Current Opportunities and Trends in the Gas Sensor Market: A Focus on e-Noses and Their Applications in Food Industry
Abstract
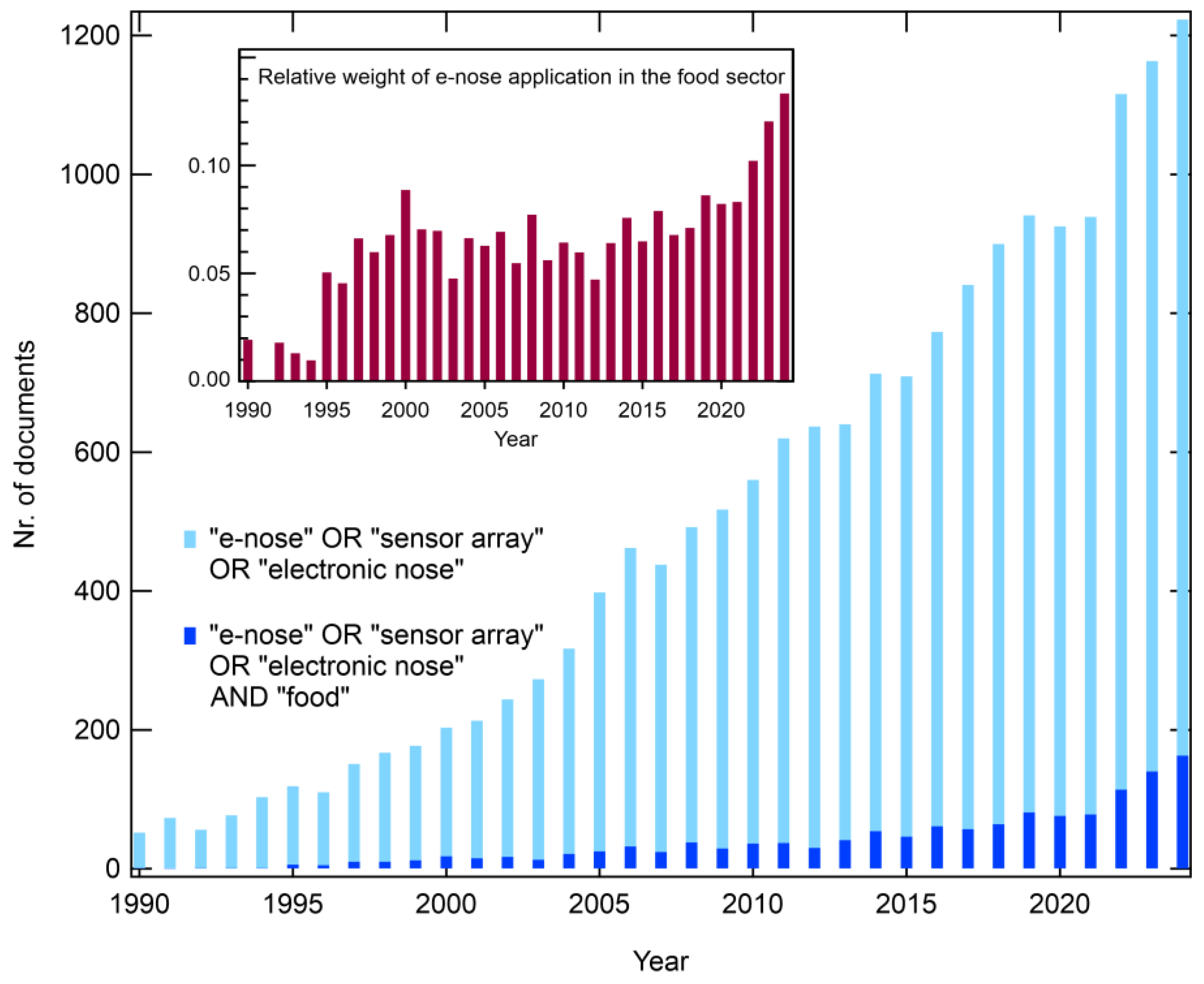
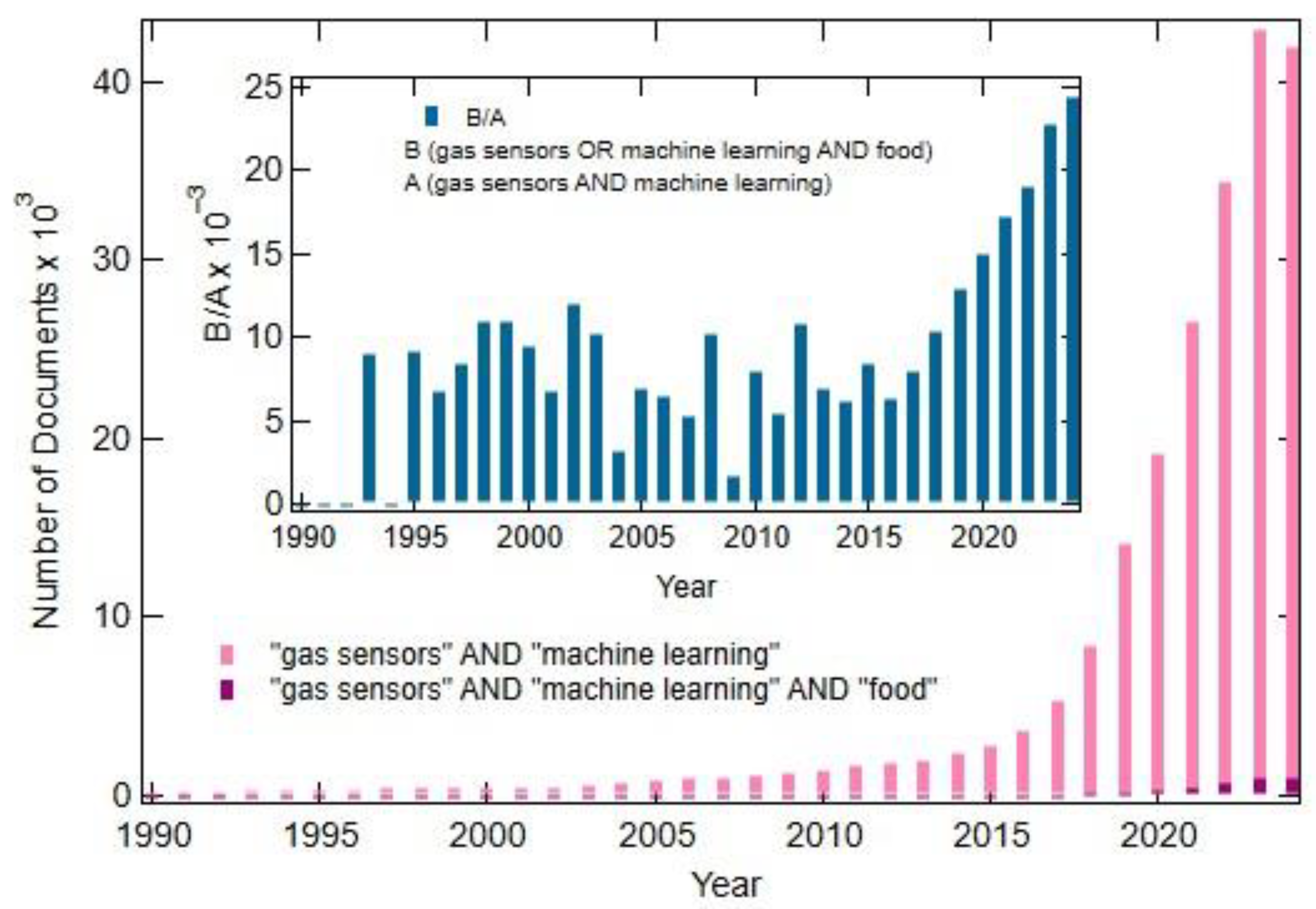
1. Introduction
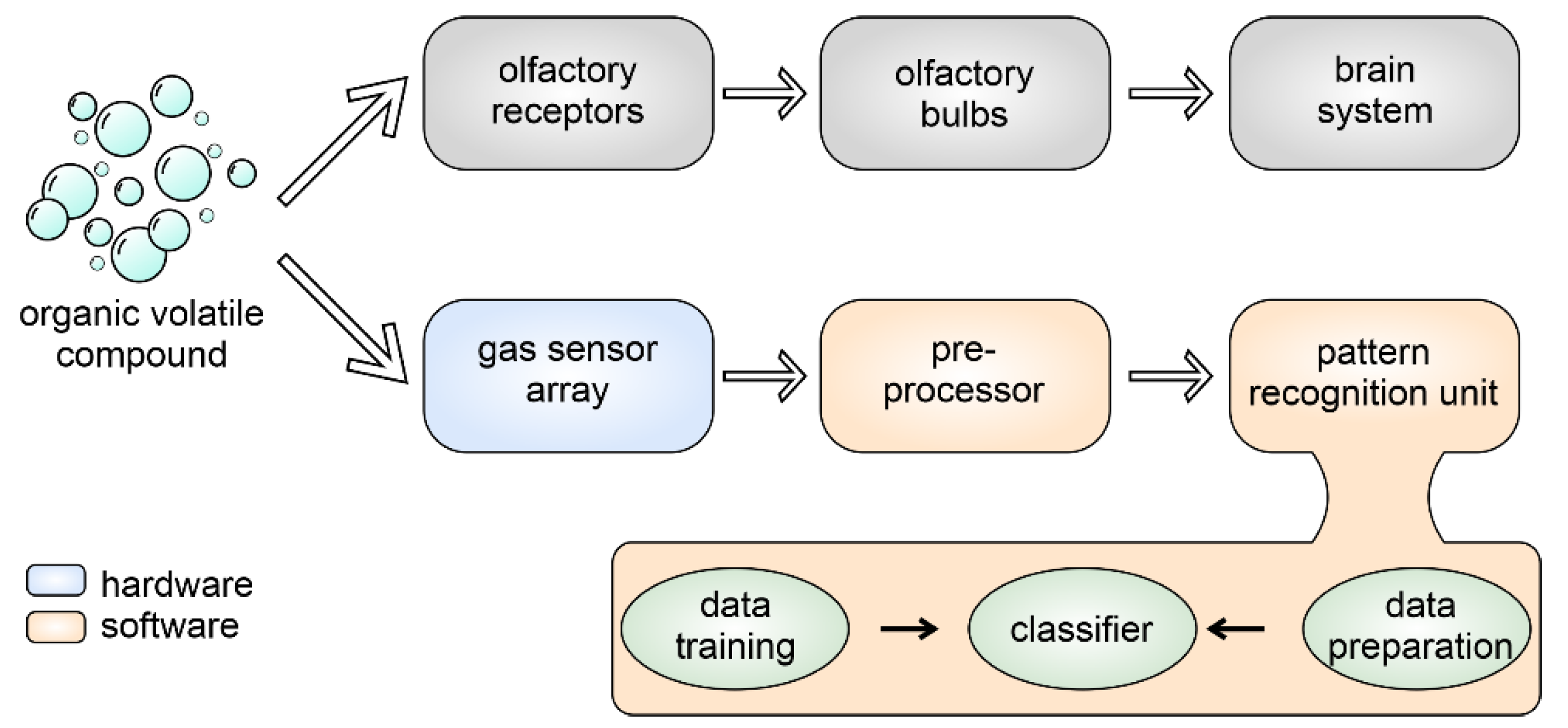
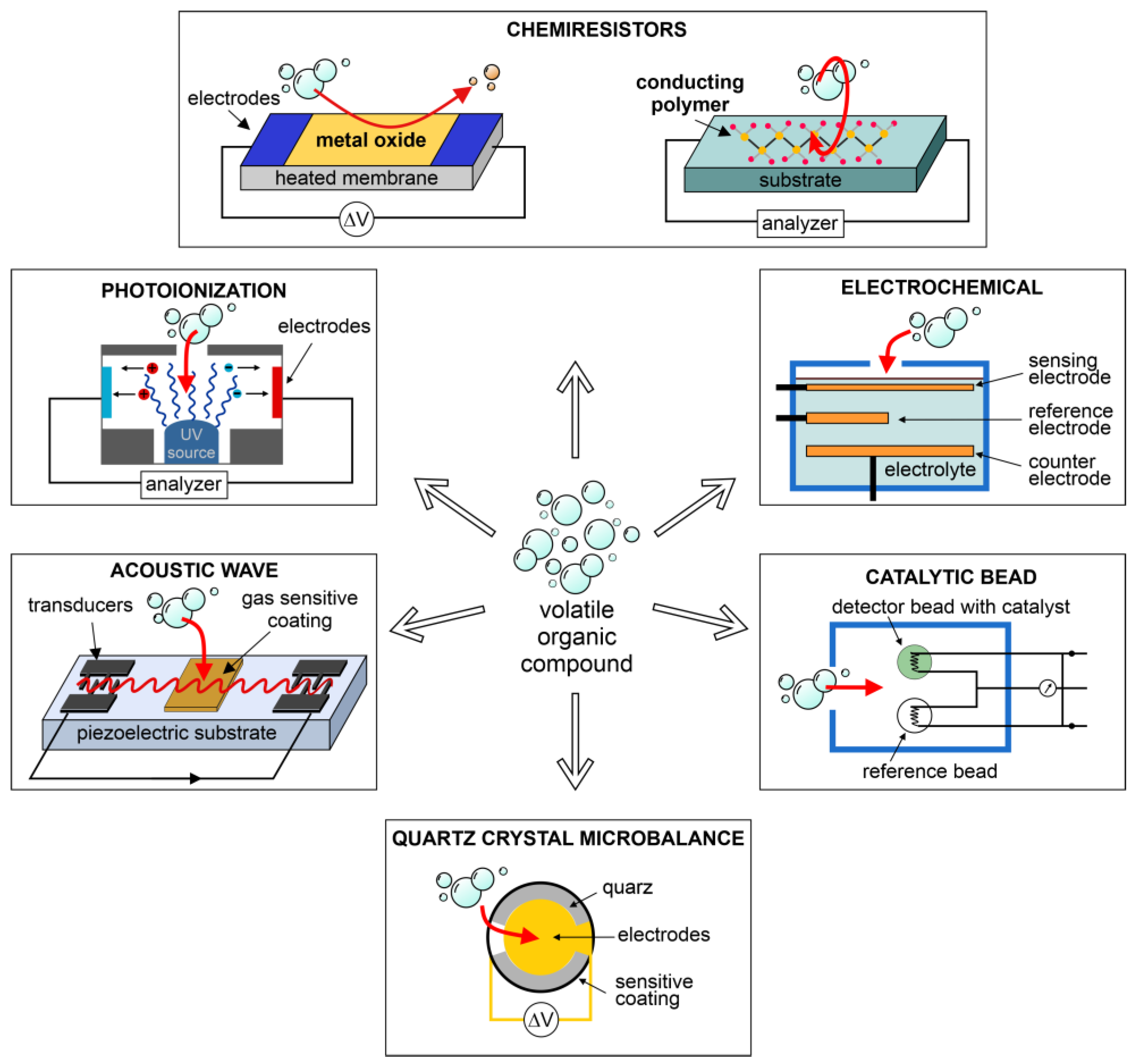
2. E-Noses: Working Principle and Sensors Classification
- The perception of odor particles, such as volatile organic compounds (VOCs), by the sensor array corresponds to the olfactory receptors in the biological olfactory system;
- The processing of the odor signal occurs in the olfactory bulbs [54];
- The delivery of the information for odor identification occurs through trained ML algorithms as an analogy to what happens in the brain cortex, matching with the response patterns stored in the brain memory [55].
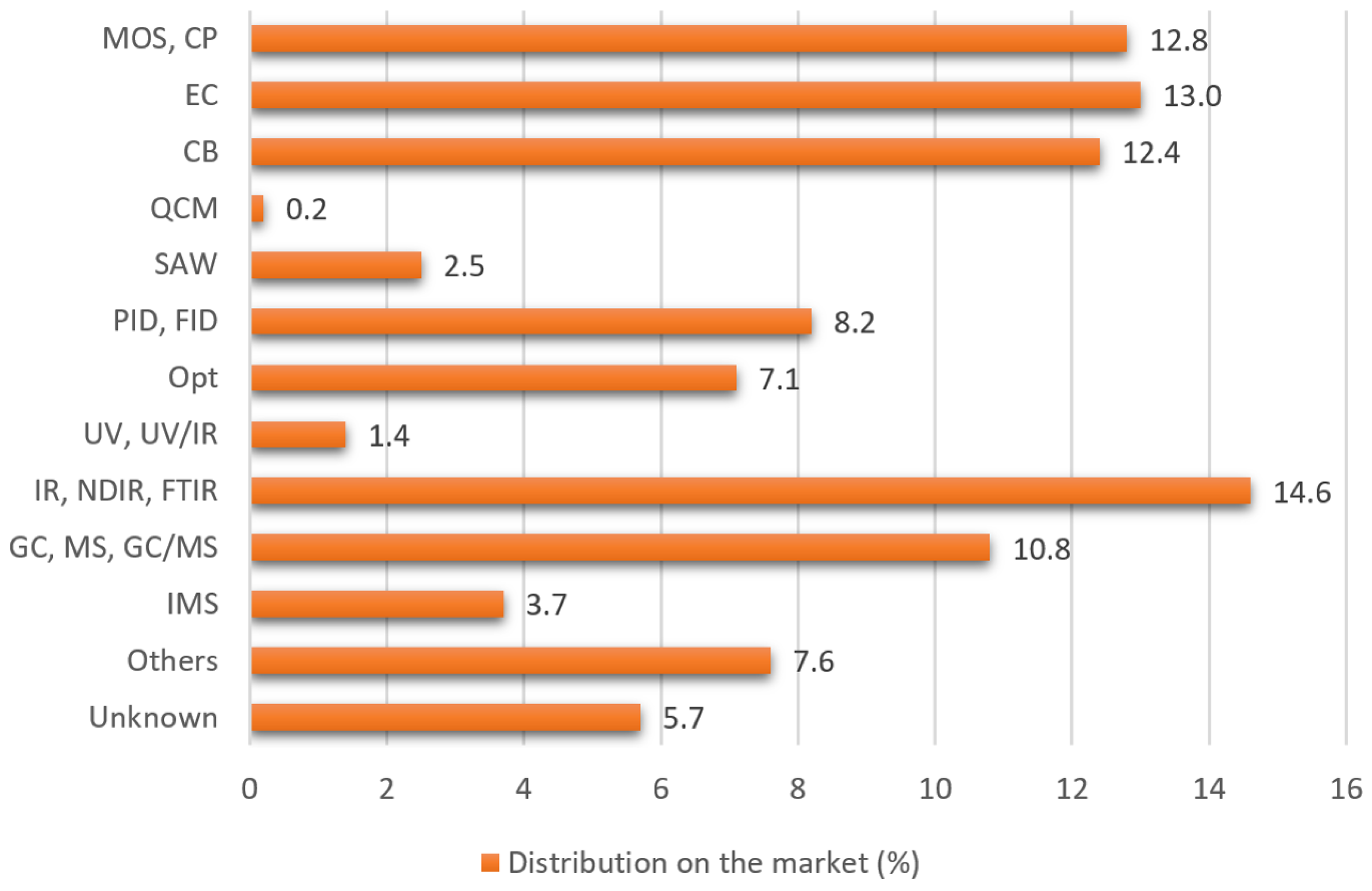
Sensors in e-Noses
