Abstract
This work provides a summary of our results in the area of the experimental development of detection paper for the detection of liquid phase chemical warfare agents (drops, aerosol), the presence of which is demonstrated by the development of characteristic coloring visible to the naked eye. The basis of the detection paper is a cellulose carrier saturated with the dithienobenzotropone monomer (RM1a)–chromogenic chemosensor sensitive to nerve agents of the G type, blister agent lewisite, or choking agent diphosgene. We achieve a higher coloring brilliance and the limit certain interferences by using this chemosensor in the mix of the o-phenylendiamine-pyronine (PY-OPD). We prove that the addition of the Bromocresol Green pH indicator even enables detection of nerve agents of the V type, or, nitrogen mustards, while keeping a high stability of the detection paper and its functions for other chemical warfare agents. We resolve the resistance against the undesirable influence of water by providing a hydrophobic treatment of the carrier surface.
1. Introduction
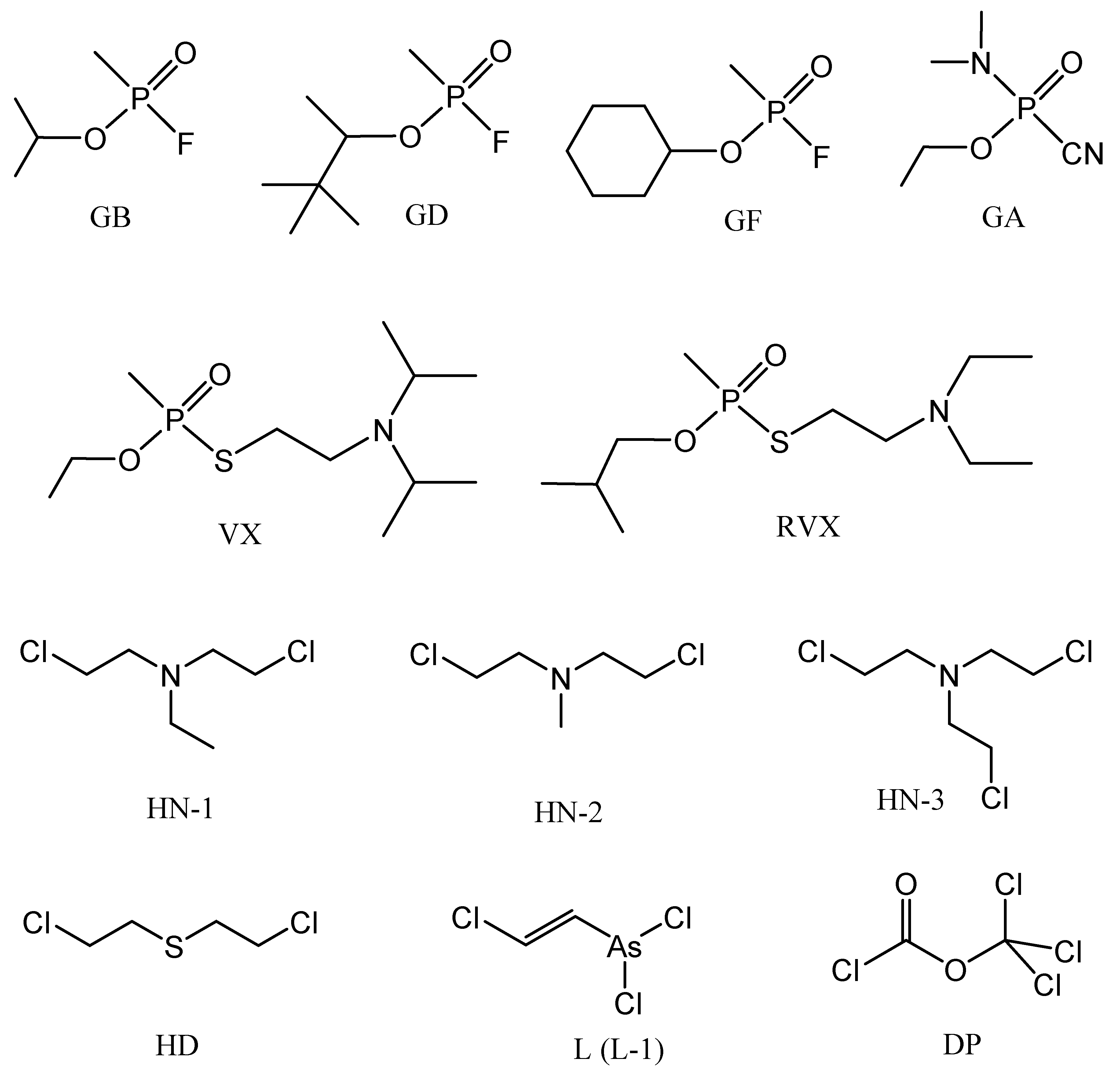
Even though the Chemical Weapons Convention came into operation in 1997, and currently 193 countries participate (as of May 2018), the risk of chemical weapons proliferation and the threat of using them is still present: They can be used in local wars, civil wars, or in terrorist attacks [1,2]. The active components of the chemical weapons are the chemical warfare agents (CWA), the combat employment of which depends to a significant extent on their state of matter. The most dangerous CWAs that have lethal effects are included within nerve agents, blister agents, and partially within choking agents. Most of them are in the liquid state, which enables their dispersion in the form of vapors, or variously dispersed liquid aerosols, with the potential of easy penetration not only through airways, but through the skin as well, resulting in serious percutaneous poisoning. Some of these CWAs are highly persistent, therefore they can contaminate the terrain for a long time, depending on actual climatic conditions and on the terrain characteristics [3]. The chemical structure of the most significant liquid CWA is shown in Figure 1. Some of their physical and toxic properties are provided in Table 1.
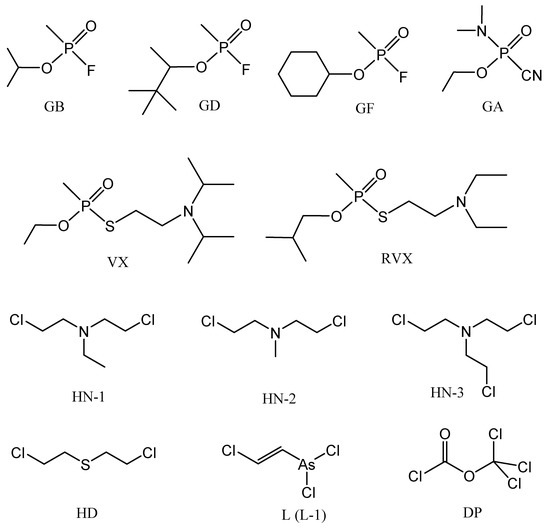
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of chemical warfare agents (CWA).

Table 1.
The summary of tested CWAs, their physical and toxic properties and reactions with detection papers (− no response, + distinct response, ++ strong response).
For the detection of settling liquid particles of the CWA aerosol cloud, or droplets or spray of a liquid CWA on the surface of the terrain, objects, machines, and persons, simple technical means are usually used, based on visual evaluation (by naked eye) of color changes. The color change results from the solubility of organic dyes, color change of pH indicator, or from the reaction with specific chromogenic agents. The organic dyes, pH indicators, and chromogenic agents are applied to the filtration paper, fabric, or another flat porous carrier, modified to the form of detection strips, papers and/or tapes.
In the past, the main focus was given to the detection of sulfur mustard, a typical poison with percutaneous effect (that is why it is called a “blister agent”). As an example, there was the detection paper saturated with 1-(p-nitrophenylazo)-2-naphtylamine, providing a red color with the sulfur mustard. Later, this dye was replaced with a less toxic compound and used not only for the detection of sulfur mustard, but also for the detection of nerve agents. Another example is the detection paper saturated with the complex of Crystal Violet with Hg2+ and Cu2+ salts, providing a dark violet color with the droplets of the sulfur mustard, due to the release of the original dye [4], or the detection paper with 4,4′-bis(N,N-dimethylamino)benzophenone and mercuric chloride, providing a red color with the sulfur mustard [5].
The introduction of nerve agents to military equipment, and the real threat of using them, also calls for the introduction of a simple means for their detection in the liquid phase. An example is the detection paper impregnated with the Bromocresol Green pH indicator, providing a blue color in contact with the VX agent. At present, multicomponent detection papers are used, intended not only for the detection of nerve agents, but also for the detection of sulfur mustard, with the option of their distinction. They are usually self-sticking paper sheets impregnated with a mixture of organic dyes, which dissolve in liquid CWA and provide characteristic colors. The Dye Red E (CAS: 60033-00-3) is used for the detection of sulfur mustard, the Dye Green EDA (CAS: 5833-18-1) is used, as an example, for the detection of nerve agents of the V type, and the Disperse Yellow 23 (CAS: 6250-23-3) dye is used for the detection of G type nerve agents, providing red, green, and yellow colours [4,6].
