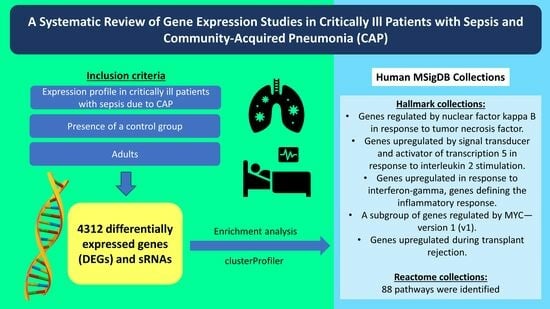
A Systematic Review of Gene Expression Studies in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Metlay, J.P.; Waterer, G.W.; Long, A.C.; Anzueto, A.; Brozek, J.; Crothers, K.; Cooley, L.A.; Dean, N.C.; Fine, M.J.; Flanders, S.A.; et al. Diagnosis and Treatment of Adults with Community-acquired Pneumonia. An Official Clinical Practice Guideline of the American Thoracic Society and Infectious Diseases Society of America. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2019, 200, e45–e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lutfiyya, M.N.; Henley, E.; Chang, L.F.; Reyburn, S.W. Diagnosis and Treatment of Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Am. Fam. Physician 2006, 73, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Womack, J.; Kropa, J. Community-Acquired Pneumonia in Adults: Rapid Evidence Review. Am. Fam. Physician 2022, 105, 625–630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Viasus, D.; Cillóniz, C.; Cardozo, C.G.; Puerta, P.; Garavito, A.; Torres, A.; Garcia-Vida, C. Early, short and long-term mortality in community-acquired pneumonia. Ann. Res. Hosp. 2018, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siljan, W.W.; Holter, J.C.; Nymo, S.H.; Husebye, E.; Ueland, T.; Aukrust, P.; Mollnes, T.E.; Heggelund, L. Cytokine responses, microbial aetiology and short-term outcome in community-acquired pneumonia. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 48, e12865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vught, L.A.; Scicluna, B.P.; Wiewel, M.A.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; Klein Klouwenberg, P.M.; Franitza, M.; Toliat, M.R.; Nürnberg, P.; Cremer, O.L.; Horn, J.; et al. Comparative Analysis of the Host Response to Community-acquired and Hospital-acquired Pneumonia in Critically Ill Patients. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care. Med. 2016, 194, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellum, J.A.; Kong, L.; Fink, M.P.; Weissfeld, L.A.; Yealy, D.M.; Pinsky, M.R.; Fine, J.; Krichevsky, A.; Delude, R.L.; Angus, D.C.; et al. Understanding the inflammatory cytokine response in pneumonia and sepsis. Arch. Intern. Med. 2007, 167, 1655–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonetti, A.F.; Garcia-Vidal, C.; Viasus, D.; García-Somoza, D.; Dorca, J.; Gudiol, F.; Carratalà, J. Declining mortality among hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 567.e1–567.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niederman, M.S.; Torres, A. Severe community-acquired pneumonia. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 220123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotchkiss, R.S.; Moldawer, L.L.; Opal, S.M.; Reinhart, K.; Turnbull, I.R.; Vincent, J.L. Sepsis and septic shock. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2016, 2, 16045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.; Perna, B.; Cesaro, A.E.; Maritati, M.; Spampinato, M.D.; Contini, C.; De Giorgio, R. 2023 Update on Sepsis and Septic Shock in Adult Patients: Management in the Emergency Department. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gyawali, B.; Ramakrishna, K.; Dhamoon, A.S. Sepsis: The evolution in definition, pathophysiology, and management. SAGE Open. Med. 2019, 7, 2050312119835043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ceccato, A.; Torres, A. Sepsis and community-acquired pneumonia. Ann. Res. Hosp. 2018, 2, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, L.; Rhodes, A.; Alhazzani, W.; Antonelli, M.; Coopersmith, C.M.; French, C.; Machado, F.R.; Mcintyre, L.; Ostermann, M.; Prescott, H.C.; et al. Surviving sepsis campaign: International guidelines for management of sepsis and septic shock 2021. Crit. Care Med. 2021, 47, 1181–1247. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, C.; Zhao, D.; Zheng, L.; Bao, X.; Yang, Q.; Jiang, S.; Zhou, X.; Tang, L.; Liu, Z. Safety and efficacy of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for the treatment of sepsis induced by pneumonia: Study protocol for a single-centre, randomised single-blind parallel group trial. BMJ Open. 2022, 12, e058444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.Y.; Ding, X.F.; Liang, H.Y.; Zhang, X.J.; Liu, S.H.; Han, B.; Duan, X.G.; Sun, T.W. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell therapy for sepsis: A meta-analysis of preclinical studies. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 11, 214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masterson, C.H.; Ceccato, A.; Artigas, A.; Dos Santos, C.; Rocco, P.R.; Rolandsson Enes, S.; Weiss, D.J.; McAuley, D.; Matthay, M.A.; English, K.; et al. Mesenchymal stem/stromal cell-based therapies for severe viral pneumonia: Therapeutic potential and challenges. Intensive Care Med. Exp. 2021, 9, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viasus, D.; Simonetti, A.F.; Nonell, L.; Vidal, O.; Meije, Y.; Ortega, L.; Arnal, M.; Bódalo-Torruella, M.; Sierra, M.; Rombauts, A.; et al. Whole-Blood Gene Expression Profiles Associated with Mortality in Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereverzeva, L.; Uhel, F.; Peters Sengers, H.; Butler, J.; van Vught, L.A.; Burnham, K.L.; Davenport, E.E.; Knight, J.C.; Cremer, O.L.; Schultz, M.J.; et al. Blood leukocyte transcriptomes in Gram-positive and Gram-negative community-acquired pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2022, 59, 2101856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano-Gamez, E.; Burnham, K.L.; Goh, C.; Allcock, A.; Malick, Z.H.; Overend, L.; Kwok, A.; Smith, D.A.; Peters-Sengers, H.; Antcliffe, D.; et al. An immune dysfunction score for stratification of patients with acute infection based on whole-blood gene expression. Sci. Transl. Med. 2022, 14, eabq4433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davenport, E.E.; Burnham, K.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Humburg, P.; Hutton, P.; Mills, T.C.; Rautanen, A.; Gordon, A.C.; Garrard, C.; Hill, A.V.; et al. Genomic landscape of the individual host response and outcomes in sepsis: A prospective cohort study. Lancet Respir. Med. 2016, 4, 259–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhury, A.; Rajkumar, A.P. Systematic review of gene expression studies in people with Lewy body dementia. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2020, 32, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Severino, P.; Silva, E.; Baggio-Zappia, G.L.; Brunialti, M.K.; Nucci, L.A.; Rigato, O., Jr.; da Silva, I.D.; Machado, F.R.; Salomao, R. Patterns of gene expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and outcomes from patients with sepsis secondary to community acquired pneumonia. PLoS. ONE 2014, 9, e91886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. ClusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria. Available online: https://www.R-project.org/ (accessed on 30 May 2023).
- Scicluna, B.P.; Klein Klouwenberg, P.M.; van Vught, L.A.; Wiewel, M.A.; Ong, D.S.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Franitza, M.; Toliat, M.R.; Nürnberg, P.; Hoogendijk, A.J.; et al. A molecular biomarker to diagnose community-acquired pneumonia on intensive care unit admission. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2015, 192, 826–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burnham, K.L.; Davenport, E.E.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Humburg, P.; Gordon, A.C.; Hutton, P.; Svoren-Jabalera, E.; Garrard, C.; Hill, A.V.S.; Hinds, C.J.; et al. Shared and Distinct Aspects of the Sepsis Transcriptomic Response to Fecal Peritonitis and Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esquerdo, K.F.; Sharma, N.K.; Brunialti, M.K.C.; Baggio-Zappia, G.L.; Assunção, M.; Azevedo, L.C.P.; Bafi, A.T.; Salomao, R. Inflammasome gene profile is modulated in septic patients, with a greater magnitude in non-survivors. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2017, 189, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, H.N.; Jongejan, A.; van Vught, L.A.; Horn, J.; Schultz, M.J.; Zwinderman, A.H.; Cremer, O.L.; Bonten, M.J.; van der Poll, T.; Scicluna, B.P. The circulatory small non-coding RNA landscape in community-acquired pneumonia on intensive care unit admission. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 7621–7630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walden, A.P.; Clarke, G.M.; McKechnie, S.; Hutton, P.; Gordon, A.C.; Rello, J.; Chiche, J.D.; Stueber, F.; Garrard, C.S.; Hinds, C.J.; et al. Patients with community acquired pneumonia admitted to European intensive care units: An epidemiological survey of the GenOSept cohort. Crit. Care 2014, 18, R58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombauts, A.; Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Cuervo, G.; Gudiol, C.; Carratalà, J. Role of the inflammatory response in community-acquired pneumonia: Clinical implications. Expert Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2022, 20, 1261–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cilloniz, C.; Torres, A. Host-targeted approaches to sepsis due to community-acquired pneumonia. EBioMedicine 2022, 86, 104335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Luo, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; Li, Q.; Feng, J.; He, D.; Zhong, Z.; Zheng, X.; Lu, J.; et al. Global transcriptional regulation of STAT3- and MYC-mediated sepsis-induced ARDS. Ther. Adv. Respir. Dis. 2019, 13, 1753466619879840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batra, S.; Balamayooran, G.; Sahoo, M.K. Nuclear factor-κB: A key regulator in health and disease of lungs. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2011, 59, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhou, J.; Wang, D.; Zhou, T. Regulation of NF-κB/MAPK signaling pathway attenuates the acute lung inflammation in Klebsiella pneumonia rats by mollugin treatment. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 132, 369–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devaney, J.; Curley, G.F.; Hayes, M.; Masterson, C.; Ansari, B.; O’Brien, T.; O’Toole, D.; Laffey, J.G. Inhibition of pulmonary nuclear factor kappa-B decreases the severity of acute Escherichia coli pneumonia but worsens prolonged pneumonia. Crit. Care 2013, 17, R82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eddy, W.E.; Gong, K.Q.; Bell, B.; Parks, W.C.; Ziegler, S.F.; Manicone, A.M. Stat5 Is Required for CD103+ Dendritic Cell and Alveolar Macrophage Development and Protection from Lung Injury. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4813–4822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, J.C.; Yamada, M.; Martin, J.R.; Dang, H.; Brickey, W.J.; Bergmeier, W.; Dinauer, M.C.; Doerschuk, C.M. Mechanisms of interferon-γ production by neutrophils and its function during Streptococcus pneumoniae pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 2015, 52, 349–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grudzinska, F.S.; Brodlie, M.; Scholefield, B.R.; Jackson, T.; Scott, A.; Thickett, D.R.; Sapey, E. Neutrophils in community-acquired pneumonia: Parallels in dysfunction at the extremes of age. Thorax 2020, 75, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soehnlein, O.; Oehmcke, S.; Ma, X.; Rothfuchs, A.G.; Frithiof, R.; van Rooijen, N.; Mörgelin, M.; Herwald, H.; Lindbom, L. Neutrophil degranulation mediates severe lung damage triggered by streptococcal M1 protein. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 32, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rendon, A.; Rendon-Ramirez, E.J.; Rosas-Taraco, A.G. Relevant Cytokines in the Management of Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Curr. Infect. Dis. Rep. 2016, 18, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- London, N.R.; Zhu, W.; Bozza, F.A.; Smith, M.C.; Greif, D.M.; Sorensen, L.K.; Chen, L.; Kaminoh, Y.; Chan, A.C.; Passi, S.F.; et al. Targeting Robo4-dependent Slit signaling to survive the cytokine storm in sepsis and influenza. Sci. Transl. Med. 2010, 2, 23ra19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gally, F.; Minor, M.N.; Smith, S.K.; Case, S.R.; Chu, H.W. Heat shock factor 1 protects against lung Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection in mice. J. Innate Immun. 2012, 4, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parnell, G.P.; McLean, A.S.; Booth, D.R.; Armstrong, N.J.; Nalos, M.; Huang, S.J.; Manak, J.; Tang, W.; Tam, O.Y.; Chan, S.; et al. A distinct influenza infection signature in the blood transcriptome of patients with severe community-acquired pneumonia. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharya, S.; Rosenberg, A.F.; Peterson, D.R.; Grzesik, K.; Baran, A.M.; Ashton, J.M.; Gill, S.R.; Corbett, A.M.; Holden-Wiltse, J.; Topham, D.J.; et al. Transcriptomic Biomarkers to Discriminate Bacterial from Nonbacterial Infection in Adults Hospitalized with Respiratory Illness. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 6548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strehlitz, A.; Goldmann, O.; Pils, M.C.; Pessler, F.; Medina, E. An Interferon Signature Discriminates Pneumococcal from Staphylococcal Pneumonia. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertrams, W.; Griss, K.; Han, M.; Seidel, K.; Klemmer, A.; Sittka-Stark, A.; Hippenstiel, S.; Suttorp, N.; Finkernagel, F.; Wilhelm, J.; et al. Transcriptional analysis identifies potential biomarkers and molecular regulators in pneumonia and COPD exacerbation. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alqutami, F.; Senok, A.; Hachim, M. COVID-19 Transcriptomic Atlas: A Comprehensive Analysis of COVID-19 Related Transcriptomics Datasets. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 755222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilieva, M.; Tschaikowski, M.; Vandin, A.; Uchida, S. The current status of gene expression profilings in COVID-19 patients. Clin. Transl. Discov. 2022, 2, e104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Liu, Y.; Cao, L.; Wang, D.; Guo, M.; Jiang, A.; Guo, D.; Hu, W.; Yang, J.; Tang, Z.; et al. Transcriptomic characteristics of bronchoalveolar lavage fluid and peripheral blood mononuclear cells in COVID-19 patients. Emerg. Microbes. Infect. 2020, 9, 761–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rombauts, A.; Bódalo Torruella, M.; Abelenda-Alonso, G.; Perera-Bel, J.; Ferrer-Salvador, A.; Acedo-Terrades, A.; Gabarrós-Subirà, M.; Oriol, I.; Gudiol, C.; Nonell, L.; et al. Dynamics of Gene Expression Profiling and Identification of High-Risk Patients for Severe COVID-19. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, J. The current landscape of microRNAs (miRNAs) in bacterial pneumonia: Opportunities and challenges. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2022, 27, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galván-Román, J.M.; Lancho-Sánchez, Á.; Luquero-Bueno, S.; Vega-Piris, L.; Curbelo, J.; Manzaneque-Pradales, M.; Gómez, M.; de la Fuente, H.; Ortega-Gómez, M.; Aspa, J. Usefulness of circulating microRNAs miR-146a and miR-16-5p as prognostic biomarkers in community-acquired pneumonia. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermann, S.; Brandes, F.; Kirchner, B.; Buschmann, D.; Borrmann, M.; Klein, M.; Kotschote, S.; Bonin, M.; Reithmair, M.; Kaufmann, I. Diagnostic potential of circulating cell-free microRNAs for community-acquired pneumonia and pneumonia-related sepsis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 12054–12064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Fleta, P.; Vera-Tomé, P.; Jiménez-Fernández, M.; Requena, S.; Roy-Vallejo, E.; Sanz-García, A.; Lozano-Prieto, M.; López-Sanz, C.; Vara, A.; Lancho-Sánchez, Á. A Differential Signature of Circulating miRNAs and Cytokines between COVID-19 and Community-Acquired Pneumonia Uncovers Novel Physiopathological Mechanisms of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 815651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| First Author, Year | Population | Control | Sample | Method | Numbers of DEGs * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Severino et al., 2014 [24] | CAP patients with sepsis | Healthy volunteers | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells | Agilent Whole Human Genome Microarray | 73 |
