Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using DNP as a Template Molecule for Explosive Sensing and Nitroaromatic Compound Discrimination
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Equipment and Software
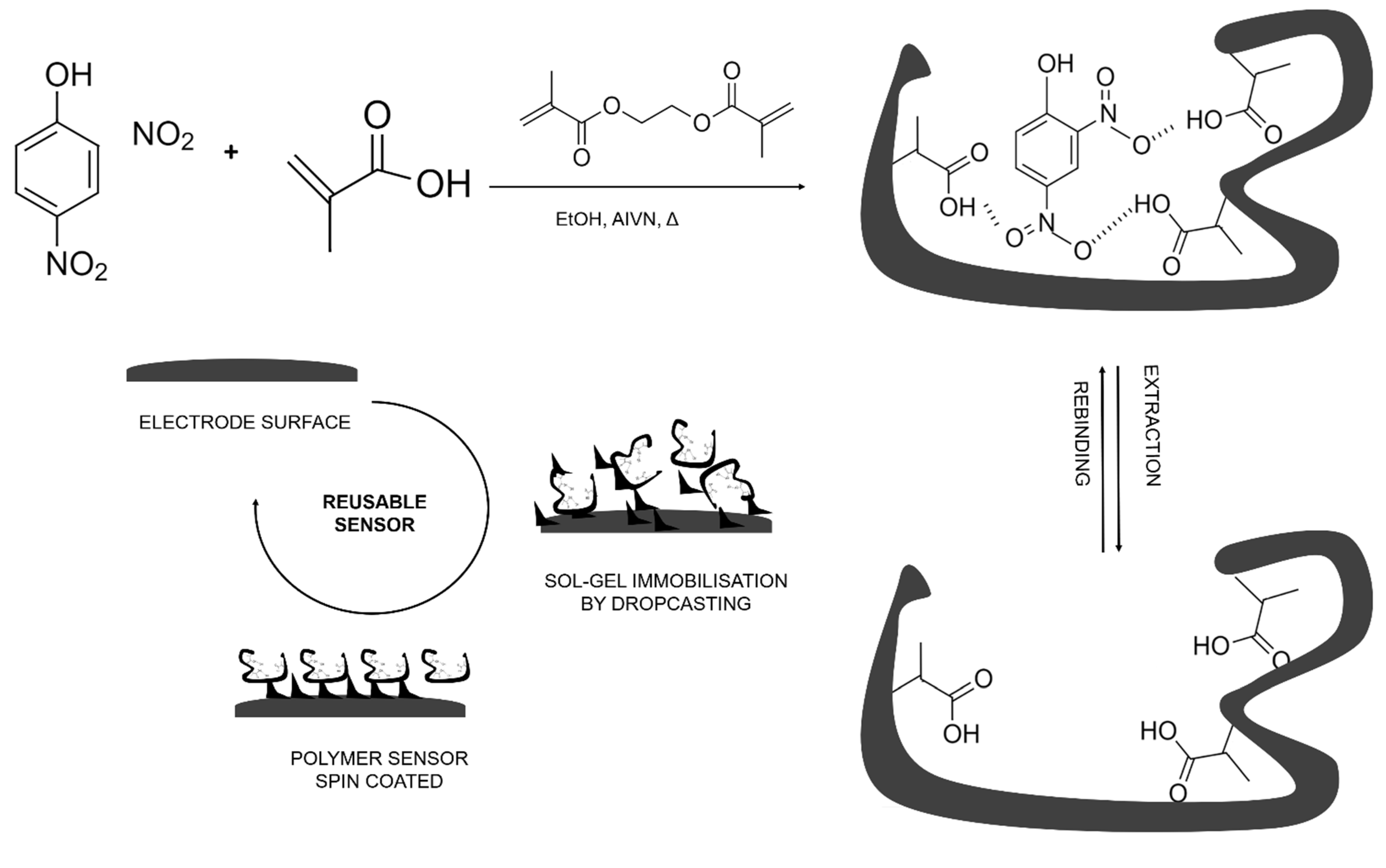
2.3. Polymer Synthesis
2.4. Sensor Preparation
2.5. MIP Modification of Electrodes by Sol–Gel Entrapment
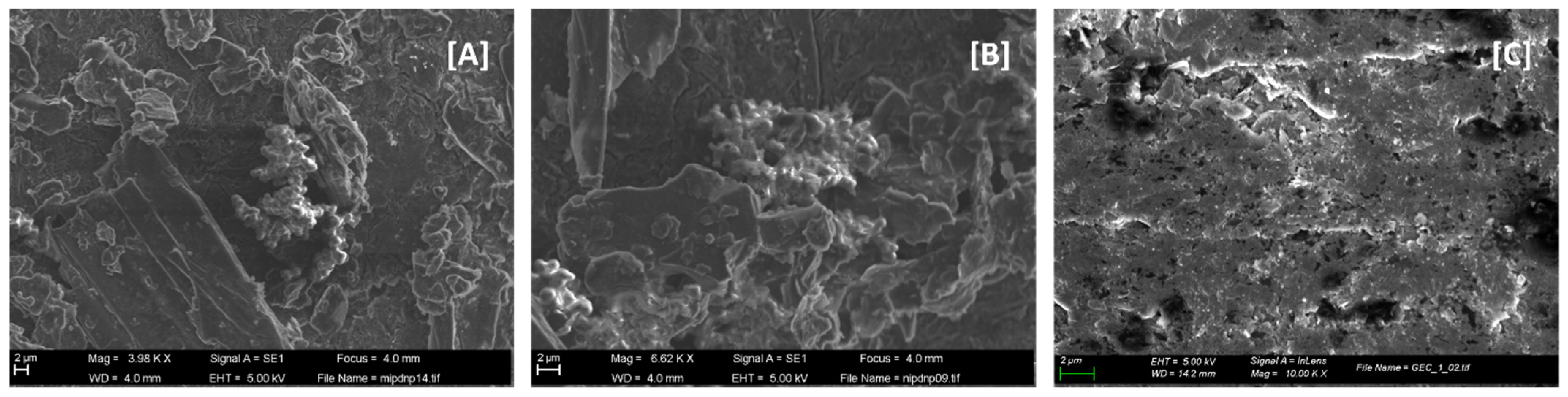
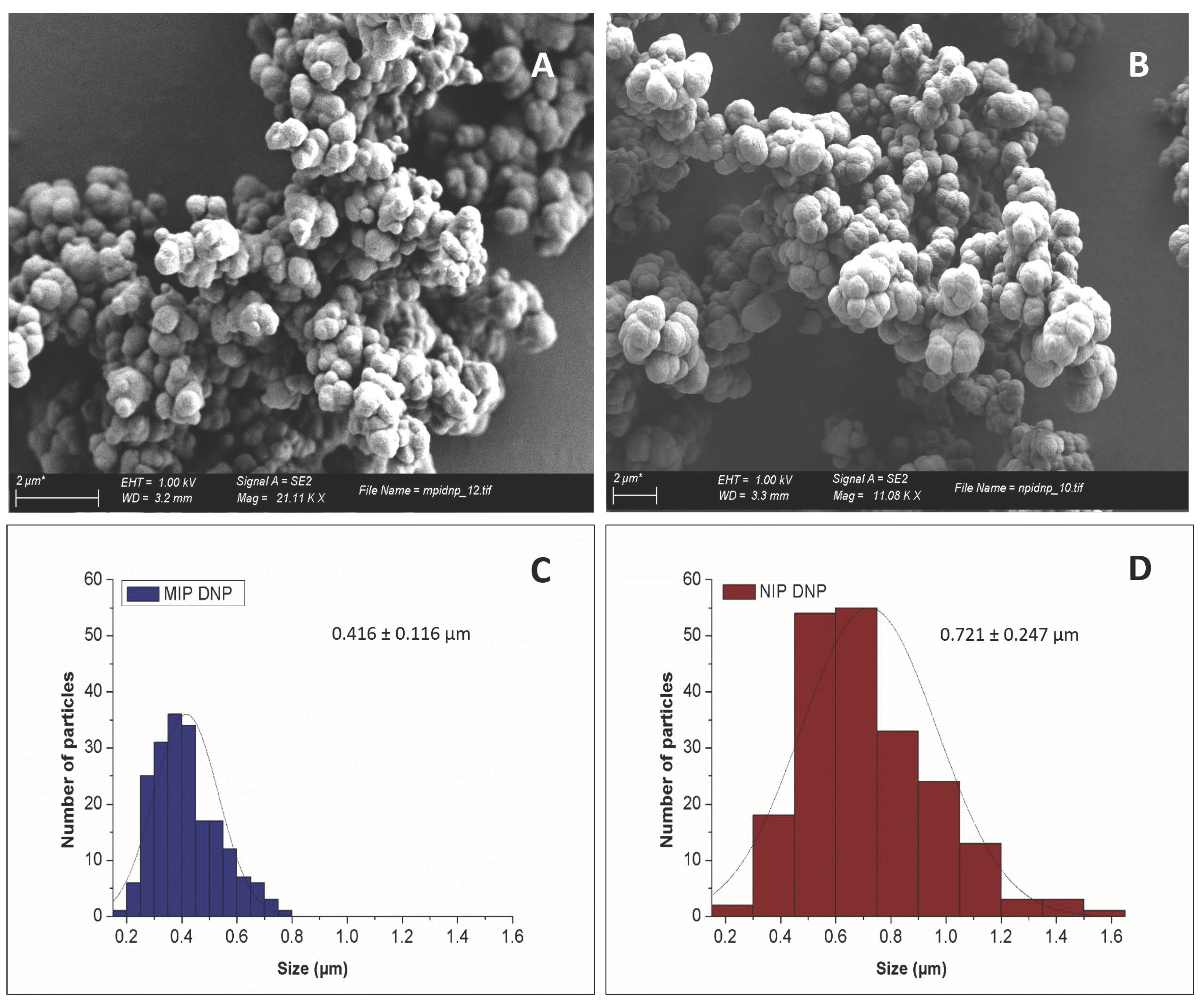
2.6. Characterisation by Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.7. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. MIP Physical Characterisation
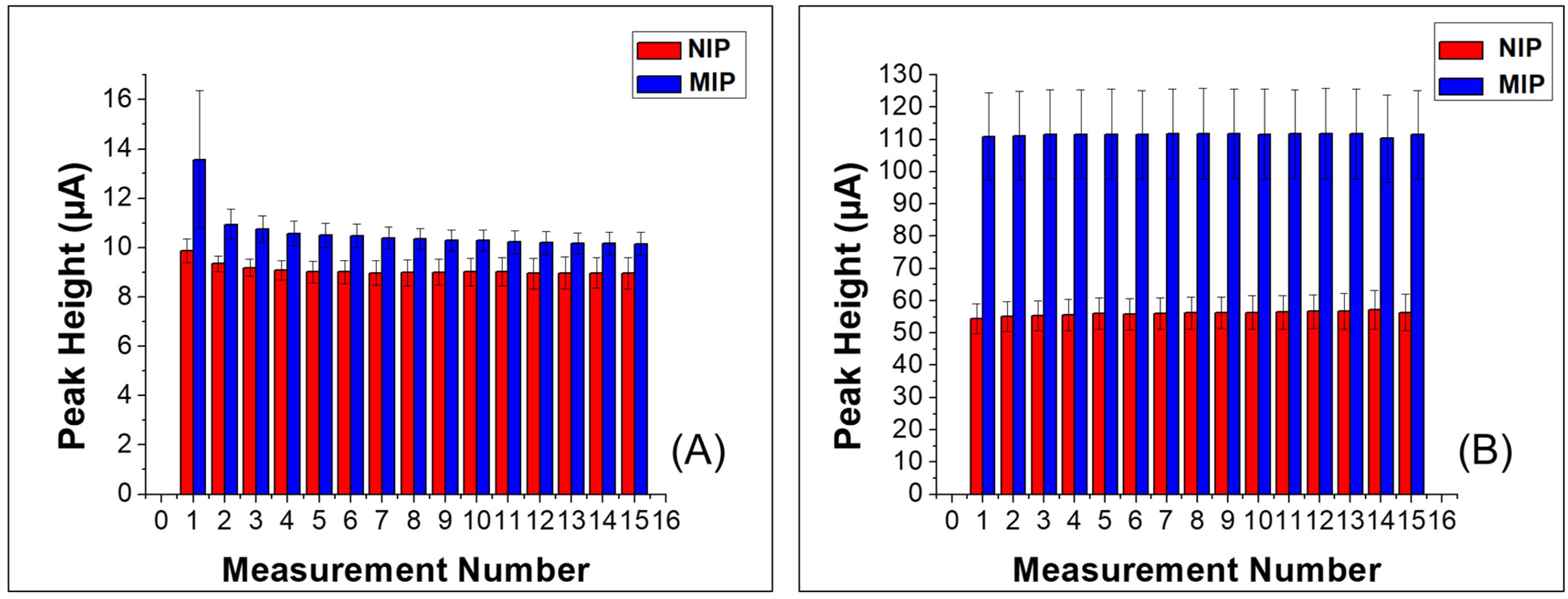
3.2. Electrochemical Response
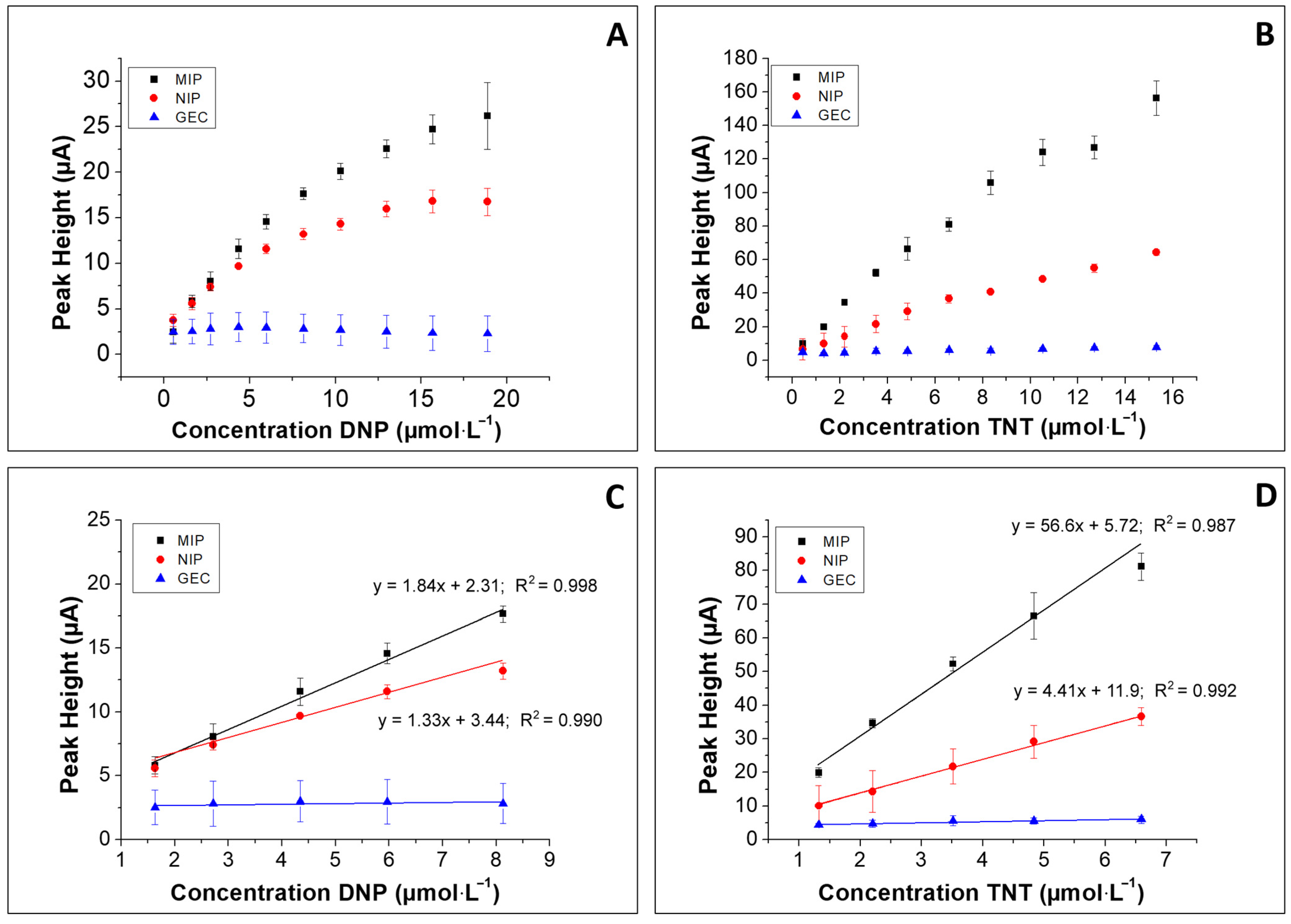
3.3. Calibration Curves
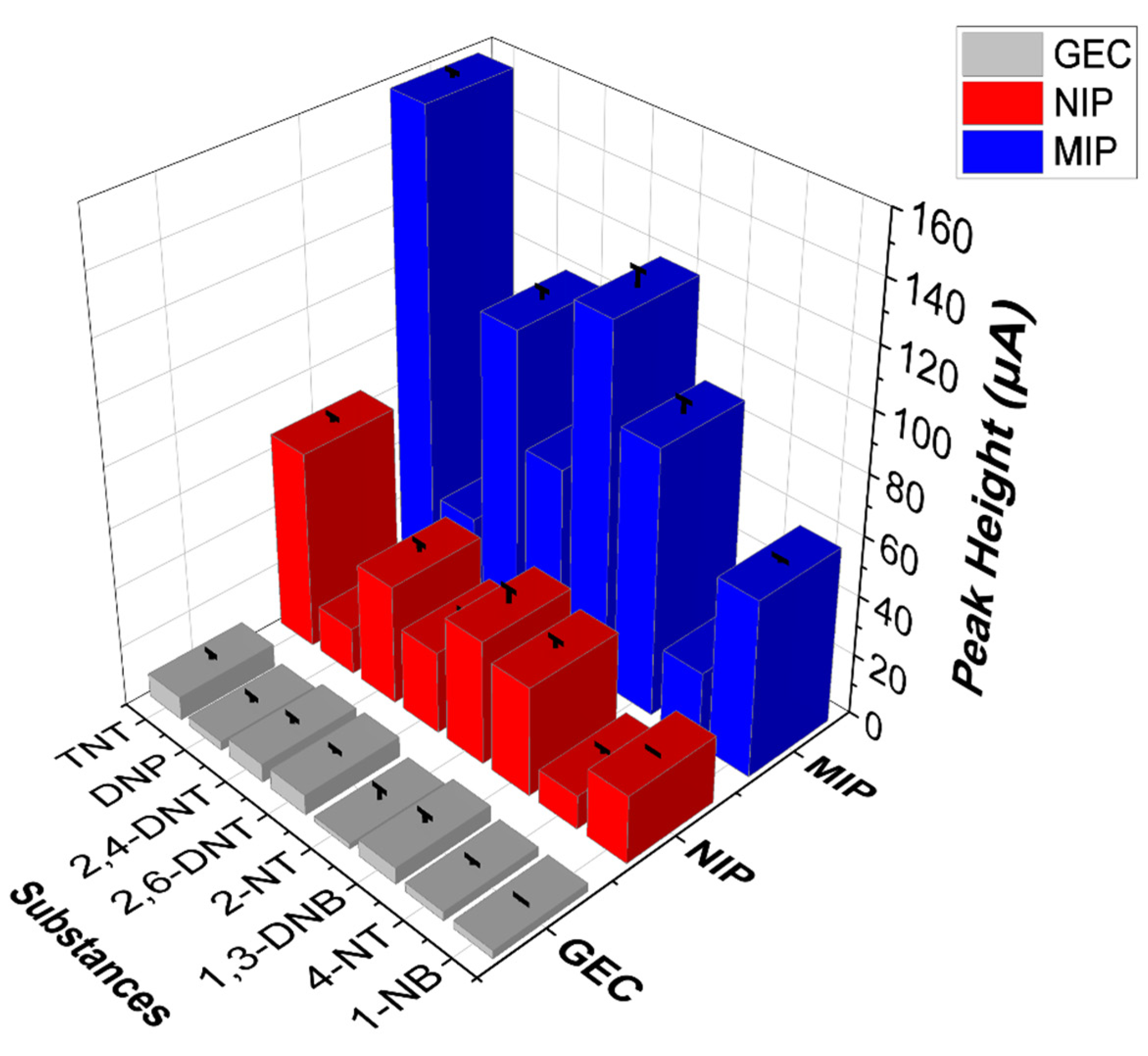
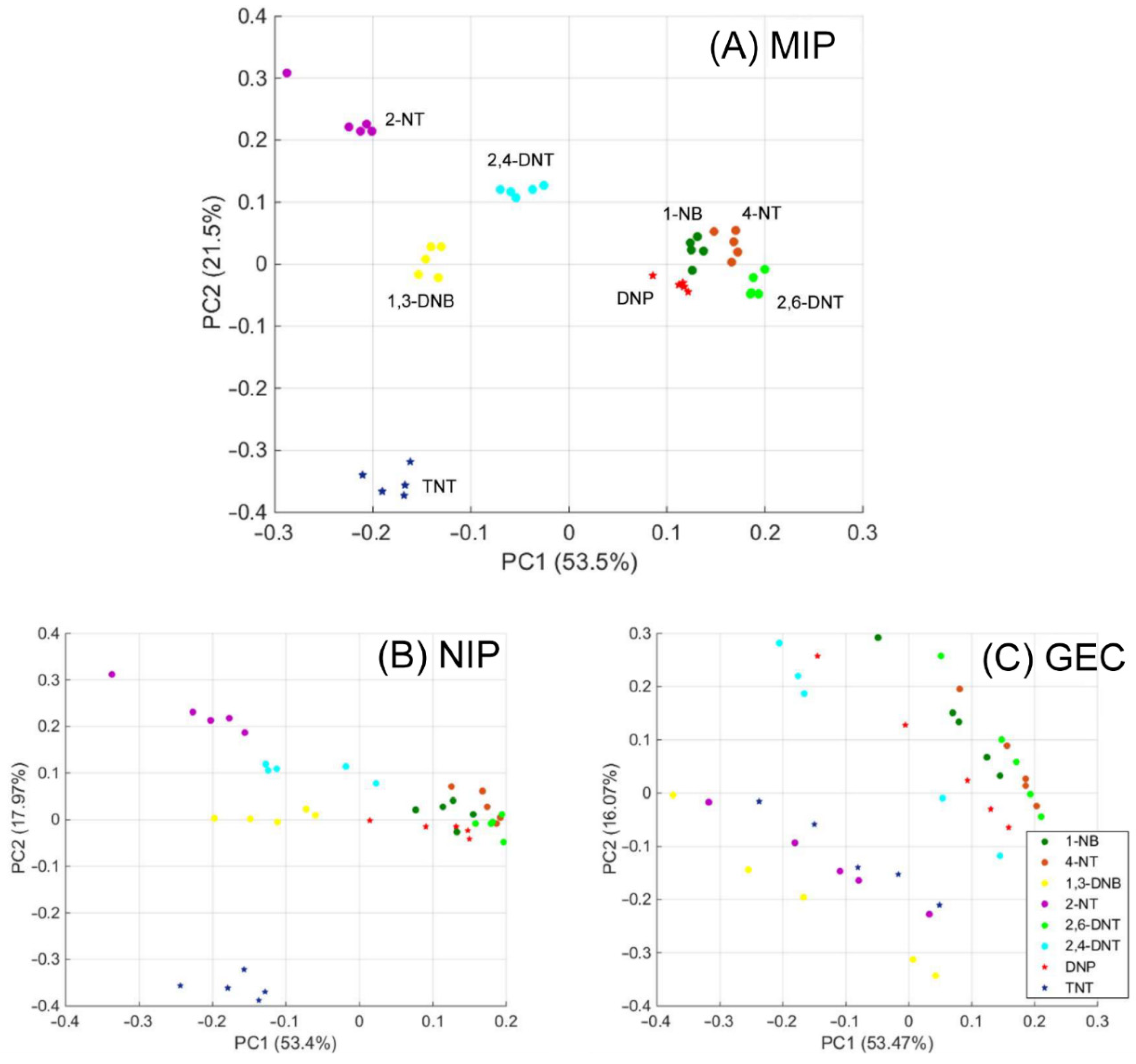
3.4. Specificity versus Other Nitroaromatic Compounds
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liang, C.; Ristic, R.; Jiranek, V.; Jeffery, D.W. Chemical and Sensory Evaluation of Magnetic Polymers as a Remedial Treatment for Elevated Concentrations of 3-Isobutyl-2-methoxypyrazine in Cabernet Sauvignon Grape Must and Wine. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 7121–7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera-Chacon, A.; González-Calabuig, A.; Campos, I.; del Valle, M. Bioelectronic tongue using MIP sensors for the resolution of volatile phenolic compounds. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 665–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yola, M.L.; Atar, N. Electrochemical Detection of Atrazine by Platinum Nanoparticles/Carbon Nitride Nanotubes with Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2017, 56, 7631–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabavi, S.A.; Vladisavljević, G.T.; Zhu, Y.; Manović, V. Synthesis of Size-Tunable CO2-Philic Imprinted Polymeric Particles (MIPs) for Low-Pressure CO2 Capture Using Oil-in-Oil Suspension Polymerization. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 11476–11483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, W.; Liu, L.; Chen, Y. Simultaneous Detection of Human C-Terminal p53 Isoforms by Single Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymers (MIPs) Coupled with Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS)-Based Targeted Proteomics. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3058–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chunta, S.; Suedee, R.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Low-Density Lipoprotein Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 1419–1425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, A.P.F.; Piletsky, S. Biosensors and Biomimetic Sensors for the Detection of Drugs, Toxins and Biological Agents. In Defense against Bioterror. NATO Security through Science Series; Morrison, D., Milanovich, F., Ivnitski, D., Austin, T.R., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Nerthlands, 2005; pp. 261–272. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Y.; Pan, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Deng, S.; Xia, Z. A SPE method with two MIPs in two steps for improving the selectivity of MIPs. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 8436–8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Huang, X. Sensitive Monitoring of Fluoroquinolones in Milk and Honey Using Multiple Monolithic Fiber Solid-Phase Microextraction Coupled to Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 8684–8693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Arribas, L.N.; Urraca, J.L.; Benito-Penìa, E.; Moreno-Bondi, M.C. Tag-specific affinity purification of recombinant proteins by using molecularly imprinted polymers. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 4100–4106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Aissa, A.; Herrera-Chacon, A.; Pupin, R.R.; Sotomayor, M.D.P.T.; Pividori, M.I. Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for the isolation and detection of biotin and biotinylated biomolecules. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 88, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Klimuntowski, M.; Alam, M.M.; Singh, G.; Howlader, M.M.R. Electrochemical Sensing of Cannabinoids in Biofluids: A Noninvasive Tool for Drug Detection. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wackerlig, J.; Schirhagl, R. Applications of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles and Their Advances toward Industrial Use: A Review. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 250–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, J.; Jin, J.; Shah, S.M.; Chen, J. Novel dummy molecularly imprinted polymers for matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction of eight fluoroquinolones from fish samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1359, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.M.; Chen, Y.P.; Wang, X.F.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.L.; Xie, M.X. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers on silica particles for selective solid-phase extraction of tetrabromobisphenol A from water samples. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1220, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagheri, A.R.; Arabi, M.; Ghaedi, M.; Ostovan, A.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Chen, L. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers based on a green synthesis strategy for magnetic solid-phase extraction of acrylamide in food samples. Talanta 2019, 195, 390–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCluskey, A.; Holdsworth, C.I.; Bowyer, M.C. Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs): Sensing, an explosive new opportunity? Org. Biomol. Chem. 2007, 5, 3233–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Lu, H.; Li, J.; Song, X.; Wang, A.; Chen, L.; Han, S. Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers-capped CdTe quantum dots for the fluorescent sensing of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8146–8154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, E.; Garipcan, B.; Patra, H.K.; Uzun, L. Molecular imprinting applications in forensic science. Sensors 2017, 17, 691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, H.; Xia, Y. Planar Is Better: Monodisperse Three-Layered MoS2 Quantum Dots as Fluorescent Reporters for 2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene Sensing in Environmental Water and Luggage Cases. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 3942–3949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Xue, M.; Xu, Z.; Dong, X.; Xue, F.; Wang, F.; Wang, Q.; Meng, Z. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Sensing of Explosives and Chemical Warfare Agents. Curr. Org. Chem. 2015, 19, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Li, H.; Meng, Z.; Liang, X.; Xue, M.; Wang, Q.; Dong, X. Detection of nitrobenzene compounds in surface water by ion mobility spectrometry coupled with molecularly imprinted polymers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 280, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortada, C.; Vidal, L.; Canals, A. Determination of nitroaromatic explosives in water samples by direct ultrasound-assisted dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Talanta 2011, 85, 2546–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Hou, A.G.; Chen, L.Y.; Wang, Z.F. Electrochemical sensor prepared from molecularly imprinted polymer for recognition of TNT. Polym. Compos. 2015, 36, 1280–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Electrochemical sensing of explosives. Electroanalysis 2007, 19, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesavento, M.; D’Agostino, G.; Alberti, G.; Biesuz, R.; Merli, D. Voltammetric platform for detection of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene based on a molecularly imprinted polymer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 3559–3570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leibl, N.; Duma, L.; Gonzato, C.; Haupt, K. Polydopamine-based molecularly imprinted thin films for electro-chemical sensing of nitro-explosives in aqueous solutions. Bioelectrochemistry 2020, 135, 107541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alizadeh, T.; Zare, M.; Ganjali, M.R.; Norouzi, P.; Tavana, B. A new molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP)-based electrochemical sensor for monitoring 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) in natural waters and soil samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2010, 25, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sağlam, Ş.; Üzer, A.; Erçağ, E.; Apak, R. Electrochemical Determination of TNT, DNT, RDX, and HMX with Gold Nanoparticles/Poly(Carbazole-Aniline) Film–Modified Glassy Carbon Sensor Electrodes Imprinted for Molecular Recognition of Nitroaromatics and Nitramines. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 7364–7370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, D.