Effects of Exercise Training on Circulating Biomarkers of Endothelial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients
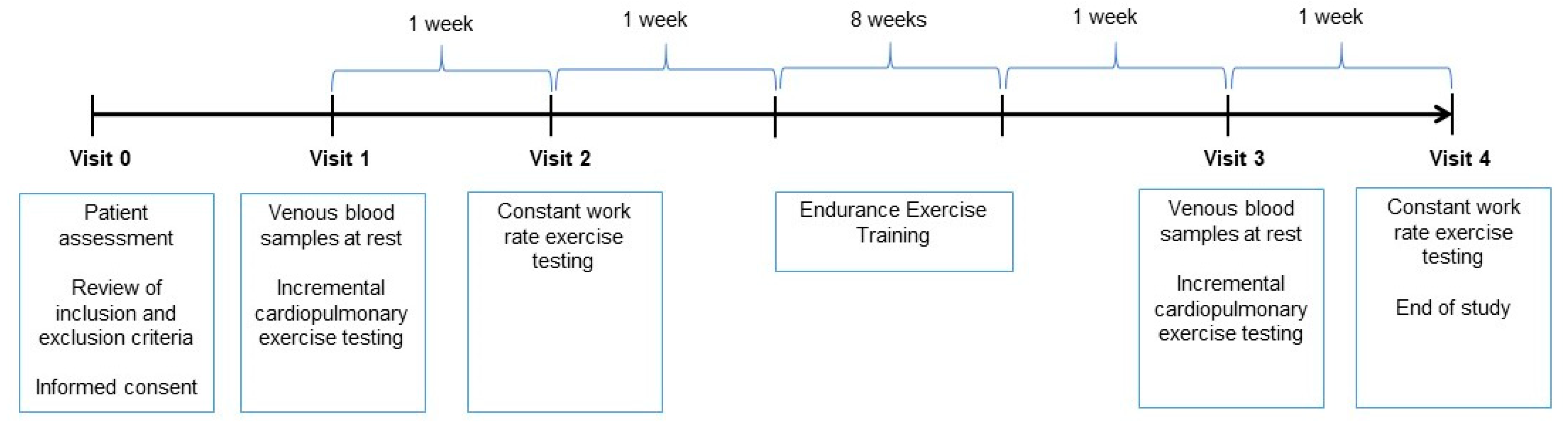
2.2. Exercise Capacity
2.3. Endurance Exercise Training
2.4. Blood Sampling
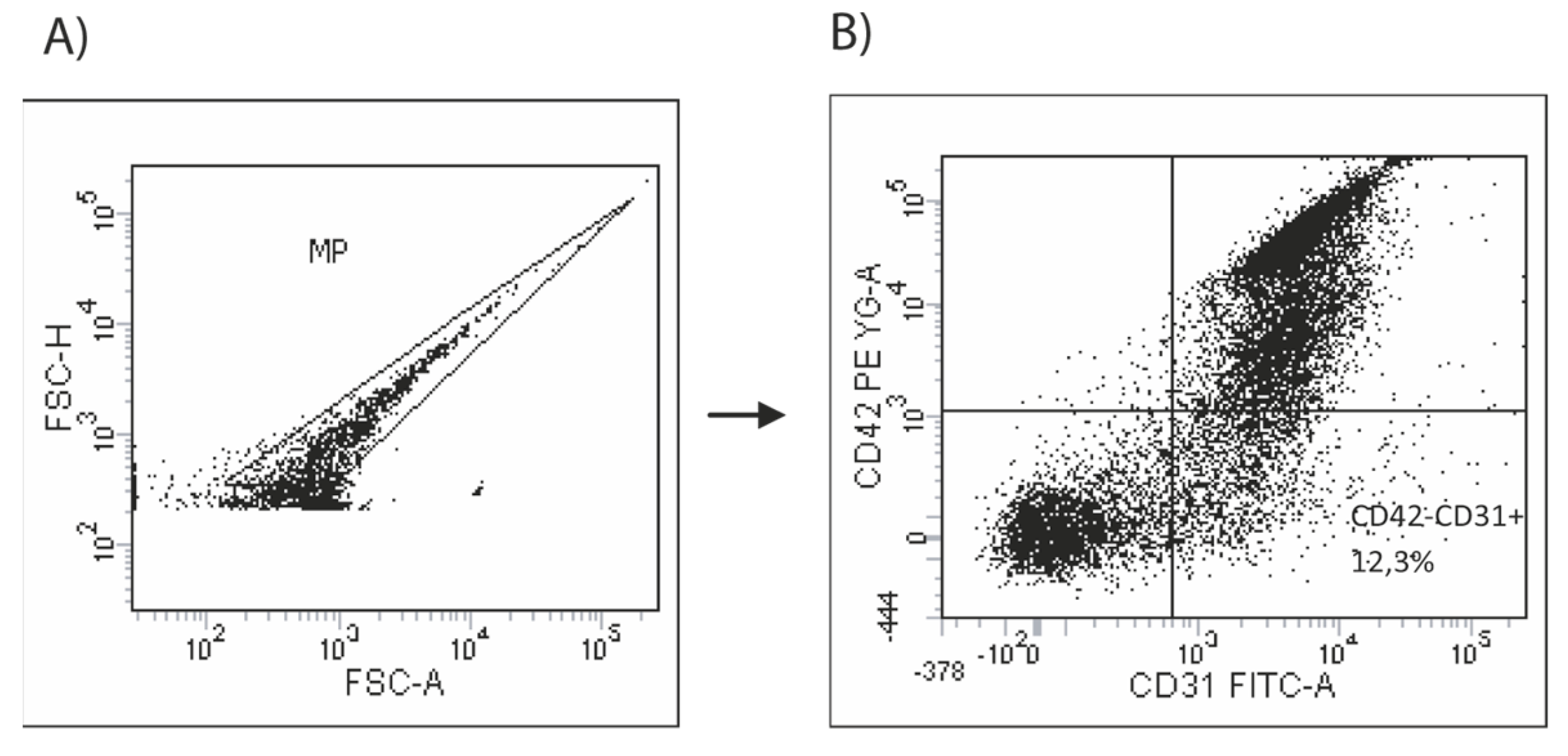
2.5. Assessment of Circulating Endothelial Microparticles
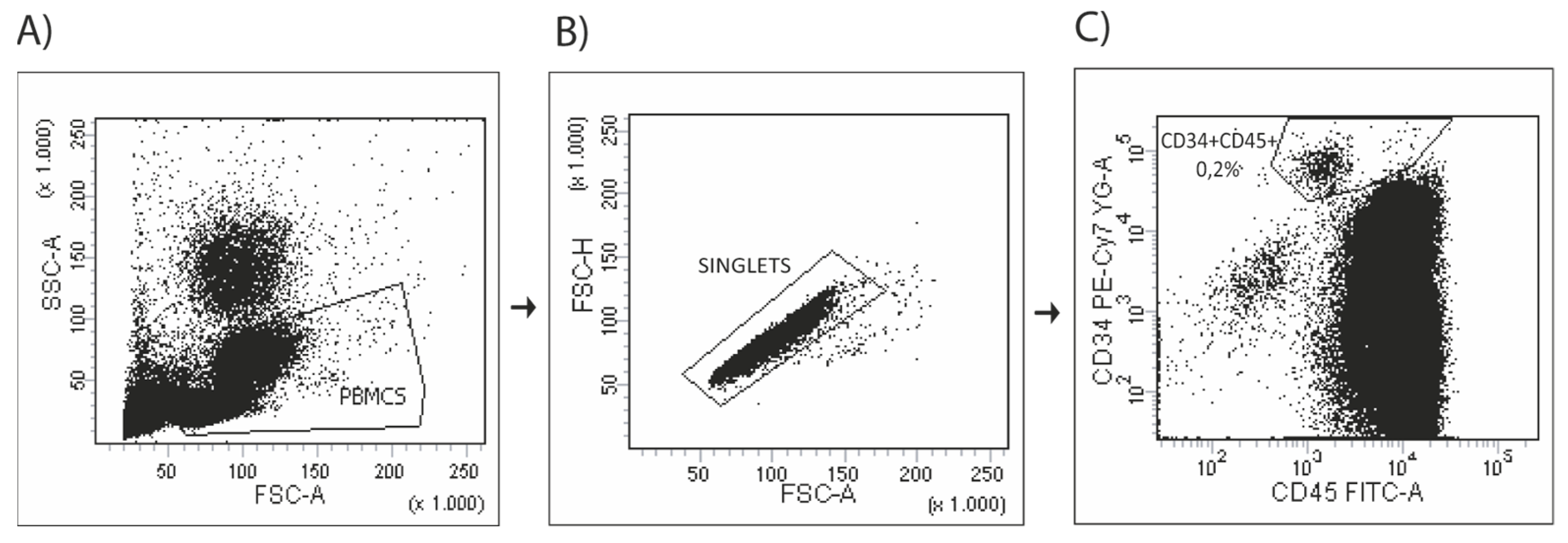
2.6. Assessment of Circulating Progenitor Cells
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
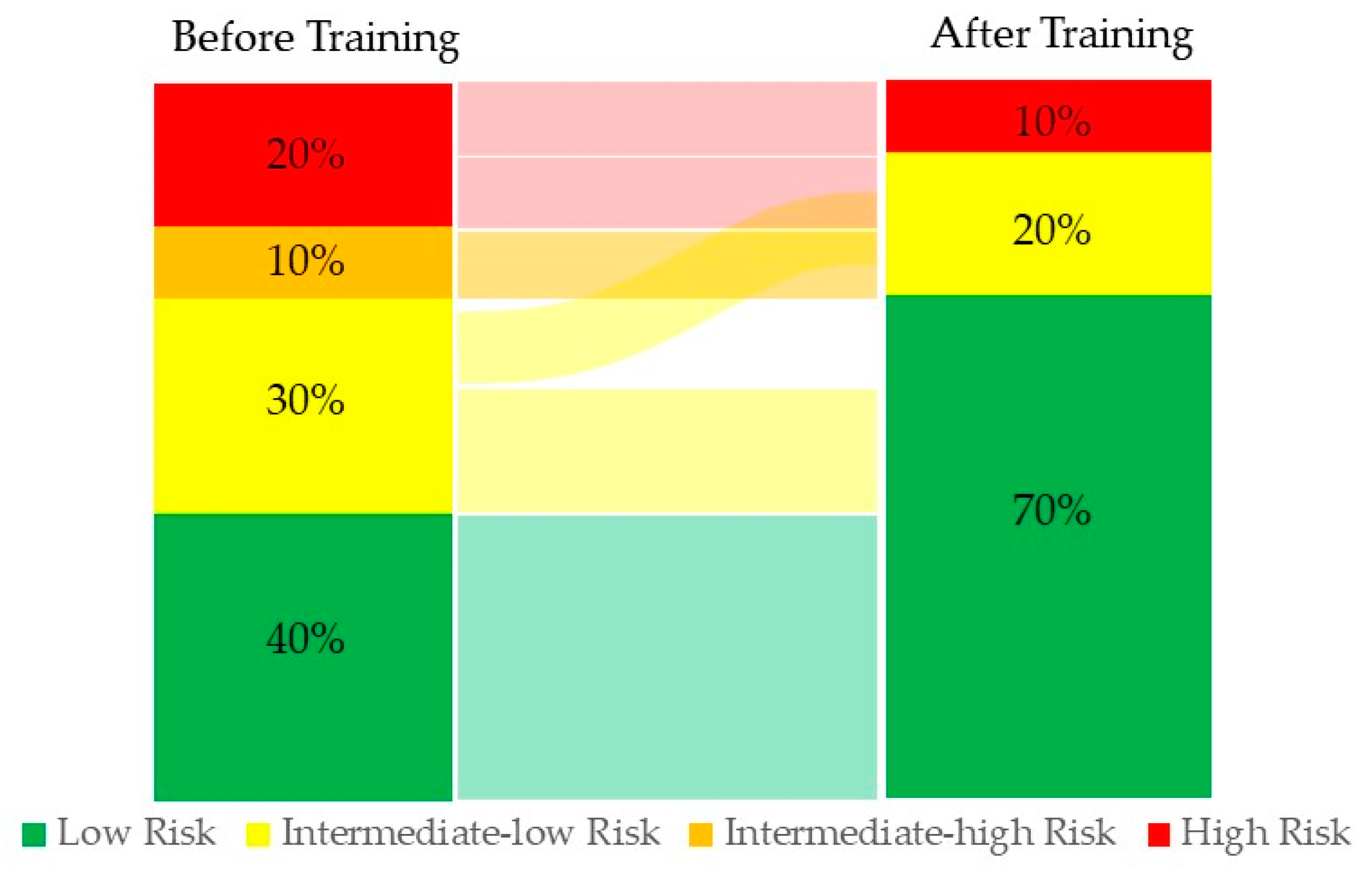
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Baseline Profiles
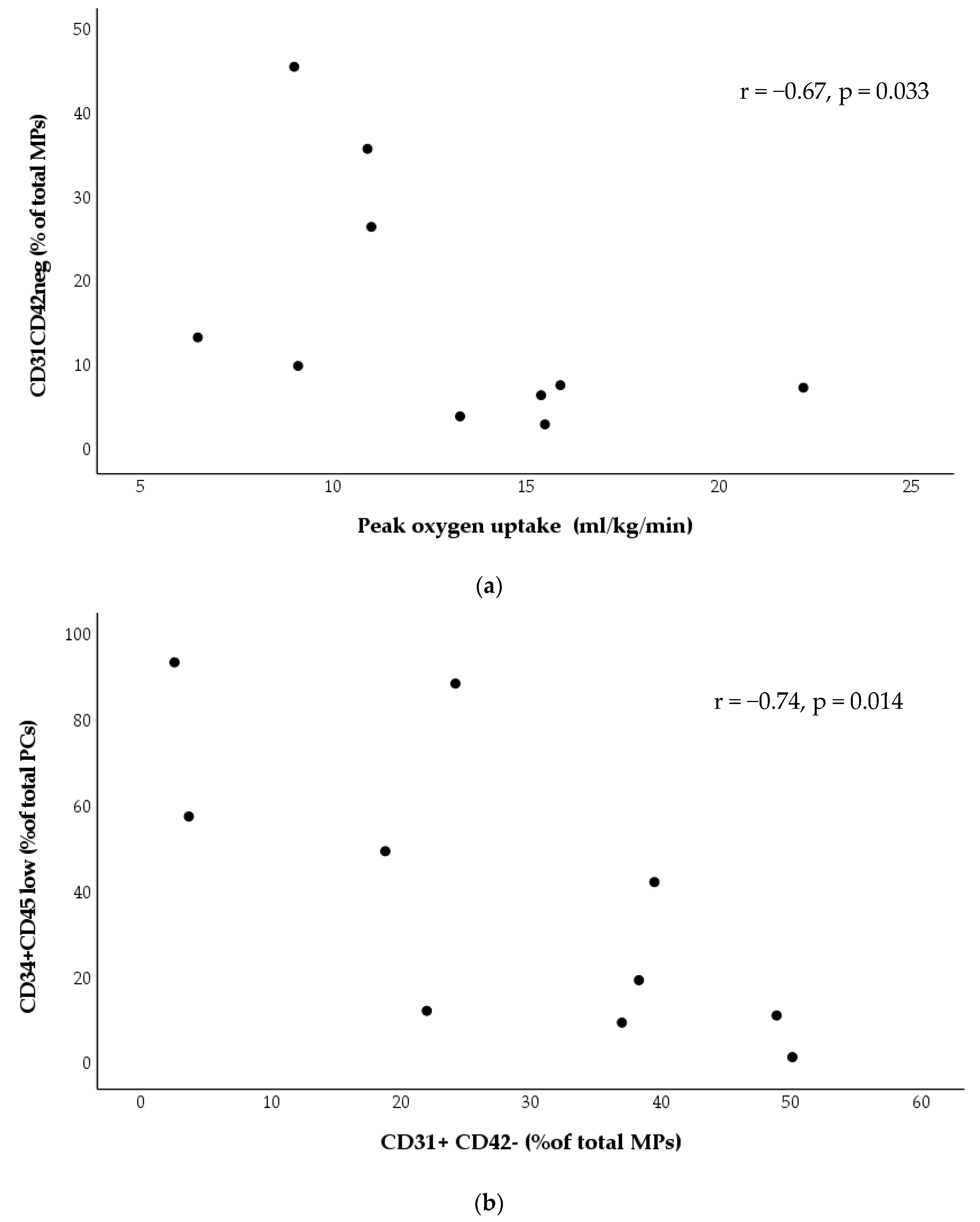
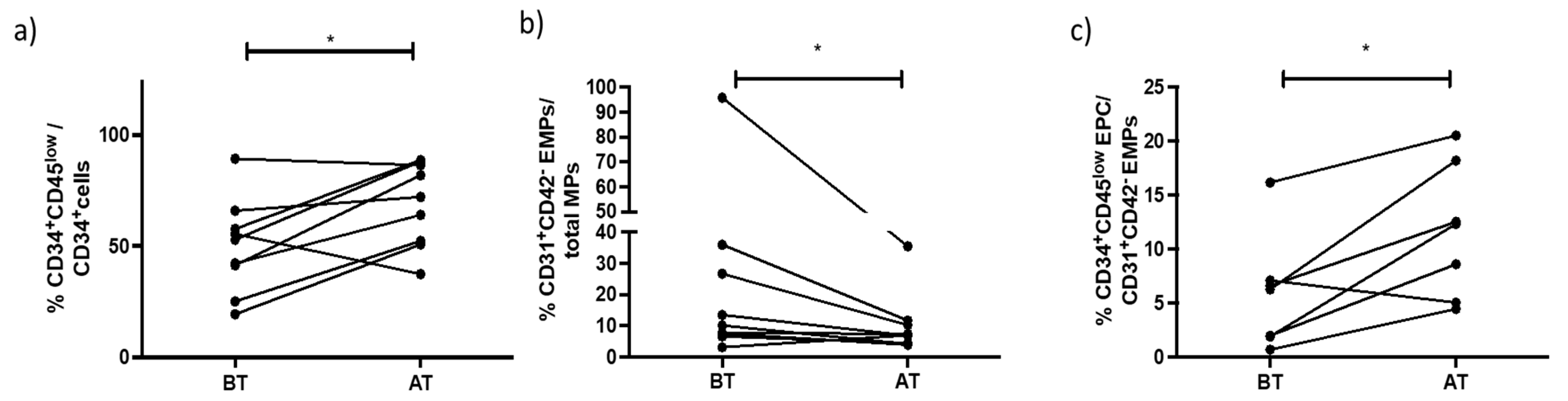
3.3. Effects of Exercise Training
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| PAH | Pulmonary arterial hypertension |
| PR | Pulmonary rehabilitation |
| PC | Circulating progenitor cells |
| EMV | Endothelial microvesicles |
| VO2 | Oxygen uptake pulmonary |
| VCO2 | Carbon dioxide output |
| RER | Respiratory exchange ratio |
| VE | Minute ventilation respiratory rate |
| RR | Respiratory rate |
| HR | Heart rate |
| SpO2 | Oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry |
| CWRET | Constant work rate exercise testing |
| Wpeak | Peak work rate |
| ET | Endurance time |
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Rosenkranz, S. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spruit, M.A.; Singh, S.J.; Garvey, C.; ZuWallack, R.; Nici, L.; Rochester, C.; Hill, K.; Holland, A.E.; Lareau, S.C.; Man, W.D.-C.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Key Concepts and Advances in Pulmonary Rehabilitation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 188, e13-642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünig, E.; Eichstaedt, C.; Barberà, J.