Nanoporous Silica-Dye Microspheres for Enhanced Colorimetric Detection of Cyclohexanone
Abstract
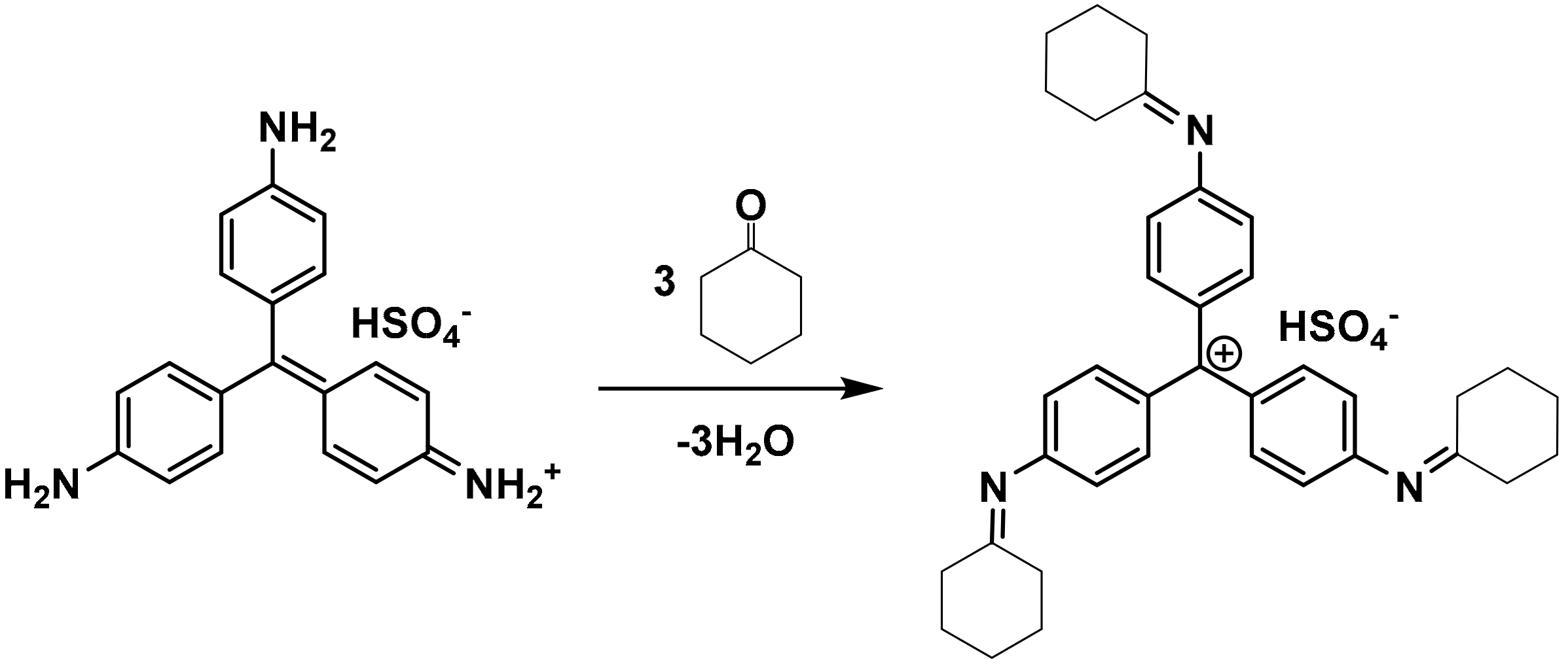
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Methods
2.1. Reagents and Materials
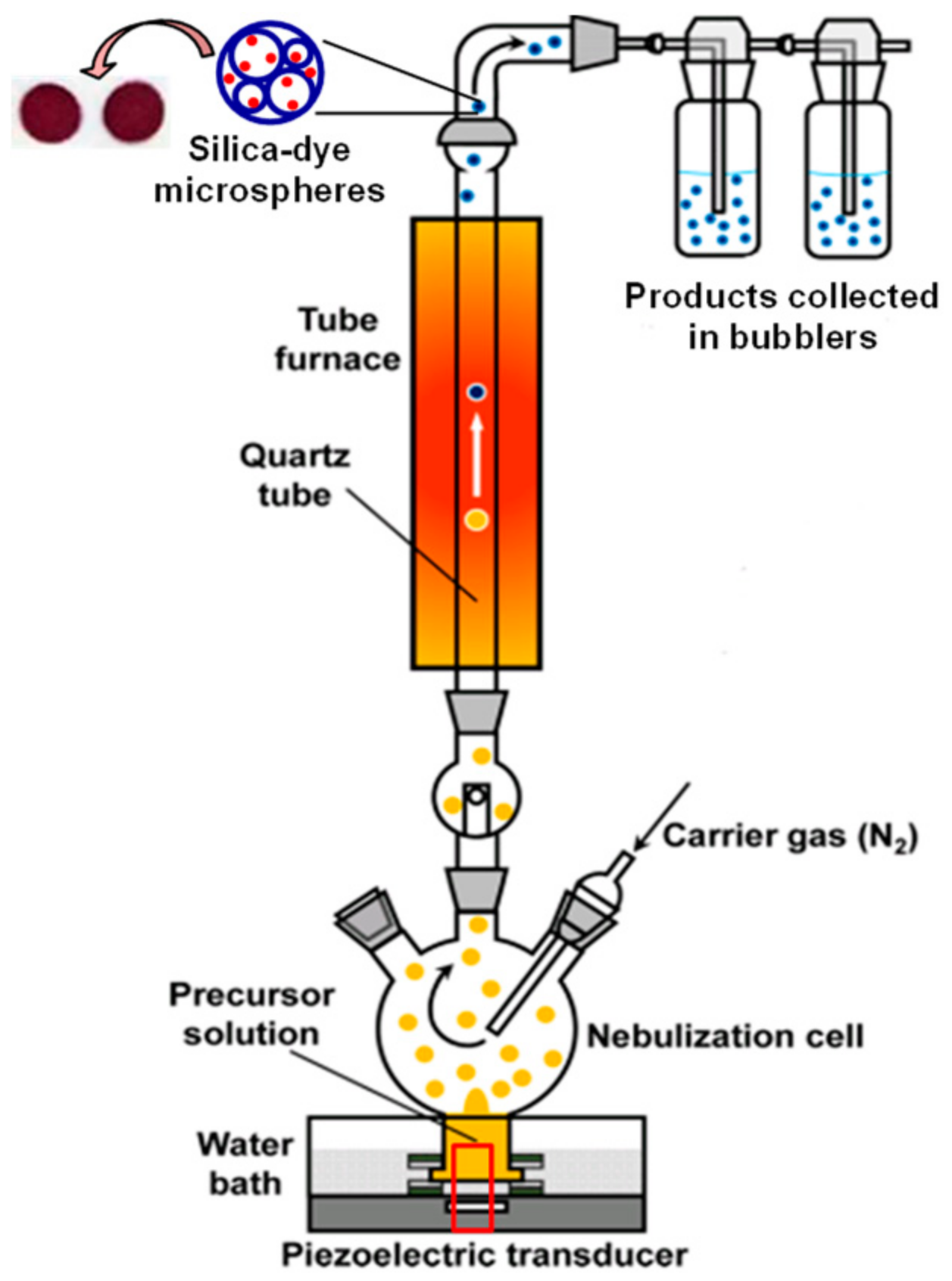
2.2. Preparation of Silica-Dye Composite Microspheres
2.3. Material Characterization
2.4. Preparation of the Paper-Based Sensor
2.5. Measurement of Gaseous Cyclohexanone
2.6. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussions
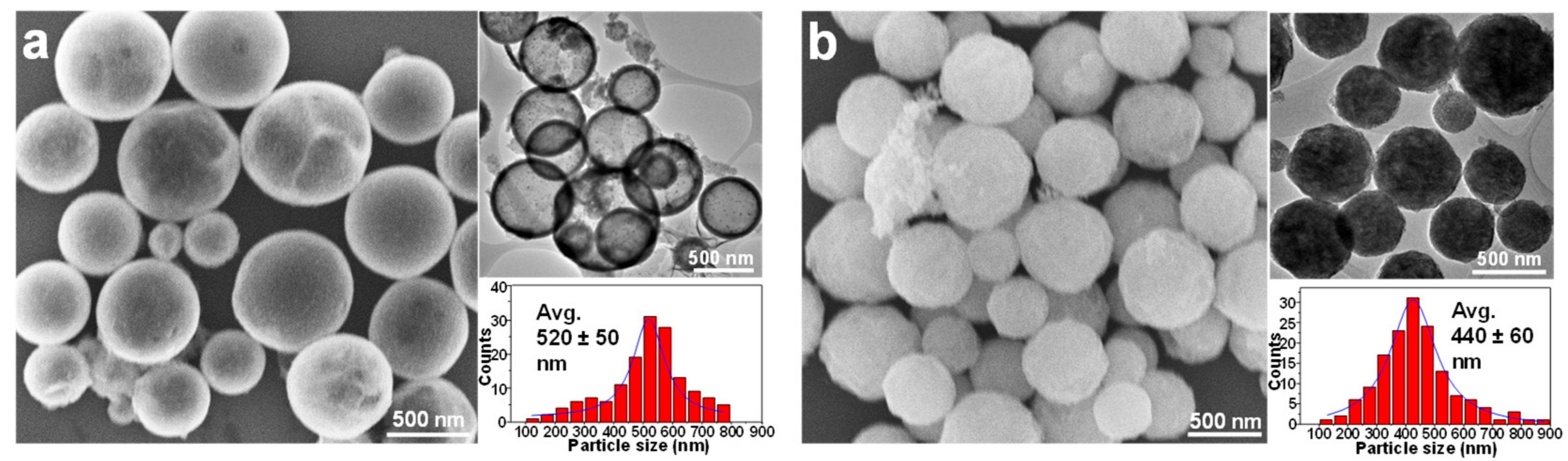
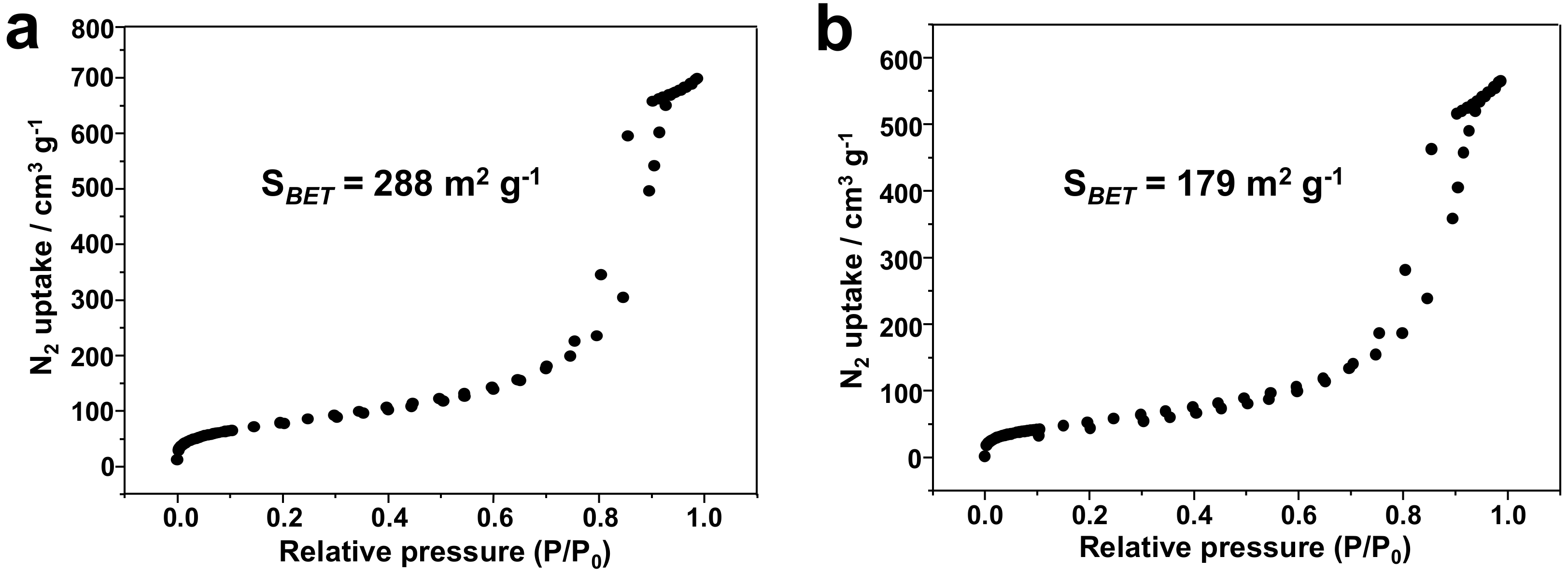
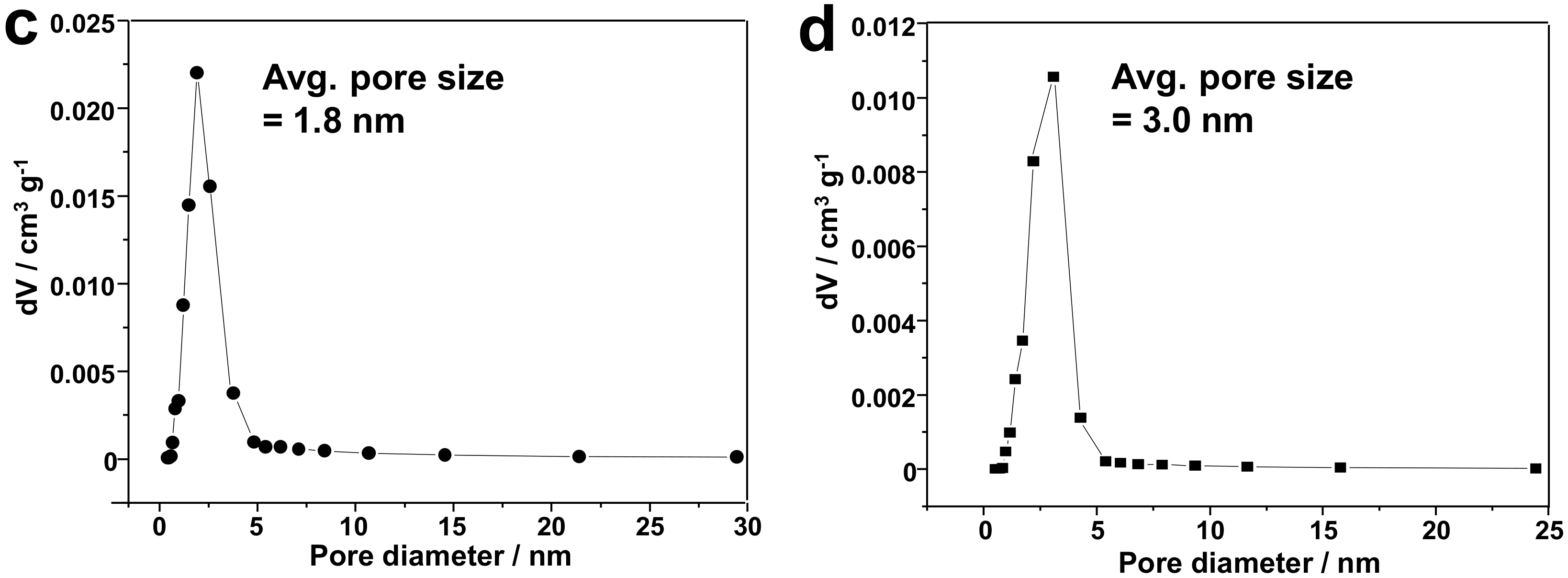
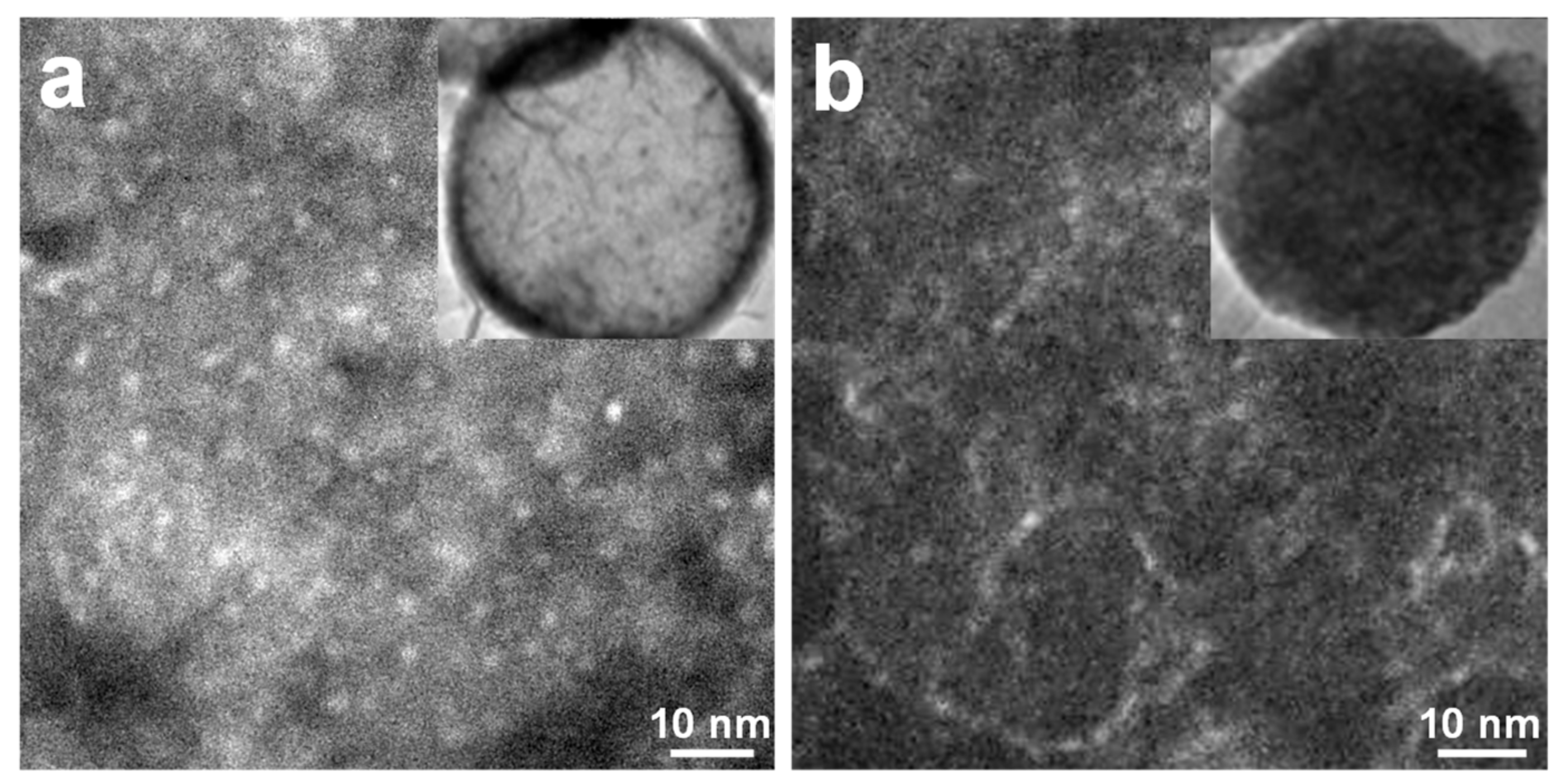
3.1. Silica-Dye Composite Microspheres
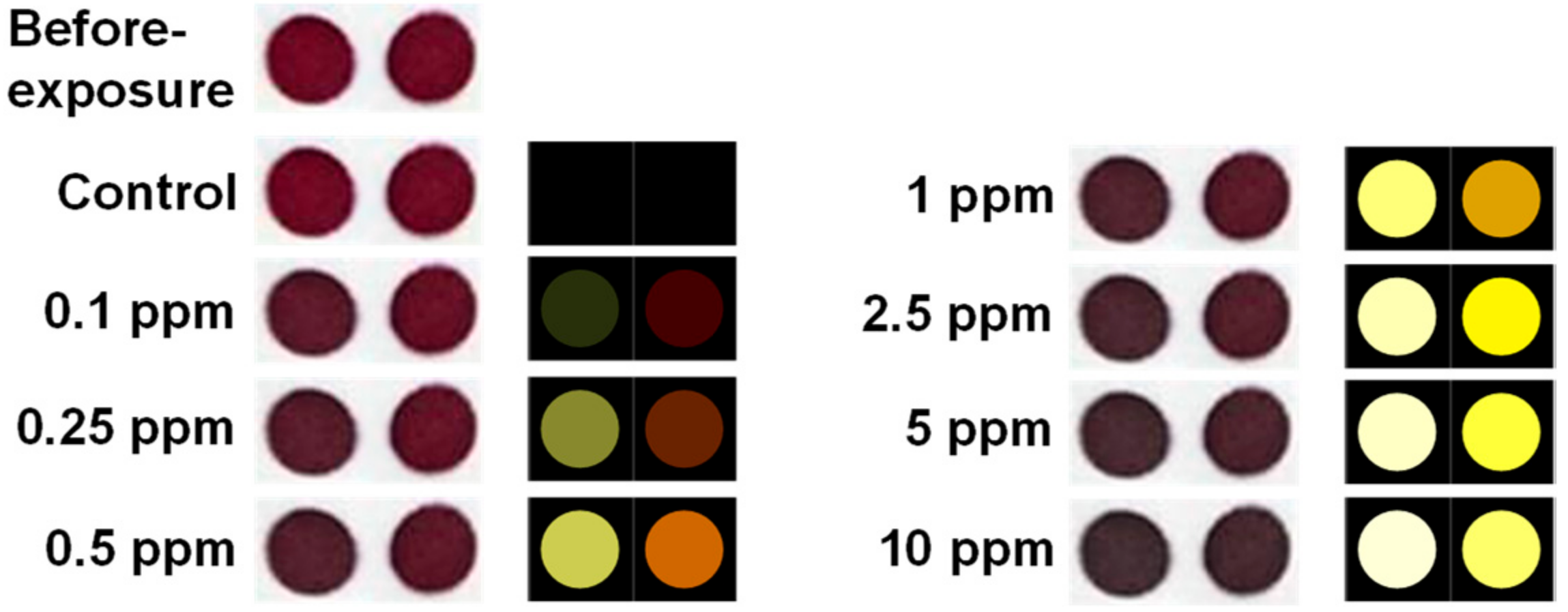
3.2. Sensor Responses of Gaseous Cyclohexanone
3.3. Discussions: Influence of Nanostructure on Sensing Properties
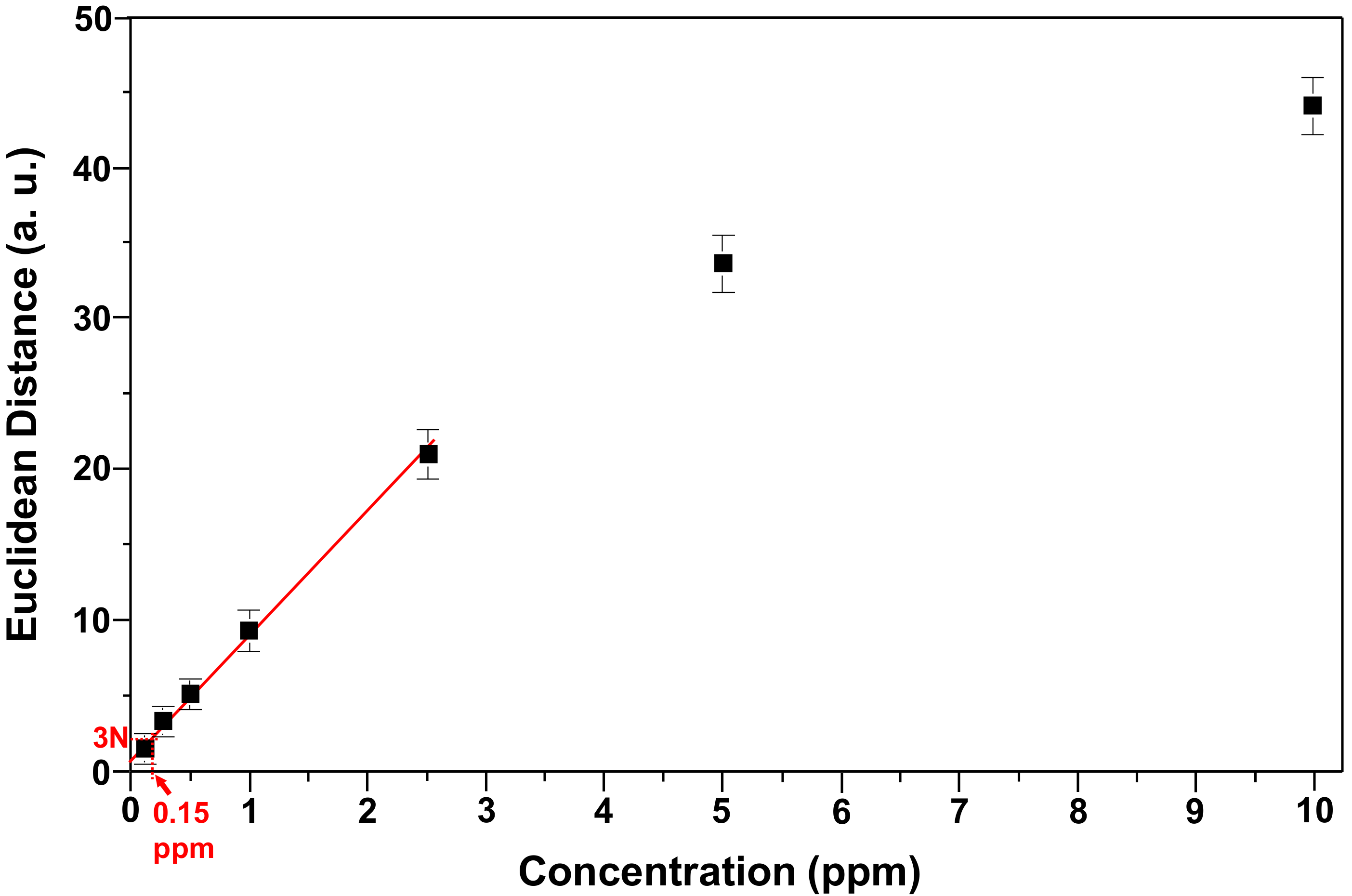
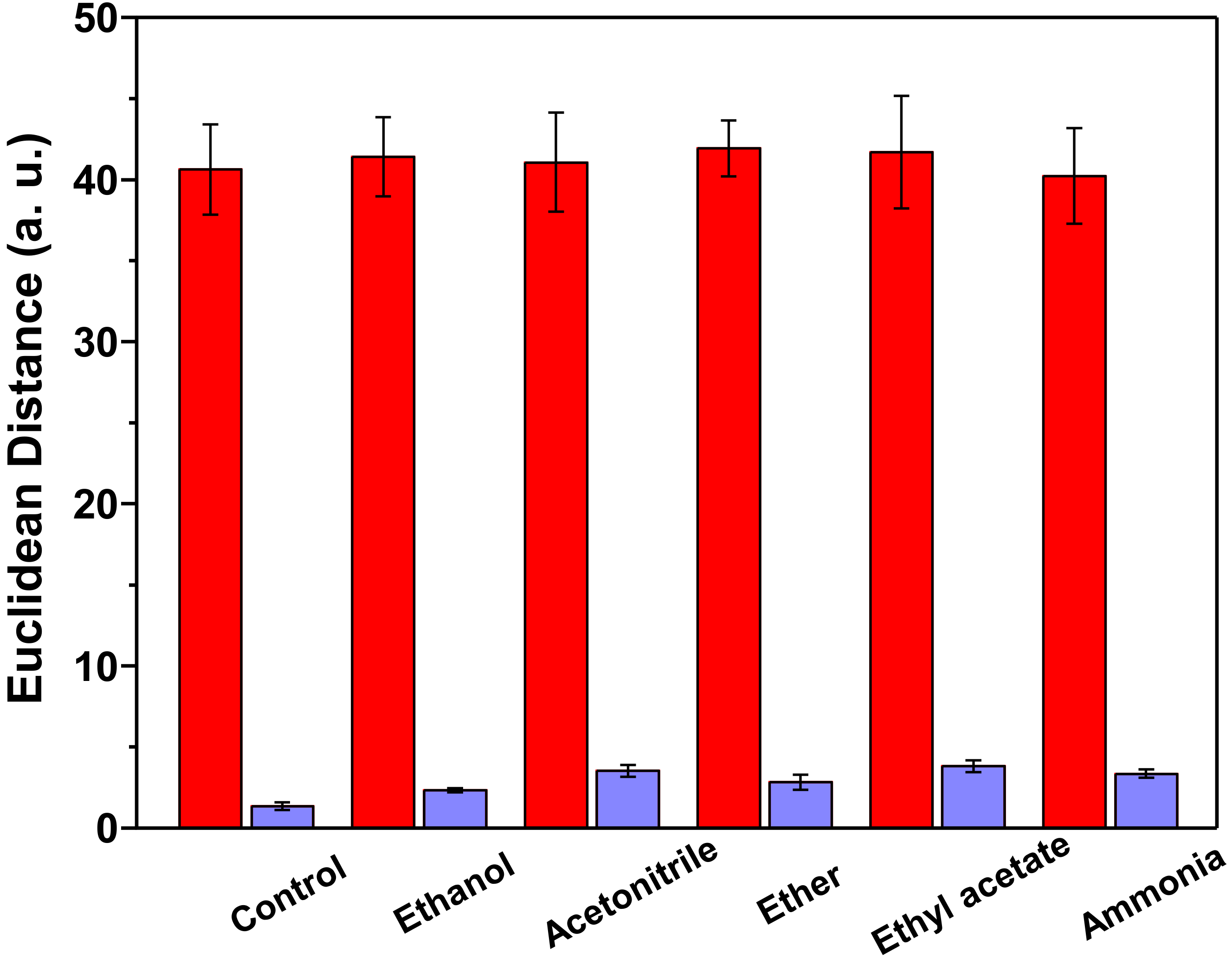
3.4. Limit of Detection and Specificity
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yinon, J. Counterterrorist Detection Techniques of Explosives; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Strobbia, P.; Odion, R.; Vo-Dinh, T. Spectroscopic chemical sensing and imaging: From plants to animals and humans. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Chen, J. Systematic study of the reaction kinetics for HMX. J. Phys. Chem. A 2015, 119, 4073–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, S.; Deb, U.; Datta, S.; Walther, C.; Gupta, D.K. Common explosives (TNT, RDX, HMX) and their fate in the environment: Emphasizing bioremediation. Chemosphere 2017, 184, 438–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, H.; Leung, A.; Magee, M.; Almirall, J.R. Identification of volatile chemical signatures from plastic explosives by SPME-GC/MS and detection by ion mobility spectrometry. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2010, 396, 2997–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.; Xia, M.; Lei, W.; Wang, F.; Gong, X. Prediction of crystal morphology of cyclotrimethylene trinitramine in the solvent medium by computer simulation: A case of cyclohexanone solvent. J. Phys. Chem. A 2014, 118, 11471–11478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, T.-H.; Mendum, T.; Geurtsen, G.; Kelley, J.; Ostrinskaya, A.; Kunz, R. Use of mass spectrometric vapor analysis to improve canine explosive detection efficiency. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6482–6490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.M.; Jiang, T.; Tang, Y.; Xu, W. A simple desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization method for enhanced non-volatile sample analysis. Anal. Chim. Acta 2018, 1002, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zamora, D.; Amo-Gonzalez, M.; Lanza, M.; Fernández de la Mora, G.; Fernández de la Mora, J. Reaching a vapor sensitivity of 0.01 parts per quadrillion in the screening of large volume freight. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 2468–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefanuto, P.-H.; Perrault, K.; Focant, J.-F.; Forbes, S. Fast chromatographic method for explosive profiling. Chromatography 2015, 2, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strle, D.; Štefane, B.; Trifkovič, M.; Van Miden, M.; Kvasić, I.; Zupanič, E.; Muševič, I. Chemical selectivity and sensitivity of a 16-channel electronic nose for trace vapour detection. Sensors 2017, 17, 2845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patil, S.J.; Duragkar, N.; Rao, V.R. An ultra-sensitive piezoresistive polymer nano-composite microcantilever sensor electronic nose platform for explosive vapor detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bassett, W.P.