The low selectivity of the known methods of the detection of liquid CWAs, based on the solubility of organic dyes or pH indicators, is a significant disadvantage. Chemical reactions are more selective, but the selection of chromogenic agents, suitable for practical applications, was very limited in the past. However, during the last two decades, a lot of original works were published, referring particularly to chromogenic chemosensors for the G type nerve agents, featuring a significant change of color as well as good selectivity and sensitivity; these chemosensors are based on hydroxyl-activation, N-activation, and contain metal ions (coordination compounds), or possibly form reactive polymers [7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15,16,17,18,19]. Many publications deal with new chemosensors for sulphur mustard [20,21,22,23,24]. The issue is that most of these chemosensors have only been verified using simulants (e.g., diethyl chlorophosphate (DCP), 2-chloroethyl ethyl sulfide (CEES), etc.), moreover, they have not been applied on the detection papers for the detection in the liquid phase.
The goal of this text is to report the results of the experimental development of detection papers for the detection of CWAs in liquid phase, using the already known chemosensor based on the dithienobenzotropone [9], in combination with the chemosensor based on the o-phenylenediamine-pyronin [11], and the Bromocresol Green pH indicator. The article provides the method of detection papers preparation, their response to real CWAs, chemical interferences and stability during storage and operational ingestion. Basically, they are simple, robust, sufficiently selective, and reliable detection systems for most of the potential liquid CWA, with the exception of the sulfur mustard.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Equipment
For the preparation of the detection papers, we used dithienobenzotropone monomer (RM1a), o-phenylendiamine-ronine (PY-OPD), both synthesized in VŠCHT Prague, Czech Republic (as per References [9,11]), Bromocresol Green (BCG), colophon resin and chloroform (all of them made by Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
We used cellulose filtration papers as carriers, with the nominal basis weight of 85 g/m2 (Whatman, Kent, UK) and 120–125 g/m2 (Filtrak, Bärenstein, Germany).
As for the CWA test we used tabun (GA), sarin (GB), soman (GD), cyclosarin (GF), VX, RVX (“Russian VX”), sulfur mustard (HD), nitrogen mustard (HN-1, HN-2, HN-3), lewisite (L-1, L-2, L-3), and diphosgene (DP), all of them provided by the Military Research Institute, Brno, Czech Republic. For the research tasks, we used DCP and CEES simulants, both made by Sigma-Aldrich. All CWAs were prepared and tested in facilities declared within OPCW (Organization for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons). Certified protection equipment was used during all experiments, and all waste was treated using chloramine solution in 10% NaOH in the water-ethanol mixture (1:1) prior to disposal.
For the objective measurement of selected parameters (detection paper ageing), we used a portable tristimulus colorimeter LMG 173 (Dr. Lange, Dusseldorf, Germany), which utilizes the color CIE-Lab system. Spectrophotometric measurement (absorption spectra) were performed using a spectrophotometer Aquamate (Thermo Spectronic, Cambridge, UK).
2.2. Preparation of the Detection Paper
We used three basic variants of the detection paper (RM1a, RM1a/PY-OPD, RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG). Sheets of filtration paper with a size of 100 × 50 mm were immersed in impregnation solution for 30 s, consisting of the following:
- (a)
- 30 mg RM1a in 100 mL of chloroform (RM1a),
- (b)
- 30 mg RM1a and 15 mg PY-OPD in 100 mL of chloroform (RM1a/PY-OPD),
- (c)
- 30 mg RM1a, 15 mg PY-OPD, 15 mg BCG in 100 mL of chloroform (RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG); the improved variant was enhanced with the addition of colophon resin (950 mg).
The impregnated filtration papers were dried in open air for 60 min and stored in a hermetically closed package and kept away from direct sunlight.
2.3. Testing the Detection Paper Functions
Droplets of test substances (5 µL) were applied using a micropipette on the detection paper and were evaluated visually (by naked eye) for color change at the point of exposure. Each test was repeated 3× using 2 lots of real CWA (the same manufacturer, different production dates). All results were documented using a photographic camera within 1 min after exposure.
2.4. Testing of Stability
For the purpose of the stability testing, the detection papers were stored in the laboratory in the open air, at a temperature of 21–23 °C, for a period of 6 months. Papers were visually monitored on a regular basis once a week for surface color change without any exposure to the CWA droplets and for their function—color change after the exposure to the CWA droplets. Thermal stability was proved with part of the samples. The samples were stored in a drying cabinet at a temperature of 80 °C for three weeks. On a regular basis, the unexposed surface color change was monitored visually using the tristimulus colorimeter (CIE-Lab color system) following the ΔE parameter as the analytical signal [25]. The ΔE values up to 0.2 cannot be perceived by the naked eye, the values of 0.2–0.5 are very slight, 0.5–1.5 are slight, 1.5–3.0 are distinct, 3.3–6.0 are very distinct, 6.0–12.0 are strong, and above 12.0, the values are very strong. In addition, the function of the detection paper (visual control of the color change after CWA exposure) was tested regularly.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Design of the RM1a Detection Paper or RM1a/PY-OPD
The first (basic) design of the novel detection paper was based on the intention of developing a detection paper with high selectivity for G type nerve agents, for which detection using existing technical means is an issue. E.g., the 3-way detection papers (M8, PDF-1, PP-3, CALID-3, and similar) provide a relatively faint yellow color with the G type nerve agents droplets (on a grey background), which is disturbed with the presence of common organic solvents and industrial chemicals; the M9 detection paper provides an even lower selectivity as we verified the selectivity of these means experimentally.
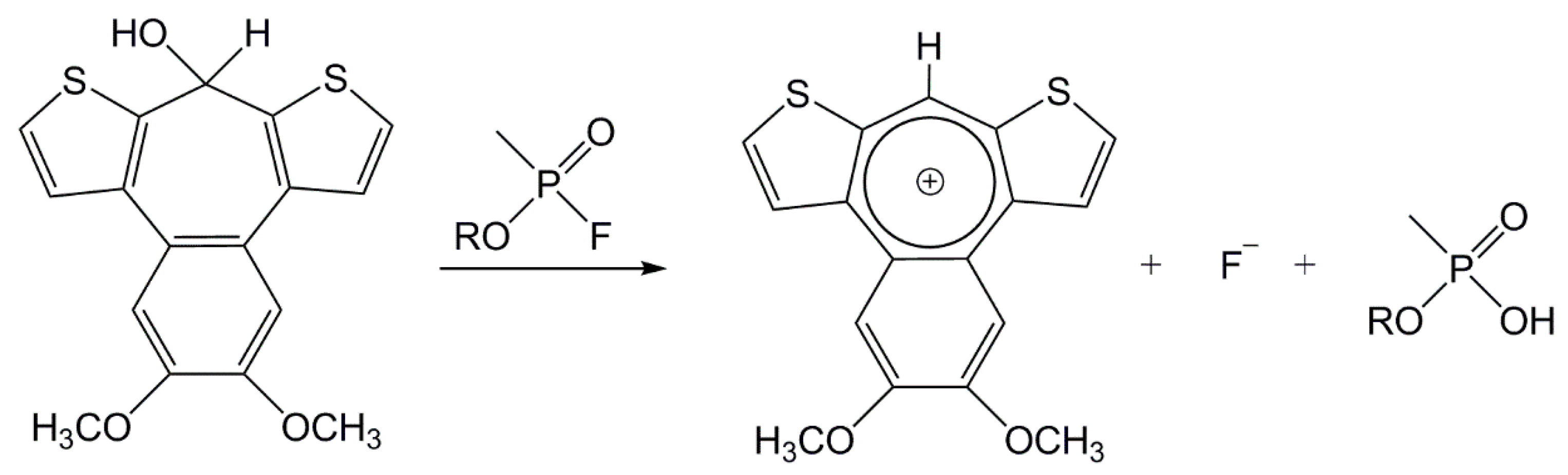
By studying the latest sources, we selected, synthesized, and verified many chemosensors, potentially sensitive to alkyl/cycloalkyl-methylphosphonofluoridates. The RM1a appeared to be the most interesting, with its colorless chloroform solution, providing red color with the DCP (according to literary data), with a bathochromic shift from 330 to 580 nm [9]. The agent was not verified against real CWA, neither on a solid carrier, nor in the form of the detection paper for the detection in the liquid phase. During the experiments, we found the RM1a was not only a good chemosensor of current G type nerve agents, but also that it is very stable and functional on the cellulose carrier. Moreover, the structurally different GA (reaction on the P-CN bond), blister agent L, and choking agent DP were giving a uniquely positive response. The reaction mechanism for the alkyl/cycloalkyl-methylphosphonofluoridates is provided in Figure 2.
