Fetal Growth Restriction Impairs Lung Function and Neurodevelopment in an Early Preterm Rabbit Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animal Model
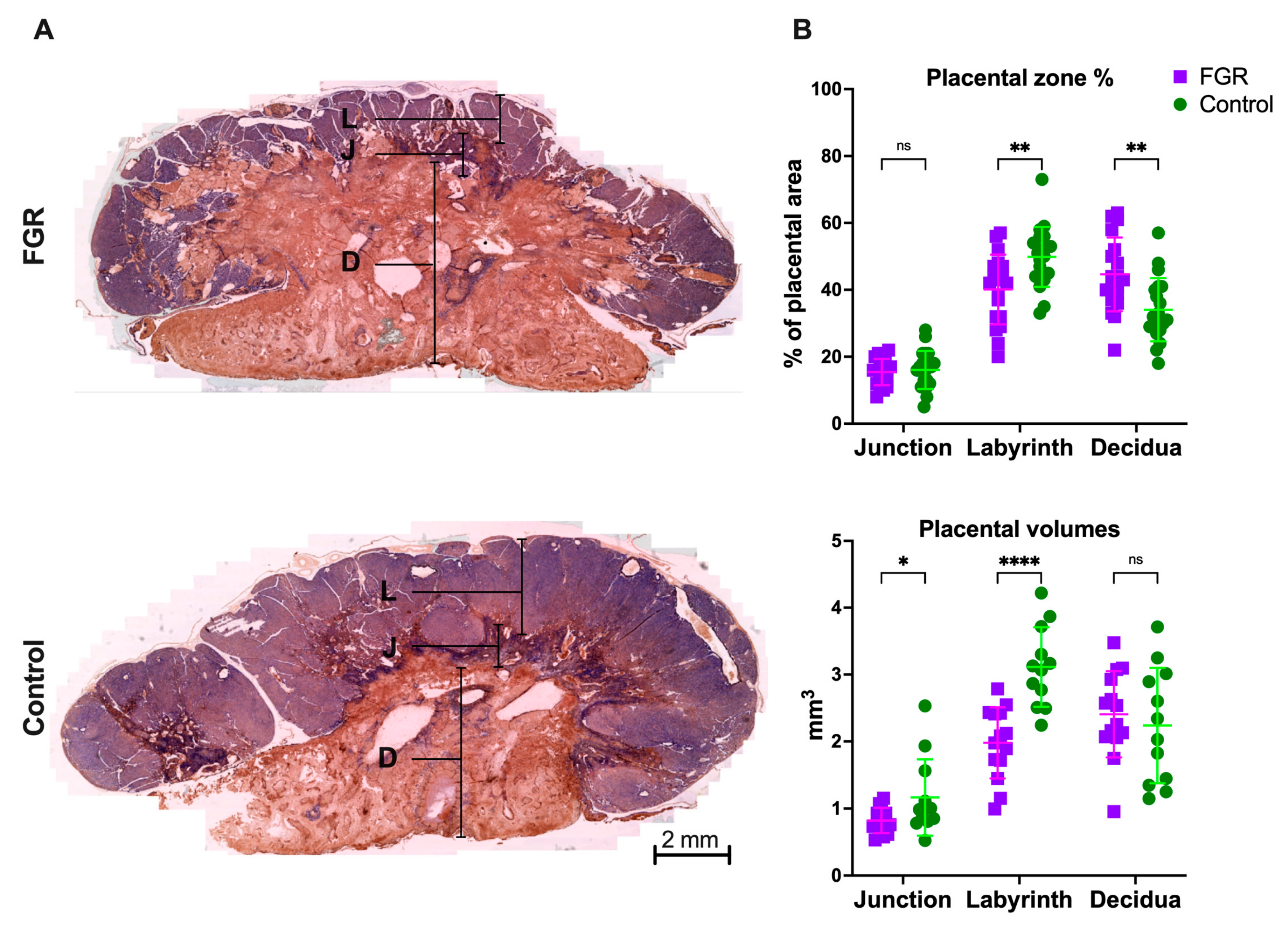
2.2. Placental Histology
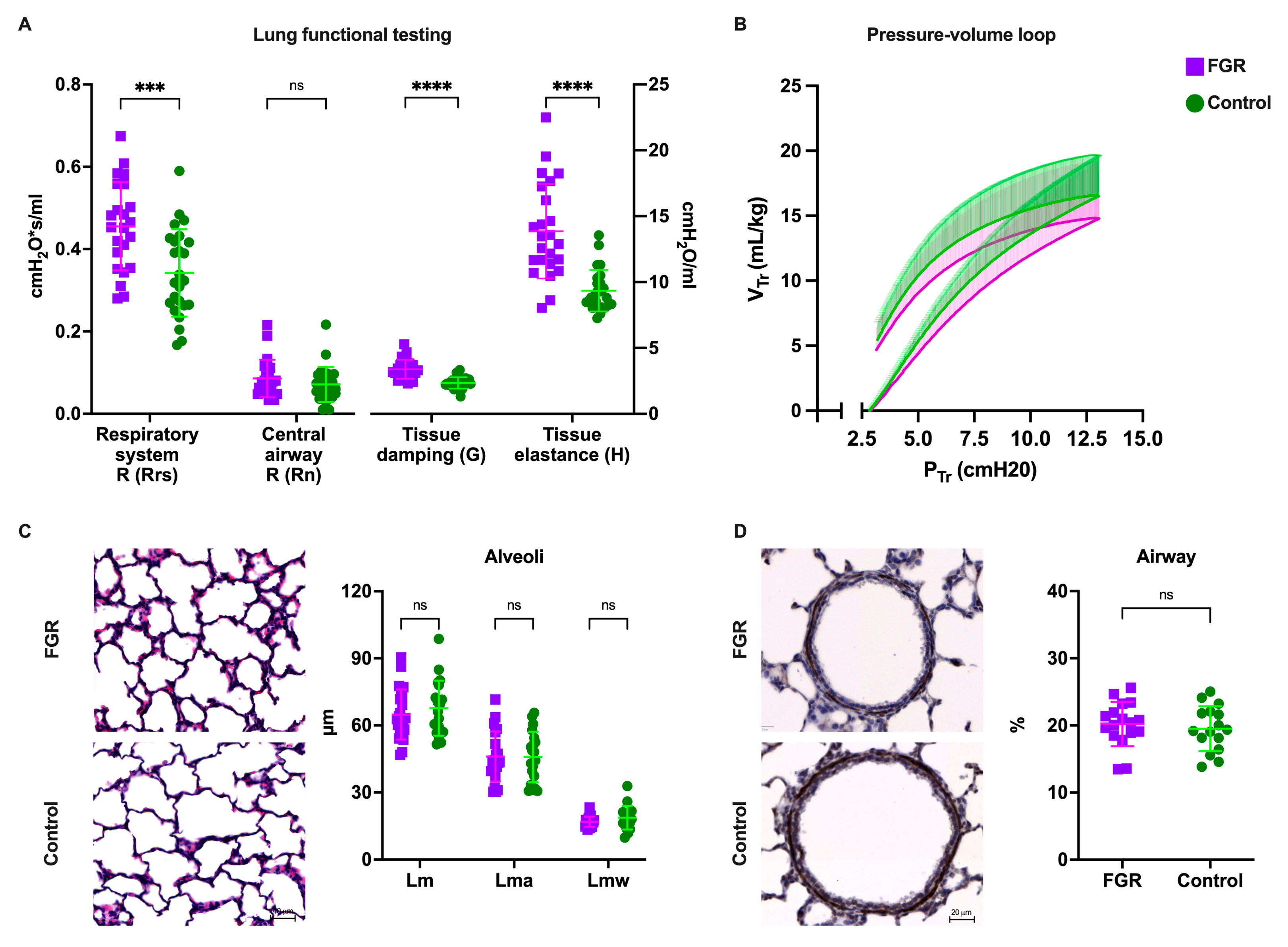
2.3. Pulmonary Function Testing (PFT)
2.4. Histological Lung Assessment
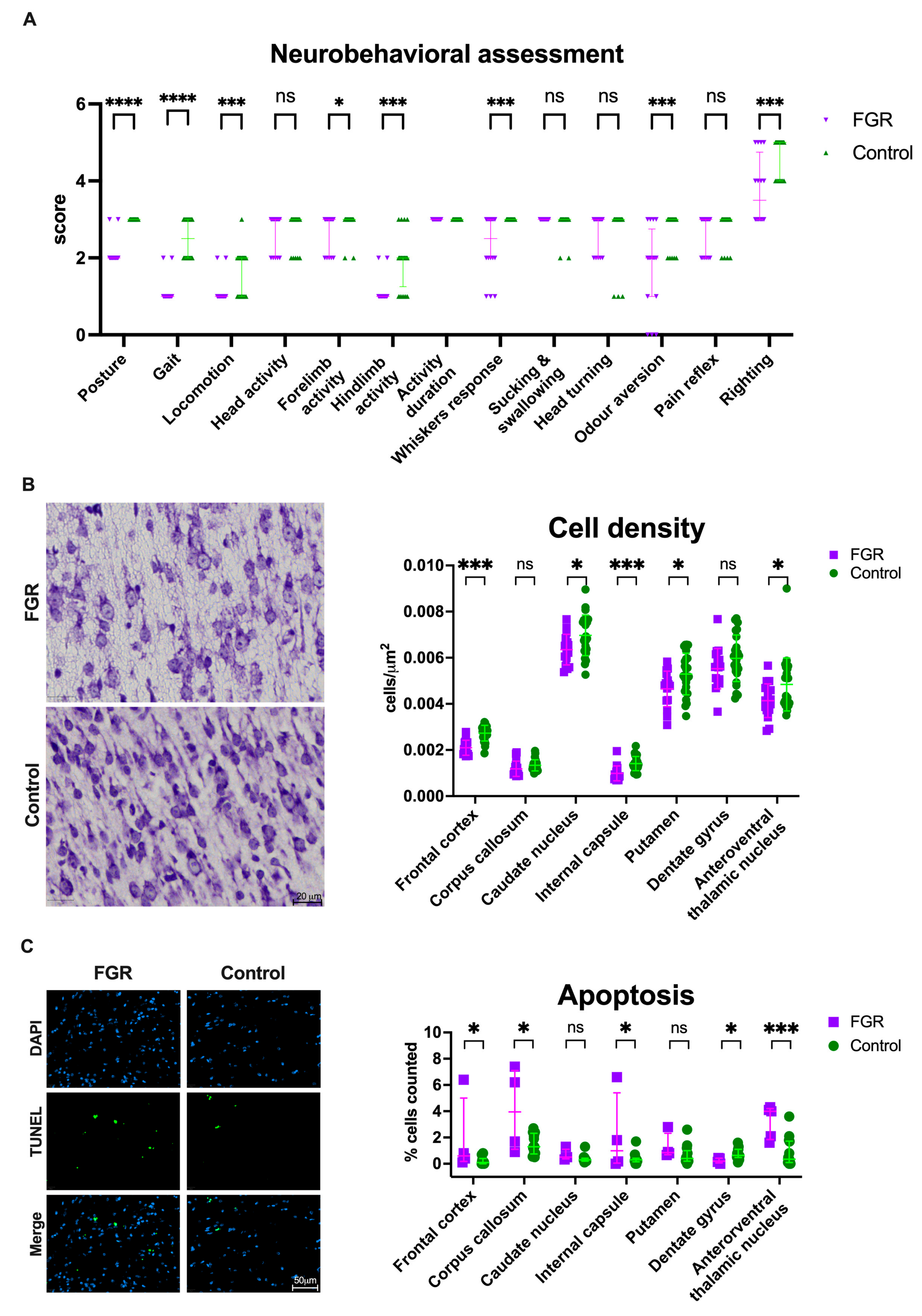
2.5. Neurobehavioral Assessment (NBA)
2.6. Brain Harvesting
2.7. Brain Histology
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. UPVL Induced Placental Alterations Leading to Fetal Growth Restriction and Increased Perinatal Mortality at GD29
3.2. FGR Lungs Had Increased Peripheral Tissue Damping and Resistance, but Similar Airway Mechanics
3.3. Alveolar Morphometry Is Comparable in Premature Lungs from FGR and Normally Grown Subjects
3.4. Neurobehavioral Impairment Coincides with Globally Reduced Cell Density in FGR Brains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fetal Growth Restriction: ACOG Practice Bulletin, Number 227. Obstet. Gynecol. 2021, 137, e16–e28. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordijn, S.J.; Beune, I.M.; Thilaganathan, B.; Papageorghiou, A.; Baschat, A.A.; Baker, P.N.; Silver, R.M.; Wynia, K.; Ganzevoort, W. Consensus definition of fetal growth restriction: A Delphi procedure. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tesfa, D.; Tadege, M.; Digssie, A.; Abebaw, S. Intrauterine growth restriction and its associated factors in South Gondar zone hospitals, Northwest Ethiopia, 2019. Arch. Public Health 2020, 78, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Onis, M.; Blössner, M.; Villar, J. Levels and patterns of intrauterine growth retardation in developing countries. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1998, 52 (Suppl. 1), S5–S15. [Google Scholar]
- Romo, A.; Carceller, R.; Tobajas, J. Intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR): Epidemiology and etiology. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2009, 6 (Suppl. 3), 332–336. [Google Scholar]
- Pels, A.; Beune, I.M.; van Wassenaer-Leemhuis, A.G.; Limpens, J.; Ganzevoort, W. Early-onset fetal growth restriction: A systematic review on mortality and morbidity. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, D.J. Adult consequences of fetal growth restriction. Clin. Obstet. Gynecol. 2006, 49, 270–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, S.L.; Huppi, P.S.; Mallard, C. The consequences of fetal growth restriction on brain structure and neurodevelopmental outcome. J. Physiol. 