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. Differentiation among peroxide explosives with an optoelectronic nose. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15312–15315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staymates, M.E.; MacCrehan, W.A.; Staymates, J.L.; Kunz, R.R.; Mendum, T.; Ong, T.-H.; Geurtsen, G.; Gillen, G.J.; Craven, B.A. Biomimetic sniffing improves the detection performance of a 3D printed nose of a dog and a commercial trace vapor detector. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roscioli, K.M.; Davis, E.; Siems, W.F.; Mariano, A.; Su, W.; Guharay, S.K.; Hill, H.H. Modular ion mobility spectrometer for explosives detection using corona ionization. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 5965–5971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senesac, L.; Thundat, T.G. Nanosensors for trace explosive detection. Mater. Today 2008, 11, 28–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Hua, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Li, H. On-site rapid detection of trace non-volatile inorganic explosives by stand-alone ion mobility spectrometry via acid-enhanced evaporization. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.-S.; Son, C.E. Analytical method for the estimation of transfer and detection efficiencies of solid state explosives using ion mobility spectrometry and smear matrix. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 2505–2510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujahid, A.; Dickert, F. Surface acoustic wave (SAW) for chemical sensing applications of recognition layers. Sensors 2017, 17, 2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, D.; Chen, X.; Wang, C.-C.; Trivedi, S.; Choa, F.-S. Stand-off chemical detection using photoacoustic sensing techniques—From single element to phase array. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimal, A.T.; Mittal, U.; Singh, M.; Khaneja, M.; Kannan, G.K.; Kapoor, J.C.; Dubey, V.; Gutch, P.K.; Lal, G.; Vyas, K.D.; et al. Development of handheld SAW vapor sensors for explosives and CW agents. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 135, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Calvo, J.; Calvo-Gredilla, P.; Ibáñez-Llorente, M.; Romero, D.C.; Cuevas, J.V.; García-Herbosa, G.; Avella, M.; Torroba, T. Surface functionalized silica nanoparticles for the off–on fluorogenic detection of an improvised explosive, tatp, in a vapour flow. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 4416–4423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.-Y.; Ruan, L.-W.; Jiang, X.; Qiu, L.-G. Trace detection of nitro aromatic explosives by highly fluorescent g-C3N4 nanosheets. Analyst 2015, 140, 637–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Liu, H.; Liu, A.; Xu, W.; Fu, Y.; He, Q.; Cao, H.; Cheng, J. Ultrasensitive and direct fluorescence detection of RDX explosive vapor via side-chain terminal functionalization of a polyfluorene probe. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Huang, H.; Bunes, B.R.; Wu, N.; Xu, M.; Yang, X.; Yu, L.; Zang, L. Trace detection of RDX, HMX and PETN explosives using a fluorescence spot sensor. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malik, A.K.; Rai, P.K. Development of a new SPME–HPLC–UV method for the analysis of nitro explosives on reverse phase amide column and application to analysis of aqueous samples. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 172, 1652–1658. [Google Scholar]