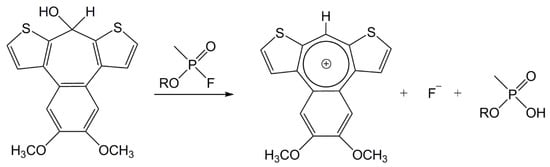
Figure 2.
The dithienobenzotropone monomer (RM1a) reaction scheme with the G type nerve agents (modified according to Reference [9]).
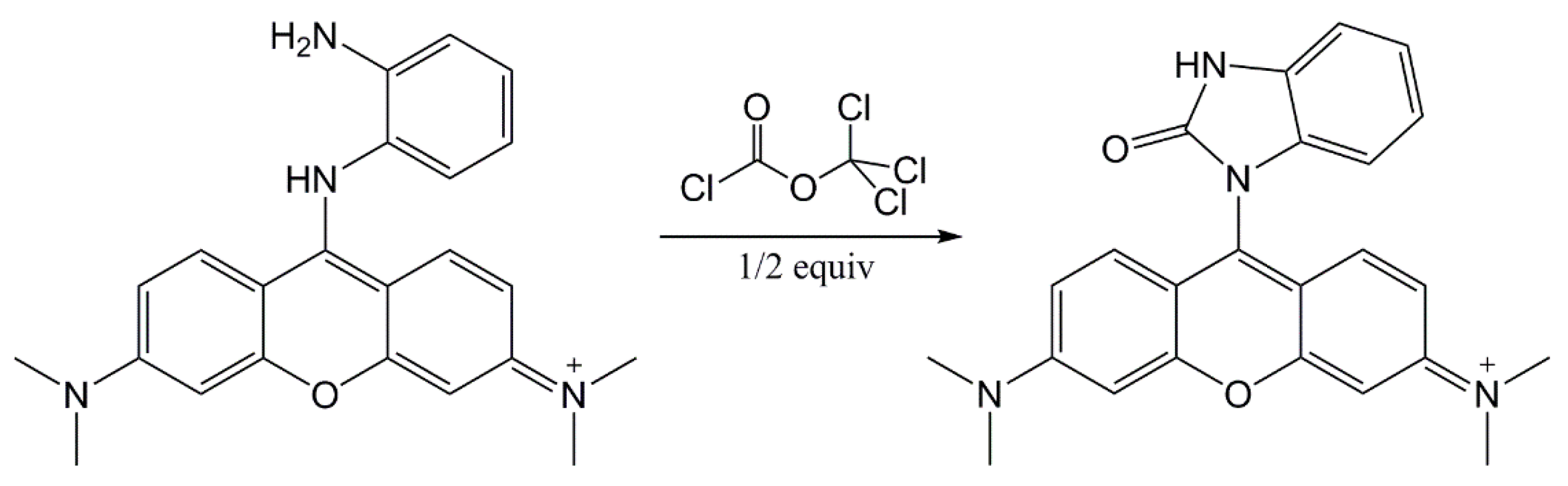
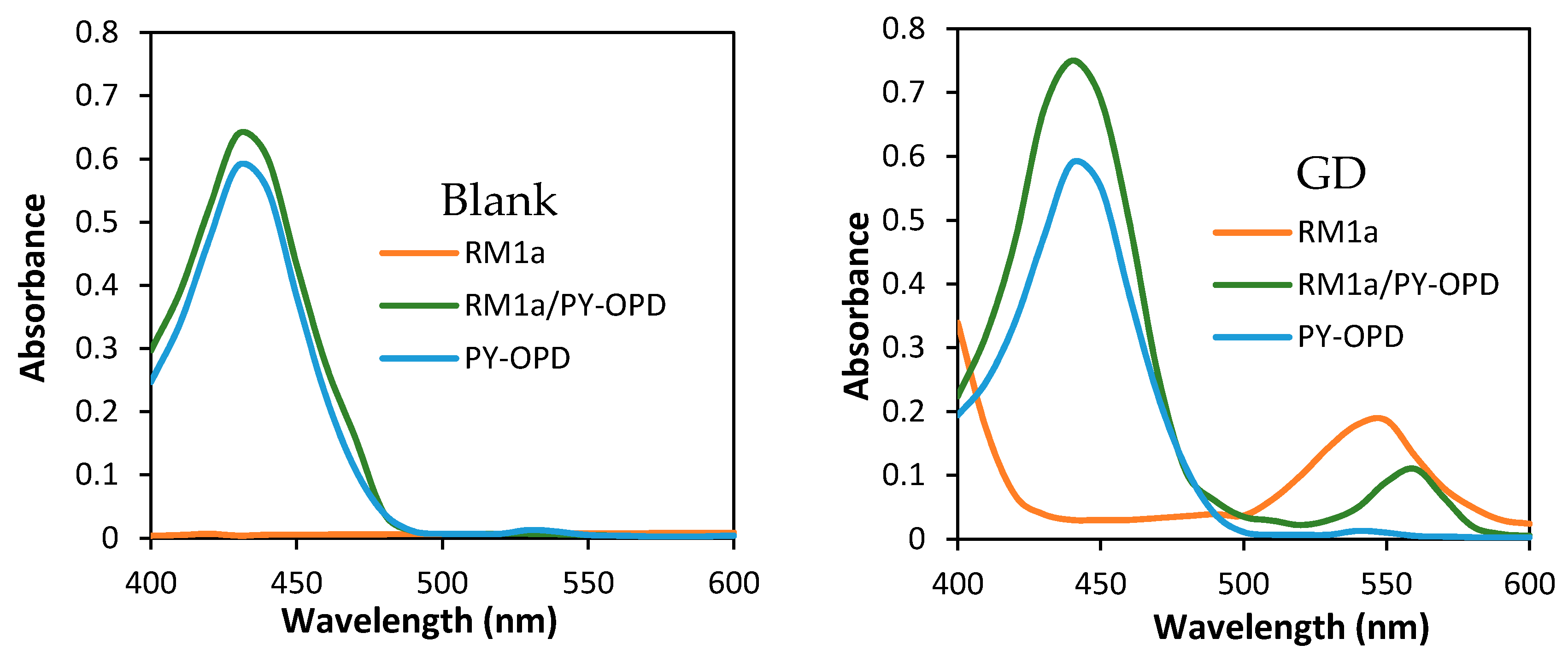
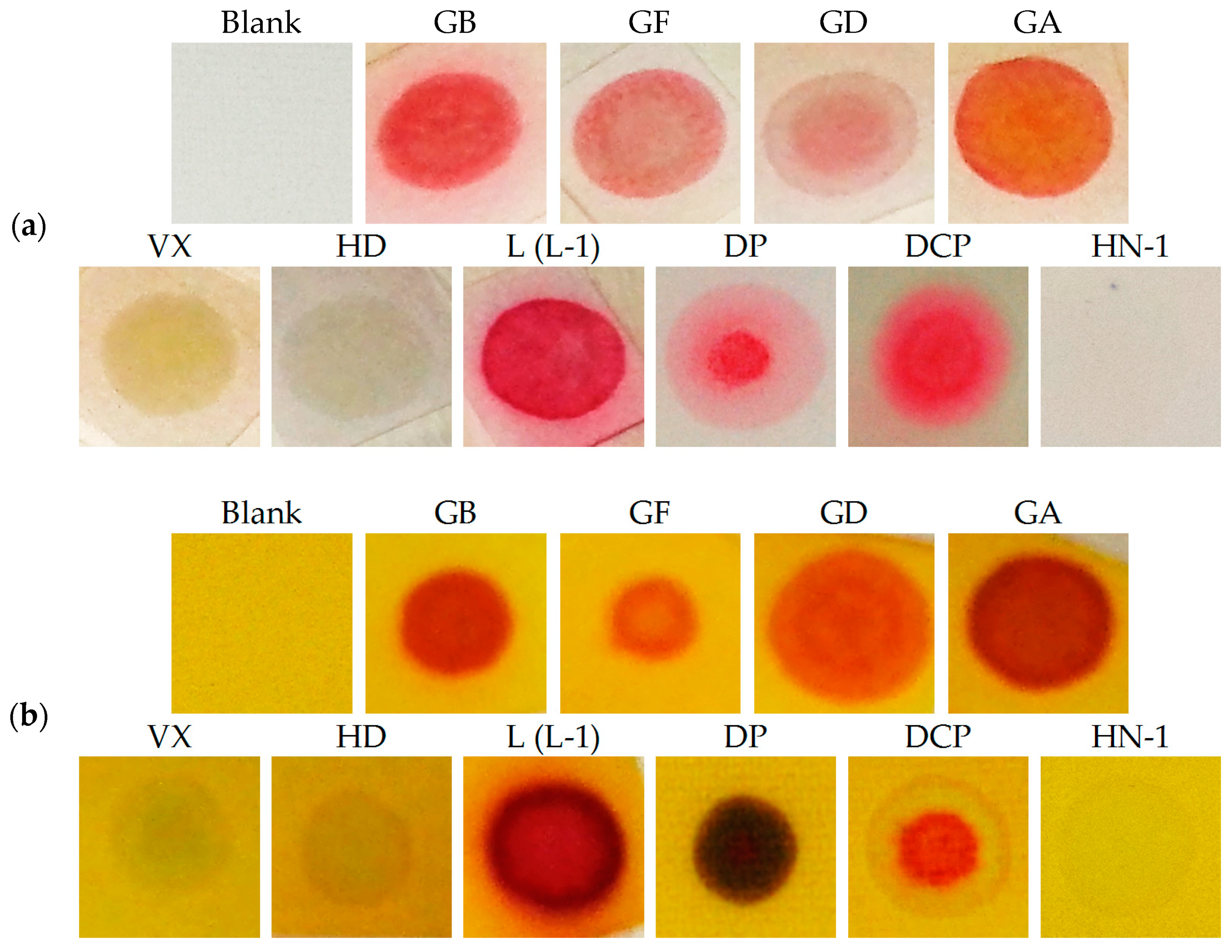
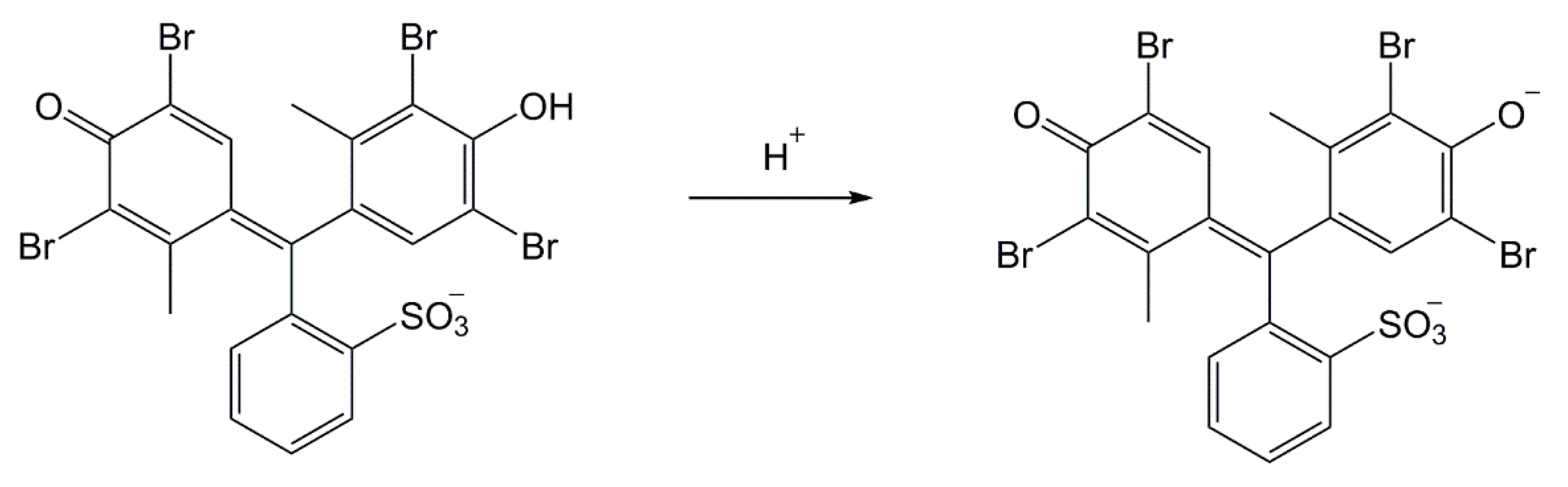
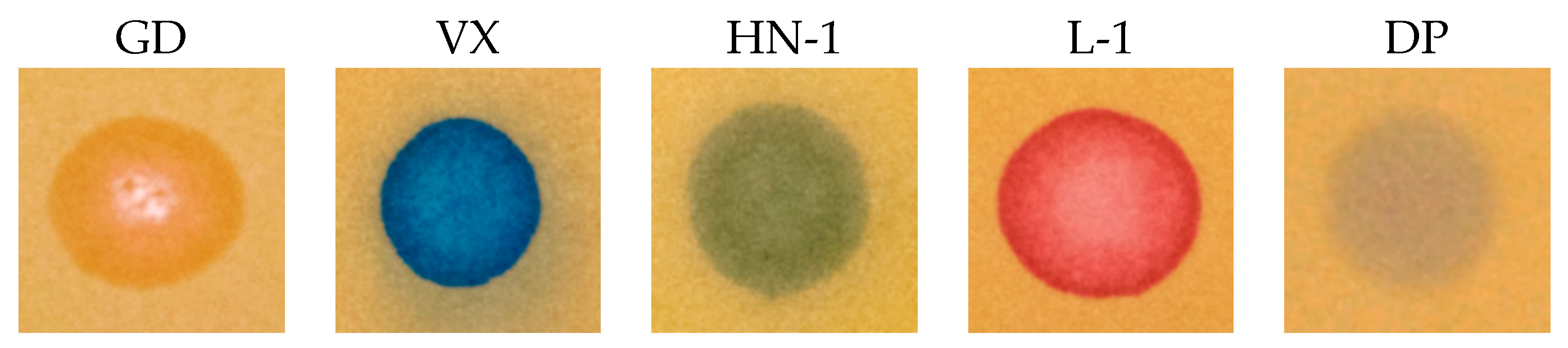
The extended design was based on two presumptions: The reaction product color intensity can be increased, or, the color contrast can be improved and the detection selectivity can be increased. With this goal, we combined the RM1a with some chemosensors for alkylating or acylating agents. The combination with the PY-OPD provided good results. This chemosensor had been designed before for the detection of DCP and phosgene, providing yellow and violet color with them in the gaseous phase, respectively [11]. The reaction mechanism with DP comprising intramolecular cyclisation is provided in Figure 3. Examples of absorption spectra of RM1a, PY-OPD