Abstract
Food manufacturers are aiming to manage the levels of cross-contamination of allergens within food processing plants and ultimately move away from precautionary labelling. Hence, the need for rapid methods to detect allergens cross-contamination. A sensitive and selective label-free nanoMIPs based sensor was developed and tested for the detection of β-lactoglobulin (BLG). NanoMIPs were synthesized using solid-phase synthesis and appeared as spherical nanoparticles with sizes ranging from 264–294 nm, using dynamic light scattering (DLS). The nanoMIPs were functionalized with amine groups and attached to the surface of the SPR gold chip via amine-coupling protocol. The SPR nanoMIPs-based sensor demonstrated a detection limit of 3 ng mL−1 (211 pM) over a linear range of 1–5000 ng mL−1, with binding affinity of 7.0 × 10−8 M and specificity towards BLG. With further testing and final optimization, the developed nanosensor can be integrated on-line or at-line cleaning-in-place (CIP) wash systems, allowing to effectively monitor milk protein allergens as a rapid, point-of-source methodology.
1. Introduction
The prevalence of individuals with food allergies has been increasing worldwide over the last few decades, affecting sufferers’ quality of life [1,2]. The accidental ingestion of allergens by the population of allergen sufferers can result in adverse allergic reactions even resulting in possible death. As there are currently no effective treatments for controlling food allergies, these sufferers must make informed decisions about what food they can eat based on precautionary labelling [3,4]. Furthermore, challenges caused by the variation in dose response across the population of allergen sufferer’s, can mean that even trace amounts of allergen present in food can lead to an adverse reaction. This has led to difficulties in defining regulatory limits on allergens [5].
This increased prevalence of allergy sufferers has prompted food manufacturers to develop more effective and rapid analytical tools to detect cross-contamination of food allergens in food products and processing equipment to allow for the effective control of allergen containing food ingredients and products [6,7]. Moreover, food manufacturers should minimise cross-contamination by: (1) ensuring the proper correct labelling and storage of allergen containing ingredients; (2) perform and monitor cleaning validation procedures of food processing equipment used for the production of allergens free food; (3) collecting samples to validate the allergen management plan [8]. This is important as the same manufacturing equipment may be used for the batch production of food items containing both allergen containing ingredients and ingredients free from allergens after performing cleaning procedures. The implementation of swab testing of equipment for the validation of cleaning is currently used to confirm the absence of allergenic ingredients. However, tests are performed infrequently and samples are often sent off-site to dedicated quality control testing labs. The measurement of allergens via the on-line or at-line cleaning in place (CIP) wash systems has been explored to further streamline the cleaning validation [9,10]. Off line testing using analytical methods such as enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and lateral flow assay devices (LFA) [11], have become more commonly used for point-of-source screening of milk protein allergens with a number of commercial kits available on the market. However, both ELISA and LFA suffer from high interlab variability and have limited shelf-lives due to the use of polyclonal antibodies [12,13]. Liquid chromatography techniques such as liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS) [14,15] and capillary electrophoresis-mass spectrometry (CE-MS) [16] have also been used as confirmation techniques to analyse protein allergens in dairy products and cleaning validation due to their superior accuracy, selectivity and robustness. Despite these advantages, liquid chromatography techniques often require expensive instrumentation and trained lab technicians to perform the assay, making analysis by these techniques costly. In addition, there are still challenges in terms of adapting methods from benchtop to lab-on-chip format for point-of-source detection [17].
Biosensors have shown great potential as alternative analytical devices to more traditional analytical techniques in the analysis of food allergens. This is due in part to their low cost of fabrication, comparable sensitivity, selectivity as well as their robustness [18,19]. In addition, they can be used at the point-of-source allowing for the rapid analysis of samples in so called lab-on-chip formats. In terms of milk protein allergens, a number of different transducers have been demonstrated for the detection of β-lactoglobulin (BLG), a major allergenic constituent of milk and dairy products. These include electrochemical [20,21], optical [22,23,24] and quartz crystal microbalance (QCM) [25,26]. Surface plasmon resonance (SPR) [27] and localised surface plasmon resonance (LSPR) [28], imaging surface plasmon resonance (iSPR)-based biosensors have also shown great potential as biosensing platforms in the detection of BLG due to their label-free, on-line detection as well as their high signal-to-noise ratio, allowing for sensitive detection [29]. Recently, our research group has developed an SPR based immunosensor for the detection of BLG which can detect BLG down to 2 μg mL−1 [30].
Lately, focus has moved to utilising biomimics as receptors for biosensing such as aptamers [31] and molecularly imprinted polymers [32]. These synthetic receptors with bio-recognition sites have demonstrated excellent thermal stability, good binding kinetics and have the potential to lower costs and increase the shelf-life of commercial kits, while being selective as antibodies [33,34,35].