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Zhou, T.; Jin, L.; Shi, G. Two-dimensional molecular imprinting approach for the electrochemical detection of trinitrotoluene. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 156, 43–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Chen, S.; Shi, R.; Ji, J.; Wang, D.; Jin, S.; Han, T.; Zhou, C.; Shu, Q. A single molecular fluorescent probe for selective and sensitive detection of nitroaromatic explosives: A new strategy for the mask-free discrimination of TNT and TNP within same sample. Talanta 2017, 166, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, L. Upconversion luminescence nanosensor for TNT selective and label-free quantification in the mixture of nitroaromatic explosives. Talanta 2014, 120, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, H.; Peng, S.; Wang, L. Highly Selective and Sensitive Fluorescent Paper Sensor for Nitroaromatic Explosive Detection. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 8415–8421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmermann, Y.; Broekaert, J.A.C. Determination of TNT and its metabolites in water samples by voltammetric techniques. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2005, 383, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drinking Water Standards and Health Advisories; EPA 822-S-12-001; United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2012; pp. 1–20.
- Technical Fact Sheet—2,4,6-Trinitrotoluene (TNT); United States Environmental Protection Agency: Washington, DC, USA, 2014; pp. 1–8.
- Wang, J.; Lu, F.; MacDonald, D.; Lu, J.; Ozsoz, M.E.S.; Rogers, K.R. Screen-printed voltammetric sensor for TNT. Talanta 1998, 46, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caygill, J.S.; Collyer, S.D.; Holmes, J.L.; Davis, F.; Higson, S.P.J. Disposable screen-printed sensors for the electrochemical detection of TNT and DNT. Analyst 2013, 138, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caygill, J.S.; Collyer, S.D.; Holmes, J.L.; Davis, F.; Higson, S.P.J. Electrochemical Detection of TNT at Cobalt Phthalocyanine Mediated Screen-Printed Electrodes and Application to Detection of Airborne Vapours. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 2445–2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, J.; Hocevar, S.B.; Ogorevc, B. Carbon nanotube-modified glassy carbon electrode for adsorptive stripping voltammetric detection of ultratrace levels of 2,4,6-trinitrotoluene. Electrochem. Commun. 2004, 6, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, J.; Guo, C.X.; Hu, F.; Yu, L.; Li, C.M. Electrochemical detection of ultratrace nitroaromatic explosives using ordered mesoporous carbon. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 683, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Wang, X.; Kang, Q.; Li, J.; Shen, D.; Chen, L. One-pot synthesis of a quantum dot-based molecular imprinting nanosensor for highly selective and sensitive fluorescence detection of 4-nitrophenol in environmental waters. Environ. Sci. Nano 2017, 4, 493–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saloni, J.; Walker, K.; Hill, G. Theoretical investigation on monomer and solvent selection for molecular imprinting of nitrocompounds. J. Phys. Chem. A 2013, 117, 1531–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Nogueroles, M.; Lordel-Madeleine, S.; Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A.; Pichon, V. Development of a selective solid phase extraction method for nitro musk compounds in environmental waters using a molecularly imprinted sorbent. Talanta 2013, 110, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindelin, J.; Arganda-Carreras, I.; Frise, E.; Kaynig, V.; Longair, M.; Pietzsch, T.; Preibisch, S.; Rueden, C.; Saalfeld, S.; Schmid, B.; et al. Fiji: An open-source platform for biological-image analysis. Nat. Methods 2019, 9, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Olivé-Monllau, R.; Baeza, M.; Bartrolí, J.; Céspedes, F. Novel amperometric sensor based on rigid near-percolation composite. Electroanalysis 2009, 21, 931–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alegret, S.; Alonso, J.; Bartrolí, J.; Céspedes, F.; Martínez-Fàbregas, E.; del Valle, M. Amperometric biosensors based on bulk-modified epoxy graphite biocomposites. Sens. Mater. 1996, 8, 147–153. [Google Scholar]
