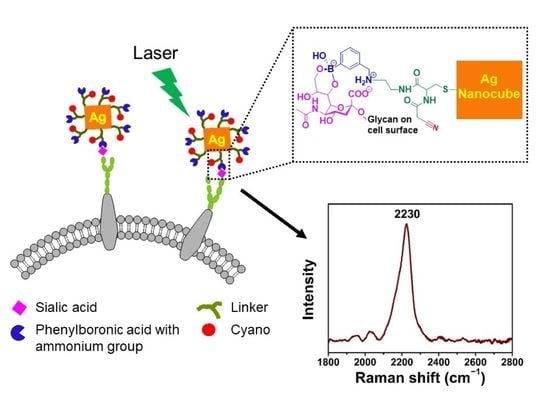
Development of a Tri-Functional Nanoprobe for Background-Free SERS Detection of Sialic Acid on the Cell Surface
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Instruments and Characterization
2.3. Synthesis of AgNCs
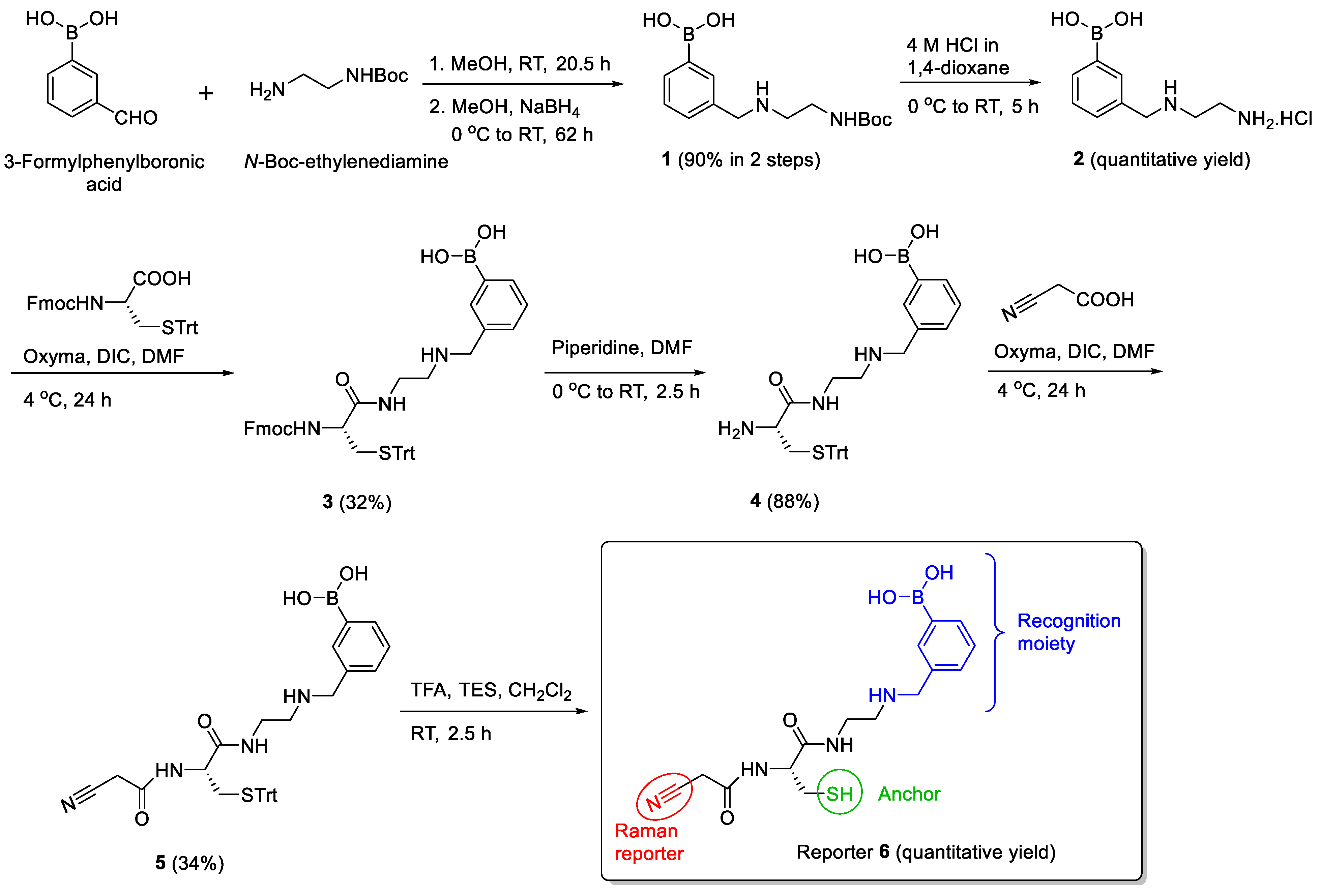
2.4. Synthetic Procedures
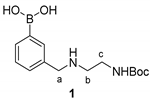
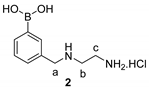
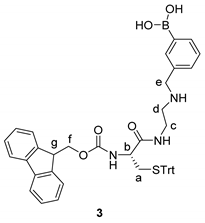
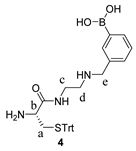
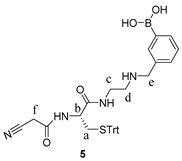

2.5. Synthesis of Tri-Functional Nanoprobe (Reporter 6 Conjugated AgNCs)
2.6. Cell Culture and Treatment with Nanoprobe
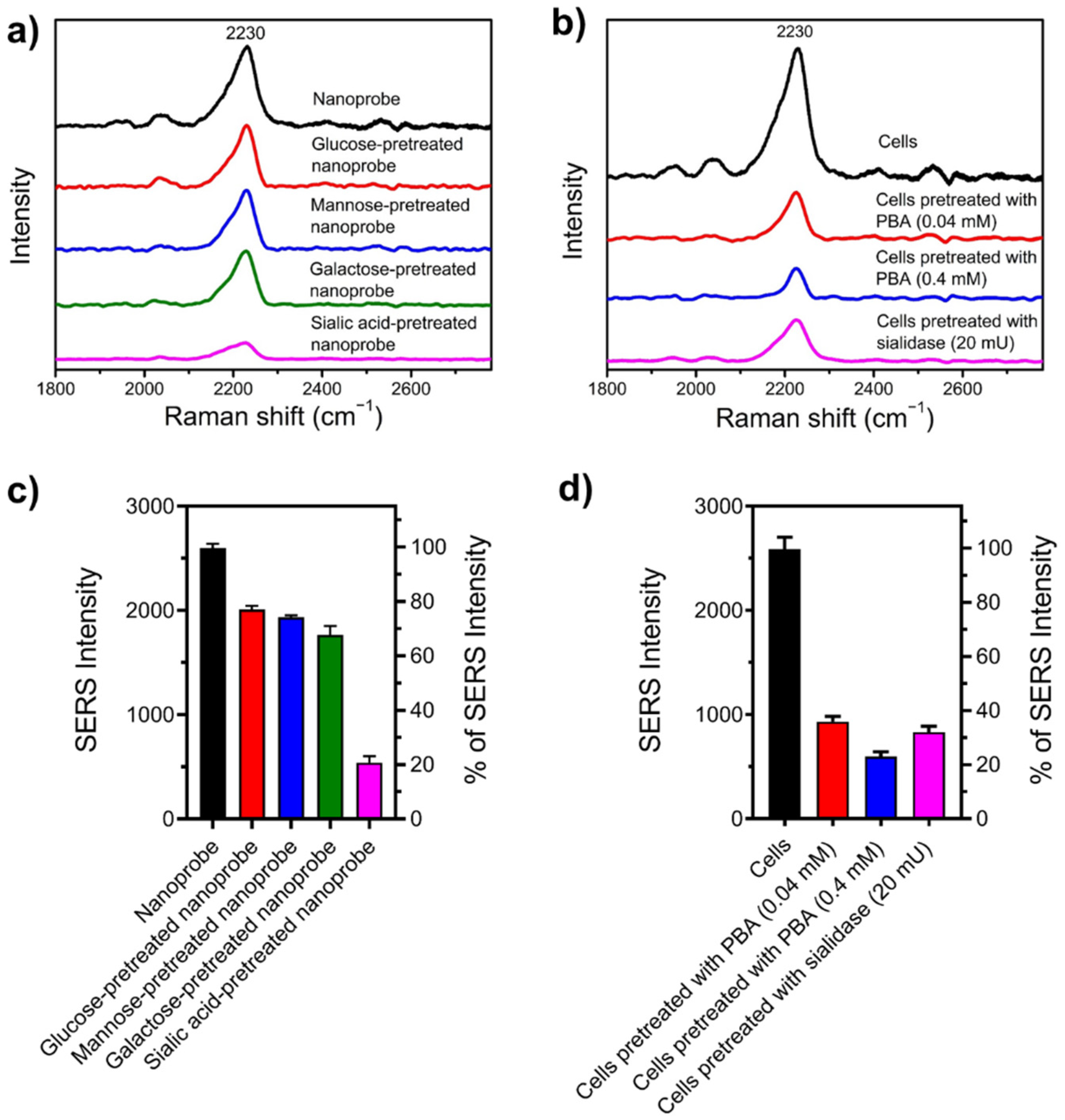
2.7. Specificity of Nanoprobe towards SA
2.8. SERS Measurement
3. Results and Discussion
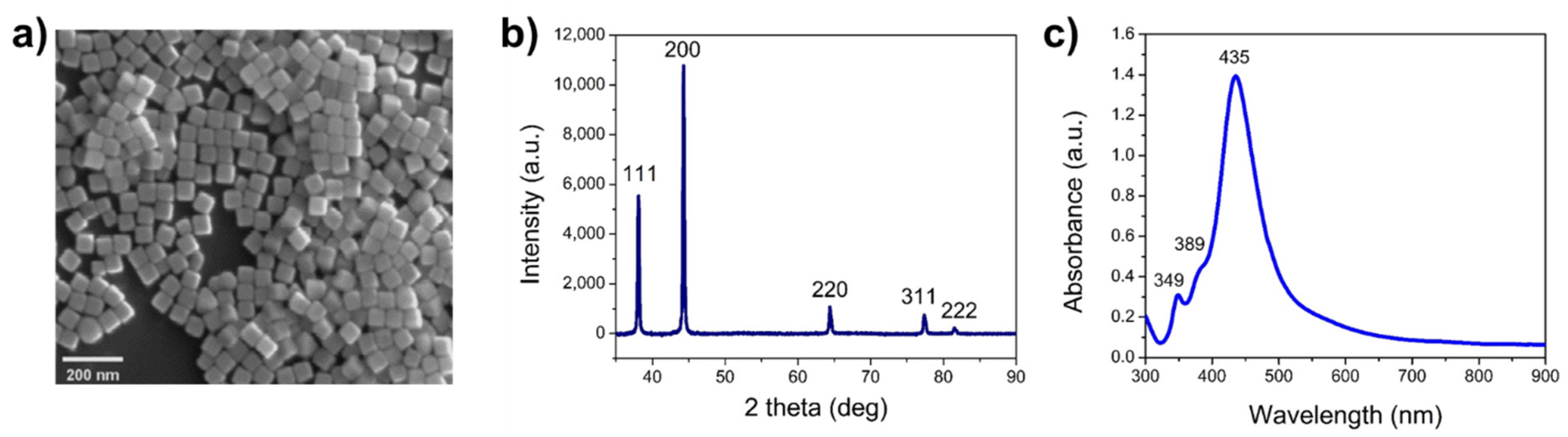
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of AgNCs
3.2. Design and Synthesis of Reporter
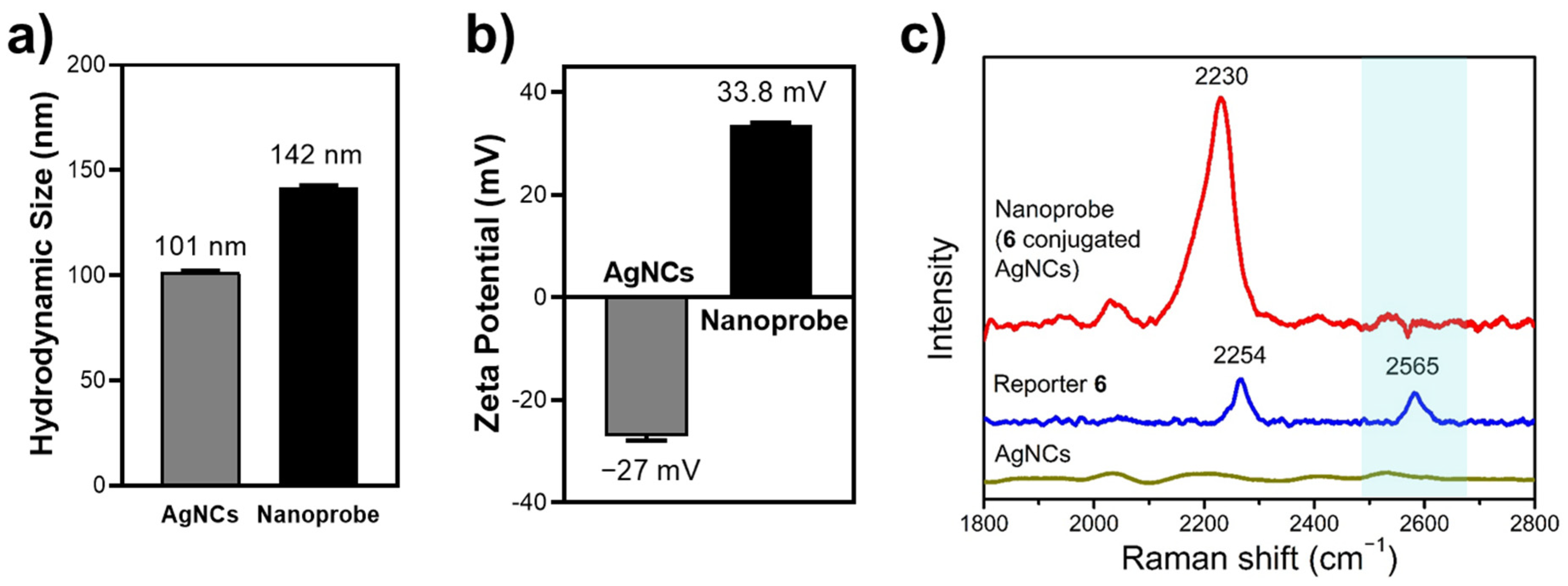
3.3. Characterization of Tri-Functional Nanoprobe
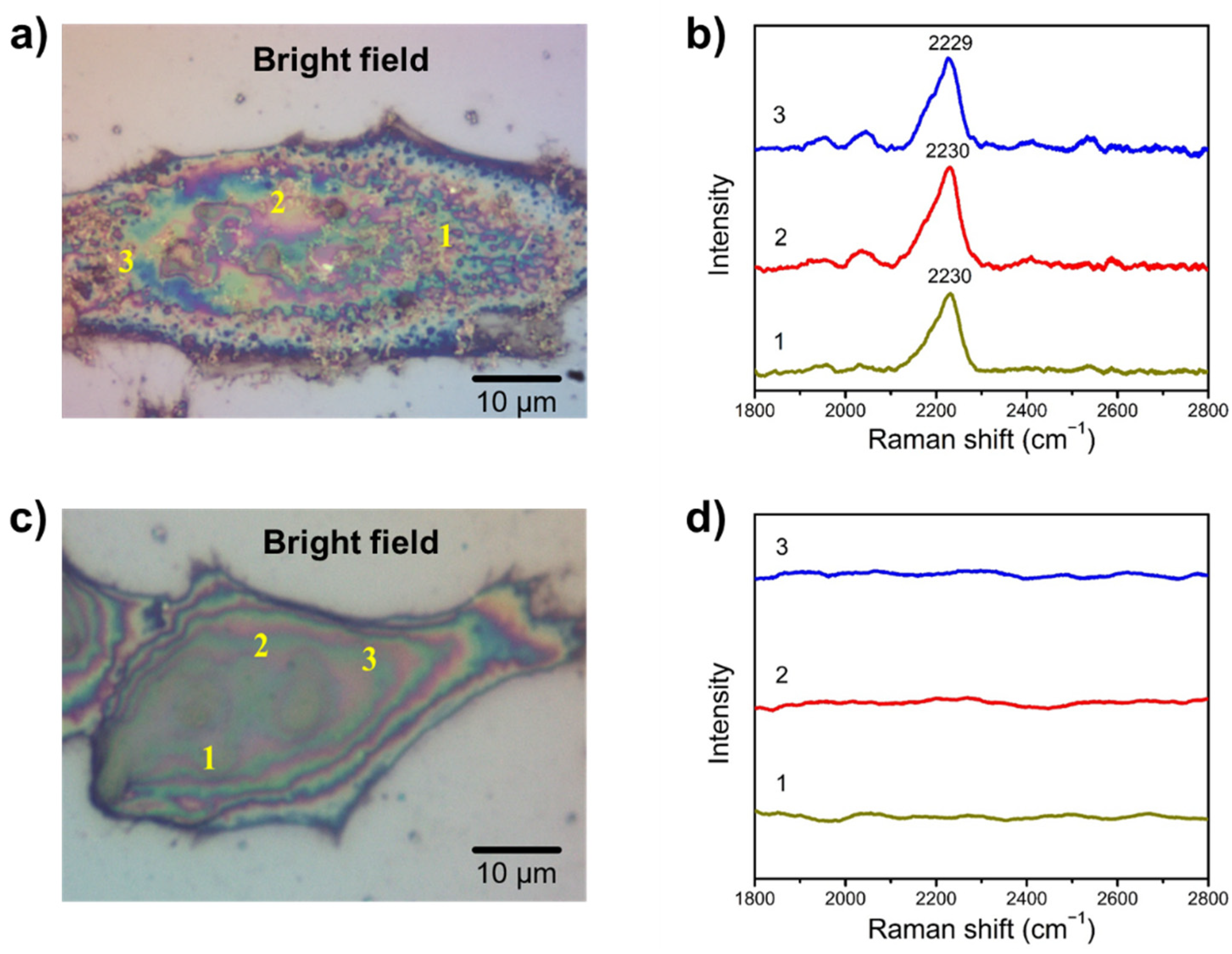
3.4. SA Expression on HeLa Cells
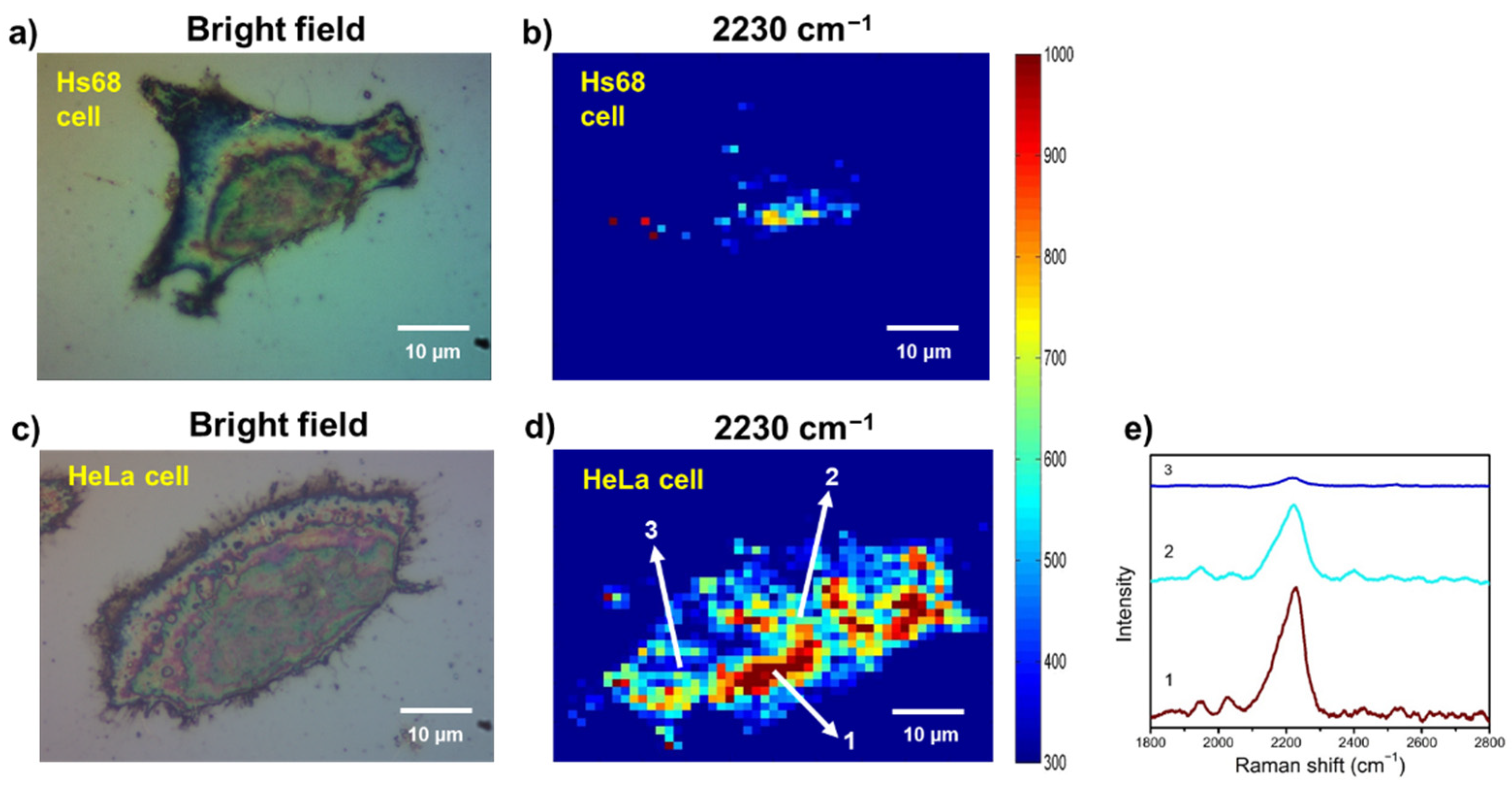
3.5. Examining SA Expression on Normal (Non-Cancerous) and Cancer Cells
