Characterization of a Novel Polypyrrole (PPy) Conductive Polymer Coated Patterned Vertical CNT (pvCNT) Dry ECG Electrode
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. pvCNT Electrode Fabrication and Coating
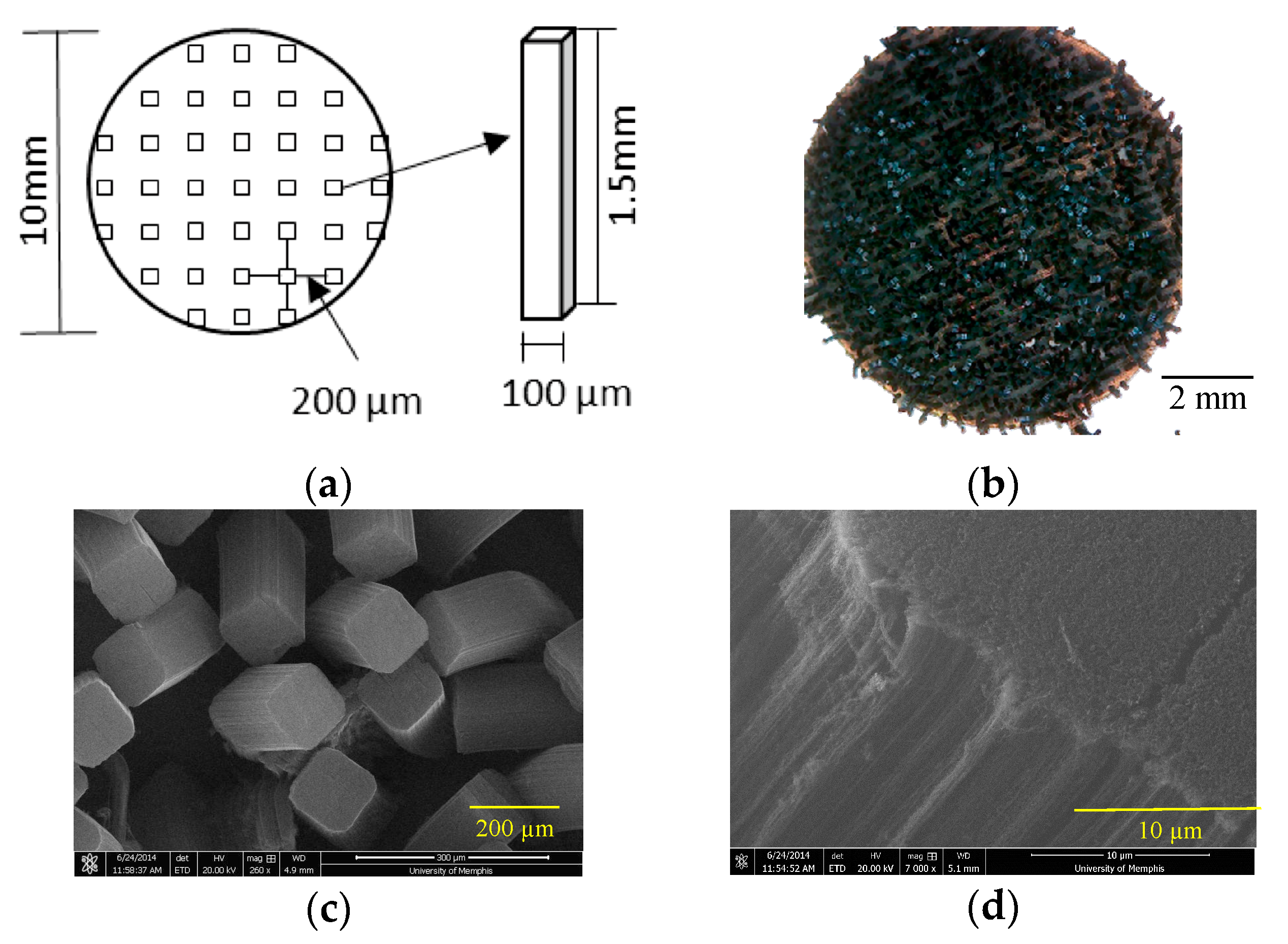
2.1. pvCNT Fabrication
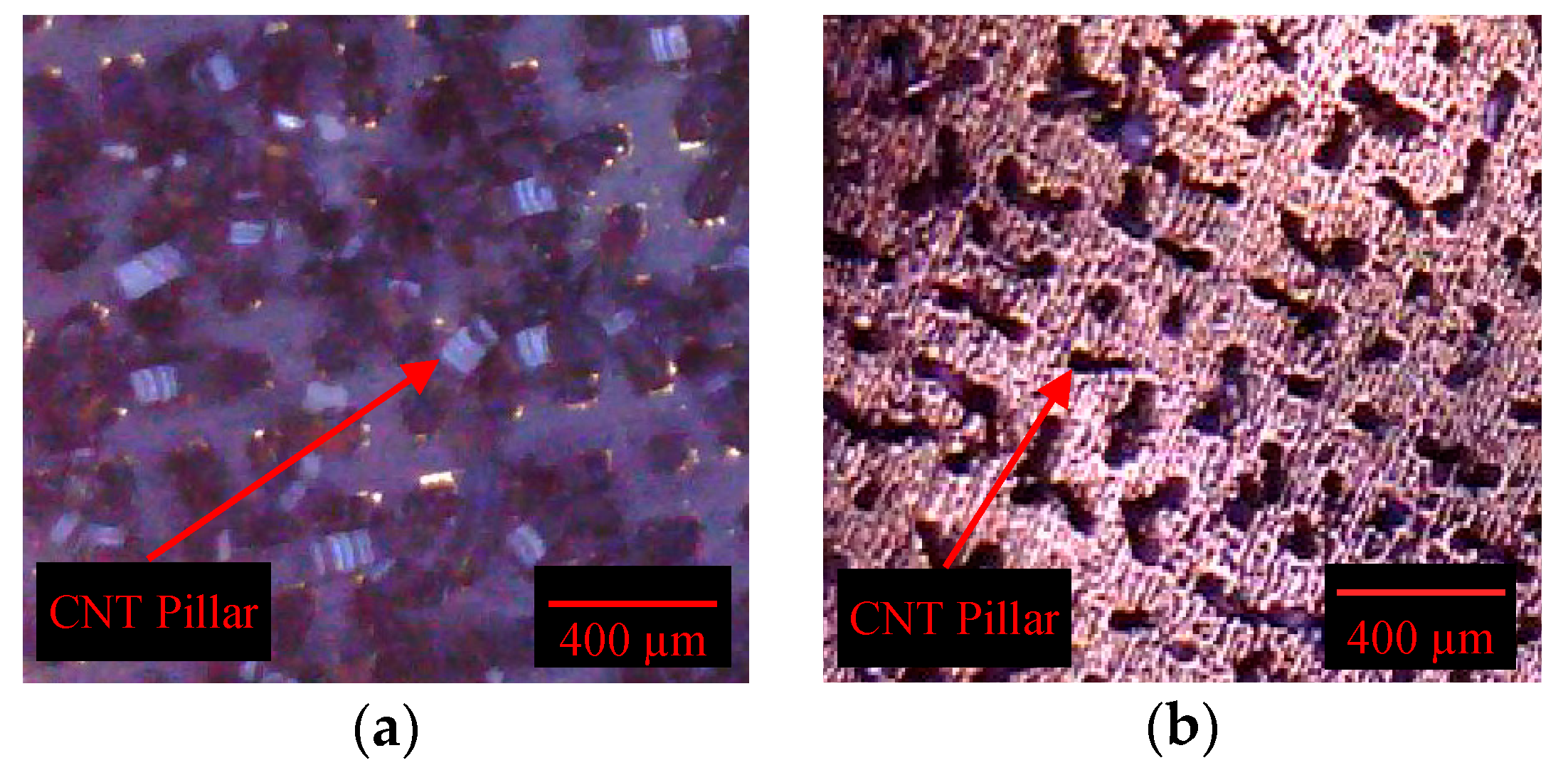
2.2. PPy Coating Procedure
3. Experimental Method and Setup
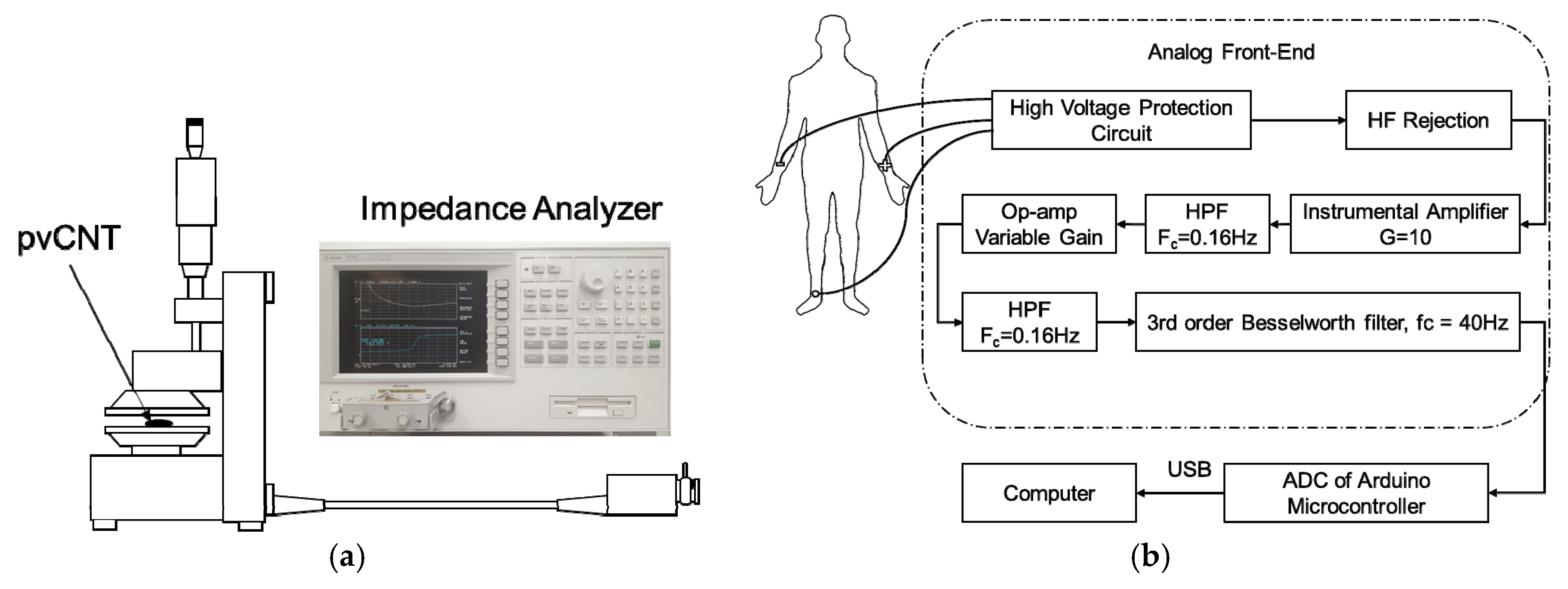
3.1. PPy-coated pvCNT Electrode Conductivity Measurement
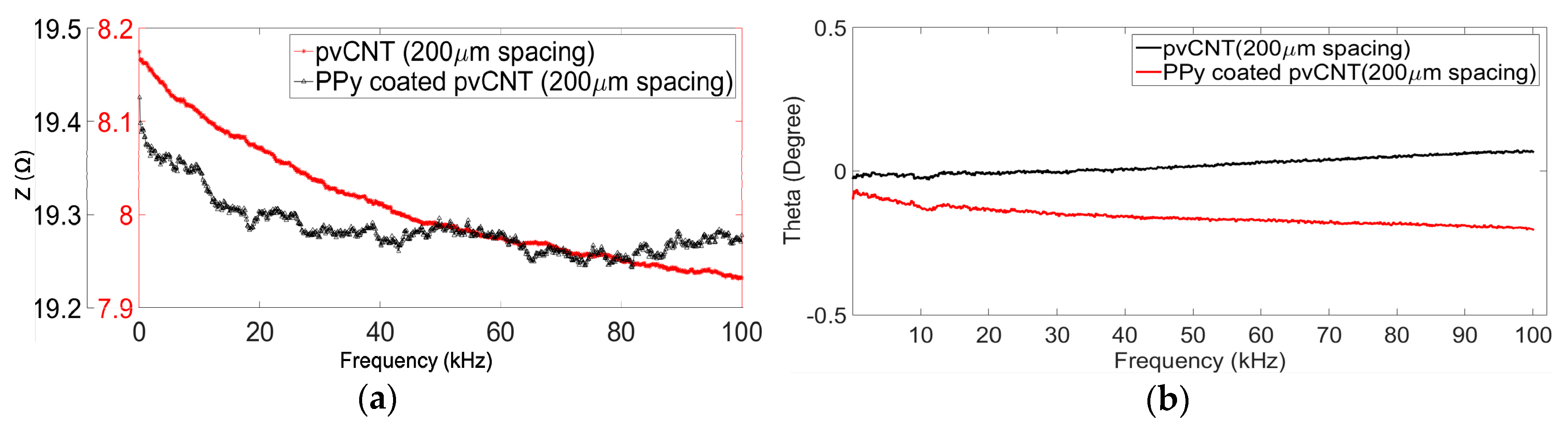
3.1.1. Impedance Measurement before and after Coating
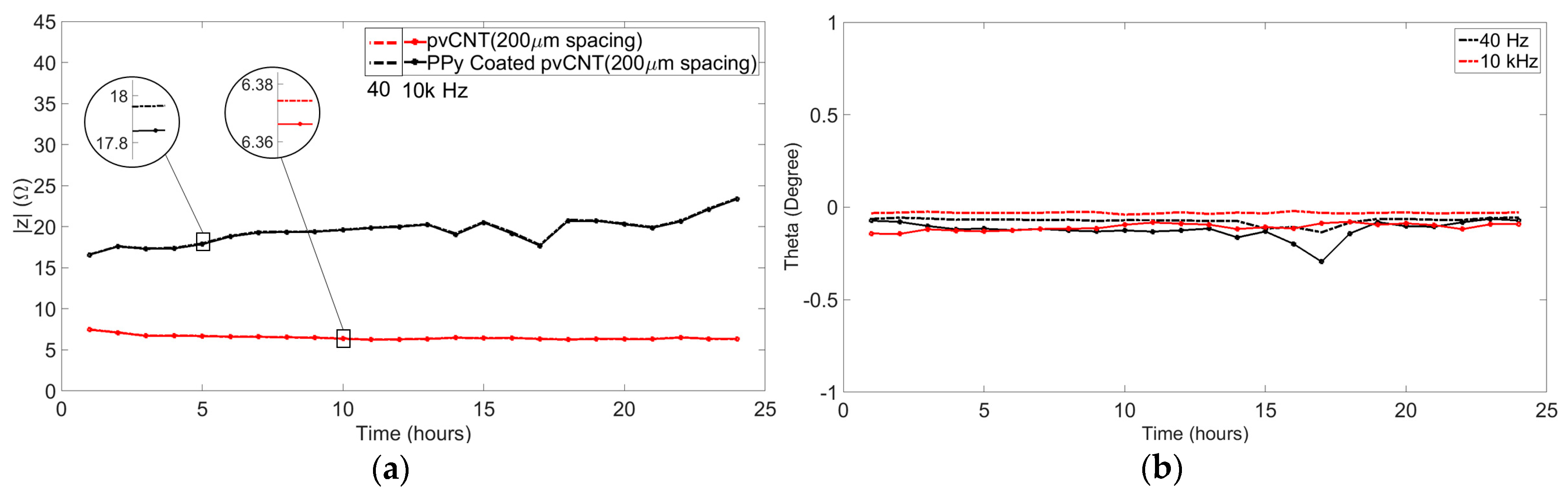
3.1.2. Long-Term Impedance Measurement
3.2. In Vitro Signal Capture
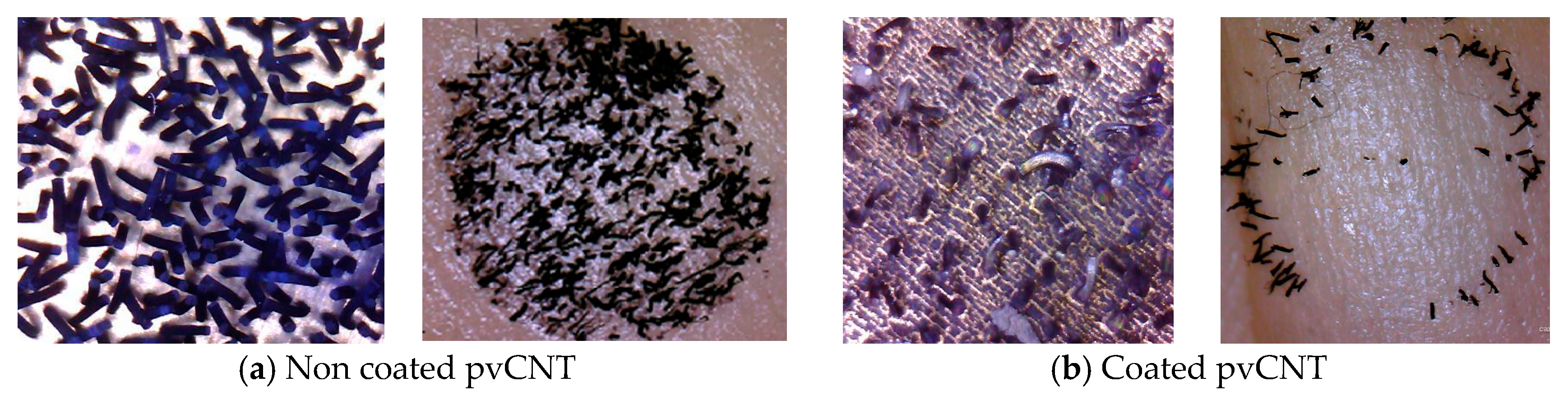
3.3. Peel-Off Tests
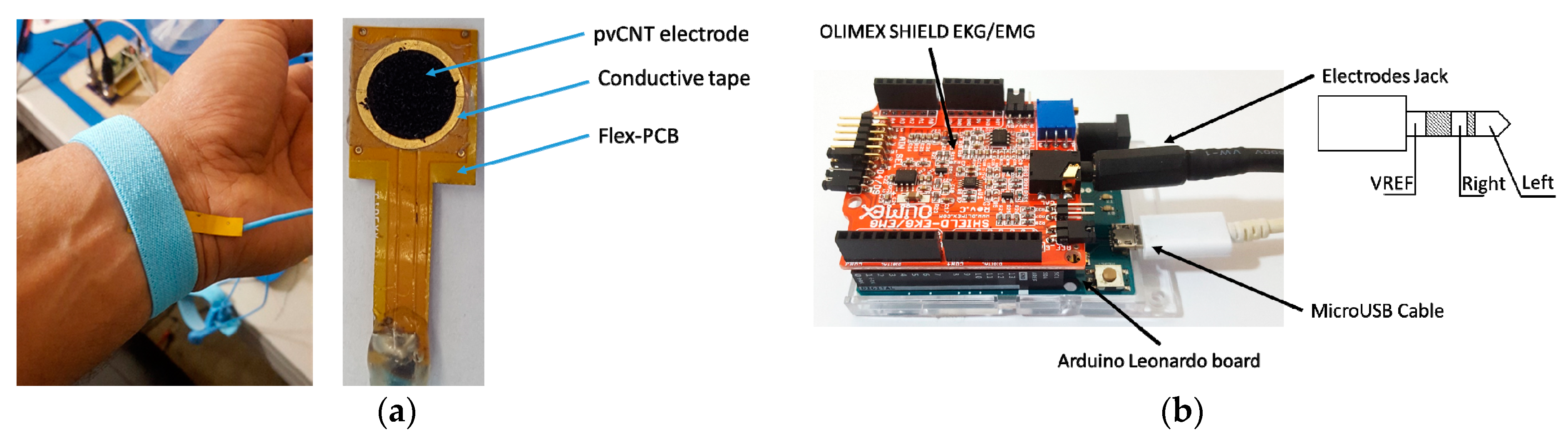
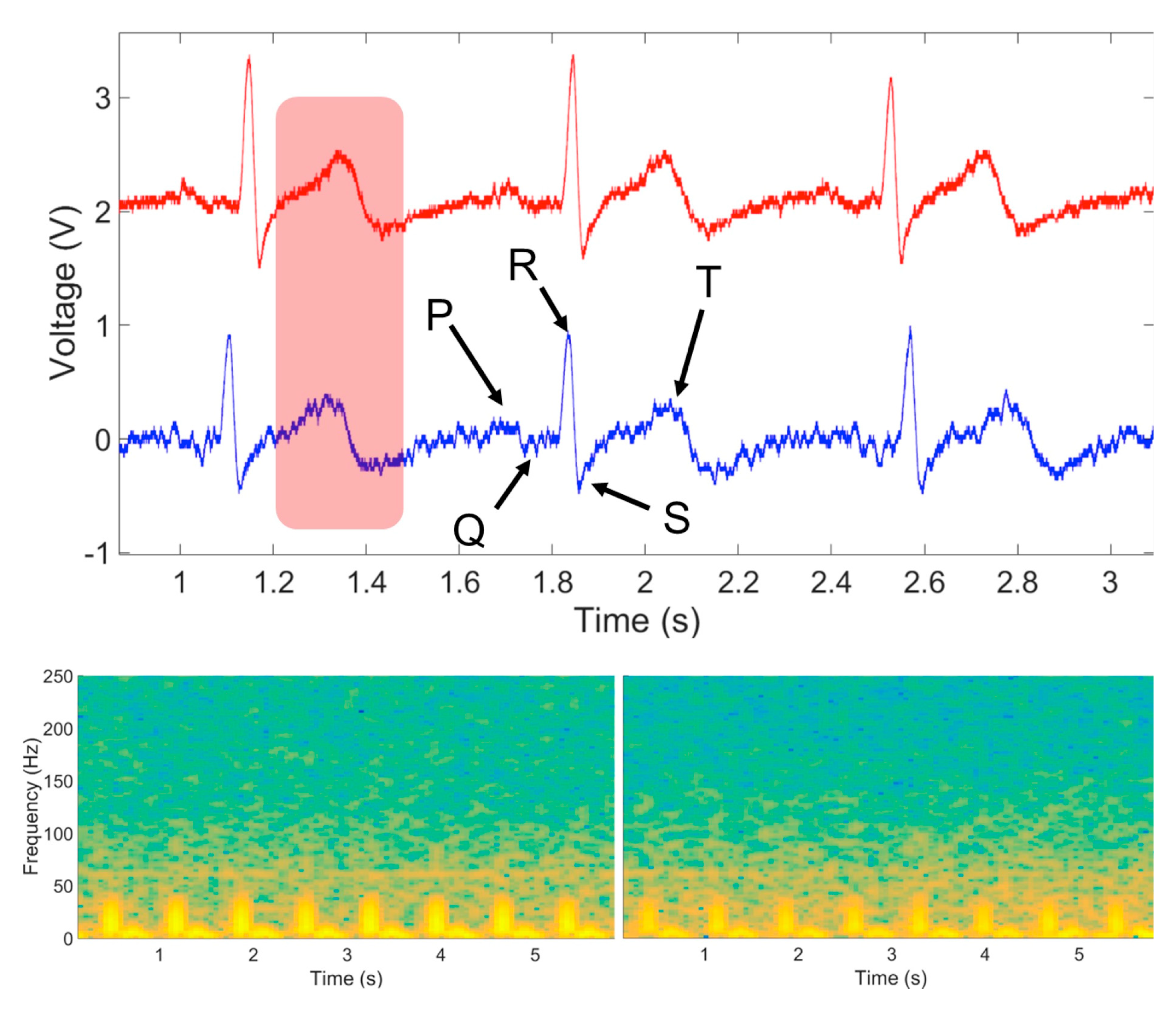
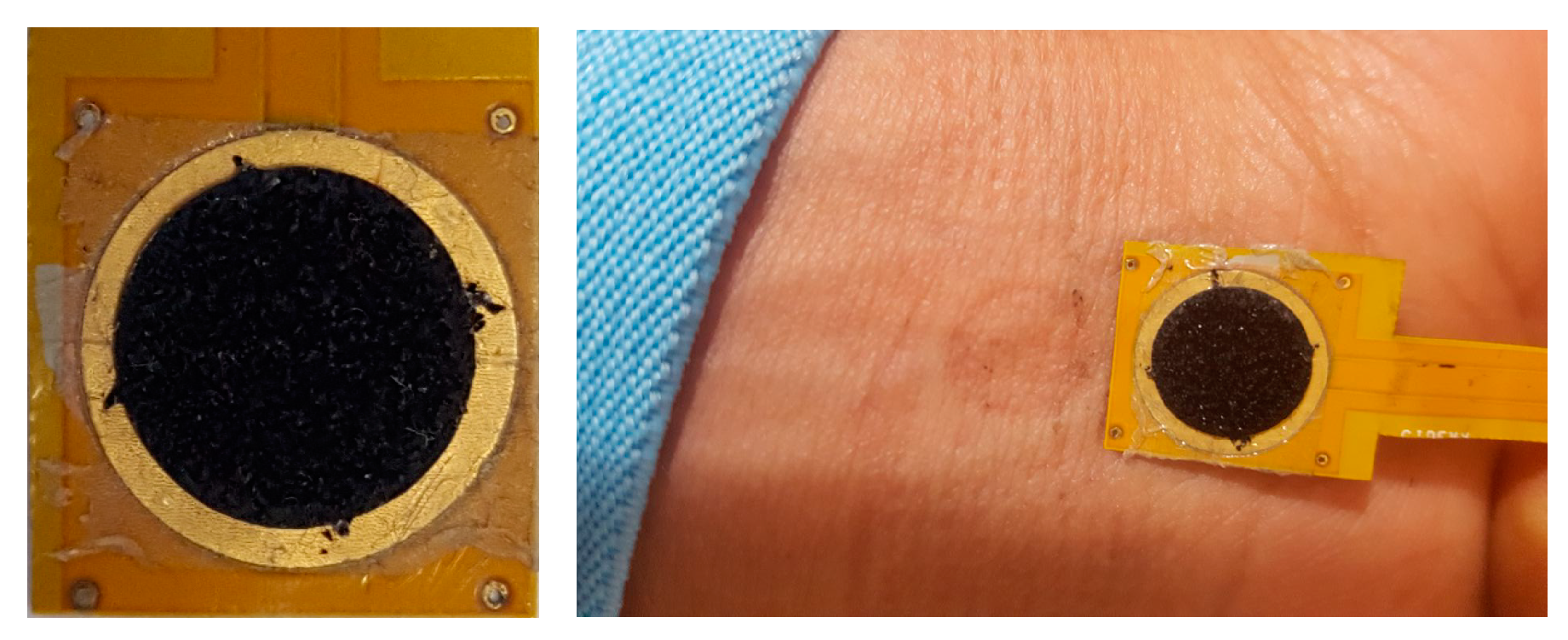
3.4. In Vivo ECG Signal Capture
4. Experimental Results
4.1. PPy-Coated pvCNT Electrode Conductivity Measurement Results
4.1.1. Impedance Measurement Results Before and After Coating
4.1.2. Long-Term Impedance Measurement Results
4.2. In Vitro Signal Capture Results
4.3. Peel-Off Test Results
4.4. In Vivo ECG Signal Capture Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yazicioglu, R.F.; VanHoof, C.; Puers, R. Bio-Potential Readout Circuits for Portable Acquisition Systems; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Thakor, N.V. Biopotentials and Electrophysiology Measurement. In The Measurement, Instrumentation and Sensors