The Possible Role of Pathogens and Chronic Immune Stimulation in the Development of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. B-Cell Receptor Signaling and the Germinal Center Reaction
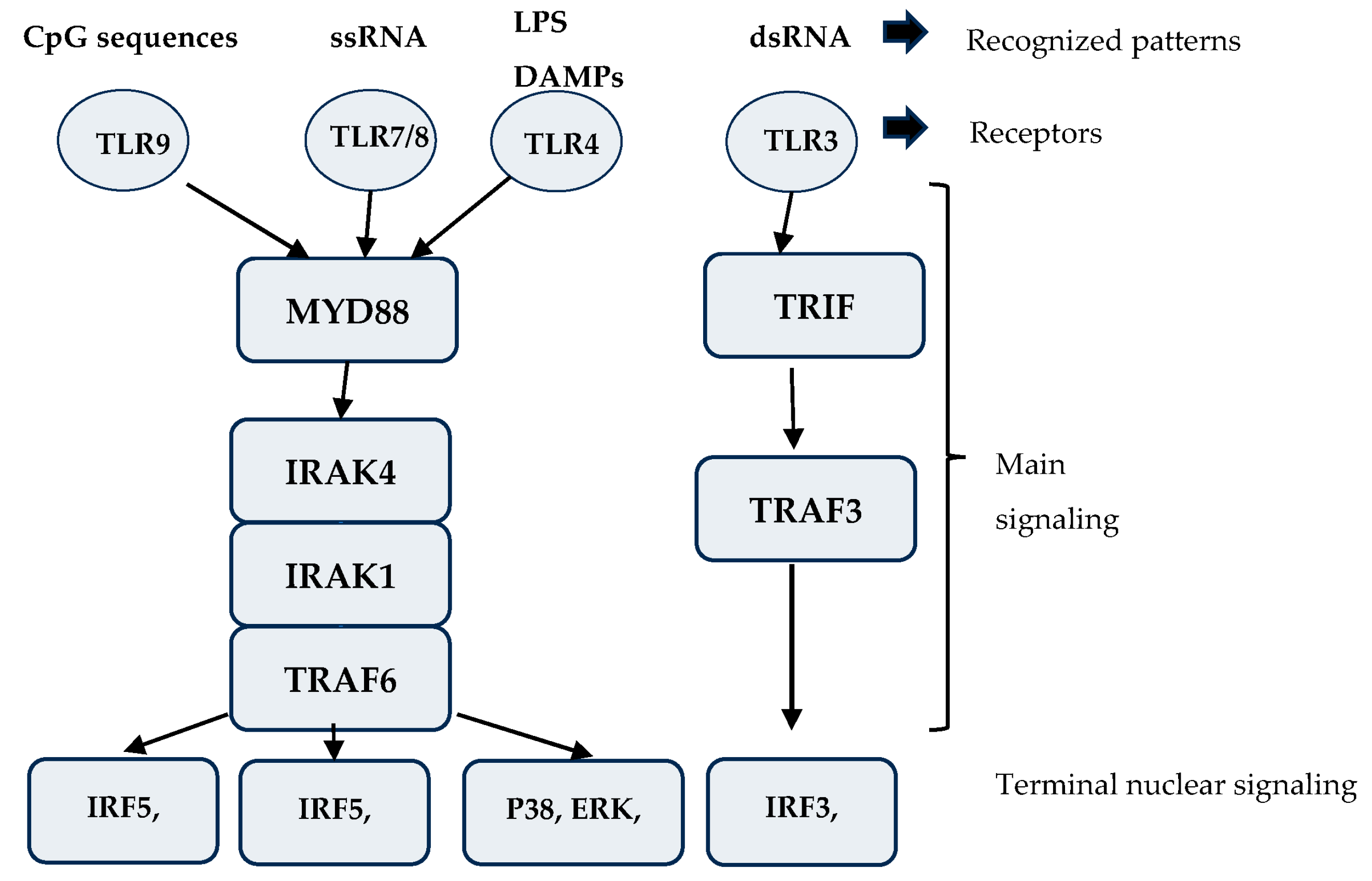
3. Toll Receptor Signaling
4. Microenvironment and the Role of Macrophages
5. Pathogens in the Development of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
6. Viral Infections
6.1. Epstein–Barr Virus (EBV)
6.2. Human Herpesvirus 8 (HHV8)
6.3. Hepatitis C Virus (HCV)
6.4. Hepatitis B Virus (HBV)
6.5. Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV)
6.6. Coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2)
6.7. Other Viruses
7. Bacterial Infections
7.1. Helicobacter pylori
7.2. Campylobacter jejuni
7.3. Borrelia burgdorferi
7.4. Chlamydia psittaci
7.5. Other Bacteria
8. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alaggio, R.; Amador, C.; Anagnostopoulos, I.; Attygalle, A.D.; Araujo, I.B.O.; Berti, E.; Bhagat, G.; Borges, A.M.; Boyer, D.; Calaminici, M.; et al. The 5th edition of the World Health Organization Classification of Haematolymphoid Tumours: Lymphoid Neoplasms. Leukemia 2022, 36, 1720–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, A.A.; Eisen, M.B.; Davis, R.E.; Ma, C.; Lossos, I.S.; Rosenwald, A.; Boldrick, J.C.; Sabet, H.; Tran, T.; Yu, X.; et al. Distinct types of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma identified by gene expression profiling. Nature 2000, 403, 503–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Redd, R.A.; Lawrence, M.S.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Li, A.J.; Ziepert, M.; et al. Molecular subtypes of diffuse large B cell lymphoma are associated with distinct pathogenic mechanisms and outcomes. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, R.; Wright, G.W.; Huang, D.W.; Johnson, C.A.; Phelan, J.D.; Wang, J.Q.; Roulland, S.; Kasbekar, M.; Young, R.M.; Shaffer, A.L.; et al. Genetics and Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1396–1407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phelan, J.D.; Young, R.M.; Webster, D.E.; Roulland, S.; Wright, G.W.; Kasbekar, M.; Shaffer, A.L.; Ceribelli, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Schmitz, R.; et al. A multiprotein supercomplex controlling oncogenic signalling in lymphoma. Nature 2018, 560, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.M.; Phelan, J.D.; Wilson, W.H.; Staudt, L.M. Pathogenic B-cell receptor signaling in lymphoid malignancies: New insights to improve treatment. Immunol. Rev. 2019, 291, 190–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lossos, I.S. The endless complexity of lymphocyte differentiation and lymphomagenesis: IRF-4 downregulates BCL6 expression. Cancer Cell 2007, 12, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.; Zhang, X.; Zang, L.; Yang, H.; Zhao, W.; Zhao, H.; Li, Q.; Xia, B.; Yu, Y.; et al. Toll-like receptor 4-induced inflammatory responses contribute to the tumor-associated macrophages formation and infiltration in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2015, 19, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.T.; Weng, S.W.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, H.C.; Tsai, P.C.; Chuang, J.H. Expression of Toll-like receptor9 in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Further exploring CpG oligodeoxynucleotide in NFκB pathway. APMIS 2012, 120, 872–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandato, E.; Yan, Q.; Ouyang, J.; Paczkowska, J.; Qin, Y.; Hao, Y.; Bojarczuk, K.; Hansen, J.; Chapuy, B.; Rodig, S.J.; et al. MYD88L265P augments proximal B-cell receptor signaling in large B-cell lymphomas via an interaction with DOCK8. Blood 2023, 142, 1219–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.C.; Liao, H.; Lin, S.X.; Xia, Y.; Wang, X.X.; Gao, Y.; Lin, Z.X.; Lu, J.B.; Huang, H.Q. High expression of tumor-infiltrating macrophages correlates with poor prognosis in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Med. Oncol. 2012, 29, 2317–2322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna, L.; Azcoaga, P.; Brahmachary, M.; Caffarel, M.M.; Braza, M.S. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma microenvironment displays a predominant macrophage infiltrate marked by a strong inflammatory signature. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1048567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godfrey, J.; Chen, X.; Sunseri, N.; Cooper, A.; Yu, J.; Varlamova, A.; Zarubin, D.; Popov, Y.; Jacobson, C.; Postovalova, E.; et al. TIGIT is a key inhibitory checkpoint receptor in lymphoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2023, 11, e006582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhuang, Y.; Shao, S.J.; Trivedi, P.; Zheng, B.; Huang, G.L.; He, Z.; Zhang, X. Essential contribution of the JAK/STAT pathway to carcinogenesis, lytic infection of herpesviruses and pathogenesis of COVID-19 (Review). Mol Med Rep. 2024, 29, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, C.Y.; Li, L.; Xu-Monette, Z.Y.; Visco, C.; Tzankov, A.; Manyam, G.C.; Montes-Moreno, S.; Dybkaer, K.; Chiu, A.; Orazi, A.; et al. Prevalence and clinical implications of epstein-barr