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Varki, A. Sialic acids in human health and disease. Trends Mol. Med. 2008, 14, 351–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, F.; Tiralongo, E.; Tiralongo, J. Sialic acid-specific lectins: Occurrence, specificity and function. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2006, 63, 1331–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angata, T.; Varki, A. Chemical diversity in the sialic acids and related α-keto acids: an evolutionary perspective. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 439–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, G.; Guan, F. Biological functions and analytical strategies of sialic acids in tumor. Cells 2020, 9, 273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearce, O.M.T.; Läubli, H. Sialic acids in cancer biology and immunity. Glycobiology 2015, 26, 111–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghosh, S. Sialic acids: Biomarkers in endocrinal cancers. Glycoconj. J. 2015, 32, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dědová, T.; Braicu, E.I.; Sehouli, J.; Blanchard, V. Sialic acid linkage analysis refines the diagnosis of ovarian cancer. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, L.A.; Qian, X.; Nie, S. SERS nanoparticles in medicine: From label-free detection to spectroscopic tagging. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 10489–10529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiles, P.L.; Dieringer, J.A.; Shah, N.C.; Duyne, R.P.V. Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2008, 1, 601–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Ru, E.C.; Blackie, E.; Meyer, M.; Etchegoin, P.G. Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: a comprehensive study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 13794–13803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Tian, X.; Hong, S.; Dai, P.; You, Q.; Wang, R.; Feng, L.; Xie, C.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Chen, X. A bioorthogonal Raman reporter strategy for SERS detection of glycans on live cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 7266–7271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, H.; Liu, H.; Li, M.; Li, J.; Liu, D. High-precision profiling of sialic acid expression in cancer cells and tissues using background-free surface-enhanced Raman scattering tags. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 5874–5881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, X.-N.; Wang, Y.-N.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.-R. Accurate quantitative detection of cell surface sialic acids with a background-free SERS probe. Talanta 2020, 209, 120579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, L.; Qu, H.