Assessment of the Role of Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle EGFR for Acute Blood Pressure Effects of Angiotensin II and Adrenergic Stimulation in Obese Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
2.2. Invasive Measurement of Blood Pressure
2.3. Statistics
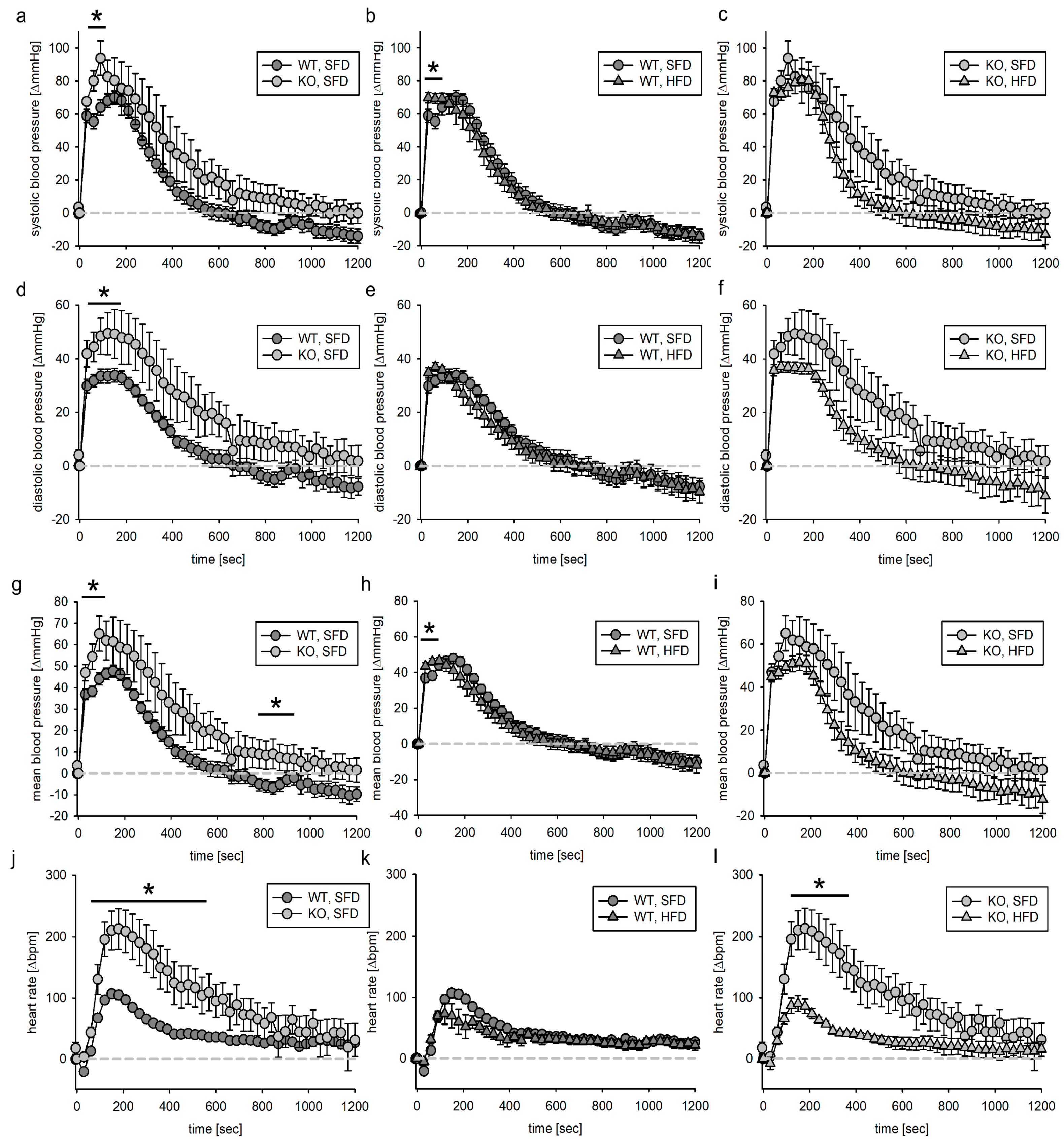
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Blood Pressure
3.1.1. Tie2 Animals
3.1.2. SMMHC Animals
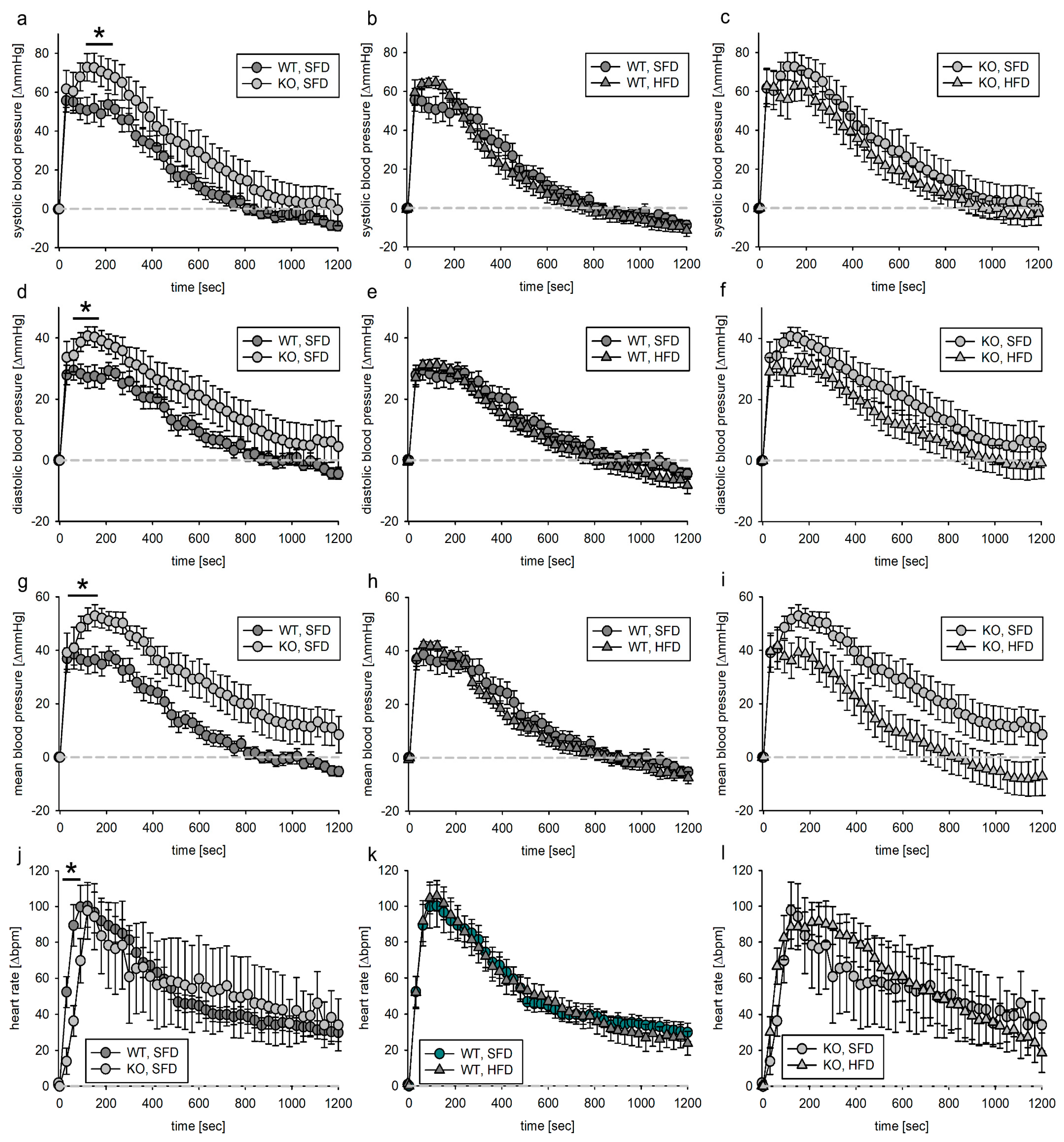
3.2. Blood Pressure Response to Volume Load
3.2.1. Tie2 Animals
3.2.2. SMMHC Animals
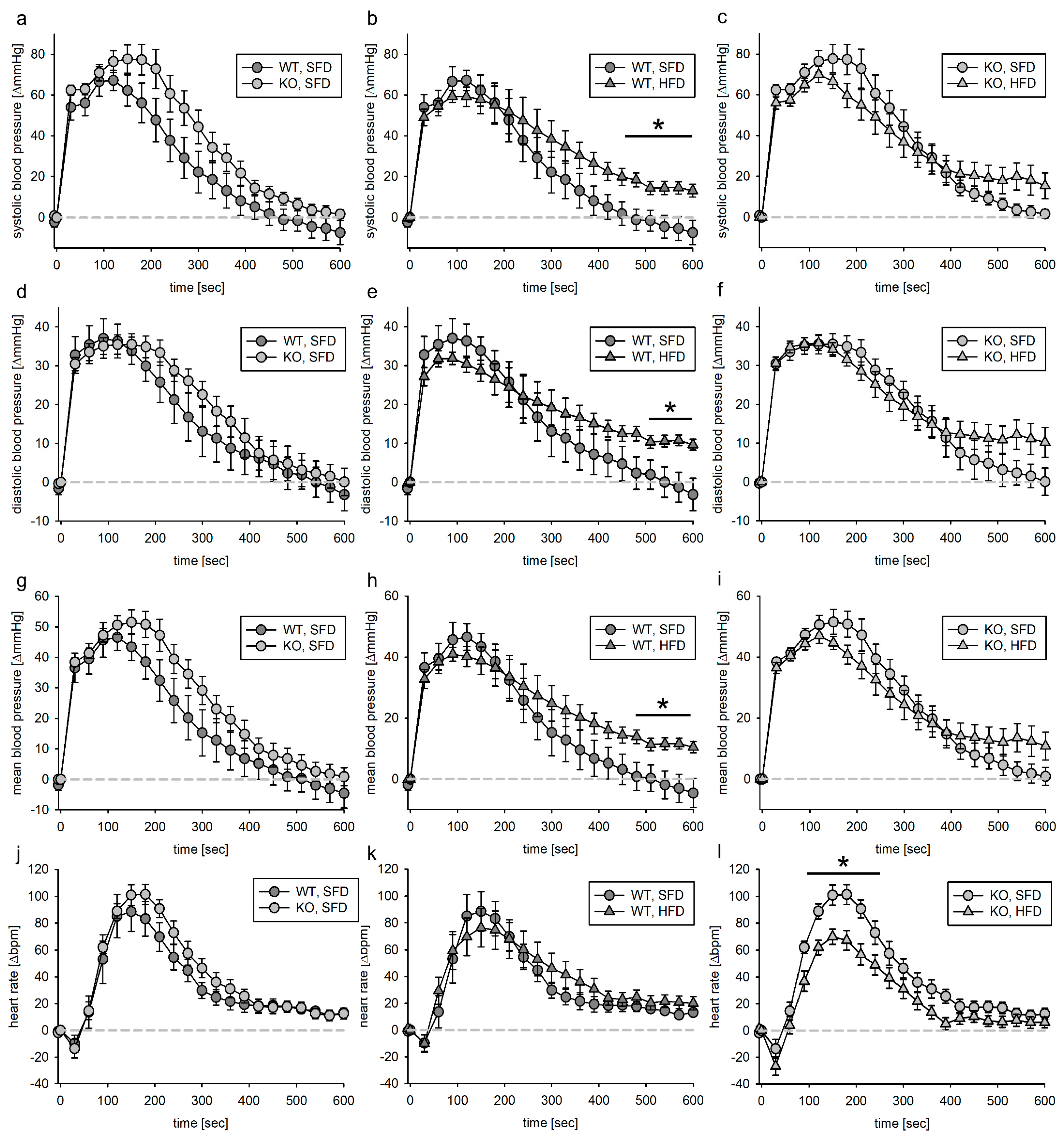
3.3. Blood Pressure Response to Acute Phenylephrine Infusion
3.3.1. Tie2 Animals
3.3.2. SMMHC Animals
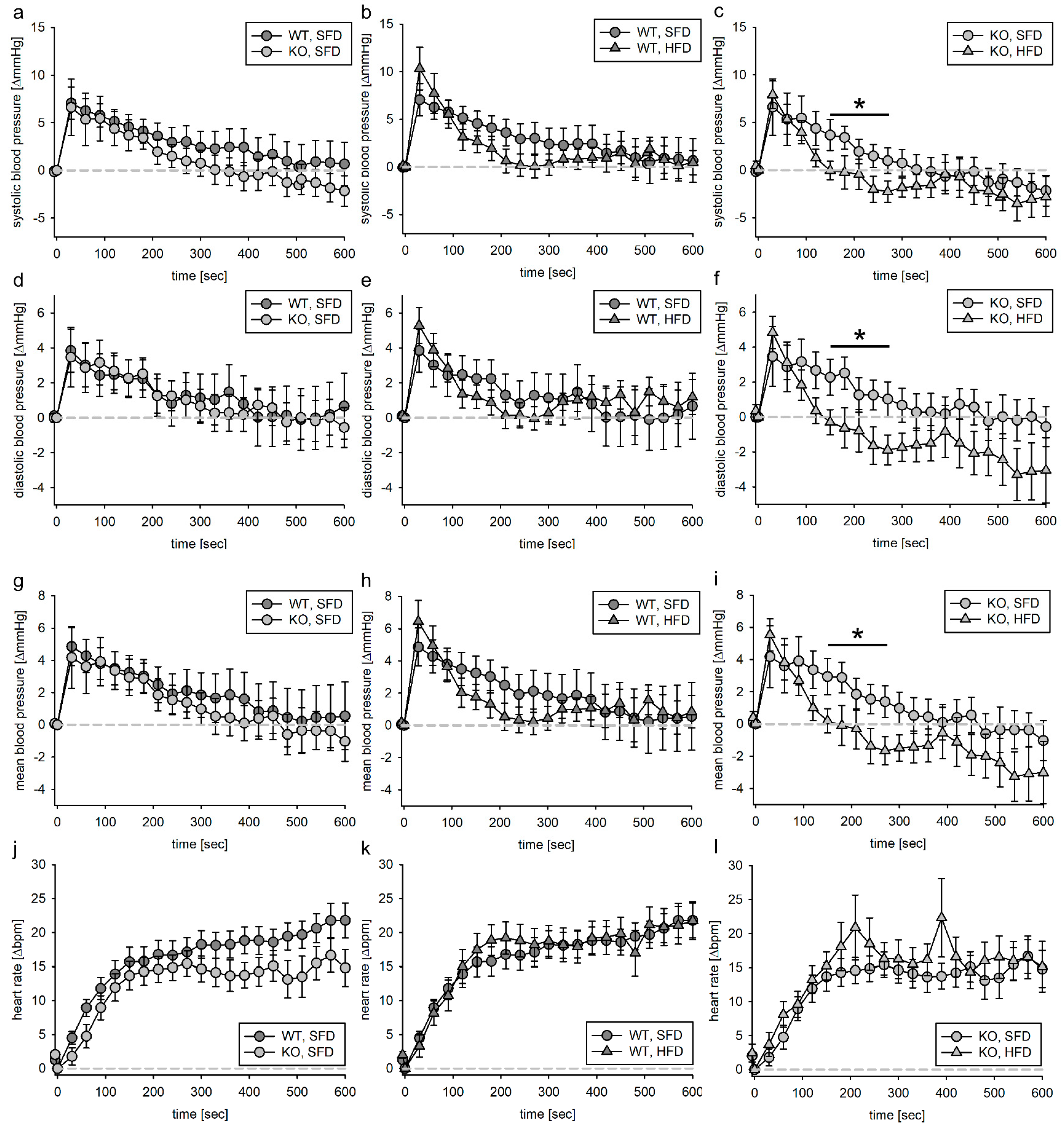
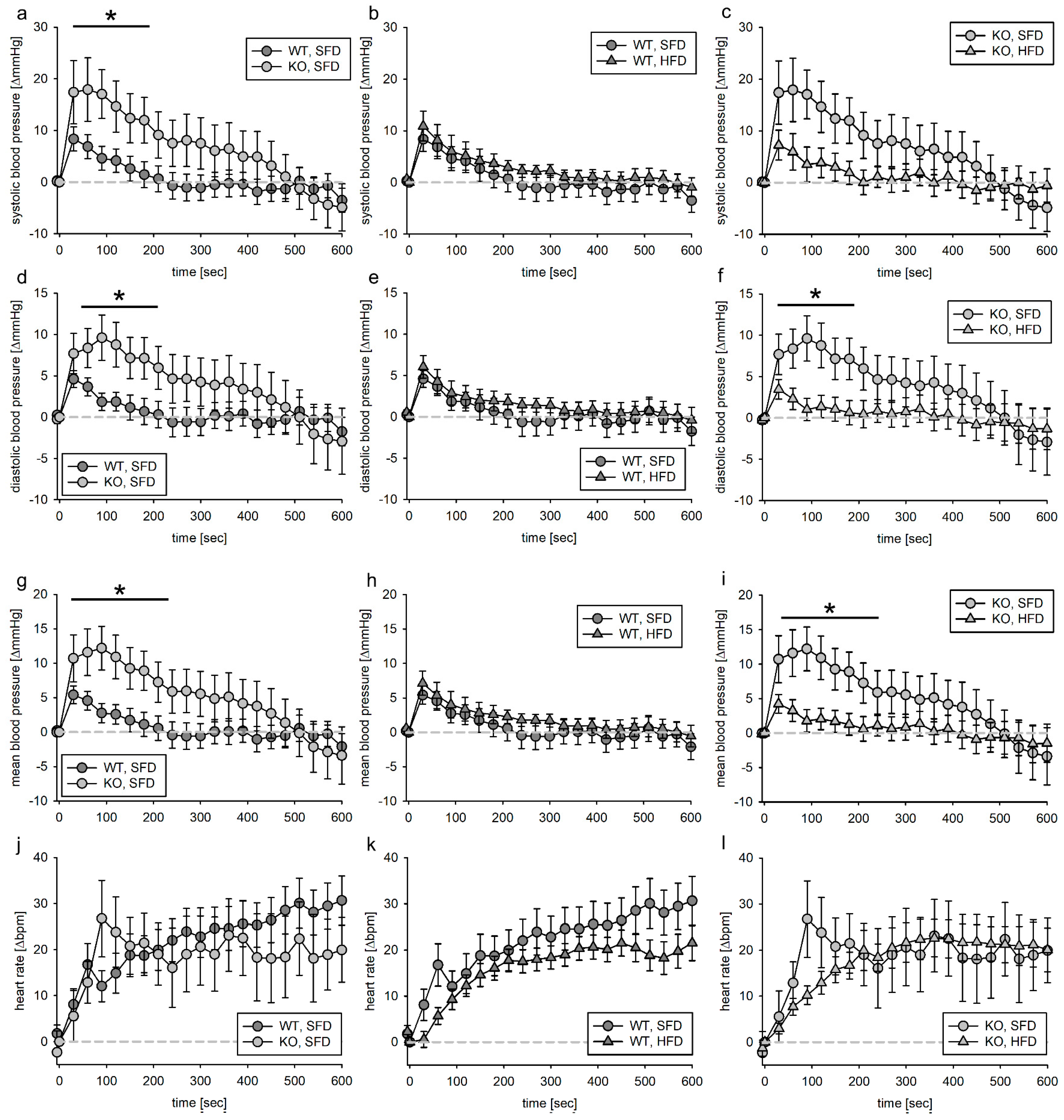
3.4. Blood Pressure Response to Acute Angiotensin II Infusion
3.4.1. Tie2 Animals
3.4.2. SMMHC Animals
4. Discussion
4.1. Baseline Blood Pressure
4.2. Vehicle Loading
4.3. Phenylephrine
4.4. Angiotensin II
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Battault, S.; Meziat, C.; Nascimento, A.; Braud, L.; Gayrard, S.; Legros, C.; de Nardi, F.; Drai, J.; Cazorla, O.; Thireau, J.; et al. Vascular endothelial function masks increased sympathetic vasopressor activity in rats with metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2018, 314, H497–H507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrannini, E.; Cushman, W.C. Diabetes and hypertension: The bad companions. Lancet 2012, 380, 601–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bełtowski, J.; Jazmroz-Wiśniewska, A. Transactivation of ErbB receptors by leptin in the cardiovascular system: Mechanisms, consequences and target for therapy. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2014, 20, 616–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreier, B.; Rabe, S.; Schneider, B.; Bretschneider, M.; Rupp, S.; Ruhs, S.; Neumann, J.; Rueckschloss, U.; Sibilia, M.; Gotthardt, M.; et al. Loss of epidermal growth factor receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells and cardiomyocytes causes arterial hypotension and cardiac hypertrophy. Hypertension 2013, 61, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrester, S.J.; Kawai, T.; O’Brien, S.; Thomas, W.; Harris, R.C.; Eguchi, S. Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Transactivation: Mechanisms, Pathophysiology, and Potential Therapies in the Cardiovascular System. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 627–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, B.; Gekle, M.; Grossmann, C. Role of epidermal growth factor receptor in vascular structure and function. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2014, 23, 113–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belmadani, S.; Palen, D.I.; Gonzalez-Villalobos, R.A.; Boulares, H.A.; Matrougui, K. Elevated epidermal growth factor receptor phosphorylation induces resistance artery dysfunction in diabetic db/db mice. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1629–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benter, I.F.; Yousif, M.H.M.; Griffiths, S.M.; Benboubetra, M.; Akhtar, S. Epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase-mediated signalling contributes to diabetes-induced vascular dysfunction in the mesenteric bed. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2005, 145, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benter, I.F.; Benboubetra, M.; Hollins, A.J.; Yousif, M.H.M.; Canatan, H.; Akhtar, S. Early inhibition of EGFR signaling prevents diabetes-induced up-regulation of multiple gene pathways in the mesenteric vasculature. Vascul. Pharmacol. 2009, 51, 236–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benter, I.F.; Sarkhou, F.; Al-Khaldi, A.T.; Chandrasekhar, B.; Attur, S.; Dhaunsi, G.S.; Yousif, M.H.M.; Akhtar, S. The dual targeting of EGFR and ErbB2 with the inhibitor Lapatinib corrects high glucose-induced apoptosis and vascular dysfunction by opposing multiple diabetes-induced signaling changes. J. Drug Target. 2015, 23, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Uttarwar, L.; Gao, B.; Charbonneau, M.; Shi, Y.; Chan, J.S.; Dubois, C.M.; Krepinsky, J.C. High Glucose up-regulates ADAM17 through HIF-1α in Mesangial Cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 21603–21614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Eguchi, S. The epidermal growth factor receptor: A missing link between endoplasmic reticulum stress and diabetic complications? Hypertension 2012, 60, 20–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Schreier, B.; Hünerberg, M.; Rabe, S.; Mildenberger, S.; Bethmann, D.; Heise, C.; Sibilia, M.; Offermanns, S.; Gekle, M. Consequences of postnatal vascular smooth muscle EGFR deletion on acute angiotensin II action. Clin. Sci. 2016, 130, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, B.; Stern, C.; Dubourg, V.; Nolze, A.; Rabe, S.; Mildenberger, S.; Wickenhauser, C.; Gekle, M. Endothelial epidermal growth factor receptor is of minor importance for vascular and renal function and obesity-induced dysfunction in mice. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, B.; Hünerberg, M.; Mildenberger, S.; Rabe, S.; Bethmann, D.; Wickenhauser, C.; Gekle, M. Deletion of the EGF receptor in vascular smooth muscle cells prevents chronic angiotensin II-induced arterial wall stiffening and media thickening. Acta Physiol. 2018, 222, e12996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, C.; Schreier, B.; Nolze, A.; Rabe, S.; Mildenberger, S.; Gekle, M. Knockout of vascular smooth muscle EGF receptor in a mouse model prevents obesity-induced vascular dysfunction and renal damage in vivo. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 2218–2234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, I.; Mundy, A.L.; Widmer, C.C.; Kretz, M.; Barton, M. Regional heterogeneity of functional changes in conduit arteries after high-fat diet. Obesity 2008, 16, 743–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacher, P.; Nagayama, T.; Mukhopadhyay, P.; Bátkai, S.; Kass, D.A. Measurement of cardiac function using pressure–volume conductance catheter technique in mice and rats. Nat. Protoc. 2008, 3, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boustany-Kari, C.M.; Gong, M.; Akers, W.S.; Guo, Z.; Cassis, L.A. Enhanced vascular contractility and diminished coronary artery flow in rats made hypertensive from diet-induced obesity. Int. J. Obes. 2007, 31, 1652–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Huang, W.; Chen, X.; Shan, P.; Zhong, P.; Khan, Z.; Wang, J.; Fang, Q.; Liang, G.; et al. Inhibition of epidermal growth factor receptor attenuates atherosclerosis via decreasing inflammation and oxidative stress. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bock, J.M.; Hughes, W.E.; Ueda, K.; Feider, A.J.; Hanada, S.; Kruse, N.T.; Iwamoto, E.; Casey, D.P. Greater α1-adrenergic-mediated vasoconstriction in contracting skeletal muscle of patients with type 2 diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2020, 319, H797–H807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, V.L.; Shi, Z.; Holwerda, S.W.; Fadel, P.J. Obesity-induced increases in sympathetic nerve activity: Sex matters. Auton. Neurosci. 2015, 187, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cooper, M.E. The role of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system in diabetes and its vascular complications. Am. J. Hypertens. 2004, 17, 16S–20S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benter, I.F.; Yousif, M.; Hollins, A.J.; Griffiths, S.M.; Akhtar, S. Diabetes-Induced Renal Vascular Dysfunction Is Normalized by Inhibition of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Tyrosine Kinase. J. Vasc. Res. 2005, 42, 284–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jewett, D.L. Activity of single efferent fibres in the cervical vagus nerve of the dog, with special reference to possible cardio-inhibitory fibres. J. Physiol. 1964, 175, 321–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pstras, L.; Thomaseth, K.; Waniewski, J.; Balzani, I.; Bellavere, F. The Valsalva manoeuvre: Physiology and clinical examples. Acta Physiol 2016, 217, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyton, A.G. Physiologic regulation of arterial pressure. Am. J. Cardiol. 