and RM1a/PY-OPD (in chloroform solution) after addition of GD are shown in Figure 4. The addition of PY-OPD featured two advantages. At first, the detection paper exposed to droplets of the G type nerve agents provided the color change of yellow–red, which is more suitable for the visual evaluation by the naked eye, compared to the white–red color change of the RM1a itself. Secondly, a different color was created upon contact with the liquid DP, compared to the G type nerve agents, thus improving the detection selectivity. The other parameters of the detection paper have been maintained. The color response of RM1a and RM1a/PY-OPD detection papers to real CWAs are documented in Figure 5.
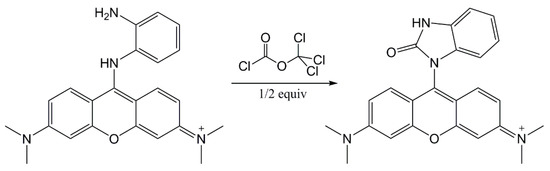
Figure 3.
The o-phenylendiamine-pyronine (PY-OPD) reaction scheme with diphosgene (DP) (modified according to Reference [11]).
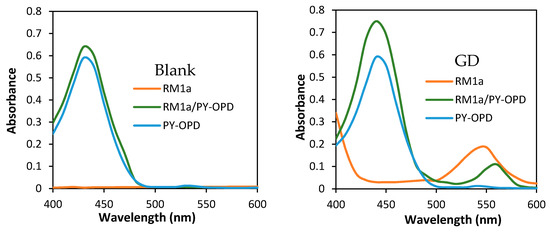
Figure 4.
Absorption spectra of RM1a, PY-OPD and RM1a/PY-OPD (in chloroform solution) for blank and addition of soman (GD).
