the Phase 1/2 BRUIN Study. Blood 2023, 142, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kater, A.; Eradat, H.; Niemann, C.; Offner, F.; Poulsen, C.B.; Hoyer, T.; Bellido, M.; Shadman, M.; Oki, T.; Kuznetsova, A.; et al. Epcoritamab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia: Results from the Phase 1b/2 EPCORE CLL-1 Trial Expansion Cohort. In Proceedings of the 2023 International Workshop on CLL, Boston, MA, USA, 6–9 October 2023; Abstract 1546171. [Google Scholar]
- Villanueva, M.T. BTK Degraders Tackle Drug Resistance. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2024, 23, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, A.R.; Wierda, W.G.; Ai, W.Z.; Flinn, I.W.; Tees, M.; Patel, M.R.; Patel, K.; O’Brien, S.; Bond, D.A.; Roeker, L.E.; et al. NX-2127-001, a First-in-Human Trial of NX-2127, a Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase-Targeted Protein Degrader, in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia and B-Cell Malignancies. Blood 2022, 140, 2329–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swerdlow, S.H.; Campo, E.; Pileri, S.A.; Harris, N.L.; Stein, H.; Siebert, R.; Advani, R.; Ghielmini, M.; Salles, G.A.; Zelenetz, A.D.; et al. The 2016 Revision of the World Health Organization Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms. Blood 2016, 127, 2375–2390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tilly, H.; Morschhauser, F.; Sehn, L.H.; Friedberg, J.W.; Trněný, M.; Sharman, J.P.; Herbaux, C.; Burke, J.M.; Matasar, M.; Rai, S.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 351–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westin, J.; Davis, R.E.; Feng, L.; Hagemeister, F.; Steiner, R.; Lee, H.J.; Fayad, L.; Nastoupil, L.; Ahmed, S.; Rodriguez, A.; et al. Smart Start: Rituximab, Lenalidomide, and Ibrutinib in Patients with Newly Diagnosed Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 41, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Westin, J.; Steiner, R.E.; Chihara, D.; Ahmed, S.; Jain, P.; Malpica, L.; Iyer, S.P.; Fayad, L.; Nair, R.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Smart Stop: Lenalidomide, Tafasitamab, Rituximab, and Acalabrutinib Alone and with Combination Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Newly Diagnosed Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Herrera, A.F.; Flowers, C.R.; Kamdar, M.K.; McMillan, A.; Hertzberg, M.; Assouline, S.; Kim, T.M.; Kim, W.S.; Ozcan, M.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 155–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sehn, L.H.; Hertzberg, M.; Opat, S.; Herrera, A.F.; Assouline, S.; Flowers, C.R.; Kim, T.M.; McMillan, A.; Ozcan, M.; Safar, V.; et al. Polatuzumab Vedotin plus Bendamustine and Rituximab in Relapsed/Refractory DLBCL: Survival Update and New Extension Cohort Data. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 533–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salles, G.; Duell, J.; Barca, E.G.; Tournilhac, O.; Jurczak, W.; Liberati, A.M.; Nagy, Z.; Obr, A.; Gaidano, G.; André, M.; et al. Tafasitamab plus Lenalidomide in Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (L-MIND): A Multicentre, Prospective, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Study. Lancet Oncol. 2020, 21, 978–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qualls, D.A.; Lambert, N.; Caimi, P.F.; Merrill, M.; Pullarkat, P.; Godby, R.C.; Bond, D.A.; Wehmeyer, G.T.; Romancik, J.; Amoozgar, B.; et al. Tafasitamab and Lenalidomide in Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Real-World Outcomes in a Multicenter Retrospective Study. Blood 2023, 142, 2327–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieblemont, C.; Phillips, T.; Ghesquieres, H.; Cheah, C.Y.; Clausen, M.R.; Cunningham, D.; Do, Y.R.; Feldman, T.; Gasiorowski, R.; Jurczak, W.; et al. Epcoritamab, a Novel, Subcutaneous CD3xCD20 Bispecific T-Cell–Engaging Antibody, in Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Dose Expansion in a Phase I/II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2238–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, M.J.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Bachy, E.; Corradini, P.; Iacoboni, G.; Khan, C.; Wróbel, T.; Offner, F.; Trněný, M.; et al. Glofitamab for Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 2220–2231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Assouline, S.; Sehn, L.H.; Schuster, S.J.; Yoon, S.-S.; Yoon, D.H.; Matasar, M.J.; Bosch, F.; Kim, W.S.; Nastoupil, L.J.; et al. Single-Agent Mosunetuzumab Shows Durable Complete Responses in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Lymphomas: Phase I Dose-Escalation Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 40, 481–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budde, L.E.; Olszewski, A.J.; Assouline, S.; Lossos, I.S.; Diefenbach, C.; Kamdar, M.; Ghosh, N.; Modi, D.; Sabry, W.; Naik, S.; et al. Mosunetuzumab with Polatuzumab Vedotin in Relapsed or Refractory Aggressive Large B Cell Lymphoma: A Phase 1b/2 Trial. Nat. Med. 2024, 30, 229–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olszewski, A.J.; Eradat, H.; Avigdor, A.; Horowitz, N.A.; Babu, S.; Levi, I.; McKinney, M.; Lee, S.T.; Burgues, J.M.B.; Izquierdo, A.R.; et al. Mosunetuzumab and Polatuzumab Vedotin Demonstrates Preliminary Efficacy in Elderly Unfit/Frail Patients with Previously Untreated Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyappan, S.; Kim, W.S.; Kim, T.M.; Walewski, J.; Cho, S.G.; Jarque, I.; Iskierka-Jazdzewska, E.; Poon, M.; Oh, S.Y.; Lim, F.L.W.I.; et al. Final Analysis of the Phase 2 ELM-2 Study: Odronextamab in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL). Blood 2023, 142, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.T.; Mensah, F.; Modi, D.; Fossa, A.; Kim, W.S.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Sawalha, Y.; Sevindik, Ö.G.; Norasetthada, L.; Santoro, A.; et al. Zilovertamab Vedotin (MK 2140) in Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma (DLBCL): Early Results from the Phase 2 waveLINE-004 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41 (Suppl. S16). [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giulino-Roth, L.; O’Donohue, T.; Chen, Z.; Bartlett, N.L.; LaCasce, A.; Martin-Doyle, W.; Barth, M.J.; Davies, K.; Blum, K.A.; Christian, B.; et al. Outcomes of Adults and Children with Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma Treated with Dose-Adjusted EPOCH-R. Br. J. Haematol. 2017, 179, 739–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Thieblemont, C.; Melnichenko, V.; Bouabdallah, K.; Walewski, J.; Majlis, A.; Fogliatto, L.M.; Martin Garcia-Sancho, A.; Christian, B.; Gulbas, Z.