Fabrication of Palladium-Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Apparatus
2.3. Fabrication of the LIG Electrodes
3. Results and Discussions
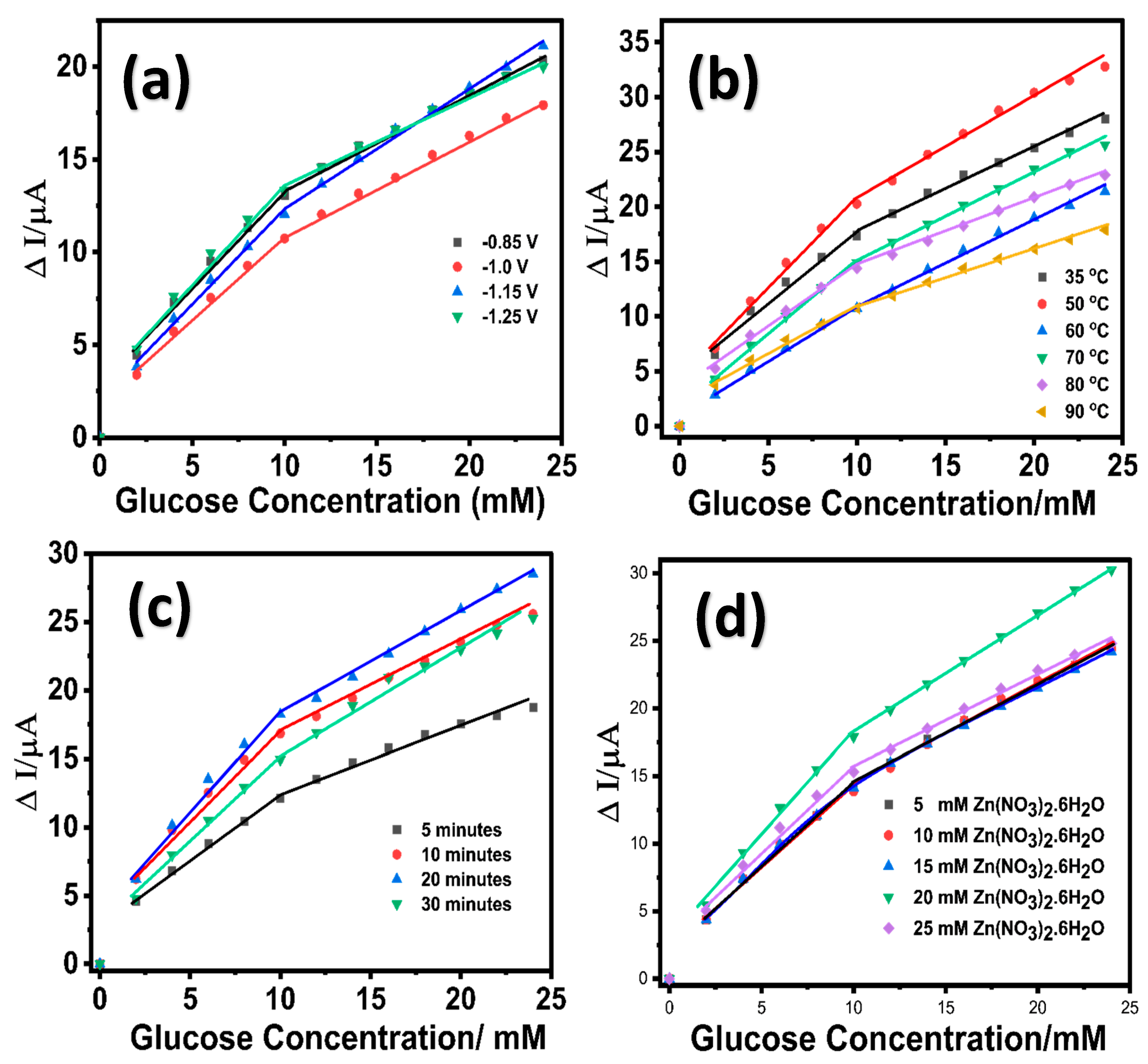
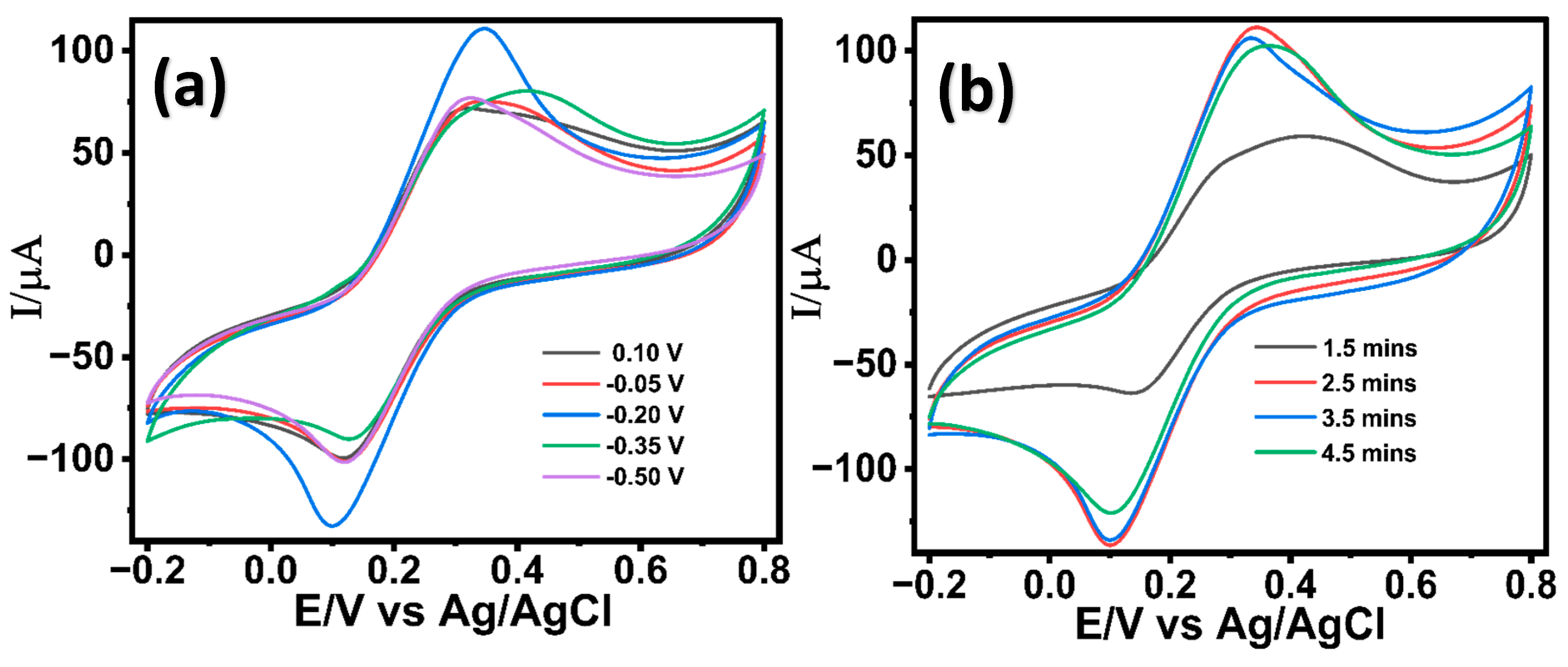
3.1. Optimization of ZnO/Pd Modified LIG Electrodes
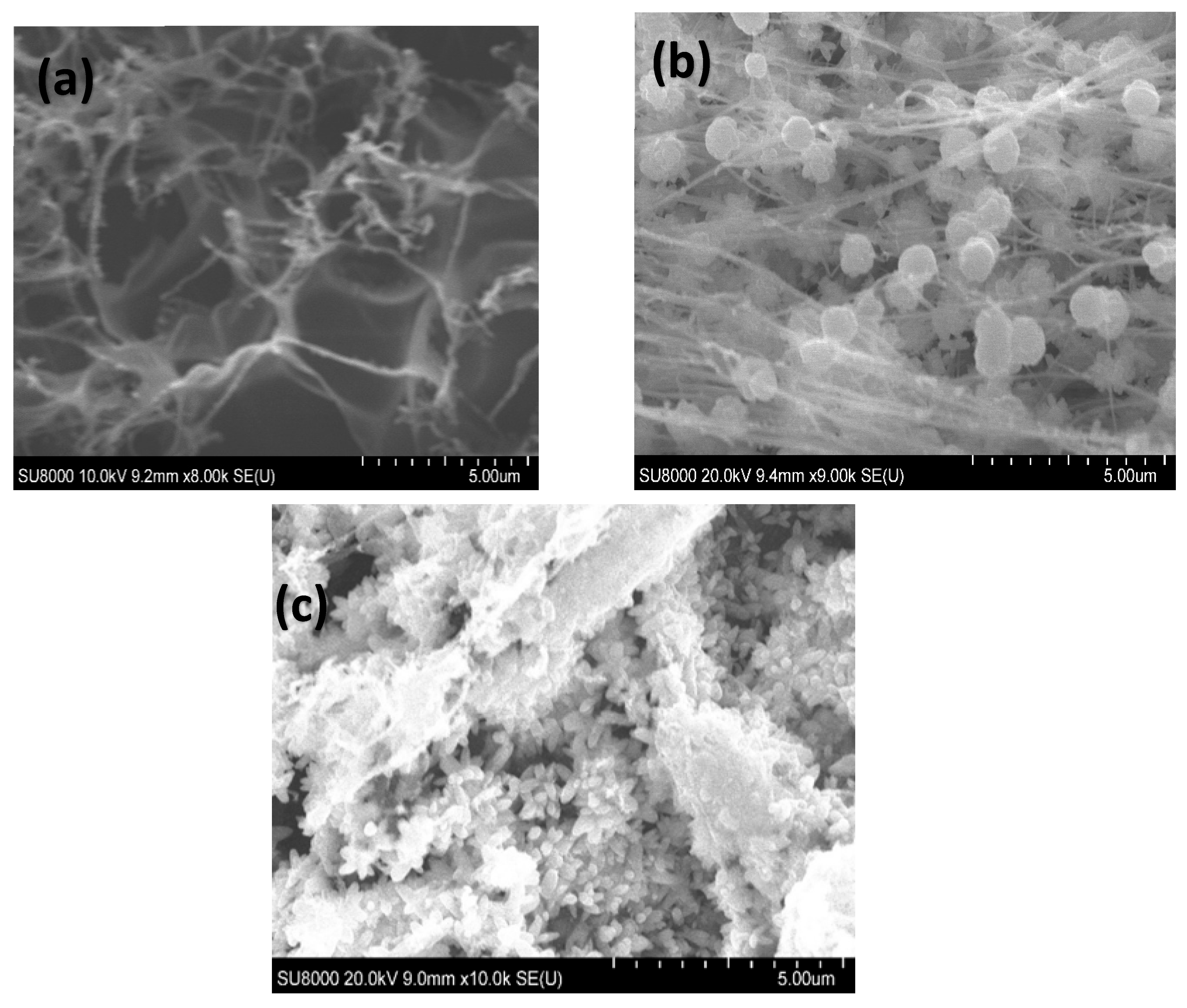
3.2. Physical Characterization of LIG-Modified Electrodes
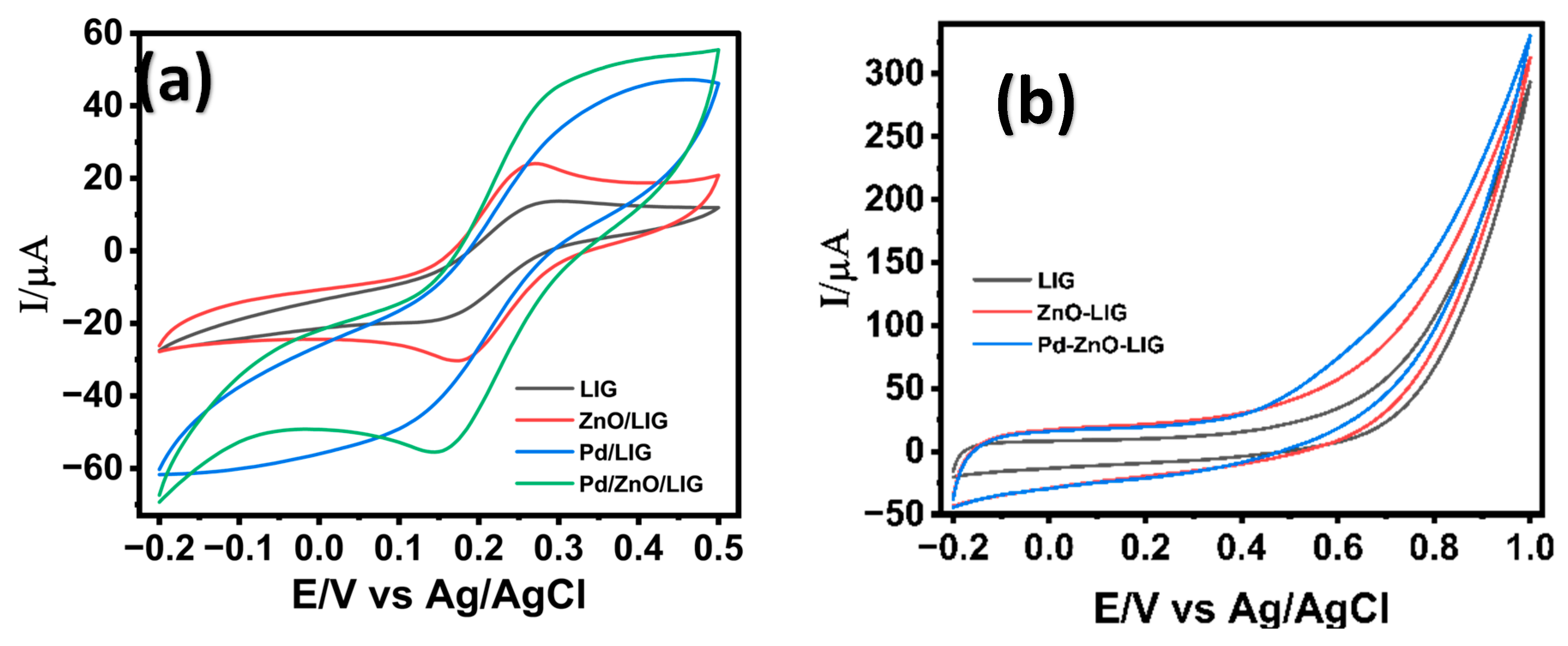
3.3. Electrochemical Characterization of LIG/ZnO/Pd Electrodes
3.4. Electrocatalytic Performance of LIG/ZnO/Pd-Based Glucose Sensor
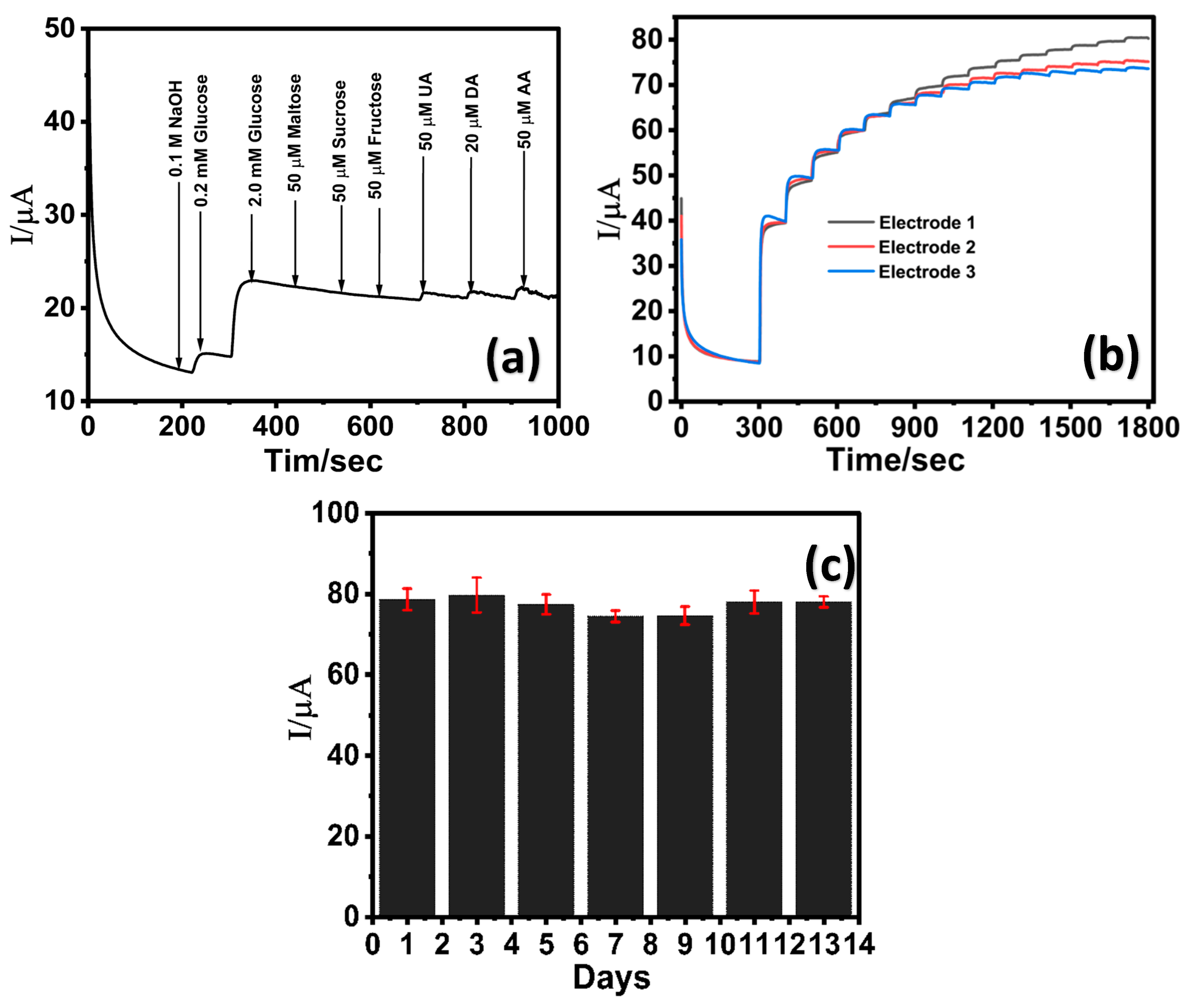
3.5. LIG/ZnO/Pd Sensor Selectivity, Reproducibility, and Shelf Life
3.6. Real Sample Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Samsu, N. Diabetic Nephropathy: Challenges in Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 1497449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Indyk, D.; Bronowicka-Szydełko, A.; Gamian, A.; Kuzan, A. Advanced glycation end products and their receptors in serum of patients with type 2 diabetes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 13264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. National Diabetes Statistics Report. 2024. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/php/data-research/index.html (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Parker, E.D.; Lin, J.; Mahoney, T.; Ume, N.; Yang, G.; Gabbay, R.A.; ElSayed, N.A.; Bannuru, R.R. Economic costs of diabetes in the US in 2022. Diabetes Care 2024, 47, 26–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, M.D.; Ong, S.C.; Rafiq, A.; Kalam, M.N.; Sajjad, A.; Abdullah, M.; Malik, T.; Yaseen, F.; Babar, Z.U.D. A systematic review of the economic burden of diabetes mellitus: Contrasting perspectives from high and low middle-income countries. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 2024, 17, 2322107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- International Diabetes Federation (IDF). IDF Diabetes Atlas 11th Edition Report 2025. IDF Diabetes Atlas 2025|Global Diabetes Data & Insights. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/resources/idf-diabetes-atlas-2025/ (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Nakrani, M.N.; Wineland, R.H.; Anjum, F. Physiology, Glucose Metabolism; StatPearls: Tampa/St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 2020. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560599/ (accessed on 19 April 2025).
