Patient-Derived Tumoroid for the Prediction of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Responses in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Human Specimens, Tissue Preparation and PDT Formation
2.2. X-ray Irradiation
2.3. Chemotherapy Treatment
2.4. Cell Viability Assay
2.5. Histological and Immunofluorescence Staining
2.6. Quantitative PCR Analyses
2.7. Droplet Digital PCR
3. Results
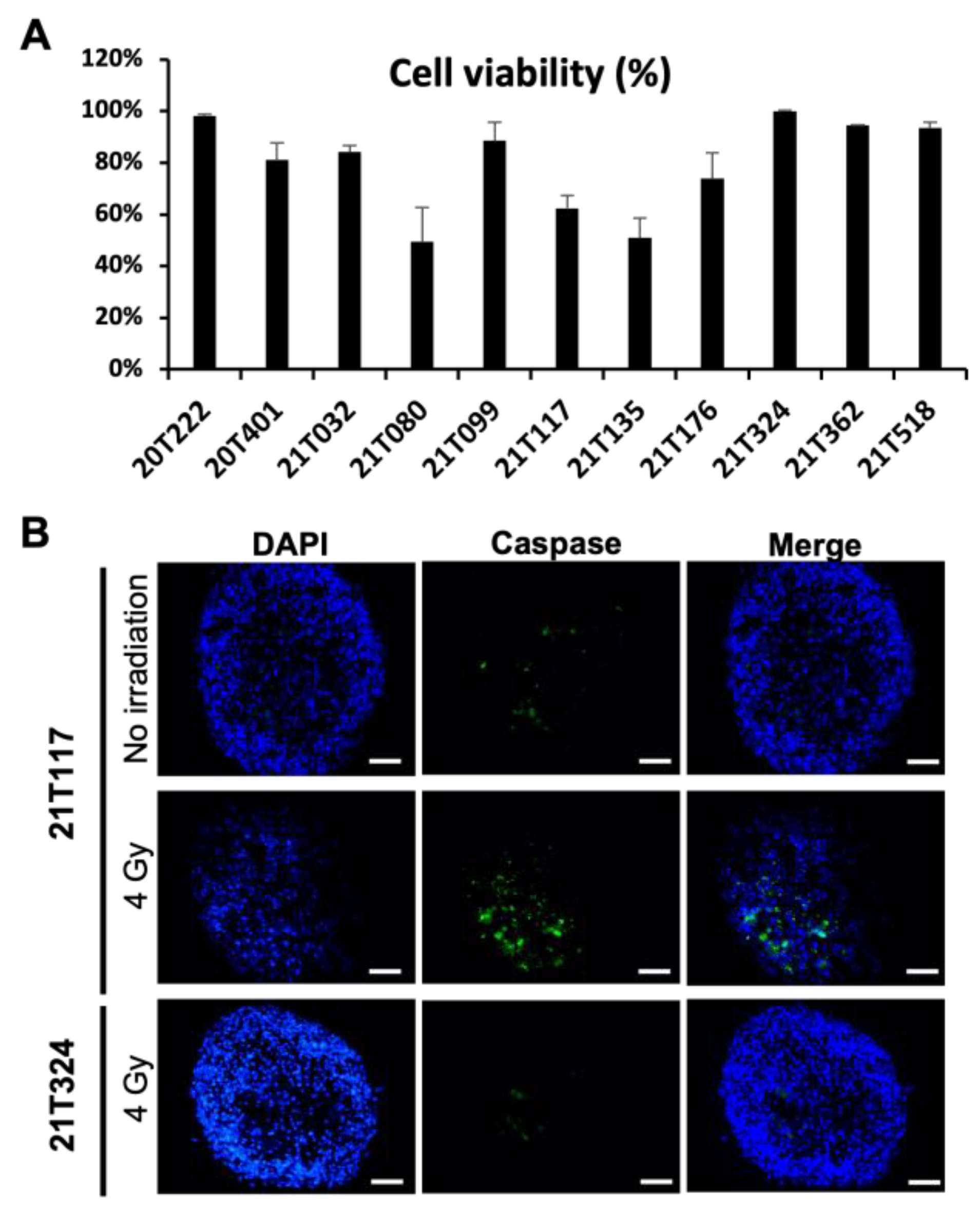
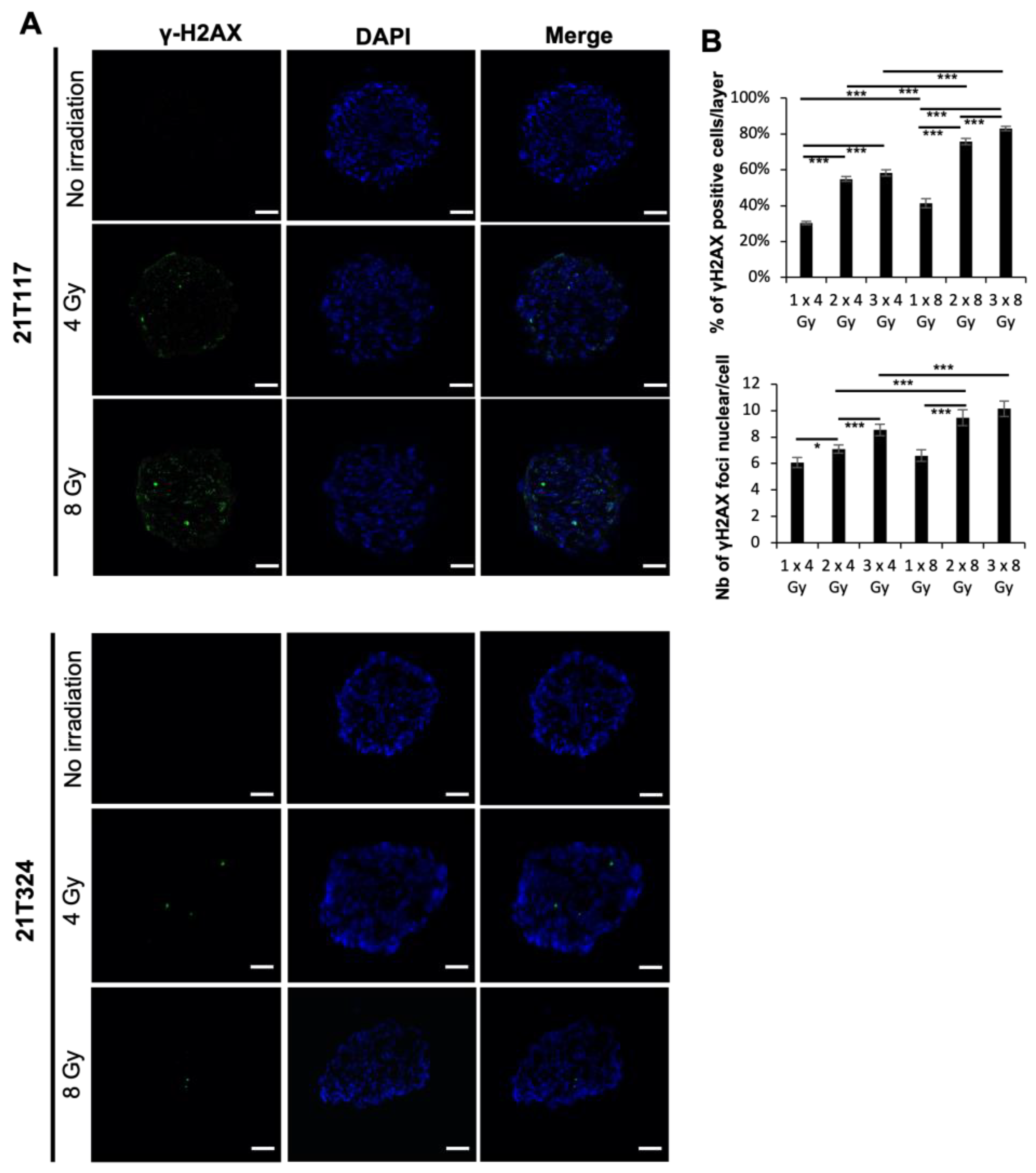
3.1. Identification of Different Dose–Responses of Lung Cancer PDTs to X-ray-Based Radiation Therapy
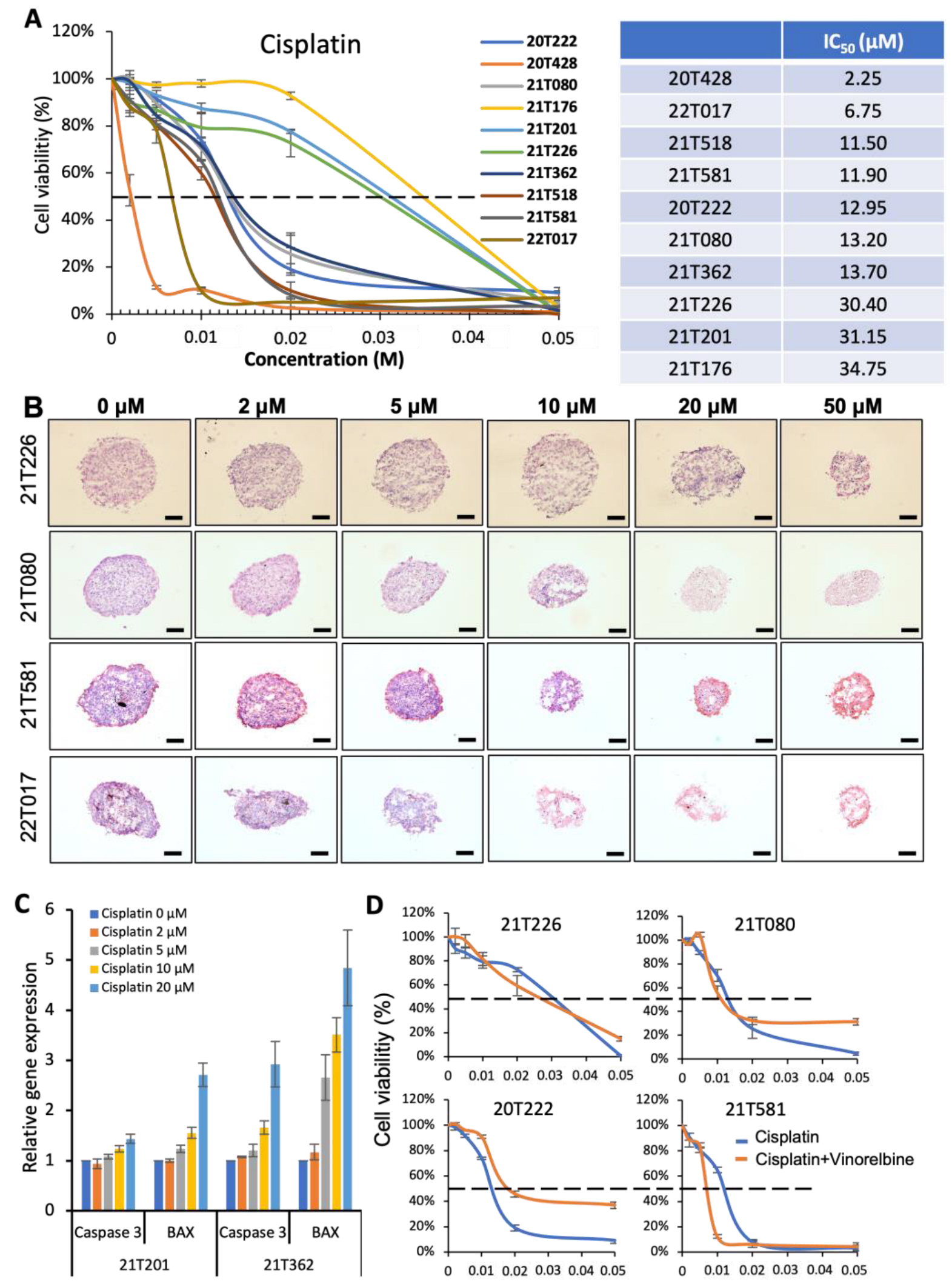
3.2. Identification of Different Dose–Responses of Lung Cancer PDTs to Cisplatin-Based Chemotherapy
3.3. Correlation of Bench Results from PDT Models with Clinical Outcome Assessment
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer Statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birring, S.S.; Peake, M.D. Symptoms and the Early Diagnosis of Lung Cancer. Thorax 2005, 60, 268–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ray, M.R.; Jablons, D.; He, B. Lung Cancer Therapeutics That Target Signaling Pathways: An Update. Expert Rev. Respir. Med. 2010, 4, 631–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liello, R.D.; Ciaramella, V.; Barra, G.; Venditti, M.; Corte, C.M.D.; Papaccio, F.; Sparano, F.; Viscardi, G.; Iacovino, M.L.; Minucci, S.; et al. Ex Vivo Lung Cancer Spheroids Resemble Treatment Response of a Patient with NSCLC to Chemotherapy and Immunotherapy: Case Report and Translational Study. ESMO Open 2019, 4, e000536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinod, S.K.; Hau, E. Radiotherapy Treatment for Lung Cancer: Current Status and Future Directions. Respirology 2020, 25, 61–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pechoux, C.L.; Pourel, N.; Barlesi, F.; Lerouge, D.; Antoni, D.; Lamezec, B.; Nestle, U.; Boisselier, P.; Dansin, E.; Paumier, A.; et al. Postoperative Radiotherapy versus No Postoperative Radiotherapy in Patients with Completely Resected Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Proven Mediastinal N2 Involvement (Lung ART, IFCT 0503): An Open-Label, Randomised, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oun, R.; Moussa, Y.E.; Wheate, N.J. The Side Effects of Platinum-Based Chemotherapy Drugs: A Review for Chemists. Dalton Trans. 