| Scicluna et al., 2015 [27] | CAP patients with sepsis | Healthy controls | Whole blood | Human Genome U219 96-array | 1966 |
| Esquerdo et al., 2017 [29] | CAP patients with sepsis | Healthy volunteers | Peripheral blood mononuclear cells | RT–PCR array of 35 genes involved in the NLR-inflammasome pathways | 3 |
| Burnham et al., 2017 [28] | CAP patients with sepsis | Subjects undergoing elective cardiac surgery | Peripheral blood leukocytes | Illumina HumanHT-12 v4 Expression BeadChips | 1198 |
| Khan et al., 2021 [30] | CAP patients with S. pneumoniae and influenza A or B | Non-infectious participants | Whole blood and plasma | Illumina TruSeq Small RNA-Seq | 42 ** |
| Gene Set Name | Gene Ratio | p-Value Adjusted | Brief Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| HALLMARK_MYC_TARGETS_V1 | 110/1190 | 7.68 × 10−16 | A subgroup of genes regulated by MYC—version 1 (v1) |
| HALLMARK_ALLOGRAFT_REJECTION | 99/1190 | 1.17 × 10−10 | Genes upregulated during transplant rejection. |
| HALLMARK_TNFA_SIGNALING_VIA_NFKB | 86/1190 | 0.000009 | Genes regulated by NF-kB in response to TNF |
| HALLMARK_IL2_STAT5_SIGNALING | 84/1190 | 0.00002 | Genes upregulated by STAT5 in response to IL2 stimulation. |
| HALLMARK_INTERFERON_GAMMA_RESPONSE | 84/1190 | 0.00002 | Genes upregulated in response to IFNG |
| HALLMARK_INFLAMMATORY_RESPONSE | 73/1190 | 0.015 | Genes defining inflammatory response |
| Gene Set Name | Gene Set Name |
|---|---|
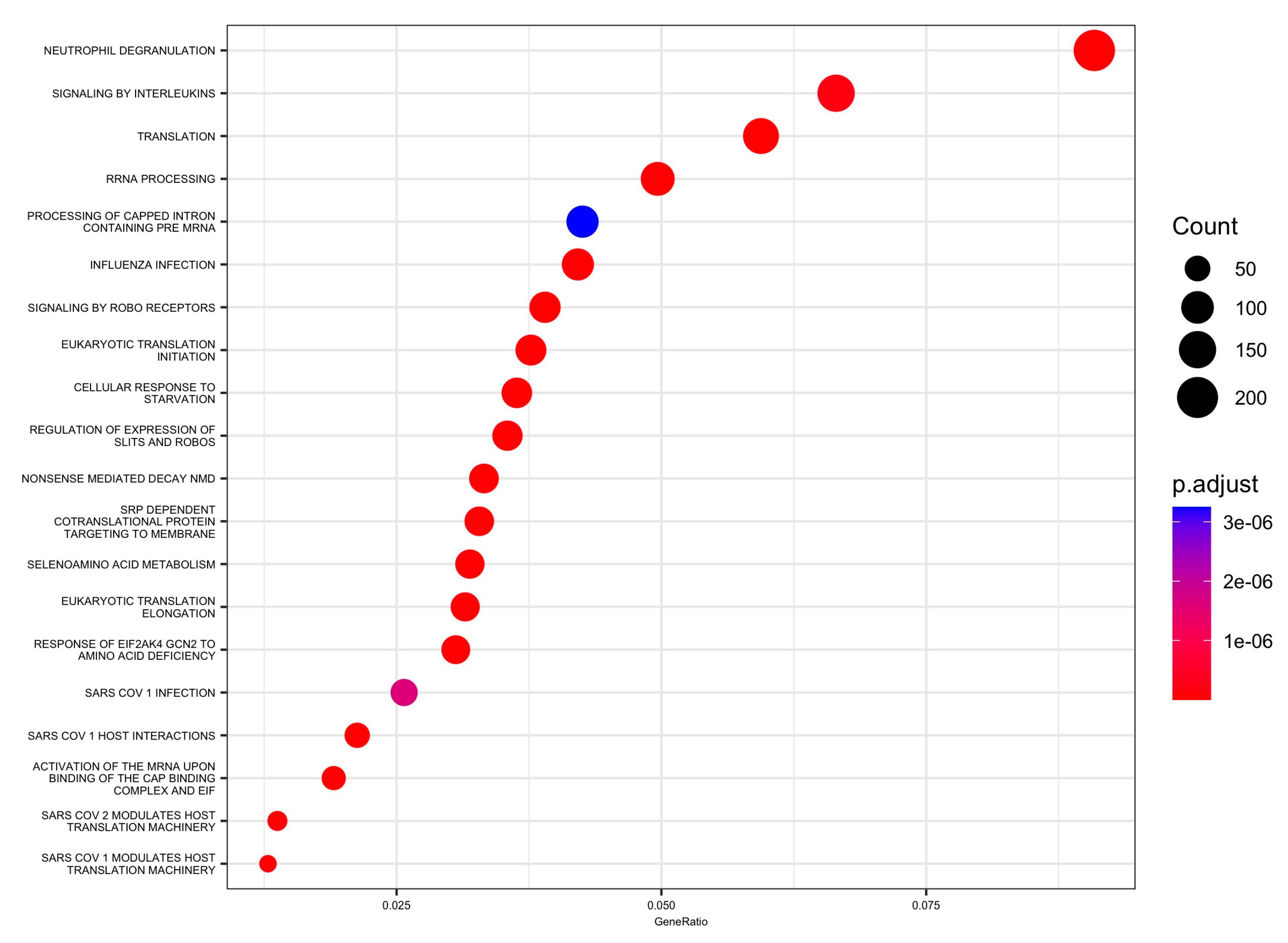
| EUKARYOTIC_TRANSLATION_INITIATION | TRANSPORT_OF_THE_SLBP_DEPENDANT_ MATURE_MRNA |
| EUKARYOTIC_TRANSLATION_ELONGATION | REGULATION_OF_HSF1_MEDIATED_ HEAT_SHOCK_RESPONSE |
| NEUTROPHIL_DEGRANULATION | KSRP_KHSRP_BINDS_AND_DESTABILIZES_ MRNA |
| INFLUENZA_INFECTION | INTERFERON_GAMMA_SIGNALING |
| RRNA_PROCESSING | NUCLEAR_ENVELOPE_BREAKDOWN |
| SRP_DEPENDENT_COTRANSLATIONAL_ PROTEIN_TARGETING_TO_MEMBRANE | SUMOYLATION_OF_RNA_BINDING_PROTEINS |
| NONSENSE_MEDIATED_DECAY_NMD | SNRNP_ASSEMBLY |
| RESPONSE_OF_EIF2AK4_GCN2_TO_AMINO_ ACID_DEFICIENCY | REGULATION_OF_GLUCOKINASE_BY_ GLUCOKINASE_REGULATORY_PROTEIN |
| TRANSLATION | TRNA_PROCESSING |
| SELENOAMINO_ACID_METABOLISM | MRNA_SPLICING |
| CELLULAR_RESPONSE_TO_STARVATION | CELLULAR_RESPONSE_TO_HEAT_STRESS |
| ACTIVATION_OF_THE_MRNA_UPON_BINDING_ OF_THE_CAP_BINDING_COMPLEX_AND_EIFS_ AND_SUBSEQUENT_BINDING_TO_43S | NUCLEAR_PORE_COMPLEX_NPC_DISASSEMBLY |
| REGULATION_OF_EXPRESSION_OF_SLITS_ AND_ROBOS | TRNA_PROCESSING_IN_THE_NUCLEUS |
| SARS_COV_1_MODULATES_HOST_ TRANSLATION_MACHINERY | NUCLEOTIDE_BINDING_DOMAIN_ LEUCINE_RICH_REPEAT_CONTAINING_ RECEPTOR_NLR_SIGNALING_PATHWAYS |
| SIGNALING_BY_ROBO_RECEPTORS | SUMOYLATION_OF_DNA_DAMAGE_ RESPONSE_AND_REPAIR_PROTEINS |
| SARS_COV_1_HOST_INTERACTIONS | IMMUNOREGULATORY_INTERACTIONS_ BETWEEN_A_LYMPHOID_AND_A_NON_LYMPHOID_CELL |
| SARS_COV_2_MODULATES_HOST_ TRANSLATION_MACHINERY | HIV_LIFE_CYCLE |
| SIGNALING_BY_INTERLEUKINS | VIRAL_MESSENGER_RNA_SYNTHESIS |