- Banday, M.Z.; Sameer, A.S.; Nissar, S. Pathophysiology of diabetes: An overview. Avicenna J. Med. 2020, 10, 174–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poznyak, A.; Grechko, A.V.; Poggio, P.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Alfieri, V.; Orekhov, A.N. The diabetes mellitus–atherosclerosis connection: The role of lipid and glucose metabolism and chronic inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolla, A.S.; Priefer, R. Blood glucose monitoring overview of current and future non-invasive devices. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2020, 14, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, A.K.; Henshaw, G.S.; Williams, D.E. Errors in ambient gas concentration measurement caused by the acoustic response of electrochemical gas sensors. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2023, 354, 114254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teymourian, H.; Barfidokht, A.; Wang, J. Electrochemical glucose sensors in diabetes management: An updated review (2010–2020). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 7671–7709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farquhar, A.K.; Henshaw, G.S.; Williams, D.E. Understanding and correcting unwanted influences on the signal electrode from electrochemical gas sensors. ACS Sens. 2021, 6, 1295–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wu, J.-T.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.-M.; Jin, H.-G.; Yang, C.; Liu, J.; Li, G.-L.; He, Q.G. Recent advances in black phosphorus-based electrochemical sensors: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1170, 338480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lingbin, O.; Liu, G.; Xia, N. Research progress and application prospects of electrochemical glucose sensors. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 210633. [Google Scholar]
- Mihai, D.A.; Stefan, D.S.; Stegaru, D.; Bernea, G.E.; Vacaroiu, I.A.; Papacocea, T.; Olaru, O.G. Continuous glucose monitoring devices: A brief presentation. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 23, 174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Y.; Chang, S.J.; Chen, C.J.; Liu, J.T. Glucose monitoring sensors: History, principle, and challenges. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 057514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thatikayala, D.; Ponnamma, D.; Sadasivuni, K.K.; Cabibihan, J.J.; Al-Ali, A.K.; Malik, R.A.; Min, B. Progress of advanced nanomaterials in nonenzymatic electrochemical sensing and H2O2. Biosensors 2020, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Liang, Z.; Chen, S.