- Aceta, Y.; del Valle, M. Graphene electrode platform for impedimetric aptasensing. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 229, 458–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocaña, C.; del Valle, M. Signal amplification for thrombin impedimetric aptasensor: Sandwich protocol and use of gold-streptavidin nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 54, 408–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Herrera-Chacón, A.; Dinç-Zor, Ş.; del Valle, M. Integrating molecularly imprinted polymer beads in graphite-epoxy electrodes for the voltammetric biosensing of histamine in wines. Talanta 2020, 208, 120348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciosek, P.; Wróblewski, W. Sensor arrays for liquid sensing—Electronic tongue systems. Analyst 2007, 132, 963–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Valle, M. Electronic Tongues Employing Electrochemical Sensors. Electroanalysis 2010, 22, 1539–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]


| Sensing Platform | Interferents | Technique | Linear Range (mol L−1) | LOD (mol L−1) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecularly imprinted polydopamine films onto gold electrodes | Trimesic acid, isopthalic acid and 4-nitrophenol | Cyclic Voltammetry | 0.1 × 10−9–10.0 × 10−9 | 50.0 × 10−12 | [27] |
| Carbon paste electrodes modified with MIP particles | Phenol, Aniline, para-Nitrophenol, Benzoic acid and Nitrobenzene | Square-Wave Voltammetry | 5.0 × 10−9–1.0 × 10−6 | 1.5 × 10−9 | [28] |
| Gold nanoparticles/poly (carbazole-aniline) film-modified glassy carbon electrode | Paracetamol-caffeine-based analgesic drug, acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin), sweetener, and sugar | Square-Wave Voltammetry | 4.4 × 10−7–4.4 × 10−6 | 1.1 × 10−7 | [29] |
| Alkanethiols self-assembled on AuNPs modified glassy carbon | Trinitrobenzene, dinitrotoluene and dinitrobenzene | Differential Pulse Voltammetry | 4.0 × 10−8–3.2 × 10−6 | 1.3 × 10−8 | [30] |
| Dummy molecularly imprinted polymers with capped CdTe quantum dots | 2,4-dinitrophenol, 4-nitrophenol, phenol, and dinitrotoluene | Fluorescence | 0.8 × 10−6–30.0 × 10−6 | 0.28 × 10−6 | [18] |
| Naphthalene based fluorescent probe | Nitrobenzene, p-Nitrotoluene, Dinitrotoluene, Trinitrophenol, cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine, cyclotetra- methylenetetranitramine and Hexanitrohexaazaisowurtzitane | UV–Vis spectroscopy | 5 × 10−9– 1 × 10−6 | 1.5 × 10−9 | [31] |
