Abstract
Addressing the lack of dynamic monitoring methods for assessing the combined toxicity of mixed pesticides, this study developed a fluorescent probe, CCHL, specifically responsive to leucine aminopeptidase (LAP). The probe utilized Cy7-COOH (CCH) as the fluorophore, with fluorescence recovery triggered by enzymatic hydrolysis. Spectral characterization confirmed a linear response between the probe and LAP activity within a concentration range of 0–0.9 μg/mL (R2 = 0.992), along with excellent selectivity in the presence of coexisting biomolecules. Application experiments demonstrated that the combination of chlorfenapyr and beta-cyfluthrin significantly reduced LAP activity, revealing a notable antagonistic effect. The novel sensing strategy developed here provides a real-time, visualized analytical tool for evaluating the combined effects of mixed pollutants, demonstrating significant potential for environmental toxicology monitoring.
1. Introduction
The rapid development of modern agriculture has witnessed the widespread use of mixed pesticides to enhance crop yields while simultaneously introducing potential risks of combined toxicity [1,2,3]. Pesticide residues accumulate through the food chain and may pose multiple health hazards to humans, including interference with enzymatic activity [4], the induction of oxidative stress [5,6], and metabolic dysregulation [7,8]. Leucine aminopeptidase (LAP), a critical proteolytic enzyme, plays essential roles in cellular metabolic regulation, immune responses, and xenobiotic detoxification processes. Abnormal LAP activity is closely associated with various pathological conditions [9,10,11]. Studies indicate that single pesticide exposure can disrupt detoxification capacity and metabolic balance by inhibiting or activating LAP activity [12,13]. However, the mechanisms underlying the combined toxicity of pesticide mixtures remain poorly understood, necessitating the development of highly sensitive and specific detection tools for the dynamic monitoring of LAP activity.
The research group led by Wang Dong [14] previously investigated the impact of a combined formulation of omethoate and chlorpyrifos on the reproductive function of male rats. Their findings revealed that omethoate and chlorpyrifos can exert a synergistically enhanced toxic effect on the reproductive function of male rats. This combined toxicity manifested in a significant inhibitory action on key testicular marker enzymes, namely acid phosphatase (ACP), gamma-glutamyl transferase (γ-GT), and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH). Consequently, these enzymatic inhibitions resulted in a marked decline in sperm motility and a concomitant increase in the sperm deformity rate among the exposed rats. Subsequently, in 2018, the research team headed by Weifeng Shen [15] conducted a study evaluating the individual toxicities and combined toxic effects of four distinct pesticides—pyraclostrobin, iprodione, pyrimethanil, and acetamiprid—on zebrafish (Danio rerio). Their experimental results demonstrated that pyraclostrobin exhibited the highest level of acute toxicity towards zebrafish among the tested compounds. The relative toxicity order of the remaining pesticides was determined to be iprodione > pyrimethanil > acetamiprid. Furthermore, their investigation into multiple pesticide combinations identified that 6 out of the 11 tested multi-component mixtures displayed statistically significant synergistic toxic effects on the zebrafish model. More recently, in 2021, the research group under the direction of Qian Yongzhong [16] quantitatively assessed the combined toxic effects of five different pesticides on the proliferation of human hepatocellular carcinoma HepG2 cells. Their analysis uncovered a critical trend: for all binary pesticide combinations tested, the nature of the combined inhibitory effect on HepG2 cell proliferation shifted from antagonism to synergy as the administered pesticide dose increased. Additionally, specific ternary combinations—namely dimethomorph + difenoconazole + cypermethrin and dimethomorph + cypermethrin + acetamiprid—exhibited a dose-dependent transition in their interaction: the combined effect switched from synergy to antagonism when the cell proliferation inhibition rate reached 60% and 18%, respectively.
Collectively, these investigations into the combined toxicological effects of pesticide mixtures underscore a crucial point: when assessing the potential health hazards posed by pesticide residues in the environment to human populations, it is imperative to account for the complex and potentially amplified toxicological consequences arising from the combined exposure to multiple pesticides, rather than solely considering the effects of individual compounds.
Conventional pesticide detection techniques, both domestically and internationally, primarily include gas chromatography (GC), high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS), liquid chromatography–mass spectrometry (LC–MS), and Biochemiluminescence [17,18,19]. While these methods offer advantages such as high selectivity, broad applicability, excellent sensitivity, and low detection limits for analyzing complex samples, they are hindered by time-consuming pretreatment procedures, expensive instrumentation, and stringent technical operator requirements. These limitations render them unsuitable for large-scale rapid screening. In contrast, fluorescence spectroscopy has recently emerged as a promising alternative due to its high sensitivity, operational simplicity, and rapid response capabilities [20,21,22,23], providing novel analytical tools for deciphering the synergistic or antagonistic toxicity effects of mixed pesticides.
In this study, a LAP-specific fluorescent probe was applied to assess the combined toxicity of pesticide mixtures. By dynamically monitoring LAP activity variations under different pesticide combinations, we aimed to elucidate the mechanisms underlying pesticide joint toxicity. This approach extends the application scope of enzyme inhibition methods from organophosphates and carbamates to pyrethroids (e.g., beta-cyfluthrin) and acaricides (e.g., chlorfenapyr). The developed technology not only provides a highly sensitive analytical method for environmental toxicology research but also establishes a theoretical foundation for formulating pesticide safety standards and developing toxicity intervention strategies.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents and Instruments
All chemical reagents were purchased from commercial suppliers and used without further purification. A magnetic stirrer (IKA, Staufen Im Breisgau, Germany), rotary evaporator (Gongyi Yuhua Instrument Co., Ltd., Gongyi City, China), nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectrometer (Bruker, Zurich, Switzerland), high-resolution time-of-flight mass spectrometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA), pH meter (Shanghai Leici Instrument Factory, Shanghai, China), multifunctional microplate reader (BioTek, Winooski, VT, USA), constant-temperature mixer (Shanghai Jingxin Industrial Development Co., Ltd., Shanghai, China), and vortex mixer (Scientific Industries, Bohemia, NY, USA) were utilized. LAP was purchased from R&D Systems (Minneapolis, MN, USA). Proteins, hydrolases, amino acids, and metal ions were obtained from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA). Pesticide standards were acquired from Beijing Wanjia Shouhua Biotechnology Co., Ltd. (Beijing, China).
