Abstract
Fluorescent sensors are indispensable tools in fields such as molecular biology, clinical diagnostics, biotechnology, and environmental monitoring, due to their high sensitivity, selectivity, biocompatibility, rapid response, and ease of use. However, conventional fluorophores often suffer from aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ), leading to diminished fluorescence in the aggregated state. The advent of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) luminogens, which exhibit enhanced fluorescence upon aggregation, offers a powerful solution to this limitation. Their unique photophysical properties have made AIE-based materials highly valuable for diverse applications, including biomedical imaging, optoelectronics, stimuli-responsive systems, drug delivery, and chemical sensing. Notably, AIE-based fluorescent probes are emerging as attractive alternatives to traditional analytical methods owing to their low cost, fast detection, and high selectivity. Over the past two decades, considerable progress has been made in the rational design and development of AIE-active small-molecule fluorescent probes for detecting a wide variety of analytes, such as biologically relevant molecules, drug compounds, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), explosives, and contaminants associated with forensic and food safety analysis. This review highlights recent advances in organic AIE-based fluorescent probes, beginning with the fundamentals of AIE and typical “turn-on” sensing mechanisms, and concluding with a discussion of current challenges and future opportunities in this rapidly evolving research area.
1. Introduction
In recent years, the development of fluorogenic and emissive compounds has emerged as a key innovation in optoelectronics, playing a pivotal role in advancing science and technology while enhancing modern life [1,2]. Initially introduced as an analytical tool for identifying various chemical species, fluorescence has rapidly evolved into a gold-standard method for detecting analytes and external stimuli due to its high sensitivity, selectivity, and superior signal-to-noise ratio [3,4]. The unique optical properties of fluorescent materials have made them indispensable in a wide range of applications, including chemical and biological sensing, anti-counterfeiting, forensic analysis, and biomedical imaging, further broadening the scope of fluorescence-based technologies [5,6]. Among all, fluorescent sensor technology has garnered significant attention as a simple and efficient method for detecting biological and chemical species due to its versatility, high selectivity, and sensitivity [7]. Fluorescent chemosensors play a vital role in identifying and quantifying metal ions, anions, biomolecules, pH fluctuations, and other specific chemical entities [8,9,10,11]. Fluorescence sensing is an ultra-sensitive detection technique that operates by inducing changes in emission intensity, enhancement, or wavelength shifts. Imbalances in these ions and molecules can lead to severe environmental repercussions and significantly impact biospheres and human health [12]. Therefore, the continuous development of advanced fluorescent chemosensors is crucial for environmental monitoring, biomedical, and optoelectronic applications.
The detection and quantification of chemical analytes traditionally rely on instrumental analysis, considered the gold standard in analytical chemistry. While portable devices exist, they remain limited in scope and affordability [13]. The fluorescent chemosensors have emerged as a low-cost, rapid, and user-friendly alternative, utilizing colorimetric and fluorescence changes for real-time detection. These sensors integrate seamlessly into paper-based probes, wearables, lateral flow assays, and smartphone-based platforms, offering practical solutions for field applications [14]. However, conventional fluorescent probes often suffer from aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ), restricting their effectiveness in solid-state sensing devices. Developing novel fluorescent sensors that effectively overcome the limitations of ACQ is highly desirable [15]. To overcome this, innovative probe designs focus on enhancing stability, sensitivity, and compatibility for real-world applications in environmental monitoring, medical diagnostics, and industrial safety [16]. The discovery of aggregation-induced emission (AIE) marked a significant breakthrough in overcoming the limitations of ACQ luminogens. Unlike ACQ fluorophores, AIE-active luminogens (AIEgens) are non-emissive in dilute solutions but exhibit strong fluorescence upon aggregation [17,18,19]. Over time, the scope of AIEgens has expanded to include a diverse range of materials, including conjugated and non-conjugated polymers [20,21,22], metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) [23,24,25], covalent-organic frameworks (COFs) [26], nanoparticles (NPs) [27,28,29,30], carbon dots (C-dots) [31,32,33], metal-hybrid nanoclusters (NCs) [34,35,36,37], and supramolecular assemblies [38,39,40,41]. Certain molecules with non-planar, congested structures, such as tetraphenylethylene (TPE) [42], hexaphenylsilole (HPS) [43], quinoline-malononitrile (QM) [44,45], tetraphenylpyrazine (TPP) [46,47], pyrene-based AIEgens [48], benzothiadiazole (BTD) [49], spirobifluorene [50], and 9,10-distyrylanthracene (DSA) [51], were initially found to have weak or negligible fluorescence in solution but showed significantly enhanced emission when aggregated.
The mechanisms of AIE explain fluorescence enhancement upon aggregation through various hypotheses. The restriction of intramolecular motion (RIM) is the most widely accepted [43,52], where suppressed rotation (RIR) and vibration (RIV) prevent non-radiative energy loss, leading to enhanced fluorescence [53]. Excimer formation occurs when aggregated luminogens form excited-state dimers, contributing to emission [54], while J-aggregate formation results from dipole–dipole interactions aligning molecules in a head-to-tail fashion, causing red-shifted fluorescence [55,56]. The inhibition of Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer (TICT) prevents fluorescence quenching [57], while Excited-State Intramolecular Proton Transfer (ESIPT) stabilizes highly emissive tautomers [58]. Unlike traditional fluorophores that experience ACQ due to strong π–π stacking, AIEgens minimize these interactions by adopting non-planar conformations. Additionally, Clusterization-Triggered Emission (CTE) arises from the clustering of non-conjugated electron-rich and deficient groups, facilitating through-space electronic interactions, while conformational planarization enhances conjugation and fluorescence by inducing molecular rigidity in the aggregated state [59].
Extensive research has led to the development of numerous AIE luminogens based on the restriction of intramolecular motion (RIM) mechanism. These AIEgens exhibit strong fluorescence in the aggregated state, along with desirable features such as a large Stokes’ shift, high photostability, and minimal background noise in dilute solutions [60]. Additionally, their integration into stimuli-responsive materials has enabled the development of next-generation functional devices with advanced optical and sensing capabilities. Their limited intramolecular motions when aggregated limit non-radiative decay and greatly increase or activate their fluorescence emission [61]. The identification of AIE events has changed our knowledge of photoluminescence by showing how high photoluminescent quantum yield (PLQY) in solid and aggregated states can be used for modern technologies and real-world applications. Beyond chemical sensing, AIEgens have shown great promise in biomedical uses, including theranostics, biosensing, and bioimaging. Furthermore, they play a promising role in the optoelectronics domain, including LEDs, organic photovoltaics, and electrofluorochrome applications [62].
A vast array of AIE-based fluorescent probes has been developed for detecting diverse analytes, including metal and inorganic ions, small molecules, drug molecule sensing, microenvironments, stimuli-responsive systems, biological macromolecules, cellular processes, and pathogens [63]. Numerous reviews have summarized progress in this field, covering general sensing as well as specific applications such as explosives, reactive oxygen and nitrogen species, metal ions, forensics, environmental monitoring, and food safety and quality control [64]. However, to the best of our knowledge, there is only a limited dedicated review focusing exclusively on AIE-based fluorescent sensors for biomolecule detection. With several recent reviews on AIEgens, this work highlights representative AIE sensors from recent years, emphasizing rational sensor design and mechanism, and is further categorized by sensing of nucleic acids, enzymes, amino acids, biogenic amines, and other biomolecules such as saccharides, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), vitamins, albumin, and collagen. Additionally, we discuss emerging trends and future advancements in AIE-based sensing technologies.
2. General Mechanism
AIEgens have been extensively developed into smart materials and devices for applications in fluorescence, phosphorescence, chemo- and colorimetric sensing, bioimaging, and therapeutic guidance. The AIE effect originates from the restriction of intramolecular motion (RIM) in propeller-like fluorophores, preventing chromophore stacking and suppressing ACQ, leading to strong luminescence in both aggregate and solid states. This intense emission has also driven interest in mechanochromic and piezochromic fluorescent materials, where external compression or grinding induces emission color changes [65]. Due to their structural simplicity, ease of synthesis, and tunable functionalities, AIEgens can be tailored into highly sensitive sensors adaptable to chemical, biological, and environmental applications. Aggregation/disaggregation control allows AIEgens to remain non-emissive in solution but fluoresce upon aggregation in response to specific analytes. Chemical modifications fine-tune optical properties for detecting ions, biomolecules, and pollutants, while enzymatic reactions convert non-luminescent precursors into emissive AIEgens for biochemical sensing [66]. Further, functional group coordination (e.g., carboxyl or pyridine groups) enhances selectivity through interactions with metal ions or biomolecules, while complex formation, supramolecular interactions, self-assembly, polymerization, encapsulation, and nano-precipitation improve stability and biocompatibility. A fundamental principle in AIE sensor design is that fluorescence intensity (F.I.) enhancement is primarily driven by restriction of intramolecular rotation (RIR), which suppresses non-radiative decay, leading to bright emission [67]. By leveraging RIR and other photophysical properties, a wide range of AIE luminogens have been synthesized for high-performance sensing. The integration of AIE-based strategies has enabled significant advancements in “turn-on” fluorescent probes and label-free detection systems, revolutionizing modern sensing and diagnostic platforms with high sensitivity, selectivity, and real-time detection capabilities [68,69].