- Sensitivity: the intensity of the sensor’s response after exposure to a target gas. This is usually defined as a relative change of the signals registered before and during the exposure to gas analytes;
- Response time: the time interval the sensor array takes to measure an analyte. It is usually defined as the time required for the sensor signal to increase from 0% to 90% of the total response;
- Recovery time: the time required by the sensor signal to decrease to 10% of the maximum response;
- Selectivity: the ability to discern the concentration of a substance in the presence of other interfering substances;
- Resolution: the minimum significant variation of the signal;
- Drift: the tendency of the output signal to monotonically vary due to a change of sensor material properties over the measurement time;
- Repeatability: the ability to provide a stable signal in repeated measurements;
- Detection Limit or Limit of Detection (LOD): the lowest analyte concentration detected by the sensor, i.e., the lowest concentration of an analyte that can be reliably distinguished from background noise;
- Limit of Quantification (LOQ): the lowest concentration that can be measured with acceptable precision and accuracy (see, e.g., Ref. [59]);
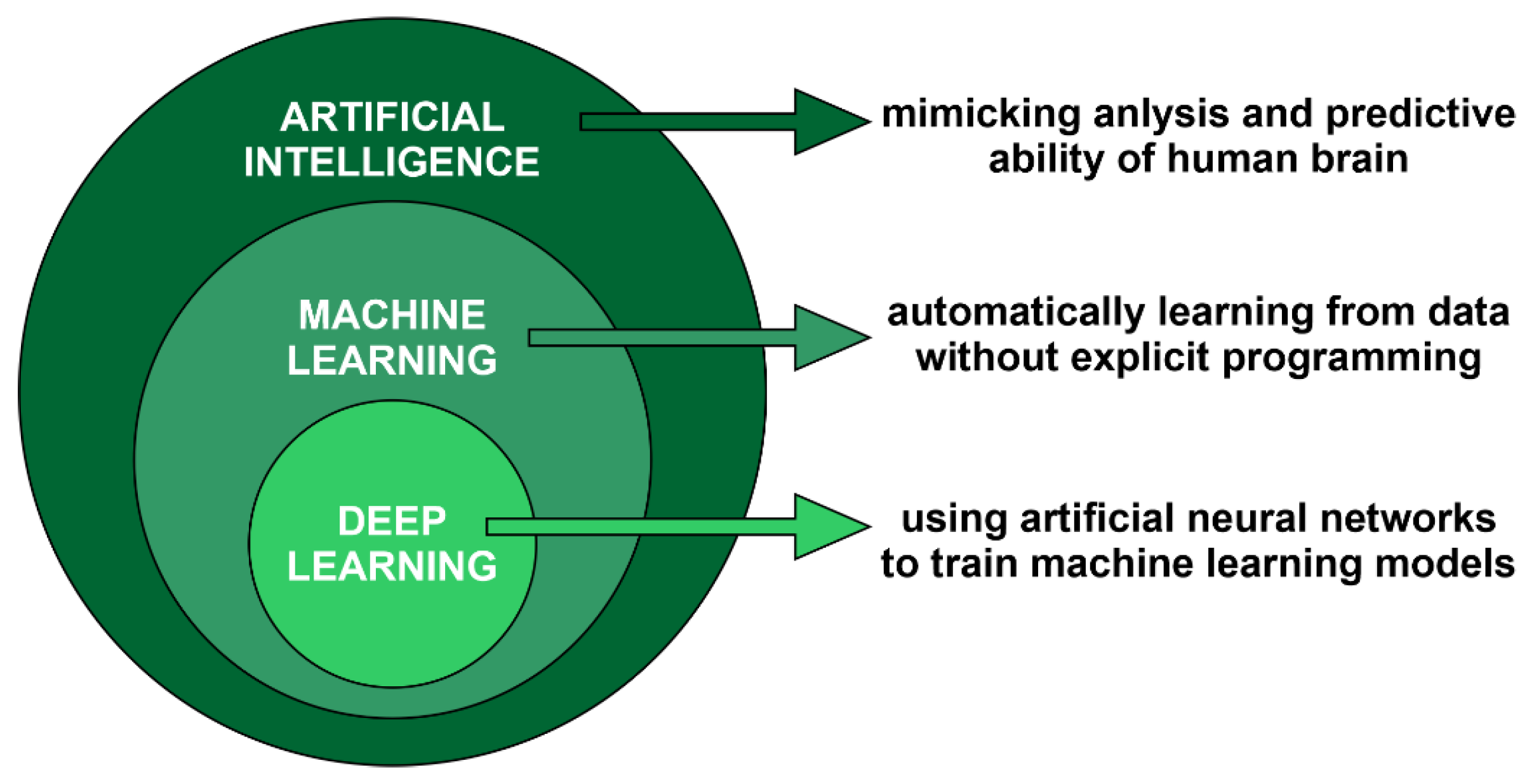
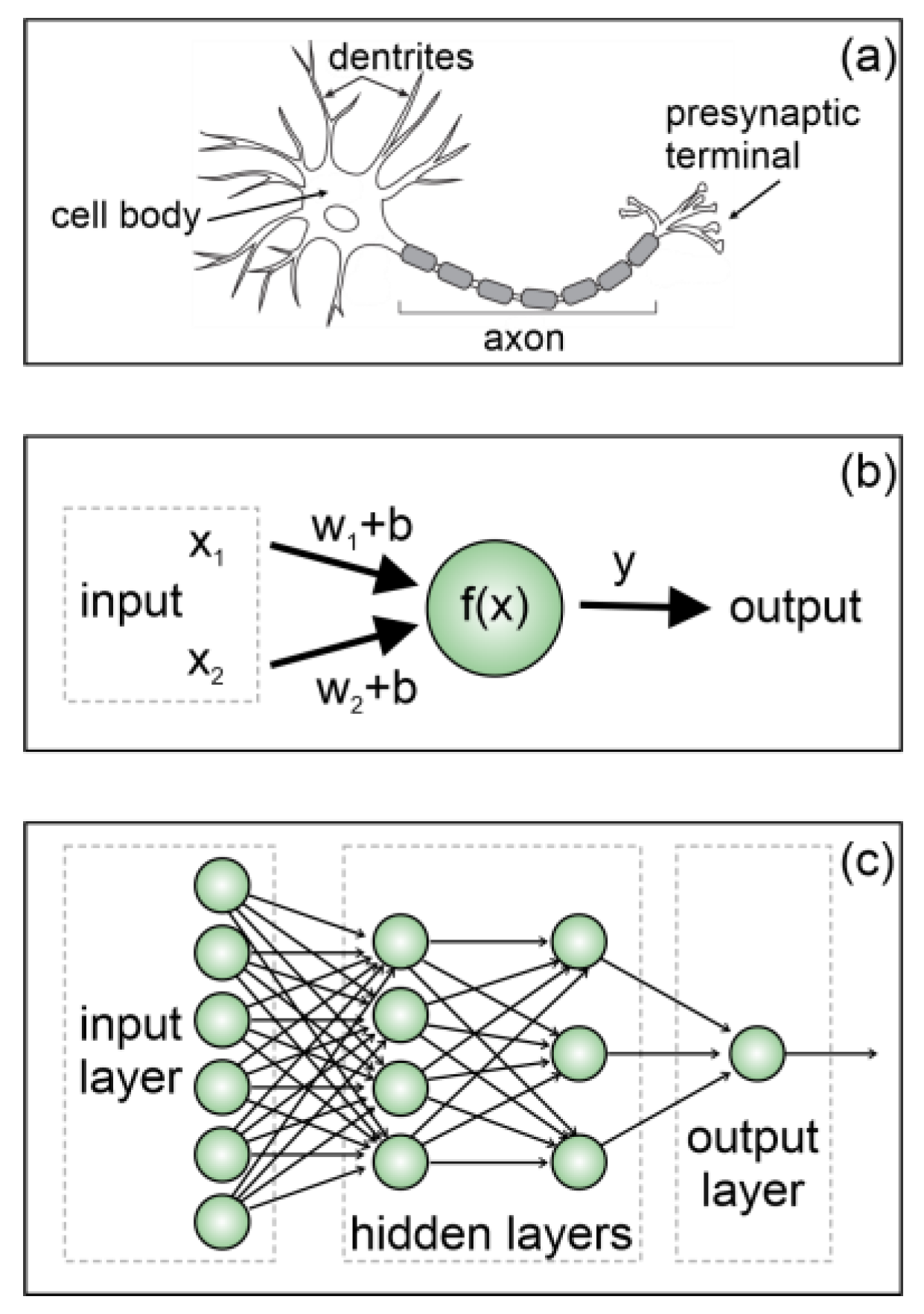
3. Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in e-Nose Technology
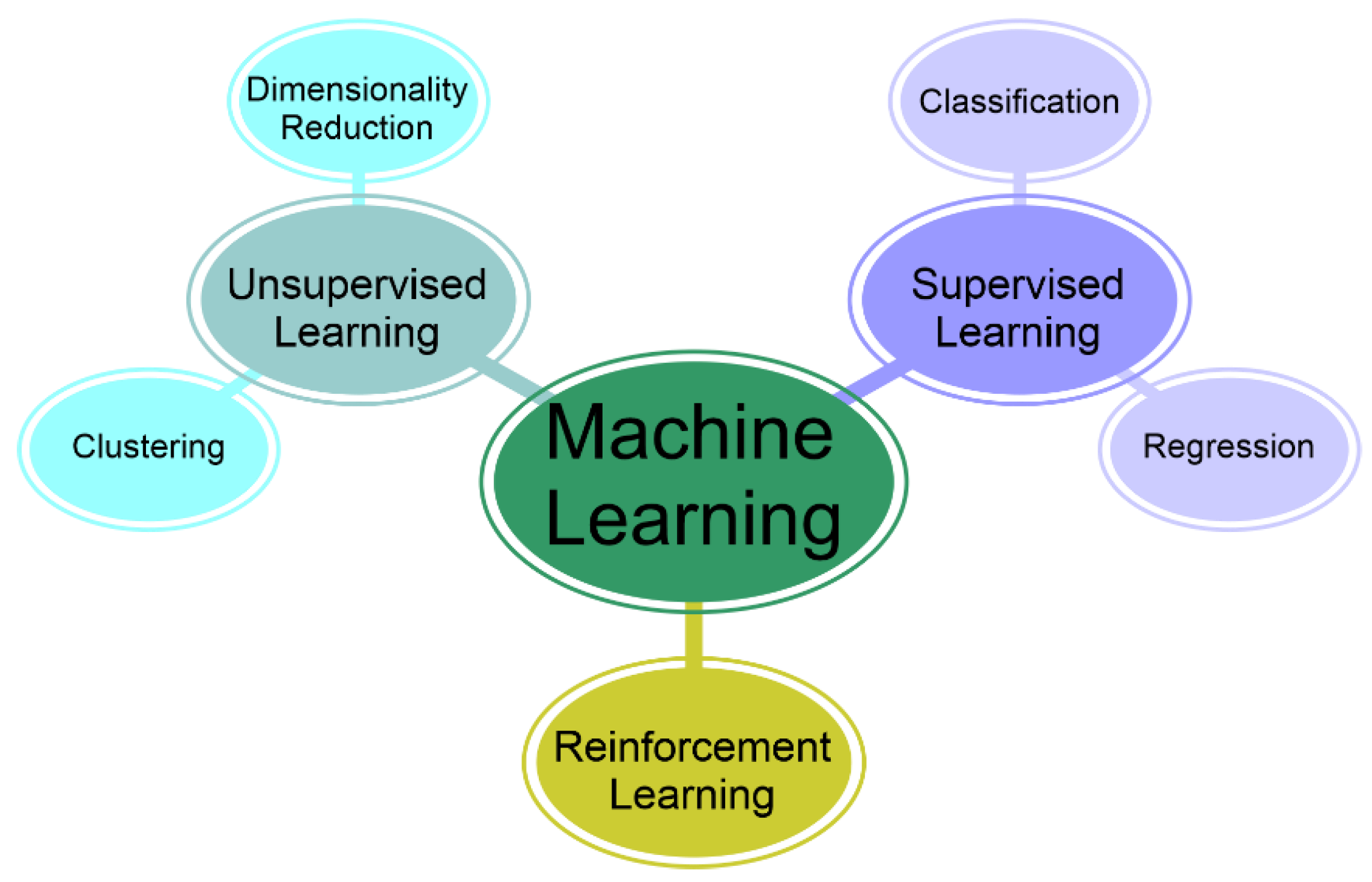
3.1. ML Paradigms
3.2. Data Preparation
3.3. Data Analysis
3.4. Model Building: Training and Evaluation
- A true positive (TP) refers to a correct prediction of an actual value of the dataset.
- A false positive (FP) refers to a wrong prediction about a value that actually belongs to the dataset.
- A true negative (TN) refers to a correct prediction about a value that does not belong to the dataset.
- A false negative (FN) corresponds to a wrong prediction of a value outside the dataset.