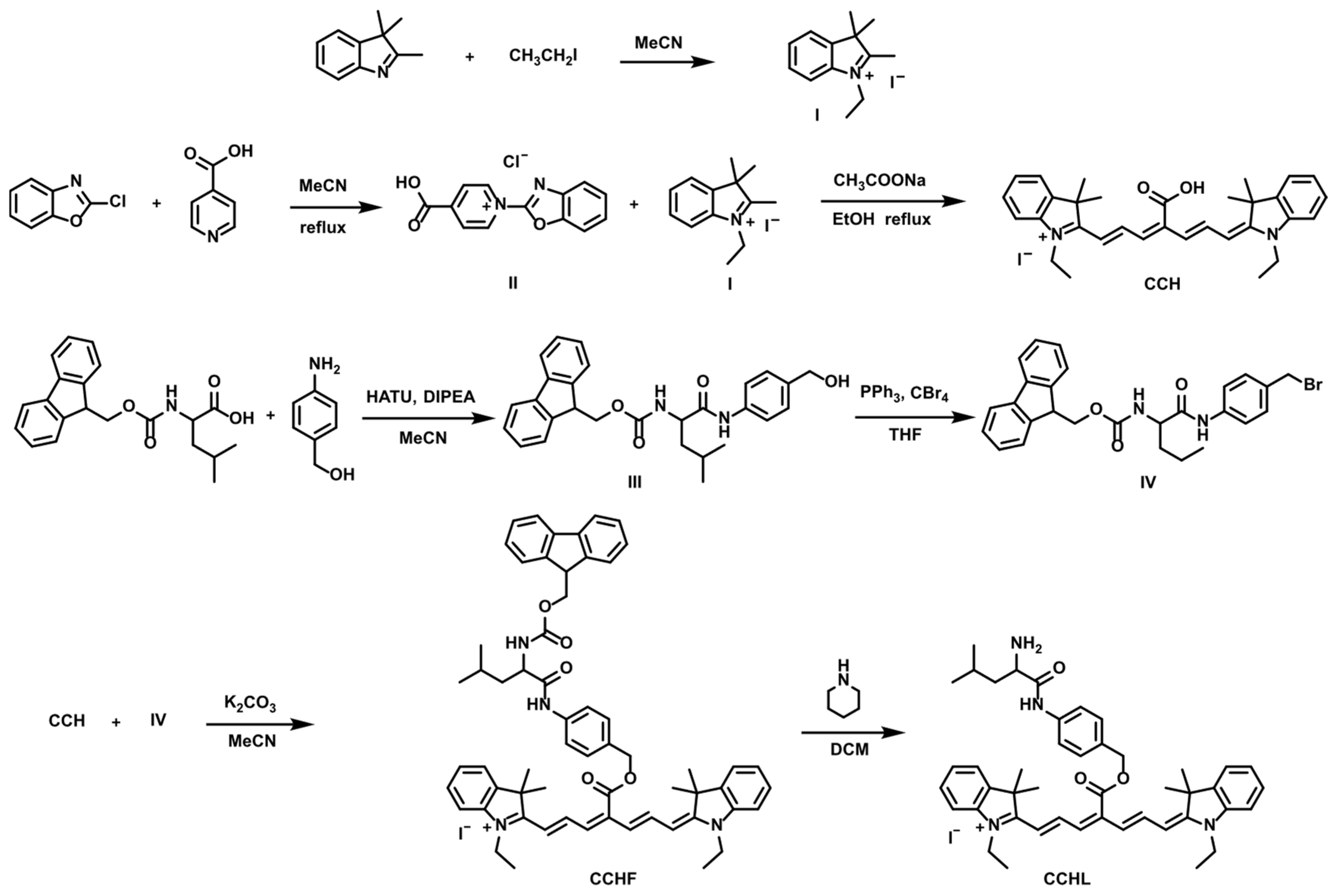
2.2. Synthesis of Novel Probe CCHL
Probe CCHL was synthesized according to the route depicted in Figure 1. Compounds I, II, III, and IV and the fluorophore CCH were prepared following previously reported methods [24,25].
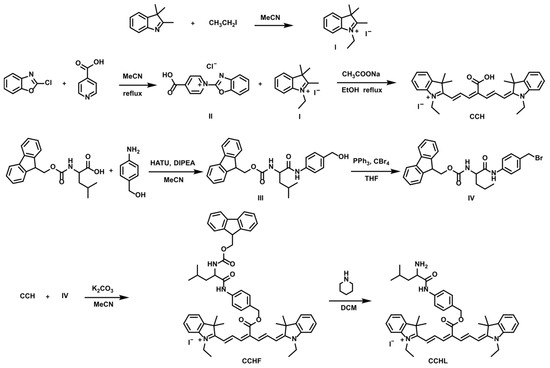
Figure 1.
Synthesis route of probe CCHL.
2.2.1. Synthesis of Compound I
A pressure-resistant flask was charged with 2,3,3-trimethyl-3H-indole (1592 mg, 10 mmol), iodoethane (3120 mg, 20 mmol), and acetonitrile (50 mL). The mixture was heated to 85 °C and stirred overnight. The next day, a large amount of pink solid precipitated. The solvent was removed by filtration, and the solid was washed with ethyl acetate to afford Compound I as a pink solid (2320 mg, 73.7% yield). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 8.10–7.95 (m, 1H), 7.95–7.78 (m, 1H), 7.77–7.48 (m, 2H), 4.53 (q, J = 7.3 Hz, 2H), 2.88 (s, 3H), 1.56 (s, 6H), 1.47 (t, J = 7.3 Hz, 3H).
2.2.2. Synthesis of Compound II
A flask was charged with 2-chlorobenzoxazole (1536 mg, 10 mmol), isonicotinic acid (1231 mg, 10 mmol), and acetonitrile (50 mL). The mixture was heated to 85 °C and stirred overnight. The following day, a large amount of yellow solid precipitated. The solvent was removed by filtration, and the residue was washed with ethyl acetate to afford Compound II as a yellow solid (2360 mg, 85.4% yield). 1H NMR (600 MHz, DMSO) δ 10.03 (d, J = 7.0 Hz, 2H), 9.04–8.79 (m, 2H), 8.67 (d, J = 6.9 Hz, 2H), 8.22–7.92 (m, 2H).
2.2.3. Synthesis of CCH
A mixture of Compound II (277 mg, 1.0 mmol), Compound I (630 mg, 2.0 mmol), and sodium acetate (328 mg, 4.0 mmol) in ethanol (20 mL) was heated under reflux overnight. The next day, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. The crude solid was purified by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: CH2Cl2/MeOH, 50:1 v/v) to afford CCH as a green solid (423 mg, 69.6% yield).
2.2.4. Synthesis of Compound III
N-(((9H-Fluoren-9-yl)methoxy)carbonyl)-L-leucine (Fmoc-Leu-OH, 3531 mg, 10 mmol), 2-(7-aza-1H-benzotriazol-1-yl)-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium hexafluorophosphate (HATU, 3802 mg, 10 mmol), and N,N-diisopropylethylamine (DIPEA, 1293 mg, 10 mmol) were dissolved in acetonitrile (20 mL). The mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 min, followed by the addition of 4-(aminomethyl)phenol (123 mg, 10 mmol). After stirring for 4 h at room temperature, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: CH2Cl2/MeOH, 100:1 v/v) to afford Compound III as a white solid (3587 mg, 78.3% yield).
2.2.5. Synthesis of Compound IV
Carbon tetrabromide (CBr4, 995 mg, 3.0 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (PPh3, 787 mg, 3.0 mmol) were dissolved in tetrahydrofuran (THF, 25 mL). Compound III (916 mg, 2.0 mmol) was added to the resulting solution, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 6 h. After the completion of the reaction, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: CH2Cl2/MeOH, 200:1 v/v) to afford Compound IV as a white solid (592 mg, 58.5% yield).
2.2.6. Synthesis of CCHF
Compound IV (202 mg, 0.2 mmol), potassium carbonate (K2CO3, 69 mg, 0.5 mmol), and CCH (91 mg, 0.15 mmol) were added to acetonitrile (MeCN, 20 mL). The reaction mixture was stirred at room temperature for 2 h. After the completion of the reaction, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. The residue was purified by silica gel column chromatography (eluent: CH2Cl2/MeOH, 100:1 v/v) to afford CCHF as a green solid (243 mg, 23.2% yield).