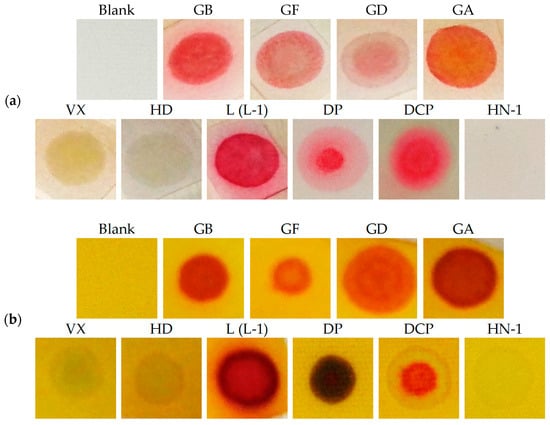
Figure 5.
RM1a (a) and RM1a/PY-OPD (b) detection paper after the exposure to a droplet of CWA.
3.2. Design of the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG Detection Paper
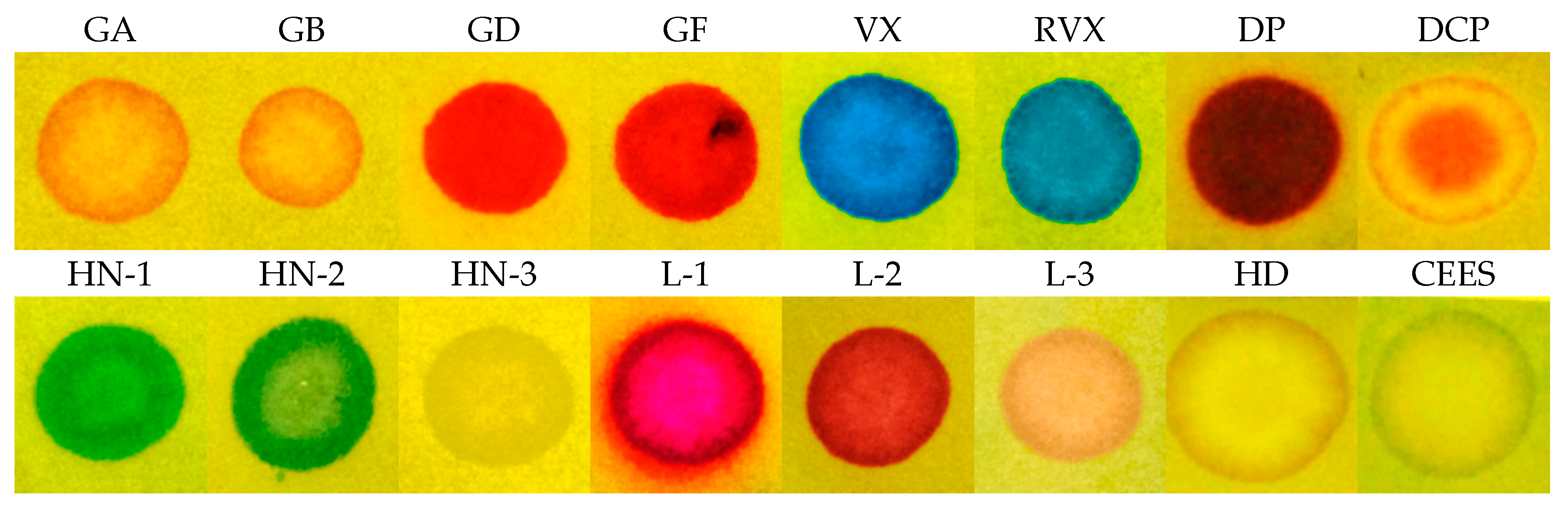
Another design covered the option of detecting droplets and aerosol of the V type nerve agents, representing the top of CWAs for their toxicity and persistence. We proceeded based on a simple plan: To the RM1a/PY-OPD detection paper, we incorporated (by adding to an impregnating solution) various chemosensors of amines, thiols, and aminothiols as precursors, or products of these CWA hydrolysis. We verified 5,5′-dithiobis(2-nitrobenzoic acid), 2,2′-dithiobis(5-nitropyridine), 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzofurazan, 4-chloro-5,7-dinitrobenzofurazan, and 4-nitro-2,1,3-benzothiadiazol as chromogenic reagents. In this investigation phase, the most promising results were provided by common color pH indicators, in particular by the triphenylmethane BCG indicator, providing the color change yellow (3.8)—blue (5.4). The BCG color change mechanism scheme is shown in Figure 6. Practically, the BCG incorporation to the RM1a/PY-OPD detection paper did not change its appearance, or dispositions to reactions with G type nerve agents (namely, the semi-persistent GD and GF), or, lewisite or DP, moreover, it provided an expressive blue color with the V type nerve agents. As expected, the HN-1 and HN-2 nitrogen mustards gave a response resulting in a green color (these vesicants are less basic than VX); the HN-3 nitrogen mustard did not react at all. The summary of color responses of RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG detection papers to CWA is shown in Figure 7. A summary overview of detection papers color changes, supplemented with selected physical and toxic properties, is provided in Table 1.
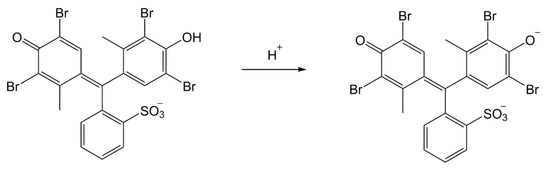
Figure 6.
The Bromocresol Green (BCG) color change mechanism scheme.
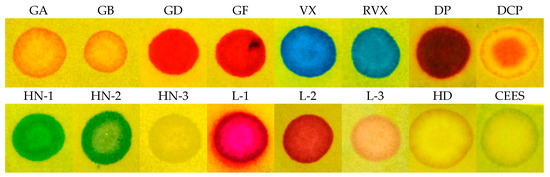
Figure 7.
Response of the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG detection paper to CWA.
3.3. Sulphur Mustard Tests
During the development of the detection paper, we also studied the option of using new specific chromogenic/fluorogenic reagents, potentially sensitive to sulfur mustard. Based on the literature, we synthesized and verified the reagents based on rhodamine-thioamide [21], benzothiazole (RHBT) [22], and pyronine (DPXT) [24]. We used solutions of reagents in common organic solvents (methanol, ethanol, chloroform) for the impregnation of the cellulose carrier, and after drying, we exposed it to droplets of sulfur mustard (HD) and simulant (CEES). However, we did not succeed in obtaining any positive color response.
3.4. Stability
In practice, the detection papers for liquid CWAs are usually stored in closed packages, at a temperature of −40 to +40 °C (at a temperature of 60 °C up to one month maximally), and they should be functional (operationally usable) at a temperature of −40 to +60 °C [26]. The samples of RM1a, RM1a/PY-OPD and RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG detection papers, stored at a common laboratory temperature, did not show any changes in their appearance or loss of functions during the full six months. At the same time, we tested the heat stability with the goal of verifying the detection paper resistance against short-term extreme temperatures, which might occur both during storage and during operational usage.