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Final Analysis of KEYNOTE-170. Blood J. 2023, 142, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Pellegrini, C.; Chiappella, A.; Di Rocco, A.; Salvi, F.; Cabras, M.G.; Argnani, L.; Stefoni, V. Brentuximab Vedotin in Relapsed Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Results from a Phase 2 Clinical Trial. Blood 2017, 129, 2328–2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Santoro, A.; Gritti, G.; Brice, P.; Barr, P.M.; Kuruvilla, J.; Cunningham, D.; Kline, J.; Johnson, N.A.; Mehta-Shah, N.; et al. Nivolumab Combined with Brentuximab Vedotin for Relapsed/Refractory Primary Mediastinal Large B-Cell Lymphoma: Efficacy and Safety from the Phase II CheckMate 436 Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 3081–3089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, L.; Hedvat, C.; Rosenblum, M.K.; Abrey, L.E.; DeAngelis, L.M. Late Relapse in Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma: Clonal Persistence. Neuro-Oncol. 2011, 13, 525–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langner-Lemercier, S.; Houillier, C.; Soussain, C.; Ghesquières, H.; Chinot, O.; Taillandier, L.; Soubeyran, P.; Lamy, T.; Morschhauser, F.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; et al. Primary CNS Lymphoma at First Relapse/Progression: Characteristics, Management, and Outcome of 256 Patients from the French LOC Network. Neuro-Oncol. 2016, 18, 1297–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Tateishi, K.; Niwa, T.; Matsushita, Y.; Tamura, K.; Kinoshita, M.; Tanaka, K.; Fukushima, S.; Takami, H.; Arita, H.; et al. Recurrent Mutations of CD79B and MYD88 Are the Hallmark of Primary Central Nervous System Lymphomas. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2016, 42, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayyar, N.; White, M.D.; Gill, C.M.; Lastrapes, M.; Bertalan, M.; Kaplan, A.; D’Andrea, M.R.; Bihun, I.; Kaneb, A.; Dietrich, J.; et al. MYD88 L265P Mutation and CDKN2A Loss Are Early Mutational Events in Primary Central Nervous System Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphomas. Blood Adv. 2019, 3, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soussain, C.; Malaise, D.; Choquet, S.; Ghesquières, H.; Houillier, C. Long-Lasting CRs after Ibrutinib Monotherapy for Relapse or Refractory Primary CNS Lymphoma (PCNSL) and Primary Vitreoretinal Lymphoma (PVRL): Long-Term Results of the iLOC Study by the Lymphoma Study Association (LYSA) and the French Oculo-Cerebral Lymphoma (LOC) Network (Clinical Trial Number: NCT02542514). Eur. J. Cancer 2023, 189, 112909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Wang, W.; Wei, C.; Zhao, D.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, W. Preliminary Evaluation of Zanubrutinib-Containing Regimens in DLBCL and the Cerebrospinal Fluid Distribution of Zanubrutinib: A 13-Case Series. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 760405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Middleton, R.E.; Sun, H.; Naniong, M.; Ott, C.J.; Mitsiades, C.S.; Wong, K.-K.; Bradner, J.E.; Kaelin, W.G. The Myeloma Drug Lenalidomide Promotes the Cereblon-Dependent Destruction of Ikaros Proteins. Science 2014, 343, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghesquieres, H.; Chevrier, M.; Laadhari, M.; Chinot, O.; Choquet, S.; Moluçon-Chabrot, C.; Beauchesne, P.; Gressin, R.; Morschhauser, F.; Schmitt, A.; et al. Lenalidomide in Combination with Intravenous Rituximab (REVRI) in Relapsed/Refractory Primary CNS Lymphoma or Primary Intraocular Lymphoma: A Multicenter Prospective ‘Proof of Concept’ Phase II Study of the French Oculo-Cerebral Lymphoma (LOC) Network and the Lymphoma Study Association (LYSA). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 621–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tun, H.W.; Johnston, P.B.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Atherton, P.J.; Pederson, L.D.; Koenig, P.A.; Reeder, C.B.; Omuro, A.M.P.; Schiff, D.; O’Neill, B.; et al. Phase 1 Study of Pomalidomide and Dexamethasone for Relapsed/Refractory Primary CNS or Vitreoretinal Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, S.; Yao, Z.; Yan, Z.; Wang, H.; Chu, J.; Zhao, S.; Zhao, X.; Liu, Y. Preliminary Results of a Phase Ⅱ Study of Lenalidomide Combined with Immunochemotherapy in Patients with Primary Central Nervous System Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wirsching, H.-G.; Weller, M.; Balabanov, S.; Roth, P. Targeted Therapies and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Primary CNS Lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayak, L.; Iwamoto, F.M.; LaCasce, A.; Mukundan, S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Chapuy, B.; Armand, P.; Rodig, S.J.; Shipp, M.A. PD-1 Blockade with Nivolumab in Relapsed/Refractory Primary Central Nervous System and Testicular Lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 3071–3073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Radford, J.; Connors, J.M.; Długosz-Danecka, M.; Kim, W.-S.; Gallamini, A.; Ramchandren, R.; Friedberg, J.W.; Advani, R.; Hutchings, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Brentuximab Vedotin in Stage III or IV Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 387, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.S.; Arnason, J.E.; LaCasce, A.S.; Redd, R.; Barnes, J.A.; Sokol, L.; Joyce, R.; Avigan, D.; Neuberg, D.; Takvorian, R.W.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin, Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine for Nonbulky Limited-Stage Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 606–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fornecker, L.-M.; Lazarovici, J.; Aurer, I.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; Gac, A.-C.; Bonnet, C.; Bouabdallah, K.; Feugier, P.; Specht, L.; Molina, L.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin Plus AVD for First-Line Treatment of Early-Stage Unfavorable Hodgkin Lymphoma (BREACH): A Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized, Phase II Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gibb, A.; Pirrie, S.J.; Linton, K.; Warbey, V.; Paterson, K.; Davies, A.J.; Collins, G.P.; Menne, T.; McKay, P.; Fields, P.A.; et al. Results of a UK National Cancer Research Institute Phase II Study of Brentuximab Vedotin Using a Response-Adapted Design in the First-Line Treatment of Patients with Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Unsuitable for Chemotherapy Due to Age, Frailty or Comorbidity (BREVITY). Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evens, A.M.; Advani, R.H.; Helenowski, I.B.; Fanale, M.; Smith, S.M.; Jovanovic, B.D.; Bociek, G.R.; Klein, A.K.; Winter, J.N.; Gordon, L.I.; et al. Multicenter Phase II Study of Sequential Brentuximab Vedotin and Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine Chemotherapy for Older Patients with Untreated Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 3015–3022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.F. Where Does PD-1 Blockade Fit in HL Therapy? Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2018, 2018, 213–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bröckelmann, P.J.; Bühnen, I.; Meissner, J.; Trautmann-Grill, K.; Herhaus, P.; Halbsguth, T.V.; Schaub, V.; Kerkhoff, A.; Mathas, S.; Bormann, M.; et al. Nivolumab and Doxorubicin, Vinblastine, and Dacarbazine in Early-Stage Unfavorable Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Analysis of the Randomized German Hodgkin Study Group Phase II NIVAHL Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 1193–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.F.; LeBlanc, M.L.; Castellino, S.M.; Li, H.; Rutherford, S.C.; Evens, A.M.; Davison, K.; Punnett, A.; Hodgson, D.C.; Parsons, S.K.; et al. SWOG S1826, a Randomized Study of Nivolumab(N)-AVD versus Brentuximab Vedotin(BV)-AVD in Advanced Stage (AS) Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, LBA4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheson, B.D.; Bartlett, N.L.; LaPlant, B.; Lee, H.J.; Advani, R.J.; Christian, B.; Diefenbach, C.S.; Feldman, T.A.; Ansell, S.M. Brentuximab Vedotin plus Nivolumab as First-Line Therapy in Older or Chemotherapy-Ineligible Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma (ACCRU): A Multicentre, Single-Arm, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e808–e815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alinari, L.; Blum, K.A. How I Treat Relapsed Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma after Autologous Stem Cell Transplant. Blood 2016, 127, 287–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fermé, C.; Mounier, N.; Diviné, M.; Brice, P.; Stamatoullas, A.; Reman, O.; Voillat, L.; Jaubert, J.; Lederlin, P.; Colin, P.; et al. Intensive Salvage Therapy with High-Dose Chemotherapy for Patients with Advanced Hodgkin’s Disease in Relapse or Failure after Initial Chemotherapy: Results of the Groupe d’Etudes Des Lymphomes de l’Adulte H89 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2002, 20, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Walewski, J.; Nademanee, A.; Masszi, T.; Agura, E.; Holowiecki, J.; Abidi, M.H.; Chen, A.I.; Stiff, P.; Viviani, S.; et al. Five-Year PFS from the AETHERA Trial of Brentuximab Vedotin for Hodgkin Lymphoma at High Risk of Progression or Relapse. Blood 2018, 132, 2639–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaCasce, A.S.; Bociek, R.G.; Sawas, A.; Caimi, P.; Agura, E.; Matous, J.; Ansell, S.M.; Crosswell, H.E.; Islas-Ohlmayer, M.; Behler, C.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin plus Bendamustine: A Highly Active First Salvage Regimen for Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 132, 40–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatoullas, A.; Ghesquières, H.; Feugier, P.; André, M.; Le Bras, F.; Gac, A.-C.; Borel, C.; Gastinne, T.; Quittet, P.; Morschhauser, F.; et al. Final Results of Brentuximab Vedotin Combined with Ifosfamide-Carboplatin-Etoposide in First Refractory/Relapsed Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Lymphoma Study Association Phase I/II Study. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 3063–3071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuelgasim, K.A.; Alzahrani, M.; Alsharhan, Y.; Khairi, M.; Hommady, M.; Gmati, G.; Salama, H.; Ali, O.; Alahmari, B.; Masuadi, E.M.; et al. Chemoimmunotherapy with Brentuximab Vedotin Combined with Ifosfamide, Gemcitabine, and Vinorelbine Is Highly Active in Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Bone Marrow Transpl. 2019, 54, 1168–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanz, R.; Sureda, A.; de la Cruz, F.; Canales, M.; Gonzalez, A.P.; Pinana, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, B.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin and ESHAP Is Highly Effective as Second-Line Therapy for Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients (Long-Term Results of a Trial by the Spanish GELTAMO Group). Ann. Oncol. 2019, 30, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kersten, M.J.; Driessen, J.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Plattel, W.J.; Morschhauser, F.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Brice, P.; Hutchings, M.; Gastinne, T.; Liu, R.; et al. Combining Brentuximab Vedotin with Dexamethasone, High-Dose Cytarabine and Cisplatin as Salvage Treatment in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: The Phase II HOVON/LLPC Transplant BRaVE Study. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, L.J.; Casulo, C.; Allen, P.B.; Smith, S.E.; Savas, H.; Dillehay, G.L.; Karmali, R.; Pro, B.; Kane, K.L.; Bazzi, L.A.; et al. Pembrolizumab Added to Ifosfamide, Carboplatin, and Etoposide Chemotherapy for Relapsed or Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Multi-Institutional Phase 2 Investigator-Initiated Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol. 2023, 9, 683–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Shah, G.; Schöder, H.; Ganesan, N.; Drill, E.; Hancock, H.; Davey, T.; Perez, L.; Ryu, S.; Sohail, S.; et al. Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab Plus Gemcitabine, Vinorelbine, and Liposomal Doxorubicin as Second-Line Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harker-Murray, P.; Mauz-Körholz, C.; Leblanc, T.; Mascarin, M.; Michel, G.; Cooper, S.; Beishuizen, A.; Leger, K.J.; Amoroso, L.; Buffardi, S.; et al. Nivolumab and Brentuximab Vedotin with or without Bendamustine for R/R Hodgkin Lymphoma in Children, Adolescents, and Young Adults. Blood 2023, 141, 2075–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, R.H.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Bartlett, N.L.; Vose, J.M.; Ramchandren, R.; Feldman, T.A.; LaCasce, A.S.; Christian, B.A.; Ansell, S.M.; Moskowitz, C.H.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin in Combination with Nivolumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: 3-Year Study Results. Blood 2021, 138, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massaro, F.; Meuleman, N.; Bron, D.; Vercruyssen, M.; Maerevoet, M. Brentuximab Vedotin and Pembrolizumab Combination in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Single-Centre Retrospective Analysis. Cancers 2022, 14, 982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Gopal, A.K.; Smith, S.E.; Ansell, S.M.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Engert, A.; Larsen, E.K.; Huebner, D.; et al. Five-Year Survival and Durability Results of Brentuximab Vedotin in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Engert, A.