2.2.7. Synthesis of Probe CCHL
CCHF (209 mg, 0.2 mmol) was dissolved in 10 mL of piperidine and stirred in 10 mL dichloromethane at room temperature for 2 h. After completion, the solvent was removed by rotary evaporation. The residue was purified via silica gel column chromatography using a mobile phase of dichloromethane/methanol (100:1, v/v) to yield CCHL as a green solid (218.3 mg, 26.4% yield). 1H NMR (400 MHz, CD3CN) δ 9.60 (s, 1H), 7.83 (t, J = 13.5 Hz, 2H), 7.75 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.56 (d, J = 8.2 Hz, 2H), 7.49 (d, J = 7.5 Hz, 2H), 7.44 (t, J = 7.7 Hz, 2H), 7.35 (s, 4H), 6.56 (d, J = 13.3 Hz, 2H), 6.35 (d, J = 13.6 Hz, 2H), 5.46 (s, 2H), 4.09 (q, J = 7.2 Hz, 4H), 3.53 (dd, J = 9.7, 4.5 Hz, 1H), 2.40–2.10 (m, 13H), 1.97 (p, J = 2.5 Hz, 11H), 1.48 (d, J = 5.9 Hz, 15H), 1.36 (t, J = 7.2 Hz, 7H), 1.30 (s, 7H), 0.98 (t, J = 6.0 Hz, 7H). HRMS (ESI) m/z found 699.4274 [M + H]+, calculated 699.4269 for C45H55N4O3+.
2.3. Fluorescence Performance Testing of CCHL
Under simulated physiological conditions (T = 37 °C, pH 7.4), the hydrolytic activity of LAP toward CCHL (final concentration: 5 μM) was measured in a 10.0 mM phosphate-buffered saline solution. Fluorescence emission at 780 nm was recorded with an excitation wavelength of 750 nm. The stability of the system under varying temperature and pH conditions was verified by monitoring changes in fluorescence intensity. The concentration-dependent response of LAP with respect to CCHL was investigated by measuring fluorescence intensity at different LAP concentrations. Reaction kinetics were studied by monitoring hydrolysis-dependent fluorescence intensity using fixed LAP concentrations with varying CCHL concentrations. Experimental data were subjected to nonlinear regression analysis according to the Michaelis–Menten kinetic equation to determine Km and Vmax values. To further evaluate the fluorescence properties of CCHL, its selectivity and stability were examined.
where Vmax represents the maximum reaction velocity, Km denotes the substrate concentration at half-maximal reaction velocity, and [S] is the substrate concentration.
2.4. Pesticide Detection Method
Pesticide detection was performed via an enzyme inhibition assay using LAP and probe CCHL. Different pesticide concentrations were mixed with LAP (0.9 μg/mL) and PBS buffer, followed by pre-incubation for 3 min. After adding the probe and reacting for 60 min, the reaction was terminated by adding acetonitrile. Fluorescence intensity was measured using a multifunctional microplate reader ( = 750 nm; = 780 nm). The inhibition rate of enzymatic activity was calculated as follows [26]:
where represents the fluorescence intensity of the control group (without pesticide), and denotes the fluorescence intensity of the experimental group (with pesticide).
To assess combined pesticide toxicity, mixtures were prepared based on the IC50 ratio (pesticide concentration inducing 50% inhibition) of individual pesticides. The measured inhibition rate at the IC50 point was normalized to 50%. Theoretical inhibition rates were calculated using the independent action (IA) model [27]:
where and E() represent the total concentration of the mixture and its corresponding combined effect, respectively; and E() denote the concentration and individual effect of the i-th component in the mixture.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Spectral Characteristics of CCHL and Its Response Mechanism
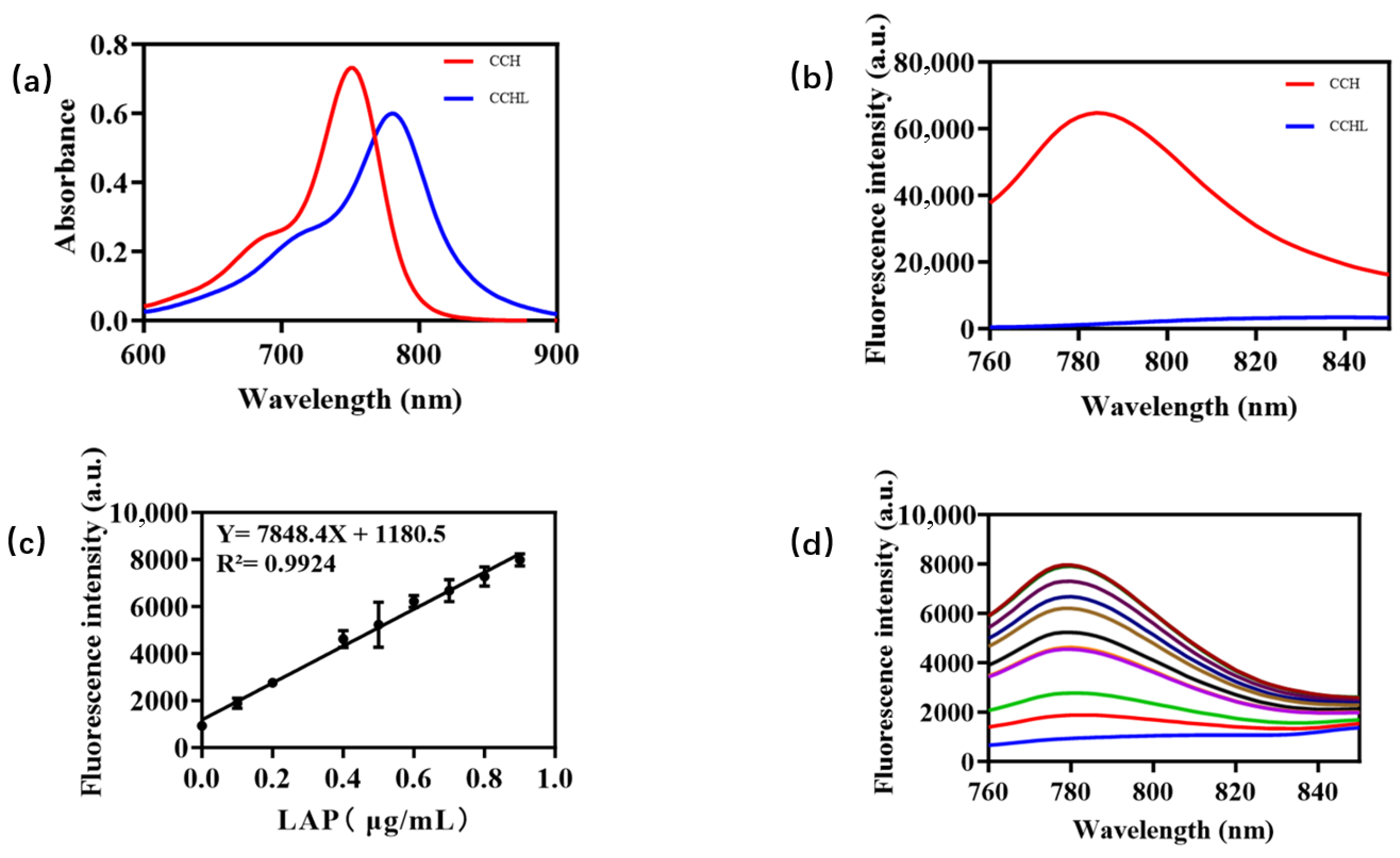
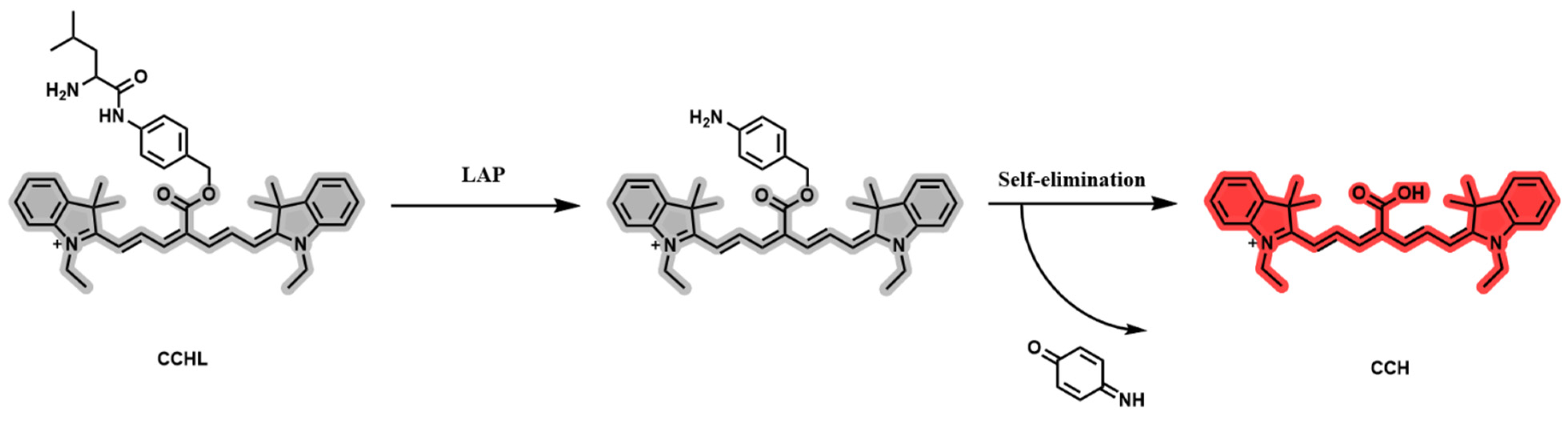
A LAP solution with a final concentration of 0.9 μg/mL was added to a PBS buffer (10.0 mM, pH = 7.4), pre-incubated for 3 min, and then mixed with 5 μM CCHL solution. The reaction proceeded at 37 °C for 60 min in a constant-temperature mixer before termination by acetonitrile. A 200 μL aliquot was taken for analysis. The control group used PBS buffer instead of LAP solution, with all other steps identical to those for the experimental group. The UV-Vis absorption spectra of CCHL and its hydrolyzed metabolite, CCH, are shown in Figure 2a. A blue shift with a strong absorption peak at 750 nm was observed after hydrolysis, confirming the occurrence of the reaction. The fluorescence emission spectrum of CCH (Figure 2b) revealed a robust fluorescence signal at 780 nm, consistent with the emission wavelength of CCH. This indicates the release of CCH, supporting the reaction mechanism illustrated in Figure 3. Upon LAP-mediated hydrolysis, CCHL undergoes the cleavage of leucine, exposing an amino group. The subsequent self-elimination of p-Benzoquinoneimine at pH 7.4 generates the CCH fluorophore, accompanied by the opening of the spiroring. This restores the conjugated system, leading to significant fluorescence enhancement.
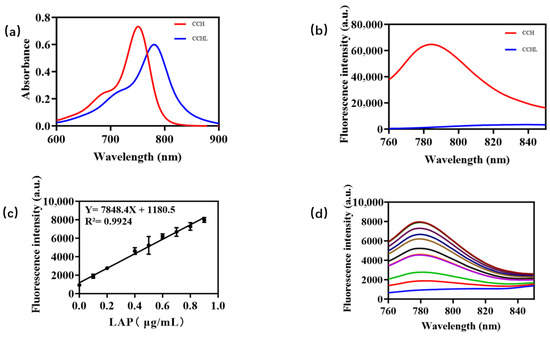
Figure 2.
(a) UV-vis absorption spectra of fluorescent probe CCHL (5 μM) before and after hydrolysis with LAP (0.9 μg/mL). (b) Fluorescence emission spectra (excitation wavelength: 750 nm; emission wavelength: 780 nm). (c) Linear relationship between LAP concentration and fluorescence intensity. (d) Fluorescence spectra of LAP at different concentrations in 760–850 nm wavelength range.
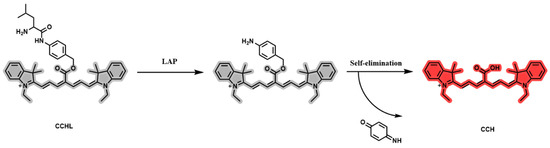
Figure 3.
Response mechanism of probe CCHL.
The fluorescence intensity measurements of LAP in the concentration range of 0–0.9 μg/mL demonstrated a linear relationship (Y = 7848.4X + 1180.5; R2 = 0.9924). As shown in Figure 2c, fluorescence intensity variations in LAP at different concentrations were measured across the wavelength range of 760–850 nm using 0.9 μg/mL LAP (within the 0–0.9 μg/mL concentration range) in subsequent steps. Based on these properties, CCHL demonstrates exceptional potential for detecting LAP activity and quantifying pesticides through enzymatic inhibition assays.
3.2. Stability, Selectivity, and Kinetic Profile of CCHL
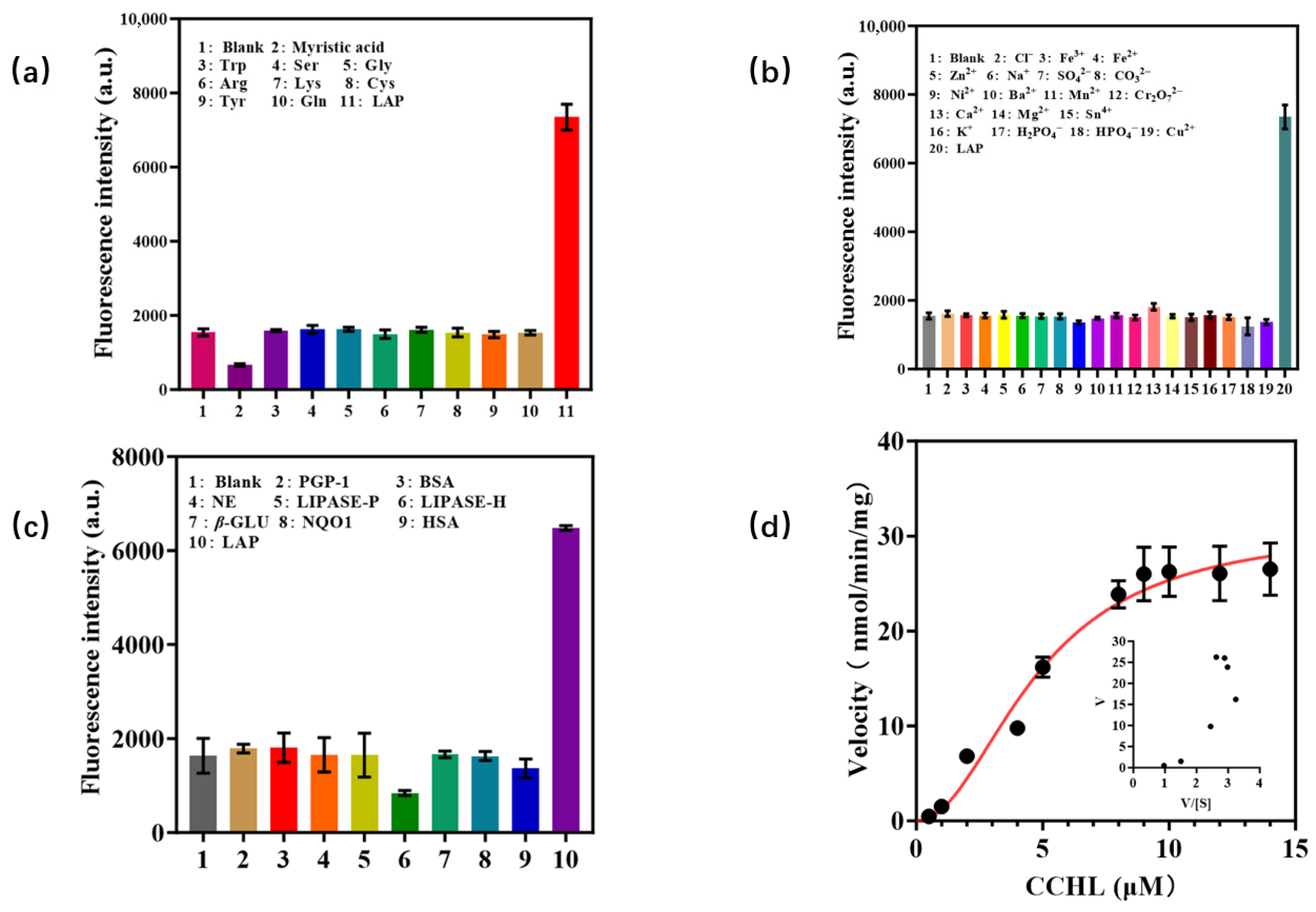
