A Naphthalimide–Sulfonylhydrazine Conjugate as a Fluorescent Chemodosimeter for Hypochlorite
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Biological Experiments
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Chemodosimeter Synthesis
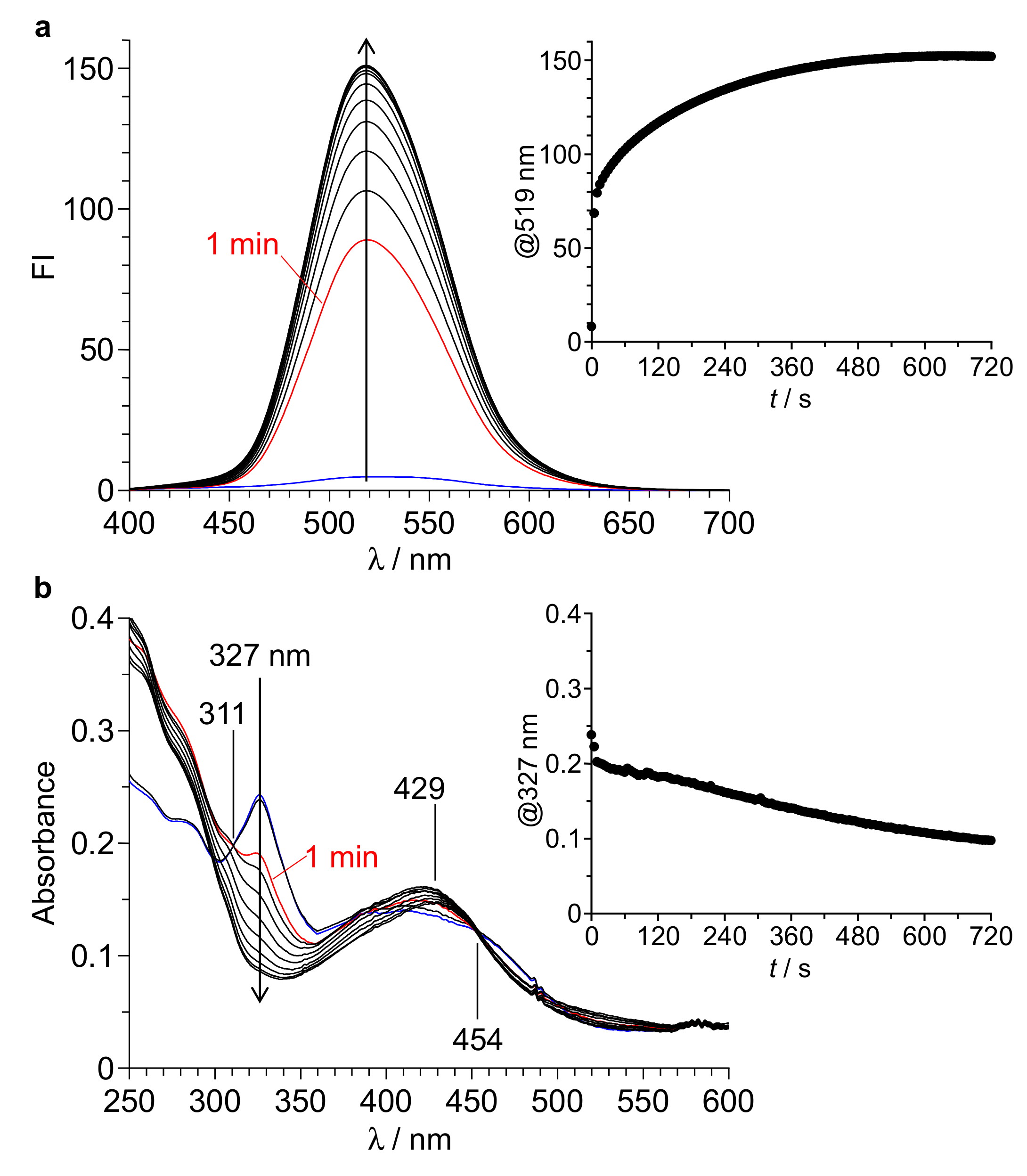
3.2. Fluorescence Properties
3.3. Emitting Species
3.4. Reaction Mechanism
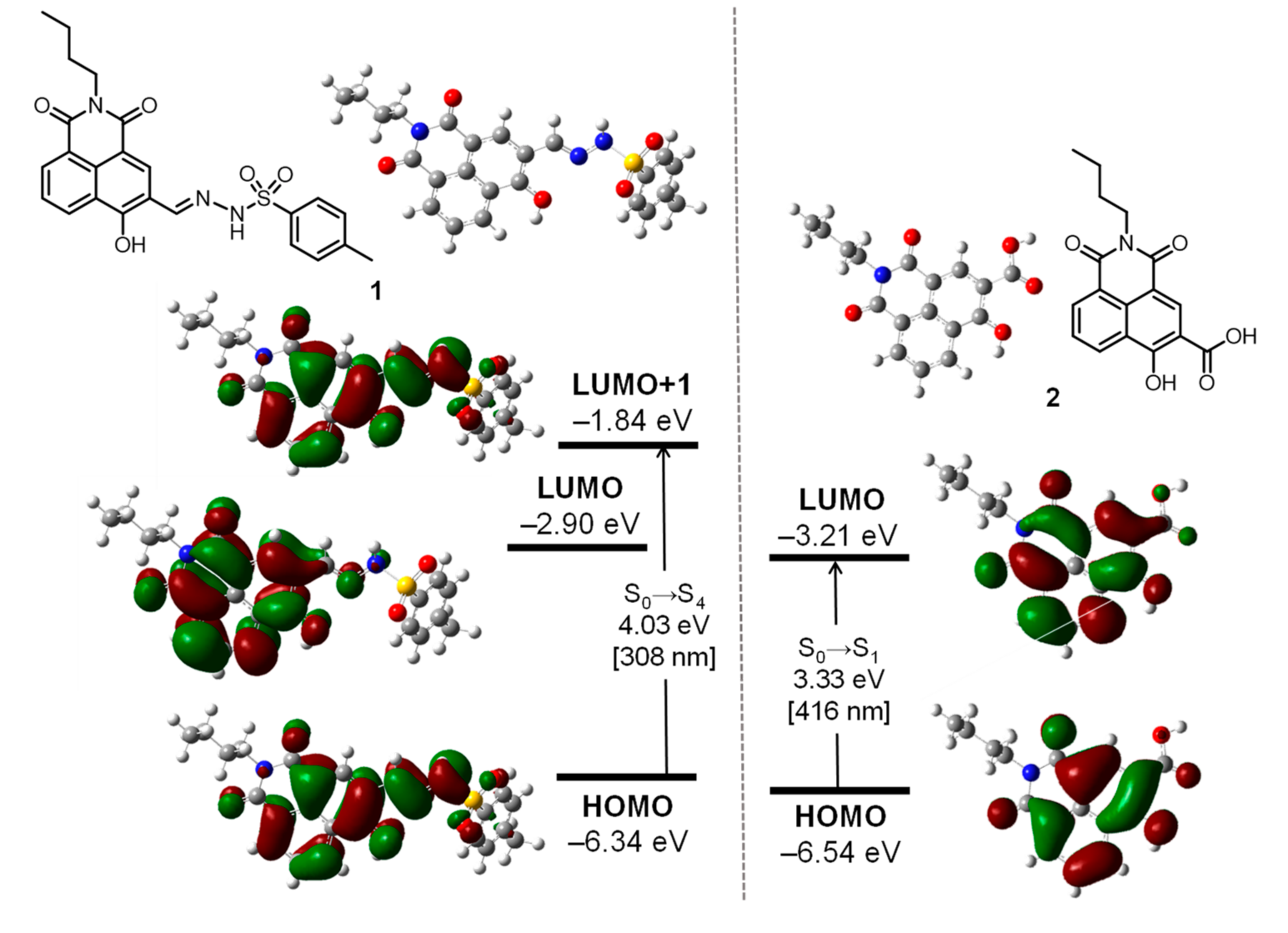
3.5. Ab Initio Calculations
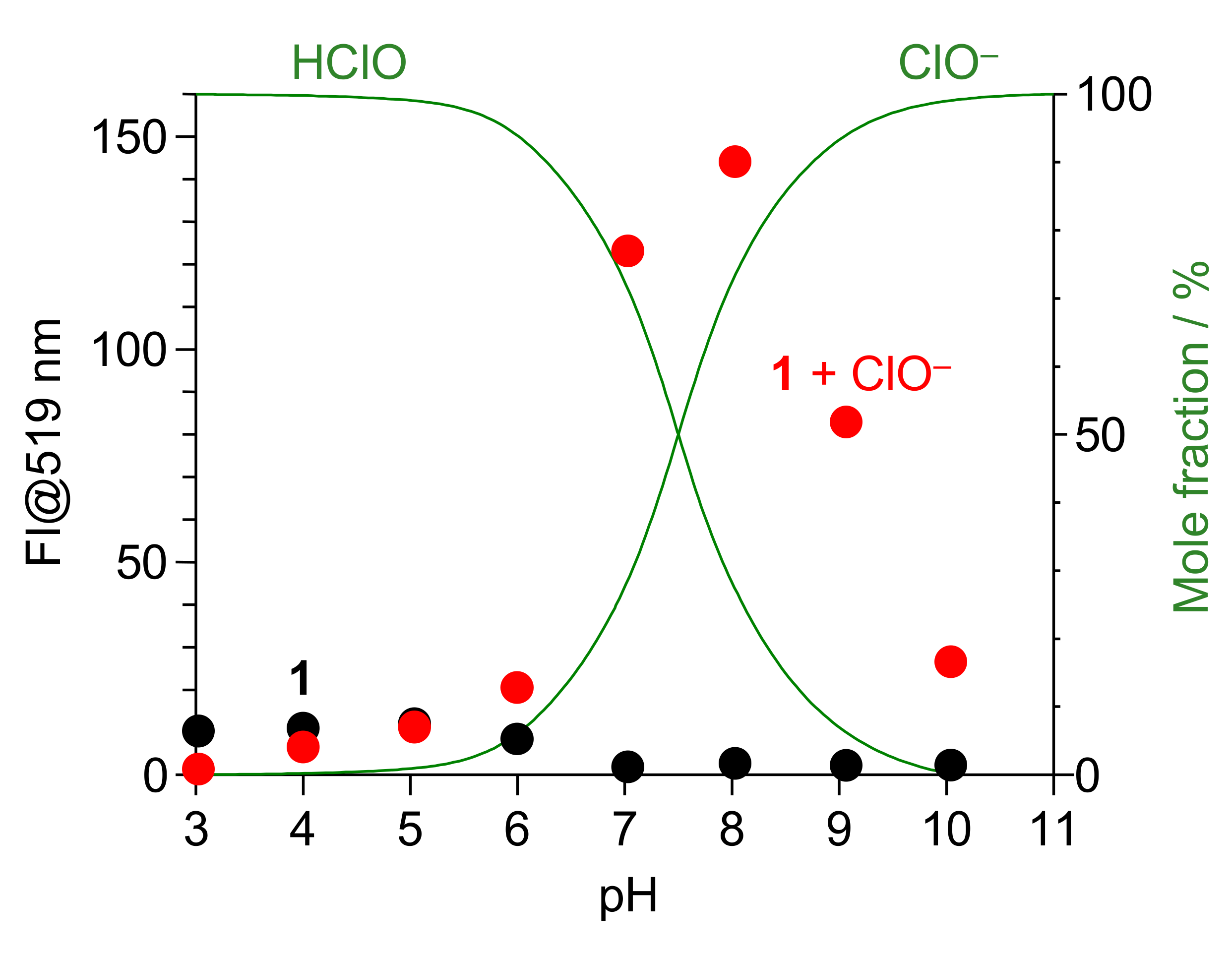
3.6. Effect of pH
3.7. Cell Imaging
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aoki, T.; Munemori, M. Continuous Flow Determination of Free Chlorine in Water. Anal. Chem. 1983, 55, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shepherd, J.; Hilderbrand, S.A.; Waternan, P.; Heinecke, J.W.; Weissleder, R.; Libby, P. A novel fluorescent probe for the detection of myeloperoxidase activity in atherosclerosis-associated macrophages. Chem. Biol. 2007, 14, 1221–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kettle, A.J.; Winterbourn, C.C. Myeloperoxidase: A key regulator of neutrophil oxidant production. Redox Rep. 1997, 3, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinbeck, M.J.; Nesti, L.J.; Sharkey, P.F.; Parvizi, J. Myeloperoxidase and chlorinated peptides in osteoarthritis: Potential biomarkers of the disease. J. Orthop. Res. 2007, 25, 1128–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, S.; Okada, Y.; Sukhova, G.K.; Virmani, R.; Heinecke, J.W.; Libby, P. Macrophage myeloperoxidase regulation by granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor in human atherosclerosis and implications in acute coronary syndromes. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 879–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiyama, T.; Fujita, M.; Koide, N.; Mori, I.; Yoshida, T.; Mori, H.; Yokochi, T. 2-Aminopurine inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced nitric oxide production by preventing IFN-β production. Microbiol. Immunol. 2004, 48, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, D.-K.; Pennathur, S.; Perier, C.; Tieu, K.; Teismann, P.; Wu, D.-C.; Lewis, V.J.; Vila, M.; Vonsattel, J.-P.; Heinecke, J.W.; et al. Ablation of the inflammatory enzyme myeloperoxidase mitigates features of parkinson’s disease in mice. J. Neurosci. 