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Timmerman, J.M.; Collins, G.P.; Ramchandren, R.; Cohen, J.B.; et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma After Failure of Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Extended Follow-Up of the Multicohort Single-Arm Phase II CheckMate 205 Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zinzani, P.L.; Lee, H.J.; Armand, P.; Johnson, N.A.; Brice, P.; Radford, J.; Ribrag, V.; Molin, D.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: 2-Year Follow-up of KEYNOTE-087. Blood 2019, 134, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Lesokhin, A.; Borrello, I.; Timmerman, J.; Gutierrez, M.; Zhu, L.; Popa McKiver, M.; Ansell, S.M. A Phase 1b Study of Dual PD-1 and CTLA-4 or KIR Blockade in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Lymphoid Malignancies. Leukemia 2021, 35, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diefenbach, C.S.; Hong, F.; Ambinder, R.F.; Cohen, J.B.; Robertson, M.J.; David, K.A.; Advani, R.H.; Fenske, T.S.; Barta, S.K.; Palmisiano, N.D.; et al. Ipilimumab, Nivolumab, and Brentuximab Vedotin Combination Therapies in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: Phase 1 Results of an Open-Label, Multicentre, Phase 1/2 Trial. Lancet Haematol. 2020, 7, e660–e670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Major, A.; Kline, J.; Karrison, T.G.; Fishkin, P.A.S.; Kimball, A.S.; Petrich, A.M.; Nattam, S.; Rao, K.; Sleckman, B.G.; Cohen, K.; et al. Phase I/II Clinical Trial of Temsirolimus and Lenalidomide in Patients with Relapsed and Refractory Lymphomas. Haematologica 2022, 107, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toukam, M.; Boni, J.P.; Hamadani, M.; Caimi, P.F.; Cruz, H.G.; Wuerthner, J. Exposure-Response Analysis of Camidanlumab Tesirine in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 2023, 91, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamadani, M.; Collins, G.P.; Caimi, P.F.; Samaniego, F.; Spira, A.; Davies, A.; Radford, J.; Menne, T.; Karnad, A.; Zain, J.M.; et al. Camidanlumab Tesirine in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Lymphoma: A Phase 1, Open-Label, Multicentre, Dose-Escalation, Dose-Expansion Study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e433–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothe, A.; Sasse, S.; Topp, M.S.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Hummel, H.; Reiners, K.S.; Dietlein, M.; Kuhnert, G.; Kessler, J.; Buerkle, C.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of the Bispecific Anti-CD30/CD16A Antibody Construct AFM13 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 125, 4024–4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasse, S.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Momotow, J.; Plütschow, A.; Hüttmann, A.; Basara, N.; Koenecke, C.; Martin, S.; Bentz, M.; Grosse-Thie, C.; et al. AFM13 in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma: Final Results of an Open-Label, Randomized, Multicenter Phase II Trial. Leuk. Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Herrera, A.F.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Mehta, A.; Forero-Torres, A.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Armand, P.; Devata, S.; Izquierdo, A.R.; Lossos, I.S.; et al. A Phase 1b Study of AFM13 in Combination with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dave, H.; Terpilowski, M.; Mai, M.; Toner, K.; Grant, M.; Stanojevic, M.; Lazarski, C.; Shibli, A.; Bien, S.A.; Maglo, P.; et al. Tumor-Associated Antigen-Specific T Cells with Nivolumab Are Safe and Persist in Vivo in Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022, 6, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, E.; Swerdlow, S.H.; Harris, N.L.; Pileri, S.; Stein, H.; Jaffe, E.S. The 2008 WHO Classification of Lymphoid Neoplasms and beyond: Evolving Concepts and Practical Applications. Blood 2011, 117, 5019–5032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouYabis, A.N.; Shenoy, P.J.; Sinha, R.; Flowers, C.R.; Lechowicz, M.J. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Front-Line Anthracycline-Based Chemotherapy Regimens for Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. ISRN Hematol. 2011, 2011, 623924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachy, E.; Camus, V.; Thieblemont, C.; Casasnovas, R.-O.; Ysebaert, L.; Damaj, G.L.; Guidez, S.; Pica, G.-M.; Kim, W.S.; Lim, S.T.; et al. Final Analysis of the Ro-CHOP Phase III Study (Conducted by LYSA): Romidepsin Plus CHOP in Patients with Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136, 32–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemonnier, F.; Safar, V.; Beldi-Ferchiou, A.; Cottereau, A.-S.; Bachy, E.; Cartron, G.; Fataccioli, V.; Pelletier, L.; Robe, C.; Letourneau, A.; et al. Integrative Analysis of a Phase 2 Trial Combining Lenalidomide with CHOP in Angioimmunoblastic T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 539–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, S.; O’Connor, O.A.; Pro, B.; Illidge, T.; Fanale, M.; Advani, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Christensen, J.H.; Morschhauser, F.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for CD30-Positive Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma (ECHELON-2): A Global, Double-Blind, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2019, 393, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, S.; O’Connor, O.A.; Pro, B.; Trümper, L.; Iyer, S.; Advani, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Christensen, J.H.; Morschhauser, F.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; et al. The ECHELON-2 Trial: 5-Year Results of a Randomized, Phase III Study of Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for CD30-Positive Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 288–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amore, F.; Relander, T.; Lauritzsen, G.F.; Jantunen, E.; Hagberg, H.; Anderson, H.; Holte, H.; Österborg, A.; Merup, M.; Brown, P.; et al. Up-Front Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma: NLG-T-01. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 3093–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellin, F.; Liestøl, K.; Mannisto, S.; Lauritzsen, G.F.; Jantunen, E.; Meyer, P.A.; Toldbod, H.; Relander, T.; Amore, F.A. Response at Interim Evaluation Predicts Survival after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Nodal Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma; A Nordic Lymphoma Group Study. Blood 2016, 128, 1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fossard, G.; Broussais, F.; Coelho, I.; Bailly, S.; Nicolas-Virelizier, E.; Toussaint, E.; Lancesseur, C.; Le Bras, F.; Willems, E.; Tchernonog, E.; et al. Role of Up-Front Autologous Stem-Cell Transplantation in Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma for Patients in Response after Induction: An Analysis of Patients from LYSA Centers. Ann. Oncol. 