Handbook; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Martinsen, O.G.; Grimnes, S. Bioimpedance & Bioelectricity Basics; Academic Press: Bodmin, UK, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Plonsey, R.; Barr, R.C. Bioelectricity: A Quantitative Approach, 3rd ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, S.; Park, H.; Bonato, P.; Chan, L.; Rodgers, M. A review of wearable sensors and systems with application in rehabitation. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2012, 9, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.T.; Liao, L.D.; Liu, Y.H.; Wang, I.J.; Lin, B.S.; Chang, J.Y. Novel dry polymer foam electrodes for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2011, 58, 1200–1207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Searle, A.; Kirkup, L. A direct comparison of wet, dry and insulating bioelectric recording electrodes. Physiol. Meas. 2000, 21, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.M.; Jung, T.G.; Cauwenberghs, G. Dry-contact and noncontact biopotential electrodes: Methodological review. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 3, 106–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurger, C.; Krausz, G.; Allison, B.Z.; Edlinger, G. Comparison of dry and gel based electrodes for P300 brain-computer interfaces. Front. Neurosci. 2012, 6, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Huigen, E.; Peper, A.; Grimbergen, C.A. Investigation into the origin of the noise of surface electrodes. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2002, 40, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Webster, J. Medical Instrumentation: Application and Design; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffini, G.; Dunne, S.; Farres, E.; Marco-Pallares, J.; Ray, C.; Mendoza, E.; Silva, R.; Grau, C. A dry electrophysiology electrode using CNT arrays. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 132, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alemdar, H.; Ersoy, C. Wireless sensor networks for healthcare: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2010, 54, 2688–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Coleman, T.; Genin, G.M.; Hu, X.; Johnson, N.; Liu, T.; Makeig, S.; Sajda, P.; Ye, K. Grand challenges in mapping the human brain: NSF workshop report. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2013, 60, 2983–2992. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Baek, J.; An, J.; Choi, J.; Park, K.; Lee, S. Flexible polymeric dry electrode for long-term monitoring of ECG. Sens. Actuators A. Phys. 2008, 143, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Yang, B.; Yang, C. PDMS based low cost flexible dry electrode for long-term EEG measurement. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 2898–2904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamadade, S.; Jadhav, S.; Puri, V. Electromagnetic properties of polypyrrole thin film on copper substrate. Phys. Res. 2010, 1, 205–210. [Google Scholar]