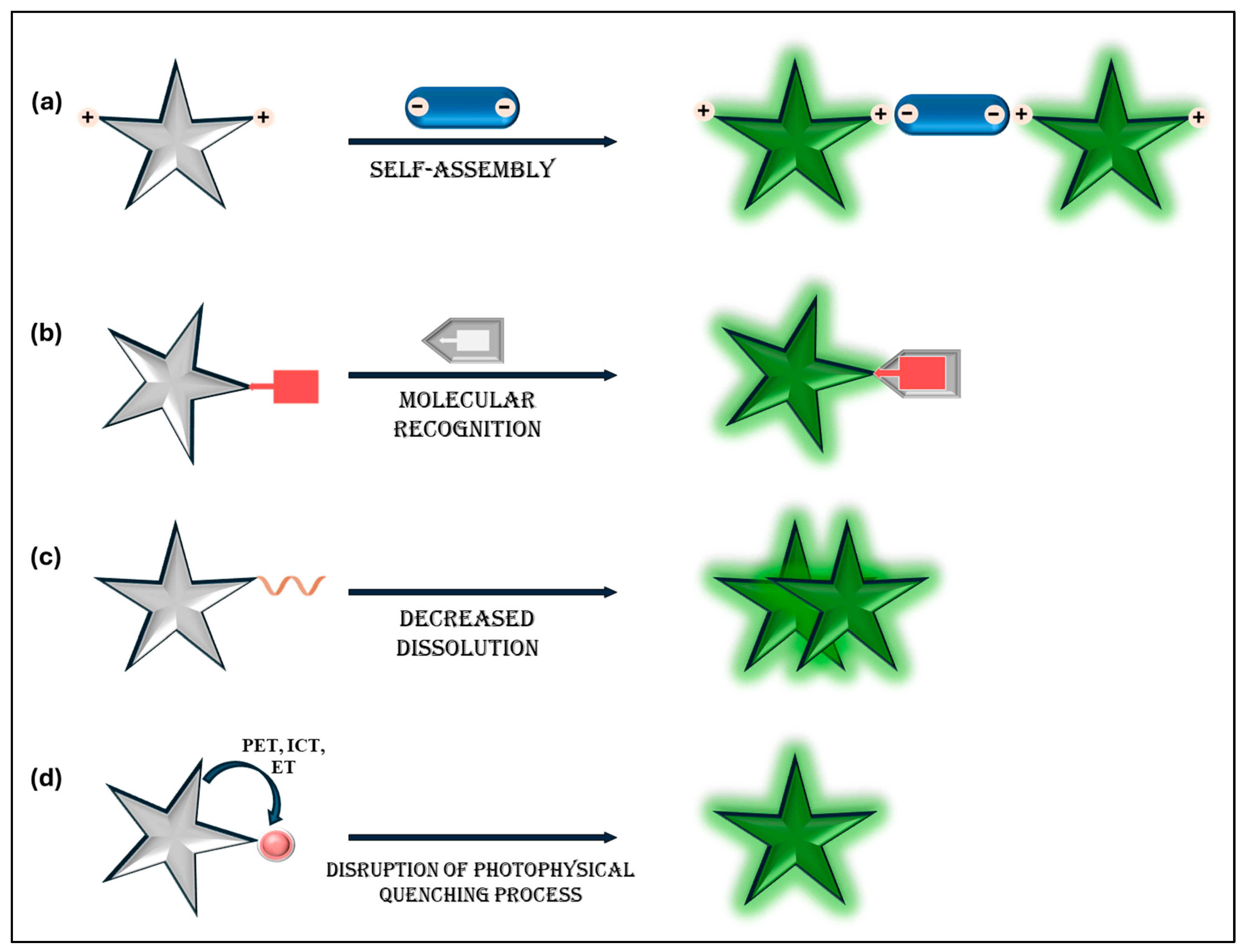
Fluorescence AIE techniques are widely employed due to their noninvasiveness, simplicity, high spatiotemporal resolution, and sensitivity. This has led to the development of numerous AIE-based probes and sensors for detection and bioimaging, utilizing various fluorescence turn-on mechanisms (Figure 1). One approach involves the conjugation of AIE fluorophores with selective ligands, enabling analyte recognition and fluorescence activation via restriction of intramolecular rotation (RIR), or fluorescence suppression through switch-off sensors. Another strategy relies on self-assembly through noncovalent interactions, such as metal–ligand coordination, van der Waals forces, hydrogen bonding, and electrostatic interactions, forming highly emissive aggregates as shown in Figure 1a. The other strategies involved are covalent conjugation with targeting ligands, triggering fluorescence by restricting intramolecular motion upon analyte recognition (Figure 1b), enzyme- or chemical-induced aggregation, where cleavage of solubility-promoting ligands reduces solubility, leading to aggregation (Figure 1c). AIE-based sensing also exploits disruptions in photophysical quenching processes, modifying electronic structures or charge transfer mechanisms to enhance fluorescence (Figure 1d). These include quenching pathways, such as photoinduced electron transfer (PET), planar intramolecular charge transfer (PICT), intramolecular charge transfer (ICT), fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET), chemiluminescence resonance energy transfer (CRET), excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT), and energy transfer (ET), activating fluorescence. Additionally, the conversion of non-conjugated to conjugated compounds plays a role in fluorescence modulation. These sensing mechanisms can also be synergistically integrated within a single sensor, enhancing sensitivity and selectivity for various analytical applications.
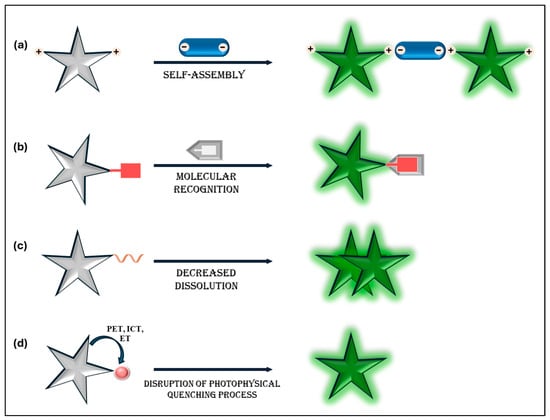
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of the turn-on sensing mechanisms of AIE sensors: (a) aggregation through self-assembly with analytes; (b) specific analyte recognition leading to restricted intramolecular motion; (c) removal of solubility-enhancing ligands, inducing aggregate formation; and (d) interruption of photophysical quenching mechanisms.
3. AIE Sensors for Biomolecule Detection
The discovery of the AIE phenomenon has led to the development of fluorescent AIE-based molecular and nanomaterial probes, offering superior photostability and high fluorescence efficiency for biological and chemical applications [70]. Among various analytical techniques, fluorescence-based detection has gained attention due to its high sensitivity, selectivity, signal-to-noise ratio, biocompatibility, strong photoluminescence quantum yield, cost-effectiveness, and ease of operation, making it highly effective for detecting diverse analytes [71]. Studies have shown that AIE-active fluorogenic sensors outperform conventional methods such as chromatography, spectroscopy, fiber optic sensors, electrochemical sensors, and colorimetric assays. AIEgens exhibit bright and stable fluorescence due to their non-planar structures, which prevent π–π stacking interactions and restrict molecular motion, reducing non-radiative decay pathways and enhancing luminescence. These properties contribute to their high quantum yield, resistance to photobleaching, and strong biophysical stability, making them ideal for sensing applications. Over the years, AIE sensors have been widely applied in detecting metal ions, anions, explosives, small biomolecules, pH variations, reactive oxygen species (ROS), bacterial detection, and disease biomarkers [72]. Moreover, fluorescent biosensors have emerged as essential tools for the precise analysis of biomolecules, including carbohydrates, enzymes, peptides, and nucleotides, offering critical insights into intricate biological and physiological processes. Since abnormal concentrations of these biomolecules are often linked to various diseases, their qualitative and quantitative detection is of great significance for biomedical research and clinical diagnostics [73]. Their low detection limits, simplicity, user-friendliness, rapid response, and robustness have positioned AIE-based detection as a superior alternative to conventional sensors, driving their commercial adoption and real-world applications [74].
The design strategies for AIE-based sensors vary due to the structural diversity of biomolecule analytes. Sensing mechanisms typically involve chemical reactions, where direct interaction with the analyte alters optical properties or solubility, leading to fluorescence activation or quenching. Supramolecular interactions, including host–guest chemistry, electrostatic forces, hydrogen bonding, π–π stacking, and metal–ligand coordination, modulate fluorescence by inducing aggregation or disassembly [75]. Additionally, photophysical processes such as intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) [76], photoinduced electron transfer (PET) [77,78], Förster resonance energy transfer (FRET) [79,80,81], excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) [82,83], and inner filter effect (IFE) [84,85] play a crucial role in tuning emission signals. Biomolecule recognition further enhances selectivity through bio-conjugation with peptides, antigens, or antibodies for targeted sensing. Mechanistically, chemical reaction-based sensing applies to analytes with reactive functional groups, while supramolecular interactions influence fluorescence through aggregation control or host–guest interactions. Photophysical processes like PET and IFE regulate fluorescence through electron transfer or spectral overlap. Biomolecule-assisted sensing, commonly used in lateral flow immunoassays, enables highly specific analyte detection via antigen–antibody interactions [86]. By integrating these diverse mechanisms, AIE-based sensors achieve high sensitivity, selectivity, and versatility, making them valuable tools for chemical sensing, biomedical diagnostics, and environmental monitoring.
AIE-based fluorescent biosensors possess distinct advantages in the detection of biomolecules compared to their applications in other areas. Proteins, nucleic acids, enzymes, and metabolites are some of the biomolecules that play crucial roles in physiological processes, and, therefore, their sensitive and selective detection is essential for disease diagnosis, biomedical research, and therapeutic monitoring [87]. Compared to quenching fluorophores that are prone to aggregation, AIE-based biosensors can show strong fluorescence in the aggregated states, enabling high-contrast imaging, real-time monitoring, and minimal background interference under complex biological conditions. Furthermore, biomolecule-specific interactions such as enzyme-mediated turn-on fluorescence, ligand-receptor binding, and aptamer-based recognition impart high specificity and versatility for biosensing. While AIE-based sensors were widely employed for environmental and chemical sensing, biosensing for biomolecules demands greater biocompatibility, minimal cytotoxicity, enhanced photostability, signal-to-noise ratio, high sensitivity, and specificity, all of which are effectively provided by AIEgens [53]. The turn-on fluorescence response, resistance to photobleaching, and ability to operate in aqueous environments make them most suitable for biosensing, differentiating them from conventional sensors applied in other areas. For internal sensing, non-invasive bioimaging is possible with the assistance of fluorescent probes. A highly effective approach is to utilize AIE-active fluorescent probes, enabling high-contrast fluorescent imaging, thereby leading to clearer and more accurate detection of the target analyte [88]. AIE sensors are constructed for the detection of various biological macromolecules, such as cholera toxin, lectin, γ-globulins, and G-quadruplex DNAs. In this review, the most recent advances in the sensing of amino acids, biogenic amines, enzymes, nucleic acids, and other biomolecules such as saccharides, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and vitamins are discussed.
3.1. Nucleic Acids
Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, play a fundamental role in life processes by serving as the primary carriers of genetic information, regulating gene expression, and directing protein synthesis and cellular metabolism [89]. They encode and transmit the instructions necessary for cell growth, differentiation, and replication, ultimately governing all biological functions. Structural or expression abnormalities, including mutations, epigenetic modifications, and RNA dysregulation, are linked to cancer, genetic disorders, viral infections, and neurological diseases [90,91]. The sensitive and rapid detection of nucleic acids is hence critical in the early diagnosis of diseases, in biomedical research, and in the precision medicine domain. Traditional techniques like PCR, electrophoresis, and microarrays are cumbersome. They require complex instrumentation, time-consuming protocols, and tagged probes, limiting their applications in real-time and point-of-care diagnostics [92,93].
Fluorescent DNA dyes are widely used tools in molecular biology, valued for their ability to exhibit significant fluorescence enhancement upon binding to DNA. Initially, dyes such as Hoechst, DAPI, and propidium iodide were employed for cellular DNA detection and quantification. Among the most extensively used are monomethine cyanine dyes, including SYBR Green, SYBR Gold, and PicoGreen. These dyes typically bind nucleic acids via intercalation or groove binding and are characterized by high fluorescence quantum yields when associated with double-stranded DNA (dsDNA). Their application has expanded to various bioassays, including cell quantification and nucleic acid detection [94].