The stability and selectivity of CCHL toward LAP were investigated. As shown in Figure 4a,b, when CCHL was co-incubated with various amino acids, ions, and LAP, the addition of amino acids or ions induced negligible fluorescence changes compared to the control group, whereas the introduction of LAP resulted in a significant increase in fluorescence intensity. This indicates that CCHL exhibits excellent stability and is unaffected by ions or amino acids. To evaluate selectivity, other hydrolases such as human serum albumin (HSA) and pyroglutamyl peptidase 1 (PGP-1) were incubated with LAP. Only LAP triggered a pronounced fluorescence enhancement (Figure 4c), demonstrating the superior selectivity of CCHL for LAP. The kinetic profile of CCHL with respect to LAP was determined through enzymatic kinetic assays (Figure 4d). The results conformed to a Hill-type kinetic model with Vmax = 31.02 nmol/min/mg and a of 4.799 μM, indicating strong affinity between CCHL and LAP. These findings suggest that CCHL is suitable for detecting LAP activity.
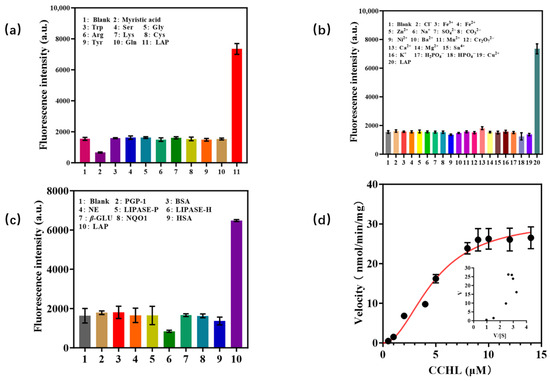
Figure 4.
(a,b) Stability of CCHL toward various amino acids and ions; (c) selectivity of CCHL toward different enzymes; (d) probe CCHL kinetic profile with respect to LAP.
3.3. Enzyme Inhibition-Based Screening of Pesticides
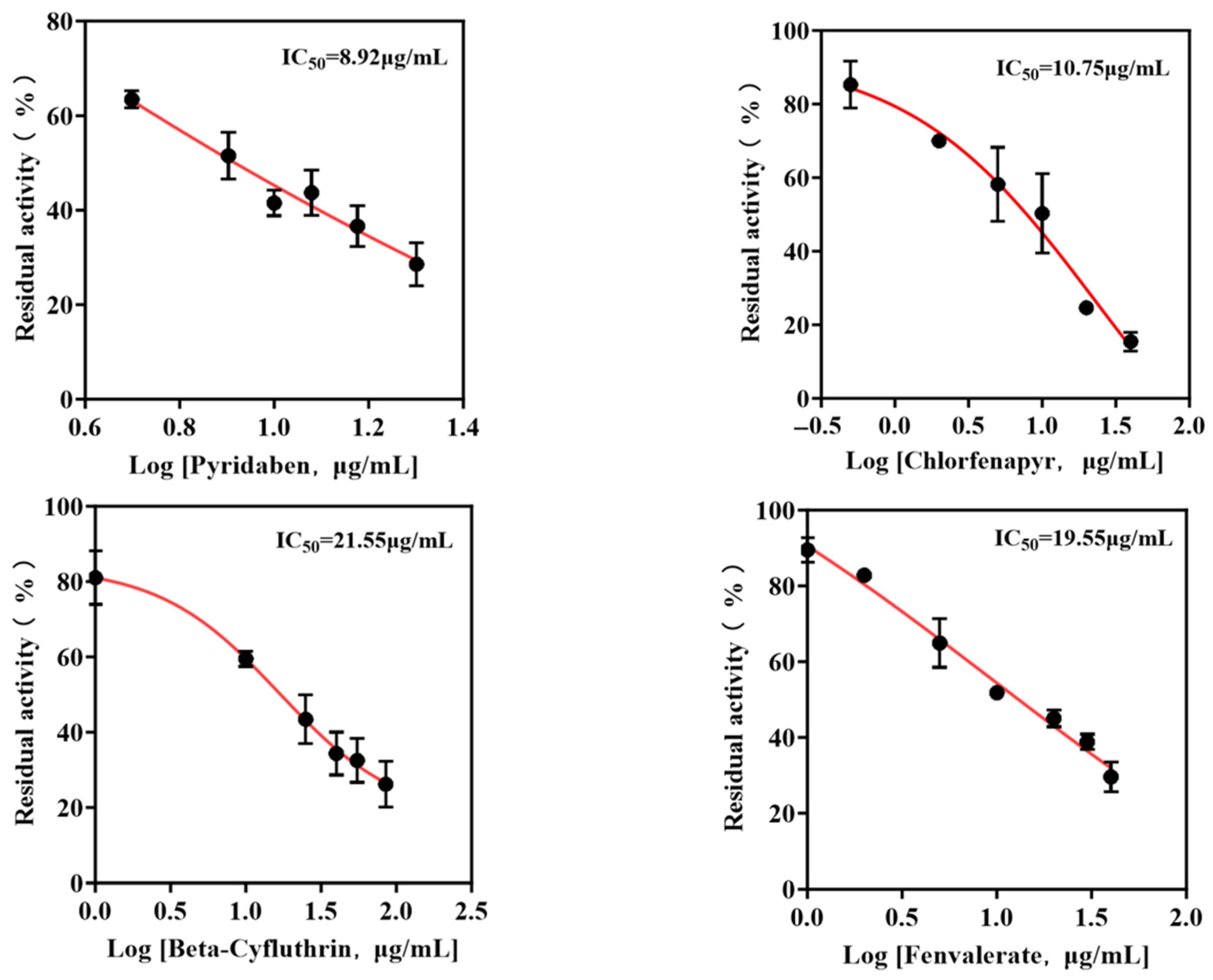
The enzyme inhibition methodology constitutes a detection approach predicated on the phenomenon wherein specific chemical substances interact with and obstruct functional moieties within enzymatic structures, consequently inducing a measurable diminution in catalytic activity or even the complete functional incapacitation of the target enzyme. Applying this principle, leucine aminopeptidase (LAP) in conjunction with the CCHL molecular probe was systematically deployed to evaluate thirteen commonly encountered agricultural pesticides enumerated in Table 1, revealing that four specific compounds—namely pyridaben, chlorfenapyr, beta-cyfluthrin, and fenvalerate—elicited a statistically significant suppression of LAP’s hydrolytic function, with their concentration-dependent inhibitory profiles meticulously quantified through residual activity assays, as systematically documented in Figure 5, facilitating the precise determination of the respective half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) values which established pyridaben as the most potent LAP inhibitor exhibiting an IC50 of 8.92 μg/mL, while the hierarchically ordered inhibitory potency sequence for the remaining pesticides demonstrated chlorfenapyr (IC50 = 10.75 μg/mL) surpassing fenvalerate (IC50 = 19.55 μg/mL) which exceeded beta-cyfluthrin (IC50 = 21.55 μg/mL), thereby conclusively validating the methodological practicality and analytical efficacy for quantitative pesticide detection while simultaneously extending the conventional detection spectrum beyond organophosphate and carbamate pesticides to incorporate pyrethroid insecticides and acaricidal agents, consequently effecting a substantial expansion in the applicability domain of enzymatic inhibition-based analytical platforms.