1961, 8, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smyth, H.S.; Sleight, P.; Pickering, G.W. Reflex Regulation of Arterial Pressure during Sleep in Man. Circ. Res. 1969, 24, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreier, B.; Döhler, M.; Rabe, S.; Schneider, B.; Schwerdt, G.; Ruhs, S.; Sibilia, M.; Gotthardt, M.; Gekle, M.; Grossmann, C. Consequences of epidermal growth factor receptor (ErbB1) loss for vascular smooth muscle cells from mice with targeted deletion of ErbB1. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2011, 31, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knapp, J.; Aleth, S.; Balzer, F.; Gergs, U.; Schmitz, W.; Neumann, J. Comparison of Contractile Responses in Isolated Mouse Aorta and Pulmonary Artery: Influence of Strain and Sex. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2006, 48, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.-J. Dual modulation of vascular function by perivascular adipose tissue and its potential correlation with adiposity/lipoatrophy-related vascular dysfunction. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 2185–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbee, J.C.; Hollander, J.M.; Brock, R.W.; Yu, H.-G.; Boegehold, M.A. Integration of skeletal muscle resistance arteriolar reactivity for perfusion responses in the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2009, 296, R1771–R1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisbee, J.C. Enhanced arteriolar alpha-adrenergic constriction impairs dilator responses and skeletal muscle perfusion in obese Zucker rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 2004, 97, 764–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, S.F.; McKendrick, J.D.; Radomski, M.W.; Davidge, S.T.; Russell, J.C. Vascular wall reactivity in conductance and resistance arteries: Differential effects of insulin resistance. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1998, 76, 72–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belin de Chantemèle, E.J.; Mintz, J.D.; Rainey, W.E.; Stepp, D.W. Impact of leptin-mediated sympatho-activation on cardiovascular function in obese mice. Hypertension 2011, 58, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreihofer, A.M.; Hair, C.D.; Stepp, D.W. Reduced plasma volume and mesenteric vascular reactivity in obese Zucker rats. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2005, 288, R253–R261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chan, S.-L.; Umesalma, S.; Baumbach, G.L. Epidermal growth factor receptor is critical for angiotensin II-mediated hypertrophy in cerebral arterioles. Hypertension 2015, 65, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inagami, T.; Eguchi, S. Angiotensin II-mediated vascular smooth muscle cell growth signaling. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2000, 33, 619–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kagiyama, S.; Eguchi, S.; Frank, G.D.; Inagami, T.; Zhang, Y.C.; Phillips, M.I. Angiotensin II-induced cardiac hypertrophy and hypertension are attenuated by epidermal growth factor receptor antisense. Circulation 