mTOR Signaling in BDNF-Treated Guinea Pigs after Ototoxic Deafening
Abstract
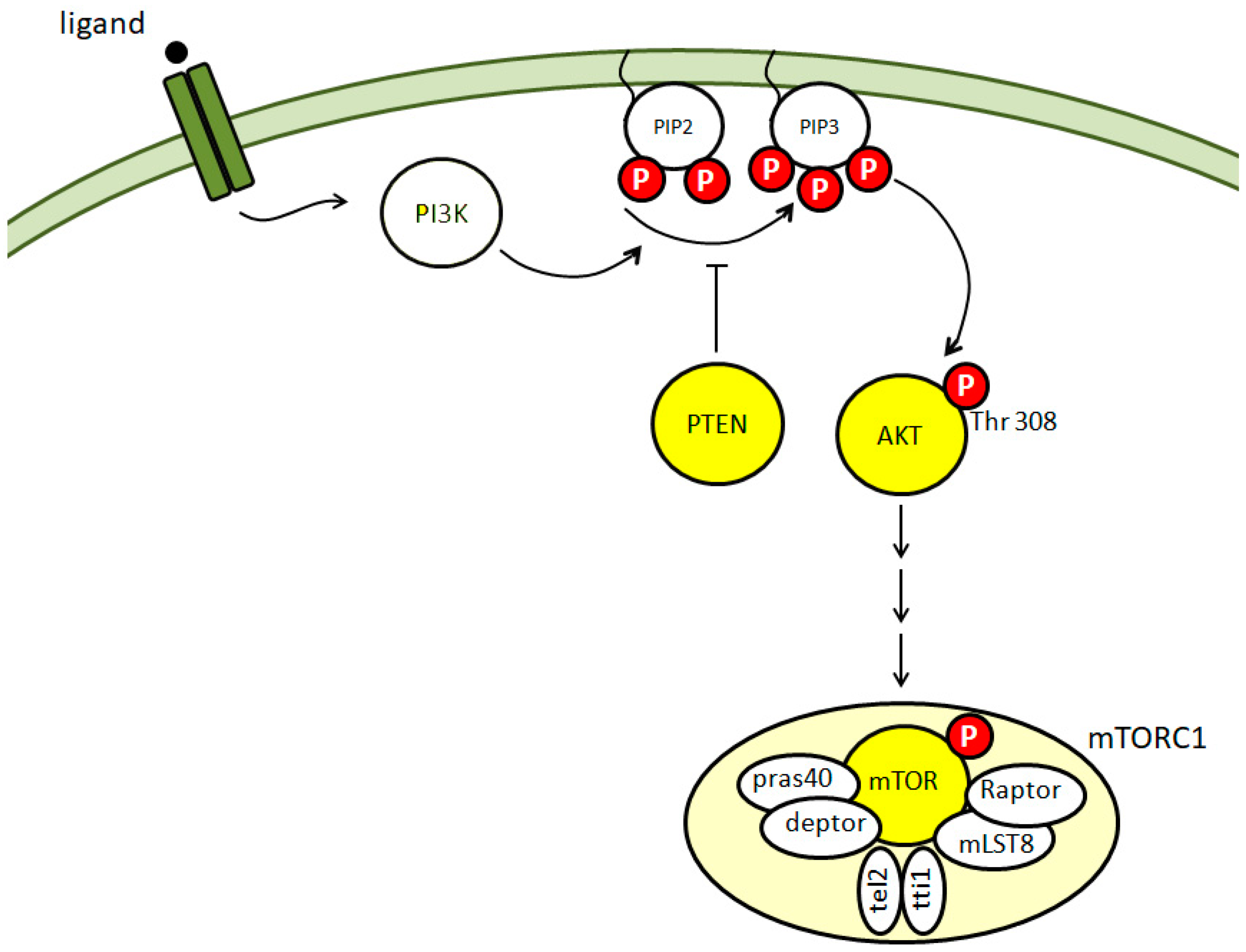
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
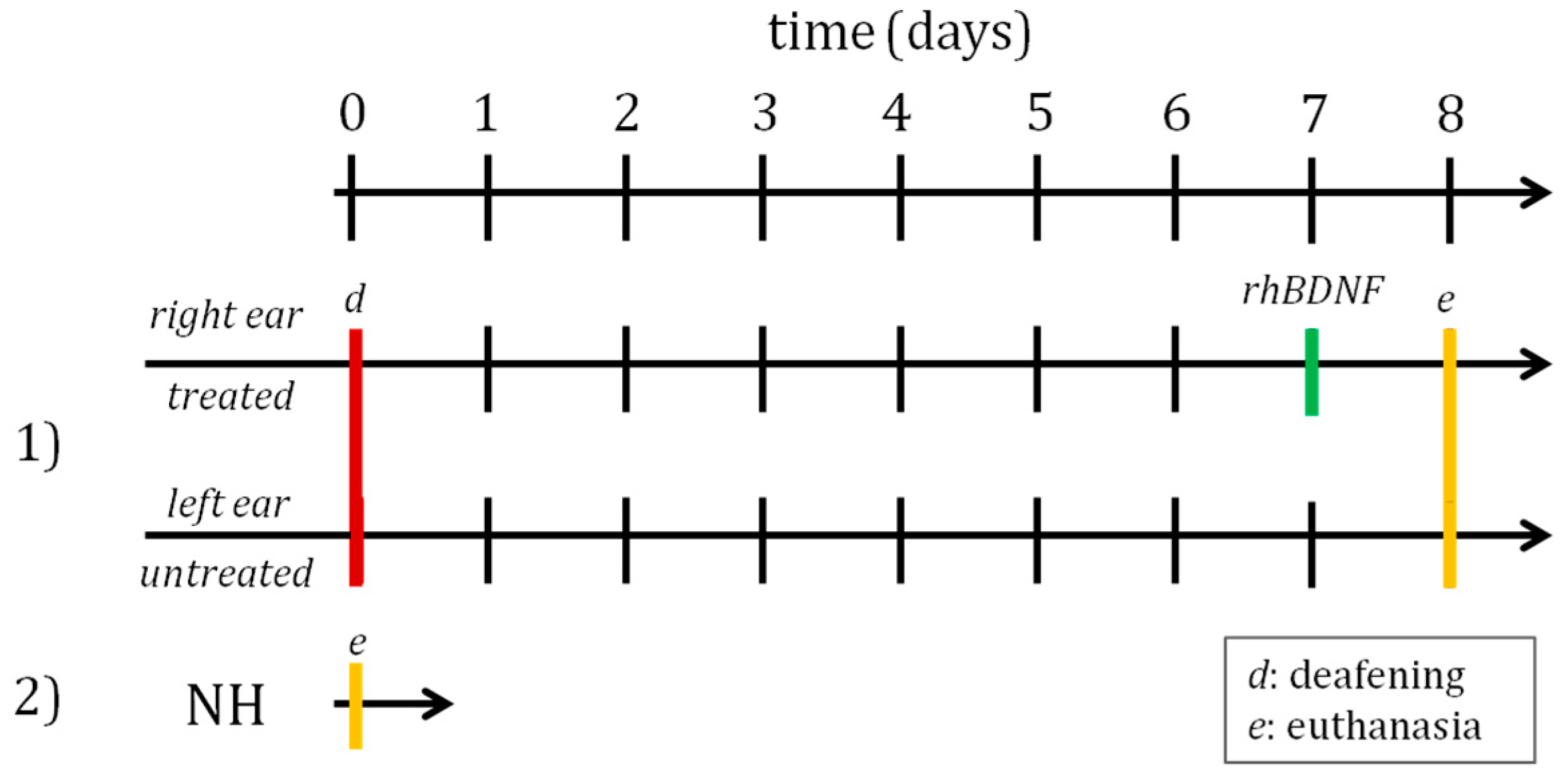
2.1. Animals and Experimental Design
2.2. Deafening Procedure, BDNF Administration and Extraction of the Cochlea
2.3. Protein Extraction
2.4. Western Blot
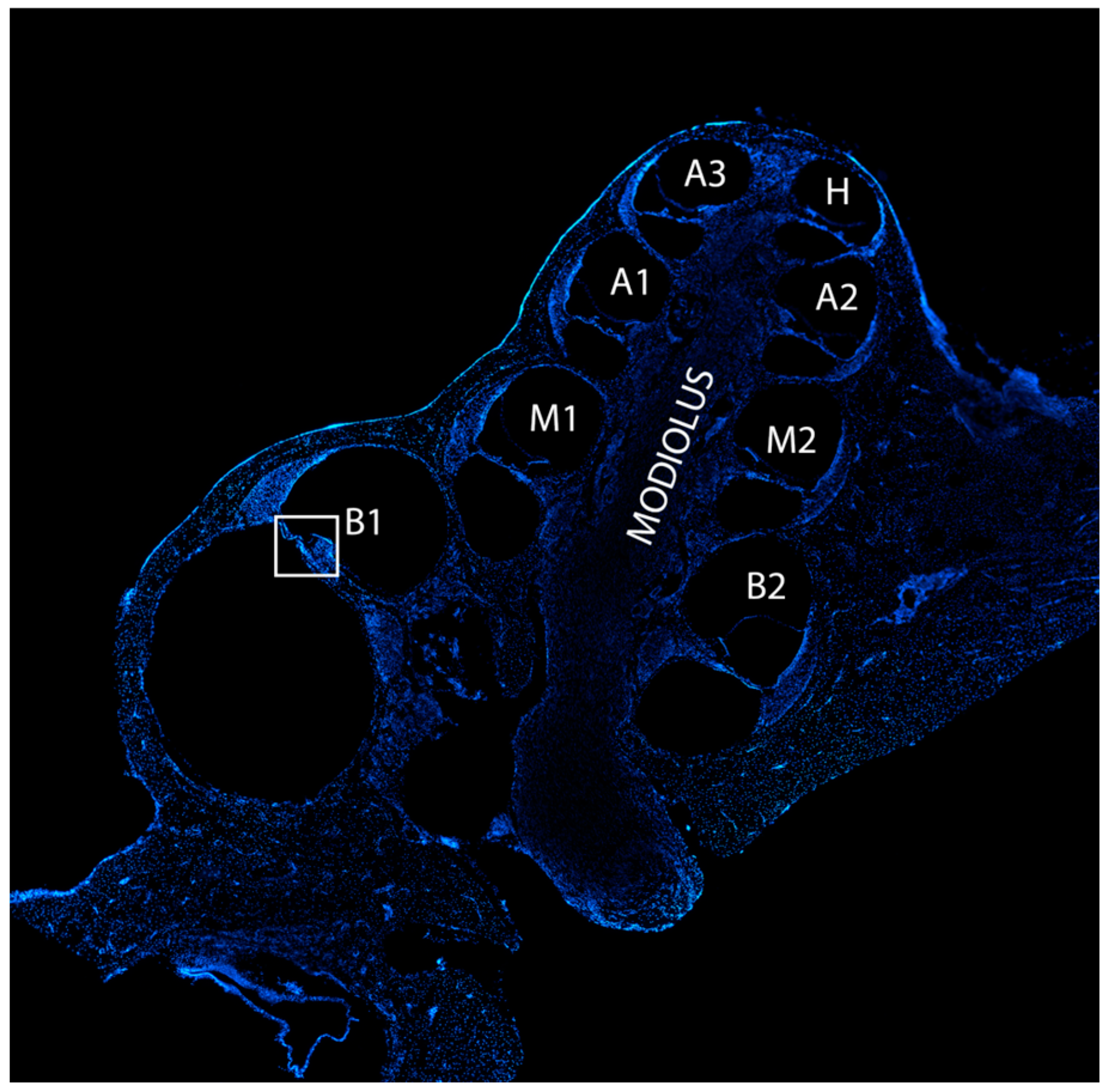
2.5. Cryosections
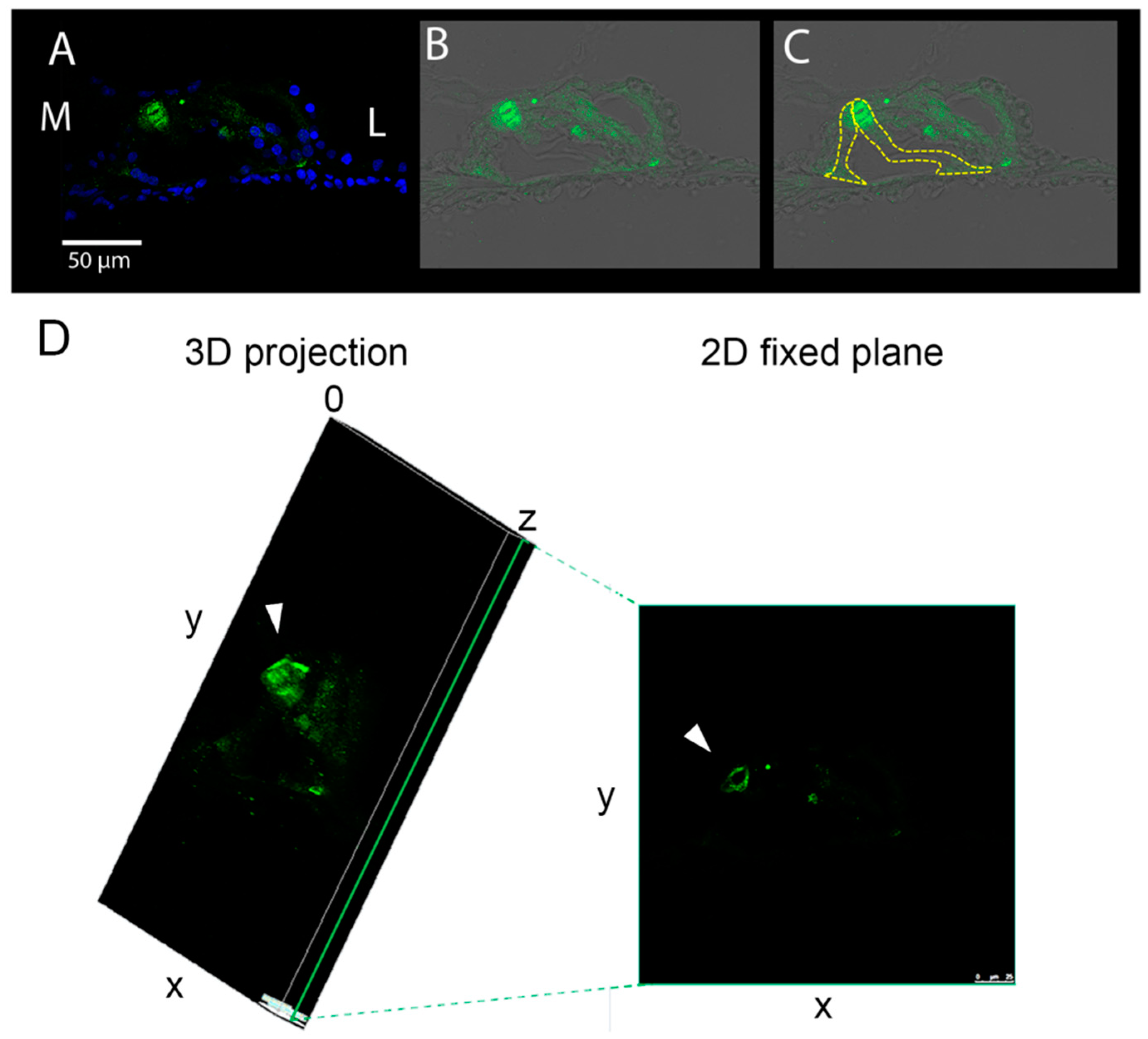
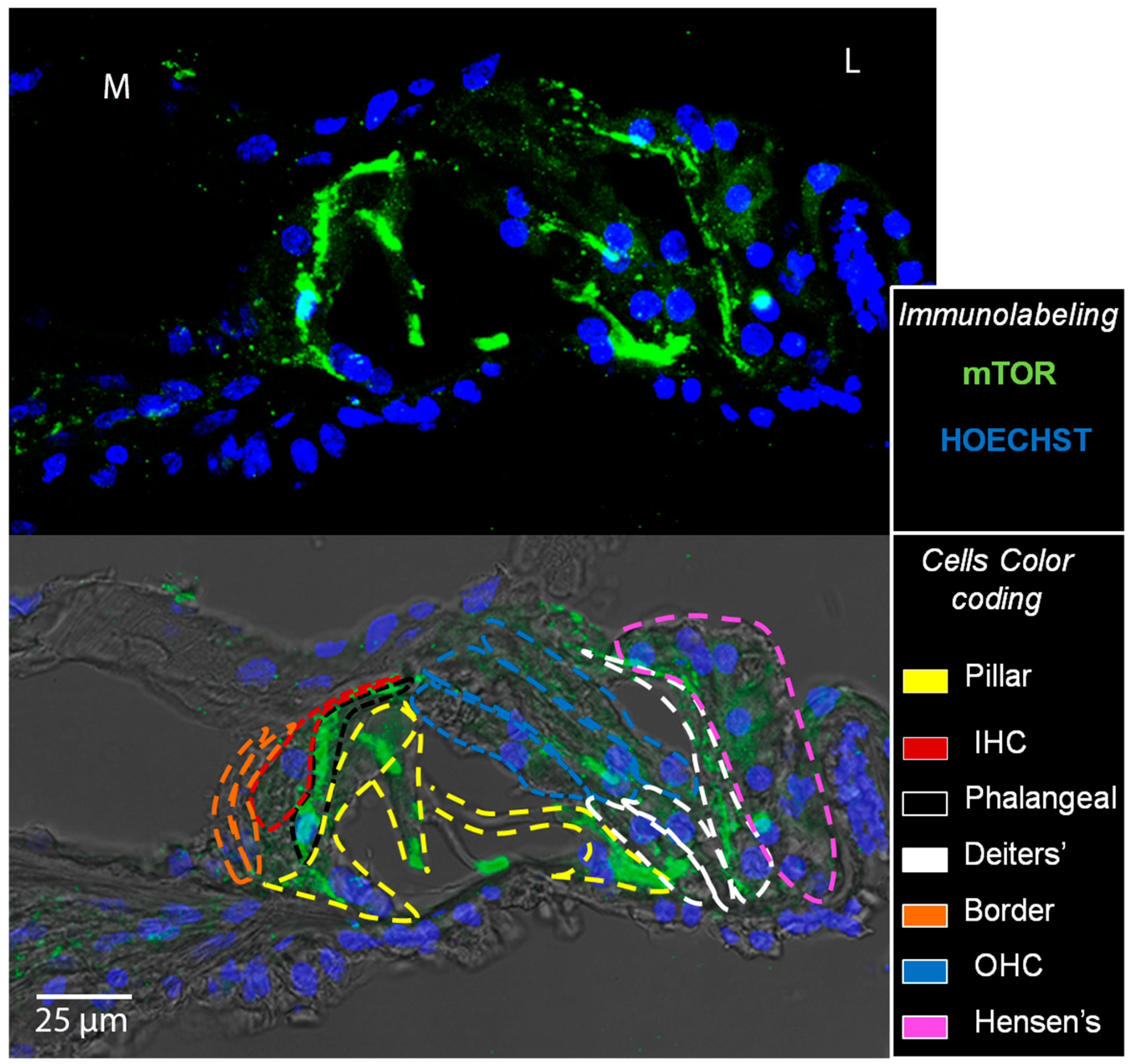
2.6. Immunofluorescence Staining
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
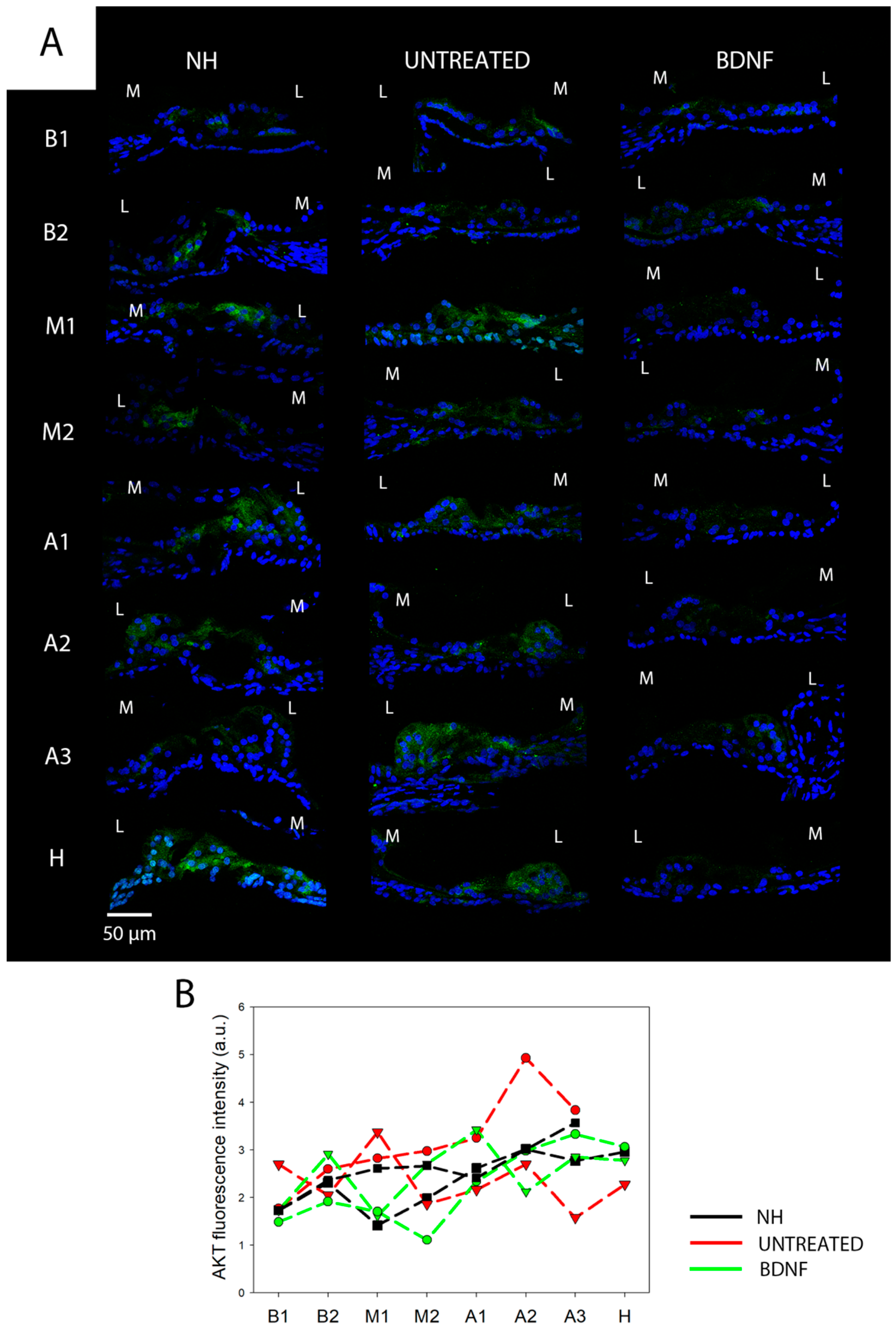
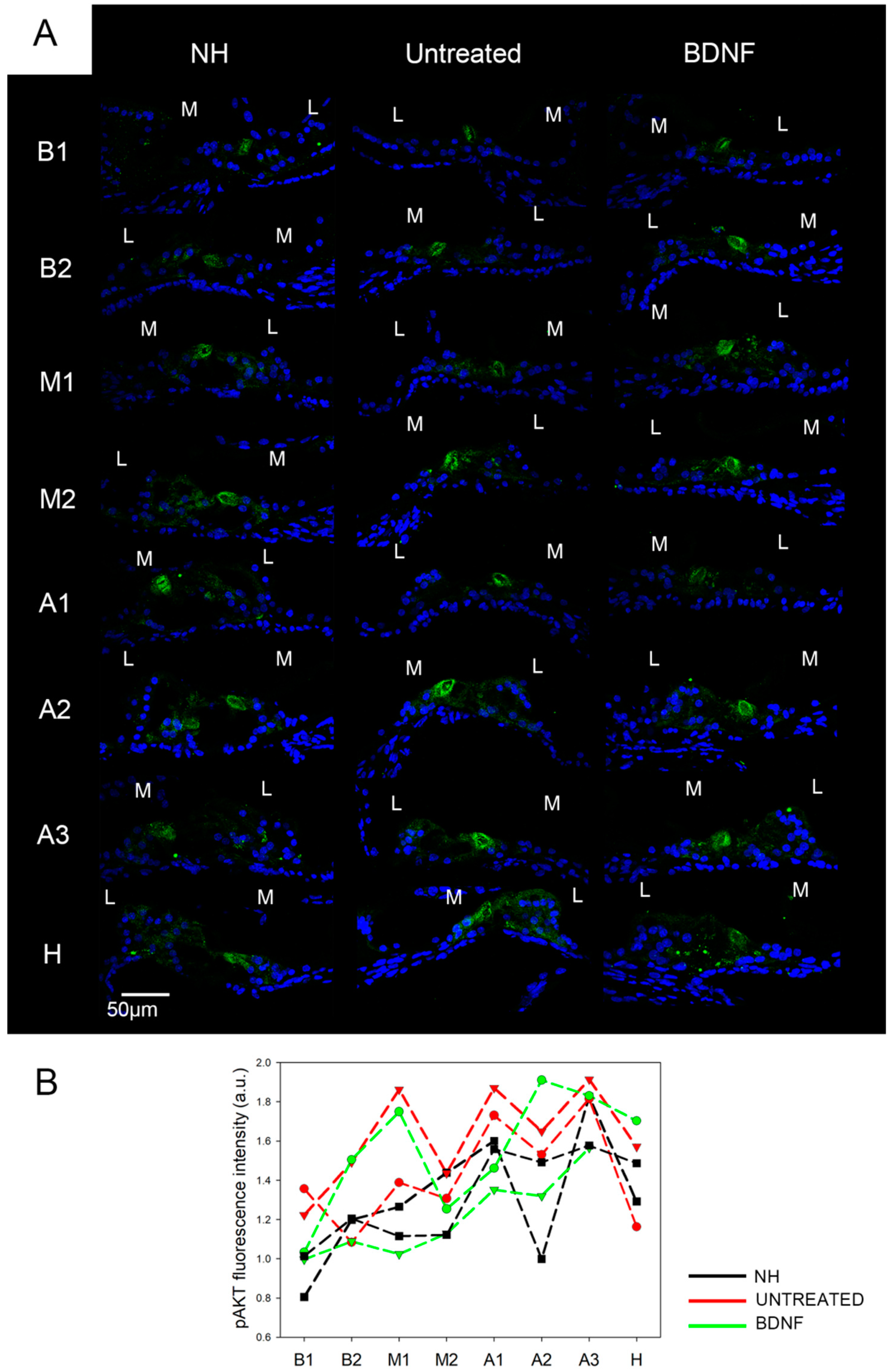
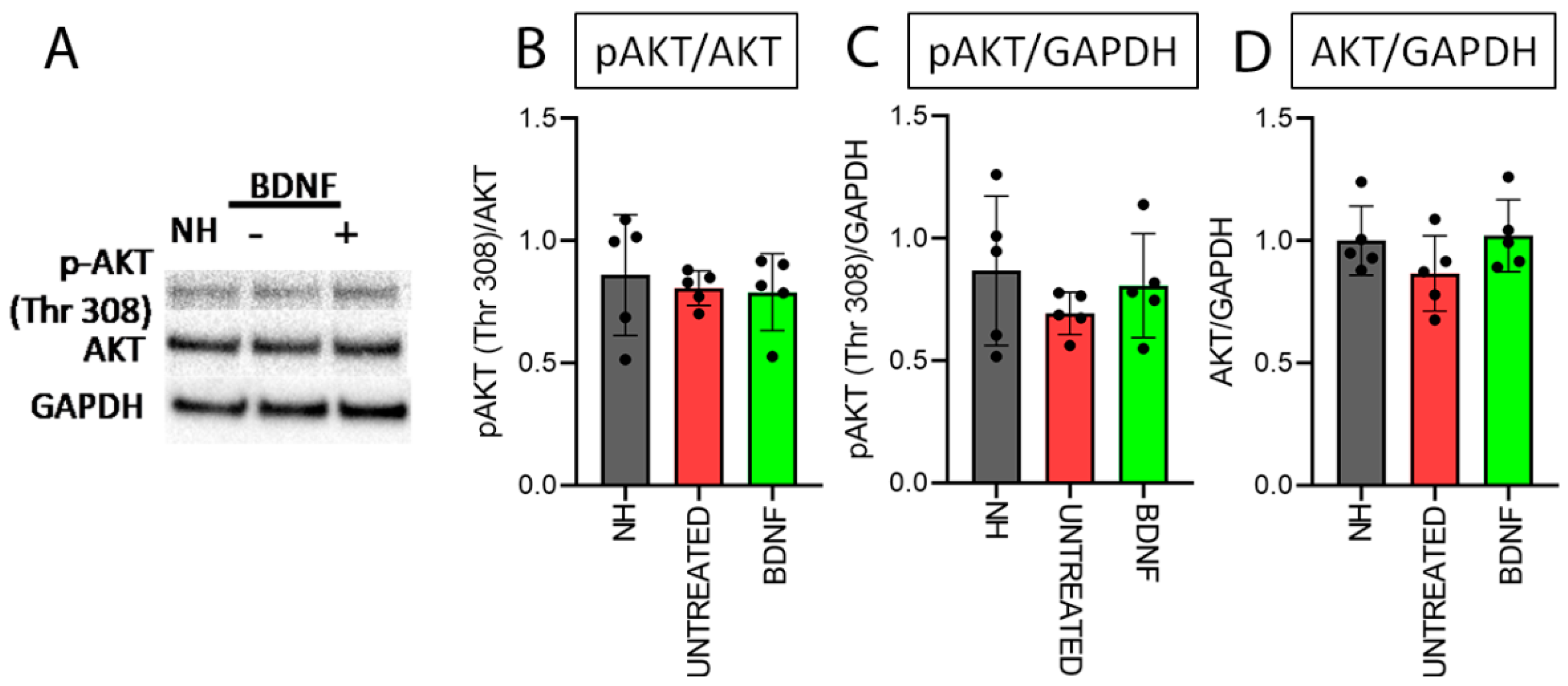
3.1. AKT and pAKT Analysis
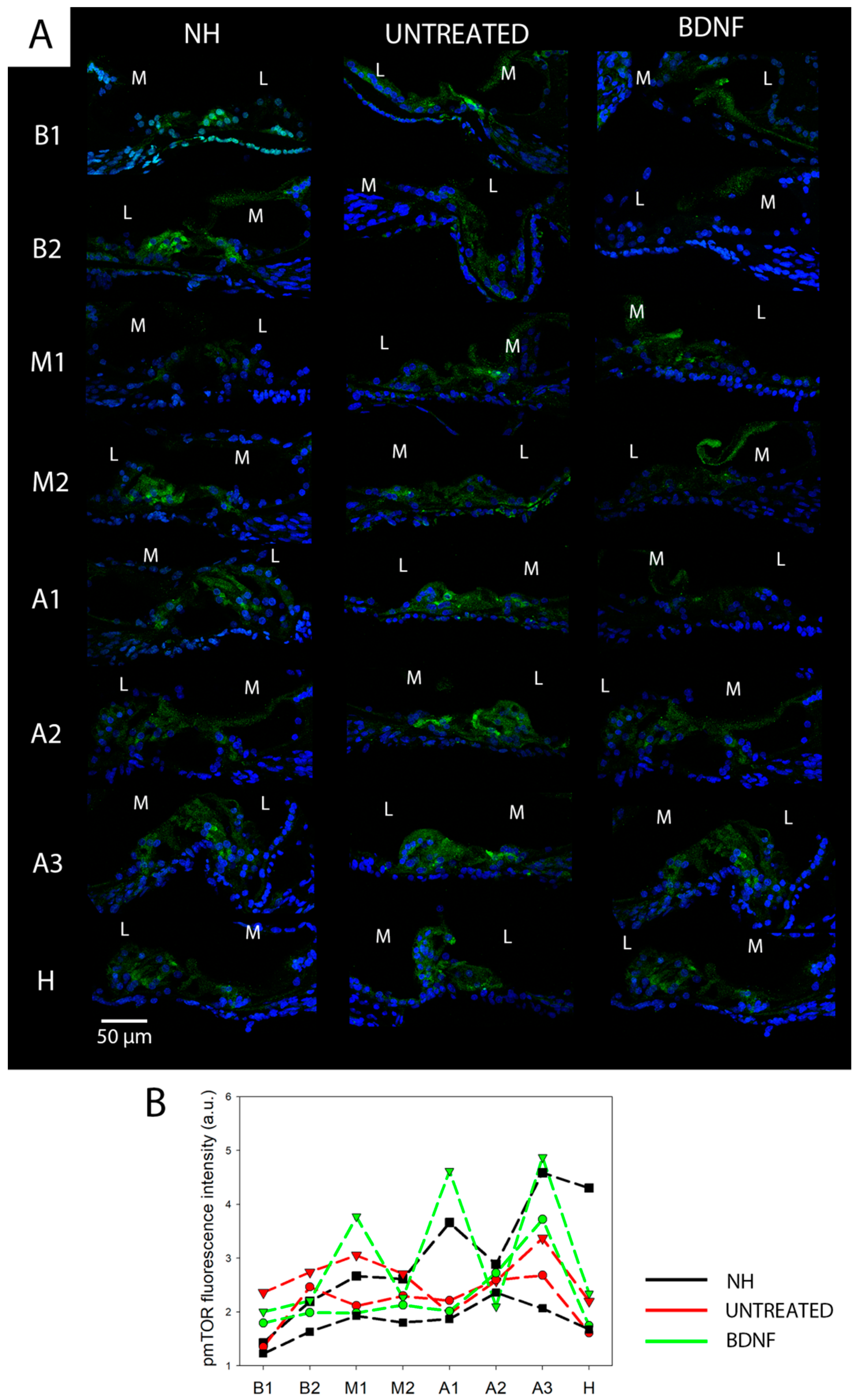
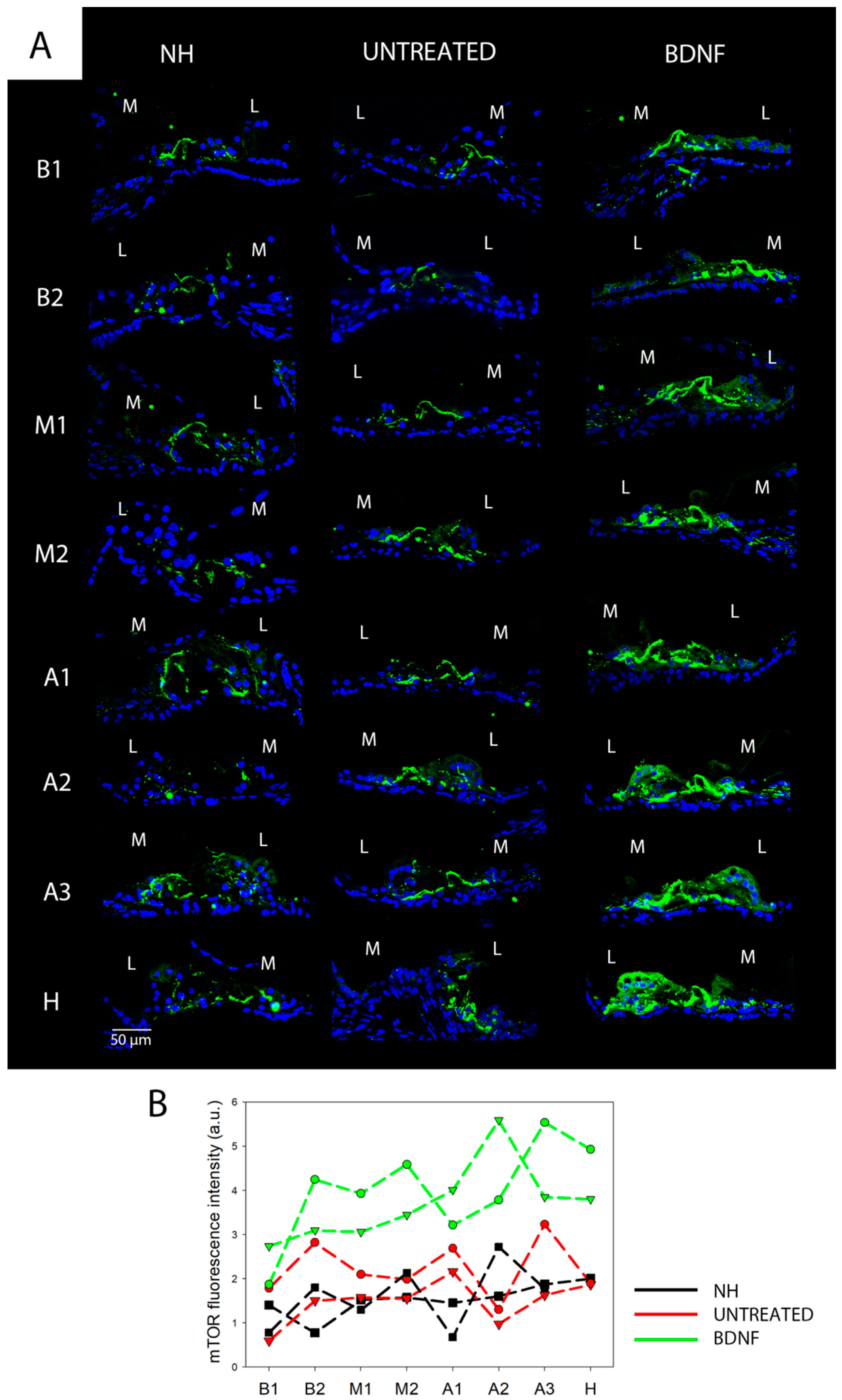
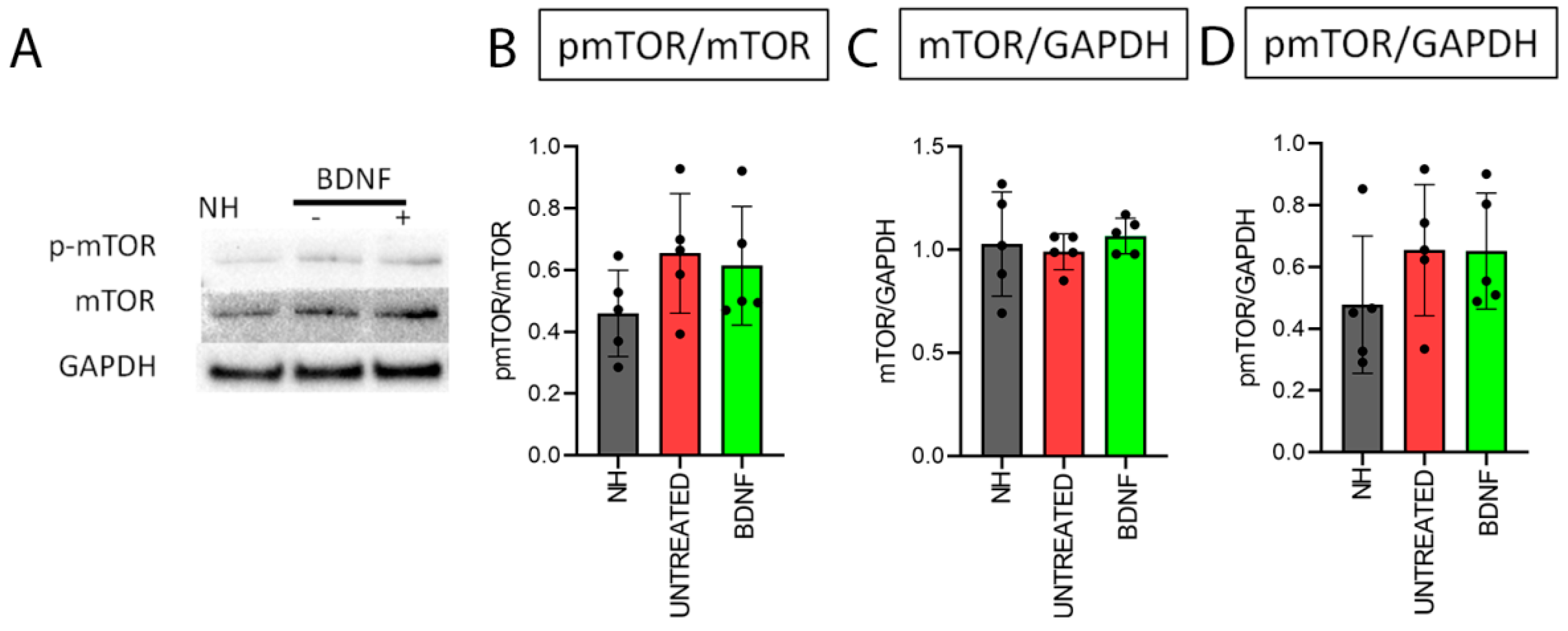
3.2. mTOR and pmTOR Analysis
3.3. PTEN Analysis
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson Chacko, L.; Blumer, M.J.F.; Pechriggl, E.; Rask-Andersen, H.; Dietl, W.; Haim, A.; Fritsch, H.; Glueckert, R.; Dudas, J.; Schrott-Fischer, A. Role of BDNF and neurotrophic