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Q.; Wang, Y. Reusable Electrochemical non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on Au-inlaid nanocages. Nano Res. 2022, 15, 6490–6499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.S.M.; Hernandez-Escobar, C.A.; Enriquez-Duran, S.K.; Estrada-Monje, A.; Zaragoza-Contreras, E.A.; Pinon-Balderrama, C.I. Non-Enzymatic Electrochemical Sensing Glucose with Silver Nanoparticles Supported on Poly(3-aminobenzoic acid). Chemosensors 2025, 13, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, A.S.; Tahira, A.; Solangi, Z.A.; Solangi, A.G.; Ibupoto, M.H.; Chang, F.; Medany, S.S.; Nafady, A.; Kasry, A.; Willander, M.; et al. Pd-Co3O4-based nanostructures for the development of enzyme-free glucose sensors. Bull. Mater. Sci. 2022, 45, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakdaphetsiri, K.; Thaweeskulchai, T.; Sukmas, W.; Wang, J.; Schulte, A.; Rodthongkum, N. Laser-Induced Graphene Electrode Modified by Platinum nanoparticle/Zein/Gelatin/Glucose Oxidase for Non-Invasive Glucose Sensor in Multiple Biofluids. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1353, 343974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayranci, R. The rapid and practical route to Cu@ PCR sensor: Modification of copper nanoparticles upon conducting polymer for a sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 268–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akter, R.; Saha, P.; Shah, S.S.; Shaikh, M.N.; Aziz, M.A.; Ahammad, A.S. Nanostructured Nickel-based Non-enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensors. Chem.–Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Chu, D.; Yan, L.; Lai, H.; Chu, X.-Q.; Ge, D.; Chen, X. Enhanced non-enzymatic glucose sensing based on porous ZIF-67 hollow nanoprisms. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 10031–10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shruthi Keerthi, D.; Vani, M.M.; Krishnamurthy, B. Green-Synthesized Nanomaterial Coatings for High-Performance Electrodes. Funct. Coat. Biomed. Energy Environ. Appl. 2024, 231–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, W.; Miao, F.; Tao, B.; Zang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Shi, C.; Chu, P.K. Hybrid ZnO–graphene electrode with palladium nanoparticles on Ni foam and application to self-powered nonenzymatic glucose sensing. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 12134–12145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aspoukeh, P.K.; Barzinjy, A.A.; Hamad, S.M. Synthesis, properties and uses of ZnO nanorods: A mini review. Int. Nano Lett. 2022, 12, 153–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayakar, T.; Rao, K.V.; Bikshalu, K.; Rajendar, V.; Park, S.-H. Novel synthesis and structural analysis of zinc oxide nanoparticles for the non-enzymatic glucose biosensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 75, 1472–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, D.H.; Romero, G.A.