2002, 106, 909–912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goossens, G.H. The Renin-Angiotensin System in the Pathophysiology of Type 2 Diabetes. Obes. Facts 2012, 5, 611–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schreier, B.; Stern, C.; Rabe, S.; Mildenberger, S.; Gekle, M. Assessment of the Role of Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle EGFR for Acute Blood Pressure Effects of Angiotensin II and Adrenergic Stimulation in Obese Mice. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082241
Schreier B, Stern C, Rabe S, Mildenberger S, Gekle M. Assessment of the Role of Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle EGFR for Acute Blood Pressure Effects of Angiotensin II and Adrenergic Stimulation in Obese Mice. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(8):2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082241
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchreier, Barbara, Christian Stern, Sindy Rabe, Sigrid Mildenberger, and Michael Gekle. 2023. "Assessment of the Role of Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle EGFR for Acute Blood Pressure Effects of Angiotensin II and Adrenergic Stimulation in Obese Mice" Biomedicines 11, no. 8: 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082241
APA StyleSchreier, B., Stern, C., Rabe, S., Mildenberger, S., & Gekle, M. (2023). Assessment of the Role of Endothelial and Vascular Smooth Muscle EGFR for Acute Blood Pressure Effects of Angiotensin II and Adrenergic Stimulation in Obese Mice. Biomedicines, 11(8), 2241. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11082241