- Bianchi, F.; Bedini, A.; Riboni, N.; Pinalli, R.; Gregori, A.; Sidisky, L.; Dalcanale, E.; Careri, M. Cavitand-based solid-phase microextraction coating for the selective detection of nitroaromatic explosives in air and soil. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 10646–10652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McEneff, G.L.; Murphy, B.; Webb, T.; Wood, D.; Irlam, R.; Mills, J.; Green, D.; Barron, L.P. Sorbent film-coated passive samplers for explosives vapour detection part A: Materials optimisation and integration with analytical technologies. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 5815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albert, K.J.; Lewis, N.S.; Schauer, C.L.; Sotzing, G.A.; Stitzel, S.E.; Vaid, T.P.; Walt, D.R. Cross-reactive chemical sensor arrays. Chem. Rev. 2000, 100, 2595–2626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Suslick, K.S. Ultrasonic preparation of porous silica-dye microspheres: Sensors for quantification of urinary trimethylamine N-oxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 15820–15828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Askim, J.R.; Li, Z.; LaGasse, M.K.; Rankin, J.M.; Suslick, K.S. An optoelectronic nose for identification of explosives. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, H.; LaGasse, M.K.; Suslick, K.S. Rapid quantification of trimethylamine. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 5615–5620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Jang, M.