Á.; Huizar, L.H.M.; Galan-Vidal, C.A.; Aguilar-Lira, G.Y. Glucose Determination Using Non-Enzymatic Sensors Based on Fe2O3 Nanoparticles. ECS Trans. 2022, 106, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, B.A.; Tsegaye, A.A.; Shifera, G.; Taddesse, A.M. A sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensor based on a ZnO/Co3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 347–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, J.; Dong, Q.; Zhou, F.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Yu, H.; Xiong, X. One-step synthesis of CuO nanoparticles based on flame synthesis: As a highly effective non-enzymatic sensor for glucose, hydrogen peroxide and formaldehyde. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 881, 114965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waqas, M.; Lan, J.; Zhang, X.; Fan, Y.; Zhang, P.; Liu, C.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, X.; Zeng, J.; Chen, W. Fabrication of Non-enzymatic Electrochemical Glucose Sensor Based on Pd-Mn Alloy Nanoparticles Supported on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Electroanalysis 2020, 32, 1226–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodnight, L.; Butler, D.; Xia, T.; Ebrahimi, A. Non-Enzymatic Detection of Glucose in Neutral Solution Using PBS-Treated Electrodeposited Copper-Nickel Electrodes. Biosensors 2021, 11, 409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, Y.; Zhang, T.; Feng, L.; Ran, J.; Ma, C.; Tan, Y.; Song, W.; Yang, B. Growth of nanostructured Cu3Al alloy films by magnetron sputtering for non-enzymatic glucose-sensing applications. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 14641–14650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, T.; Li, W.; Shang, R.; Lei, Y.; Liu, Y.; Ma, C. Experimental and theoretical study on one-step synthesis of AuAg alloy nanoparticle catalytic layer as highly stable non-enzymatic glucose sensing interface. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2023, 950, 117898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakhdari, D.; Guittoum, A.; Benbrahim, N.; Belgherbi, O.; Berkani, M.; Vasseghian, Y.; Lakhdari, N. A novel non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on NiFe (NPs)–polyaniline hybrid materials. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2021, 151, 112099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.; Gupta, V.K.; Huseinov, A.; Rahm, C.E.; Gazica, K.; Alvarez, N.T. Highly sensitive non-enzymatic glucose sensor based on carbon nanotube microelectrode set. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dey, B.; Ahmad, W.; Sarkhel, G.; Yang, D.