SYBR Green I shows a greater than 1000-fold increase in fluorescence following binding to dsDNA, which results from inhibiting intramolecular motion [95]. SYBR Gold offers even more comprehensive nucleic acid discrimination and binds dsDNA, ssDNA, and RNA with higher sensitivity up to 100-fold greater than with ethidium bromide and is thus extremely selective with hardly any background fluorescence [96]. PicoGreen is a commonly used dye that shows a ~1000-fold increase in fluorescence upon binding to dsDNA but is impermeable to membranes and requires fixed or enzymatically lysed cells. It is extensively used in quantitative DNA assays where sensitivity is needed [97]. While these dyes work well, they are plagued by shortcomings such as photobleaching, non-specific background signals, and interference with polymerase activity at high concentrations. On the contrary, AIE-based fluorescent probes exhibit a “turn-on” emission mechanism, which is inherently non-fluorescent in solution but highly emissive in the aggregated or upon binding to the target. This provides low background fluorescence, high signal-to-noise ratios, and excellent photostability. Unlike conventional dyes, AIE-based sensors are particularly of high utility for real-time imaging, monitoring, and biosensing applications, bypassing most of the pitfalls intrinsic to conventional fluorescent probes. A comparative analysis of AIE-based sensors and monomethine cyanine-based fluorescent dyes for DNA detection is given in Table 1.

Table 1.
Comparative analysis of AIE-based sensors and conventional fluorescent dyes for DNA detection.
AIE-based fluorescent biosensors provide a sensitive and efficient alternative for nucleic acid detection. AIEgens functional nucleic acids (AFNAs) are utilized to detect targeted analytes, e.g., Hg2+ ions, via fluorescence induction on molecular interaction. Restriction of intramolecular motion in structural variants in AFNAs enables greater fluorescence intensity and selectivity. The biosensors leverage hybridization-induced aggregation, electrostatic interaction with phosphate backbones, and enzymatic fluorescence activation to enable turn-on detection [98]. Compared to conventional fluorophores, which are prone to self-quenching and photobleaching, AIE-based probes exhibit high signal-to-noise ratios, superior photostability, and real-time monitoring. Their integration with nanomaterials, microfluidic devices, and portable sensors enables high-throughput screening, rapid diagnostics, and point-of-care diagnosis, rendering them a promising tool for clinical and biomedical applications [93].
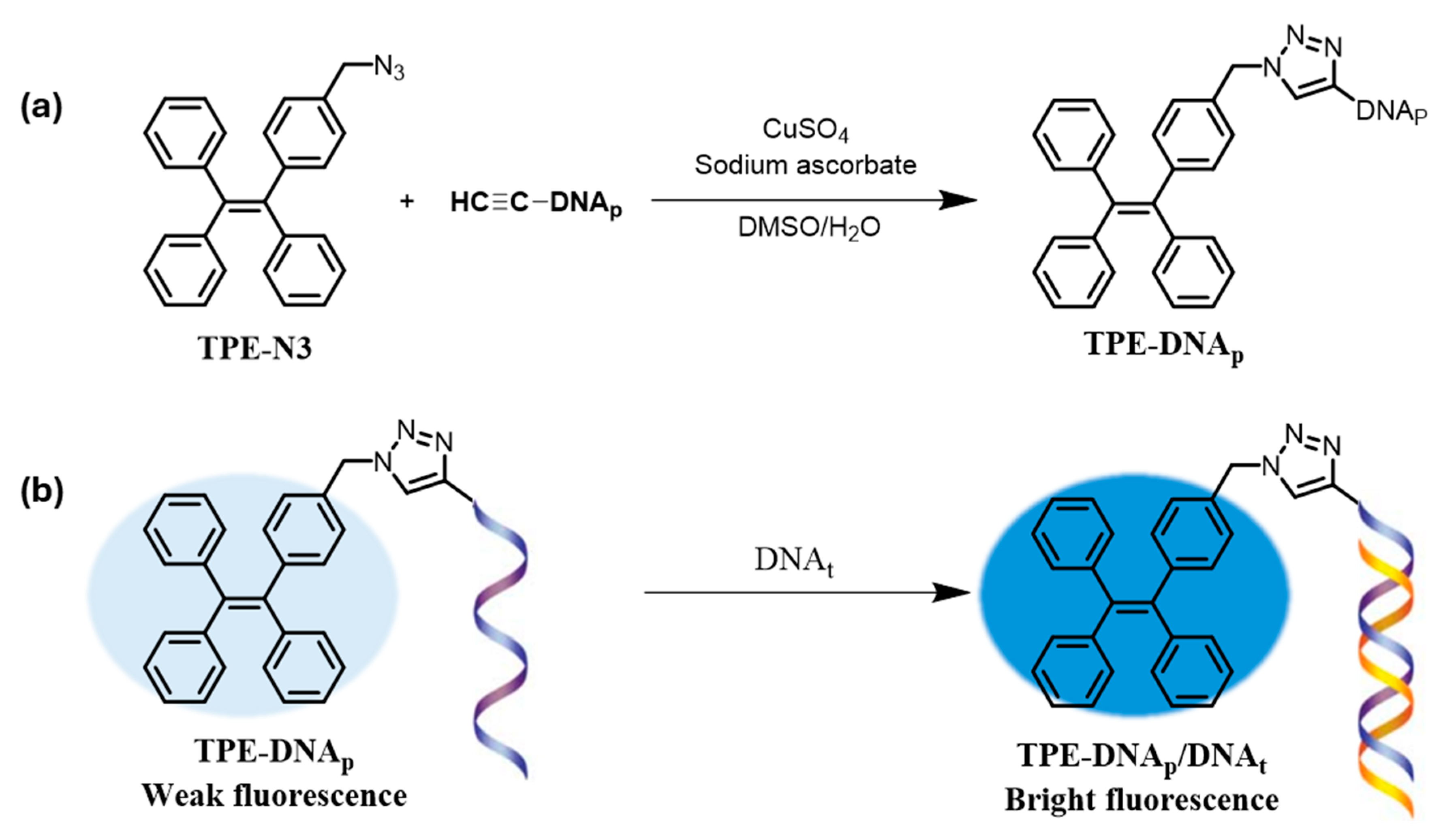
The development of highly selective and sensitive fluorescent probes is vital for detecting nucleic acids. As shown in Figure 2, TPE–DNAp was synthesized for nucleic acid hybridization detection, where DNAp and DNAt act as probe DNA to form a complementary DNA complex [99]. Using Hg2+-DNA complexes to stimulate AIE of a tetraphenylethene derivative, Xu et al. developed a label-free fluorescence sensor for Hg2+ and glutathione (GSH) [100]. Fluorescence sensors were water-soluble AIE probes complexed with anti-Hg2+ aptamer ssDNA. Selective Hg2+ detection was made possible by the hairpin-like aptamer structure that was created by Hg2+ binding. GSH detection was made easier by the disruption of the T-Hg2+-T complex caused by the GSH addition, which released Hg2+, unfolded the structure, and quenched fluorescence. Similarly, Hong et al. introduced non-emissive tetraphenylethene derivatives (TTAPE), which become fluorescent upon interaction with DNA/RNA, enabling quantification and visualization in both liquid and electrophoretic gels, making them useful for chromosome and nuclear labeling in fixed cells [101]. Due to its high DNA-binding affinity, TTAPE selectively labels chromosomes and nuclei in fixed cells, offering a quick and straightforward method for observing cell mitosis.
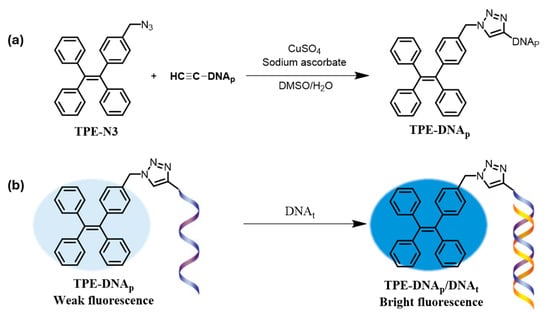
Figure 2.
(a) Synthesis of TPE–DNAp and (b) a schematic representation of its application in nucleic acid hybridization detection [95].
Hu et al. developed carboxyl-modified TPE conjugated with amino-modified DNA (TPE/DNA), which was immobilized on magnetic beads (MBs) through biotin-modified influenza virus hemagglutinin peptide (HA) and biotin-DNA-amino interactions to form MB/DNA/HA/TPE, and realized an enhanced fluorescence response and attained a detection limit of 1.0 × 10−9 M, outperforming traditional AIE systems [102]. Kawamura et al., in another work, reported an AIE-based method for DNA detection by using dye-labeled peptide nucleic acid (PNA) to enhance target recognition and signal emission [103]. This label-free PNA probe can efficiently separate target DNA from similar sequences or structural variants, allowing quantitative DNA detection without the use of intercalators or additives. Reliable detection was ensured by the fluorescence intensity remaining inversely proportional to target concentration, even though the fluorescence quenching ratio decreased with longer telomere DNA. High sensitivity detection of repetitive long-chain target DNA is a good fit for this system. Additionally, because this detection method supports detection via a particular dye for each sequence, it will allow the detection of multiple DNA targets within a single system.