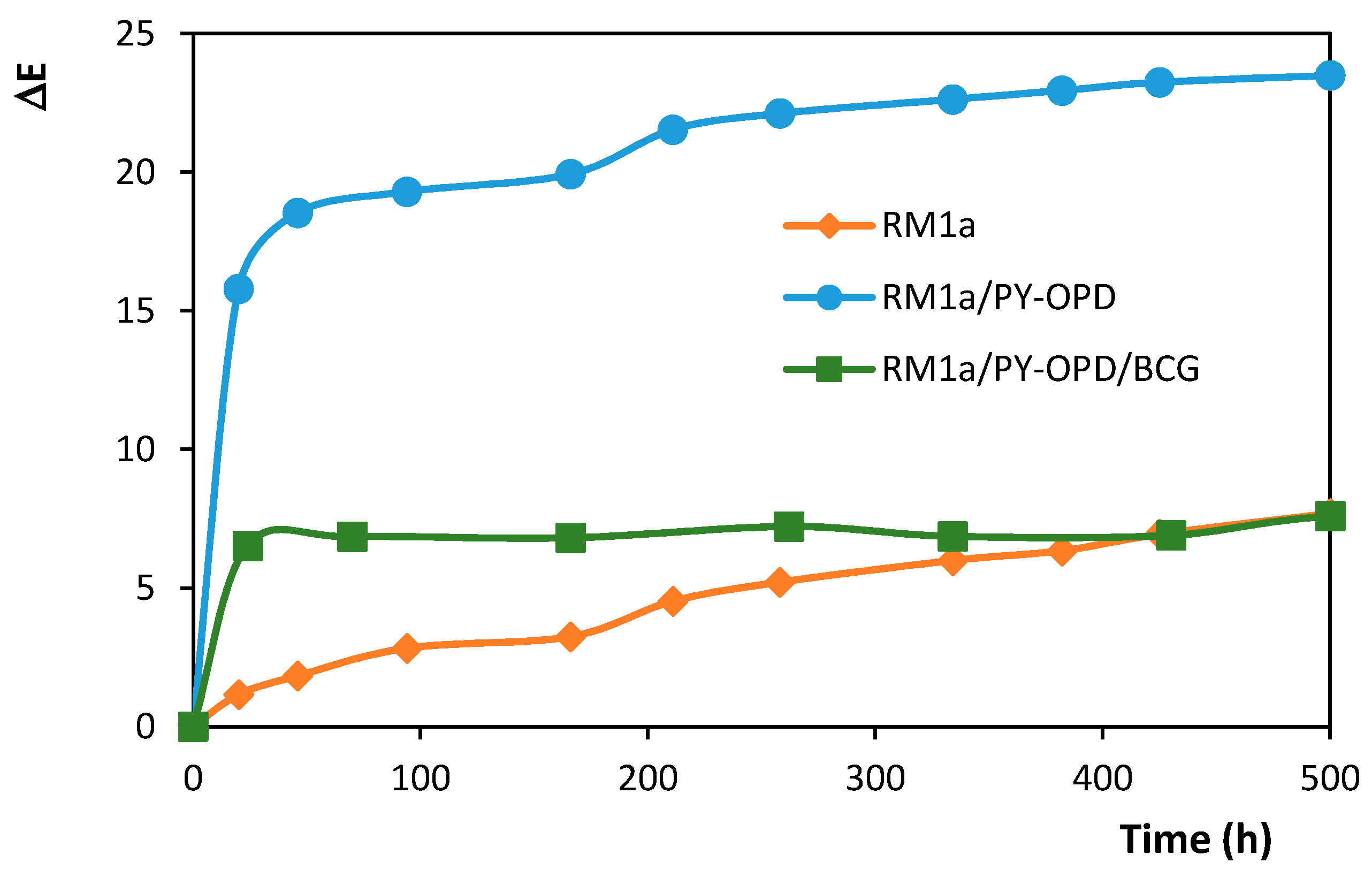
The change of detection papers appearance exposed to a temperature of 80 °C is shown in Figure 8. The charts show that a more significant darkening of the combined systems occurred during the first 24 h, then their appearance was stabilized. In the case of the RM1a detection paper, a slow darkening occurred from the very beginning. Yet, the detection papers maintained their functions, as noticeable on the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG complex system example in Figure 9.
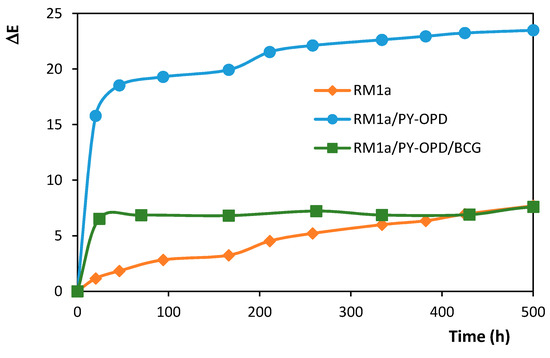
Figure 8.
Color stability of detection papers during storage at a temperature of 80 °C (tristimulus colorimetric measurement of the surface color change).
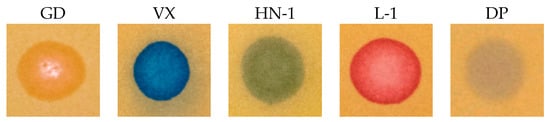
Figure 9.
Functional stability of the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG detection paper after 20 days of storage at a temperature of 80 °C.
3.5. Interferences
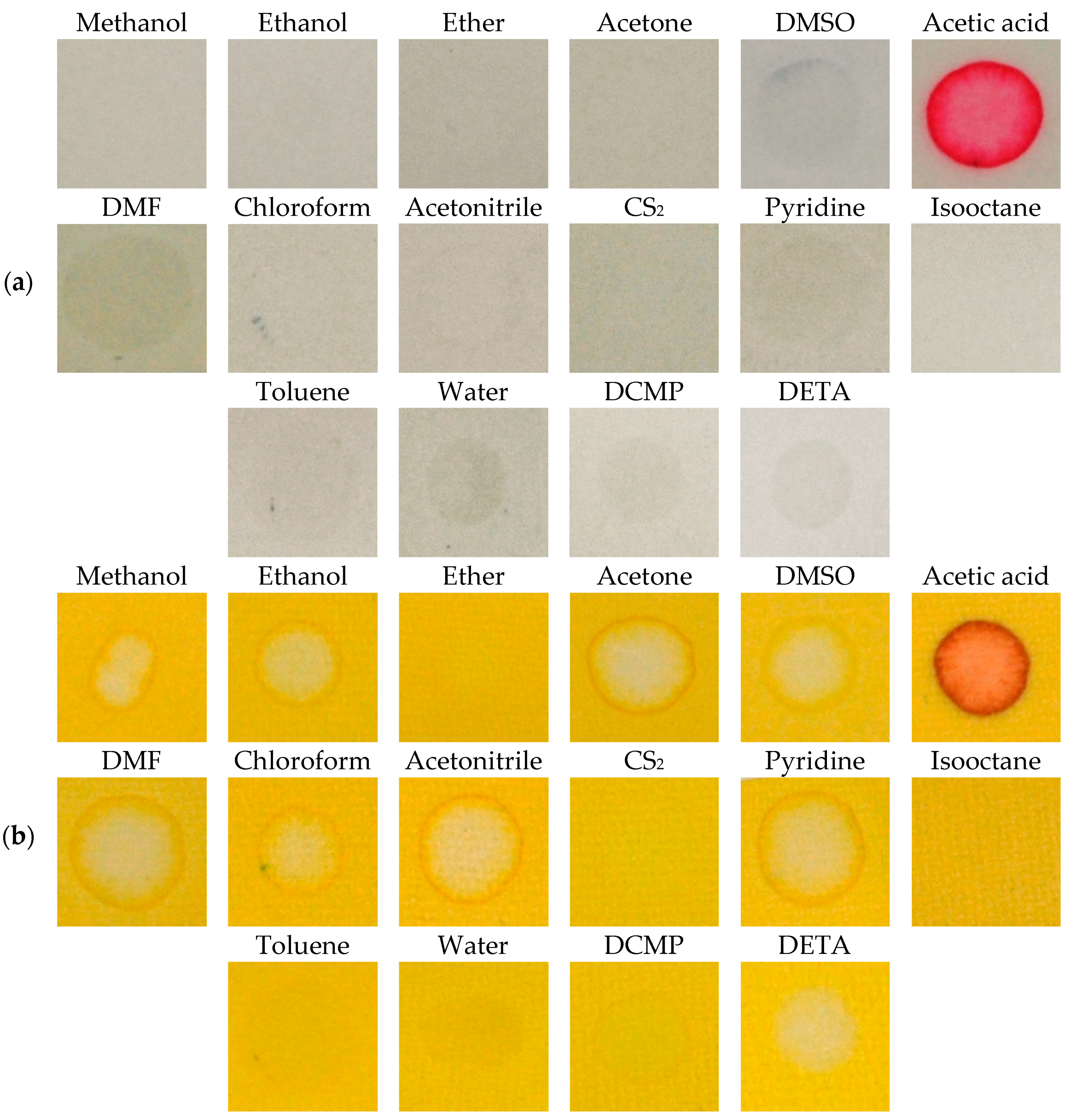
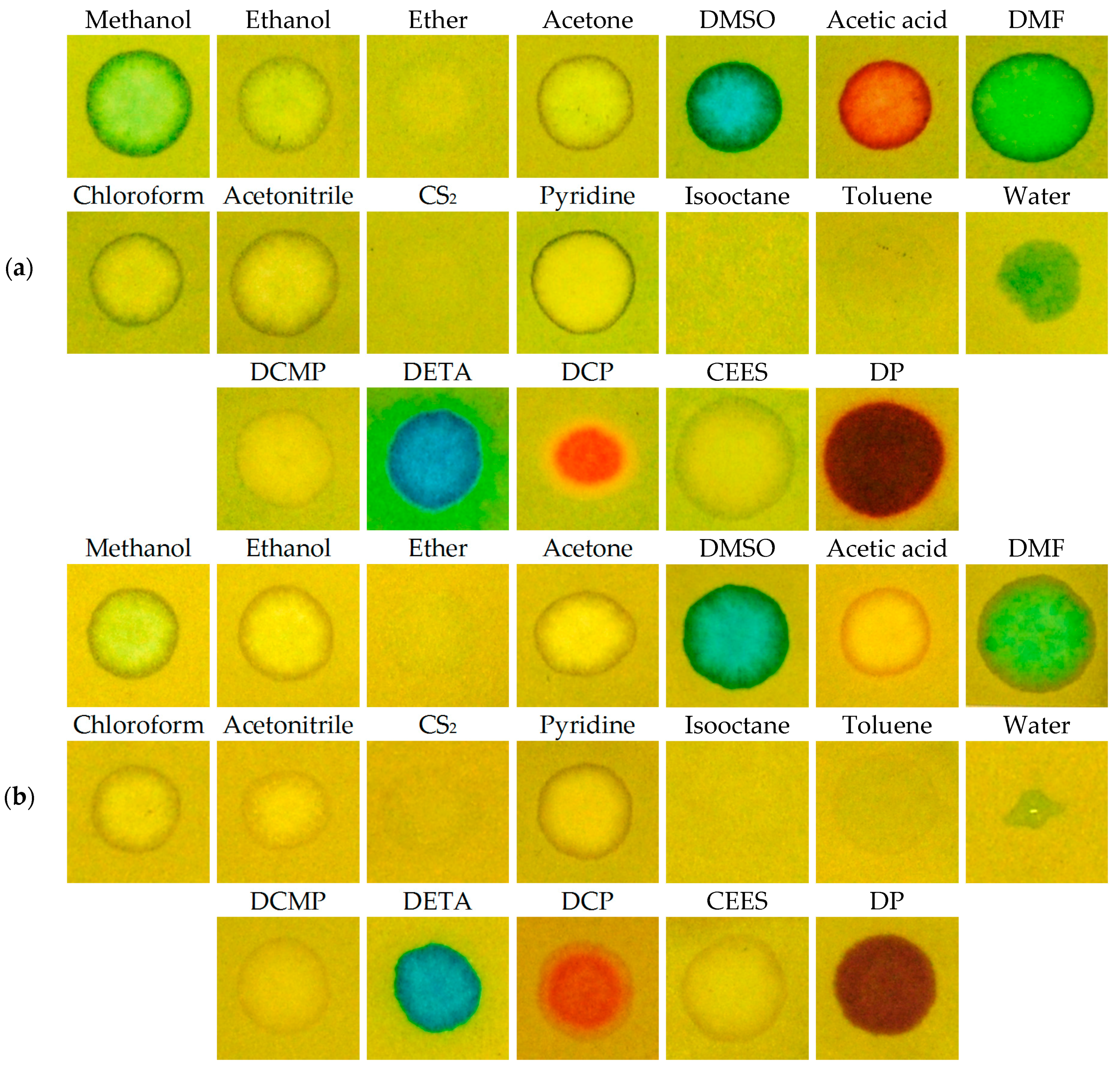
We also paid attention to the study of interferences of chemical substances, which are not CWAs, but might be present as stabilizers, tactical ingredients, or might be present for other reasons. We verified the representatives of all types of organic solvents (polar, non-polar, aprotic) for causing interferences, as well as other chemicals. The RM1a detection papers, or, the RM1a/PY-OPD detection papers proved themselves as being highly resistant against the interferences, only the acetic acid provided a color response; the circles at RM1a/PY-OPD were created due to “reagent elution” (Figure 10). The RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG detection papers were less resistant against the interference with these organic compounds, but still much more resistant than known M8, M9, CALID-3 detectors (we verified the selectivity of these detectors experimentally).