-J.; Choudhury, A. Fabrication of porous nickel (II)-based MOF@ carbon nanofiber hybrid mat for high-performance non-enzymatic glucose sensing. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2022, 142, 106500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Sánchez, M.-I.; Khadhraoui, H.; Jiménez-Pérez, R.; Iniesta, J.; Valero, E. non-enzymatic glucose sensor using mesoporous carbon screen-printed electrodes modified with cobalt phthalocyanine by phase inversion. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Zhao, P.; Li, J.; Sun, Z.; Huang, W. Construction of a novel Co-based coordination polymer and its study of non-enzymatic glucose sensors. J. Solid-State Chem. 2022, 311, 123115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ariyasajjamongkol, N.; Phasuksom, K.; Paradee, N.; Sirivat, A. Negative current response of non–enzymatic glucose sensor based on pure PEDOT: PSS conductive polymer. Synth. Met. 2023, 297, 117413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raha, S.; Ahmaruzzaman, M. ZnO nanostructured materials and their potential applications: Progress, challenges and perspectives. Nanoscale Adv. 2022, 4, 1868–1925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.; Huang, J.H.; Gao, L.F.; Qi, Z.K.; Chen, K.F. Green synthesis of Nano-ZnO/N-Doped porous carbon composites for High-Performance Non-Enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensing. Microchem. J. 2025, 113272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.; Echabaane, M.; Omri, K.; Boudon, J.; Saviot, L.; Millot, N.; Chaabane, R.B. Cu-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Molecules 2021, 26, 929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, A.K.; Guha, P.; Srivastava, S.K.; Varma, S. Non-enzymatic glucose sensors based on electrodeposited CuxO–ZnO composite nanostructures. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Tangsuwanjinda, S.; Cheng, H.; Lee, P. Copper Oxide Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for the Production of a Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor. Coatings 2021, 11, 936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk Doğan, H.; Çepni, E.; Öznülüer Özer, T. Non-enzymatic Amperometric Detection of Glucose on One-Pot Electrochemical Fabricated Pd Nanoparticles-Graphene Modified Electrodes. Iran. J. Sci. 2024, 48, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-H.; Young, S.-J.; Hsien, C.-Y.; Chu, Y.-L.; Wang, Z.-H.; Chang, S.-J. Improved Non-enzymatic Glucose Sensors of ZnO Nanorods by Adsorb Pt Nanoparticles. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2024, 23, 303–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-H.; Sivakumar, C.; Balraj, B.; Murugesan, G.; Nagarajan, S.K.; Ho, M.