virus infection in de novo diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in Western countries. Clin. Cancer Res. 2014, 20, 2338–2349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uner, A.; Akyurek, N.; Saglam, A.; Abdullazade, S.; Uzum, N.; Onder, S.; Barista, I.; Benekli, M. The presence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in diffuse large B-cell lymphomas (DLBCLs) in Turkey: Special emphasis on ‘EBV-positive DLBCL of the elderly’. APMIS 2011, 119, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, M.; Traverse-Glehen, A.; Combes, J.D.; Clifford, G.M.; de Martel, C. Estimating the prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus in primary gastric lymphoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Infect. Agents Cancer 2023, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Napoli, A.; Soma, L.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L.; de Leval, L.; Leoncini, L.; Zamò, A.; Ng, S.B.; Ondrejka, S.L.; Climent, F.; Wotherspoon, A.; et al. Cavity-based lymphomas: Challenges and novel concepts. A report of the 2022 EA4HP/SH lymphoma workshop. Virchows Arch. 2023, 483, 299–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qunaj, L.; Castillo, J.J.; Olszewski, A.J. Survival of patients with CD20-negative variants of large B-cell lymphoma: An analysis of the National Cancer Data Base. Leuk. Lymphoma 2018, 59, 1375–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gisbert, J.P.; García-Buey, L.; Pajares, J.M.; Moreno-Otero, R. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 1723–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canioni, D.; Michot, J.M.; Rabiega, P.; Molina, T.J.; Charlotte, F.; Lazure, T.; Davi, F.; Settegrana, C.; Berger, F.; Alric, L.; et al. In Situ Hepatitis C NS3 Protein Detection Is Associated with High Grade Features in Hepatitis C-Associated B-Cell Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0156384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visentini, M.; Pica, A.; D’Ippolito, G.; Sculco, E.; La Gualana, F.; Gragnani, L.; Miglionico, M.; Mazzaro, C.; Fiorilli, M.; Basili, S.; et al. High prevalence of past hepatitis B virus infection in diffuse large B cell lymphoma: A retrospective study from Italy. Ann. Hematol. 2023, 102, 3457–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, X.; Jemal, A.; Hulland, E.; Simard, E.P.; Nastoupil, L.; Ward, E.; Flowers, C.R. HIV Infection and Survival of Lymphoma Patients in the Era of Highly Active Antiretroviral Therapy. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2017, 26, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiels, M.S.; Engels, E.A.; Linet, M.S.; Clarke, C.A.; Li, J.; Hall, H.I.; Hartge, P.; Morton, L.M. The epidemic of non-Hodgkin lymphoma in the United States: Disentangling the effect of HIV, 1992–2009. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2013, 22, 1069–1078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lu, C.; Jiang, F.; Wang, C.; Yu, L. The association of COVID-19 with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2023, 27, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krajden, M.; Yu, A.; Braybrook, H.; Lai, A.S.; Mak, A.; Chow, R.; Cook, D.; Tellier, R.; Petric, M.; Gascoyne, R.D.; et al. GBV-C/hepatitis G virus infection and non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A case control study. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 126, 2885–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Xia, B.; Guo, S.; Zhan, Z.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, D.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y. A retrospective analysis of primary gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma with or without concomitant mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT) lymphoma components. Ann. Hematol. 2013, 92, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ewers, E.C.; Sheffler, R.L.; Wang, J.; Ngauy, V. Immunoproliferative Small Intestinal Disease Associated with Overwhelming Polymicrobial Gastrointestinal Infection with Transformation to Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2016, 94, 1177–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colli, C.; Leinweber, B.; Müllegger, R.; Chott, A.; Kerl, H.; Cerroni, L. Borrelia burgdorferi-associated lymphocytoma cutis: Clinicopathologic, immunophenotypic, and molecular study of 106 cases. J. Cutan. Pathol. 2004, 31, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melenotte, C.; Million, M.; Audoly, G.; Gorse, A.; Dutronc, H.; Roland, G.; Dekel, M.; Moreno, A.; Cammilleri, S.; Carrieri, M.P.; et al. B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma linked to Coxiella burnetii. Blood 2016, 127, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoyama, S.; Masaki, A.; Sakamoto, Y.; Takino, H.; Murase, T.; Ohshima, K.; Yoshino, T.; Kato, S.; Inagaki, H. Achromobacter Infection Is Rare in Japanese Patients with Pulmonary B-cell Lymphoma. Intern. Med. 2018, 57, 789–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ross, A.M.; Leahy, C.I.; Neylon, F.; Steigerova, J.; Flodr, P.; Navratilova, M.; Urbankova, H.; Vrzalikova, K.; Mundo, L.; Lazzi, S.; et al. Epstein-Barr Virus and the Pathogenesis of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Life 2023, 13, 521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Robertson, E.S. Epstein-Barr Virus History and Pathogenesis. Viruses 2023, 15, 714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.T.; Kim, K.D. Topological implications of DNA tumor viral episomes. BMB Rep. 2022, 55, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gebauer, N.; Künstner, A.; Ketzer, J.; Witte, H.M.; Rausch, T.; Benes, V.; Zimmermann, J.; Gebauer, J.; Merz, H.; Bernard, V.; et al. Genomic insights into the pathogenesis of Epstein-Barr virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by whole-genome and targeted amplicon sequencing. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zapatka, M.; Borozan, I.; Brewer, D.S.; Iskar, M.; Grundhoff, A.; Alawi, M.; Desai, N.; Sültmann, H.; Moch, H.; PCAWG Pathogens; et al. The landscape of viral associations in human cancers. Nat. Genet. 2020, 52, 320–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, T.; Noda, C.; Narita, Y.; Watanabe, T.; Yoshida, M.; Ashio, K.; Sato, Y.; Goshima, F.; Kanda, T.; Yoshiyama, H.; et al. Induction of Epstein-Barr Virus Oncoprotein LMP1 by Transcription Factors AP-2 and Early B Cell Factor. J. Virol. 2016, 90, 3873–3889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Stroopinsky, D.; Alimperti, S.; Jiao, A.L.; Pyzer, A.R.; Cippitelli, C.; Pepe, G.; Severa, M.; Rosenblatt, J.; Etna, M.P.; et al. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded EBNA2 alters immune checkpoint PD-L1 expression by downregulating miR-34a in B-cell lymphomas. Leukemia 2019, 33, 132–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.T.; Kuo, S.H.; Kuo, Y.C.; Lin, C.W. miR-155-regulated mTOR and Toll-like receptor 5 in gastric diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Med. 2022, 11, 555–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Triyatni, M.; Saunier, B.; Maruvada, P.; Davis, A.R.; Ulianich, L.; Heller, T.; Patel, A.; Kohn, L.D.; Liang, T.J. Interaction of hepatitis C virus-like particles and cells: A model system for studying viral binding and entry. J. Virol. 2002, 76, 9335–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Knight, G.B.; Gao, L.; Gragnani, L.; Elfahal, M.M.; De Rosa, F.G.; Gordon, F.D.; Agnello, V. Detection of WA B cells in hepatitis C virus infection: A potential prognostic marker for cryoglobulinemic vasculitis and B cell malignancies. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 2152–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Du, Z. Demographic characteristics and prognosis of HHV8-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: Insights from a population-based study with a 10-year follow-up. Medicine 2023, 102, e36464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cacoub, P.; Comarmond, C.; Vieira, M.; Régnier, P.; Saadoun, D. HCV-related lymphoproliferative disorders in the direct-acting antiviral era: From mixed cryoglobulinaemia to B-cell lymphoma. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 174–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Locarnini, S. Molecular virology of hepatitis B virus. Semin. Liver Dis. 2004, 24 (Suppl. 1), 3–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.Y.; Gao, F.; Zhao, Y.W.; Ni, B.W.; Huang, H.H.; Hou, J. Inferior survival and frequent hepatic dysfunction in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients with HBV infection: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Hematology 2022, 27, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Liu, J.; Lei, H.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Guo, B.; Hu, R.; Liu, T.; Wu, J.; Ding, Y.; et al. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of newly diagnosed patients with HIV-associated aggressive B-cell NHL in China. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2022, 26, 5067–5077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, X.; Liu, T.; Wang, Z.; Ma, M.; Lei, J.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, S.; Fu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Ding, H.; et al. Expression of the Inhibitory Receptor TIGIT Is Up-Regulated Specifically on NK Cells With CD226 Activating Receptor From HIV-Infected Individuals. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, A.; Chen, X.; Wisner, L.; Malasi, S.; Ramsower, C.; Kendrick, S.; Barrett, M.T.; Glinsmann-Gibson, B.; McGrath, M.; Rimsza, L.M. Enhanced DNA repair and genomic stability identify a novel HIV-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma signature. Int. J. Cancer 2019, 145, 3078–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi Anari, S.R.; Kheirkhah, B.; Amini, K.; Roozafzai, F. Expression of MicroRNA-155 in Patients with Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma, Coronavirus Disease 2019, or Both: A Cross-Sectional Study. Iran J. Med. Sci. 2023, 48, 26–34. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-Ampudia, Y.; Monsalve, D.M.; Rojas, M.; Rodríguez, Y.; Zapata, E.; Ramírez-Santana, C.; Anaya, J.M. Persistent Autoimmune Activation and Proinflammatory State in Post-Coronavirus Disease 2019 Syndrome. J. Infect Dis. 2022, 225, 2155–2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Kost, J.; Sulovari, A.; Wong, N.; Liang, W.S.; Cao, J.; Li, D. A virome-wide clonal integration analysis platform for discovering cancer viral etiology. Genome Res. 2019, 29, 819–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.M.; Stapleton, J.T.; Klinzman, D.; McLinden, J.H.; Purdue, M.P.; Katki, H.A.; Engels, E.A. GBV-C infection and risk of NHL among U.S. adults. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5553–5560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belshaw, R.; Pereira, V.; Katzourakis, A.; Talbot, G.; Paces, J.; Burt, A.; Tristem, M. Long-term reinfection of the human genome by endogenous retroviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 4894–4899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, B.; Dopkins, N.; Fei, T.; Marston, J.L.; Michael, S.; Reyes-Gopar, H.; Curty, G.; Heymann, J.J.; Chadburn, A.; Martin, P.; et al. Locus specific human endogenous retroviruses reveal new lymphoma subtypes. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biernat, M.M.; Wróbel, T. Bacterial Infection and Non-Hodgkin B-Cell Lymphoma: Interactions between Pathogen, Host and the Tumor Environment. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torisu, T.; Kawano, S.; Miyawaki, K.; Yamamoto, H.; Ihara, Y.; Matsuno, Y.; Torisu, K.; Sugio, T.; Sasaki, K.; Shimakawa, T.; et al. B cell receptor signaling related to resistance to Helicobacter pylori eradication therapy in gastric diffuse large B cell lymphoma. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 39, 145–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Younes, K.; Doghri, R.; Mrad, K.; Bedhiafi, W.; Benammar-Elgaaied, A.; Sola, B.; Ben Aissa-Fennira, F. PTENLoss Cyclin A2 Upregulation Define a PI3K/AKTPathway Activation in Helicobacter pylori-induced MALT and DLBCL Gastric Lymphoma with Features of MALT. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2021, 29, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saleem, T.; Al-Mondhiry, H. Immunoproliferative small intestinal disease (IPSID): A model for mature B-cell neoplasms. Blood 2005, 105, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreling, V.; Falcone, F.H.; Kehrenberg, C.; Hensel, A. Campylobacter sp.: Pathogenicity factors and prevention methods-new molecular targets for innovative antivirulence drugs. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 104, 10409–10436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalogeropoulos, D.; Papoudou-Bai, A.; Kanavaros, P.; Kalogeropoulos, C. Ocular adnexal marginal zone lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18, 151–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behdad, A.; Zhou, X.Y.; Gao, J.; Raparia, K.; Dittman, D.; Green, S.J.; Qi, C.; Betz, B.; Bryar, P.; Chen, Q.; et al. High Frequency of MYD88 L265P Mutation in Primary Ocular Adnexal Marginal Zone Lymphoma and Its Clinicopathologic Correlation: A Study From a Single Institution. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2019, 143, 483–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyapichev, K.A.; Ivashkevich, Y.; Chernov, Y.; Chinenov, D.; Shpot, E.; Bessonov, A.A.; Dabaja, B.S.; Konoplev, S. MALT Lymphoma of the Urinary Bladder Shows a Dramatic Female Predominance, Uneven Geographic Distribution, and Possible Infectious Etiology. Res. Rep. Urol. 2021, 13, 49–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adam, P.; Czapiewski, P.; Colak, S.; Kosmidis, P.; Tousseyn, T.; Sagaert, X.; Boudova, L.; Okoń, K.; Morresi-Hauf, A.; Agostinelli, C.; et al. Prevalence of Achromobacter xylosoxidans in pulmonary mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma in different regions of Europe. Br. J. Haematol. 2014, 164, 804–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, G.L.; Stylianou, J.; Rasaiyaah, J.; Wei, W.; Thomas, W.; Croom-Carter, D.; Kohler, C.; Spang, R.; Woodman, C.; Kellam, P.; et al. Different patterns of Epstein-Barr virus latency in endemic Burkitt lymphoma (BL) lead to distinct variants within the BL-associated gene expression signature. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 2882–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Studstill, C.J.; Mac, M.; Moody, C.A. Interplay between the DNA damage response and the life cycle of DNA tumor viruses. Tumour Virus Res. 2023, 16, 200272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vets, J.; Marcelis, L.; Schepers, C.; Dorreman, Y.; Verbeek, S.; Vanwalleghem, L.; Gieraerts, K.; Meylaerts, L.; Lesaffer, J.; Devos, H.; et al. Breast implant associated EBV-positive Diffuse Large B-cell lymphoma: An underrecognized entity. Diagn. Pathol. 2023, 18, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beltran, B.E.; Castro, D.; Paredes, S.; Miranda, R.N.; Castillo, J.J. EBV-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma, not otherwise specified: 2020 update on diagnosis, risk-stratification and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2020, 95, 435–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofscheier, A.; Ponciano, A.; Bonzheim, I.; Adam, P.; Lome-Maldonado, C.; Vela, T.; Cortes, E.; Ortiz-Hidalgo, C.; Fend, F.; Quintanilla-Martinez, L. Geographic variation in the prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus-positive diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the elderly: A comparative analysis of a Mexican and a German population. Mod. Pathol. 