In our previous work, we have developed a nanoMIP-based SPR sensor for the detection of α-casein in cleaning in place system (CIP) waste water [10] to replace the use of antibodies and increase the stability of the sensor. Since the casein-based sensor cannot detect whey proteins allergens (like BLG), a new sensor needed to be developed to overcome this drawback. In this work, we set out to develop a new SPR nanosensor, utilising nanoMIPs as the receptor for the detection of BLG to widen the range of allergens that can be detected using the sensor. NanoMIPs against BLG were therefore synthesized using solid-phase synthesis and functionalised with primary amines on the outside of the nanoMIP. The nanoMIPs were characterized and immobilized onto an SPR sensor chip and demonstrated excellent sensitivity and selectivity for the detection of BLG. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported nanoMIP based SPR sensor for the detection of BLG.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Equipment
Sulfuric acid (H2SO4), sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), acetone, methanol, 3-aminopropyltrimethoxysilane (APTMS), toluene anhydrous, 2,4,6, trinitrobenzene sulfonic acid, glutaraldehyde, 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid (MUDA), ethanolamine hydrochloride, N-isopropylacrylamide (NIPAm), N,N′-methylenebisacrylamide (BIS), phosphate buffered saline (PBS, 0.01M), N-tert-butylacrylamide (TBAm), ethanol, acrylic acid (AAc), N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-ethylenediamine (TEMED), lactoferrin, α-casein, κ-casein and β-lactoglobulin (BLG), and vancomycin were purchased from Sigma Aldrich (Dorset, UK). Ammonium persulphate (APS), 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl) carbodiimide (EDC), N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS), N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylamide hydrochloride (APM), bicinchoninic acid solution, copper (II) sulfate solution 4% (w/v) were sourced from Fisher Scientific (Loughborough, UK). All protein standards were standardized by measuring the absorbance at 280 nm, using DU 7000 spectrophotometers (Beckman Coulter, Brea, CA, US). Glass beads (75 μm glass beads acid washed, Supelco (Dorset, UK) used as the solid phase for the synthesis of nanoMIPs were purchased Sigma Aldrich. Milli-Q® water (18.5 MΩ cm) was sourced using a Barnstead™ Smart2Pure™ Water Purification System (Fisher Scientific).
All buffers and solutions were filtered through 0.2 µm or 0.45 µm (nanoMIP solution) filter paper (Whatman® qualitative filter paper, Sigma Aldrich, Dorset, UK) or 0.2 µm or 0.45 µm syringe filter (Minisart® plus syringe filters, Sartorius Stedim UK Ltd., Epsom, UK). Furthermore, samples and proteins dilutions were prepared and stored into low binding Eppendorf tubes (Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany). The yield was assessed using Eppendorf Concentrator 5301 (Eppendorf AG, Hamburg, Germany).
Characterization of the nanoMIPs was performed using dynamic light scattering (DLS, S-nanosizer, Malvern Ltd., Malvern, UK) and transmission electron microscope (TEM, CM20, Philips, Amsterdam, The Netherlands). All SPR experiments were performed on a SPR-4 instrument (Sierra Sensors, Hamburg, Germany) using SIA sensor chips.
2.2. Preparation of BLG Immobilized Glass Beads
The nanoMIPs were synthesized manually using cleaned and lab grade glassware. BLG was immobilised onto the silanised glass beads prior to the nanoMIP synthesis. Briefly, glass beads (70 g) were cleaned with piranha solution (3:1 H2SO4 and H2O2). The glass beads were then neutralized by washing with Milli-Q water and activated by boiling in NaOH (1 M) for 5 min and washed thoroughly with Milli-Q water pre-heated at 60 °C. The beads were then washed with acetone and dried in the oven at 80 °C for 2.5 h. The glass beads were then silanised with 2% v/v APTMS in anhydrous toluene (50 mL) overnight at room temperature, under a gentle stirring (10 RPM). Finally, silanised glass beads were washed thoroughly with acetone and reconditioned by washing with Milli-Q water. The presence of the amine groups was determined by a colorimetric assay using 2,4,6, trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid in PBS (5% v/v, pH 7.4). The resultant amine functionalised glass beads were incubated with a 50 mL solution of glutaraldehyde in PBS of (5% v/v, pH 7.4) for 2 h. Subsequently, the glass beads were rinsed with milli-Q water and allowed to dry under vacuum, using a large funnel, Erlenmeyer flask and a vacuum pump. The subsequent glass beads were then incubated overnight at 4 °C with the template solution, prepared by dissolving BLG (3 mg mL−1) in PBS (50 mL) and adjusting the pH to 7.4. The beads were then rinsed with double distilled deionized water and dried well under vacuum. The remaining unreacted aldehydes groups were blocked with 50 mL ethanolamine (0.01 M, pH 7.4).
2.3. The Solid-Phase Synthesis of NanoMIPs
A solution containing the monomers was prepared by weighing out NIPAm (39 mg; 3.45 × 10−4 mol), BIS (2 mg; 1.3 × 10−5 mol) dissolved in 90 mL PBS (10 mM, pH 7.4). TBAm (33 mg; 2.59 × 10−4 mol) was dissolved in ethanol (1 mL) and carefully added to the monomer solution. 22 µL (2.60 × 10−5 mol) of acrylic acid was diluted in 1 mL of water and 100 µL were added to the monomer solution. The monomer solution was then made up to 100 mL with PBS (pH 7.4). The resultant solution was degassed under vacuum, sonication for 10 min followed by purging with nitrogen for 30 min. A solution containing 60 mg of APS dissolved in 1 mL of Milli-Q water was prepared. The templated glass beads were transferred to a column and the monomer solution was added. The polymerization was initiated by adding the solution containing APS (800 µL) and TEMED (24 µL) to the column. The polymerisation was carried out at room temperature. After 2 h, the monomer solution was discarded from the glass beads and 54 mg of APM (3.20 × 10−4 mol) pre-dissolved in PBS (40 mL, pH 7.4) was quickly added and left for a further 20 min, thus introducing primary amino group onto the external surface of the pre-formed nanoMIP. The APM solution was then discarded.