Table 1.
Types of pesticides.
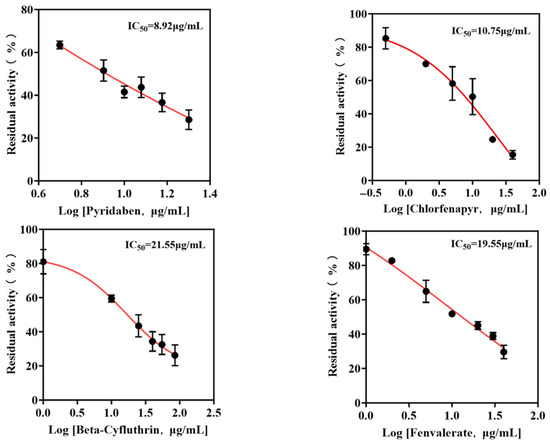
Figure 5.
Effect of single pesticides on LAP residual activity.
3.4. Enzyme Inhibition Assay for Detecting Binary and Ternary Pesticide Combinations
Within the context of contemporary practical agricultural production activities, pesticide formulations are frequently designed and employed in the form of mixtures combining two active ingredients (binary mixtures) or three active ingredients (ternary mixtures). This strategic combination of multiple pesticidal active substances is implemented to enhance pest control efficacy and address potential issues of pesticide resistance. This approach, when contrasted with the application of a single pesticide Compound In isolation, characteristically engenders biological effects that are considerably more intricate and diverse in nature. These combined effects are predominantly categorized into three distinct types: antagonistic effects (where the actual observed efficacy of the mixture is demonstrably lower than the theoretically calculated sum of the efficacies of the individual components applied separately), additive effects (where the mixture’s efficacy is essentially equivalent to the sum of the efficacies of the individual components), and synergistic effects (where the mixture’s actual efficacy significantly exceeds the sum of the efficacies expected from the individual components acting alone).
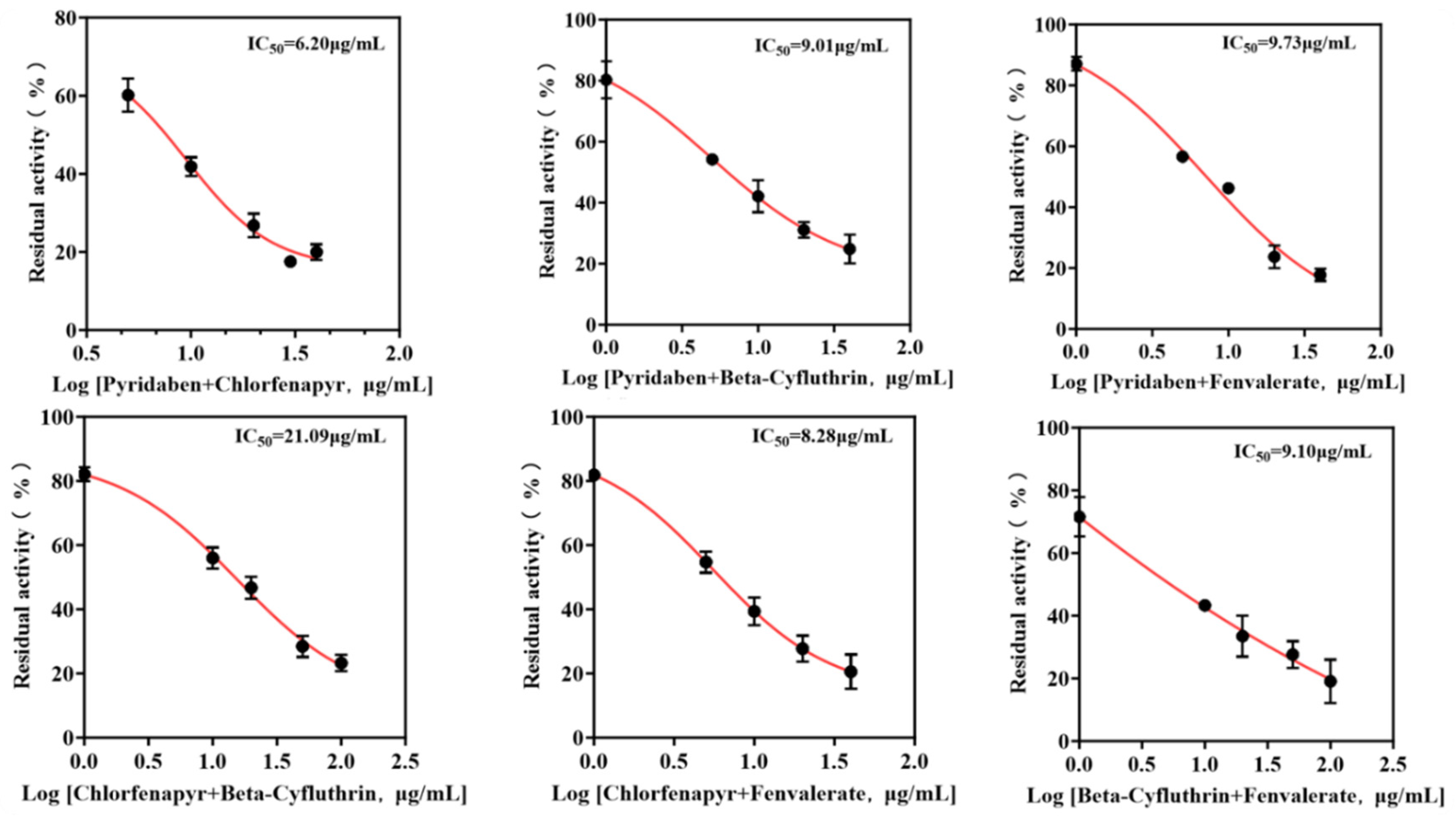
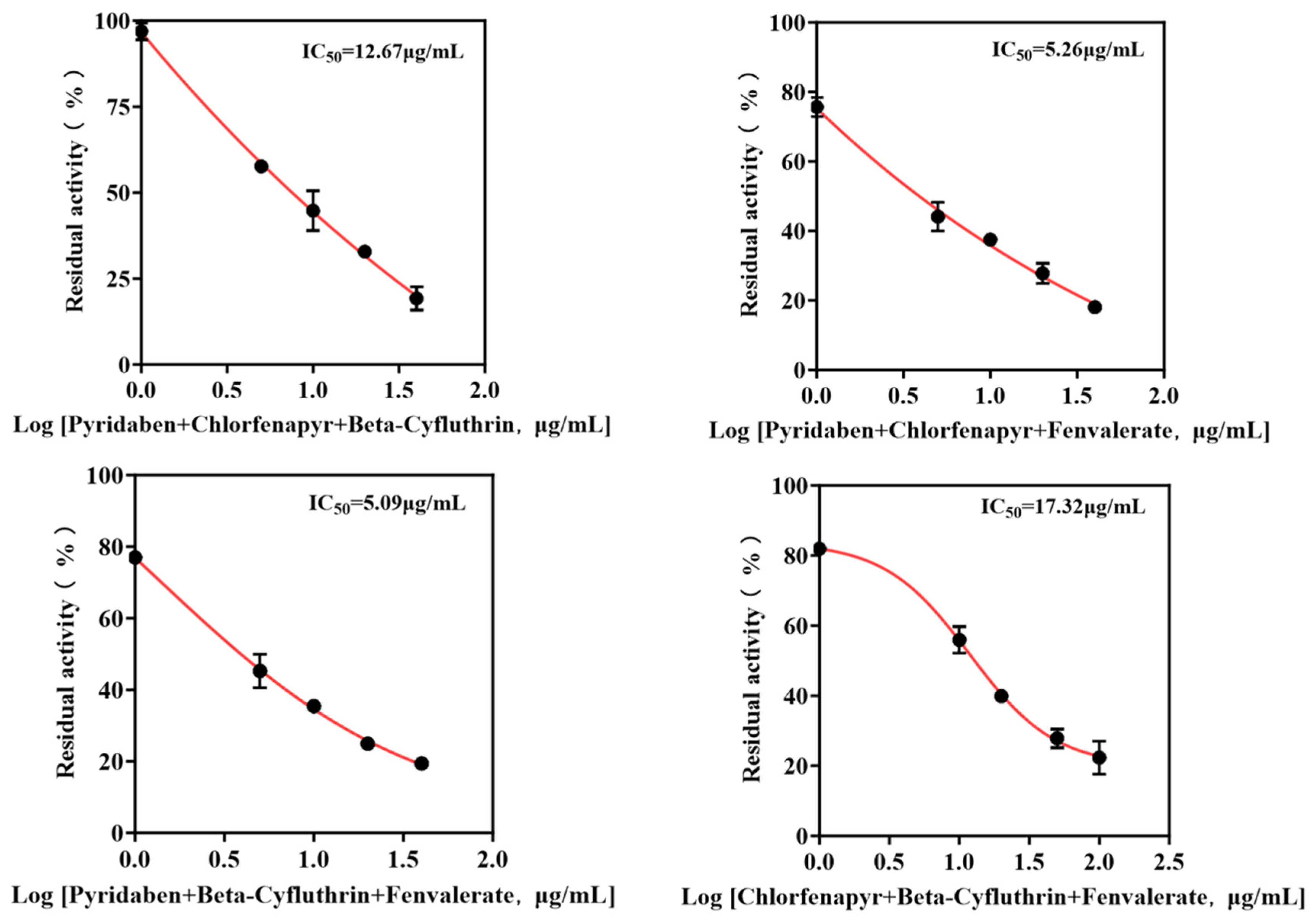
Mixtures were formulated based on the individual IC50 values of each pesticide. The IC50 values of binary and ternary mixtures were determined (Figure 6 and Figure 7) to assess combined toxicity effects. The research results derived from the aggregate analysis of the experimental data clearly indicate the following: Across all instances tested within this study, encompassing pairwise combinations (binary mixtures) and triple combinations (ternary mixtures) involving the four distinct pesticides, the nature of the joint action consistently and unambiguously manifested as antagonism (specific quantitative data reflecting the degree of antagonism observed are detailed in Table 2). It is particularly noteworthy that, among the binary pesticide mixtures, the combination constituted by the active ingredients beta-cyfluthrin