2011, 24, 1046–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Lee, J.; Ko, Y.H.; Han, A.; Jun, H.J.; Lee, S.C.; Hwang, I.G.; Park, Y.H.; Ahn, J.S.; Jung, C.W.; et al. The impact of Epstein-Barr virus status on clinical outcome in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2007, 110, 972–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyer, D.F.; McKelvie, P.A.; de Leval, L.; Edlefsen, K.L.; Ko, Y.H.; Aberman, Z.A.; Kovach, A.E.; Masih, A.; Nishino, H.T.; Weiss, L.M.; et al. Fibrin-associated EBV-positive Large B-Cell Lymphoma: An Indolent Neoplasm With Features Distinct From Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Associated With Chronic Inflammation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2017, 41, 299–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Hashida, Y.; Matsuo, K.; Kitahata, K.; Ujihara, T.; Murakami, I.; Nakayama, T.; Daibata, M. EBV-positive pyothorax-associated lymphoma expresses CXCL9 and CXCL10 chemokines that attract cytotoxic lymphocytes via CXCR3. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2622–2633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrò, M.L.; Sarid, R. Human Herpesvirus 8 and Lymphoproliferative Disorders. Mediterr. J. Hematol. Infect. Dis. 2018, 10, e2018061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, T.F.; Freise, A.; Stein, S.C. Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpesvirus latency-associated nuclear antigen: More than a key mediator of viral persistence. Curr. Opin. Virol. 2023, 61, 101336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casato, M.; Mecucci, C.; Agnello, V.; Fiorilli, M.; Knight, G.B.; Matteucci, C.; Gao, L.; Kay, J. Regression of lymphoproliferative disorder after treatment for hepatitis C virus infection in a patient with partial trisomy 3, Bcl-2 overexpression, and type II cryoglobulinemia. Blood 2002, 99, 2259–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arcari, A.; Tabanelli, V.; Merli, F.; Marcheselli, L.; Merli, M.; Balzarotti, M.; Zilioli, V.R.; Fabbri, A.; Cavallo, F.; Casaluci, G.M.; et al. Biological features and outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma associated with hepatitis C virus in elderly patients: Results of the prospective ‘Elderly Project’ by the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 201, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visco, C.; Finotto, S. Hepatitis C virus and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Pathogenesis, behavior and treatment. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 11054–11061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merli, M.; Visco, C.; Spina, M.; Luminari, S.; Ferretti, V.V.; Gotti, M.; Rattotti, S.; Fiaccadori, V.; Rusconi, C.; Targhetta, C.; et al. Outcome prediction of diffuse large B-cell lymphomas associated with hepatitis C virus infection: A study on behalf of the Fondazione Italiana Linfomi. Haematologica 2014, 99, 489–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persico, M.; Aglitti, A.; Caruso, R.; De Renzo, A.; Selleri, C.; Califano, C.; Abenavoli, L.; Federico, A.; Masarone, M. Efficacy and safety of new direct antiviral agents in hepatitis C virus-infected patients with diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Hepatology 2018, 67, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masarone, M.; Persico, M. Hepatitis C virus infection and non-hepatocellular malignancies in the DAA era: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 1292–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, M.; Poluch, M.; Thomas, C.; Sindaco, P.; Khoo, A.; Porcu, P. Hepatitis B Virus and B-cell lymphoma: Evidence, unmet need, clinical impact, and opportunities. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1275800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Shen, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gao, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, Q.; Fan, C.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Cong, H.; et al. Characterization of hepatitis B virus infection and viral DNA integration in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 147, 2199–2209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Pan, H.; Yang, P.; Ye, P.; Cao, H.; Zhou, H. Both chronic HBV infection and naturally acquired HBV immunity confer increased risks of B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Gan, Y.; Fan, C.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, X.; Shen, Y.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Z.; Xu, D.; Tu, H. Hepatitis B virus and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: An updated meta-analysis of 58 studies. J. Viral Hepat. 