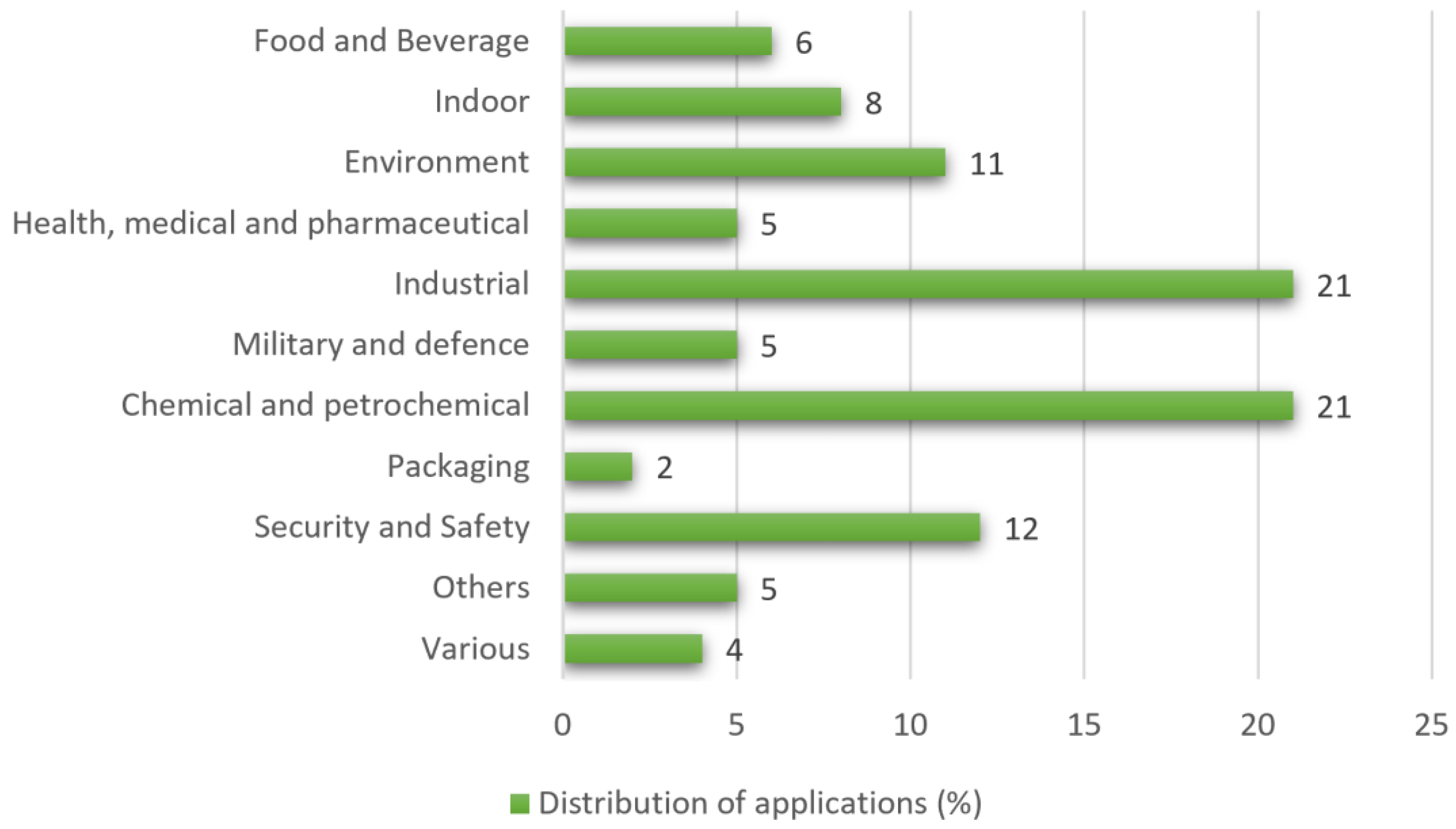
4. Application Fields of e-Nose Technology
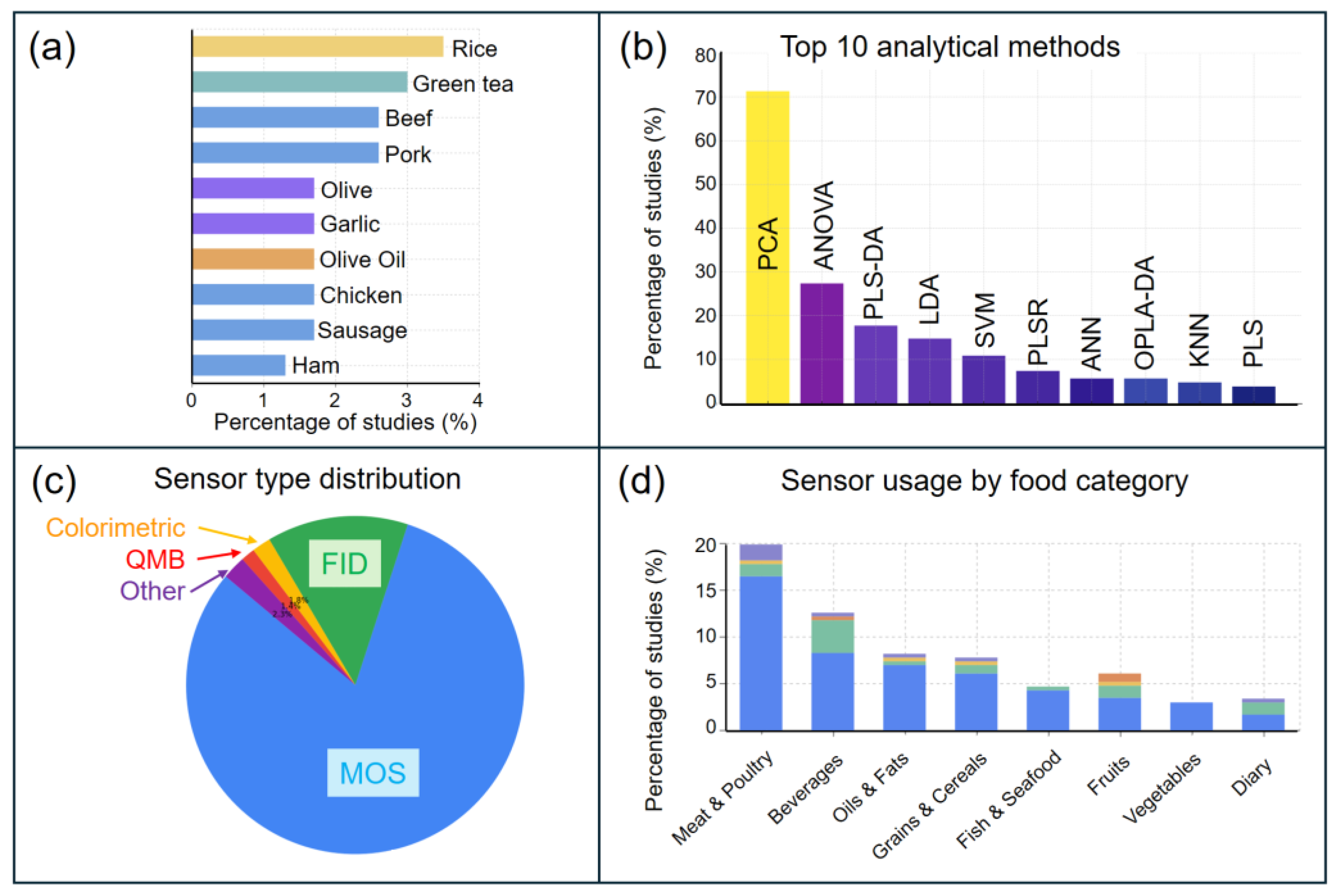
4.1. Food and Beverage
| Manufacturer | Product | Sensor Technology | Application Area | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AIRSENSE Analytics GmbH & PCA Technologies | Portable Electronic Nose (PEN3) | MOS | Quality control: food freshness, oil rancidity, off-odor of packaging materials, flavor degradation, aroma characterization in beverages; Process control: spice dosage in food production, inspection of fermentation processes, monitoring of coffee roasting | [173] |
| Alpha MOS | Heracles Neo | Flash GC technology | Quality control: Food flavor, fraud detection on product origin, detection of food adulteration, gelatin quality | [174] |
| Aryballe Technologies | NeOse Advance | Optical sensor based on array of Mach-Zehnder Interferometers | Discrimination of flavored beverages and of coffee samples, vanillin quality, automation of home cooking by detecting odor changes, determination of food ripeness or freshness | [175] |
| FOODSniffer | The FOODsniffer | Optoelectronic sensor (LED self-aligned to a broadband Mach–Zehnder interferometer and a photodetector array) | Determination of food ripeness or freshness, detection of poisoned food | [167] |
| Gerstel GmbH & Co. KG | ChemSensor 4440A | Headspace GC and quadrupole MS | Routine quality control and measurements of flavors | [168] |
| Honeywell Analytics | GasAlertMicro 5 | EC, CB | NH3 from refrigerants, PH3 from fumigation in food & beverage industry | [176] |
| GasAlertMicro 5 IR | EC, IR | By-product of yeast fermentation in wineries and breweries; Solid CO2 (dry ice) used as a refrigerant and for carbonation; CO2 used in packaging to extend storage shelf life in food industry and cold storage | [176] | |
| Sensepoint XCD RTD | EC | No detailed information | [177] | |
| Manning AirScan IRF9 | IR | Quality control: banana ripeness, food processing, wineries; Process monitoring: beverage and gas bottling plants, product coolers, rack houses, refrigeration systems | [178] | |
| RAE Systems by Honeywell | Honeywell BW™ Ultra | PID, IR | Detection of NH3 in refrigeration and agriculture, of CO2 in wineries and breweries, of HCN in perishable food shipping | [179] |
| International Gas Detectors Ltd. | TOC-750X Series | EC, IR, PID, CB | Process monitoring: beverage plants, breweries, food processing, refrigeration in commercial kitchens | [180] |
| TOC-30 | IR, EC, and CB | Refrigeration, hospitality/beverage and breweries; used in freezers/coolers and commercial kitchens, bottle stores, and more | [181] | |
| POLI | PID, EC, CB, NDIR | Beverage industry and agriculture | [182] | |
| Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT) | SAGAS | SAW sensor array | Coffee analysis | [159] |
| Owlstone Inc. | Lonestar | Field Asymmetric Ion Mobility Spectrometer (FAIMS) | Detection of food and beverage taints, food freshness, and odors | [183] |
| RipeSense Limited (by Jenkins Group Ltd.) | ripeSense® | Colorimetric | Detection of food ripeness | [169] |
| Sacmi Imola Scarl | EOS Aroma | 6 MOS sensors | Analysis of flavors and aromas of olive oil | [161] |
| Sensigent | Cyranose® 320 | NoseChip™ Nanocomposite sensor array | Microbiological food spoilage screening, detection of foodborne bacteria on beef | [184] |
| eNose Aqua | NoseChip™ Nanocomposite sensor array | Detection of contamination in bottled water, wine, beer, distilled spirits, soda, and juices | [185] | |
| eNose QA | NoseChip™ Nanocomposite sensor array | Detection of contamination in bottled water, food and beverage containers, and in bottles for recycling and reusing | [185] | |
| Shimadzu Co. | Nexis GC-2030 | GC | Aroma components analysis in essential oils and beers, determination of volatile substances in liquors, analysis of components in kimchi, identification of sulfur compounds | [186] |
| GC-2010 Pro | GC, FID | Check for residual solvent in food packaging; analysis of vegetable oils, alcohol congeners in alcoholic beverages, mineral oil residues in food, aroma components in Japanese sake, fatty acid content ratio in polysorbate 80, THP in soil, residual pesticides in agriproducts, volatile substances in the headspace of wine | [187] | |
| Nexis SCD-2030 | GC | Analysis of volatile sulfur compounds and hydrogen sulfide in beer | [188] | |
| GCMS-TQ8050 NX | Triple Quadrupole GC/MS | Analysis of residual pesticides, mineral oil residues, dioxins in foods and animal feed | [189] | |
| GCMS-TQ8040 NX | Triple Quadrupole GC/MS | Quality control: metabolites analysis in tomato juice and beer, pesticide residues, food deterioration, chemical contaminants in marine fish, determination of geographical origin of agricultural products; Analysis of fragrance components in aroma oils | [190] | |
| GCMS-QP2010 SE | GC/MS | Determination of organophosphorus pesticide in herbal products; analysis of VOCs in drinking water | [191] | |
| Multi-Dimensional GC/GCMS System | GC, GC/MS | Analysis of fragrance components in food and beverages | [192] | |
| TD-30 Series | GC/MS | Analysis of fragrance components in food | [193] | |
| Agilent | 7000D Triple Quadrupole GC/MS | Quadrupole GC/MS | Quantitative analysis of ethylene oxide and ethylene chlorohydrin in sesame seeds, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) compounds in salmon and beef, pesticides in strawberries and complex food matrices, PAH compounds in edible oil, nitrosamines in drinking water | [194] |
| 7010D Triple Quadrupole GC/MS | Quadrupole GC/MS | Quantitative analysis of multiresidue pesticides in salmon, strawberries, and olive oil | [195] | |
| 7250 GC/Q-TOF | GC/MS | Quantitative analysis of pesticides and other contaminants in food matrices | [196] | |
| 8860 GC System | GC | Measurement of purgeable organic compounds in drinking water; Analysis of alcohols, aldehydes, and esters in spirits | [197] | |
| Intuvo 9000 GC System | GC | Dioxin analysis in food and animal feed, analysis of fatty acid methyl esters (FAME), test of drinking water, and food safety | [198] | |
| 8890 GC System | GC | Detection of benzene and derivatives in water, semi-volatile organic compounds in drinking water, organophosphorus and organochlorine pesticides in fruit and vegetables, FAME analysis | [199] | |
| 7890B GC System | GC | FAME analysis, detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) compounds in salmon, drinking water, pumpkin seed oil and other edible oil, off-odor compounds in drinking water, multiple pesticide residues in complex food matrices | [200] | |
| 7820A GC System | GC | Quantitative analysis of food preservatives, pesticide residues in food products, organochlorine pesticides in drinking water | [201] | |
| 5977C GC/MSD | Quadrupole GC/MS | Analysis of endrin and DDT stability, and of semi-volatile organic compounds in drinking water | [202] | |
| Plasmion GmbH | SICRIT® ionization | MS, GC/MS | Aroma profiling of coffee beans | [203] |
4.2. Other Application Areas
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AI | Artificial Intelligence |
| ANN | Artificial Neural Network |
| BAW | Bulk Acoustic Wave |
| CB | Catalytic Bead |
| CP | Conducting Polymer |
| DBS | Deep Brain Stimulation |
| DDT | Dichloro Diphenyl Trichloroethane |
| DFA | Deterministic Finite Automata |
| DL | Deep Learning |
| DQN | Deep Q-Networks |
| E-nose | Electronic Nose |
| EC | Electrochemical |
| FAIMS | Field Asymmetric Ion Mobility Spectrometry |
| FAME | Fatty Acids Methyl Ester |
| FID | Flame Ionization Detector |
| FN | False Negative |
| FP | False Positive |
| FPW | Flexural Plate Wave |
| FTIR | Fourier Transform Infrared |
| GC | Gas Chromatography |
| GC/MS | Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry |
| IMS | Ion Mobility Spectrometry |
| IR | Infrared |
| IoT | Internet of Things |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbor |
| LDA | Linear Discriminant Analysis |
| LOD | Limit of Detection |
| LOQ | Limit of Quantification |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| MOS | Metal Oxide Semiconducting |
| NDIR | Non-Dispersive Infrared |
| OPC | Optical Particle Counter |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Projections to Latent Structures Discriminant Analysis |
| Opt | Optical |
| PAH | Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbon |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PID | Photoionization Detector |
| PLS | Partial Least-Squares |
| PLS-DA | Partial Least-Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| PLSR | Partial Least-Squares Regression |
| ppm | Parts Per Million |
| QCM | Quartz Crystal Microbalance |
| ReLu | Rectified Linear Unit |
| SAW | Surface Acoustic Wave |
| SVM | Support Vector Machine |
| TMD | Transition Metal Dichalcogenides |
| TN | True Negative |
| TP | True Positive |
| t-SNE | t-distributed Stochastic Neighbor Embedding |
| U-MAP | Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
| VOC | Volatile Organic Compound |
References