2018, 47, 6645–6653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The Cancer Genome Atlas Research Network. Comprehensive Molecular Profiling of Lung Adenocarcinoma. Nature 2014, 511, 543–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, M.; Xu, X.; Fan, Y. KRAS-Mutant Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: An Emerging Promisingly Treatable Subgroup. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 672612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.L.; Bang, Y.-J.; Camidge, D.R.; Shaw, A.T.; Solomon, B.; Maki, R.G.; Ou, S.-H.I.; Dezube, B.J.; Jänne, P.A.; Costa, D.B.; et al. Anaplastic Lymphoma Kinase Inhibition in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergethon, K.; Shaw, A.T.; Ignatius Ou, S.-H.; Katayama, R.; Lovly, C.M.; McDonald, N.T.; Massion, P.P.; Siwak-Tapp, C.; Gonzalez, A.; Fang, R.; et al. ROS1 Rearrangements Define a Unique Molecular Class of Lung Cancers. J. Clin. Oncol. 2012, 30, 863–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drilon, A.; Wang, L.; Hasanovic, A.; Suehara, Y.; Lipson, D.; Stephens, P.; Ross, J.; Miller, V.; Ginsberg, M.; Zakowski, M.F.; et al. Response to Cabozantinib in Patients with RET Fusion-Positive Lung Adenocarcinomas. Cancer Discov. 2013, 3, 630–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.; Hunter, C.; Bignell, G.; Edkins, S.; Davies, H.; Teague, J.; Stevens, C.; O’Meara, S.; Smith, R.; Parker, A.; et al. Intragenic ERBB2 Kinase Mutations in Tumours. Nature 2004, 431, 525–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massarelli, E.; Papadimitrakopoulou, V.; Welsh, J.; Tang, C.; Tsao, A.S. Immunotherapy in Lung Cancer. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2014, 3, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Topalian, S.L.; Hodi, F.S.; Brahmer, J.R.; Gettinger, S.N.; Smith, D.C.; McDermott, D.F.; Powderly, J.D.; Carvajal, R.D.; Sosman, J.A.; Atkins, M.B.; et al. Safety, Activity, and Immune Correlates of Anti–PD-1 Antibody in Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2443–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.M.; Hwu, W.