-S. Ag-Decorated Vertically Aligned ZnO Nanorods for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensor Applications. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vélez, C.A.; Soto-Pérez, J.J.; Corchado-García, J.; Larios, E.; Fulvio, P.F.; Echegoyen, L.; Cabrera, C.R. Glucose oxidation reaction at palladium-carbon nano-onions in alkaline media. J. Solid-State Electrochem. 2021, 25, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhara, K.; Mahapatra, D.R. Electrochemical nonenzymatic sensing of glucose using advanced nanomaterials. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 1–32, Erratum in: Fuel 2023, 345, 128182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Astruc, D. Recent trends and perspectives in palladium nanocatalysis: From nanoparticles to frameworks, atomically precise nanoclusters and single-atom catalysts. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2024, 34, 2903–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eswaran, M.; Rahimi, S.; Pandit, S.; Chokkiah, B.; Mijakovic, I. A flexible multifunctional electrode based on conducting PANI/Pd composite for non-enzymatic glucose sensor and direct alcohol fuel cell applications. Fuel 2023, 345, 128182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wang, W.; Zhao, H.; Meng, P.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Y. A flexible electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of glucose (Glu) and ethanol (Eth) using ZnO and Pd nanoparticles. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2023, 53, 2013–2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maťátková, O.; Michailidu, J.; Miškovská, A.; Kolouchová, I.; Masák, J.; Čejková, A. Antimicrobial properties and applications of metal nanoparticles biosynthesized by green methods. Biotechnol. Adv. 2022, 58, 107905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaweeskulchai, T.; Sakdaphetsiri, K.; Schulte, A. Ten years of laser-induced graphene: Impact and future prospects on biomedical, healthcare, and wearable technology. Microchim. Acta 2024, 191, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moon, H.-R.; Ryu, B. Review of Laser-Induced Graphene (LIG) Produced on Eco-Friendly Substrates. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf.-Green. Tech. 2024, 11, 1279–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sunday, J.; Amoah, K.; Slaughter, G. Growth of electrodeposited ZnO nanowires. Thin Solid Films 2015, 592, 76–80. [Google Scholar]