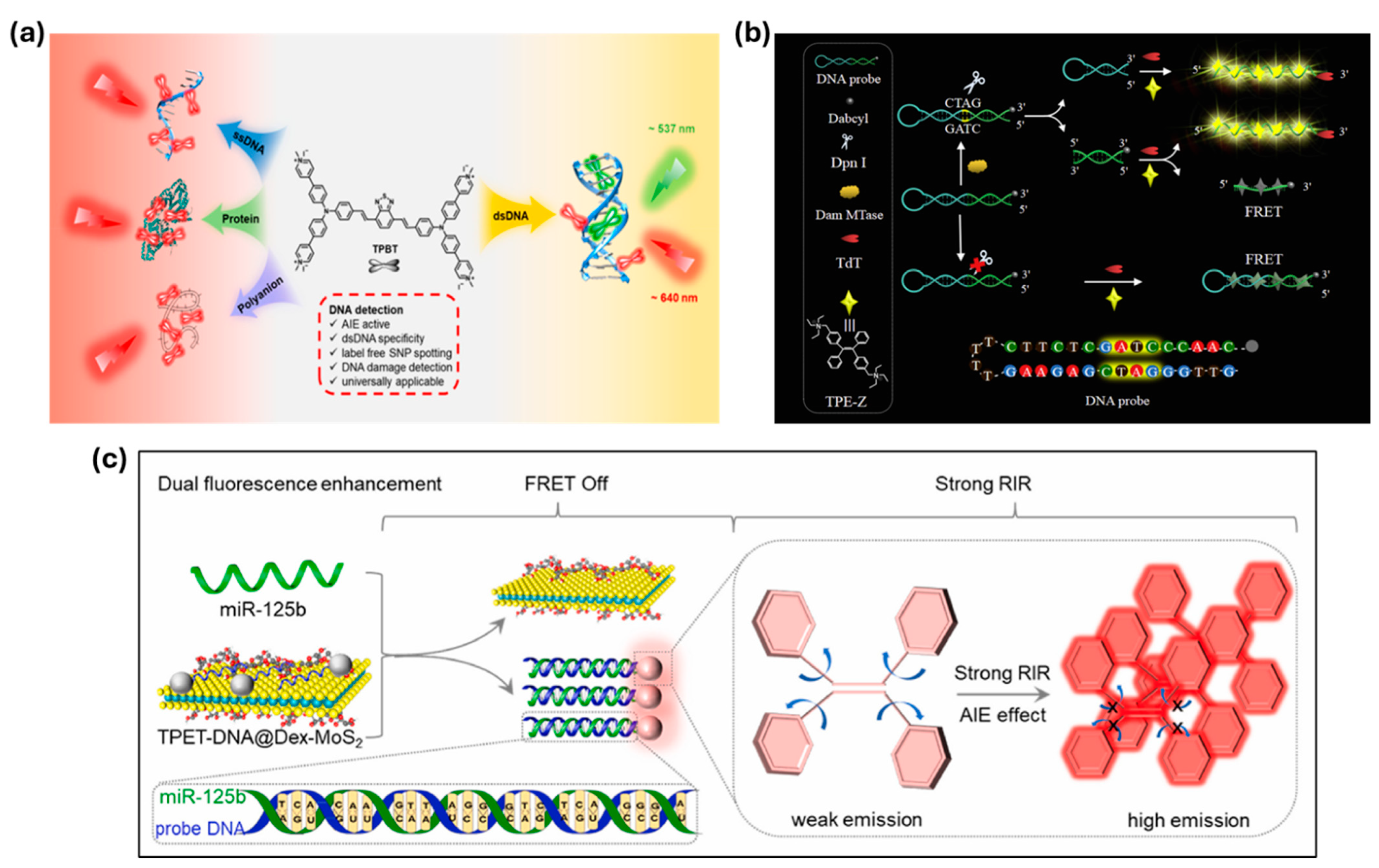
Gao et al. have designed a TPBT assay capable of detecting double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) based on dual-color fluorescence emission red (640 nm) and green (537 nm) for single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) detection and UV-induced DNA damage analysis for disease diagnostics and genomics research [104]. This unique property of TPBT presents a promising opportunity for high-throughput screening of gene variations, particularly for detecting unknown mutation sites with high efficiency (Figure 3a). Other advancements include Zhang and co-workers’ AIE-based SDA system for the analysis of patulin (PAT) toxin via DNA G-quadruplex assembly with a sensitivity of 0.42 pg mL−1. This system competes with cDNA aptamers on aptamer-modified magnetic beads for highly specific PAT detection [105]. Furthermore, Niu et al. developed an AIE-based fluorescence assay for the detection of DNA methyltransferase (MTase) based on quaternized TPE salts that bind to ssDNA via electrostatic interactions. A hairpin probe was used to cause DNA methylation, causing DNA polymerization with terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) enzymes, causing fluorescence with a detection limit of 0.16 U mL−1 (Figure 3b) [106]. These advances highlight AIE-based biosensors as powerful tools for nucleic acid sensing, which have the potential to offer high sensitivity, specificity, and real-time detection for biomedical and diagnostic applications.
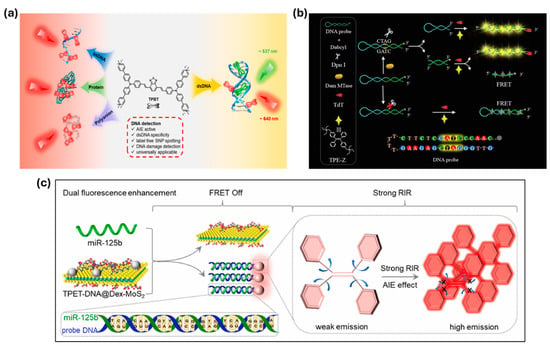
Figure 3.
(a) Molecular structure of TPBT and its various emissions upon binding with different polyanionic macromolecules, (b) illustration of Dam MTase activity assay based on AIE and template-free DNA polymerization, (c) schematic illustrations of the working mechanism (dual fluorescence enhancement) of TPET-DNA@Dex-MoS2 nanoprobes for the detection of miR-125b in vitro. Reprinted with permission from [100,102,103].
Yang et al. designed AIEgen-based biosensors that detect miR-125b through the immobilization of AIEgen-labeled oligonucleotide (TPET-DNA) probes on a nanocomposite via a cationic dextran modified molybdenum disulfide surface, namely PET-DNA@Dex-MoS2. The TPET-DNA composites exhibited maximum fluorescence at 668 nm (excitation: 480 nm), which blue-shifted to 618 nm upon introducing ssDNA. When miR-125b interacted with the system, it formed a DNA/RNA complex, causing TPET-DNA detachment from Dex-MoS2 (Figure 3c) [107]. This activated fluorescence by restoring the TPET-DNA signal and enhancing AIE fluorescence through restricted intramolecular rotation. In vitro, this sensor detected miR-125b at concentrations as low as 20.82 pM, showing a strong linear correlation with fluorescence at 618 nm (R2 = 0.994). It also effectively detected miR-125b in PC12 cells and AD model mice, highlighting TPET-DNA@Dex-MoS2 as a promising tool for real-time in situ monitoring of AD-associated miRNAs, offering new insights into early-stage Alzheimer’s disease prognosis [107,108].
Recently, AIEgen-based nanoparticles (AIE dots) have been utilized for biomolecule detection, imaging, and sensing. Xu et al. designed and synthesized AIE-based probes capable of detecting DNA and RNA, demonstrating their ability to identify both single-stranded and double-stranded DNA sequences, making them promising candidates for nucleus staining [98]. A microchip AIE sensing system was also created for the quantification of microRNA (miRNA). The platform employed miRNA and TPE-DNA in microwells, where the controlled evaporation of water allowed analyte concentration to a minute detection zone, significantly amplifying fluorescence intensity and sensitivity. These results show that AIE-based RNA sensing has excellent potential to promote RNA biology research by enhancing detection and analysis tools for RNA. As AIE technology continues to evolve, it is expected to further expand applications in RNA biology, offering deeper insights and enhanced diagnostic capabilities [109,110].
3.2. Detection of Enzyme
Enzymes, predominantly protein molecules synthesized by living organisms, exhibit remarkable substrate specificity and catalytic efficiency. Enzymes are involved in fundamental life processes and are closely associated with the development of numerous diseases [111]. As biocatalysts, enzymes use their complex protein structures to control major life-sustaining processes. Thus, the development of accurate techniques for the identification of disease-causing enzymes becomes very important [112]. AIE-based biosensors have attracted great attention because of their extraordinary characteristics, including superb photostability, high luminescence efficiency in the aggregated state, a large Stokes shift, and exceptional biocompatibility [113]. Small-molecule AIEgens have effective permeability through cell membranes and provide simplicity of synthesis with low requirements for raw materials [114,115,116]. After being internalized, the aggregates emit steady-state fluorescence signals, enabling long-term in situ imaging and detection, which are closely linked to their molecular structure [117]. AIE sensors have been used with success to detect a wide range of enzymes, such as acetylcholinesterase (AChE), alkaline phosphatase (ALP), esterase, caspases, chymase, furin, β-galactosidase, hyaluronidase, and telomerase, etc. [14]. The fluorescence mechanisms of AIE-active biosensors in enzyme activity assays are hydrolysis, electrostatic adsorption, biological redox reactions, and pH responsiveness. Intensive research work is ongoing in the creation of enzyme activity sensing based on AIE-active sensors [117].
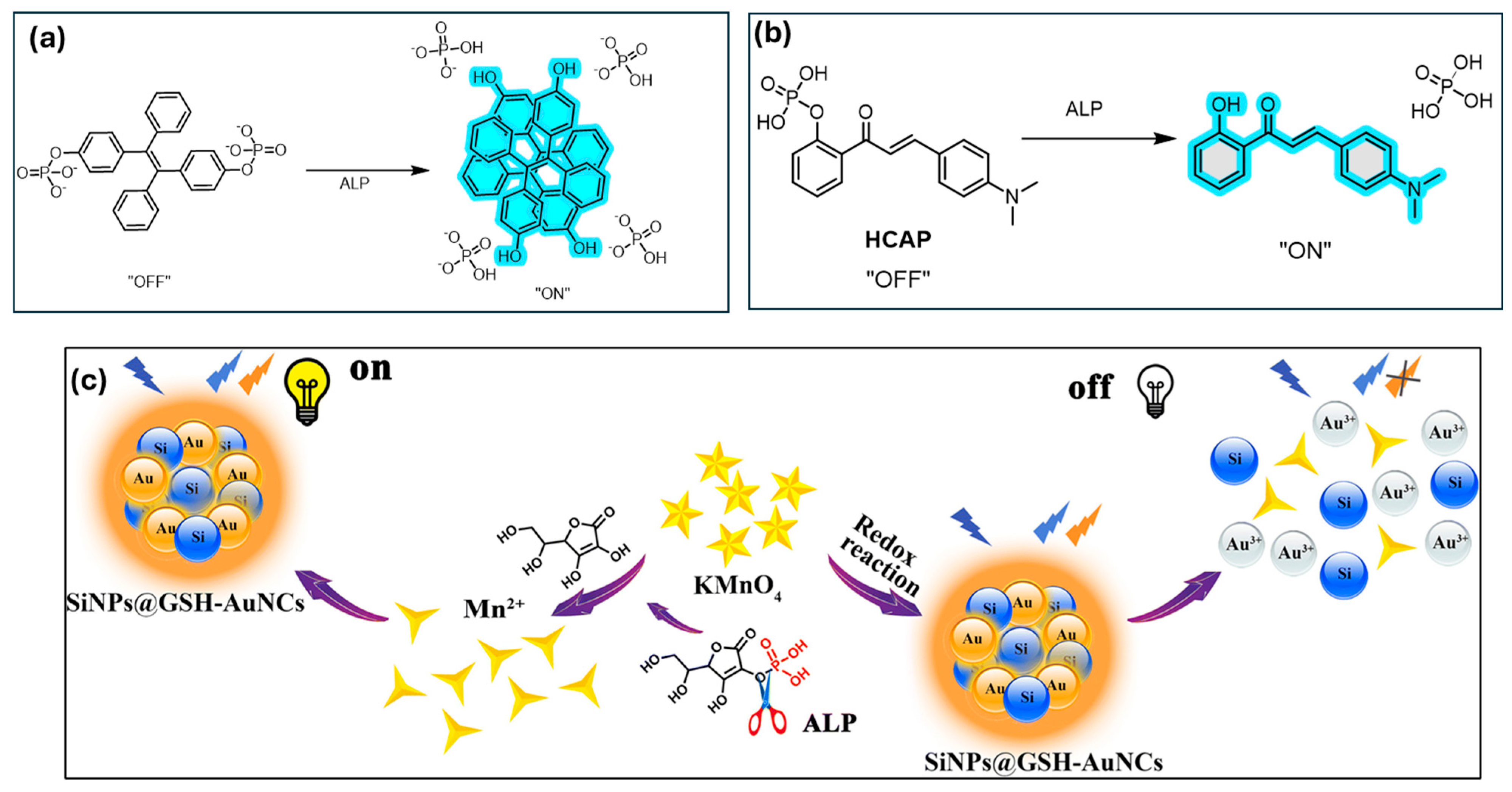
Alkaline phosphatase (ALP) is a non-specific phosphate monoesterase and an important biomarker for diseases like hypothyroidism and hepatobiliary disorders in clinical diagnosis. In situ detection of endogenous ALP and examination of its cellular localization are very important aspects for the diagnosis of ALP-related diseases. Liu et al. independently developed tetraphenylethylene (TPE)-based probes for the highly sensitive detection of ALP through the introduction of phosphate groups on the TPE core to enhance its water solubility (Figure 4a). In the presence of enzymatic hydrolysis, the cleavage of the phosphate group occurs, resulting in the generation of highly emissive aggregates. The system is capable of ultra-sensitive detection of ALP, achieving a detection limit as low as 11.4 pM or 0.2 U/L [118]. Further, Zhang and co-workers also developed a novel fluorescent probe, (E)-2-(((9H-fluoren-9-ylidene)hydrazono)methyl) phenyl dihydrogen phosphate (FAS-P), for the detection of ALP, based on the excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) mechanism. The probe consists of a phosphate binding unit and fluorophore, (E)-2-(((9H-fluoren-9-ylidene)hydrazono)methyl)phenol (FAS). FAS was selected based on its greater solubility in water, decent permeability in cellular environments, selective targeting towards lipid droplets (LDs), and efficient fluorescence quenching aided by hydroxyl substitution. The FAS-P probe exhibits high selectivity and sensitivity for ALP detection, with a linear fluorescence response in the 1–100 U L−1 range and a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.6 U/L [119].