-J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and Activity of Anti–PD-L1 Antibody in Patients with Advanced Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.A.; Hughes, B.G.M. Targeted Therapy for Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Current Standards and the Promise of the Future. Transl. Lung Cancer Res. 2015, 4, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Maldegem, F.; Downward, J. Mutant KRAS at the Heart of Tumor Immune Evasion. Immunity 2020, 52, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkstra, K.K.; Cattaneo, C.M.; Weeber, F.; Chalabi, M.; van de Haar, J.; Fanchi, L.F.; Slagter, M.; van der Velden, D.L.; Kaing, S.; Kelderman, S.; et al. Generation of Tumor-Reactive T Cells by Co-Culture of Peripheral Blood Lymphocytes and Tumor Organoids. Cell 2018, 174, 1586–1598.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Mun, H.; Sung, C.O.; Cho, E.J.; Jeon, H.-J.; Chun, S.-M.; Jung, D.J.; Shin, T.H.; Jeong, G.S.; Kim, D.K.; et al. Patient-Derived Lung Cancer Organoids as in Vitro Cancer Models for Therapeutic Screening. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yokota, E.; Iwai, M.; Yukawa, T.; Yoshida, M.; Naomoto, Y.; Haisa, M.; Monobe, Y.; Takigawa, N.; Guo, M.; Maeda, Y.; et al. Clinical Application of a Lung Cancer Organoid (Tumoroid) Culture System. NPJ Precis Oncol. 2021, 5, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delom, F.; Begiristain, I.; Grenier, T.; Begueret, H.; Soulet, F.; Siegfried, G.; Khatib, A.-M.; Robert, J.; Fessart, D. Patients Lung Derived Tumoroids (PLDTs) to Model Therapeutic Response. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2020, 1867, 118808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitlinger, J.; Nounsi, A.; Idoux-Gillet, Y.; Santos Pujol, E.; Lê, H.; Grandgirard, E.; Olland, A.; Lindner, V.; Zaupa, C.; Balloul, J.-M.; et al. Vascularization of Patient-Derived Tumoroid from Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer and Its Microenvironment. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Qian, Y.; Li, W.; Liu, L.; Yu, L.; Liu, X.; Wu, G.; Wang, Y.; Luo, W.; Fang, F.; et al. Human Lung Adenocarcinoma-Derived Organoid Models for Drug Screening. iScience 2020, 23, 101411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moroni, M.; Maeda, D.; Whitnall, M.H.; Bonner, W.M.; Redon, C.E. Evaluation of the Gamma-H2AX Assay for Radiation Biodosimetry in a Swine Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 14119–14135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Xu, X.; Yang, L.; Zhu, J.; Wan, J.; Shen, L.; Xia, F.; Fu, G.; Deng, Y.; Pan, M.; et al. Patient-Derived Organoids Predict Chemoradiation Responses of Locally Advanced Rectal Cancer. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 17–26.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Sheng, Z.; Deng, W.; Yuan, H.; Wang, S.; Liu, Y. Advances of Patient-Derived Organoids in Personalized Radiotherapy. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 888416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, K.; Wu, C.; O’Rourke, K.P.; Szeglin, B.C.; Zheng, Y.; Sauvé, C.-E.G.; Adileh, M.; Wasserman, I.; Marco, M.R.; Kim, A.S.; et al. A Rectal Cancer Organoid Platform to Study Individual Responses to Chemoradiation. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1607–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakasheva, T.A.; Gabre, J.T.; Sachdeva, U.M.; Cruz-Acuña, R.; Lin, E.W.; DeMarshall, M.; Falk, G.W.; Ginsberg, G.G.; Yang, Z.; Kim, M.M.; et al. Patient-Derived Organoids as a Platform for Modeling a Patient’s Response to Chemoradiotherapy in Esophageal Cancer. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubert, C.G.; Rivera, M.; Spangler, L.C.; Wu, Q.; Mack, S.C.; Prager, B.C.; Couce, M.; McLendon, R.E.; Sloan, A.E.; Rich, J.N. A Three-Dimensional Organoid Culture System Derived from Human Glioblastomas Recapitulates the Hypoxic Gradients and Cancer Stem Cell Heterogeneity of Tumors Found in Vivo. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 2465–2477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundar, S.J.; Shakya, S.; Barnett, A.; Wallace, L.C.; Jeon, H.; Sloan, A.; Recinos, V.; Hubert, C.G. Three-Dimensional Organoid Culture Unveils Resistance to Clinical Therapies in Adult and Pediatric Glioblastoma. Transl. Oncol. 2021, 15, 101251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Driehuis, E.; Kolders, S.; Spelier, S.; Lõhmussaar, K.; Willems, S.M.; Devriese, L.A.; de Bree, R.; de Ruiter, E.J.; Korving, J.; Begthel, H.; et al. Oral Mucosal Organoids as a Potential Platform for Personalized Cancer Therapy. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 852–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putker, M.; Millen, R.; Overmeer, R.; Driehuis, E.; Zandvliet, M.M.J.M.; Clevers, H.; Boj, S.F.; Li, Q.