- El Hafidi, Z.; Outaleb, N.; Naimi, Y. Electrodeposition of ZnO thin films at low temperature: Effects of deposition potential on properties for ZnO/CuO heterojunction solar cells. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2024, 35, 1861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patella, B.; Moukri, N.; Regalbuto, G.; Cipollina, C.; Pace, E.; Di Vincenzo, S.; Aiello, G.; O’Riordan, A.; Inguanta, R. Electrochemical synthesis of zinc oxide nanostructures on flexible substrate and application as an electrochemical immunoglobulin-G immunosensor. Materials 2022, 15, 713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, S.R.; Mukherjee, P.; Bhattacharya, S.K. A highly sensitive nonenzymatic glucose sensor based on carbon electrode amplified with PdxCuy catalyst. Electroanalysis 2021, 33, 820–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.K.; Mahbub, H.; Nowrin, F.H.; Malmali, M. Highly robust laser-induced graphene (LIG) ultrafiltration membrane with a stable microporous structure. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 46884–46895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarode, A.; Torati, S.R.; Hossain, M.F.; Slaughter, G. A photo-driven bioanode based on MXene-decorated graphene. Electrochimica Acta 2024, 498, 144637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Tao, B.; Miao, F.; Zang, Y. Electrodeposited Pd/graphene/ZnO/nickel foam electrode for the hydrogen evolution reaction. RSC Adv. 2019, 9, 33814–33822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movaghgharnezhad, S.; Kang, P. Laser-induced graphene: Synthesis advances, structural tailoring, enhanced properties, and sensing applications. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 6718–6742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, N.; Mehta, D.; Chaturvedi, A.; Mandal, D.; Nagaiah, T.C. Glucose oxidation assisted hydrogen and gluconic/glucaric acid production using NiVP/Pi bifunctional electrocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. A 2023, 11, 15868–15877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caglar, A.; Düzenli, D.; Onal, I.; Tezsevin, I.; Sahin, O.; Kivrak, H. A novel experimental and density functional theory study on palladium and nitrogen doped few-layer graphene surface towards glucose adsorption and electrooxidation. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2021, 150, 109684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Lin, Y.; Kang, K.; Meng, Y.; Feng, Z.; Wang, J. A non-enzymatic amperometric glucose sensor based on the use of graphene frameworks-promoted ultrafine platinum nanoparticles. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Lv, H.W.; Peng, H.L.; Li, Q.F. Development of a non-enzymatic glucose electrode based on Au nanoparticles decorated single-walled carbon nanohorns. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2021, 32, 12705–12715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, C.E. Strategies for assessing the limit of detection in voltametric methods: Comparison and evaluation of approaches. Analyst 2024, 149, 4295–4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.P.; Hong, B.D.; Lin, Y.M.; Lee, C.L. Catalysis of the D-glucose oxidation reaction using octahedral, rhombic dodecahedral, and cubic Pd@Pt core–shell nanoparticles. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 260, 118140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.S.; Hsu, S.Y.; Lee, C.L. Sequential and transient electrocatalysis of glucose oxidation reactions by octahedral, rhombic dodecahedral, and cubic palladium nanocrystals. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 211, 1024–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Electrode | Method | Sensitivity (µA mM−1cm−2) | LoD (μM) | Linear Range (mM) | Synthesis Time (hrs) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO/Co3O4/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite | Amperometric | 1551.38 | 0.043 | 0.015–10 | 59 | [31] |
| Pd-Mn alloy nanoparticles supported on reduced graphene oxide | Amperometric | 52.16 | 1.25 | 0.0161–1.152 | 49.08 | [33] |
| 22.55 | 1.152–4.875 | |||||
| Nano-ZnO/N-doped porous carbon composites | Amperometric | 255.99 | 0.39 | 0.002–3.28 | 29.5 | [44] |
| Cu-doped ZnO nanoparticles | Cyclic Voltammetry | Not provided | 0.0007 | 10−6–0.1 | 4.5 | [45] |
| CuxO-ZnO composite nanostructures | Amperometric | 384.6 | 0.7 | 0.03–3 | Not provided | [46] |
| Copper oxide decorated zinc oxide | Amperometric | 1142 | 13.9 | 1–7 | 3 | [47] |
| PANI/Pd composite | Cyclic Voltammetry | 2140 | 0.3 | 0.01–0.1 | 0.63 | [54] |
| LIG/ZnO/Pd | Amperometric | 25.625 | 130 | 2–24 | 0.46 | This work |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aviha, R.; Joshi, A.; Slaughter, G. Fabrication of Palladium-Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060201
Aviha R, Joshi A, Slaughter G. Fabrication of Palladium-Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(6):201. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060201
Chicago/Turabian StyleAviha, Reagan, Anju Joshi, and Gymama Slaughter. 2025. "Fabrication of Palladium-Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing" Chemosensors 13, no. 6: 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060201
APA StyleAviha, R., Joshi, A., & Slaughter, G. (2025). Fabrication of Palladium-Decorated Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Non-Enzymatic Glucose Sensing. Chemosensors, 13(6), 201. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13060201