-A.; Benjamin, N.; Blanco, I.; Bossone, E.; Cittadini, A.; Coghlan, G.; Corris, P.; D’Alto, M.; et al. ERS statement on exercise training and rehabilitation in patients with severe chronic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1800332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, R.; Siqueira, R.; Becker, C.U.; Fernandes, T.G.; Pires, K.M.; Valença, S.S.; Souza-Rabbo, M.P.; Araujo, A.S.; Belló-Klein, A. Effects of exercise on monocrotaline-induced changes in right heart function and pulmonary artery remodeling in rats. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2013, 91, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soares, L.L.; Drummond, F.R.; Rezende, L.M.T.; Costa, A.J.L.D.; Leal, T.F.; Fidelis, M.R.; Neves, M.M.; Prímola-Gomes, T.N.; Carneiro-Junior, M.A.; Reis, E.C.C.; et al. Voluntary running counteracts right ventricular adverse remodeling and myocyte contraction impairment in pulmonary arterial hypertension model. Life Sci. 2019, 238, 116974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harbaum, L.; Renk, E.; Yousef, S.; Glatzel, A.; Lüneburg, N.; Hennigs, J.K.; Oqueka, T.; Baumann, H.J.; Atanackovic, D.; Grünig, E.; et al. Acute effects of exercise on the inflammatory state in patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension. BMC Pulm. Med. 2016, 16, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mainguy, V.; Maltais, F.; Saey, D.; Gagnon, P.; Martel, S.; Simon, M.; Provencher, S. Effects of a Rehabilitation Program on Skeletal Muscle Function in Idiopathic Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2010, 30, 238–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.M.A.; Tucci, P.J.F.; Conzatti, A.; de Lima Seolin, B.G.; Fernandes, T.R.G.; da Rosa Araújo, A.S.; Belló-Klein, A. Exercise training contributes to H2O2/VEGF signaling in the lung of rats with monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension. Vasc. Pharm. 2016, 87, 49–59. [Google Scholar]