2018, 25, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, K.; Imamura, H.; Watahiki, Y.; Hazama, H.; Hashimoto, T.; Mukae, S.; Ohhira, H. A Hepatitis B Virus Reactivation Case Potentially Triggered by the Onset of Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma. Intern. Med. 2023, 62, 1611–1615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Song, Y.; Young, K.H.; Hu, S.; Ding, N.; Song, W.; Li, X.; Shi, Y.; Huang, H.; Liu, W.; et al. Hepatitis B virus-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: Unique clinical features, poor outcome, and hepatitis B surface antigen-driven origin. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 25061–25073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, X.; Xing, L.; Yue, W.; Yin, H.; He, M.; Wang, J.; Yang, J.; Chen, J. HBV infection potentiates resistance to S-phase arrest-inducing chemotherapeutics by inhibiting CHK2 pathway in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pather, S.; Patel, M. HIV-associated DLBCL: Clinicopathological factors including dual-colour chromogenic in situ hybridisation to assess MYC gene copies. Ann. Diagn. Pathol. 2022, 58, 151913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Besson, C.; Lancar, R.; Prevot, S.; Algarte-Genin, M.; Delobel, P.; Bonnet, F.; Meyohas, M.C.; Partisani, M.; Oberic, L.; Gabarre, J.; et al. Outcomes for HIV-associated diffuse large B-cell lymphoma in the modern combined antiretroviral therapy era. AIDS 2017, 31, 2493–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baptista, M.J.; Garcia, O.; Morgades, M.; Gonzalez-Barca, E.; Miralles, P.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Abella, E.; Moreno, M.; Sancho, J.M.; Feliu, E.; et al. HIV-infection impact on clinical-biological features and outcome of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated with R-CHOP in the combination antiretroviral therapy era. AIDS 2015, 29, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.J.C.; Di Ciaccio, P.; Polizzotto, M.N.; Milliken, S.; Cochrane, T.; Goh, Z.; Shaw, B.; Perry, E.; Gilbertson, M.; Kermode, W.; et al. Outcomes of human immunodeficiency virus-associated Burkitt lymphoma and diffuse large B-cell lymphoma treated in Australia: A report from the Australasian Lymphoma Alliance. Br. J. Haematol. 2023, 201, 865–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howlader, N.; Shiels, M.S.; Mariotto, A.B.; Engels, E.A. Contributions of HIV to Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma Mortality Trends in the United States. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2016, 25, 1289–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenart, M.; Górecka, M.; Bochenek, M.; Barreto-Duran, E.; Szczepański, A.; Gałuszka-Bulaga, A.; Mazur-Panasiuk, N.; Węglarczyk, K.; Siwiec-Koźlik, A.; Korkosz, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 infection impairs NK cell functions via activation of the LLT1-CD161 axis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1123155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giladi, O.; Bagnato, G.; Gentilini, M.; Shimony, S.; Pasvolsky, O.; Berger, T.; Itchaki, G.; Raanani, P.; Lolli, G.; Stefoni, V.; et al. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma characteristics and outcomes during the COVID-19 pandemic in two tertiary centers—An Israeli/ Italian study. Ann. Hematol. 2024, 103, 803–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cattaneo, C.; Cancelli, V.; Imberti, L.; Dobbs, K.; Sottini, A.; Pagani, C.; Belotti, A.; Re, A.; Anastasia, A.; Quaresima, V.; et al. Production and persistence of specific antibodies in COVID-19 patients with hematologic malignancies: Role of rituximab. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishna, J.P.; Bhavsar, T.; Nicolae, A.; Raffeld, M.; Jaffe, E.S.; Pittaluga, S. Human Herpes Virus 6 (HHV-6)-associated Lymphadenitis: Pitfalls in Diagnosis in Benign and Malignant Settings. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2018, 42, 1402–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, A.; Patel, N.; Morris, N.A. Diffuse large B cell lymphoma secondary to JC virus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J. Neurovirol. 2019, 25, 883–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, C.E.; Yeh, C.M.; Fang, C.Y.; Shay, J.; Chen, P.L.; Lin, M.C.; Chang, D.; Wang, M. Detection of human JCPyV and BKPyV in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the GI tract. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 33, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolosi Guidicelli, S.; Lopez-Guillermo, A.; Falcone, U.; Conconi, A.; Christinat, A.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Grisanti, S.; Lobetti-Bodoni, C.; Piffaretti, J.C.; Johnson, P.W.; et al. Hepatitis C virus and GBV-C virus prevalence among patients with B-cell lymphoma in different European regions: A case-control study of the International Extranodal Lymphoma Study Group. Hematol. Oncol. 2012, 30, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yu, K.; Li, M.; Zeng, K.; Wei, J.; Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Fan, L.; Yu, Z.; et al. EZH2 overexpression in primary gastrointestinal diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and its association with the clinicopathological features. Hum. Pathol. 