2005, 25, 6594–6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazen, S.L.; Hsu, F.F.; Duffin, K.; Heinecke, J.W. Molecular Chlorine Generated by the Myeloperoxidase-Hydrogen Peroxide-Chloride System of Phagocytes Converts Low Density Lipoprotein Cholesterol into a Family of Chlorinated Sterols. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23080–23088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adam, L.C.; Gordon, G. Direct and sequential potentiometric determination of hypochlorite, chlorite, and chlorate ions when hypochlorite ion is present in large excess. Anal. Chem. 1995, 67, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Lee, K.A.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, W.J.; Yoon, J.A. A Highly Specific Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorous Acid and Its Application in Imaging Microbe-Induced HOCl Production. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9944–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Tian, X.; Shin, I.; Yoon, J. Fluorescent and luminescent probes for detection of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 4783–4804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yoon, J. Design Principles, Sensing Mechanisms, and Applications of Highly Specific Fluorescent Probes for HOCl/OCl−. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabchev, I.; Petkov, C.; Bojinov, V. 1,8-Naphthalimides as blue emitting fluorophores for polymer materials. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2002, 287, 904–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, K.; Huo, F.; Yin, C.; Chao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, M. A highly selective fluorescent bioimaging probe for hypochloritebased on 1,8-naphthalimide derivative. Sens. Actuators B 2015, 221, 1508–1514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhang, Z.; Meng, Q.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R. Rapid Response Fluorescence Probe Enabled In Vivo Diagnosis and Assessing Treatment Response of Hypochlorous Acid-Mediated Rheumatoid Arthritis. Adv. Sci. 2018, 5, 1800397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.C.; Kim, C. Naphthalimide-based probe for the detection of hypochlorite in a near-perfect aqueous solution. Anal. Sci. 2019, 35, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, S.; Maity, S.; Maity, A.C.; Das, A.K. Chemical Fluorometric and Naked-Eye Detectable