Sensitive Gold Nanostar-Based Adsorption Sensor for the Determination of Dexamethasone
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Electrochemical Behaviour of Dexamethasone
3.2. Adsorptive Detection of Dexamethasone Under Anaerobic Conditions
3.3. Effect of pH—Acidic, Neutral, and Basic—On the Detection of DEX
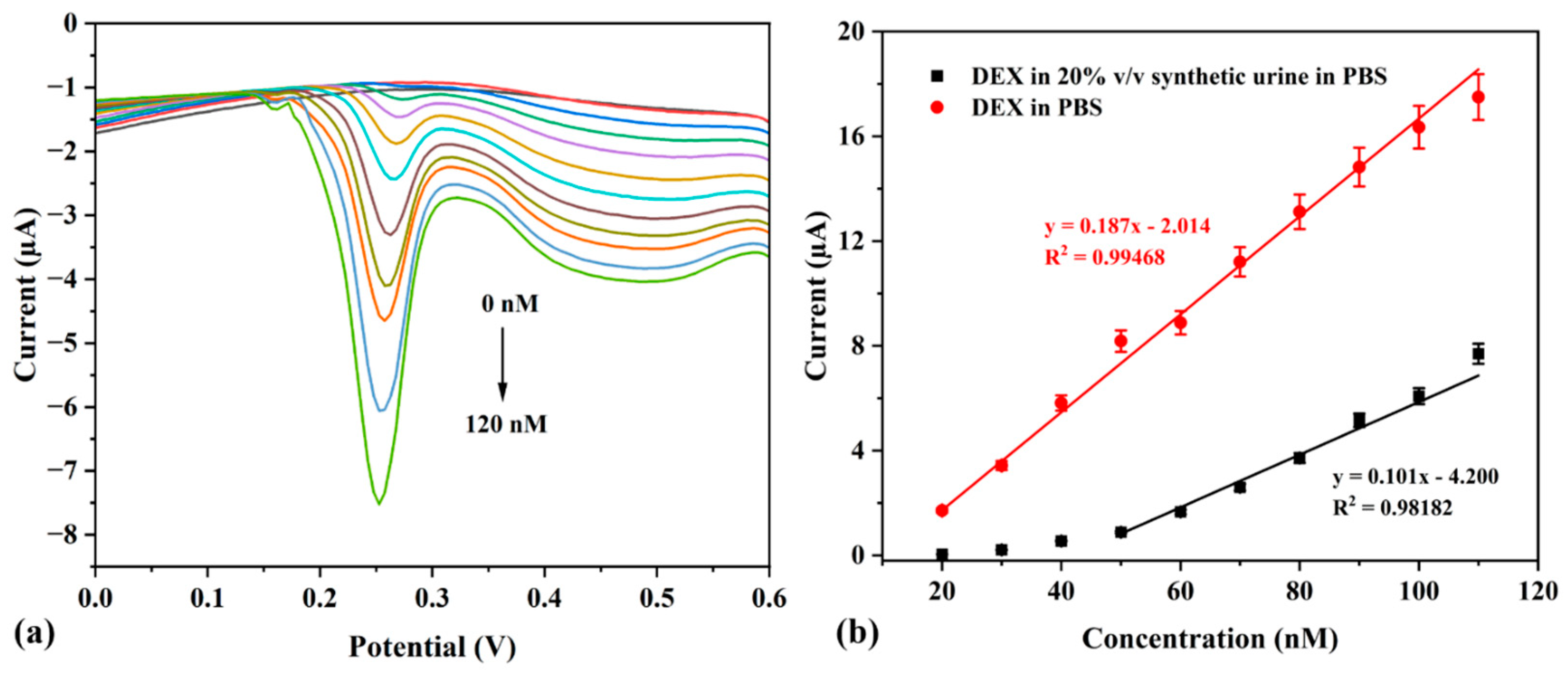
3.4. Determination of Sensor Sensitivity Towards DEX
3.5. Interference of Other Drugs—INH, PAR, and STR
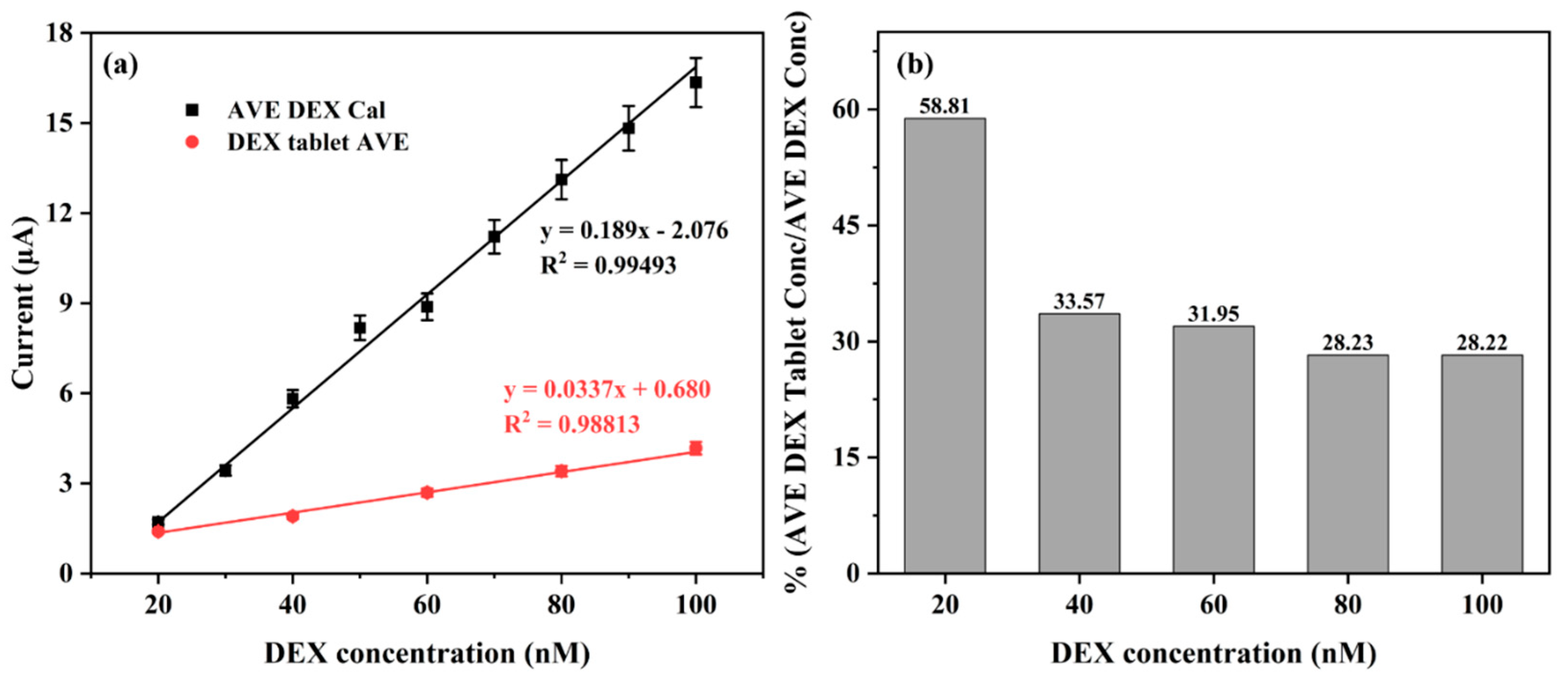
3.6. Detection of DEX in Commercial DEX-Containing Tablet—Perazone
3.7. Real Sample Analysis of DEX
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| DEX | Dexamethasone |
| AuNSs | Gold nanostars |
| GCE | Glassy carbon electrode |
| NMGA | N–methyl–D–glucamine |
| LOD | Limit of detection |
| CV | Cyclic voltammetry |
| DPV | Differential pulse voltammetry |
| SWV | Square wave voltammetry |
| WE | Working electrode |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffer solution |
| HR-TEM | High–resolution transmission electron microscopy |
| TB | Tuberculosis |
References
- Gaze, D.C. Dexamethasone: What Is the Breakthrough Treatment for COVID-19? Available online: https://theconversation.com/dexamethasone-what-is-the-breakthrough-treatment-for-covid-19-140966 (accessed on 21 June 2020).
- National Center for Biotechnology Information Dexamethasone|C22H29FO5-PubChem. Available online: http://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/dexamethasone#section=Top (accessed on 21 June 2020).