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Deng, R.; Shen, Y.; Xu, S.; Liang, C.; Xu, W. Tracing sialoglycans on cell membrane via surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy with a phenylboronic acid-based nanosensor in molecular recognition. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 148–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, R.; Yue, J.; Qu, H.; Liang, L.; Sun, D.; Zhang, J.; Liang, C.; Xu, W.; Xu, S. Glucose-bridged silver nanoparticle assemblies for highly sensitive molecular recognition of sialic acid on cancer cells via surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy. Talanta 2018, 179, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, T.; Cui, Y.; Goh, D.; Voon, K.K.; Shum, P.P.; Humbert, G.; Auguste, J.-L.; Dinh, X.-Q.; Yong, K.-T.; Olivo, M. Highly sensitive SERS detection and quantification of sialic acid on single cell using photonic-crystal fiber with gold nanoparticles. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 227–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schütz, M.; Müller, C.I.; Salehi, M.; Lambert, C.; Schlücker, S. Design and synthesis of Raman reporter molecules for tissue imaging by immuno-SERS microscopy. J. Biophotonics 2011, 4, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlücker, S. SERS microscopy: Nanoparticle probes and biomedical applications. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2009, 10, 1344–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, G.; Ng, S.P.; Wu, C.-M.L. Bimetallic Au-Ag alloy nanoislands for highly sensitive localized surface plasmon resonance biosensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 265, 459–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanoff, D.D., Jr.; Chumanov, G. Synthesis and optical properties of silver nanoparticles and arrays. Chem. Phys. Chem. 2005, 6, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evanoff, D.D.; Chumanov, G. Size-controlled synthesis of nanoparticles. 2. Measurement of extinction, scattering, and absorption cross sections. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 13957–13962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rycenga, M.; Kim, M.H.; Camargo, P.H.C.; Cobley, C.; Li, Z.-Y.; Xia, Y. Surface-enhanced Raman scattering: Comparison of three different molecules on single-crystal nanocubes and nanospheres of silver. J. Phys. Chem. A 2009, 113, 3932–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kha, N.M.; Chen, C.-H.; Su, W.-N.; Rick, J.; Hwang, B.-J. Improved Raman and photoluminescence sensitivity achieved using bifunctional Ag@SiO2 nanocubes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2015, 17, 21226–21235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Li, W.; Wen, L.