-X. Medium-Throughput Drug- and Radiotherapy Screening Assay Using Patient-Derived Organoids. J. Vis. Exp. 2021, 170, e62495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lucky, S.S.; Law, M.; Lui, M.H.; Mong, J.; Shi, J.; Yu, S.; Yoon, D.K.; Djeng, S.K.; Wang, J.; Lim, C.M.; et al. Patient-Derived Nasopharyngeal Cancer Organoids for Disease Modeling and Radiation Dose Optimization. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 622244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacker, B.C.; Rafat, M. Organoids as Complex In Vitro Models for Studying Radiation-Induced Cell Recruitment. Cell Mol. Bioeng. 2020, 13, 341–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hua, G.; Wang, C.; Pan, Y.; Zeng, Z.; Lee, S.G.; Martin, M.L.; Haimovitz-Friedman, A.; Fuks, Z.; Paty, P.B.; Kolesnick, R. Distinct Levels of Radioresistance in Lgr5+ Colonic Epithelial Stem Cells versus Lgr5+ Small Intestinal Stem Cells. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2124–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasch, C.A.; Favreau, P.F.; Yueh, A.E.; Babiarz, C.P.; Gillette, A.A.; Sharick, J.T.; Karim, M.R.; Nickel, K.P.; DeZeeuw, A.K.; Sprackling, C.M.; et al. Patient-Derived Cancer Organoid Cultures to Predict Sensitivity to Chemotherapy and Radiation. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 5376–5387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reita, D.; Pabst, L.; Pencreach, E.; Guérin, E.; Dano, L.; Rimelen, V.; Voegeli, A.-C.; Vallat, L.; Mascaux, C.; Beau-Faller, M. Direct Targeting KRAS Mutation in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Focus on Resistance. Cancers 2022, 14, 1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Han, J.; Marcar, L.; Black, J.; Liu, Q.; Li, X.; Nagulapalli, K.; Sequist, L.V.; Mak, R.H.; Benes, C.H.; et al. Radiation Resistance in KRAS-Mutated Lung Cancer Is Enabled by Stem-like Properties Mediated by an Osteopontin-EGFR Pathway. Cancer Res. 2017, 77, 2018–2028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Shen, C.; Estrada-Bernal, A.; Robb, R.; Chatterjee, M.; Sebastian, N.; Webb, A.; Mo, X.; Chen, W.; Krishnan, S.; et al. Oncogenic KRAS Drives Radioresistance through Upregulation of NRF2-53BP1-Mediated Non-Homologous End-Joining Repair. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 11067–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalcman, G.; Beau-Faller, M.; Creveuil, C.; de Fraipont, F.; Mounawar, M.; Richard, N.; Bergot, E.; Favrot, M.; Morin, F.; Milleron, B. Use of Ras Effector RASSF1A Promoter Gene Methylation and Chromosome 9p Loss of Heterozygosity (LOH) to Predict Progression-Free Survival (PFS) in Perioperative Chemotherapy (CT) Phase III Trial IFCT-0002 in Resectable Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2008, 26, 7500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsao, M.-S.; Aviel-Ronen, S.; Ding, K.; Lau, D.; Liu, N.; Sakurada, A.; Whitehead, M.; Zhu, C.-Q.; Livingston, R.; Johnson, D.H.; et al. Prognostic and Predictive Importance of P53 and RAS for Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Non Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2007, 25, 5240–5247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimessy, A.; Radeczky, P.; Laszlo, V.; Hegedus, B.; Renyi-Vamos, F.; Fillinger, J.; Klepetko, W.; Lang, C.; Dome, B.; Megyesfalvi, Z. Current Therapy of KRAS-Mutant Lung Cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2020, 39, 1159–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gene Product | Forward Primer Sequence | Reverse Primer Sequence |
|---|---|---|
| GAPDH | CTGACTTCAACAGCGACACC | GTGGTCCAGGGGTCTTACTC |
| Caspase 3 | AGAACTGGACTGTGGCATTGAG | GCTTCTCGGCATACTGTTTCAG |
| BAX | GATGCGTCCACCAAGAAGCT | CGGCCCCAGTTGAAGTTG |
| Patient Identity | Sourcing | Gender | Age | NSCLC Subtype and TNM Score | Mutational Status | Decision MDTMs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20T222 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 80 | AC cT4N2Mx | KRAS G12C | Died quickly after surgery |
| 20T401 | CRB Strasbourg | F | 64 | AC cT3N0M0 | KRAS G12V | Adjuvant chemotherapy |
| 20T428 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 66 | AC pT3N3M0 | No mutation | Surveillance |
| 21T032 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 77 | SCC cT2aN0M0 | Unknown | Surveillance |
| 21T080 | CRB Strasbourg | F | 48 | AC cT1cN0M0 | EGFR deletion exon 19 | Adjuvant chemotherapy |
| 21T099 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 60 | AC cT2bN0M0 | KRAS G12D | Adjuvant chemotherapy |
| 21T117 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 69 | SCC cT3N0M0 | Unknown | Adjuvant radiotherapy |
| 21T135 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 71 | AC cT1bN0M1a | No mutation | Adjuvant chemotherapy |
| 21T176 | CRB Strasbourg | F | 55 | AC cT1cN0M0 | KRAS G12C | Surveillance |