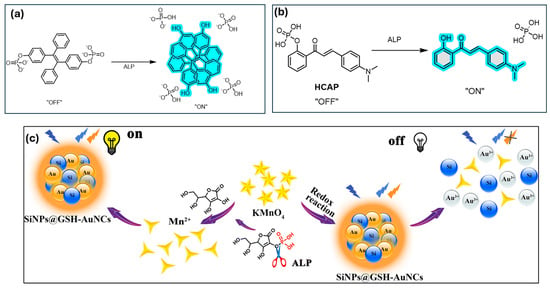
Figure 4.
(a) Schematic illustration of the light-up detection for ALP [118], (b) schematic illustration of HCAP for ALP activity assay in solution and living cells [120], (c) schematic of the ratiometric detection of ALP based on the SiNPs@GSH-AuNCs-KMnO4 system. Reprinted with permission from ref. [121]. Copyright © 2019, Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany, part of Springer. Nature.
Song et al. synthesized and further developed a phosphorylated chalcone derivative for the ratiometric measurement of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity. Through the modification of 2′-hydroxychalcone, they created a new ratiometric fluorescent bioprobe (HCAP) with AIE feature and excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) property for ALP detection in buffer solutions and serum samples (Figure 4b). The aqueous-soluble probe is greenish-yellow fluorescent in aqueous buffers but switches to red in the presence of ALP. This bioprobe facilitates the detection of ALP in the concentration range 0–150 mU/mL with a detection limit of 0.15 mU/mL, hence showing better sensitivity than in earlier reports. Additionally, the red fluorescence of the enzymatic residue reduces autofluorescence interferences from serum samples. Apart from serum assays, the probe is also applicable to the detection of ALP in intercellular fluids and imaging ALP activity in living cells [120].
You et al. developed an electrostatically driven self-assembly system using glutathione-capped gold nanoclusters (GSH-AuNCs) with AIE and amino-modified silicon nanoparticles (SiNPs) to create a hybrid probe (SiNPs@GSH-AuNCs). This system enables highly sensitive and selective detection of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity via an enzymatic reaction involving SiNPs@GSH-AuNCs-KMnO4 (Figure 4c) [121]. In this setup, GSH-AuNCs fluorescence serves as the signal, KMnO4 acts as a quencher, and SiNPs provide a stable internal reference. Initially, KMnO4 quenches the AIE, but fluorescence is restored upon the addition of ascorbic acid through an oxidation–reduction reaction, while SiNP fluorescence remains unaffected. With excellent sensitivity and selectivity, this hybrid probe successfully detects ALP in serum samples and assesses ALP inhibitors. In the enzymatic reaction, ALP hydrolyzes ascorbic acid 2-phosphate to generate ascorbic acid, which reduces KMnO4, leading to fluorescence recovery. This ratiometric detection system offers a linear range of 0.5–10 U/L and a limit of detection (LOD) of 0.23 U/L [121].
Caspases are a family of cysteine proteases that play fundamental roles in programmed cell death and inflammation. Their activation, substrate specificity, and biological roles are important factors to be explored in order to understand their role in different cellular mechanisms. In 2016, Liu et al. designed and developed a self-validating fluorescent probe through the utilization of coumarin (Cou) as an energy donor and tetraphenylethenethiophene (TPETP) as an AIE-based quencher, which were connected by a caspase-3-responsive DEVD peptide. The probe is non-fluorescent in aqueous solution because of the energy transfer between Cou and TPETP. After being cleaved by caspase-3, the energy transfer is interrupted, resulting in the simultaneous turn-on of green and red fluorescence from Cou and TPETP, respectively. The dual fluorescence turn-on mode improves the accuracy of detection based on self-validation [122].
Ding et al. developed a simple strategy to improve AIE light-up probe sensitivity through the incorporation of self-assembling peptide GFFY between the AIE luminogen and the recognition unit. The probes are non-emissive in water but emissive when caspase-3 is activated, where DEVD cleavage eliminates hydrophilic groups to activate fluorescence. GFFY promotes ordered self-assembly of AIEgen to inhibit intramolecular motion and greatly improve fluorescence. In comparison to the non-assembling probes, this strategy is more sensitive in solution and cancer cells. TPE-GFFYK residues self-assemble into filamentous networks, and TPE-K residues self-assemble into nanoparticles under enzyme-catalyzed hydrolysis. The ordered self-assembly of TPE-GFFYK more effectively suppresses the rotation of phenyl rings, resulting in enhanced fluorescence, reduced detection limits, and better caspase-3 imaging. The TPE-GFFYK(DVEDEE-Ac) probe has an ultra-low detection limit of 0.54 pM in caspase-3 detection. Moreover, TPE-GFFYE-SS-EE exhibited enhanced GSH sensing and intracellular thiol imaging compared to its control TPE-SS-EE, revealing a versatile strategy for the design of highly sensitive AIE fluorescent probes through GFFY-mediated self-assembly. Research on AIE-based strategies for enzyme activity detection broadens the application of AIE luminogen-based assays and advances the development of disease-targeted diagnostics [123].
3.3. Detection of Amino Acids
Amino acids, as the building blocks of protein, are essential raw materials for biosynthesis and play critical roles in physiological and pathological processes, including epigenetic regulation and tumor metabolism. Amino acids are essential for the synthesis of hormones, peptides, enzymes, and other biological proteins [124]. Given their significance, high spatiotemporal resolution sensing of amino acids is crucial. The disruption of amino acid dynamics leads to dramatic biological consequences, and, therefore, in vivo sensing is relevant. Fluorophore-based strategies allow selective modification of specific amino acids, such as cysteine, homocysteine, and lysine, with fluorescent molecules for selective monitoring and analysis [125].