- Chiou, J.C.; Ko, L.W.; Lin, C.T.; Hong, C.T.; Jung, T.P.; Liang, S.F.; Jeng, J.L. Using novel MEMS EEG sensors in detecting drowsiness application. In Proceedings of the Biomedical Circuits and Systems Conference, London, UK, 29 November–1 December 2006; pp. 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Matthews, R.; Turner, P.J.; McDonald, N.J.; Ermolaev, K.; Mc Manus, T.; Shelby, R.A.; Steindorf, M. Real time workload classification from an ambulatory wireless EEG system using hybrid EEG electrodes. In Proceedings of the 2008 30th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 20–25 August 2008; pp. 5871–5875. [Google Scholar]
- Grozea, C.; Voinescu, C.D.; Fazli, S. Bristle-sensors—Low-cost flexible passive dry EEG electrodes for neurofeedback and BCI applications. J. Neural Eng. 2011, 8, 025008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruetzmann, A.; Hansen, S.; Muller, J. Novel dry electrodes for ECG monitoring. Physiol. Meas. 2007, 28, 1375–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gondran, C.; Siebert, E.; Fabry, P.; Novakov, E.; Gumery, P.Y. Non-polarisable dry electrode based on NASICON ceramic. Med. Biol. Eng. Comput. 1995, 33, 452–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, L.; Geng, Y.; Mäntysalo, M.; Xu, L.L.; Jonsson, F.; Zheng, L.R. Heterogeneous Integration of Bio-Sensing System-on-Chip and Printed electronics. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Syst. 2012, 2, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.S.; Rai, P.; Oh, S.; Kwon, H.; Varadan, V.K. Flexible capacitive electrodes using carbon nanotube and acrylic polymer nanocomposites for healthcare textiles. Smart Nanosyst. Eng. Med. 2012, 2, 18–24. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.M.; Pearce, F.; Hibbs, A.D.; Matthews, R.; Morrissette, C. Evaluation of a capacitively-coupled, non-contact (through clothing) electrode or ECG monitoring and life signs detection for the objective force warfighter. In Proceedings of the Combat Casualty Care in Ground Based Tactical Situations: Trauma Technology and Emergency Medical Procedures, DTIC Document, St. Pete Beach, FL, USA, 16–18 August 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Ding, X.; Zhang, J.; Duan, Y.; Hu, J.; Yang, X. Fabrication of conductive fabric as textile electrode for ECG monitoring. Fibers Polym. 2014, 15, 2260–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yapici, M.K.; Alkhidir, T.; Samad, Y.A.; Liao, K. Graphene-clad textile electrodes for electrocardiogram monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 1469–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, T.J.; Deiss, S.R.; Cauwenberghs, G.; Jung, T. A low-noise, low-power EEG acquisition node for scalable brain-machine interfaces. SPIE Bioeng. Bioinspir. Syst. III 2007, 6592, 659203. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, S.; Kim, C.; Chi, Y.M.; Akinin, A.; Maier, C.; Ueno, A.; Cauwenberghs, G. Integrated circuits and electrode interfaces for noninvasive physiological monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2014, 61, 1522–1537. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yan, B. Functionalized carbon nanotubes for potential medicinal applications. Drug Discov. Today 2010, 15, 428–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, C.T.; Todorov, T.N. Carbon nanotubes as long ballistic conductors. Nature 1998, 393, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, T.Q.; Headrick, R.J.; Bengio, E.A.; Myo Myint, S.; Khoshnevis, H.; Jamil, V.; Duong, H.M.; Pasquali, M. Purification and Dissolution of Carbon Nanotube Fibers Spun from the Floating Catalyst Method. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 37112–37119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bareket-Keren, L.; Hanein, Y. Carbon nanotube-based multi electrode arrays for neuronal interfacing: Progress and prospects. Front. Neural Circuits 2013, 6, 1–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smart, S.K.; Cassady, A.I.; Lu, G.Q.; Martin, D.J. The biocompatibility of carbon nanotubes. Carbon 2006, 44, 1034–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chlopek, J.; Czajkowska, B.; Szaraniec, B.; Frackowiak, E.; Szostak, K.; Beduin, F. In vitro studies of carbon nanotubes biocompatibility. Carbon 2006, 44, 1106–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruffini, G.; Dunne, S.; Farres, E.; Watts, P.C.P.; Mendoza, E.; Silva, S.R.P.; Grau, C.; Marcho-Pallares, J.; Fuentemilla, L.; Vandecasteele, B. ENOBIO—First tests of a dry electrophysiology electrode using carbon nanotubes. In Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, New York, NY, USA, 30 August–3 September 2006; pp. 1826–1829. [Google Scholar]