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. Identification of accelerants, fuels and post-combustion residues using a colorimetric sensor array. Analyst 2015, 140, 5929–5935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nery, E.W.; Kubota, L.T. Sensing approaches on paper-based devices: A review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 7573–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Suslick, K.S. Portable optoelectronic nose for monitoring meat freshness. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 1330–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodasevych, I.; Parmar, S.; Troynikov, O. Flexible sensors for pressure therapy: Effect of substrate curvature and stiffness on sensor performance. Sensors 2017, 17, 2399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burleigh, M.C.; Markowitz, M.A.; Spector, M.S.; Gaber, B.P. Porous organosilicas: An acid-catalyzed approach. Langmuir 2001, 17, 7923–7928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Yan, F.; Yao, M.; Wei, Z.; Zhou, D.; Yao, H.; Zheng, H.; Chen, H.; Shi, J. Template-free synthesis of hollow/porous organosilica–Fe3O4 hybrid nanocapsules toward magnetic resonance imaging-guided high-intensity focused ultrasound therapy. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29986–29996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, G.; Peng, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Lü, J.; Fang, Y. One-step synthesis of hydrophobic multicompartment organosilica microspheres with highly interconnected macro-mesopores for the stabilization of liquid marbles with excellent catalysis. Langmuir 2017, 33, 5223–5235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiang, Z.; Guo, Y.; Liu, H.; Cheng, S.Z.D.; Cakmak, M.; Cavicchi, K.A.; Vogt, B.D. Large-scale roll-to-roll fabrication of ordered mesoporous materials using resol-assisted cooperative assembly. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 4306–4310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skrabalak, S.E.; Suslick, K.S. Porous MoS2 synthesized by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. JACS 2005, 127, 9990–9991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bang, J.H.; Helmich, R.J.; Suslick, K.S. Nanostructured ZnS: Ni2+ photocatalysts prepared by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 2599–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zeiger, B.W.; Suslick, K.S. Sonochemical synthesis of nanomaterials. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 2555–2567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jerónimo, P.C.A.; Araújo, A.N.; Montenegro, M.C.B.S.M. Optical sensors and biosensors based on sol-gel films. Talanta 2007, 72, 13–27. [Google Scholar]
- Yao, N.; Xiong, G.; Yeung, K.L.; Sheng, S.; He, M.; Yang, W.; Liu, X.; Bao, X. Ultrasonic synthesis of silica-alumina nanomaterials with controlled mesopore distribution without using surfactants. Langmuir 2002, 18, 4111–4117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Halder, S.; Guha, A.; Bandyopadhyay, S. Highly selective sub-ppm naked-eye detection of hydrazine with conjugated-1,3-diketo probes: Imaging hydrazine in Drosophila larvae. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10625–10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Tu, J.; Sun, S.; Pei, Z.; Pei, Y.; Pang, Y.; Xu, Y. A fluorescent probe for hydrazine and its in vivo applications. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 41807–41811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baud, D.; Ladkau, N.; Moody, T.S.; Ward, J.M.; Hailes, H.C. A rapid, sensitive colorimetric assay for the high-throughput screening of transaminases in liquid or solid-phase. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 17225–17228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dilek, O.; Bane, S. Turn on fluorescent probes for selective targeting of aldehydes. Chemosensors 2016, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Suslick, K.S. A hand-held optoelectronic nose for the identification of liquors. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrett, E.P.; Joyner, L.G.; Halenda, P.P. The determination of pore volume and area distributions in porous substances. I. Computations from nitrogen isotherms. JACS 1951, 73, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, K.M.; Swager, T.M. Robust cyclohexanone selective chemiresistors based on single-walled carbon nanotubes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7154–7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Fang, M.; LaGasse, M.K.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. Colorimetric recognition of aldehydes and ketones. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 56, 9860–9863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, Z. Nanoporous Silica-Dye Microspheres for Enhanced Colorimetric Detection of Cyclohexanone. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030034
Li Z. Nanoporous Silica-Dye Microspheres for Enhanced Colorimetric Detection of Cyclohexanone. Chemosensors. 2018; 6(3):34. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030034
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Zheng. 2018. "Nanoporous Silica-Dye Microspheres for Enhanced Colorimetric Detection of Cyclohexanone" Chemosensors 6, no. 3: 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030034
APA StyleLi, Z. (2018). Nanoporous Silica-Dye Microspheres for Enhanced Colorimetric Detection of Cyclohexanone. Chemosensors, 6(3), 34. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030034