and chlorfenapyr exhibited a relatively more pronounced and prominent antagonistic effect. Quantitatively, this antagonism was evidenced by the fact that the experimentally observed inhibition rate recorded during the actual bioassays for this specific binary mixture was markedly lower—by a substantial margin of 19.4%—than the theoretically predicted inhibition rate calculated based on the dose–response relationships and efficacies of the individual components. Focusing further on the outcomes pertaining to the ternary pesticide mixtures, two specific combinations demonstrated notably significant antagonistic effects: the ternary mixture composed of pyridaben, chlorfenapyr, and beta-cyfluthrin and the ternary mixture composed of chlorfenapyr, beta-cyfluthrin, and fenvalerate. Quantifiable data revealed that the actual measured inhibition rates for these two ternary mixtures were significantly reduced compared to their respective theoretically calculated expected inhibition rates, exhibiting decreases of 24.4% and 24.6%, respectively. Given that the aforementioned mixed combinations unequivocally demonstrated antagonistic interactions, therefore, the simultaneous mixing and use of these specific pesticide combinations exhibiting significant antagonism should be strictly avoided.
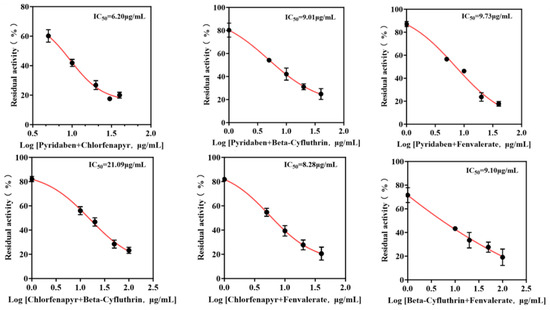
Figure 6.
IC50 curves of binary pesticide mixtures.
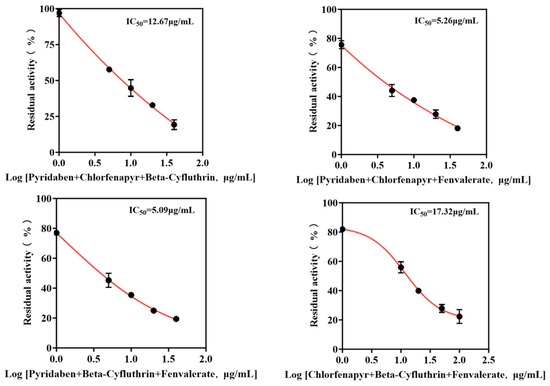
Figure 7.
IC50 curves of ternary pesticide mixtures.

Table 2.
Combined toxicity detection data of binary and ternary pesticides on LAP.
In summary, the LAP inhibition assay methodology employed in this research was substantiated as a reliable and practical technical approach. This method proved its effectiveness for application in both the preliminary screening and the subsequent more precise detection of potential toxicological interaction effects (encompassing antagonism, additivity, and synergy) that may arise from the combined application of multiple pesticides. The successful implementation of this methodology thereby offers an efficient technical pathway for achieving the rapid and accurate identification, discrimination, and assessment of the composite pollution risks and associated joint toxicological effects that mixed pesticides could potentially introduce into real-world environments.