- Ruffini, G.; Dunne, S.; Fuentemilla, L.; Grau, C.; Farres, E.; Marco-Pallares, J.; Watts, P.C.P.; Silva, S.R.P. First human trials of a dry electrophysiology sensor using a carbon nanotube array interface. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 144, 275–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radhakrishana, J.K.; Bhusan, H.; Pandian, P.S.; Rao, K.U.B.; Padaki, V.C.; Aatre, K.; Xie, J.; Abraham, J.K.; Varadan, V.K. Growth of CNT array, for physiological monitoring applications. Proc. SPIE 2008, 6931, 69310. [Google Scholar]
- Baskey, H.B. Development of carbon nanotube based sensor for wireless monitoring of electroencephalogram. DRDO Sci. Spectr. 2009, 59, 161–163. [Google Scholar]
- Jung, H.; Moon, J.; Baek, D.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.; Hong, J.; Lee, S. CNT/PDMS composite flexible dry electrodes for long-term ECG monitoring. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2012, 59, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abu-Saude, M.; Consul-Pacareu, S.; Morshed, B.I. Feasibility of Patterned Vertical CNT for Dry Electrode Sensing of Physiological Parameters. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Topical Conference on Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireleSS), San Diego, CA, USA, 25–28 January 2015; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Abu-Saude, M.; Morshed, B.I. Patterned Vertical Carbon Nanotube (pvCNT) Dry Electrodes for Impedimetric Sensing and Stimulation. IEEE Sens. J. 2015, 15, 5851–5858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Saude, M.; Morshed, B.I. Polypyrrole (PPy) Conductive Polymer Coating of Dry Patterned Vertical CNT (pvCNT) Electrode to Improve Mechanical Stability. In Proceedings of the IEEE Topical Conf. Biomedical Wireless Technologies, Networks, and Sensing Systems (BioWireleSS), Austin, TX, USA, 24–27 January 2016; pp. 84–87. [Google Scholar]

© 2018 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Abu-Saude, M.; Morshed, B.I. Characterization of a Novel Polypyrrole (PPy) Conductive Polymer Coated Patterned Vertical CNT (pvCNT) Dry ECG Electrode. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030027
Abu-Saude M, Morshed BI. Characterization of a Novel Polypyrrole (PPy) Conductive Polymer Coated Patterned Vertical CNT (pvCNT) Dry ECG Electrode. Chemosensors. 2018; 6(3):27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030027
Chicago/Turabian StyleAbu-Saude, Mohammad, and Bashir I. Morshed. 2018. "Characterization of a Novel Polypyrrole (PPy) Conductive Polymer Coated Patterned Vertical CNT (pvCNT) Dry ECG Electrode" Chemosensors 6, no. 3: 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030027
APA StyleAbu-Saude, M., & Morshed, B. I. (2018). Characterization of a Novel Polypyrrole (PPy) Conductive Polymer Coated Patterned Vertical CNT (pvCNT) Dry ECG Electrode. Chemosensors, 6(3), 27. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors6030027