-P.; Chen, J.; Xia, Y. Facile synthesis of Ag nanocubes of 30 to 70 nm in edge length with CF3COOAg as a precursor. Chem. Eur. J. 2010, 16, 10234–10239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Stephenson-Brown, A.J.; Khan, T.; Miyazawa, T.; Cabral, H.; Kataoka, K.; Miyahara, Y. Heterocyclic boronic acids display sialic acid selective binding in a hypoxic tumor relevant acidic environment. Chem. Sci. 2017, 8, 6165–6170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Springsteen, G.; Wang, B. A detailed examination of boronic acid–diol complexation. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 5291–5300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djanashvili, K.; Koning, G.A.; van der Meer, A.J.G.M.; Wolterbeek, H.T.; Peters, J.A. Phenylboronate 160Tb complexes for molecular recognition of glycoproteins expressed on tumor cells. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2007, 2, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, J.A. Interactions between boric acid derivatives and saccharides in aqueous media: Structures and stabilities of resulting esters. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 268, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldys, E.M.; Drozdowicz-Tomsia, K. Gold and silver nanowires for fluorescence enhancement. In Nanowires—Fundamental Research; Hashim, A.A., Ed.; IntechOpen Limited: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Madeira, A.; Plissonneau, M.; Servant, L.; Goldthorpe, I.A.; Tréguer-Delapierre, M. Increasing silver nanowire network stability through small molecule passivation. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loza, K.; Diendorf, J.; Sengstock, C.; Ruiz-Gonzalez, L.; Gonzalez-Calbet, J.M.; Vallet-Regi, M.; Köller, M.; Epple, M. The dissolution and biological effects of silver nanoparticles in biological media. J. Mater. Chem. B 2014, 2, 1634–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pearson, D.A.; Blanchette, M.; Baker, M.L.; Guindon, C.A. Trialkylsilanes as scavengers for the trifluoroacetic acid deblocking of protecting groups in peptide synthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1989, 30, 2739–2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wehner, J.W.; Lindhorst, T.K. Glycocluster synthesis by native chemical ligation. Synthesis 2010, 2010, 3070–3082. [Google Scholar]
- Song, W.; Ding, L.; Chen, Y.; Ju, H. Plasmonic coupling of dual gold nanoprobes for SERS imaging of sialic acids on living cells. Chem. Comm. 2016, 52, 10640–10643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.-E.; Yan, J.; Jiang, J.; Liu, X.; Tian, C.; Xu, J.; Yuan, M.