Low affinity NanoMIPs and unreacted monomers were discarded by washing the beads four times using 40 mL aliquots of Milli-Q water, previously cooled down to 15 °C, for 10 min. The high affinity NanoMIPs were collected in three consecutive cycles of incubation and elution. Briefly, the beads were incubated for 15 min with 60 °C Milli-Q water (30 mL) in an incubator, pre-heated at 60 °C. The NanoMIPs-containing eluate was then collected in a glass bottle and stored at 4 °C. Control MIPs were prepared in the same manner as described for the NanoMIPs using vancomycin as a template instead of BLG.
2.4. NanoMIPs Characterization
The nanoMIP yield was obtained using an Eppendorf Concentrator 530. The NanoMIP solution (10 mL) was filtered using 0.45 µm paper filter and placed in a 15 mL falcon tube, which was previously accurately weighed by an analytical balance (Mettler Toledo, Greifensee, Switzerland). The falcon tube was placed in the Eppendorf Concentrator set at 60 °C and the solvent was allowed to evaporate. The falcon tube was then allowed to equilibrate to room temperature and weighed to obtain a yield from the weight difference.
For DLS measurements, nanoMIPs were filtered through a 0.45 µm syringe filter prior to analysis. The DLS was used to determine hydrodynamic diameter (dH). Briefly, each collected elution were analysed in 3 cm3 disposable polystyrene cuvettes by using Zetasizer Nano (Nano-S, Malvern Ltd.) at 25 °C. Furthermore, the thermo-responsive behaviour of the nanoMIP was assessed by setting the temperature of the analysis and of the sample to 4 °C and 37 °C. The samples were allowed to equilibrate at the set temperature prior to start the analysis. For TEM analysis, 10 µL of NanoMIP solution was deposited on a TEM holder and allowed to dry. The collected TEM images were processed by ImageJ (National Institutes of Health, US) to derive the nanoMIP morphology.
2.5. Development of the SPR Sensor Surface
The gold surface of a bare SIA chip was firstly cleaned by immersion in piranha solution (H2SO4/H2O2, 3:1 v/v) for 5 min. The piranha solution was then carefully discarded and the gold surface was washed to neutrality with water. The surface was rinsed with ethanol three times and then dried with nitrogen. A self-assembled monolayer (SAM) was then formed on the sensor surface. This was accomplished by first drying the surface under a gentle stream of N2 and then submerging the sensor in 50 mL of ethanol solution containing 11-mercaptoundecanoic acid 95% (MUDA) (10 mM, w/v) and incubating under dark conditions for 24 h. The chips were then removed from the solution and washed with ethanol, dried under nitrogen and immediately docked into the SPR instrument. When not immediately used, chips were stored at 4 °C until use and for no longer than seven days.
2.6. Development of the BLG nanoMIP Based Sensor
The nanoMIPs (BLG and vancomycin) solutions were filtered using a 0.45 µm syringe filter, whereas all the other solutions were degassed and filtered using a 0.2 µm filter paper under vacuum conditions. All SPR experiments were carried out with PBS (pH 7.4, 10 mM) as the running buffer, whilst the flow rate and the temperature were kept constant at 25 µL min−1 and 25 °C, respectively. The sensor surface was primed with PBS until a stable SPR signal was achieved. The sensor surface was then stabilized by injecting NaCl (25 µL, 1 M) followed by NaOH (25 µL, 10 mM) for 1 min (flow rate 25 µL min−1). The carboxylated surface was activated by injecting 100 µL of a mixture of EDC and NHS (0.2 M and 0.05 M, respectively) for 1 min (flow rate 25 µL min−1). The amino functionalized BLG-nanoMIPs (100 µL, 1.5 mg mL−1) solution was then injected on spot 1 for four minutes (flow rate 25 µL min−1). Amino functionalized vancomycin nanoMIPs (100 µL, 1.5 mg mL−1) solution was then injected on spot 2 for four minutes (flow rate 25 µL min−1) and used as a sensor control spot. Both sensor spots were then blocked using ethanolamine (1M, pH 8.5, 50 µL). A schematic of the SPR sensor is shown in Scheme 1.
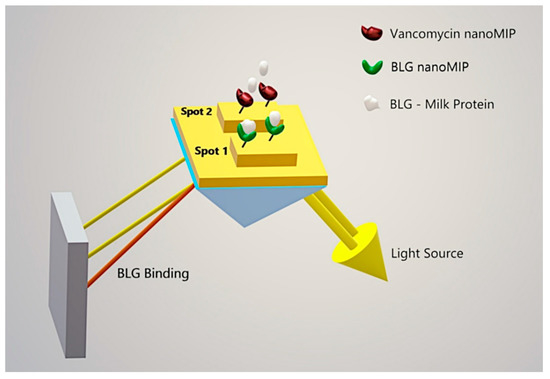
Scheme 1.
A schematic of the MIP assay on the SPR sensor. BLG nanoMIPs and Vancomycin nanoMIPs were covalently attached via amine coupling onto the SPR active (1) and control (2) spots, respectively.
2.7. Development of the BLG nanoMIP Cumulative Assay
Calibration curves were constructed by sequentially injecting increasing concentrations of BLG (1–5000 ng mL−1) standard (50 µL) in PBS buffer (pH 7.4) on the active (spot 1) and control (spot 2) sensor surface and measuring the response. The absolute response was then normalized by subtracting the reference and control channel responses from the active nanoMIP to give the relative response. A non-linear calibration plot was obtained by plotting the double subtracted sensor response (relative RU values) against the BLG concentrations. A linear calibration plot was obtained by measuring the response of the sensor and plotting against the BLG concentration, expressed as a LOG. The low limit of detection (LOD) was determined by measuring 3× the SD of the blank SPR signal.