2018, 29, 715–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, N.; Truemper, L.H.; Bouabdallah, K.; Ziepert, M.; Leclerc, M.; Cartron, G.; Jaccard, A.; Reimer, P.; Wagner-Drouet, E.M.; Wilhelm, M.; et al. A Randomized Phase 3 Trial of Auto vs. Allo Transplantation as Part of First-Line Therapy in Poor-Risk Peripheral T-NHL. Blood 2020, 137, 2646–2656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mak, V.; Hamm, J.; Chhanabhai, M.; Shenkier, T.; Klasa, R.; Sehn, L.H.; Villa, D.; Gascoyne, R.D.; Connors, J.M.; Savage, K.J. Survival of Patients with Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma After First Relapse or Progression: Spectrum of Disease and Rare Long-Term Survivors. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 1970–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, O.A.; Pro, B.; Pinter-Brown, L.; Bartlett, N.; Popplewell, L.; Coiffier, B.; Jo Lechowicz, M.; Savage, K.J.; Shustov, A.R.; Gisselbrecht, C.; et al. Pralatrexate in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma: Results from the Pivotal PROPEL Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011, 29, 1182–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coiffier, B.; Pro, B.; Prince, H.M.; Foss, F.; Sokol, L.; Greenwood, M.; Caballero, D.; Borchmann, P.; Morschhauser, F.; Wilhelm, M.; et al. Results from a Pivotal, Open-Label, Phase II Study of Romidepsin in Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma After Prior Systemic Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 631–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, O.A.; Horwitz, S.; Masszi, T.; Van Hoof, A.; Brown, P.; Doorduijn, J.; Hess, G.; Jurczak, W.; Knoblauch, P.; Chawla, S.; et al. Belinostat in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma: Results of the Pivotal Phase II BELIEF (CLN-19) Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 2492–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damaj, G.; Gressin, R.; Bouabdallah, K.; Cartron, G.; Choufi, B.; Gyan, E.; Banos, A.; Jaccard, A.; Park, S.; Tournilhac, O.; et al. Results from a Prospective, Open-Label, Phase II Trial of Bendamustine in Refractory or Relapsed T-Cell Lymphomas: The BENTLY Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 31, 104–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Connor, O.A.; Özcan, M.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Roncero, J.M.; Trotman, J.; Demeter, J.; Masszi, T.; Pereira, J.; Ramchandren, R.; Beaven, A.; et al. Randomized Phase III Study of Alisertib or Investigator’s Choice (Selected Single Agent) in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2019, 37, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, S.M.; Koch, R.; Porcu, P.; Oki, Y.; Moskowitz, A.; Perez, M.; Myskowski, P.; Officer, A.; Jaffe, J.D.; Morrow, S.N.; et al. Activity of the PI3K-δ,γ Inhibitor Duvelisib in a Phase 1 Trial and Preclinical Models of T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 888–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, J.; Cen, H.; Zhou, K.; Xu, X.; Li, F.; Wu, T.; Yang, H.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z.; Qiu, L.; et al. A Phase Ib Study of a PI3K δ Inhibitor Linperlisib in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 7531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dreyling, M.; Morschhauser, F.; Bouabdallah, K.; Bron, D.; Cunningham, D.; Assouline, S.E.; Verhoef, G.; Linton, K.; Thieblemont, C.; Vitolo, U.; et al. Phase II Study of Copanlisib, a PI3K Inhibitor, in Relapsed or Refractory, Indolent or Aggressive Lymphoma. Ann. Oncol. 2017, 28, 2169–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Witzig, T.E.; Reeder, C.; Han, J.J.; LaPlant, B.; Stenson, M.; Tun, H.W.; Macon, W.; Ansell, S.M.; Habermann, T.M.; Inwards, D.J.; et al. The mTORC1 Inhibitor Everolimus Has Antitumor Activity in Vitro and Produces Tumor Responses in Patients with Relapsed T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Musuraca, G.; Tani, M.; Stefoni, V.; Marchi, E.; Fina, M.; Pellegrini, C.; Alinari, L.; Derenzini, E.; de Vivo, A.; et al. Phase II Trial of Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Cutaneous T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 4293–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boonstra, P.S.; Polk, A.; Brown, N.; Hristov, A.C.; Bailey, N.G.; Kaminski, M.S.; Phillips, T.; Devata, S.; Mayer, T.; Wilcox, R.A. A Single Center Phase II Study of Ixazomib in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Cutaneous or Peripheral T-Cell Lymphomas. Am. J. Hematol. 2017, 92, 1287–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishitsuka, K.; Izutsu, K.; Maruyama, D.; Makita, S.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Horwitz, S.; Kusumoto, S.; Allen, P.; Porcu, P.; Imaizumi, Y.; et al. First-in-human study of the ezh1 and ezh2 dual inhibitor valemetostat tosylate (ds-3201b) in patients with relapsed or refractory non-hodgkin lymphomas. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amengual, J.E.; Lichtenstein, R.; Lue, J.; Sawas, A.; Deng, C.; Lichtenstein, E.; Khan, K.; Atkins, L.; Rada, A.; Kim, H.A.; et al. A Phase 1 Study of Romidepsin and Pralatrexate Reveals Marked Activity in Relapsed and Refractory T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 397–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falchi, L.; Ma, H.; Klein, S.; Lue, J.K.; Montanari, F.; Marchi, E.; Deng, C.; Kim, H.A.; Rada, A.; Jacob, A.T.; et al. Combined Oral 5-Azacytidine and Romidepsin Are Highly Effective in Patients with PTCL: A Multicenter Phase 2 Study. Blood 2021, 137, 2161–2170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, S.M.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Jacobsen, E.D.; Mehta-Shah, N.; Khodadoust, M.S.; Fisher, D.C.; Myskowski, P.; Wang, E.B.K.; Tawa, M.; Davey, T.; et al. The Combination of Duvelisib, a PI3K-δ,γ Inhibitor, and Romidepsin Is Highly Active in Relapsed/Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma with Low Rates of Transaminitis: Results of Parallel Multicenter, Phase 1 Combination Studies with Expansion Cohorts. Blood 2018, 132, 683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyer, S.P.; Huen, A.; Ai, W.Z.; Jagadeesh, D.; Lechowicz, M.J.; Okada, C.; Feldman, T.A.; Sundaram, S.; Alderuccio, J.P.; Reddy, N.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Tenalisib Given in Combination with Romidepsin in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory T-Cell Lymphoma: Final Results from a Phase I/II Open Label Multi-Center Study. Blood 2021, 138, 1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta-Shah, N.; Lunning, M.A.; Boruchov, A.M.; Ruan, J.; Nair, S.; Lynch, P.; Byrne, R.