receptors in human inner ear development. Cell Tissue Res. 2017, 370, 347–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singer, W.; Panford-Walsh, R.; Knipper, M. The function of BDNF in the adult auditory system. Neuropharmacology 2014, 76, 719–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbacid, M. The Trk family of neurotrophin receptors. J. Neurobiol. 1994, 25, 1386–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramekers, D.; Versnel, H.; Grolman, W.; Klis, S.F.L. Neurotrophins and their role in the cochlea. Hear. Res. 2012, 288, 19–33. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, J.; Staecker, H.; Wedekind, D.; Lenarz, T.; Warnecke, A. Expression pattern of brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its associated receptors: Implications for exogenous neurotrophin application. Hear. Res. 2020, 413, 108098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, H.A.; Versnel, H.; Kroon, S.; Klis, S.F.L.; Ramekers, D. BDNF-mediated preservation of spiral ganglion cell peripheral processes and axons in comparison to that of their cell bodies. Hear. Res. 2021, 400, 108114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramekers, D.; Versnel, H.; Strahl, S.B.; Klis, S.F.L.; Grolman, W. Temporary neurotrophin treatment prevents deafness- induced auditory nerve degeneration and preserves function. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 12331–12345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, J.M.; Chi, D.H.; O’Keeffe, L.J.; Kruszka, P.; Raphael, Y.; Altschuler, R.A. Neurotrophins can enhance spiral ganglion cell survival after inner hair cell loss. Int. J. Dev. Neurosci. 1997, 15, 631–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gillespie, L.N.; Clark, G.M.; Marzella, P.L. Delayed neurotrophin treatment supports auditory neuron survival in deaf guinea pigs. Neuroreport 2004, 15, 1121–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agterberg, M.J.H.; Versnel, H.; de Groot, J.C.M.J.; Smoorenburg, G.F.; Albers, F.W.J.; Klis, S.F.L. Morphological changes in spiral ganglion cells after intracochlear application of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in deafened guinea pigs. Hear. Res. 2008, 244, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGuinness, S.L.; Shepherd, R.K. Exogenous BDNF rescues rat spiral ganglion neurons in vivo. Otol. Neurotol. 