Dual Signaling Chemodosimeter for Hypochlorite. Sens. Actuators B 2014, 204, 741–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.J.; Ryu, H.; Lee, H.J.; Chang, S. Chemical Selective Fluorescence Signaling of Hypochlorite in Tap Water by Oxidative Hydrolysis of Sulfonhydrazone. Sens Actuators B 2017, 241, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, L.; Nie, H.; Wu, Y.; Xin, F.; Gao, C.; Jing, J.; Zhang, X. An ultrafast responsive BODIPY-based fluorescent probe for the detection of endogenous hypochlorite in live cells. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 525–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Setsukinai, K.; Urano, Y.; Kakinuma, K.; Majima, H.J.; Nagano, T. Development of novel fluorescence probes that can reliably detect reactive oxygen species and distinguish specific species. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3170–3175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Z.-N.; Liu, F.-Q.; Chen, Y.; Tam, P.K.H.; Yang, D. A Highly Specific BODIPY-Based Fluorescent Probe for the Detection of Hypochlorous Acid. Org. Lett. 2008, 10, 2171–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Nakamura, M.; Hayashi, N.; Hirai, T. Coumarin-spyropyran dyad with a hydrogenated pyran moiety for rapid, selective, and sensitive fluorometric detection of cyanide anion. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6805–6811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Hashimoto, M.; Chishiro, K.; Moriyama, K.; Tanaka, S.; Hirai, T. Photocatalytic dinitrogen fixation with water on bismuth oxychloride in chloride solutions for solar-to-chemical energy conversion. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 7574–7583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bag, B.; Bharadwaj, P.K. Perturbation of the PET process in fluorophore-spacer-receptor systems through structural modification: Transition metal induced fluorescence enhancement and selectivity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 4377–4390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Proutiere, A.; Megnassan, E.; Hucteau, H. Refractive index and density variations in pure liquids: A new theoretical relation. J. Phys. Chem. 1992, 96, 3485–3489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W. Synthesis and photochromism of naphthopyrans bearing naphthalimide