- World Health Organization. WHO Welcomes Preliminary Results About Dexamethasone Use in Treating Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/detail/16-06-2020-who-welcomes-preliminary-results-about-dexamethasone-use-in-treating-critically-ill-covid-19-patients (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Goyal, R.N.; Gupta, V.K.; Chatterjee, S. Fullerene-C60-Modified Edge Plane Pyrolytic Graphite Electrode for the Determination of Dexamethasone in Pharmaceutical Formulations and Human Biological Fluids. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1649–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alimohammadi, S.; Kiani, M.A.; Imani, M.; Rafii-Tabar, H.; Sasanpour, P. Electrochemical Determination of Dexamethasone by Graphene Modified Electrode: Experimental and Theoretical Investigations. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehennaoui, S.; Poorahong, S.; Jimenez, G.C.; Siaj, M. Selection of High Affinity Aptamer-Ligand for Dexamethasone and Its Electrochemical Biosensor. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 6600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherlet, M.; De Baere, S.; De Backer, P. Quantitative Determination of Dexamethasone in Bovine Milk by Liquid Chromatography-Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2004, 805, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reig, M.; Mora, L.; Navarro, J.L.; Toldrá, F. A Chromatography Method for the Screening and Confirmatory Detection of Dexamethasone. Meat Sci. 2006, 74, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, E.M.; El-Attar, M.A.; Ghoneim, M.M. Adsorptive Cathodic Stripping Voltammetric Determination of Dexamethasone in Formulations and Biological Fluids. J. AOAC Int. 2009, 92, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piskin, E.; Korkut, F.A.; Cetinkaya, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Highly Selective and Sensitive Detection of Atorvastatin from Using a MIP-Based Electrochemical Sensor. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2025, 5, 100061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fdez-Sanromán, A.; Ben Messaoud, N.; Pazos, M.; Rosales, E.; Barbosa Queirós, R. Development of Eco-Friendly and Cost-Effective Electrochemical Sensor for the Simultaneous Detection of 4-Aminophenol and Paracetamol in Water. Sens. Biosensing Res. 2025, 48, 100782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckschlegel, C.; Fleischmann, V.; Gajovic-Eichelmann, N.; Wongkaew, N. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensors for Point-of-Care Testing: Current Status, Challenges, and Future Prospects. Talanta 2025, 291, 127850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidli, W.; Fumagalli, D.; Pifferi, V.; Falciola, L. From Dual-Mode to Multi-Modal Electrochemical Based Sensors: A Path toward Accurate Sensing. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2025, 50, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeyaseelan, C.; Joshi, A.P. Trace Determination of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate in Pharmaceutical Formulations by Differential Pulse Polarography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2002, 373, 772–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, T.M.B.F.; Ribeiro, F.W.P.; Soares, J.E.S.; De Lima-Neto, P.; Correia, A.N. Square-Wave Adsorptive Voltammetry of Dexamethasone: Redox Mechanism, Kinetic Properties, and Electroanalytical Determinations in Multicomponent Formulations. Anal. Biochem. 2011, 413, 148–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karuwan, C.; Wisitsoraat, A.; Chaisuwan, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Tuantranont, A. Screen-Printed Graphene-Based Electrochemical Sensors for a Microfluidic Device. Anal. Methods 2017, 9, 3689–3695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, B.; Zare, S.Z.M.; Ensafi, A.A. Square Wave Voltammetric Determination of Dexamethasone on a Multiwalled Carbon Nanotube Modified Pencil Electrode. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2011, 22, 897–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, E.; Inam, O.; Inam, R.; Aboul-Enein, H.Y. Voltammetric Determination of Ophthalmic Drug Dexamethasone Using Poly-Glycine Multi Walled Carbon Nanotubes Modified Paste Electrode. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2018, 14, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, K.; Jiang, S.; Chen, S.; Xing, Y.; Wu, J.; Guo, Y. Nanomaterial-Assisted Electrochemical Detection Platforms for Lung Cancer Diagnosis. Alex Eng. J. 2024, 102, 82–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Song, Y.; Yu, J.; Tong, C. Electrochemical Detection Platform Based on Graphene-Zinc Oxide Composite Nanomaterials for 17β-Estradiol Determination in Milk. Alex Eng. J. 2024, 100, 170–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, H.; Archana, N.; Noumani, A.; Himanshu, J.K.; Chakravorty, S.; Solanki, P.R. Recent Advancement in the Detection of Potential Cancer Biomarkers Using the Nanomaterial Integrated Electrochemical Sensing Technique: A Detailed Review. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 475–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, A.P.; Chakravorty, A.; Mini, A.A.; Das, S.; Rajendiran, M.; Raghavan, V. Emerging Trends on Nanomaterial-Based Simultaneous Electrochemical Sensing of Dopamine and Acetaminophen. Results Chem. 2024, 7, 101489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Huang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Feng, M.; Liu, X.; Geng, C.; Zhao, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, B.; Miao, Y. Nanomaterials Promote the Fast Development of Electrochemical MiRNA Biosensors. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 17929–17944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madagalam, M.; Rosito, M.; Blangetti, N.; Etzi, M.; Padovano, E.; Bonelli, B.; Carrara, S.; Tagliaferro, A.; Bartoli, M. Unveiling the Effect of Bi in ZnFe2O4 Nanoparticles in Electrochemical Sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 673, 160870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, R.; Rana, D.S.; Awasthi, A.; Singh, D.; Ibrahim, A.A.; Umar, A.; Baskoutas, S. Nitrogen Functionalized Biomass Derived Mesoporous Carbon Nanomaterials for Electrochemical Detection of Lead (II) Ions. Heliyon 2024, 10, e39090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Shen, R.; Xu, J.; Feng, Z. Progress in Electrochemical Sensing of Epinephrine Using Carbon Nanomaterials: A Review. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabrielle Sutanto, L.; Sabilla, S.; Wardhana, B.Y.; Ramadani, A.; Sari, A.P.; Anjani, Q.K.; Basirun, W.J.; Amrillah, T.; Amalina, I.; Jiwanti, P.K. Carbon Nanomaterials as Electrochemical Sensors for Theophylline: A Review. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 28927–28942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalambate, R.P.; Kalambate, P.K.; Khosropour, H.; Thummarati, P.; Chiabchalard, A.; Boonlue, W.; Laiwattanapaisal, W. Exploring Advanced Functional Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins in Food Matrices: A Comprehensive Review. Chem. Inorg. Mater. 2024, 3, 100044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jebril, S.; Fredj, Z.; Saeed, A.A.; Gonçalves, A.M.; Kaur, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, B. Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Chemo(Bio)Sensors for the Detection of Nanoplastic Residues: Trends and Future Prospects. RSC Sustain. 2024, 2, 832–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geleta, G.S. Recent Advances in Electrochemical Sensors Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers and Nanomaterials for Detection of Ascorbic Acid, Dopamine, and Uric Acid: A Review. Sens. Biosensing Res. 2024, 43, 100610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, S.; Ahmadi, S.; Kerman, K. Electrochemical Biosensors for the Detection of SARS-CoV-2 and Other Viruses. Micromachines 2021, 12, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pingarrón, J.M.; Yáñez-Sedeño, P.; González-Cortés, A. Gold Nanoparticle-Based Electrochemical Biosensors. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5848–5866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegel, A.L.; Polo-Parada, L.; Baker, G.A. Plasmon-Controlled Shaping of Gold Nanostar Photothermal Therapy Agents. ChemComm 2022, 58, 13119–13122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyal, R.N.; Chatterjee, S.; Rana, A.R.S. Effect of Cetyltrimethyl Ammonium Bromide on Electrochemical Determination of Dexamethasone. Electroanal 2010, 22, 2330–2338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venditti, I.; Fontana, L.; Fratoddi, I.; Battocchio, C.; Cametti, C.; Sennato, S.; Mura, F.; Sciubba, F.; Delfini, M.; Russo, M.V. Direct Interaction of Hydrophilic Gold Nanoparticles with Dexamethasone Drug: Loading and Release Study. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2014, 418, 52–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blizzard, C.; McLaurin, E.B.; Driscoll, A.; Silva, F.Q.; Vantipalli, S.; Metzinger, J.L.; Goldstein, M.H. Plasma Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Dexamethasone Following Administration of a Dexamethasone Intracanalicular Insert in Healthy Adults. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 2055–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hichens, M.; Hogans, A.F. Radioimmunoassay for Dexamethasone in Plasma. Clin. Chem. 1974, 20, 266–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrero, P.; Borrull, F.; Pocurull, E.; Marcé, R.M. Determination of Glucocorticoids in Sewage and River Waters by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography–Tandem Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2012, 1224, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, P. Development of a Highly Sensitive Electrochemical Sensor for Dexamethasone Detection Using Fe3O4/Polyaniline-Cu(II) Microspheres and Hematite Nanoparticles. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2024, 19, 100622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloum-Ardakani, M.; Sadri, N.; Eslami, V. Detection of Dexamethasone Sodium Phosphate in Blood Plasma: Application of Hematite in Electrochemical Sensors. Electroanal 2020, 32, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purnama, S.K.; Doewes, R.I.; Elumalai, G.; Azmi, S.H.; Nuryadin, I. Manshuralhudlori Biosensor Development in Sports Doping with Dexamethasone. Rev. Bras. Med. Esporte 2023, 29, e2022_0416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smajdor, J.; Piech, R.; Paczosa-Bator, B. Highly Sensitive Voltammetric Determination of Dexamethasone on Amalgam Film Electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 809, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Platform | Measurement Technique | Linear Range (M) | LOD (M) | Detection Potential (V) | Sample | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| - | RIA † | 1 × 10−9–1 × 10−7 | 1.3 × 10−10 | N/A | Rabbit plasma | [37] |
| - | SPE-UHPLC–MS/MS † | 3.8 × 10−12–2.5 × 10−10 | 1.3 × 10−11 | N/A | River water, effluent, and influent sewage | [38] |
| MWCNT|PE † | SWV | 1.5 × 10−7–1 × 10−4 | 9 × 10−8 | +0.8 | Urine samples | [17] |
| Fe3O4|PANI–CuII|α–Fe3O4|CILE † | CV | 5 × 10−8–1 × 10−4 | 1.5 × 10−8 | +0.6 | Human serum and urine samples | [39] |
| GCE|GNP † | DPV | 1 × 10−7–5 × 10−3 | 1.5 × 10−8 | −1.3 | Human plasma | [5] |
| GCE|Nano–porous | DPV | 2 × 10−8–2.2 × 10−5 | 5 × 10−9 | +0.6 | Pharmaceutical samples (tablet) | [40] |
| MnO2|rGO|CPE † | Amperometry | 0–2.6 × 10−4 | 5 × 10−9 | N/A (ferricyanide used as redox probe) | Pharmacological and human urine samples | [41] |
| HMDE (hanging mercury drop electrode) | DPV | 8.5 × 10−5–1.4 × 10−5 | 7.6 × 10−6 | −1.14 | pharmaceutical formulations | [14] |
| Hg(Ag)FE (amalgam film silver-based electrode) | DPV | 2.5 × 10−9–2.25 × 10−7 | 1.6 × 10−9 | −1.05 | tablets and eye drops | [42] |
| GCE|GO|α–Fe2O3 | DPV | 1 × 10−7–0.1 × 10−4 | 4.6 × 10−8 | +1.05 | blood serum | [40] |
| GCE|GNS † | DPV | 2 × 10−8–1.1 × 10−7 2 × 10−8–1.2 × 10−7 | 1.1 × 10−9 2 × 10−9 | +0.2 | PBS 20 % v/v urine in PBS | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
MacDonald, R.T.; Pokpas, K.; Iwuoha, E.; Cupido, C. Sensitive Gold Nanostar-Based Adsorption Sensor for the Determination of Dexamethasone. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060208
MacDonald RT, Pokpas K, Iwuoha E, Cupido C. Sensitive Gold Nanostar-Based Adsorption Sensor for the Determination of Dexamethasone. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(6):208. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060208
Chicago/Turabian StyleMacDonald, Riccarda Thelma, Keagan Pokpas, Emmanuel Iwuoha, and Candice Cupido. 2025. "Sensitive Gold Nanostar-Based Adsorption Sensor for the Determination of Dexamethasone" Chemosensors 13, no. 6: 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060208
APA StyleMacDonald, R. T., Pokpas, K., Iwuoha, E., & Cupido, C. (2025). Sensitive Gold Nanostar-Based Adsorption Sensor for the Determination of Dexamethasone. Chemosensors, 13(6), 208. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060208