- Moreira-Gonçalves, D.; Ferreira, R.; Fonseca, H.; Padrão, A.I.; Moreno, N.; Silva, A.F.; Vasques-Nóvoa, F.; Gonçalves, N.; Vieira, S.; Santos, M.; et al. Cardioprotective effects of early and late aerobic exercise training in experimental pulmonary arterial hypertension. Basic Res. Cardiol. 2015, 110, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, A.; Teixeira, R.B.; Bonetto, J.H.P.; Siqueira, R.; Carraro, C.C.; Donatti, L.M.; Hickmann, A.; Litvin, I.E.; Godoy, A.E.G.; Araujo, A.S.; et al. Effects of aerobic exercise training on metabolism of nitric oxide and endothelin-1 in lung parenchyma of rats with pulmonary arterial hypertension. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2017, 429, 73–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Potus, F.; Malenfant, S.; Graydon, C.; Mainguy, V.; Tremblay, È.; Breuils-Bonnet, S.; Ribeiro, F.; Porlier, A.; Maltais, F.; Bonnet, S.; et al. Impaired Angiogenesis and Peripheral Muscle Microcirculation Loss Contribute to Exercise Intolerance in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2014, 190, 318–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandoo, A.; Veldhuijzen van Zanten, J.J.C.; Metsios, G.S.; Carroll, D.; Kitas, G.D. The Endothelium and Its Role in Regulating Vascular Tone. Open Cardiovasc. Med. J. 2015, 4, 302–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pober, J.S.; Min, W.; Bradley, J.R. Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction, injury, and death. Annual Review of Pathology: Mechanisms of Disease. Annu. Rev. Pathol. 2009, 4, 71–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huertas, A.; Guignabert, C.; Barberà, J.A.; Bärtsch, P.; Bhattacharya, J.; Bhattacharya, S.; Wilkins, M.R. Pulmonary vascular endothelium: The orchestra conductor in respiratory diseases Highlights from basic research to therapy. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1700745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabatier, F.; Camoin-Jau, L.; Anfosso, F.; Sampol, J.; Dignat-George, F. Circulating endothelial cells, microparticles and progenitors: Key players towards the definition of vascular competence. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 454–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, D.; Touyz, R.M. Cellular biomarkers of endothelial health: Microparticles, endothelial progenitor cells, and circulating endothelial cells. J. Am. Soc. Hypertens. 2012, 6, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutroumpi, M. Circulating endothelial and progenitor cells: Evidence from acute and long-term exercise effects. World J. Cardiol. 2012, 4, 312–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Highton, P.J.; Martin, N.; Smith, A.C.; Burton, J.; Bishop, N.C. Microparticles and Exercise in Clinical Populations. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 24, 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Radtke, T.; Crook, S.; Kaltsakas, G.; Louvaris, Z.; Berton, D.; Urquhart, D.S.; Kampouras, A.; Rabinovich, R.A.; Verges, S.; Kontopidis, D.; et al. ERS statement on standardisation of cardiopulmonary exercise testing in chronic lung diseases. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2019, 28, 180101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puente-Maestu, L.; Palange, P.; Casaburi, R.; Laveneziana, P.; Maltais, F.; Neder, J.A.; O’Donnell, D.E.; Onorati, P.; Porszasz, J.; Rabinovich, R.; et al. Use of exercise testing in the evaluation of interventional efficacy: An official ERS statement. Eur. Respir. J. 2016, 47, 