| Amine functionalised nanoparticles | Nitrobenzene, dinitrotoluene and trinitrophenol | Fluorescence | 4.4 × 10−11–4.0 × 10−8 | 4.3 × 10−11 | [32] |
| Fluorescent paper | Nitrobenzene, dinitrotoluene and trinitrophenol | Fluorescence | 2.2 × 10−10–3.1 × 10−8 | 1.4 × 10−10 | [33] |
| MIP functionalised carbon graphite epoxy composite electrodes | Paracetamol, serotonin, tryptamine | Differential pulse voltammetry | 1.5 × 10−6–8 × 10−6 | 0.29 × 10−6 | The present work |
| MIP | NIP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DNP | TNT | DNP | TNT | |
| Sensitivity (µA µmol−1 L) | 1.84 | 56.6 | 1.33 | 4.41 |
| Intercept (µA) | 2.31 | 5.72 | 3.44 | 11.9 |
| R2 | 0.99 | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.99 |
| LOD (µmol−1 L) | 0.59 | 0.29 | 1.38 | 0.95 |
| LOQ (µmol−1 L) | 1.79 | 0.88 | 4.18 | 2.87 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Herrera-Chacon, A.; Gonzalez-Calabuig, A.; del Valle, M. Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using DNP as a Template Molecule for Explosive Sensing and Nitroaromatic Compound Discrimination. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090255
Herrera-Chacon A, Gonzalez-Calabuig A, del Valle M. Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using DNP as a Template Molecule for Explosive Sensing and Nitroaromatic Compound Discrimination. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(9):255. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090255
Chicago/Turabian StyleHerrera-Chacon, Anna, Andreu Gonzalez-Calabuig, and Manel del Valle. 2021. "Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using DNP as a Template Molecule for Explosive Sensing and Nitroaromatic Compound Discrimination" Chemosensors 9, no. 9: 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090255
APA StyleHerrera-Chacon, A., Gonzalez-Calabuig, A., & del Valle, M. (2021). Dummy Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Using DNP as a Template Molecule for Explosive Sensing and Nitroaromatic Compound Discrimination. Chemosensors, 9(9), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9090255