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Matasar, M.J.; Gerecitano, J.F.; et al. A Phase I/II Trial of the Combination of Romidepsin and Lenalidomide in Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Lymphoma and Myeloma: Activity in T-Cell Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2015, 33, 8521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalac, M.; Jain, S.; Tam, C.S.; Xiao, Z.; Montanari, F.; Kanakry, J.; Huber, B.D.; Goldfinger, M.; O’Connor, O.A.; Marchi, E. Real-World Experience of Combined Treatment with Azacitidine and Romidepsin in Patients with Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 3760–3763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Feldman, T.; Collins, G.; Zain, J.; Khot, A.; Kim, J.S.; Morschhauser, F.; Kim, T.M.; Roderick, J.; Yoon, J.L.; et al. Encouraging Complete Responses (CRs) with CDK9 Inhibitor AZD4573 in Patients (Pts) with Relapsed/Refractory (r/r) Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma (PTCL): Early Trial Analysis. Hematol. Oncol. 2023, 41, 568–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, H.; Zhang, M.; Peng, Z.; Shen, J.; Shuang, Y.; Zhou, H.; Guo, H.; Huang, H.; Li, F.; Qian, Z.; et al. A Multicenter, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase Ib Clinical Trial of HH2853 in the Treatment of Patients with Relapsed and/or Refractory Peripheral T-Cell Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Cai, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zou, L.; Li, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, K.; Qiu, L.; Su, L.; Ding, K.; et al. Phase 2 Study of Golidocitinib, a JAK1 Selective Inhibitor, As Maintenance Therapy in Patients with Peripheral T Cell Lymphomas after First-Line Systemic Therapy (JACKPOT26). Blood 2023, 142, 4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Perales, M.-A.; Kersten, M.-J.; Oluwole, O.O.; Ghobadi, A.; Rapoport, A.P.; McGuirk, J.; Pagel, J.M.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel as Second-Line Therapy for Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 640–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Bishop, M.R.; Tam, C.S.; Waller, E.K.; Borchmann, P.; McGuirk, J.P.; Jäger, U.; Jaglowski, S.; Andreadis, C.; Westin, J.R.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larson, R.C.; Maus, M.V. Recent Advances and Discoveries in the Mechanisms and Functions of CAR-T Cells. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2021, 21, 145–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghilardi, G.; Braendstrup, P.; Chong, E.A.; Schuster, S.J.; Svoboda, J.; Ruella, M. CAR-T TREK through the Lymphoma Universe, to Boldly Go Where No Other Therapy Has Gone Before. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 193, 449–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanber, K.; Savani, B.; Jain, T. Graft-versus-Host Disease Risk after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy: The Diametric Opposition of T Cells. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 195, 660–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimitri, A.; Herbst, F.; Fraietta, J.A. Engineering the Next-Generation of CAR-T-Cells with CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khurana, A.; Lin, Y. Allogeneic Chimeric Antigen Receptor Therapy in Lymphoma. Curr. Treat. Options Oncol. 2022, 23, 171–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locke, F.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Eradat, H.; Munoz, J.; Tees, M.T.; De Vos, S.; Nath, R.; Stevens, D.A.; Malik, S.; Popplewell, L.; et al. Phase 1 Results with Anti-CD19 Allogeneic CAR-T ALLO-501/501A in Relapsed/Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma (r/r LBCL). J. Clin. Oncol. 2023, 41, 2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Rossi, J.M.; Jacobson, C.A.; Locke, F.L.; Miklos, D.B.; Reagan, P.M.; Rodig, S.J.; Lekakis, L.J.; Flinn, I.W.; Zheng, L.; et al. CD19-Loss with Preservation of Other B Cell Lineage Features in Patients with Large B Cell Lymphoma Who Relapsed Post-Axi-Cel. Blood 2019, 134, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.P.; Coleman, M.; Ketas, J.C.; Chadburn, A.; Furman, R.; Schuster, M.W.; Feldman, E.J.; Ashe, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Wegener, W.A.; et al. Epratuzumab, a Humanized Anti-CD22 Antibody, in Aggressive Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2004, 10, 5327–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, A.; Ye, S.; Li, P.; Huang, J.; Zhu, S.; Yao, X.; Zhou, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Zheng, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of a Novel Anti-CD20 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR)-T Cell Therapy in Relapsed/Refractory (r/r) B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (B-NHL) Patients after Failing CD19 CAR-T Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2021, 39, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, H.; Wang, Y.; Nagler, A.; Chang, A.H.; Huang, H. CD19/CD22 Dual-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy for Relapsed/Refractory Aggressive B-Cell Lymphoma: A Safety and Efficacy Study. Blood 2020, 136, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, N.N.; Maatman, T.; Hari, P.; Johnson, B. Multi Targeted CAR-T Cell Therapies for B-Cell Malignancies. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spiegel, J.Y.; Patel, S.; Muffly, L.; Hossain, N.M.; Oak, J.; Baird, J.H.; Frank, M.J.; Shiraz, P.; Sahaf, B.; Craig, J.; et al. CAR-T Cells with Dual Targeting of CD19 and CD22 in Adult Patients with Recurrent or Refractory B Cell Malignancies: A Phase 1 Trial. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1419–1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaeger, U.; Worel, N.; McGuirk, J.P.; Riedell, P.A.; Fleury, I.; Du, Y.; Han, X.; Pearson, D.; Redondo, S.; Waller, E.K. Safety and Efficacy of Tisagenlecleucel plus Pembrolizumab in Patients with r/r DLBCL: Phase 1b PORTIA Study Results. Blood Adv. 2023, 7, 2283–2286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, E.A.; Svoboda, J.; Dwivedy Nasta, S.; Landsburg, D.J.; Winchell, N.; Napier, E.; Mato, A.R.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Ruella, M.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Sequential Anti-CD19 Directed Chimeric Antigen Receptor Modified T-Cell Therapy (CART19) and PD-1 Blockade with Pembrolizumab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. Blood 2018, 132, 4198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, T.; Abramson, J.S.; Lee, H.J.; Schuster, S.; Hasskarl, J.; Montheard, S.; Dell Aringa, J.; Thompson, E.; Ananthakrishnan, R.; Lunning, M. Safety of lisocabtagene maraleucel given with durvalumab in patients with relapsed/refractory aggressive b-cell non hodgkin lymphoma: First results from the platform study. Hematol. Oncol. 