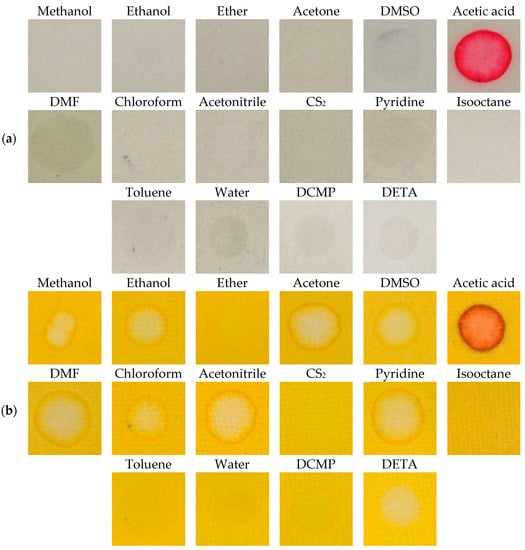
Figure 10.
Color response (a) RM1a, (b) RM1a/PY-OPD to selected chemicals (DMSO—dimethyl sulfoxide, DMF—dimethylformamide, DCMP diethyl cyanomethylphosphonate, DETA—diethylenetriamine).
The influence of water is shown to be an issue. In liquid CWAs, there is no water present, so its interference can practically be neglected from this point of view. However, water can be present as a medium of other toxic substances (such as pesticides), which may be sprayed, or it can be present as a rain or fog. We proved the RM1a and RM1a/PY-OPD detection papers were resistant against water drops. Unlike the reaction of the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG, detection paper’s reaction to water created only smaller, but relatively intensive green dots. For this reason, we modified the surface of the detection paper with hydrophobic colophon resin, which prevents the contact of chemosensors (preferentially with BCG) with water, but it lets the liquid CWA get through and does not block their color response. The disadvantage of the colophon resin is its content of an acid ingredient (abietic acid), which affects the color hues of the stains to a certain extent (this was apparent at V agents, showing a blue–green shift). The appearance of color stains before and after the modification of the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG detection paper using the colophon is documented in Figure 11.
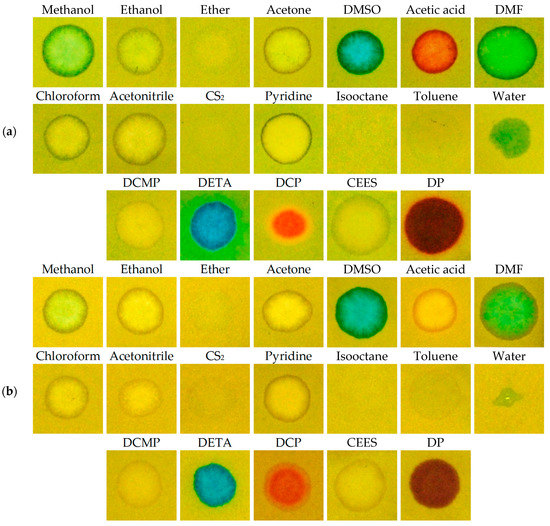
Figure 11.
Color response (a) RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG, (b) RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG/colophon to selected chemicals (DMSO—dimethyl sulfoxide, DMF—dimethylformamide, DCMP—diethyl cyanomethylphosphonate, DETA—diethylenetriamine).