2.8. Selectivity Studies of the BLG nanoMIP Sensor
The selectivity of the BLG nanoMIP sensor was also determined by measuring the binding affinity (KD) of BLG, α-casein, k-casein and lactoferrin toward the BLG nanoMIP sensor respectively. This was conducted by injecting a 100 µL of each protein (1–5000 ng mL−1) in PBS buffer over the two sensor spots and measuring the response. The binding affinity was then determined for each protein by fitting the results using the 1:1 Langmuir binding model and calculating the KD value from both the kon and koff rates.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. NanoMIPs Solid-phase Synthesis
NanoMIPs were successfully synthesized using a solid phase synthesis method, which was adapted from a protocol developed by Canfarotta et al. [36]. The glass beads were silanised and functionalised with the primary amine group. Glutaraldehyde was used as a cross-linker, which allowed the subsequent attachment of the BLG template using the Schiff-base route. To this aim, a BLG solution (3 mg mL−1) was incubated with the glass beads overnight in the fridge. The unreacted groups were capped by the addition of ethanolamine (1 M) in PBS, adjusted at pH 7.4 to prevent BLG conformation changes. Indeed, a BLG conformational transition occurs at a pH ranging from 8 to 10 due to the neutralization of a lysine residue [37].
The monomer solution composition was adopted from previous studies using protein as template and the protocol [10,38] was optimized for BLG nanoMIPs production. The solid-phase precipitation polymerization, methodology allows for the facile separation of the formed nanoMIP from the template, which is often considered the bottle neck in MIP synthesis protocols. Furthermore, the methodology is affinity selective and can allow for further functionalisation of the pre-formed nanoMIP. The surface of the nanoMIPs were functionalised with amino group self -assembly monolayer, which is required for the direct immobilisation of the nanoMIP onto the SPR sensor surface. The cold wash (15 °C) allowed the removal of unreacted monomers and low affinity nanoMIPs. Then, the highly specific BLG nanoMIP were collected during the elution performed at 60 °C. This temperature triggered the nanoMIP desorption from the template and, therefore, using a temperature above this value may be explored as a regeneration strategy for specific application, e.g., where high temperature will not affect the sensor performance and surface chemistry.
3.2. NanoMIP Characterization
The BLG nanoMIPs solution was filtered using a 0.45 µm syringe filter since: 1) the estimate size of the nanoMIPs previously synthesized via a similar protocol and towards a protein template has been reported to be between 100 and 300 nm and, 2) a size below 450 nm was considered suitable to prevent the blocking of the microfluidic system of the automated SPR machine used in this work. The filtered solution was then analysed via DLS and TEM to assess the average hydrodynamic diameter (dH) and the morphological size and structure, respectively.
The DLS results (Figure 1A,B) show that the hydrodynamic diameter of batches 1, 2 and 3 of nanoMIPs was 287, 265 and 294 nm, respectively, while the PDI (polydispersity index) values were 0.30, 0.20, and 0.14, respectively. The one-way ANOVA (F (2, 7) = 11.13; p = 0.007) revealed that there was a batch to batch variation. The Sheffe’s post hoc test revealed that the dH of batch 2 was significantly smaller than the dH of batches 1 and 3 and was due to the manual synthesis process.
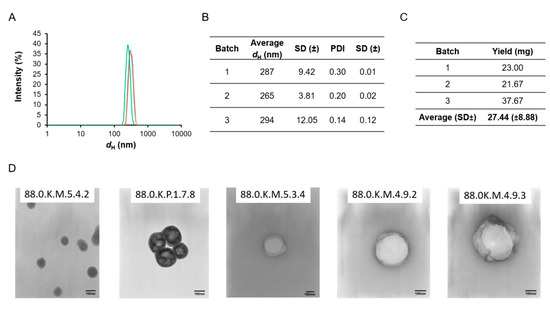
Figure 1.
(A) Typical intensity (%) results of nanoMIPs and (B) Average (SD±) of dH (nm) and PDI (SD±) of each nanoMIP batches obtained during DLS analysis. (C) Results of yield (expressed in mg) obtained across the three batches. (D) Typical BLG nanoMIP morphology obtained by TEM analysis (650,000–880,000×) (The size bars are equal to 100 nm).
The TEM image (Figure 1D) for the nanoMIPs showed a slightly smaller nanoMIP diameter, which was due to shrinkage of the polymer upon drying. These results suggest that the nanoMIPs synthesized were well dispersed and had an acceptable size making them ideal for the attachment to the SPR gold sensor surface. The filtered solution was then used to assess the yield. The average yield across the three produced batches was found to be 36.11% (±11.68) and these are detailed in Figure 1C. The yield was found to be consistent with previously reported nanoMIP synthesized towards other proteins template and high enough for future application in real case scenarios. As the thermo-responsive monomer NIPam was included in the nanoMIP formulation, the DLS was used to investigate the thermal behaviour of the nanoMIPs. The analysis was run at refrigeration temperature (4 °C), room temperature (25 °C) and a higher temperature (37 °C). The results (Figure 2) showed that the average nanoMIPs dH increased when the analysis temperature was set at 4 °C and decrease when the temperature was risen to 37 °C. These findings provide insight of the thermo-responsive behaviour of the nanoMIP and are consistent with previous study [37]. The thermo-responsive behaviour can be further investigated and optimised for sensor regeneration purpose (“catch and release”) or to add smart feature to the sensor surface.