2005, 26, 1064–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruan, R.S.; Leong, S.K.; Mark, I.; Yeoh, K.H. Effects of BDNF and NT-3 on hair cell survival in guinea pig cochlea damaged by kanamycin treatment. Neuroreport 1999, 10, 2067–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoji, F.; Miller, A.L.; Mitchell, A.; Yamasoba, T.; Altschuler, R.A.; Miller, J.M. Differential protective effects of neurotrophins in the attenuation of noise-induced hair cell loss. Hear. Res. 2000, 146, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tisi, A.; Rovers, J.; Vink, H.A.; Ramekers, D.; Maccarone, R.; Versnel, H. No Protective Effects of Hair Cells or Supporting Cells in Ototoxically Deafened Guinea Pigs upon Administration of BDNF. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ranum, P.T.; Goodwin, A.T.; Yoshimura, H.; Kolbe, D.L.; Walls, W.D.; Koh, J.Y.; He, D.Z.Z.; Smith, R.J.H. Insights into the Biology of Hearing and Deafness Revealed by Single-Cell RNA Sequencing. Cell Rep. 2019, 26, 3160–3171.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, Y.; Li, W.; Huang, M.; Quan, Y.Z.; Scheffer, D.; Tian, C.; Tao, Y.; Liu, X.; Hochedlinger, K.; Indzhykulian, A.A.; et al. Renewed proliferation in adult mouse cochlea and regeneration of hair cells. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 5530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldhaus, J.; Durruthy-Durruthy, R.; Heller, S. Quantitative High-Resolution Cellular Map of the Organ of Corti. Cell Rep. 2015, 11, 1385–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.D.; Wu, C.L.; Hwang, W.C.; Yang, D.I. More insight into BDNF against neurodegeneration: Anti-apoptosis, anti-oxidation, and suppression of autophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 545. [Google Scholar]
- Bockaert, J.; Marin, P. mTOR in Brain Physiology and Pathologies. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 1157–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, W.J.; Jacinto, E. mTOR complex 2 signaling and functions. Cell Cycle 2011, 10, 2305–2316. [Google Scholar]