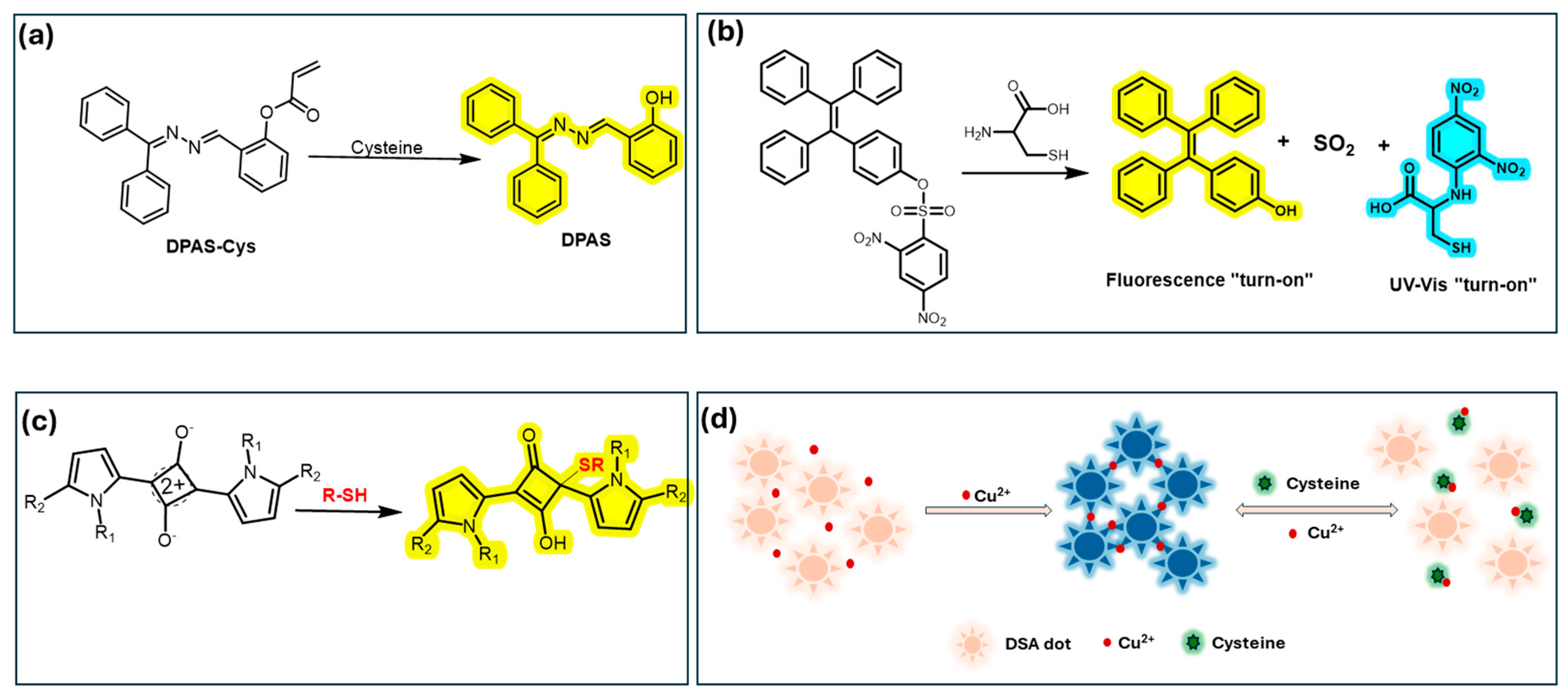
Cysteine (Cys) is a non-essential amino acid that plays a vital role in protein synthesis and redox regulation, and serves as a precursor to biothiols like glutathione. Similarly, homocysteine (Hcy), a byproduct of methionine metabolism, is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease when present at elevated levels in the blood. Given their biological significance, detecting Cys and Hcy is crucial for early disease diagnosis [126]. To address this, AIE chemosensors have been developed for thiol-containing amino acids, utilizing specific reactive sites and sensing mechanisms. Cheng and co-workers developed the smart fluorescent probe DPAS-Cys, designed with AIEgen DPAS and an acrylate moiety, which enables selective cysteine (Cys) detection with a large Stokes shift (200 nm) and a low detection limit (2.4 μM), as shown in Figure 5a. It is appropriate for bioimaging in physiological systems because it also avoids excessive organic solvents and demonstrates lipid droplet (LD) targeting [126]. In continuation, Stang et al. designed a tetragonal prismatic Pt(II) metallacage featuring benzoate-TPE groups as structural components. This metallacage, initially non-emissive in a methanol/water solution (1:1, v/v), undergoes strong fluorescence enhancement upon disruption by thiol-containing amino acids. The breakdown of the metallacage results in the formation of highly emissive TPE-based aggregates, allowing for highly sensitive detection of Cys and glutathione (GSH), with detection limits of 2.78 × 10−7 M for Cys and 1.89 × 10−7 M for GSH. This study not only contributes to fluorescent materials research but also offers insights into the development of stimuli-responsive supramolecular coordination complexes [127]. Feng and Ding et al. incorporated a 2,4-dinitrobenzenesulfonyl group to enhance aqueous solubility and quench fluorescence via photoinduced electron transfer (PET) as displayed in Figure 5b. To address these challenges, they developed a novel colorimetric and turn-on fluorescent probe based on salicylaldehyde azine, integrating AIE and excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) properties for Cys/Hcy detection, achieving a detection limit (LOD) of 2.84 mM [128]. Further, Chua et al. synthesized a reactive squaraine center (1,3-Bis(pyrrol-2-yl)squaraine dyes) where Cys undergoes Michael addition, disrupting conjugation and causing blue decolorization. Notably, a squaraine-based solid-state device was fabricated, effectively detecting Cys and GSH through pale yellow fluorescence (Figure 5c) [129]. Furthermore, a nano-precipitation technique was used by Jiang et al. to create a novel on-off-on fluorescent chemosensor for Cu2+, Fe3+, and cysteine. Through aggregation-induced fluorescence quenching (on-off), the AIE dots selectively detect Cu2+ and Fe3+ (Figure 5d). Cysteine breaks up these agglomerations and restores fluorescence (off-on). This sensor is a promising probe for metal ion and biothiol detection because it has a broad linear range with detection limits of 107 nM (Cu2+), 120 nM (Fe3+), and 78 nM (cysteine) [130].
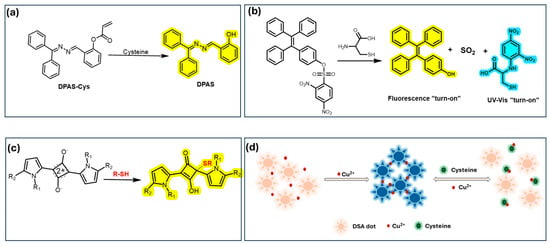
Figure 5.
Four main sensing mechanisms in the detection of Cys: (a) cleaving of acrylate quenching group [126], (b) cleaving of sulfonic ester linkers [128], (c) formation of sensor-Cys adducts: mechanism of reaction between thiol compounds and 1,3-Bis(pyrrol-2-yl)squaraine Dyes [129], and (d) coordination of Cys to metal complexes [130].
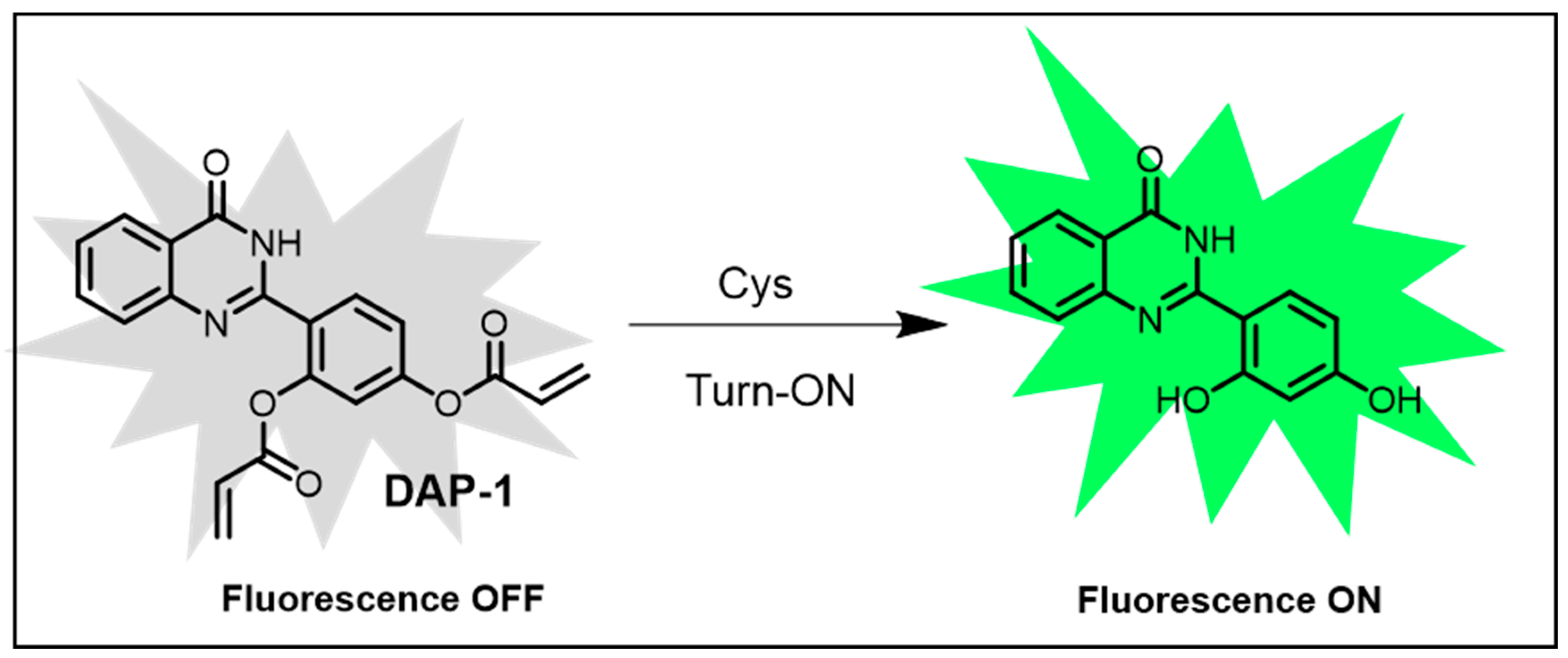
Further, glutathione (GSH), a tripeptide consisting of glutamate, cysteine, and glycine, is one of the most abundant biothiols in cells. It has a prominent role as an antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and reactive oxygen species (ROS) while also facilitating the detoxification of harmful compounds through conjugation and elimination. In addition, cysteamine (CSH), a cysteine-derived small molecule, is widely used in medicine, particularly for the treatment of cystinosis. In 2018, Zhou et al. developed a ratiometric fluorescence nanoprobe for label-free biothiol detection, leveraging Au3+-triggered AIE behavior of Ag nanoclusters (Ag NCs). The probe, created by loading Au3+ onto g-C3N4 nanosheets and aggregating Ag NCs via ion binding, enabled biothiol detection by altering its emission ratio upon Au3+ removal by biothiol coordination. It showed high sensitivity for GSH with a detection limit of 0.8 μM and performed well in human serum samples [131]. In 2021, Li’s team synthesized 2-(benzo [d]thiazol-2-yl)-4-hydroxyphthalazin-1(2H)-one hydrate (TP), a phthalazinetrione derivative with multi-detection capabilities. It formed a dimer with TEA vapor for GSH sensing and underwent J-aggregation with acetic acid for Zn2+ and Cd2+ detection. A green fluorescence was observed under a green channel in the presence of GSH, demonstrating its versatile sensing potential [132]. In 2018, Yang et al. developed DAP-1, a hydroxyphenylquinazolinone-based fluorescent probe (Figure 6) with a large Stokes shift (162 nm) for cysteine (Cys) detection. Upon Cys addition, fluorescence increased significantly due to a conjugated addition/cyclization sequence mechanism. DAP-1 exhibited high selectivity and sensitivity for Cys over homocysteine (Hcy) and glutathione (GSH), producing a 65-fold fluorescence enhancement upon interaction with Cys. The probe achieved a detection limit as low as 0.03 μM, demonstrating its ultrasensitive detection capabilities [133].
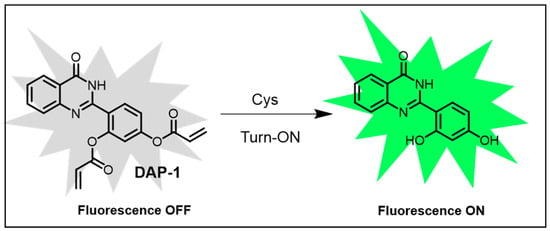
Figure 6.
Rational design of fluorescent probe DAP-1 [133].