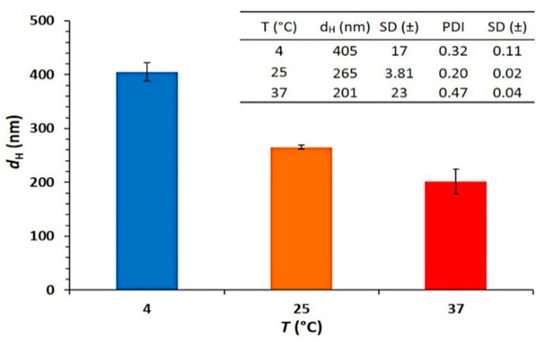
Figure 2.
Average (SD±) dH (nm) of nanoMIPs batch 2 obtained by DLS analysis carried out at different temperatures (4 °C, 25 °C, 37 °C). The inset table reports the average dH (SD±) and the PDI (SD±) obtained at each temperature (n = 10).
3.3. Development of the BLG nanoMIP Sensor
The BLG nanoMIPs were then used to fabricate the SPR sensor. The MUDA coated gold SPR sensor was firstly activated with EDC-NHS thus allowing the covalent immobilization of the amino functionalized BLG nanoMIPs. The concentration of the nanoMIPs solution was optimized at 1.5 mg mL−1. Vancomycin nanoMIPs were attached on the control sensor spot using the same procedure and these showed a similar degree of attachment to the sensor surface as shown for the BLG nanoMIPs, which was consistent to our previous study [10].
The real-time binding analysis shown by the SPR sensorgram (Figure 3) confirmed the attachment of the nanoMIPs to the surface of the sensor chip due to the large change in response observed after the start of the MIP solution injection, which then levelled off after the end of the injection period (1320 ± 221 RU).
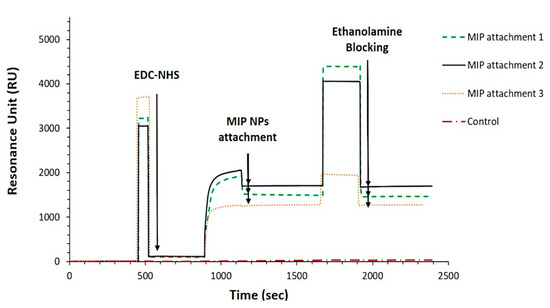
Figure 3.
On-line sensorgrams showing the attachment of the nanoMIPs onto the sensor chip (triplicates). The average of the RU value achieved over three replicates was 1320 (±221).
Furthermore, the BLG nanoMIPs attachment was found to be reproducible and can be considered mainly covalent to the sensor surface as suggested from the stable sensorgram signal over the time. The sensor chip was blocked using ethanolamine (1 M, pH 8.5). The ethanolamine can act as a blocking agent of unreacted activated ester groups on the sensor surface, thus preventing false sensor response due to non-specific binding of unwanted chemical species towards the sensor surface.
To test the performance of the fabricated nanoMIPs sensor, a cumulative concentration assay was performed by injecting increasing concentrations of BLG (1–5000 ng mL−1) dissolved in PBS (pH 7.4). The BLG demonstrated the higher binding affinity towards the BLG nanoMIPs compared to the vancomycin control nanoMIPs as demonstrated in Figure 4.
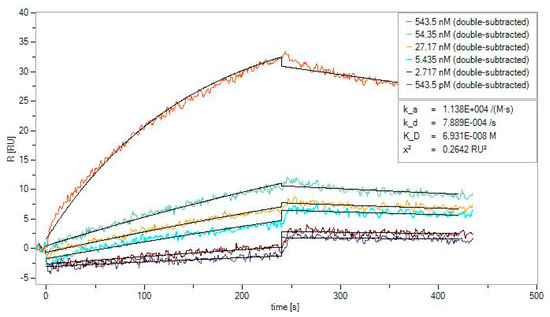
Figure 4.
The affinity binding assay for BLG nanoMIPs. Signals were subtracted from the blank and the control signals (double-subtracted). Black lines represent the fitting of the Langmuir model (1:1 binding) obtained using the SPR Sensor Analyser software. The kinetic fitting parameters are reported under the bottom left inset.
The sensor response towards the BLG injections were subtracted from the response of the control spot and the blank injections. The non-linear and semi-LOG linear calibration plots are shown in Figure 5. The non-linear calibration plot showed an exponential increase in sensor response at different concentrations of BLG reaching a point of saturation at about 30 RU. A good linear correlation was observed (R2 = 0.99) demonstrating an excellent sensitivity in optimal conditions (LOD of 3.10 ng mL−1, 211 pM). The selectivity of the sensor was evaluated by comparing the BLG nanoMIPs binding affinities against BLG and other common milk proteins.
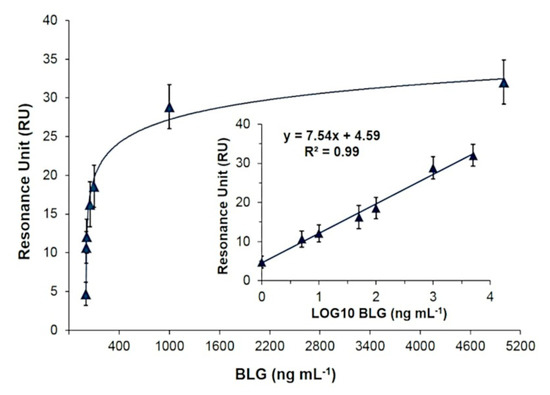
Figure 5.