2019, 37, 171–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, N.H.; Dickinson, M.; Dreyling, M.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Kolstad, A.; Butler, J.; Ghosh, M.; Popplewell, L.; Chavez, J.C.; Bachy, E.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Adult Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma: The Phase 2 ELARA Trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, C.A.; Chavez, J.C.; Sehgal, A.R.; William, B.M.; Munoz, J.; Salles, G.; Munshi, P.N.; Casulo, C.; Maloney, D.G.; de Vos, S.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Relapsed or Refractory Indolent Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma (ZUMA-5): A Single-Arm, Multicentre, Phase 2 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuster, S.J.; Fowler, N.; Dickinson, M.; Martinez-Lopez, J.; Kolstad, A.; Butler, J.; Ghosh, M.; Popplewell, L.L.; Chavez, J.C.; Bachy, E.; et al. Clinical Outcomes of Patients with Relapsed/Refractory Follicular Lymphoma Treated with Tisagenlecleucel: Phase 2 Elara 3-Year Follow-Up. Blood 2023, 142, 601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morschhauser, F.; Dahiya, S.; Palomba, M.L.; Martin Garcia-Sancho, A.; Reguera, J.L.; Kuruvilla, J.; Jaeger, U.; Cartron, G.; Izutsu, K.; Dreyling, M.; et al. TRANSCEND FL: Phase 2 Study Primary Analysis of Lisocabtagene Maraleucel as Second-Line Therapy in Patients with High-Risk Relapsed or Refractory Follicular Lymphoma. Blood 2023, 142, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqi, T.; Maloney, D.G.; Kenderian, S.S.; Brander, D.M.; Dorritie, K.; Soumerai, J.; Riedell, P.A.; Shah, N.N.; Nath, R.; Fakhri, B.; et al. Lisocabtagene Maraleucel in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukaemia and Small Lymphocytic Lymphoma (TRANSCEND CLL 004): A Multicentre, Open-Label, Single-Arm, Phase 1–2 Study. Lancet 2023, 402, 641–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavez, J.C.; Dickinson, M.; Munoz, J.L.; Ulrickson, M.L.; Thieblemont, C.; Oluwole, O.O.; Herrera, A.F.; Ujjani, C.S.; Lin, Y.; Riedell, P.A.; et al. 3-Year Analysis of ZUMA-12: A Phase 2 Study of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel (Axi-Cel) As First-Line Therapy in Patients with High-Risk Large B-Cell Lymphoma (LBCL). Blood 2023, 142, 894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.S.; Palomba, M.L.; Gordon, L.I.; Lunning, M.A.; Wang, M.; Arnason, J.; Mehta, A.; Purev, E.; Maloney, D.G.; Andreadis, C.; et al. Lisocabtagene Maraleucel for Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphomas (TRANSCEND NHL 001): A Multicentre Seamless Design Study. Lancet 2020, 396, 839–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crombie, J.L.; Nastoupil, L.J.; Redd, R.A.; Tang, K.; Shouse, G.; Herrera, A.F.; Chow, V.A.; Shadman, M.; Castaneda Puglianini, O.; Saucier, A.; et al. Real-World Outcomes of Axicabtagene Ciloleucel in Adult Patients with Primary Mediastinal B-Cell Lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3563–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigault, M.J.; Dietrich, J.; Gallagher, K.; Roschewski, M.; Jordan, J.T.; Forst, D.; Plotkin, S.R.; Cook, D.; Casey, K.S.; Lindell, K.A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Tisagenlecleucel in Primary CNS Lymphoma: A Phase 1/2 Clinical Trial. Blood 2022, 139, 2306–2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.A.; Grover, N.S.; Beaven, A.W.; Lulla, P.D.; Wu, M.-F.; Ivanova, A.; Wang, T.; Shea, T.C.; Rooney, C.M.; Dittus, C.; et al. Anti-CD30 CAR-T Cell Therapy in Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, L.C.; Rouce, R.H.; Wu, M.; Wang, T.; Ma, R.; Zhang, H.; Mehta, B.; Lapteva, N.; Mei, Z.; Smith, T.S.; et al. Anti-Tumor Efficacy and Safety of Unedited Autologous CD5.CAR-T Cells in Relapsed/Refractory Mature T-Cell Lymphomas. Blood J. 2023, 143, 1231–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, R.; Zhao, Y.; Sun, R.; Guo, S.; Lu, W.; Zhao, M. Targeted CD7 CAR-T-Cells for Treatment of T-Lymphocyte Leukemia and Lymphoma and Acute Myeloid Leukemia: Recent Advances. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1170968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Du, M.; Jiang, H.; Luo, W.; Tang, L.; Kang, Y.; Xu, J.; Wu, Z.; Wang, X.; et al. Allogenic and Autologous Anti-CD7 CAR-T Cell Therapies in Relapsed or Refractory T-Cell Malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 2023, 13, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Target | ORR | CR | mDoR |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Golcadomide | I/II | Ikaros/Aiolos | 50% | 13% | 17.4 w |
| LP-168 | I | BTK | 65% (MCL: 77%, DLBCL: 70%, MZL: 73%) | MCL: 39%, DLBCL: 40%, MZL: 9% | / |
| Emavusertib | I | IRAK4 | 38% | 31% | / |
| HZ-H08905 | I | CK1ε/PI3Kδ | 60% | 17% | NR |
| ZD8586 | I | LYN/BTK | 69% | / | / |
| Zilovertamab | I | ROR1 | MCL: 53%, DLBCL: 29%, RT: 57% | / | / |
| AR160 | I | CD20 | 85% | 14% | / |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | DoR | PFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acalabrutinib− Rituximab− Lenalidomide | II | First-line FL | BTK/CD20/ IMiD | 100% | 92% | / | |
| Mosunetuzumab ± Lenalidomide | II | First-line FL | CD20xCD3/ IMiD | 96% (M) 89% (M + L) | 81% (M) 82% (M + L) | / | / |
| Epcoritamab | II | R/R FL | CD20xCD3 | 90% | 50% | / | / |
| Glofitamab | II | R/R FL | CD20xCD3 | 81% | 70% | / | / |
| Odronextamab | II | R/R FL | CD20xCD3 | 91% | 72% | / | / |
| Zanubrutinib− Obinutuzumab | II | R/R FL | BTK/CD20 | 69% | 39% | 18 m: 69% | mPFS: 28 m |
| Loncastuximab tesirine | II | R/R FL | CD19 | 95% | 67% | / | / |
| Zanubrutinib− Venetoclax− Obinutuzumab | II | R/R MCL | BTK/BCL2/ CD20 | 96% | 88% | / | 2y: 72% |
| Ibrutinib− Venetoclax | III | R/R MCL | BTK/BCL2 | 82% | 54% | mDoR: 42 m | mPFS: 32 m |
| Pirtobrutinib | I/II | R/R MCL | BTK | 2y: 86% (cBTKn) vs. 90% (cBTKexp) |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | DoR | PFS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ibrutinib− Venetoclax | III | First line | BTK/BCL2 | 95% | 92% | / | 3y: 97% |
| Obinutuzumab− Venetoclax ± Ibrutinib | III | First line | CD20/BCL2/ BTK | 96% (O + V) vs. 94% (O + V + I) | 57% (O + V) vs. 62% (O + V + I) | / | 4y: 82% (O + V) vs. 86% (O + V + I) |
| Venetoclax− Rituximab | III | R/R retreatment cohort | BCL2/CD20 | 72% | 56% | / | mPFS: 23 m |
| Ibrutinib− Venetoclax | II | R/R Retreatment cohort | BTK/BCL2 | 86% | 5% | / | / |
| Pirtobrutinib | I/II | R/R | BTK | 83% (cBTKn) vs. 80% (cBTKexp) | / | mDoR: 25 m (cBTKn) vs. 15 m (cBTKexp) | mPFS: 23 m (cBTKn) vs. 16 m (cBTKexp) |