- Wilson, A.D.; Baietto, M. Applications and Advances in Electronic-Nose Technologies. Sensors 2009, 9, 5099–5148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Kim, Y.; Kim, T.; Eom, T.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Jang, H.W. Chemoresistive materials for electronic nose: Progress, perspectives, and challenges. InfoMat 2019, 1, 289–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwaardemaker, H.; Hogewind, F. On Spray-Electricity and Waterfall-Electricity. KNAW Proc. 1920, 22, 429–437. [Google Scholar]
- Arshak, K.; Moore, E.; Lyons, G.; Harris, J.; Clifford, S. A review of gas sensors employed in electronic nose applications. Sens. Rev. 2004, 24, 181–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- S & S Insider. Available online: https://www.snsinsider.com/reports/electronic-nose-market-1303 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Hartman, J. A possible method for the rapid estimation of flavours in vegetables. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 1954, 64, 335–342. [Google Scholar]
- Moncrieff, R. An instrument for measuring and classifying odours. J. Appl. Physiol. 1961, 16, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buck, T.M.; Allen, F.G.; Dalton, J.V. Detection of Chemical Species by Surface Effects on Metals and Semiconductors. In Surface Effects in Detection; Bell Telephone Laboratories: Murray Hill, NJ, USA, 1965. [Google Scholar]
- Dravnieks, A.; Trotter, P.J. Polar vapour detector based on thermal modulation of contact potential. J. Sci. Instrum. 1965, 42, 624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pybus, D.; Sell, C. The Chemistry of Fragrances; RSC Paperbacks: Cambridge, UK, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Persaud, K.C.; Dodd, G. Analysis of discrimination mechanisms in the mammalian olfactory system using a model nose. Nature 1982, 299, 352–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikegami, A.; Kaneyasu, M. Olfactory detection using integrated sensors. In Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Solid-State Sensors and Actuators, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 11–14 June 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Gardner, J.W.; Bartlett, P.N. A brief history of electronic noses. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1994, 18, 210–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakaya, D.; Ulucan, O.; Turkan, M. Electronic Nose and Its Applications: A Survey. Int. J. Autom. Comput. 2020, 17, 179–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvani, M.; Freddi, S.; Sangaletti, L. Disclosing Fast Detection Opportunities with Nanostructured Chemiresistor Gas Sensors Based on Metal Oxides, Carbon, and Transition Metal Dichalcogenides. Sensors 2024, 24, 584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabchinskii, M.K.; Sysoev, V.V.; Glukhova, O.E.; Brzhezinskaya, M.; Stolyarova, D.Y.; Varezhnikov, A.S.; Solomatin, M.A.; Barkov, P.V.; Kirilenko, D.A.; Pavlov, S.I.; et al. Guiding Graphene Derivatization for the On-Chip Multisensor Arrays: From the Synthesis to the Theoretical Background. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2022, 7, 2101250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, A.; Ehlert, C.; Gryn, G. Sensing and sensitivity: Computational chemistry of graphene-based sensors. WIREs Comput. Mol. Sci. 2021, 1111, e1526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paghi, A.; Mariani, S.; Barillaro, G. 1D and 2D Field Effect Transistors in Gas Sensing: A Comprehensive Review. Small 2023, 19, 2206100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Benedetti, S.; Casiraghi, E.; Buratti, S. E-sensing systems for shelf life evaluation: A review on applications to fresh food of animal origin. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 40, 101221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarra, T.; Galang, M.G.; Ballesteros, F., Jr.; Balgiorno, V.; Naddeo, V. Environmental odour management by artificial neural network—A review. Environ. Int. Part B 2019, 133, 105189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonezzer, M.; Thi Thanh Le, D.; Van Duy, L.; Hoa, N.D.; Gasperi, F.; Van Duy, N.; Biasioli, F. Electronic noses based on metal oxide nanowires: A review. Nanotechnol. Rev. 2022, 11, 897–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, A.D. Application of Electronic-Nose Technologies and VOC-Biomarkers for the Noninvasive Early Diagnosis of Gastrointestinal Diseases. Sensors 2018, 18, 2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freddi, S.; Sangaletti, L. Trends in the development of electronic noses based on carbon nanotubes chemiresistors for breathomics. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 2992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abideen, Z.U.; Arifeen, W.U.; Nuwan, Y.M. Emerging trends in metal oxide-based electronic noses for healthcare applications: A review. Nanoscale 2024, 16, 9259–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Na, M.; Yu, J.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Hu, C. Sniffing Like a Wine Taster: Multiple Overlapping Sniffs (MOSS) Strategy Enhances Electronic Nose Odor Recognition Capability. Adv. Sci. 2023, 11, 2305639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hierlemann, A.; Gutierrez-Osuna, R. Higher-Order Chemical Sensing. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 563–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ao, S.; Liu, M.; Wang, D.; Zhu, E.; Liu, K.; Wang, W.; Ling, Y.; Fu, W.; Zhang, Z. Dual-parameter gas sensing with functional graphene field-effect transistors. Cell Rep. Phys. Sci. 2023, 4, 101564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.W.; Kim, B.H.; Seo, Y.H. Olfactory system-inspired electronic nose system using numerous low-cost homogenous and hetrogenous sensors. PLoS ONE 2022, 18, e0295703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parichencko, A.; Huang, S.; Pang, J.; Ibarlucea, B.; Cuniberti, G. Recent Advances in technologies toward the development of 2D matarials-based electronic noses. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Huang, Y.; Kam, K.W.; Cheung, W.F.; Zhao, N.; Zheng, B. Functionalized graphene-based chemiresistive electronic nose for discrimination of disease-related volatile organic compounds. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2019, 1, 100016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nallon, E.C.; Schnee, V.P.; Bright, C.; Polcha, M.P.; Li, Q. Chemical Discrimination with an Unmodified Graphene Chemical Sensor. ACS Sens. 2016, 1, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, K.L.; Rose-Pehrsson, S.L. Sensor Array Design for Complex Sensing Tasks. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2015, 8, 287–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayasaka, T.; Lin, A.; Copa, V.C.; Lopez, L.P., Jr.; Loberternos, R.; Ballesteros, L.I.M.; Kubota, Y.; Liu, Y.; Salvador, A.A.; Lin, L. An electronic nose using a single graphene FET and machine learning for water, methanol, and ethanol. Microsyst. Microengineering 2002, 6, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Askim, J.R.; Suslick, K.S. The Optoelectronic Nose: Colorimetric and Fluorometric Sensor Arrays. Chem. Rev. 2019, 1, 231–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannone, A.; Raj, A.; Ravichandran, H.; Das, S.; Chen, Z.; Price, C.A.; Sultana, M.; Das, S. Robust chemical analysis with graphene chemosensors and machine learning. Nature 2024, 634, 572–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, S.; Croy, A.; Bierling, A.L.; Khavrus, V.; Panes-Ruiz, L.A.; Dianat, A.; Ibarlucea, B.; Cuniberti, G. Machine learning-eneabled graphene-based electronic olfactation sensors and their olfactory performance assessmen. Appl. Phys. Rev. 2023, 10, 021406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, C.; Li, H.-Y.; Li, L.; Su, H.-Y.; Tang, J.; Bai, X.; Liu, H. Smart electronic Nose Enabled by an All-Feature Olfactory Algorithm. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leon-Medina, J.X.; Parés, N.; Anaya, M.; Tibaduiza, D.; Pozo, F. Data classification Methodology for Electronic Nose Using Uniform Manifold Approximation and Projection and Extreme Learning Machine. Mathematics 2022, 10, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sagar, M.S.I.; Allison, N.R.; Jalajamony, H.M.; Fernandez, R.E.; Sekhar, P.K. Modern Data Analysis in Gas Sensors. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 127512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Guo, L.; Wang, M.; Su, C.; Wang, D.; Dong, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, W. Review on algorithm Design in Electronic Noses: Challenges, Status, and Trends. Intell. Comput. 2023, 3, 0012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaqoob, U.; Younis, M.I.; Sensors, C.G. Challenges, and the Potential of Machine Learning—A Review. Sensors 2021, 21, 2877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Li, Z.; Sun, Y. An E-nose system for identification and quantification of hazardousgas mixtures using a combined strategy of CNNs and attentional mechanisms. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 096001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.K.; Mayhew, E.J.; Sanchez-Lengeling, B.; Wei, J.N.; Quian, W.W.; Little, K.A.; Andres, M.; Nguyen, B.B.; Yasonik, J.; Parker, J.K.; et al. A principal odor map unifies diverse tasks in olfactory perception. Science 2023, 381, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Röck, F.; Barsan, N.; Weimar, U. Electronic Nose: Current Status and Future Trends. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 705–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staerz, A.; Roeck, F.; Weimar, U.; Barsan, N.; Nose, E. Electronic Nose. Surf. Interface Sci. 2020, 9, 335–379. [Google Scholar]