429–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maltais, F.; Celli, B.; Casaburi, R.; Porszasz, J.; Jarreta, D.; Seoane, B.; Caracta, C. Aclidinium bromide improves exercise endurance and lung hyperinflation in patients with moderate to severe COPD. Respir. Med. 2011, 105, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García-Lucio, J.; Peinado, V.I.; de Jover, L.; del Pozo, R.; Blanco, I.; Bonjoch, C.; Paul, T. Imbalance between endothelial damage and repair capacity in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0195724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tura-Ceide, O.; Blanco, I.; Garcia-Lucio, J.; del Pozo, R.; García, A.R.; Ferrer, E.; Crespo, I.; Rodríguez-Chiaradia, D.A.; Simeon-Aznar, C.P.; López-Meseguer, M.; et al. Circulating Cell Biomarkers in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Relationship with Clinical Heterogeneity and Therapeutic Response. Cells 2021, 10, 1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feher, K.; Kirsch, J.; Radbruch, A.; Chang, H.-D.; Kaiser, T. Cell population identification using fluorescence-minus-one controls with a one-class classifying algorithm. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 3372–3378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Lucke, C.; Fichtlscherer, S.; Aicher, A.; Tschöpe, C.; Schultheiss, H.-P.; Zeiher, A.M.; Dimmeler, S. Quantification of Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells Using the Modified ISHAGE Protocol. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e13790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, N.; Kosiol, S.; Schiegl, T.; Ahlers, P.; Walenta, K.; Link, A.; Böhm, M.; Nickenig, G. Circulating Endothelial Progenitor Cells and Cardiovascular Outcomes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 353, 