2016, 594, 807–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levine, T.A.; Grunau, R.E.; McAuliffe, F.M.; Pinnamaneni, R.; Foran, A.; Alderdice, F.A. Early Childhood Neurodevelopment After Intrauterine Growth Restriction: A Systematic Review. Pediatrics 2015, 135, 126–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cruz-Lemini, M.; Crispi, F.; Valenzuela-Alcaraz, B.; Figueras, F.; Sitges, M.; Bijnens, B.; Gratacos, E. Fetal cardiovascular remodeling persists at 6 months in infants with intrauterine growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2016, 48, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pike, K.; Jane Pillow, J.; Lucas, J.S. Long term respiratory consequences of intrauterine growth restriction. Semin. Fetal Neonatal Med. 2012, 17, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lees, C.C.; Stampalija, T.; Baschat, A.; da Silva Costa, F.; Ferrazzi, E.; Figueras, F.; Hecher, K.; Kingdom, J.; Poon, L.C.; Salomon, L.J.; et al. ISUOG Practice Guidelines: Diagnosis and management of small-for-gestational-age fetus and fetal growth restriction. Ultrasound Obstet. Gynecol. 2020, 56, 298–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, I.; Kinoshita, M.; van der Merwe, J.; Marsal, K.; Deprest, J. Prenatal interventions for fetal growth restriction in animal models: A systematic review. Placenta 2022, 126, 90–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Tello, J.; Arias-Alvarez, M.; Gonzalez-Bulnes, A.; Sferuzzi-Perri, A.N. Models of Intrauterine growth restriction and fetal programming in rabbits. Mol. Reprod. Dev. 2019, 86, 1781–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, A.M.; David, A.L. Animal models of fetal growth restriction: Considerations for translational medicine. Placenta 2015, 36, 623–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.; Chavatte-Palmer, P.; Viebahn, C.; Navarrete Santos, A.; Duranthon, V. Rabbit as a reproductive model for human health. Reproduction 2012, 144, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaets, T.; Gie, A.; Tack, B.; Deprest, J.; Toelen, J. Modelling Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia in Animals: Arguments for the Preterm Rabbit Model. Curr Pharm Des. 2017, 23, 5887–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harel, S.; Watanabe, K.; Linke, I.; Schain, R.J. Growth and development of the rabbit brain. Biol. Neonate 1972, 21, 381–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, I.; Basurto, D.; Regin, Y.; Gie, A.; van der Veeken, L.; Vergote, S.; Muñoz-Moreno, E.; Leszczynski, B.; Tielemans, B.; Velde, G.V.; et al. Placental vascular alterations are associated with early neurodevelopmental and pulmonary impairment in the rabbit fetal growth restriction model. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 19720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Merwe, J.; van der Veeken, L.; Inversetti, A.; Galgano, A.; Toelen, J.; Deprest, J. Earlier preterm birth is associated with a worse neurocognitive outcome in a rabbit model. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Percie du Sert, N.; Hurst, V.; Ahluwalia, A.; Alam, S.; Avey, M.T.; Baker, M.; Browne, W.J.; Clark, A.; Cuthill, I.C.; Dirnagl, U.; et al. The ARRIVE guidelines 2.0: Updated guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol. 2020, 18, e3000410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eixarch, E.; Figueras, F.; Hernandez-Andrade, E.; Crispi, F.; Nadal, A.; Torre, I.; Oliveira, S.; Gratacos, E. An experimental model of fetal growth restriction based on selective ligature of uteroplacental vessels in the pregnant rabbit. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2009, 26, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bankhead, P.; Loughrey, M.B.; Fernandez, J.A.; Dombrowski, Y.; McArt, D.G.; Dunne, P.D.; McQuaid, S.; Gray, R.T.; Murray, L.J.; Coleman, H.G.; et al. QuPath: Open source software for digital pathology image analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richter, J.; Toelen, J.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Kakigano, A.; Dekoninck, P.; Verbeken, E.; Deprest, J. Functional assessment of hyperoxia-induced lung injury after preterm birth in the rabbit. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2014, 306, L277–L283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salaets, T.; Tack, B.; Gie, A.; Pavie, B.; Sindhwani, N.; Jimenez, J.; Regin, Y.; Allegaert, K.; Deprest, J.; Toelen, J. A semi-automated method for unbiased alveolar morphometry: Validation in a bronchopulmonary dysplasia model. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salaets, T.; Aertgeerts, M.; Gie, A.; Vignero, J.; de Winter, D.; Regin, Y.; Jimenez, J.; Vande Velde, G.; Allegaert, K.; Deprest, J.; et al. Preterm birth impairs postnatal lung development in the neonatal rabbit model. Respir. Res. 2020, 21, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrick, M.; Luo, N.L.; Bregman, J.C.; Jilling, T.; Ji, X.; Fisher, K.; Gladson, C.L.; Beardsley, D.J.; Murdoch, G.; Back, S.A.; et al. Preterm fetal