-S.; Han, X.; Wang, J. Polydiacetylene liposomes with phenylboronic acid tags: A fluorescence turn-on sensor for sialic acid detection and cell-surface glycan imaging. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 4570–4578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Renata, S.; Verma, N.; Tu, Z.; Pan, R.-L.; Hofmann, M.; Lin, C.-H. Development of a Tri-Functional Nanoprobe for Background-Free SERS Detection of Sialic Acid on the Cell Surface. Chemosensors 2021, 9, 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050092
Renata S, Verma N, Tu Z, Pan R-L, Hofmann M, Lin C-H. Development of a Tri-Functional Nanoprobe for Background-Free SERS Detection of Sialic Acid on the Cell Surface. Chemosensors. 2021; 9(5):92. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050092
Chicago/Turabian StyleRenata, Septila, Nitish Verma, Zhijay Tu, Rong-Long Pan, Mario Hofmann, and Chun-Hung Lin. 2021. "Development of a Tri-Functional Nanoprobe for Background-Free SERS Detection of Sialic Acid on the Cell Surface" Chemosensors 9, no. 5: 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050092
APA StyleRenata, S., Verma, N., Tu, Z., Pan, R.-L., Hofmann, M., & Lin, C.-H. (2021). Development of a Tri-Functional Nanoprobe for Background-Free SERS Detection of Sialic Acid on the Cell Surface. Chemosensors, 9(5), 92. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors9050092