- Sberveglieri, G.; Genzardi, D.; Greco, G.; Nunez-Carmona, E.; Pezzottini, S.; Sberveglieri, V. The Electronic Nose: Review on Sensor Arrays and Future Perspectives. Chem. Eng. Trans. 2022, 95, 265–270. [Google Scholar]
- Wilson, A.D. Review of Electronic-nose Technologies and Algorithms to Detect Hazardous Chemicals in the Environment. Procedia Technol. 2012, 1, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowdhaman, P.; Venkatesan, T.; Banupriya, R.; Nimal, A.T.; Pandya, H.M. Comprehensive Review of Latest e-Nose Sensor Technologies. J. Environ. Nanotechnol. 2020, 9, 31–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jońca, J.; Pawnuk, M.; Arsen, A.; Sówka, I. Electronic Noses and Their Applications for Sensory and Analytical Measurements in the Waste Management Plants—A Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojnowski, W.; Dymerski, T.; Gębicki, J.; Namieśnik, J. Electronic Noses in Medical Diagnostics. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 197–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanaeifar, A.; ZakiDizaji, H.; Jafari, A.; de la Guardia, M. Early detection of contamination and defect in foodstuffs by electronic nose: A review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 87, 257–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabehi, A.; Helal, H.; Zappa, D.; Comini, E. Advancements and Prospects of Electronic Nose in Various Applications: A Comprehensive Review. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 4506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boeker, P. On ‘Electronic Nose’ methodology. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 204, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.; Magan, N. Electronic noses and disease diagnostics. Nat Rev. Microbiol. 2004, 2, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schaller, E.; Bosset, J.O.; Escher, F. Electronic Noses and Their Application to Food. LWT—Food Sci. Technol. 1998, 31, 305–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.B.; Subramian, V. Electronic Noses Sniff Success. Available online: https://spectrum.ieee.org/electronic-noses-sniff-success (accessed on 29 February 2008).
- Gardner, J.W.; Bartlett, P.N.; Principles, E.N. Electronic Noses. Principles and Applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2000, 11, 1087. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, W.; Wan, L.; Jian, Y.; Ren, C.; Jin, K.; Su, X.; Bai, X.; Haick, H.; Yao, M.; Wu, W. Electronic Noses: From Advanced Materials to Sensors Aided with Data Processing. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2018, 4, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruse, J.; Worner, J.; Schneider, J.; Dorksen, H.; Pein-Hackelbusch, M. Methods for Estimating the Detection and Quantifica-tion Limits of Key Substances in Beer Maturation with Electronic Noses. Sensors 2024, 24, 3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Örnek, Ö.; Karlık, B. An Overview of Metal Oxide Semiconducting Sensors in Electronic Nose Applications. IBU Repos. 2024, 2, 506–515. [Google Scholar]
- Brattoli, M.; Gennaro, G.D.; Pinto, V.D.; Loiotilde, A.D.; Lovascio, S.; Penza, M. Odour Detection Methods: Olfactometry and Chemical Sensors. Sensors 2011, 11, 5290–5322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Javid, I.; Konwar, S.; Singh, P.K.; Sahni, M.; Bhattacharya, B. Solid state gas sensor. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 34, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J. Highly sensitive and selective gas sensors using p-type oxide semiconductors: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 192, 607–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Yin, L.; Zhang, L.; Xiang, D.; Gao, R. Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors. Sensors 2010, 10, 2088–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna, A. Metal Oxide Sensors for Electronic Noses and Their Application to Food Analysis. Sensors 2010, 10, 3882–3910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Shon, I.; Shin, D.; Yoo, H.; Park, J.; Chung, S.; Kim, H. Recent Advances in Functionalization and Hybridization of Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Dichalcogenide for Gas Sensor. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2023, 26, 2301063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SmartNanotubes. Available online: https://smart-nanotubes.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Peters, R.; Beijer, N.; ‘t Hul, B.; Bruijns, B.; Munniks, S.; Knotter, J. Evaluation of a Commercial Electronic Nose Based on Carbon Nanotube Chemiresistors. Sensors 2023, 23, 5302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torad, N.L.; Ayad, M.M. Gas Sensors Based on Conducting Polymers. In Gas Sensors; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Lange, U.; Mirsky, V.M. Chemiresistors based on conducting polymers: A review on measurement techniques. Anal. Chim. Acta vol. 2011, 687, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machungo, C.; Berna, A.Z.; McNevin, D.; Wang, R.; Trowell, S. Comparison of the performance of metal oxide and conducting polymer electronic noses for detection of aflatoxin using artificially contaminated maize. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 360, 131681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, S.; Si, Y.; Liu, R.; Guo, X. Flexible Organic Polymer Gas Sensor and System Integration for Smart Packaging. Adv. Sens. Res. 2023, 2, 2300030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sierra-Padilla, A.; García-Guzmán, J.J.; López-Iglesias, D.; Palacios-Santander, J.M.; Cubillana-Aguilera, L. E-Tongues/Noses Based on Conducting Polymers and Composite Materials: Expanding the Possibilities in Complex Analytical Sensing. Sensors 2021, 21, 4976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deshmukh, S.; Bandyopadhyay, R.; Bhattacharyya; Pandey, R.; Jana, A. Application of electronic nose for industrial odors and gaseous emissions measurement and monitoring—An overview. Talanta 2015, 144, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- James, D.; Scott, S.M.; Ali, Z.; O’Hare, W.T. Chemical Sensors for Electronic Nose Systems. Microchim. Acta 2004, 149, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecunia, V.; Petti, L.; Andrews, J.B.; Ollearo, R.; Gelinck, G.H.; Nasrollahi, B.; Jailani, J.M.; Li, N.; Kim, J.H.; Ng, T.N.; et al. Roadmap on printable electronic materials for next-generation. Nano Futures 2024, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strike, D.J.; Meijerink, M.G.; Koudelka-Hep, M. Electronic noses—A mini-review. J. Anal. Chem. 1999, 364, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hobbs, B.; Tantrum, A.; Chan-Henry, R. Liquid electrolyte fuel cells. In Techniques and Mechanisms in Gas Sensing; Moseley, P.T., Norris, I.O.W., Williams, D.E., Eds.; Taylor & Francis: Bristol, UK, 1991; pp. 161–188. [Google Scholar]
- Man, G.; Stoeber, B.; Walus, K. Detecting and Identifying Clandestine Drug Laboratories: Sensing Technology Assessment; Technical Report TR-04; Government of Canada Publications: Ottawa, ON, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Figaro Engineering. Available online: https://www.figaro.co.jp/en/technicalinfo/principle/catalytic-type.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Yuwono, A.S.; Lammers, P.S. Odor pollution in the environment and the detection instrumentation. Agric. Eng. Int. CIGR J. Sci. Res. Dev. 2004, 6, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Electronic Sensor Technology. Available online: https://www.estcal.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Tomandl, A.; Wolpers, M.; Ogle, K. Investigations of the kinetics of surface treatments by advanced methods. In Directorate-General for Research and Innovation; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Cheeke, J.; Wang, Z. Acoustic wave gas sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1999, 59, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KIT—The Research University in the Helmholtz Association. Novel Detection Methods in Biological and Chemical Sensing. Available online: https://www.imt.kit.edu/m_rapp.php (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Spinelle, L.; Gerboles, M.; Kok, G.; Sauerwald, T. Sensitivity of VOC Sensors for Air Quality Monitoring Within the EURAMET Key-VOC Project. In Proceedings of the Fourth Eunetair Scientific Meeting, Linköping, Sweden, 3 June 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Safeopedia. What is a Photoionization Detector (PID)? Available online: https://www.safeopedia.com/definition/7120/photoionization-detector-pid (accessed on 11 August 2019).