999–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahhan, A.S.; Hammadah, M.; Sandesara, P.B.; Hayek, S.S.; Kalogeropoulos, A.P.; Alkhoder, A.; Kelli, H.M.; Topel, M.; Ghasemzadeh, N.; Chivukula, K.; et al. Progenitor Cells and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Heart Failure. Circ. Hear Fail. 2017, 10, e004106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandri, M.; Viehmann, M.; Adams, V.; Rabald, K.; Mangner, N.; Höllriegel, R.; Lurz, P.; Erbs, S.; Linke, A.; Kirsch, K.; et al. Chronic heart failure and aging—effects of exercise training on endothelial function and mechanisms of endothelial regeneration: Results from the Leipzig Exercise Intervention in Chronic heart failure and Aging (LEICA) study. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2015, 23, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Handoko, M.; Man, F.H.-D.; Happé, C.; Schalij, I.; Musters, R.; Westerhof, N.; Postmus, P.; Paulus, W.; van der Laarse, W.; Vonk-Noordegraaf, A. Opposite Effects of Training in Rats with Stable and Progressive Pulmonary Hypertension. Circulation 2009, 120, 42–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehlken, N.; Lichtblau, M.; Klose, H.; Weidenhammer, J.; Fischer, C.; Nechwatal, R.; Uiker, S.; Halank, M.; Olsson, K.; Seeger, W.; et al. Exercise training improves peak oxygen consumption and haemodynamics in patients with severe pulmonary arterial hypertension and inoperable chronic thrombo-embolic pulmonary hypertension: A prospective, randomized, controlled trial. Eur. Heart J. 2016, 37, 35–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lansford, K.A.; Shill, D.D.; Dicks, A.B.; Marshburn, M.P.; Southern, W.M.; Jenkins, N.T. Effect of acute exercise on circulating angiogenic cell and microparticle populations. Exp. Physiol. 2016, 101, 155–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnier, L.; Fontana, P.; Kwak, B.R.; Angelillo-Scherrer, A. Cell-derived microparticles in haemostasis and vascular medicine. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 101, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mezentsev, A.; Merks, R.M.; O’Riordan, E.; Chen, J.; Mendelev, N.; Goligorsky, M.S.; Brodsky, S.V. Endothelial microparticles affect angiogenesis in vitro: Role of oxidative stress. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005, 289, H1106–H1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, E.N.; Mourot, L.; Rakobowchuk, M. Exercise-Derived Microvesicles: A Review of the Literature. Sports Med. 2018, 48, 2025–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Age (years) | 54 (12.6) |
| Male (%) | 20 |
| Body Mass Index (kg/m2) | 26.5 (10) |
| Mean Pulmonary Arterial Pressure (mmHg) | 39.4 (8.6) |
| Pulmonary Vascular Resistance (Wood unit) | 6.8 (3) |
| Cardiac Index (L/m2) | 2.5 (0.6) |
| Pulmonary Arterial Wedge Pressure (mmHg) | 9.5 (4) |
| Right Atrial Pressure (mmHg) | 8 (3.8) |
| FEV1/FVC (% pred) | 69.4 (7) |
| FEV1 (% pred) | 68 (6.8) |
| FVC (% pred) | 77 (9) |
| DLCO (% pred) | 63 (20) |
| TLC (% pred) | 98 (15) |
| FC II (%) | 90 |
| Double therapy (%) | 80 |
| GROUP (n) | |
| CHD | 2 |
| SS | 2 |
| HIV | 2 |
| Idiopathic | 3 |
| SLE | 1 |
| Exercise Parameters | Basal | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| ICPET | |||
| Workload (Watts) peak | 59 (29) | ||
| Workload (% predicted) peak | 55 (16) | ||
| VO2 (mL/kg/min) peak | 13 (4) | ||
| VO2 (% predicted) peak | 50 (14) | ||
| VO2 (% predicted) AT | 28 (17) | ||
| VE (% max) peak | 60 (16) | ||
| HR peak (beat per minute) | 126 (19) | ||
| HR (% predicted) peak | 76 (12) | ||
| O2 pulse peak | 6.3 (2) | ||
| VE/VCO2 AT | 35 (2) | ||
| Borg dyspnea final | 6 (3) | ||
| Borg leg final | 5 (2) | ||
| CWRET | Before ET | After ET | p value |