3.6. Effects of Dilution
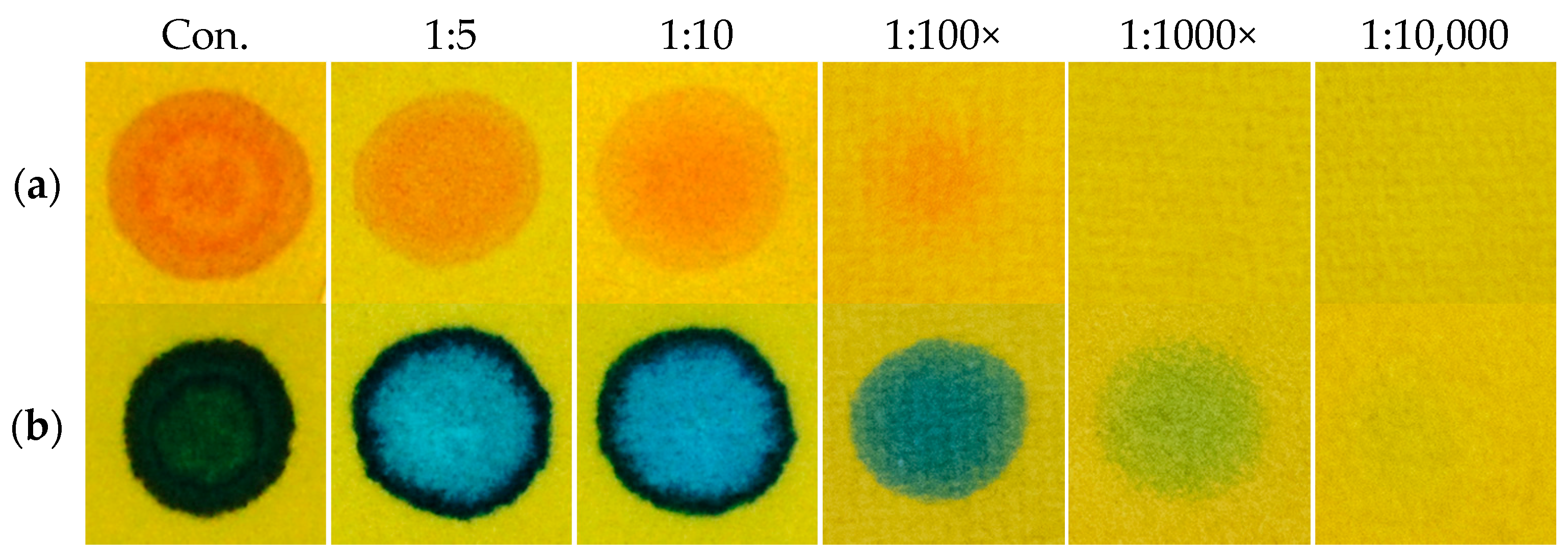
One of the basic characteristics of CWA detection papers is that they must allow the detection of substances in their concentrated form, or in mixture with stabilizers or thickeners. By this, the issue of the detection limit gets significantly simplified. You might even say that the relatively lower sensitivity is rather an advantage for the detection of droplets, since many potential interferences are eliminated in this way. Despite this, we verified the influence of the dilution of real CWA (in chloroform) to the intensity of generated color, or, to the detection paper function. In Figure 12, it is proved that the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG/colophon detection paper (as the most complex of all designed detectors) provided a color response even after the 100-fold dilution of GD or 1000-fold dilution of VX. In conclusion, the detection limits of CWAs (nerve agents, lewisite, DP) range from 0.001 to 0.1 mg/µL, which satisfies the requirements for their detection in the liquid phase (for example, primary liquid aerosol cloud) in field conditions.
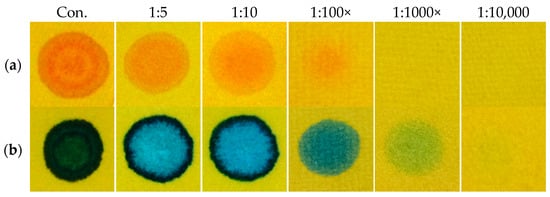
Figure 12.
Influence of CWA dilution to the RM1a/PY-OPD/BCG/colophon detection paper colour intensity, (a) GD, (b) VX.
4. Conclusions
The results of the experimental development of detection paper for the detection of CWAs in liquid phase showed that the strategy of usage and the combination of the latest world findings in the area of the investigation of chromogenic sensors (RM1a, PY-OPD) with traditional analytical agents (BCG) is highly effective. This strategy enabled the authors to design and verify the detection papers for a whole range of potential CWA, which might occur in the form of droplets, or variously dispersed aerosol, even with the possibility of their color distinction. Practically, the only CWA which did not provide a positive color response, was sulfur mustard. Greater efforts will therefore be dedicated to this resolving this issue in the future.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, V.P. and L.M.; methodology, V.P., L.M. and M.D.; validation, V.P., L.M. and M.D.; formal analysis, L.M. and M.D.; resources, M.U., K.L. and L.K.; data curation, V.P., L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, V.P.; writing—review and editing, V.P., L.M. and K.L.; visualization, V.P., L.M. and M.D.; supervision, V.P., M.U. and L.K.; project administration, V.P.
Funding
The work was funded in the framework of a security research project of the Ministry of Interior of the Czech Republic, No. VI20172019101.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guidotti, M.; Trifirò, F. Chemical risk and chemical warfare agents: Science and technology against humankind. Toxicol. Environ. Chem. 2016, 98, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciottone, G.R. Toxidrome recognition in chemical weapons attacks. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 1611–1620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lillie, S.H.; Hanlon, E., Jr.; Kelly, J.M.; Rayburn, B.B. Potential military chemical (biological) agents and compounds. In Field Manual FM 3-11.9; Exidyne: Wentzeville, MO, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Halámek, E.; Kobliha, Z.; Pitschmann, V. Analysis of Chemical Warfare Agents; University of Defence: Brno, Czech Republic, 2009; p. 39. [Google Scholar]
- Franke, S. Lehrbuch der Militärchemie; Militärverlag der DDR: Berlin, Germany, 1977; Volume 2, p. 494. [Google Scholar]
- Thoraval, D.; Bovenkamp, J.W. Paper Chemical Agent Detectors. EP 0 334 668 B1, 23 December 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.; Wu, D.; Yoon, J. Recent advances in the developments of chromophore-based chemosensors for nerve agents and phosgene. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 27–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kangas, M.J.; Burks, R.M.; Atwater, J.; Lukowicz, R.M.; Williams, P.; Holmes, A.E. Colorimetric sensor arrays for the detection and identification of chemical weapons and explosives. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2017, 47, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weis, J.G.; Swager, T.M. Thiophene-fused tropones as chemical warfare agent-responsive building blocks. ACS Macro Lett. 2015, 4, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ordroneau, L.; Carella, A.; Pohanka, M.; Simonato, J.P. Chromogenic detection of sarin by discolouring decomplexation of a metal coordination complex. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 8946–8948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Zeng, Y.; Liyan, C.; Wu, X.; Yoon, J. A fluorescent sensor for dual-channel discrimination betwen phosgene and a nerve-gas mimic. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 4729–4733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belger, C.; Weis, J.G.; Egap, E.; Swager, T.M. Colorimetric stimuli-responsive hydrogel polymers for the detection of nerve agent surrogates. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 7990–7994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Yu, J.; Wang, K.; Kiu, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, A.; Peng, X.; He, Q.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J. Simple and efficient chromophonic-fluorogenic probes for diethylchlorophosphate vapor. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 1445–1450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.C.; Song, Q.H. Fluorescent chemosensors with varying degrees of intramolecular charge transfer for detection of a nerve agent mimic in solution and in vapor. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, Z.; Han, S. Chromogenic and fluorogenic detection of a nerve agent simulants with a rhodamine-deoxylactam based sensor. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 11468–11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Raviraju, G.; Rana, H.; Rao, V.K.; Gupta, A.K. Highly selective and sensitive chromogenic detection of nerve agents (sarin, tabun and VX): A multianalyte detection approach. Chem. Commun. 2017, 53, 12954–12957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, Z.; Yang, Y. A concise colorimetric and fluorimetric probe for sarin related threats designed via the “covalent-assembly” approach. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 6594–6597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barba-Bon, A.; Costero, A.M.; Gil, S.; Martínez-Manez, R.; Sancenón, F. Selective chromo-fluorogenic detection of DFP (a sarin and soman mimic) and DCNP (a tabun mimic) with unique probe based on a boron dipyrromethene (BODIPY) dye. Organ. Biomol. Chem. 2014, 43, 8745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Royo, S.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S.; Martínez-Manez, R.; Sancenón, F. Chromogenic, specific detection of the nerve-agent mimic DCNP (a tabun mimic). Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 6931–6934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Anslyn, E.V. A selective and sensitive chromogenic and fluorogenic detection of a sulfur mustard simulant. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 4292–4297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goud, D.R.; Purohit, A.K.; Tak, V.; Dubey, D.K.; Kumar, P.; Pardasani, D. A highly selective and sensitive “turn-on” fluorescence chemodosimeter for the detection of mustard gas. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12363–12366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Guan, J.; Han, X.; Chen, S.-W.; Li, T.; Zhang, Y.; Yuan, M.-S.; Wang, J. Benzothiazole modified rhodol as chemodosimetr for the detection of sulfur mustard simulant. Talanta 2018, 189, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, V.; Rana, H.; Raviraju, G.; Gupta, A.K. Chemodosimetr for selective and sensitive chromogenic and fluorogenic detection of mustard gas for real time analysis. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 1417–1422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Lv, Y.; Wang, X.; Peng, A.; Zhang, K.; Jie, X.; Huanh, J.; Tian, Z. A turn-on fluorescent probe for detection of sub-ppm levels of a sulfur-mustard simulant with high selectivity. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5481–5488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitschmann, V.; Matějovský, L. New carrier made from glass nanofibers for the colorimetric biosensor of cholinesterase inhibitors. Biosensors 2018, 8, 51. [Google Scholar]
- CALID-3 & CALID-3P. Available online: https://www.oritest.cz/wp-content/uploads/2017/12/CALID-3and3P.pdf (accessed on 4 April 2019).
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).