| 21T201 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 68 | AC cT2aN1M0 | KRAS G12C | Adjuvant chemotherapy |
| 21T226 | CRB Strasbourg | F | 62 | AC cT2aN2M0 | KRAS G12C | Surveillance |
| 21T324 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 69 | AC cT2bN2M0 | Unknown | Immunotherapy |
| 21T362 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 65 | AC cT2bN2M0 | EGFR deletion exon 19 | Adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy |
| 21T518 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 84 | AC cT2bN0M1a | No mutation | No chemotherapy |
| 21T581 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 63 | AC cT1bN0M0 | Unknown | Surveillance |
| 22T017 | CRB Strasbourg | M | 79 | AC cT2bN2M0 | ROS 1 | Adjuvant chemotherapy and radiotherapy |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nounsi, A.; Seitlinger, J.; Ponté, C.; Demiselle, J.; Idoux-Gillet, Y.; Pencreach, E.; Beau-Faller, M.; Lindner, V.; Balloul, J.-M.; Quemeneur, E.; et al. Patient-Derived Tumoroid for the Prediction of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Responses in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071824
Nounsi A, Seitlinger J, Ponté C, Demiselle J, Idoux-Gillet Y, Pencreach E, Beau-Faller M, Lindner V, Balloul J-M, Quemeneur E, et al. Patient-Derived Tumoroid for the Prediction of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Responses in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071824
Chicago/Turabian StyleNounsi, Anasse, Joseph Seitlinger, Charlotte Ponté, Julien Demiselle, Ysia Idoux-Gillet, Erwan Pencreach, Michèle Beau-Faller, Véronique Lindner, Jean-Marc Balloul, Eric Quemeneur, and et al. 2023. "Patient-Derived Tumoroid for the Prediction of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Responses in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071824
APA StyleNounsi, A., Seitlinger, J., Ponté, C., Demiselle, J., Idoux-Gillet, Y., Pencreach, E., Beau-Faller, M., Lindner, V., Balloul, J.-M., Quemeneur, E., Burckel, H., Noël, G., Olland, A., Fioretti, F., Falcoz, P.-E., Benkirane-Jessel, N., & Hua, G. (2023). Patient-Derived Tumoroid for the Prediction of Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy Responses in Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1824. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071824