hypoxia-ischemia causes hypertonia and motor deficits in the neonatal rabbit: A model for human cerebral palsy? J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 24–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Merwe, J.; van der Veeken, L.; Ferraris, S.; Gsell, W.; Himmelreich, U.; Toelen, J.; Ourselin, S.; Melbourne, A.; Vercauteren, T.; Deprest, J. Early neuropathological and neurobehavioral consequences of preterm birth in a rabbit model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgiadis, P.; Xu, H.; Chua, C.; Hu, F.; Collins, L.; Huynh, C.; LaGamma, E.F.; Ballabh, P. Characterization of acute brain injuries and neurobehavioral profiles in a rabbit model of germinal matrix hemorrhage. Stroke 2008, 39, 3378–3388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannan, S.; Dai, H.; Navath, R.S.; Balakrishnan, B.; Jyoti, A.; Janisse, J.; Romero, R.; Kannan, R.M. Dendrimer-based postnatal therapy for neuroinflammation and cerebral palsy in a rabbit model. Sci. Transl. Med. 2012, 4, 130ra146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Veeken, L.; Van der Merwe, J.; Devroe, S.; Inversetti, A.; Galgano, A.; Bleeser, T.; Meeusen, R.; Rex, S.; Deprest, J. Maternal surgery during pregnancy has a transient adverse effect on the developing fetal rabbit brain. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2019, 221, 355-e351–355-e319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toelen, J.; Carlon, M.; Claus, F.; Gijsbers, R.; Sandaite, I.; Dierickx, K.; Devlieger, R.; Devriendt, K.; Debeer, A.; Proesmans, M.; et al. The fetal respiratory system as target for antenatal therapy. Facts Views Vis. Obstet. Gynecol. 2011, 3, 22–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schittny, J.C. Development of the lung. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 367, 427–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gie, A.G.; Regin, Y.; Salaets, T.; Casiraghi, C.; Salomone, F.; Deprest, J.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Toelen, J. Intratracheal budesonide/surfactant attenuates hyperoxia-induced lung injury in preterm rabbits. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 319, L949–L956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gie, A.G.; Salaets, T.; Vignero, J.; Regin, Y.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Deprest, J.; Toelen, J. Intermittent CPAP limits hyperoxia-induced lung damage in a rabbit model of bronchopulmonary dysplasia. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2020, 318, L976–L987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jimenez, J.; Richter, J.; Nagatomo, T.; Salaets, T.; Quarck, R.; Wagennar, A.; Wang, H.; Vanoirbeek, J.; Deprest, J.; Toelen, J. Progressive Vascular Functional and Structural Damage in a Bronchopulmonary Dysplasia Model in Preterm Rabbits Exposed to Hyperoxia. Int J. Mol. Sci 2016, 17, 1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illa, M.; Brito, V.; Pla, L.; Eixarch, E.; Arbat-Plana, A.; Batalle, D.; Munoz-Moreno, E.; Crispi, F.; Udina, E.; Figueras, F.; et al. Early Environmental Enrichment Enhances Abnormal Brain Connectivity in a Rabbit Model of Intrauterine Growth Restriction. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2018, 44, 184–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illa, M.; Eixarch, E.; Batalle, D.; Arbat-Plana, A.; Munoz-Moreno, E.; Figueras, F.; Gratacos, E. Long-term functional outcomes and correlation with regional brain connectivity by MRI diffusion tractography metrics in a near-term rabbit model of intrauterine growth restriction. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e76453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illa, M.; Eixarch, E.; Munoz-Moreno, E.; Batalle, D.; Leal-Campanario, R.; Gruart, A.; Delgado-Garcia, J.M.; Figueras, F.; Gratacos, E. Neurodevelopmental Effects of Undernutrition and Placental Underperfusion in Fetal Growth Restriction Rabbit Models. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2017, 42, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buser, J.R.; Segovia, K.N.; Dean, J.M.; Nelson, K.; Beardsley, D.; Gong, X.; Luo, N.L.; Ren, J.; Wan, Y.; Riddle, A.; et al. Timing of appearance of late oligodendrocyte progenitors coincides with enhanced susceptibility of preterm rabbit cerebral white matter to hypoxia-ischemia. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2010, 30, 1053–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, S.E.; Miller, J.A.; Blackwell, J.M.; West, J.R. Fetal alcohol exposure and temporal vulnerability: Regional differences in cell loss as a function of the timing of binge-like alcohol exposure during brain development. Alcohol Clin. Exp. Res. 1999, 23, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patten, A.R.; Gil-Mohapel, J.; Wortman, R.C.; Noonan, A.; Brocardo, P.S.; Christie, B.R. Effects of Ethanol Exposure during Distinct Periods of Brain Development on Hippocampal Synaptic Plasticity. Brain Sci. 2013, 3, 1076–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spinillo, A.; Gardella, B.; Adamo, L.; Muscettola, G.; Fiandrino, G.; Cesari, S. Pathologic placental lesions in early and late fetal growth restriction. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2019, 98, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burton, G.J.; Jauniaux, E. Pathophysiology of placental-derived fetal growth restriction. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, S745–S761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savchev, S.; Figueras, F.; Sanz-Cortes, M.; Cruz-Lemini, M.; Triunfo, S.; Botet, F.; Gratacos, E. Evaluation of an optimal gestational age cut-off for the definition of early- and late-onset fetal growth restriction. Fetal Diagn. Ther. 2014, 36, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| N = 18 Dams | FGR | Control | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Survival at birth | 63/114 (55.3%) | 86/89 (96.6%) | <0.0001 |
| Survival at PND1 | 46/114 (40.3%) | 77/89 (86.5%) | <0.0001 |
| Birth weight (g) | 32.09 ± 6.15 | 40.01 ± 5.94 | <0.0001 |
| Placental weight (g) | 5.14 ± 1.19 | 5.78 ± 1.10 | 0.008 |
| Brain weight (g) | 1.53 ± 0.19 | 1.72 ± 0.19 | 0.0001 |
| Brain/body weight ratio | 0.048 ± 0.008 | 0.045 ± 0.006 | 0.09 |
| Fetal/placental weight ratio | 6.40 ± 1.11 | 7.08 ± 1.20 | 0.008 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Valenzuela, I.; Zapletalova, K.; Greyling, M.; Regin, Y.; Gie, A.; Basurto, D.; Deprest, J.; van der Merwe, J. Fetal Growth Restriction Impairs Lung Function and Neurodevelopment in an Early Preterm Rabbit Model. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010139
Valenzuela I, Zapletalova K, Greyling M, Regin Y, Gie A, Basurto D, Deprest J, van der Merwe J. Fetal Growth Restriction Impairs Lung Function and Neurodevelopment in an Early Preterm Rabbit Model. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(1):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010139
Chicago/Turabian StyleValenzuela, Ignacio, Katerina Zapletalova, Marnel Greyling, Yannick Regin, Andre Gie, David Basurto, Jan Deprest, and Johannes van der Merwe. 2023. "Fetal Growth Restriction Impairs Lung Function and Neurodevelopment in an Early Preterm Rabbit Model" Biomedicines 11, no. 1: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010139
APA StyleValenzuela, I., Zapletalova, K., Greyling, M., Regin, Y., Gie, A., Basurto, D., Deprest, J., & van der Merwe, J. (2023). Fetal Growth Restriction Impairs Lung Function and Neurodevelopment in an Early Preterm Rabbit Model. Biomedicines, 11(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11010139