The non-linear and linear calibration plots (inset plot) for the BLG cumulative assay. Relative responses were normalised by subtracting the control response. The error bars refer to the SD (±) of three replicates. The achieved LOD was as low as 3.10 ng mL−1.
The results listed (Table 1), show that the BLG nanoMIP demonstrated a binding affinity which was at least four orders of magnitude higher than observed for α-casein, k-casein and lactoferrin confirming that the developed nanoMIP based SPR nanosensor can discriminate BLG from other whey proteins (lactoferrin) and casein milk fractions (α-casein, k-casein).

Table 1.
Selectivity of the developed BLG nanoMIPs sensor based on the binding affinities for BLG, LF, α-casein, k-casein.
According to the food labelling regulations in force in several countries, food business operators (FBOs) have to indicate in the food label when an allergen (such as milk or milk by-products) is voluntarily used as a food ingredient. However, an allergen may be present in a food as a result of a cross-contamination. On this instance, FBOs have the option to use a precautionary allergen labelling (PAL) on food packaging to alert the consumer, often expressed with “may contain” statements [39]. However, threshold values concerning allergen residues are not regulated as this varies on case by case basis. Hence, FBOs are recommended to perform a quantitative risk assessment to assess if and the amount of food allergens that may occur in each produced food and if a PAL statement needs to be included in the labelling. This is crucial for FBOs producing dairy-free food, who have to take control over accidental cross-contaminations, as well for food control authorities, who need to refer to allergen residues threshold values to protect the health of food allergy suffers [40].
The quantitative risk assessment should take into consideration: (1) the amount of possible milk proteins occurring in the food; (2) intake or the serving size (i.e., the amount of food eaten in a typical eating occasion), and (3) the reference dose expressed as the allergic reaction eliciting dose (Edp = dose calculated to elicit an allergic reaction in p% of allergic individuals) [41]. Australian food industry’s allergen bureau provide FBOs with a scientific based action level (expressed in ppm) for applying PAL. Concerning milk allergens, the latest Voluntary Incidental Trace Allergen Labelling (VITAL®) guideline suggests a reference does equal to 0.2 mg (previously fixed at 0.1 mg) [42]. By applying the following formula, it is possible to assess whether a precautionary statement should be used or not:
The required action level for cow’s milk allergens span from 0.4 to 40 ppm, according to the serving size. VITAL provides a reference dose of 0.02 mg BLG in a 500 g portion size. Therefore, a PAL statements should be included in the food label when BLG occurs at a level above 0.04 ppm in the final food [43]. Consequently, there is the need for a fast and accurate analytical tool able to detect trace level of BLG occurring on surfaces where foods are produced and in food itself. The LOD (=3.10 ppb) achieved in this work is below the VITAL BLG action level and competitive towards other analytical methods as reported in the literature (Table 2). Compared to sandwich ELISA and mass spectrometry methods, the nanoMIPs BLG sensor is based on a direct assay format, is faster and easier to execute. Furthermore, upon further testing, optimisation and technical developments, it would be a valid candidate for on-line integration in dairy food industry equipment, allowing for a continuous monitoring of cleaning procedures and unwanted cross-contamination application. Compared to other biosensor platforms, the nanoMIP sensor is more environmentally stable as it is not affected by enzymatic activity or by temperature changes.

Table 2.
List of recent developed analytical methods for BLG detection, including LOD and linear range.
4. Conclusions
In this paper, a sensitive, yet selective, BLG nanoMIPs-based SPR-sensor for the detection of BLG, a marker for milk and whey protein was demonstrated. BLG nanoMIPs with minimal batch-to-batch variation were designed and successfully synthesized using solid phase synthesis. Furthermore, the nanoMIP were used to develop the SPR affinity sensor achieving an LOD of 3.10 ng mL−1 (3.10 ppb). This is well below the action level required for cow allergens and specifically, for BLG. Kinetic study results suggest that the sensor has the ability to selectively bind BLG, thus discriminating it from other whey proteins (lactoferrin) and casein milk fractions (α-casein, k-casein). The nanoMIP-based nanosensor demonstrated a selectivity of four orders of magnitude towards BLG. Compared to other technologies, the developed BLG nanoMIPs SPR sensor offers a valid, environmentally resistant, rapid, real-time analytical platform for allergen detection. To conclude, the developed nanoMIP-based sensor is a valid detection tool candidate for unintentional BLG cross-contamination events at the point of source and could be used in conjunction with other allergen mitigation strategies [48].