4. Conclusions
In this study, we designed a LAP fluorescent probe CCHL using CCH as the fluorophore and leucine as the active site. CCHL exhibited good stability and selectivity for LAP. By integrating LAP with the CCHL probe through an enzymatic inhibition method, we established a rapid detection approach for pesticides. Among the 13 tested pesticides, pyridaben, chlorfenapyr, beta-cyfluthrin, and fenvalerate demonstrated significant inhibitory effects on LAP activity. Furthermore, this method was applied to evaluate the combined toxicity of binary and ternary mixtures of these pesticides, providing a novel strategy for screening and monitoring the joint toxicity of mixed pesticides.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at https://www.mdpi.com/article/10.3390/chemosensors13080310/s1, Figure S1: 1H NMR spectrum of CCHL in CD3CN; Figure S2: 13C NMR spectrum of CCHL in CDCl3; Figure S3: HRMS spectrum of CCHL; Figure S4: FT-IR of CCHL; Figure S5: pH-dependent changes in fluorescence emission intensity of the system; Figure S6: Temperature-dependent fluorescence emission profile of the CCHL-LAP system; Figure S7: Inhibition profiles of multiple pesticides on the CCHL-LAP enzymatic system.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Z.X. and X.Z.; methodology, Z.X., X.Z., and M.Z.; validation, Z.X., X.Z., and M.Z.; formal analysis, Z.X., X.Z., and Y.G.; investigation, Z.X. and X.Z.; data curation, Z.X. and M.Z.; writing—original draft preparation, Z.X.; writing—review and editing, Z.X. and J.C.; supervision, J.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key R&D Program of China [grant number 2018YFC1603001].
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article and Supplementary Materials.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Belden, J.B.; Brain, R.A. Incorporating the joint toxicity of co-applied pesticides into the ecological risk assessment process. Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2017, 14, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Chen, C.; Zhao, H.; Shao, K. Quantitative ecotoxicity analysis for pesticide mixtures using benchmark dose methodology. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2018, 159, 94–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, X.; Chen, L.; Liu, T.; He, S.; Zhao, X.; Tian, Y.; Fang, Y.; Cui, J. Detecting the combined toxicity of 18 binary and 24 ternary pesticide combinations to carboxylesterase based on fluorescence probe technology. J. Environ. Sci. Health Part B 2022, 57, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, D.; Lei, L.; Tian, T.; Yang, X.; Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. A novel strategy for identification of pesticides in different categories by concentration-independent model based on a nanozyme with multienzyme-like activities. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 237, 115458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, C.; Miozzi, E.; Teodoro, M.; Fenga, C. Influence of genetic polymorphism on pesticide-induced oxidative stress. Curr. Opin. Toxicol. 2019, 13, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, T.; Zhang, L.; Li, H.; Liu, S.; Yang, S.; An, Q.; Pan, C.; Zou, N. Exogenous salicylic acid alleviates the accumulation of pesticides and mitigates pesticide-induced oxidative stress in cucumber plants (Cucumis sativus L.). Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 208, 111654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, B.; Ni, Y.; Jin, Y.; Fu, Z. Pesticides-induced energy metabolic disorders. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 729, 139033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonel Javeres, M.N.; Habib, R.; Judith Laure, N.; Abbas Shah, S.T.; Valis, M.; Kuca, K.; Muhammad Nurulain, S. Chronic Exposure to Organophosphates Pesticides and Risk of Metabolic Disorder in Cohort from Pakistan and Cameroon. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Tian, M.; Wang, J.; Tian, X.; Liu, J.; Feng, L.; Ma, X.; Cui, J. Rational design of a fluorescent probe for the detection of LAP and its application in drug-induced liver injury. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 251, 119362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, L.N.; Yadav, S.P.; Lal, H. Serum leucine aminopeptidase in head and neck cancer. J. Laryngol. Otol. 2007, 108, 660–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, U.C.; Ganguly, N.K.; Sharma, S.; Bhatnagar, R. New sensitive markers for the detection of experimental ascending pyelonephritis. Life Sci. 1987, 41, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Lu, T.; Sun, L.; Peijnenburg, W.; Qian, H. Effect of chlorpyrifos on freshwater microbial community and metabolic capacity of zebrafish. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2023, 262, 115230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gangola, S.; Bhatt, P.; Kumar, A.J.; Bhandari, G.; Joshi, S.; Punetha, A.; Bhatt, K.; Rene, E.R. Biotechnological tools to elucidate the mechanism of pesticide degradation in the environment. Chemosphere 2022, 296, 133916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, T.; Gao, Z.; Zhu, G.; Wang, D.; Pan, J. Joint Toxicity of Omethoate and Chlorpyrifos Mixture on Male Reproductive Function in Rats. Asian J. Ecotoxicol. 2013, 8, 945–954. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Wu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, C.; Xu, Z.; Li, G.; Cai, L.; Shen, W.; Wang, Q. Single and joint toxicity assessment of four currently used pesticides to zebrafish (Danio rerio) using traditional and molecular endpoints. Chemosphere 2018, 192, 14–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Chen, C.; Ma, M.; Yang, X.; Li, Y.; Qian, Y. Combined Toxic Effects of Five Pesticides and Their Binary/Ternary Mixtures on Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma HepG2 Cells. Chin. J. Pestic. Sci. 2021, 23, 499–508. [Google Scholar]
- Sur, S.; Sathiavelu, M. A concise overview on pesticide detection and degradation strategies. Environ. Pollut. Bioavailab. 2022, 34, 112–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, N.; Khunger, A.; Wallen, S.L.; Kaushik, A.; Chaudhary, G.R.; Varma, R.S. Advanced green analytical chemistry for environmental pesticide detection. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2021, 30, 100488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watthaisong, P.; Kamutira, P.; Kesornpun, C.; Pongsupasa, V.; Phonbuppha, J.; Tinikul, R.; Maenpuen, S.; Wongnate, T.; Nishihara, R.; Ohmiya, Y.; et al. Luciferin Synthesis and Pesticide Detection by Luminescence Enzymatic Cascades. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2022, 61, e202203489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Ji, R.; Wang, T.; He, Y.; Bian, H.; Wang, X.; Hu, W. Mixed pesticide recognition based on three-dimensional fluorescence spectroscopy and a convolutional neural network. Appl. Opt. 2023, 62, 9018–9027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Jun, S.; Zhang, B.; Jun, W. Classification of different kinds of pesticide residues on lettuce based on fluorescence spectra and WT–BCC–SVM algorithm. Mod. Phys. Lett. B 2017, 31, 1740082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Ma, S.; Yao, H.; Han, Y.; Yang, X.; Chen, R.; Yu, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, T.; et al. Multiple kinds of pesticide residue detection usingfluorescence spectroscopy combined with partial leastsquares models. Appl. Opt. 2020, 59, 1524–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.-X.; Wei, R.-B.; Chen, C.-Z.; Tuo, X.-L.; Wang, X.-G. A novel fluorescent epoxy resin for organophosphate pesticide detection. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2015, 26, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guan, L.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Huang, D.; Sun, M.; Wang, S. A cyanine-based near-infrared fluorescent probe for highly sensitive and selective detection of hypochlorous acid and bioimaging. Talanta 2016, 161, 592–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usama, S.M.; Marker, S.C.; Li, D.-H.; Caldwell, D.R.; Stroet, M.; Patel, N.L.; Tebo, A.G.; Hernot, S.; Kalen, J.D.; Schnermann, M. Method To Diversify Cyanine Chromophore Functionality Enables Improved Biomolecule Tracking and Intracellular Imaging. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 14647–14659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins-Gomes, C.; Coutinho, T.E.; Silva, T.L.; Andreani, T.; Silva, A.M. Neurotoxicity Assessment of Four Different Pesticides Using In Vitro Enzymatic Inhibition Assays. Toxics 2022, 10, 448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nys, C.; Van Regenmortel, T.; Janssen, C.R.; Oorts, K.; Smolders, E.; De Schamphelaere, K.A. A framework for ecological risk assessment of metal mixtures in aquatic systems. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2018, 37, 623–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).