2017, 64, 213–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, S.H.; Yeh, K.H.; Chen, L.T.; Lin, C.W.; Hsu, P.N.; Hsu, C.; Wu, M.S.; Tzeng, Y.S.; Tsai, H.J.; Wang, H.P.; et al. Helicobacter pylori-related diffuse large B-cell lymphoma of the stomach: A distinct entity with lower aggressiveness and higher chemosensitivity. Blood Cancer J. 2014, 4, e220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roncati, L.; Maiorana, A. IgA plasmablastic large B-cell lymphoma. Diagnosis 2017, 4, 105–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishikawa, E.; Nakamura, M.; Satou, A.; Shimada, K.; Nakamura, S. Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue (MALT) Lymphoma in the Gastrointestinal Tract in the Modern Era. Cancers 2022, 14, 446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuo, S.H.; Yeh, K.H.; Lin, C.W.; Liou, J.M.; Wu, M.S.; Chen, L.T.; Cheng, A.L. Current Status of the Spectrum and Therapeutics of Helicobacter pylori-Negative Mucosa-Associated Lymphoid Tissue Lymphoma. Cancers 2022, 14, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreri, A.J.; Govi, S.; Ponzoni, M. Marginal zone lymphomas and infectious agents. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2013, 23, 431–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goteri, G.; Ranaldi, R.; Simonetti, O.; Capretti, R.; Menzo, S.; Stramazzotti, D.; Morichetti, D.; Offidani, A.M.; Rupoli, S.; Leoni, P. Clinicopathological features of primary cutaneous B-cell lymphomas from an academic regional hospital in central Italy: No evidence of Borrelia burgdorferi association. Leuk. Lymphoma 2007, 48, 2184–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaddu-Mulindwa, D.; Thurner, L.; Christofyllakis, K.; Bewarder, M.; Kos, I.A. Management of Extranodal Marginal Zone Lymphoma: Present and Upcoming Perspectives. Cancers 2022, 14, 3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vela, V.; Juskevicius, D.; Gerlach, M.M.; Meyer, P.; Graber, A.; Cathomas, G.; Dirnhofer, S.; Tzankov, A. High throughput sequencing reveals high specificity of TNFAIP3 mutations in ocular adnexal marginal zone B-cell lymphomas. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 38, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, U.; Cho, I.; Lee, S.H.; Yang, S.W.; Cho, S.G.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, H.W.; Park, G. Lack of Association between Chlamydophila psittaci and Ocular Adnexal MALT Lymphoma in Korean Patients-Is the Geographic or Genetic Difference Significant. Diagnostics 2021, 11, 2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, H.U.; Son, J.H. Ocular adnexal mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphoma: A narrative review. J. Yeungnam Med. Sci. 2022, 39, 3–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van Roeden, S.E.; van Houwelingen, F.; Donkers, C.M.J.; Hogewoning, S.J.; de Lange, M.M.A.; van der Hoek, W.; Kampschreur, L.M.; Bonten, M.J.M.; Hoepelman, A.I.M.; Bleeker-Rovers, C.P.; et al. Exposure to Coxiella burnetii and risk of non-Hodgkin lymphoma: A retrospective population-based analysis in the Netherlands. Lancet Haematol. 2018, 5, e211–e219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melenotte, C.; Mezouar, S.; Mège, J.L.; Gorvel, J.P.; Kroemer, G.; Raoult, D. Bacterial infection and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 2020, 46, 270–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiesewetter, B.; Lamm, W.; Dolak, W.; Lukas, J.; Mayerhoefer, M.E.; Weber, M.; Schiefer, A.I.; Kornauth, C.; Bayer, G.; Simonitsch-Klupp, I.; et al. Transformed mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue lymphomas: A single institution retrospective study including polymerase chain reaction-based clonality analysis. Br. J. Haematol. 2019, 186, 448–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeshima, A.M.; Taniguchi, H.; Toyoda, K.; Yamauchi, N.; Makita, S.; Fukuhara, S.; Munakata, W.; Maruyama, D.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tobinai, K. Clinicopathological features of histological transformation from extranodal marginal zone B-cell lymphoma of mucosa-associated lymphoid tissue to diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: An analysis of 467 patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2016, 174, 923–931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Váróczy, L.; Páyer, E.; Kádár, Z.; Gergely, L.; Miltényi, Z.; Magyari, F.; Szodoray, P.; Illés, A. Malignant lymphomas and autoimmunity-a single center experience from Hungary. Clin. Rheumatol. 2012, 31, 219–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.S.; Vajdic, C.M.; Linet, M.S.; Slager, S.L.; Voutsinas, J.; Nieters, A.; Casabonne, D.; Cerhan, J.R.; Cozen, W.; Alarcón, G.; et al. B-Cell NHLSubtype Risk Associated with Autoimmune Conditions and PRS. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomark. Prev. 2022, 31, 1103–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bende, R.J.; Slot, L.M.; Kwakkenbos, M.J.; Wormhoudt, T.A.; Jongejan, A.; Verstappen, G.M.; van Kampen, A.C.; Guikema, J.E.; Kroese, F.G.; van Noesel, C.J. Lymphoma-associated mutations in autoreactive memory B cells of patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. J. Pathol. 2023, 259, 264–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujita, N.; Ando, M.; Goto, A.; Sakata, M.; Ogata, M.; Usagawa, Y.; Yoshikawa, H.; Yamasue, M.; Komiya, K.; Umeki, K.; et al. Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma Arising from the Lesion of Chronic Lobar Atelectasis. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 2020, 250, 129–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, J.; Ma, K.; Guo, J.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Q.; Sun, H. Clinical significance of elevated antinuclear antibodies in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: A single center study. J. Cancer Res. Ther. 2018, 14, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pósfai, É.; Irsai, G.; Illés, Á.; Méhes, G.; Marton, I.; Molnár, C.; Csípő, I.; Baráth, S.; Gergely, L. Evaluation of significance of lymphocyte subpopulations and non-specific serologic markers in B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma patients. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2014, 20, 649–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Chen, N. The Roles of IRF-8 in Regulating IL-9-Mediated Immunologic Mechanisms in the Development of DLBCL: A State-of-the-Art Literature Review. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 817069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand, N.; Ly, T.L.; Sonstein, J.; Medeiros, L.J. Microscopic diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) occurring in pseudocysts: Do these tumors belong to the category of DLBCL associated with chronic inflammation. Am. J. Surg. Pathol. 2012, 36, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filip, D.; Mraz, M. The role of MYC in the transformation and aggressiveness of ‘indolent’ B-cell malignancies. Leuk. Lymphoma 2020, 61, 510–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions, and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content. |
| Pathogen | WHO 2022 Category, Lymphoma Type | Frequency (Cases Reported) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| EBV | EBV positive DLBCL DLBCL (NOS) DLBCL (NOS)—gastric lymphoma EBV positive mucocutaneous ulcer | 80–100% 4–5% 11% 100% | [1] [15,16] [17] [1] |
| KSHV/HHV8 | Primary effusion lymphoma KSHV/HHV8-positive DLBCL KSHV/HHV8-positive germinotrophic lymphoproliferative ulcer DLBCL (NOS) | 100% 100% 100% 0.1% | [1,18] [1] [1] [19] |
| HCV | B-cell NHL (non MALT) DLBCL | 13% 36% of HCV+ lymphomas | [20] [21] |
| HBV | DLBCL (NOS) | 16.8% (serological test) | [22] |
| HIV | DLBCL (NOS) | 5.4% 7.8% | [23] [24] |
| SARS-CoV-2 | DLBCL (NOS) | Severe COVID: OR:1.765 (no percentage reported) | [25] |
| GBV-C | NHL (all types) | 4.5% | [26] |
| Helicobacter pylori | DLBCL (NOS) gastric MALT/DLBCL gastric | 36% 75% | [27] [27] |
| Campylobacter jejuni | DLBCL (NOS) | 1 case reported | [28] |
| Borrelia burgdorferi | DLBCL-like proliferation in the skin | 5 cases reported | [29] |
| Coxiella burnetti | DLBCL (NOS) | Among Q-fever cases: 0.48% | [30] |
| Achomobacter xylosoxidans | DLBCL (NOS) | 2 cases reported | [31] |
| Pathogen | Inflammation | BCR Signaling | Microenvironment Modulation | Interaction with Cytoplasmic Signaling | Genetic Alteration | Genome Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EBV | + [32,33,34,35] | +/− [36] | + [37,38] | + [32,38] | + [34,36] | + [33] |
| HHV8 | - | - | - | + [39] | + [39] | +/− [18] |
| HCV | + [40] | +/− [41] | + [40,41,42] | +/− [43] | - | - |
| HBV | - | - | +/− [20,44] | +/− [45] | +/− [20] | + [20,35] |
| HIV | - | - | + [46] | + [47] | +/− [22,48] | - |
| SARS-CoV-2 | + [49] | - | + [25,50] | +[25] | - | - |
| JCPyV, BKPyV | - | - | - | - | +/− [51] | +/− [51] |
| HHV6 | - | - | - | - | +/− [51] | +/− [51] |
| GBV-C | +/− [52] | - | - | - | - | - |
| endogenous retroviruses | - | - | - | - | +/− [53,54] | + [53,54] |
| Helicobacter pylori | + [55] | + [56] | + [55] | + [55,57] | - | - |
| Campylobacter jejuni | + [28,58,59] | - | +/− [59] | +/− [59] | - | - |
| Borrelia burgdorferi | + [29] | - | +/− [29] | - | - | - |
| Chlamydia psittaci | + [60] | +/− [61] | - | +/− [61] | - | - |
| Coxiella burnetti | +/− [30] | - | - | - | - | - |
| Escherischia coli | +/− [62] | - | - | - | - | - |
| Achromobacter xylosoxidans | +/− [63] | - | - | - | - | - |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gergely, L.; Udvardy, M.; Illes, A. The Possible Role of Pathogens and Chronic Immune Stimulation in the Development of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030648
Gergely L, Udvardy M, Illes A. The Possible Role of Pathogens and Chronic Immune Stimulation in the Development of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Biomedicines. 2024; 12(3):648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030648
Chicago/Turabian StyleGergely, Lajos, Miklos Udvardy, and Arpad Illes. 2024. "The Possible Role of Pathogens and Chronic Immune Stimulation in the Development of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma" Biomedicines 12, no. 3: 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030648
APA StyleGergely, L., Udvardy, M., & Illes, A. (2024). The Possible Role of Pathogens and Chronic Immune Stimulation in the Development of Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma. Biomedicines, 12(3), 648. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines12030648