- Kalit, M.T.; Marković, K.; Kalit, N.; Havranek, J. Application of electronic nose and electronic tongue in the dairy industry. Mljekarstvo 2014, 64, 228–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Natale, C.; Salimbeni, D.; Paolesse, R.; Macagnano, A.; D’Amico, A. Porphyrins-based opto-electronic nose for volatile compounds detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 65, 220–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rakow, N.A.; Suslick, K.S. A colorimetric sensor array for odour visualization. Nature 2000, 406, 710–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tromberg, B.J.; Sepaniak, M.J.; Alarie, J.P.; Vo-Dinh, T.; Santella, R.M. Development Of Antibody-Based Fiber-Optic Sensors for detection of a benzo[a]pyrene metabolite. Anal. Chem. 1988, 60, 1901–1908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kangas, M.J.; Burks, R.M.; Atwater, J.; Lukowicz, R.M.; Williams, P.; Holmes, A.E. Colorimetric Sensor Arrays for the Detection and Identification of Chemical Weapons and Explosives. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 47, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laffort, P. Models for describing intensity interactions in odor mixtures: A reappraisal. In Perception of Complex Smells and Tastes; Laing, D.G., Cam, W.S., McBride, R.L., Ache, B.W., Eds.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1989; pp. 20–223. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Newport, D.; Le Calvé, S. Gas Detection Using Portable Deep-UV Absorption Spectrophotometry: A Review. Sensors 2019, 19, 5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dr. Födisch Umweltmesstechnik AG. Available online: https://www.foedisch.de/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- MSA Safety Italy. Available online: https://www.it.msasafety.com/?r=NA&locale=en (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- AZO Sensor. Available online: https://www.azosensors.com/article.aspx?ArticleID=1327 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Honeywell International Inc. Available online: https://www.honeywell.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- International Gas Detectors Ltd. Available online: https://www.internationalgasdetectors.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Thermo Fisher Scientific Inc. Available online: https://www.thermofisher.com/it/en/home.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Thermo Fisher Scientific. Gas Chromatography—How a Gas Chromatography Machine Works, How to Read a Chromatograph and GC × GC. Available online: https://www.technologynetworks.com/analysis/articles/gas-chromatography-how-a-gas-chromatography-machine-works-how-to-read-a-chromatograph-and-gcxgc-335168 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Hajšlová, J.; Čajka, T.; Chromatography, G. Gas Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry (GC–MS). In Food Toxicants Analysis; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 419–473. [Google Scholar]
- Shimadzu Corporation. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Kienitz, H.; Brunner, E. Experimental Thermodynamics Volume II—Reference Materials for Thermometric Fixed Points; International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry: Zürich, Switzerland, 1968; pp. 71–85. [Google Scholar]
- Plasmion GmbH. Available online: https://plasmion.com/industrial-sensory-system/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Ant Teknik. Available online: https://www.antteknik.com/tr/urun-kategori/?c=gaz-kromatografi-gc-gcms (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Eiceman, G.A.; Karpas, Z.; Hill, H.H., Jr. Ion Mobility Spectrometry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 205–230. [Google Scholar]
- Maestre, R.F. Ion Mobility Spectrometry: History, Characteristics and Applications. Rev. UDCA Actual. Divulg. Científica 2012, 15, 2. [Google Scholar]
- Bertin Environics. Available online: https://www.environics.fi/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Smiths Detection Group Ltd. Available online: https://www.smithsdetection.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Owlstone Inc. Available online: https://www.owlstoneinc.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Inst Tools. Flame Ionization Detector (FID) Principle. Available online: https://instrumentationtools.com/flame-ionization-detector-fid-principle/?utm_content=cmp-true (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- RAE Systems by Honeywell. The PID Handbook; Honeywell: Charlotte, NC, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Drägerwerk AG & Co. KGaA. Available online: https://www.draeger.com/en-us_us/Home (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Ye, Z.; Liu, Y.; Li, Q. Recent Progress in Smart Electronic Nose Technologies Enabled with Machine Learning Method. Sensors 2021, 21, 7620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papp, S.; Weidinger, W.; Munro, K.; Ortner, B.; Cadonna, A.; Langs, G.; Licandro, R.; Meir-Huber, M.; Nikolić, D.; Toth, Z.; et al. The Handbook of Data Science and AI; Carl Hanser Verlag GmbH & Co. KG: Munich, Germany, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Barbierato, E.; Gatti, A.; Incremona, A.; Pozzi, A.; Toti, D. Breaking Away From AI: The Ontological and Ethical Evolution of Machine Learning. IEEE Access 2025, 13, 55627–55647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.-Y.; Wu, C.-C.; Chou, T.-I.; Chiu, S.-W. Development of a Dual MOS Electronic Nose/Camera System for Improving Fruit Ripeness Classification. Sensors 2018, 18, 3256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, F.S.; Yaqin, A.; Krasnikov, D.V.; Kondrashov, V.A.; Ovchinnikov, G.; Kostyukevich, Y.; Osipenko, S.; Nasibulin, A.G. Detecting cooking state of grilled chicken by electronic nose and computer vision techniques. Food Chem. 2021, 350, 128747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingos, P. A few useful things to know about machine learning. Commun. ACM 2012, 55, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortes, C.; Vapnik, V. Support-vector networks. Mach. Learn. 1995, 20, 273–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frey, B.J.; Dueck, D. Clustering by passing messages between data points. Science 2007, 315, 972–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, C.M. Pattern Recognition and Machine Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Castelletti, F.; Niro, F.; Denti, M.; Tessera, D.; Pozzi, A. Bayesian Learning of Causal Networks for Unsupervised Fault Diagnosis in Distributed Energy Systems. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 61185–61197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Mnih, V.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Silver, D.; Rusu, A.A.; Veness, J.; Bellemare, M.G.; Graves, A.; Riedmiller, M.; Fidjeland, A.K.; Ostrovski, G.; et al. Human-level control through deep reinforcement learning. Nature 2015, 518, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, A.; Toti, D. Imitation Learning for Agnostic Battery Charging: A DAGGER-Based Approach. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 115190–115203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matrone, S.; Pozzi, A.; Ogliari, E.; Leva, S. Deep Learning-Based Predictive Control for Optimal Battery Management in Microgrids. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 141580–141593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berthold, M.R.; Borgelt, C.; Hoppner, F.; Klawonn, F. Guide to Intelligent Data Analysis; Springer: London, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T. Machine Learning-Based Inverse Solution for Predictions of Impact Conditions Buring Car Collisions; University of California: Berkeley, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- T. A. Team. How, When, and Why Should You Normalize/Standardize/Rescale Your Data? Available online: https://towardsai.net/p/data-science/how-when-and-why-should-you-normalize-standardize-rescale-your-data-3f083def38ff (accessed on 29 May 2020).
- Manthani, S. Data Normalization and Standardization. Available online: https://sathish-manthani.medium.com/data-normalization-and-standardization-7ce8cb6472ae (accessed on 31 January 2020).
- Burkov, A. The Hundred-Page Machine Learning Book; Andriy Burkov: Quebec City, QC, Canada, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Geller, S. Normalization vs. Standardization—Quantitative Analysis. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/normalization-vs-standardization-quantitative-analysis-a91e8a79cebf (accessed on 5 April 2019).
- Shao, X.; Li, H.; Wang, N.; Zhang, Q. Comparison of Different Classification Methods for Analyzing Electronic Nose Data to Characterize Sesame Oils and Blends. Sensors 2015, 15, 26726–26742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Estakhroueiyeh, H.R.; Rashedi, E. Detecting moldy Bread using an E-nose and the KNN classifier. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computer and Knowledge Engineering (ICCKE), Mashhad, Iran, 29–30 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Papadopoulou, O.S.; Panagou, E.Z.; Mohareb, F.R.; Nychas, G.E. Sensory and microbiological quality assessment of beef fillets using a portable electronic nose in tandem with support vector machine analysis. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harifi, S.; Khalilian, M.; Mohammadzadeh, J.; Ebrahimnejad, S. Using Metaheuristic Algorithms to Improve k-Means Clustering: A Comparative Study. Rev. D’Intelligence Artif. 2020, 34, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finance, T. Support Vector Machine Algorithm Explained. 2023. Available online: https://financetrain.com/support-vector-machine-algorithm-explained (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Ihl, P.D. Machine Learning Fundamentals. Available online: https://www.startupengineer.io/_repos/_transfer/data_science/06_ml_fund/ (accessed on 16 March 2021).
- Flomo, G. How to Cluster Images Based on Visual Similarity. Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/how-to-cluster-images-based-on-visual-similarity-cd6e7209fe34 (accessed on 13 October 2020).
- Galarnyk, M. PCA Using Python (Scikit-Learn). Available online: https://towardsdatascience.com/pca-using-python-scikit-learn-e653f8989e60 (accessed on 17 November 2021).
- Serrano, L. Principal Component Analysis (PCA). Available online: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=g-Hb26agBFg&t=1057s (accessed on 9 February 2019).
- Yan, J.; Guo, X.; Duan, S.; Jia, P.; Wang, L.; Peng, C.; Zhang, S. Electronic Nose Feature Extraction Methods: A Review. Sensors 2015, 15, 27804–27831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roussel, S.; Forsberg, G.; Steinmetz, V.; Grenier, P.; Bellon-Maurel, V. Optimisation of electronic nose measurements. Part I: Methodology of output feature selection. J. Food Eng. 1998, 37, 207–222. [Google Scholar]
- Sawla, S.; Analysis, L.D. Available online: https://medium.com/@srishtisawla/linear-discriminant-analysis-d38decf48105 (accessed on 5 June 2018).
- James, G.; Witten, D.; Hastie, T.; Tibshirani, R. An Introduction to Statistical Learning with Applications in R; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Izenman, A.J. Modern Multivariate Statistical Techniques: Regression, Classification, and Manifold Learning; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Blatt, R.; Bonarini, A.; Calabro, E.; Torre, M.D.; Matteucci, M.; Pastorino, U. Lung Cancer Identification by an Electronic Nose based on an Array of MOS Sensors. In Proceedings of the 2007 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Orlando, FL, USA, 12–17 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Aouada, S.; Zoubir, A.; See, C.M. Source detection in the presence of nonuniform noise. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech, and Signal Processing, Montreal, QC, Canada, 17–21 May 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Scott, S.M.; James, D.; Ali, Z. Data analysis for electronic nose systems. Microchim. Acta 2006, 156, 183–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhujel, S. KNN and Naïve Bayes—Data Science. Available online: https://sudipbhujel.com.np/knn-nb-classifier/ (accessed on 6 August 2020).