| Epcoritamab− Venetoclax | I/II | R/R | CD20xCD3/ BCL2 | 82% | 33% | 9 m: 83% | / |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | PFS | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polatuzumab vedotin− Rituximab−CHP | III | First-line DLBCL | CD79b | 86% | 78% | 2y: 77% | 2y: 89% |
| Rituximab− Lenalidomide− Ibrutinib− CHOP/EPOCH | II | First-line DLBCL | CD20/IMiD/ BTK | 100% | 94% | 31m: 91% | 31m: 97% |
| Lenalidomide− Tafasitamab− Rituximab− Acalabrutinib | II | First-line DLBCL | IMiD/CD19/ CD20/BTK | 100% | 64% | / | / |
| Polatuzumab vedotin− Rituximab− Bendamustine | III | R/R DLBCL | CD79b/CD20 | / | 43% | mPFS: 9m | mOS: 12m |
| Tafasitamab− Lenalidomide | II | R/R DLBCL | CD79b/IMiD | 60% | 43% | mPFS: 11m | mOS: 33m |
| Epcoritamab | II | R/R DLBCL | CD20xCD3 | 63% | 39% | mPFS: 4m | mOS: NR |
| Glofitamab | II | R/R DLBCL | CD20xCD3 | 52% | 39% | mPFS: 5m | 1y: 50% |
| Pembrolizumab | II | R/R PMBCL | PD-L1 | 41% | 21% | 4y: 33% | 4y: 45% |
| Brentuximab Vedotin | II | R/R PMBCL | CD30 | 70% | 43% | mPFS: NR | mOS: NR |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | PFS | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lenalidomide− Rituximab− Methotrexate− Temozolomide | II | First line | IMiD/CD20 | 92% | 79% | 2y: 62% | 2y: 67% |
| Ibrutinib | II | R/R | BTK | 59% | 19% | mPFS: 5m | mOS: 20m |
| Lenalidomide− Rituximab | II | R/R | IMiD/CD20 | 67% | / | mPFS: 8m | mOS: 18m |
| Pomalidomide− Dexamethasone | I | R/R | IMiD | 48% | / | mPFS: 6m | / |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | PFS | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brentuximab vedotin− AVD | III | First-line advanced stage | CD30 | / | / | 6y: 82% | 6y: 94% |
| Brentuximab vedotin | II | First-line frail | CD30 | 84% | 26% | mPFS: 7m | mOS: 20m |
| Brentuximab vedotin− AVD (sequential) | II | First-line Frail | CD30 | 82% | 36% | 2y: 84% | 2y: 93% |
| Nivolumab− AVD | III | First-line advanced | PD-L1 | / | / | 1y: 94% | / |
| Brentuximab vedotin− Nivolumab | II | First-line Frail | CD30/ PD-L1 | 61% | 48% | / | / |
| Brentuximab vedotin−ICE | I/II | R/R | CD30 | / | 62% | 3y: 64% | 3y: 100% |
| Brentuximab vedotin−IGEV | I/II | R/R | CD30 | 96% | 71% | / | / |
| Brentuximab vedotin−ESHAP | I/II | R/R | CD30 | 91% | 70% | 30m: 71% | 30m: 91% |
| Brentuximab vedotin−DHAP | I/II | R/R | CD30 | 91% | 81% | 2y: 74% | 2y: 95% |
| Pembrolizumab− ICE | II | R/R | PD-L1 | 97% | 87% | 2y: 87% | 2y: 95% |
| Pembrolizumab− GVD | II | R/R | PD-L1 | 100% | 95% | 14m: 100% | 14m: 100% |
| Brentuximab vedotin− Nivolumab | II | R/R | CD30/ PD-L1 | 85% | 67% | 3y: 77% | 3y: 93% |
| Brentuximab vedotin− Pembrolizumab | II | R/R | CD30/ PD-L1 | / | 80% | / | / |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | PFS | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Duvelisib | II | R/R | PI3K | 49% | 34% | mPFS: 4m | / |
| Linperlisib | Ib | R/R | PI3K | 60% | 35% | mPFS: 10m | mOS: NR |
| Copanlisib | II | R/R | PI3K | 21% | 14% | / | / |
| Bortezomib | II | R/R | Proteasome | 67% | 17% | / | / |
| Ixazomib | II | R/R | Proteasome | 14% | 14% | / | / |
| Valemetostat | I | R/R | EZH1/2 | 55% | 31% | mPFS: 7.7m | / |
| Romidepsin− pralatrexate | I | R/R | HDAC | 71% | / | / | / |
| Romidepsin− Duvelisib | II | R/R | HDAC/ PI3K | 47% | 29% | / | / |
| Romidepsin− lenalidomide | II | R/R | HDAC/ IMiD | 65% | 26% | 2y: 32% | 2y: 50% |
| Romidepsin− azacitidine | II | R/R | HDAC/ DNA methylation | 80% | 67% | / | / |
| AZD4573 | II | R/R | CDK9 | 25% | 25% | / | / |
| HH2853 | Ib | R/R | EZH1/2 | 61% | 39% | 3m: 74% | 6m: 92% |
| Golidocitinib | II | R/R | JAK1 | 39% | 33% | NR | / |
| Treatment | Trial Phase | Setting | Target | ORR | CR | PFS | OS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tisa-cel | III | R/R FL | CD19 | 69% | 76% | mPFS: 37m | 3y: 82% |
| Liso-cel | II | R/R FL | CD19 | 96% | 96% | 12m: 90% | 12m: 91% |
| Liso-cel | I/II | R/R CLL | CD19 | 47% | 19% | mPFS: 18m | / |
| Axi-cel | II | Refractory (two cycles of chemotherapy) DLBCL | CD19 | 92% | 86% | 3y: 75% | 3y: 81% |
| Liso-cel | II | R/R PMBCL | CD19 | 79% | 50% | / | / |
| Axi-cel | II | R/R PMBCL | CD19 | 76% | 67% | 2y: 64% | / |
| Tisa-cel | I/II | R/R PCNSL | CD19 | 58% | 50% | / | / |
| Early phase | New molecular pathways (Ikaros/Aiolos, IRAK4, and ROR1) and new delivery systems (nanotechnology) are currently being evaluated in phase I/II trials for various types of NHL. |
| FL/MCL | Bispecific antibodies showed important activity in R/R settings and are now moving to first line in FL. In MCL, new chemo-free regimens combining a cBTKi and a BCL2i also showed promising activity in patients with TP53 aberrations. |
| CLL | Fixed-duration schemes and continuous treatments with cBTKi are available options for CLL. New randomized trials directly comparing these different approaches and/or evaluating MRD-driven strategies are ongoing. |
| DLBCL/ PMBCL | Targeted therapies such as polatuzumab vedotin and bispecific antibodies are changing the management of DLBCL. Chemo-free regimens based on checkpoint inhibitors seem promising in PMBCL. |
| PCNSL | Targeted therapies like ibrutinib and immunomodulation with lenalidomide emerge for PCNSL, with studies showing encouraging initial responses. |
| HL | The use of BV and checkpoint inhibitors improves outcomes in HL, with new combinations and sequential approaches demonstrating efficacy and tolerability. |
| PTCL-NOS | New agents such as azacitidine, romidepsin, and JAK inhibitors showed promising outcomes for PTCL-NOS in phase I/II studies. |
| Cellular therapy | CAR-T cell treatment is emerging as a revolution for R/R NHL, with studies showing high efficacy and a curative potential. New approaches, like the development of CAR-NK cells or allogenic CAR-T cells, are currently under investigation. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Massaro, F.; Andreozzi, F.; Abrassart, T.; Castiaux, J.; Massa, H.; Rizzo, O.; Vercruyssen, M. Beyond Chemotherapy: Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050977
Massaro F, Andreozzi F, Abrassart T, Castiaux J, Massa H, Rizzo O, Vercruyssen M. Beyond Chemotherapy: Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(5):977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050977
Chicago/Turabian StyleMassaro, Fulvio, Fabio Andreozzi, Tom Abrassart, Julie Castiaux, Hanne Massa, Ornella Rizzo, and Marie Vercruyssen. 2024. "Beyond Chemotherapy: Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders" Biomedicines 12, no. 5: 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050977
APA StyleMassaro, F., Andreozzi, F., Abrassart, T., Castiaux, J., Massa, H., Rizzo, O., & Vercruyssen, M. (2024). Beyond Chemotherapy: Present and Future Perspectives in the Treatment of Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Biomedicines, 12(5), 977. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12050977