Author Contributions
R.D. performed all the experimental work, analysed the data and created the graphics. R.D. and J.A. wrote the draft of the paper; J.T. and M.P. supported the research and provided industrial input on legislations and experimental design; L.T. and T.L.R. provided collaborative input on the research; I.E.T. supervised and directed the research and finalized the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors would like to thank Innovate UK and the VILLUM FONDEN for partial funding of this work (Project no: 34312-241239) and (Project no: 00022912).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Abbreviations
| BLG | β-lactoglobulin |
| nanoMIP(s) | molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticle(s) |
| SPR | surface plasmon resonance |
| LOD | limit of detection |
| QCM | quartz crystal microbalance |
| ELISA | enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| SD | standard deviation |
| DLS | dynamic light scattering |
| TEM | transmission electron microscope |
| PDI | polydispersity index |
| KD | dissociation constant |
| FBOs | food business operators |
| PAL | precautionary allergen labelling |
| VITAL | voluntary incidental trace allergen labelling |
References
- Tang, M.L.K.; Mullins, R.J. Food allergy: Is prevalence increasing? Intern. Med. J. 2017, 47, 256–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sicherer, S.H.; Sampson, H.A. Food allergy: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gendel, S.M. Comparison of international food allergen labeling regulations. Regul. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2012, 63, 279–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muraro, A.; Hoffmann-Sommergruber, K.; Holzhauser, T.; Poulsen, L.K.; Gowland, M.H.; Akdis, C.A.; Mills, E.N.C.; Papadopoulos, N.; Roberts, G.; Schnadt, S.; et al. EAACI Food Allergy and Anaphylaxis Guidelines. Protecting consumers with food allergies: Understanding food consumption, meeting regulations and identifying unmet needs. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 69, 1164–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madsen, C.B.; Hattersley, S.; Allen, K.J.; Beyer, K.; Chan, C.-H.; Godefroy, S.B.; Hodgson, R.; Mills, E.N.C.; Muñoz-Furlong, A.; Schnadt, S.; et al. Can we define a tolerable level of risk in food allergy? Report from a EuroPrevall/UK Food Standards Agency workshop. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2012, 42, 30–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubert-Ullrich, P.; Rudolf, J.; Ansari, P.; Galler, B.; Führer, M.; Molinelli, A.; Baumgartner, S. Commercialized rapid immunoanalytical tests for determination of allergenic food proteins: An overview. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2009, 395, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivens, K.O.; Baumert, J.L.; Taylor, S.L. Commercial Milk Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA) Kit Reactivities to Purified Milk Proteins and Milk-Derived Ingredients. J. Food Sci. 2016, 81, T1871–T1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, L.S.; Al-Taher, F.M.; Moorman, M.; DeVries, J.W.; Tippett, R.; Swanson, K.M.J.; Fu, T.-J.; Salter, R.; Dunaif, G.; Estes, S.; et al. Cleaning and other control and validation strategies to prevent allergen cross-contact in food-processing operations. J. Food Prot. 2008, 71, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, O.; Weisz, N.; Vieths, S.; Weiser, T.; Rabe, B.; Vatterott, W. Protein quantification, sandwich ELISA, and real-time PCR used to monitor industrial cleaning procedures for contamination with peanut and celery allergens. J. AOAC Int. 2004, 87, 1448–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; Shukor, Y.; D’Aurelio, R.; Trinh, L.; Rodgers, T.L.; Temblay, J.; Pleasants, M.; Tothill, I.E. Synthesis of MIP Nanoparticles for α-Casein Detection using SPR as a Milk Allergen Sensor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 418–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.; Yang, Y.; Ni, X.; Peng, J.; Lai, W. Fluorescent microspheres lateral flow assay for sensitive detection of the milk allergen casein. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017, 28, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Courtney, R.C.; Taylor, S.L.; Baumert, J.L. Evaluation of Commercial Milk-Specific Lateral Flow Devices. J. Food Prot. 2016, 79, 1767–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, P.E.; Rigby, N.M.; Dainty, J.R.; Mackie, A.R.; Immer, U.U.; Rogers, A.; Titchener, P.; Shoji, M.; Ryan, A.; Mata, L.; et al. A multi-laboratory evaluation of a clinically-validated incurred quality control material for analysis of allergens in food. Food Chem. 2014, 148, 30–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groves, K.; Cryar, A.; Walker, M.; Quaglia, M. Assessment of Recovery of Milk Protein Allergens from Processed Food for Mass Spectrometry Quantification. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 152–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monaci, L.; Losito, I.; Palmisano, F.; Visconti, A. Identification of allergenic milk proteins markers in fined white wines by capillary liquid chromatography–electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2010, 1217, 4300–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasilova, N.; Gassner, A.-L.; Girault, H.H. Analysis of major milk whey proteins by immunoaffinity capillary electrophoresis coupled with MALDI-MS. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 2390–2398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desmet, G.; Eeltink, S. Fundamentals for LC miniaturization. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 543–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilolli, R.; Monaci, L.; Visconti, A. Advances in biosensor development based on integrating nanotechnology and applied to food-allergen management. TrAC—Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 47, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neethirajan, S.; Weng, X.; Tah, A.; Cordero, J.O.; Ragavan, K.V. Nano-biosensor platforms for detecting food allergens—New trends. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2018, 18, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eissa, S.; Tlili, C.; L’Hocine, L.; Zourob, M. Electrochemical immunosensor for the milk allergen β-lactoglobulin based on electrografting of organic film on graphene modified screen-printed carbon electrodes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 38, 308–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surucu, O.; Abaci, S. Electrochemical determination of β-lactoglobulin in whey proteins. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 14, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohensinner, V.; Maier, I.; Pittner, F. A “gold cluster-linked immunosorbent assay”: Optical near-field biosensor chip for the detection of allergenic ß-lactoglobulin in processed milk matrices. J. Biotechnol. 2007, 130, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wen, F.; Li, Z.; Zheng, N.; Jiang, J.; Xu, D. Simultaneous detection of α-Lactoalbumin, β-Lactoglobulin and Lactoferrin in milk by Visualized Microarray. BMC Biotechnol. 2017, 17, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zang, J.; Li, C.; Zhou, K.; Dong, H.; Chen, B.; Wang, F.; Zhao, G. Nanomolar Hg 2+ Detection Using β-Lactoglobulin-Stabilized Fluorescent Gold Nanoclusters in Beverage and Biological Media. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 10275–10283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, N.W.; Liu, X.; Piletsky, S.A.; Hlady, V.; Britt, D.W. Recognition of conformational changes in β-lactoglobulin by molecularly imprinted thin films. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ito, T.; Aoki, N.; Tsuchiya, A.; Kaneko, S.; Suzuki, K. Sequential Analysis of β-Lactoglobulin for Allergen Check Using QCM with a Passive Flow System. Chem. Lett. 2015, 44, 981–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Indyk, H.E.; Hart, S.; Meerkerk, T.; Gill, B.D.; Woollard, D.C. The β-lactoglobulin content of bovine milk: Development and application of a biosensor immunoassay. Int. Dairy J. 2017, 73, 68–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minh Hiep, H.; Endo, T.; Kerman, K.; Chikae, M.; Kim, D.K.; Yamamura, S.; Takamura, Y.; Tamiya, E. A localized surface plasmon resonance based immunosensor for the detection of casein in milk. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2007, 8, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebe Raz, S.; Liu, H.; Norde, W.; Bremer, M.G.E.G. Food allergens profiling with an imaging surface plasmon resonance-based biosensor. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 8485–8491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashley, J.; D’Aurelio, R.; Piekarska, M.; Temblay, J.; Pleasants, M.; Trinh, L.; Rodgers, T.L.; Tothill, I.E. Development of a β-Lactoglobulin sensor based on SPR for milk allergens detection. Biosensors 2018, 8, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amaya-González, S.; De-los-Santos-Alvarez, N.; Miranda-Ordieres, A.J.; Lobo-Castañón, M.J. Aptamer-based analysis: A promising alternative for food safety control. Sensors (Basel) 2013, 13, 16292–16311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Sun, X.; Su, X.; Wang, T. Advancements of molecularly imprinted polymers in the food safety field. Analyst 2016, 141, 3540–3553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, J.; Feng, X.; Halder, A.; Zhou, T.; Sun, Y. Dispersive solid-phase imprinting of proteins for the production of plastic antibodies. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 3355–3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashley, J.; Shukor, Y.; Tothill, I.E. The use of differential scanning fluorimetry in the rational design of plastic antibodies for protein targets. Analyst 2016, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berghaus, M.; Mohammadi, R.; Sellergren, B. Productive encounter: Molecularly imprinted nanoparticles prepared using magnetic templates. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 8993–8996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canfarotta, F.; Poma, A.; Guerreiro, A.; Piletsky, S. Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles. Nat. Protoc. 2016, 11, 443–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, K.; Lesel, B.K.; Yonamine, Y.; Beierle, J.M.; Hoshino, Y.; Shea, K.J. Temperature-responsive “catch and release” of proteins by using multifunctional polymer-based nanoparticles. Angew. Chemie Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 2405–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoshino, Y.; Kodama, T.; Okahata, Y.; Shea, K.J. Peptide Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles: A Plastic Antibody. October 2008, 130, 15242–15243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soon, J.M.; Manning, L. “May Contain” Allergen Statements: Facilitating or Frustrating Consumers? J. Consum. Policy 2017, 40, 447–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waiblinger, H.-U.; Schulze, G. Action Levels for Food Allergens: An Approach for Official Food Control in Germany. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crevel, R.W.R.; Baumert, J.L.; Baka, A.; Houben, G.F.; Knulst, A.C.; Kruizinga, A.G.; Luccioli, S.; Taylor, S.L.; Madsen, C.B. Development and evolution of risk assessment for food allergens. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 67, 262–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Limited, T.A.B. Food Industry Guide to the Voluntary Incidental Trace Allergen Labelling (VITAL®) Program Version 3.0; Allergen Bureau Ltd.: Auckland, New Zealand, 2019; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Holzhauser, T.; Johnson, P.; Hindley, J.P.; O’Connor, G.; Chan, C.-H.; Costa, J.; Fæste, C.K.; Hirst, B.J.; Lambertini, F.; Miani, M.; et al. Are current analytical methods suitable to verify VITAL® 2.0/3.0 Allergen Reference doses for EU Allergens in Foods? Food Chem. Toxicol. 2020, 145, 111709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, S.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Development of a H2O2-sensitive quantum dots-based fluorescent sandwich ELISA for sensitive detection of bovine β-lactoglobulin by monoclonal antibody. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Li, X.; Gao, J.; Tong, P.; Chen, H. Development of sandwich ELISA for testing bovine β-lactoglobulin allergenic residues by specific polyclonal antibody against human IgE binding epitopes. Food Chem. 2017, 227, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, J.; Zhu, P.; Pi, F.; Sun, C.; Sun, J.; Jia, M.; Ying, C.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, X. Development of a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous detection of the main milk allergens. Food Control. 2017, 74, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel, V.; Campuzano, S.; Conzuelo, F.; Torrente-Rodríguez, R.M.; Gamella, M.; Reviejo, A.J.; Pingarrón, J.M. Electrochemical magnetoimmunosensing platform for determination of the milk allergen β-lactoglobulin. Talanta 2015, 131, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, F.; Shi, A.; Ashley, J.; Kronfel, C.; Wang, Q.; Maleki, S.J.; Adhikari, B.; Zhang, J. Peanut Allergy: Characteristics and Approaches for Mitigation. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1361–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).