- Ungu, V.J. Biological Neural Network (BNN) to Artificial Neural Network (ANN). Available online: https://medium.com/@vjuugm18/biological-neural-network-bnn-to-artificial-neural-network-ann-91ddd0080d5 (accessed on 23 May 2020).
- Cassani, R. Code for a Simple MLP (Multi-Layer Perceptron). Available online: https://github.com/rcassani/mlp-example (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Jain, A.; Mao, J.; Mohiuddin, K. Artificial neural networks: A tutorial. Computer 1996, 29, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, J.; Kvaal, K. Electronic nose and artificial neural network. Meat Sci. 1998, 49, S273–S286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, A.C.; Guido, S. Introduction to Machine Learning with Python a Guide for Data Scientists; O’Reilly.: Springfield, MI, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- SAGAS by Karlsruher Institut für Technologie (KIT). Available online: https://www.kit-technology.de/en/technology-offers/details/331 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Sensigent LLC. Available online: https://www.sensigent.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- EOS Aroma by Sacmi Imola Scarl. Available online: https://sacmi.com/en-US/corporate/news/5827/The-Sacmi-made-‘electronic-nose’-for-olive-oil (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- World Health Organization. Foodborne Diseases. Available online: https://www.who.int/health-topics/foodborne-diseases#tab=tab_1 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- European Commission. Food Waste. Available online: https://www.ec.europa.eu/food/safety/food-waste_en (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- AirSense Analytics GmbH. Available online: https://airsense.com/en (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Alpha MOS. Available online: https://www.alpha-mos.com/electronic-nose (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Aryballe. Available online: https://aryballe.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- FOODSniffer. Available online: https://www.myfoodsniffer.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- GERSTEL GmbH & Co. KG. Available online: https://gerstel.com/en (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- The New Zealand Institute for Plant and Food Research Limited. Available online: https://www.plantandfood.com/en-nz/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Wang, M.; Chen, Y. Electronic nose and its application in the food industry: A review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2024, 250, 21–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, H.; Anwar, T.; Murtaza, S. Review on food quality assessment using machine learning and electronic nose system. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2023, 14, 100365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mordor Intelligence. Electronic Nose Market Size & Share Analysis—Growth Trends & Forecasts (2025–2030). Available online: https://www.mordorintelligence.com/industry-reports/electronic-nose-market (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Portable Electronic Nose (PEN3) by AIRSENSE Analytics GmbH & PCA Technologies. Available online: https://airsense.com/en/products/portable-electronic-nose (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Heracles Neo by Alpha MOS. Available online: https://www.alpha-mos.com/smell-analysis-heracles-electronic-nose (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- NeOse Advance by Aryballe Technologies. Available online: https://aryballe.com/our-products/device-solutions/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- GasAlertMicro 5 Series by Honeywell Analytics. Available online: https://sps.honeywell.com/us/en/products/safety/gas-and-flame-detection/portables/gasalertmicro-5-series (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Sensepoint XCD RTD by Honeywell Analytics. Available online: https://sps.honeywell.com/us/en/products/safety/gas-and-flame-detection/industrial-fixed/sensepoint-xcd-rtd (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Manning AirScan IRF9 by Honeywell Analytics. Available online: https://www.honeywellanalytics.com/en/products/2014/05/08/09/42/irf9-manning-airscan.
- Honeywell BW™ Ultra by RAE Systems RAE Systems by Honeywell. Available online: https://sps.honeywell.com/us/en/products/safety/gas-and-flame-detection/portables/honeywell-bw-ultra (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- TOC-750X Series by International Gas Detectors Ltd. Available online: https://www.internationalgasdetectors.com/product/750-atex-addressable-gas-detector/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- TOC-30 by International Gas Detectors Ltd. Available online: https://www.internationalgasdetectors.com/product/toc-30-analogue-gas-detector/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- POLI by International Gas Detectors Ltd. Available online: https://www.internationalgasdetectors.com/product/multi-gas-monitor-poli/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Lonestar by Owlstone Inc. Available online: https://www.owlstoneinc.com/products/lonestar/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Cyranose® 320 by Sensigent. Available online: https://www.sensigent.com/cyranose-320.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- eNose Aqua and QA by Sensigent. Available online: https://www.sensigent.com/enoseproducts.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Nexis GC-2030 by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatography/gas-chromatograph/nexis-gc-2030/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- GC-2010 Pro by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatography/gas-chromatograph/gc-2010-pro/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Nexis SCD-2030 by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatography/gc-accessories-components/nexis-scd-2030/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- GCMS-TQ8050 NX by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatograph-mass-spectrometry/triple-quadrupole-gc-msms/gcms-tq8050-nx/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- GCMS-TQ8040 NX by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatograph-mass-spectrometry/triple-quadrupole-gc-msms/gcms-tq8040-nx/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- GCMS-QP2010 SE by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatograph-mass-spectrometry/single-quadrupole-gc-ms/gcms-qp2010-se/applications.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Multi-Dimensional GC/GCMS System by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatography/gc-accessories-components/advanced-flow-technology-series/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- TD-30 Series by Shimadzu Co. Available online: https://www.shimadzu.com/an/products/gas-chromatograph-mass-spectrometry/gc-ms-system/td-30-series/index.html (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 7000D Triple Quadrupole GC/MS by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography-mass-spectrometry-gc-ms/gc-ms-instruments/7000d-triple-quadrupole-gc-ms (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 7010D Triple Quadrupole GC/MS by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography-mass-spectrometry-gc-ms/gc-ms-instruments/7010d-triple-quadrupole-gc-ms (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 7250 GC/Q-TOF by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography-mass-spectrometry-gc-ms/gc-ms-instruments/7250-gc-q-tof (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 8860 GC System by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography/gc-systems/8860-gc-system (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Intuvo 9000 GC System by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography/gc-systems/intuvo-9000-gc-system (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 8890 GC System by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography/gc-systems/8890-gc-system (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 7890B GC System by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography/gc-systems/7890b-gc-system (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 7820A GC System by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography/gc-systems/7820a-gc-system (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- 5977C GC/MSD by Agilent. Available online: https://www.agilent.com/en/product/gas-chromatography-mass-spectrometry-gc-ms/gc-ms-instruments/5977c-gc-msd (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- SICRIT® Ionization by Plasmion GmbH. Available online: https://plasmion.com/technology/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Altitude Technologies Ltd. Sensly—A Smart, Portable Pollution Sensor for Your Home by Altitude Tech Ltd.—Kickstarter. Available online: https://www.kickstarter.com/projects/sensly/sensly-a-smart-portable-pollution-sensor-for-your (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- IQAir. AirVisual Series Air Quality Monitors. Available online: https://www.iqair.com/commercial-air-quality-monitors (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- MyDx. Available online: https://www.mydxlife.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Atmotech Inc. Available online: https://atmotube.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Sensit Technologies. Available online: https://gasleaksensors.com/it/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- SGX Sensortech. Available online: https://www.sgxsensortech.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Gentex (Ex-Vaporsense). Available online: https://www.gentex.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Sciosense, B.V. Available online: https://www.sciosense.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Roboscientific. Available online: https://www.roboscientific.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- AerNos Inc. Available online: https://www.aernos.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Noze. Available online: https://www.noze.ca/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Muñoz, R.; Sivret, E.C.; Parcsi, G.; Lebrero, R.; Wang, X.; Suffet, I.H.; Stuetz, R.M. Monitoring Techniques for Odour Abatement Assessment. Water Res. 2010, 44, 5129–5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PCA Technologies. Available online: https://www.pcatechnologies.com/en (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Envirosuite Ltd. Available online: https://envirosuite.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Pem-Tech Inc. Available online: https://www.pem-tech.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Sensidyne LP. Available online: https://sensidyne.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Crowcon Detection Instruments Ltd. Available online: https://www.crowcon.com/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Teledyne Gas and Flame Detection. Available online: https://www.teledynegasandflamedetection.com/en-us (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- NASA—Jet Propulsion Laboratory—California Institute of Technology. Available online: https://enose.jpl.nasa.gov/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Proengin. Available online: https://www.proengin.com/en/ (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- European Commission—CORDIS. Monitoring Networks and Autonomous Platforms for Odor Impact Assessment Using Electronic Noses. Available online: https://cordis.europa.eu/project/id/101033564 (accessed on 11 March 2025).
- Li, Y.; Wei, X.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; You, R. Research progress of electronic nose technology in exhaled breath disease analysis. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2023, 9, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cipriano, D.; Capelli, L. Evolution of Electronic Noses from Research Objects to Engineered Environmental Odour Monitoring Systems: A Review of Standardization Approaches. Biosensors 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanotti, M.; Freddi, S.; Sangaletti, L. Physical Virtualization of a GFET for a Versatile, High-Throughput, and Highly Discriminating Detection of Target Gas Molecules at Room Temperature. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2024, 10, 2400985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Croy, A.; Panes-Ruiz, L.A.; Khavrus, V.; Bezugly, V.; Ibarlucea, B.; Cuniberti, G. Machine Learning-Enabled Smart Gas Sensing Platform for Identification of Industrial Gases. Adv. Intell. Syst. 2022, 4, 2200016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, R.; Shi, L.; Dai, C. An effective method fusing electronic nose and fluorescence hyperspectral imaging for the detection of pork freshness. Food Biosci. 2024, 59, 103880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-Y.; Jung, H.-T. Artificial Intelligence: A Game Changer in Sensor Research. ACS Sens. 2023, 8, 1371–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masson, J.-F. Roadmap for the Use of Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence in Sensing. ACS Sens. 2024, 9, 3805–3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mor, S.; Gunay, B.; Zanotti, M.; Galvani, M.; Pagliara, S.; Sangaletti, L. Current Opportunities and Trends in the Gas Sensor Market: A Focus on e-Noses and Their Applications in Food Industry. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050181
Mor S, Gunay B, Zanotti M, Galvani M, Pagliara S, Sangaletti L. Current Opportunities and Trends in the Gas Sensor Market: A Focus on e-Noses and Their Applications in Food Industry. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(5):181. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050181
Chicago/Turabian StyleMor, Selene, Buse Gunay, Michele Zanotti, Michele Galvani, Stefania Pagliara, and Luigi Sangaletti. 2025. "Current Opportunities and Trends in the Gas Sensor Market: A Focus on e-Noses and Their Applications in Food Industry" Chemosensors 13, no. 5: 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050181
APA StyleMor, S., Gunay, B., Zanotti, M., Galvani, M., Pagliara, S., & Sangaletti, L. (2025). Current Opportunities and Trends in the Gas Sensor Market: A Focus on e-Noses and Their Applications in Food Industry. Chemosensors, 13(5), 181. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13050181