| SARS_COV_1_INFECTION | NS1_MEDIATED_EFFECTS_ON_ HOST_PATHWAYS |
| PROCESSING_OF_CAPPED_INTRON_ CONTAINING_PRE_MRNA | DISEASES_OF_MITOTIC_CELL_CYCLE |
| METABOLISM_OF_AMINO_ACIDS_AND_ DERIVATIVES | TCR_SIGNALING |
| SARS_COV_2_HOST_INTERACTIONS | ONCOGENE_INDUCED_SENESCENCE |
| SARS_COV_INFECTIONS | PYRUVATE_METABOLISM_AND_CITRIC_ACID_TCA_CYCLE |
| SARS_COV_2_INFECTION | TRANSPORT_OF_MATURE_TRANSCRIPT_TO_CYTOPLASM |
| INTERFERON_SIGNALING | ASSOCIATION_OF_TRIC_CCT_WITH_ TARGET_PROTEINS_DURING_BIOSYNTHESIS |
| RRNA_MODIFICATION_IN_THE_ NUCLEUS_AND_CYTOSOL | SUMOYLATION_OF_UBIQUITINYLATION_PROTEINS |
| INTERLEUKIN_10_SIGNALING | FOLDING_OF_ACTIN_BY_CCT_TRIC |
| GENE_AND_PROTEIN_EXPRESSION_BY_ JAK_STAT_SIGNALING_AFTER_INTERLEUKIN_ 12_STIMULATION | REACTOME_HIV_INFECTION |
| INTERLEUKIN_12_SIGNALING | HOST_INTERACTIONS_OF_HIV_FACTORS |
| INTERLEUKIN_12_FAMILY_SIGNALING | GLYCOLYSIS |
| INTERACTIONS_OF_REV_WITH_HOST_ CELLULAR_PROTEINS | TRANSCRIPTIONAL_ACTIVITY_OF_SMAD2_ SMAD3_SMAD4_HETEROTRIMER |
| INTERLEUKIN_4_AND_INTERLEUKIN_13_SIGNALING | MITOCHONDRIAL_TRANSLATION |
| POSTMITOTIC_NUCLEAR_PORE_ COMPLEX_NPC_REFORMATION | DEADENYLATION_DEPENDENT_MRNA_DECAY |
| EXPORT_OF_VIRAL_ RIBONUCLEOPROTEINS_FROM_NUCLEUS | PERK_REGULATES_GENE_EXPRESSION |
| GENERATION_OF_SECOND_MESSENGER_ MOLECULES | SUMOYLATION_OF_CHROMATIN_ ORGANIZATION_PROTEINS |
| PD_1_SIGNALING | NUCLEOTIDE_SALVAGE |
| NUCLEAR_IMPORT_OF_REV_PROTEIN | PLATELET_ACTIVATION_SIGNALING_ AND_AGGREGATION |
| INTERACTIONS_OF_VPR_WITH_HOST_ CELLULAR_PROTEINS | SMAD2_SMAD3_SMAD4_HETEROTRIMER_ REGULATES_TRANSCRIPTION |
| SUMOYLATION_OF_DNA_REPLICATION_ PROTEINS | ABERRANT_REGULATION_OF_MITOTIC_G1_ S_TRANSITION_IN_CANCER_DUE_TO_RB1_DEFECTS |
| TRANSPORT_OF_MATURE_MRNAS_ DERIVED_FROM_INTRONLESS_TRANSCRIPTS | BUTYRATE_RESPONSE_FACTOR_1_BRF1_ BINDS_AND_DESTABILIZES_MRNA |
| ANTIVIRAL_MECHANISM_BY_IFN_ STIMULATED_GENES | TRISTETRAPROLIN_TTP_ZFP36_BINDS_AND_ DESTABILIZES_MRNA |
| METABOLISM_OF_NUCLEOTIDES | TRANSLATION_OF_SARS_COV_2_ STRUCTURAL_PROTEINS |
| SUMOYLATION_OF_SUMOYLATION_PROTEINS | CONVERSION_FROM_APC_C_CDC20_TO_ APC_C_CDH1_IN_LATE_ANAPHASE |
| SUMOYLATION | REGULATION_OF_MRNA_STABILITY_BY_ PROTEINS_THAT_BIND_AU_RICH_ELEMENTS |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Viasus, D.; Nonell, L.; Restrepo, C.; Figueroa, F.; Donado-Mazarrón, C.; Carratalà, J. A Systematic Review of Gene Expression Studies in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102755
Viasus D, Nonell L, Restrepo C, Figueroa F, Donado-Mazarrón C, Carratalà J. A Systematic Review of Gene Expression Studies in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102755
Chicago/Turabian StyleViasus, Diego, Lara Nonell, Carlos Restrepo, Fabian Figueroa, Carla Donado-Mazarrón, and Jordi Carratalà. 2023. "A Systematic Review of Gene Expression Studies in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102755
APA StyleViasus, D., Nonell, L., Restrepo, C., Figueroa, F., Donado-Mazarrón, C., & Carratalà, J. (2023). A Systematic Review of Gene Expression Studies in Critically Ill Patients with Sepsis and Community-Acquired Pneumonia. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2755. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102755