- Melick, C.H.; Jewell, J.L. Regulation of mtorc1 by upstream stimuli. Genes 2020, 11, 989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabanal-Ruiz, Y.; Otten, E.G.; Korolchuk, V.I. MTORC1 as the main gateway to autophagy. Essays Biochem. 2017, 61, 565–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Cortada, M.; Levano, S.; Bodmer, D. mTOR Signaling in the Inner Ear as Potential Target to Treat Hearing Loss. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 6368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Sun, X.; Zhang, L.; Jin, Y.; Chai, R.; Yang, L.; Zhang, A.; Liu, X.; Bai, X.; Li, J.; et al. Tuberous sclerosis complex-mediated mTORC1 overactivation promotes age-related hearing loss. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 4938–4955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leitmeyer, K.; Glutz, A.; Radojevic, V.; Setz, C.; Huerzeler, N.; Bumann, H.; Bodmer, D.; Brand, Y. Inhibition of mTOR by Rapamycin Results in Auditory Hair Cell Damage and Decreased Spiral Ganglion Neuron Outgrowth and Neurite Formation In Vitro. Biomed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 925890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, Z.; Liu, Y.; Cao, H.; Yang, J.; Wang, B. PIN1 Protects Hair Cells and Auditory HEI-OC1 Cells against Senescence by Inhibiting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2021, 2021, 9980444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramekers, D.; Benav, H.; Klis, S.F.L.; Versnel, H. Changes in the Electrically Evoked Compound Action Potential over time After Implantation and Subsequent Deafening in Guinea Pigs. JARO-J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baar, E.L.; Carbajal, K.A.; Ong, I.M.; Lamming, D.W. Sex- and tissue-specific changes in mTOR signaling with age in C57BL/6J mice. Aging Cell 2016, 15, 155–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vink, H.A.; van Dorp, W.C.; Thomeer, H.G.X.M.; Versnel, H.; Ramekers, D. Bdnf outperforms trkb agonist 7,8,3′-thf in preserving the auditory nerve in deafened guinea pigs. Brain Sci. 2020, 10, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Antibody | Company | Catalogue Number | MW (kDa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| anti-mTOR | Rockland | #600-401-897 | 250 |
| anti-pmTOR | Rockland | #600-401-422 | 250 |
| anti-AKT | Cell Signaling | #9272S | 60 |
| anti-pAKT (Thr 308) | Cell Signaling | #2965S | 60 |
| anti-PTEN | Cell Signaling | #9552S | 54 |
| anti-GAPDH | Thermo Fisher | #AM4300 | 37 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tisi, A.; Ramekers, D.; Flati, V.; Versnel, H.; Maccarone, R. mTOR Signaling in BDNF-Treated Guinea Pigs after Ototoxic Deafening. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112935
Tisi A, Ramekers D, Flati V, Versnel H, Maccarone R. mTOR Signaling in BDNF-Treated Guinea Pigs after Ototoxic Deafening. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(11):2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112935
Chicago/Turabian StyleTisi, Annamaria, Dyan Ramekers, Vincenzo Flati, Huib Versnel, and Rita Maccarone. 2022. "mTOR Signaling in BDNF-Treated Guinea Pigs after Ototoxic Deafening" Biomedicines 10, no. 11: 2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112935
APA StyleTisi, A., Ramekers, D., Flati, V., Versnel, H., & Maccarone, R. (2022). mTOR Signaling in BDNF-Treated Guinea Pigs after Ototoxic Deafening. Biomedicines, 10(11), 2935. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10112935