Further, Shu et al. demonstrated stimuli-responsive behavior in AIE-type Ag NCs, where pH and salinity modulation-controlled photoluminescence without affecting UV-vis absorption. The shrunk oligomer shell selectively inhibited cysteamine-induced etching, protecting the Ag(0) core from larger etchants like glutathione. Utilizing this property, a highly selective and sensitive luminescent sensor for cysteamine was developed, enabling rapid detection (minutes) with a detection limit of 15.7 nM, offering a new strategy for AIE-based nanocluster sensing [134]. In another approach, Qu et al. developed a label-free fluorescent “turn-on” nanoprobe for GSH detection, using MnO2 nanosheets and AIE-silica nanospheres (SiO2 NPs). The anionic tetraphenylethylene derivative (TPE3) functioned as an AIE-active probe, aggregating on amino-functionalized SiO2 NPs to form AIE-SiO2 NPs, which emitted strong fluorescence. The MnO2 nanosheets acted as charge protectors for SiO2 NPs and recognition units for GSH. When GSH selectively reduced MnO2 nanosheets to Mn2+, the positively charged SiO2 NPs were exposed, allowing TPE3 aggregation and triggering a fluorescence turn-on response. This approach demonstrated a detection limit of 200 nM for GSH and was successfully applied for GSH detection in human serum samples, showcasing its high sensitivity and practical applicability [135].
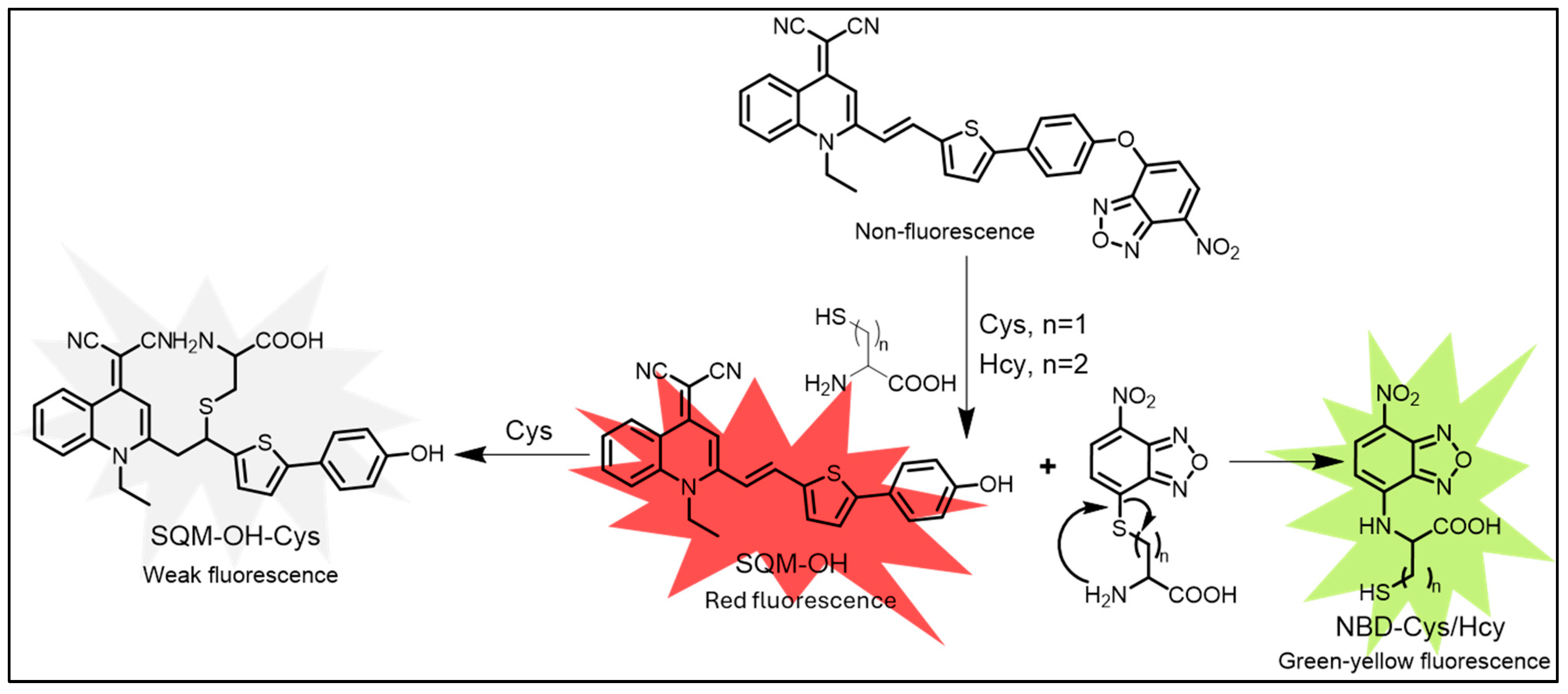
Further in 2022, Wang et al. developed an AIE fluorescent probe, SQM-NBD, by linking 7-nitro-2,1,3-benzoxadiazole (NBD) to the hydroxyl group of the fluorophore SQM-OH for selective Cys/Hcy detection. SQM-NBD itself was non-fluorescent, but in the presence of Cys/Hcy, fluorescence was activated, while GSH had no effect. Mechanistic studies revealed that SQM-NBD released both SQM-OH and Cys/Hcy-NBD upon reaction with Cys/Hcy. However, Cys/Hcy further quenched the fluorescence of SQM-OH through Michael addition and an ion-rich environment, allowing only the fluorescence signal of Cys/Hcy-NBD to be observed (Figure 7). The probe demonstrated high sensitivity, with detection limits of 54 nM for Cys and 72 nM for Hcy. Notably, SQM-NBD enabled fluorescence imaging of Cys/Hcy in HeLa cells, showcasing its potential for detecting Cys/Hcy in physiological and pathological conditions [136].
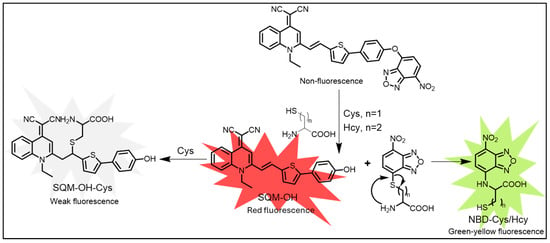
Figure 7.
The mechanism of Cys/Hcy detected by probe SQM-NBD [132].
Furthermore, various AIE chemosensors have been developed for detecting specific amino acids, including arginine (Arg), lysine (Lys), tryptophan (Trp), trypsin (Try), and histidine (His), with some exhibiting multipurpose detection capabilities. Enhancing amino acid and protein detection methods enables more accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of imbalances, as their regulation is essential for maintaining homeostasis in the human body.
3.4. Detection of Biogenic Amines
Biogenic amines (BAs) are amine-containing molecules made from amino acids that are crucial for neurotransmission, hormonal control, immunity, and digestion. They are important for the viability of cells as well as predominant metabolic activities, including protein and hormone production, and replication of DNA. Altered levels of BA have been implicated in neurological conditions including depression, Parkinson’s disease, and migraine headaches. Common BAs, including histamine, tyramine, putrescine, cadaverine, agmatine, spermidine, and spermine, are organic, nitrogenous compounds found in plants, microbes, and animals. Dopamine, norepinephrine, epinephrine, histamine, and serotonin also serve as neurotransmitters, highlighting their significance in physiological processes [137,138,139].
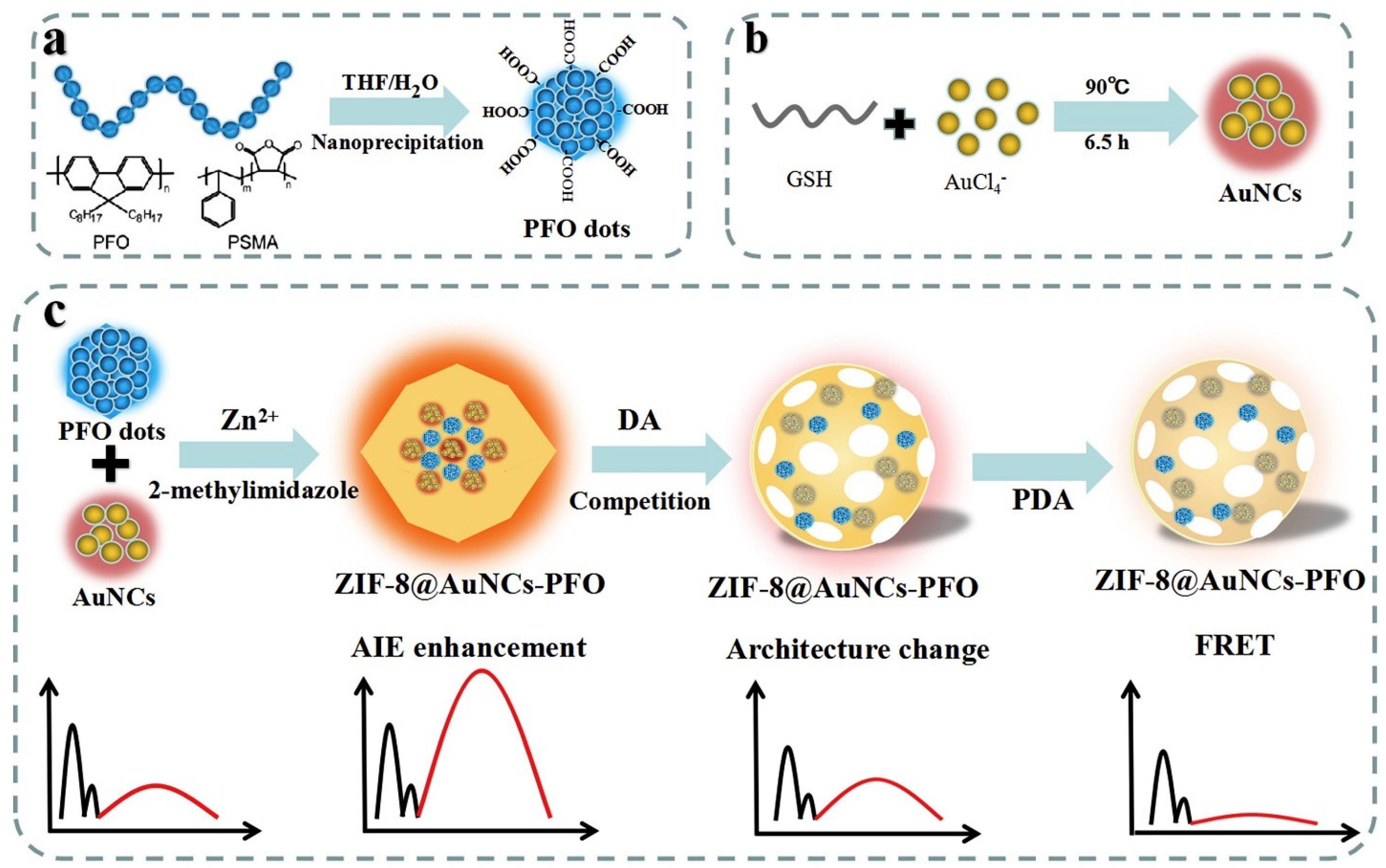
Dopamine (DA) is a neurotransmitter associated with pleasure, motivation, and contentment, as well as learning, memory, and attention. Parkinson’s disease, anxiety, depression, and other neurological and psychiatric conditions are linked to abnormalities in dopamine signaling. Gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) and poly(9,9-dioctylfluorenyl-2,7-diyl) (PFO) dots were added to zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) by Shao et al. to create a dual-emission fluorescence probe (ZIF-8@AuNCs-PFO) for ratiometric detection of DA. A “two-in-one” ratiometric fluorescence probe was designed by encapsulating gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) and PFO dots within zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8). Figure 8 illustrates the synthesis of AuNCs (orange fluorescence) and carboxyl-functionalized PFO dots (blue fluorescence) using chemical reduction and nanoprecipitation, respectively. After that, the ZIF-8@AuNCs-PFO nanoprobe was put together using a chemically uncoupled self-assembly process that involved AuNCs, PFO dots, Zn2+, and 2-methylimidazole. With three fluorescence peaks at 438 nm and 465 nm (PFO dots) and 600 nm (AuNCs), the probe demonstrated high selectivity and sensitivity toward DA. PFO dots underwent a slight quenching upon DA interaction, whereas AuNC fluorescence was sharply quenched, allowing for ratiometric sensing with superior analytical performance. Encapsulation allowed for DA-triggered asynchronous fluorescence responses and increased AuNCs AIE by five times. With a detection limit of 4.8 nmol L−1, the probe demonstrated high sensitivity and selectivity, detecting DA from 0.01 to 10,000 μmol L−1 [139].