| Endurance time (seconds) | 260 (125) | 527 (299) | 0.004 |
| VO2 (isotime) (L/min) | 0.61 (0.1) | 0.75 (0.2) | 0.042 |
| VE (isotime) | 36 (11) | 35 (11) | 0.534 |
| HR (isotime) | 132 (15) | 122 (13) | 0.042 |
| O2 pulse (isotime) | 4 (0.5) | 6 (1) | 0.038 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rodríguez-Chiaradía, D.A.; Khilzi, K.; Blanco, I.; Rodó-Pin, A.; Martin-Ontiyuelo, C.; Herranz Blasco, A.; Garcia-Lucio, J.; Molina, L.; Marco, E.; Barreiro, E.; et al. Effects of Exercise Training on Circulating Biomarkers of Endothelial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071822
Rodríguez-Chiaradía DA, Khilzi K, Blanco I, Rodó-Pin A, Martin-Ontiyuelo C, Herranz Blasco A, Garcia-Lucio J, Molina L, Marco E, Barreiro E, et al. Effects of Exercise Training on Circulating Biomarkers of Endothelial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(7):1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071822
Chicago/Turabian StyleRodríguez-Chiaradía, Diego A., Karys Khilzi, Isabel Blanco, Anna Rodó-Pin, Clara Martin-Ontiyuelo, Anna Herranz Blasco, Jessica Garcia-Lucio, Lluis Molina, Ester Marco, Esther Barreiro, and et al. 2023. "Effects of Exercise Training on Circulating Biomarkers of Endothelial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension" Biomedicines 11, no. 7: 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071822
APA StyleRodríguez-Chiaradía, D. A., Khilzi, K., Blanco, I., Rodó-Pin, A., Martin-Ontiyuelo, C., Herranz Blasco, A., Garcia-Lucio, J., Molina, L., Marco, E., Barreiro, E., Piccari, L., Peinado, V. I., Garcia, A. R., Tura-Ceide, O., & Barberà, J. A. (2023). Effects of Exercise Training on Circulating Biomarkers of Endothelial Function in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. Biomedicines, 11(7), 1822. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11071822