chromophore: Predominant thermal reversibility in color-fading and fluorescence switch. J. Phys. Chem. B 2011, 115, 14648–14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Nie, H.; Yang, W.; Tian, Y.; Jing, J.; Zhang, X. A highly sensitive and rapidly responding fluorescent probe with alarge Stokes shift for imaging intracellular hypochlorite. Sens. Actuators B 2016, 236, 459–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Sakai, S.; Kawa, S.; Taya, M. Identification of Hydrogen Peroxide-Secreting Cells by Cytocompatible Coating with a Hydrogel Membrane. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 11592–11598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiraishi, Y.; Hayashi, N.; Nakahata, M.; Sakai, S.; Hirai, T. Naphthalimide-Coumarin Conjugate: Ratiometric Fluorescent Receptor for Self-Calibrating Quantification of Cyanide Anion in Cells. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 32304–32309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Reja, S.I.; Bhalla, V.; Kumar, M. A new thiacalix[4]arene-fluorescein based probe for detection of CN− and Cu2+ ions and construction of a sequential logic circuit. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 15929–15936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.C.; Kairdolf, B.A.; Smith, A.M.; Nie, S. Oxidative Quenching and Degradation of Polymer-Encapsulated Quantum Dots: New Insights into the Long-Term Fate and Toxicity of Nanocrystals In Vivo. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10836–10837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greim, H.; Ahlers, J.; Bias, R.; Broecker, B.; Hollander, H.; Gelbke, H.P.; Klimisch, H.J.; Mangelsdorf, I.; Paetz, A.; Schön, N.; et al. Toxicity and Ecotoxicity of Sulfonic Acids: Structure-Activity Relationship. Chemosphere 1994, 28, 2203–2236. [Google Scholar]
- Ortiz, G.; Liu, P.; Naing, S.H.H.; Muller, V.R.; Miller, E.W. Synthesis of Sulfonated Carbofluoresceins for Voltage Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 14, 6631–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Peng, J.; An, B.; Qiao, Z.; Wei, N.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, W. Highly Efficient Cell Membrane Tracker Based on a Solvatochromic Dye with Near-Infrared Emission. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 11829–11835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, R.E.; Scuseria, G.E.; Frisch, M.J. An efficient implementation of time-dependent density-functional theory for the calculation of excitation energies of large molecules. J. Chem. Phys. 1998, 109, 8218–8224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawara, S.; Goto, T.; Nara, M.; Ozawa, Y.; Hotta, K.; Arata, Y. Spectroscopic characterization and the pH dependence of bactericidal activity of the aqueous chlorine solution. Anal. Sci. 1998, 14, 691–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Yuan, H.; Qin, C.; Zeng, L.; Bao, G.-M. A mitochondria-targeted near-infrared probe for colorimetric and ratiometric fluorescence detection of hypochlorite in living cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 107525–107532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Huo, F.; Chao, J.; Yin, C. A near-infrared ratiometric fluorescent probe with large stokes based on isophorone for rapid detection of ClO− and its bioimaging in cell and mice. Sens. Actuators B 2019, 287, 453–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, J.; Fu, B.; Qin, C.; Zeng, L.; Hu, X. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for rapid and sensitive visualization of hypochlorite in living cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 43110–43113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shiraishi, Y.; Nakatani, R.; Takagi, S.; Yamada, C.; Hirai, T. A Naphthalimide–Sulfonylhydrazine Conjugate as a Fluorescent Chemodosimeter for Hypochlorite. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040123
Shiraishi Y, Nakatani R, Takagi S, Yamada C, Hirai T. A Naphthalimide–Sulfonylhydrazine Conjugate as a Fluorescent Chemodosimeter for Hypochlorite. Chemosensors. 2020; 8(4):123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040123
Chicago/Turabian StyleShiraishi, Yasuhiro, Rikako Nakatani, Shunsuke Takagi, Chiharu Yamada, and Takayuki Hirai. 2020. "A Naphthalimide–Sulfonylhydrazine Conjugate as a Fluorescent Chemodosimeter for Hypochlorite" Chemosensors 8, no. 4: 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040123
APA StyleShiraishi, Y., Nakatani, R., Takagi, S., Yamada, C., & Hirai, T. (2020). A Naphthalimide–Sulfonylhydrazine Conjugate as a Fluorescent Chemodosimeter for Hypochlorite. Chemosensors, 8(4), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors8040123