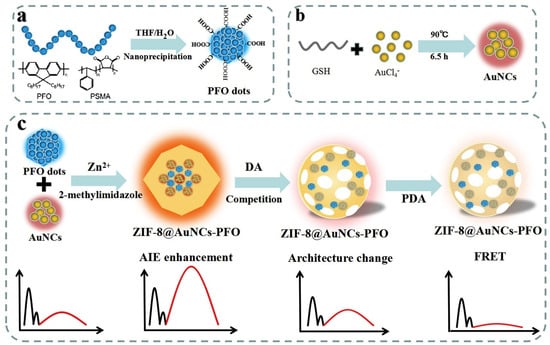
Figure 8.
Schematic illustration of ZiF-8@AuNCs-PFO nanoprobe-based ratiometric fluorescent sensing of DA. (a) Schematic illustration of the preparation of PFO dots, (b) Synthesis of gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) through the reduction of HAuCl4 by glutathione (GSH), (c) Fabrication and sensing mechanism of ZIF-8@AuNCs-PFO nanohybrids. Reprinted with permission from ref. [139]. Copyright 2019 Elsevier B.V.
Qu et al. reported lead halide perovskites (LHPs) with AIE characteristics. They are non-emissive in DMF but exhibit strong fluorescence when they aggregate in water. As the water fraction increases, their form changes from irregular nanoparticles to needle-like and finally stick-like structures. At pM levels, AuNPs suppress LHP fluorescence; however, DA causes AuNP aggregation, which restores AIE. A linear DA detection range of 0.5–50 μM with a LOD of 0.12 μM was attained by the approach [140]. Further investigation of a ratiometric fluorescence methodology by Ling et al. revealed its great sensitivity for DA analysis, finding DA within the range of 0–800 nM with a LOD of 10 nM (3δ/s method) [141]. Naturally occurring polyamines with numerous amine (-NH2) groups, spermidine (SPD), and spermine (SPM) are essential for DNA synthesis, cell division, and apoptosis. Because they signify aberrant biological processes, their higher levels in urine act as biomarkers for early cancer identification. Using an AIE-active molecule encapsulated in cucurbit[7]uril (CB[7]), Jiang et al. created a supramolecular fluorescence probe called 1@CB[7], which demonstrated high selectivity for spermine with a linear detection range of 0–12 μM and a LOD of 1.0 μM, which corresponds to the range needed for early cancer diagnosis (1–10 μM urinary spermine) [142].
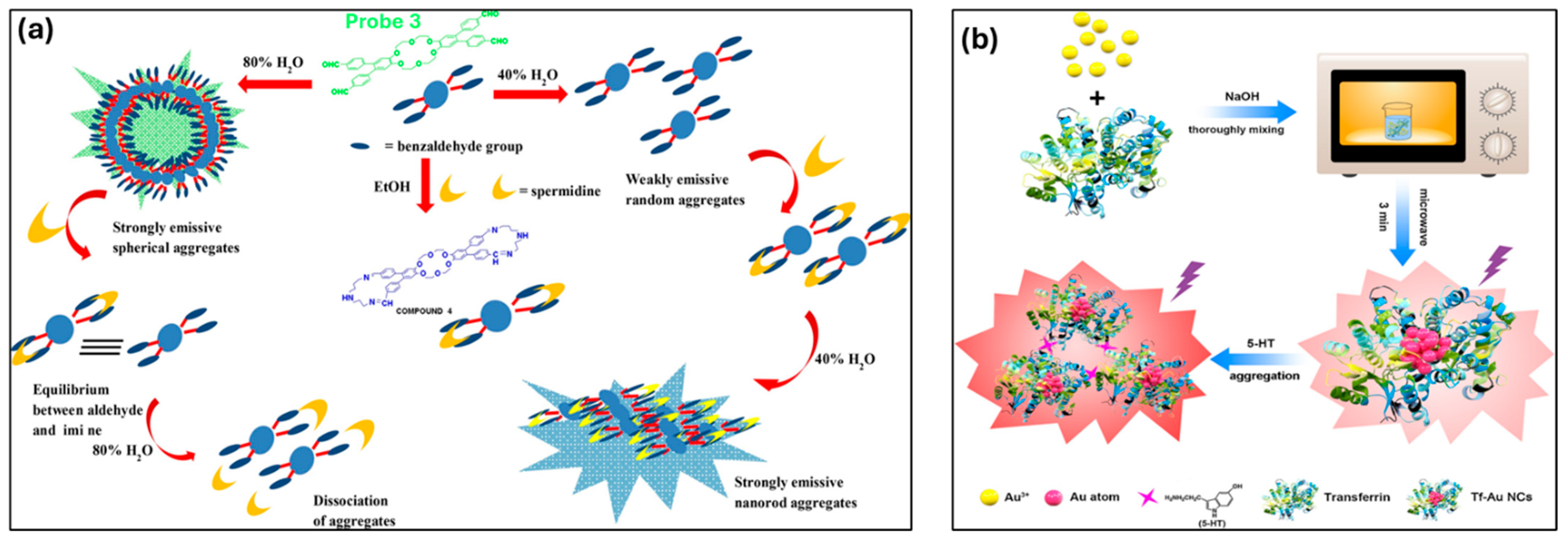
In order to improve the AIE effect of a tetraphenylethylene (TPE)-based water-soluble probe and enable quick and precise detection of SP and SPD in water, Naik and colleagues developed a solid-supported amplification technique. Through spectroscopic, microscopic, and isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC) investigations, the assembly–disassembly sensing process was verified. This system’s LOD values for SP and SPD were 1.4 × 10−8 M and 3.6 × 10−8 M, respectively, which are significantly below the cutoff point required for early cancer detection [143]. Building on this, Tejpal et al. utilized Suzuki–Miyaura cross-coupling to synthesize a terphenyl-based AIE-active molecule (probe 3), which exhibits AIE behavior upon aggregation in 80% H2O (Figure 9a). Spermidine further reorganized the structure into a random aggregation pattern by inducing the creation of imine linkages. This AIE-active probe 3 acted as a fluorescent assay for nanomolar-level SPD detection (46 nM), making it highly suitable for cancer diagnostics [144]. In 2019, Sha et al. developed a fluorescence turn-on biosensor for the sensitive detection of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) using transferrin-encapsulated gold nanoclusters (Tf-Au NCs). These monodisperse, red-emissive nanoclusters were rapidly synthesized through microwave-assisted preparation as shown in Figure 9b. The detection mechanism was based on aggregation-enhanced emission, triggered by the strong affinity between 5-HT and the sialic acid (SA) residues of transferrin. The sensor achieved quantitative 5-HT detection in the 0.2–50 μM range (R2 = 0.994) with a detection limit of 0.049 μM (S/N = 3) and was successfully applied to 5-HT detection in human serum, yielding recovery rates of 96.20–108.6% [145]. In 2020, Zang et al. developed a water-soluble AIE fluorescent probe for the specific detection of the CK-B subunit of cytosolic creatine kinase isoenzyme. Leveraging its AIE properties, the probe exhibited significantly enhanced fluorescence upon CK-B interaction, with a fast response time and minimal interference from other analytes. Its high selectivity (LOD: 93 U L−1) was attributed to differences in cavity sizes among isomers, which prevented hydrogen bond formation, ensuring precise CK-B detection. These studies introduce a new design strategy for developing fluorescent probes tailored for subunit-specific enzyme detection in future research [146].
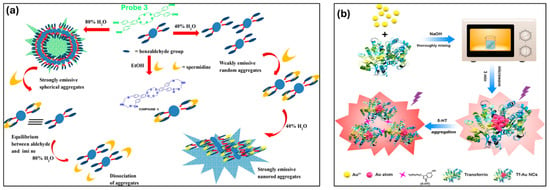
Figure 9.
(a) Illustration of the aggregation behavior of probe 3 in the presence of spermidine across different solvent environments. Reprinted with permission from ref. [144]. Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. (b) Schematic representation of the synthesis process and application of fluorescent transferrin-stabilized gold nanoclusters (Tf-Au NCs) for the detection of 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT). Reprinted with permission from ref. [145]. Copyright © 2019 Elsevier B.V.
3.5. Detection of Other Biological Molecules
The fluorescent sensing of biological macromolecules has gained significant attention due to their crucial role in clinical diagnostics. In this section, we highlight other important small biological molecules, including saccharides, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and vitamins, which will be discussed further.
3.5.1. Saccharides
Glucose, the most abundant monosaccharide, plays a crucial role in metabolic homeostasis, serving as the primary energy source for cellular respiration and ATP production. Body anomalies like diabetes and hypoglycemia are associated with aberrant glucose levels, which are important markers of human health. For a clinical diagnosis, ongoing glucose monitoring is therefore crucial [147]. To detect glucose levels, several approaches have been developed, such as electrochemical, fluorescent, and absorptiometry-based technologies. Fluorescence-based techniques have become more popular because of their high sensitivity, stability, affordability, and quick reaction time, even though electrochemical approaches are well-established. The majority of fluorescence sensors use indirect glucose detection, in which glucose oxidation is catalyzed by glucose oxidase (GOx), resulting in H2O2, which chemosensors then detect to measure glucose levels [148,149].
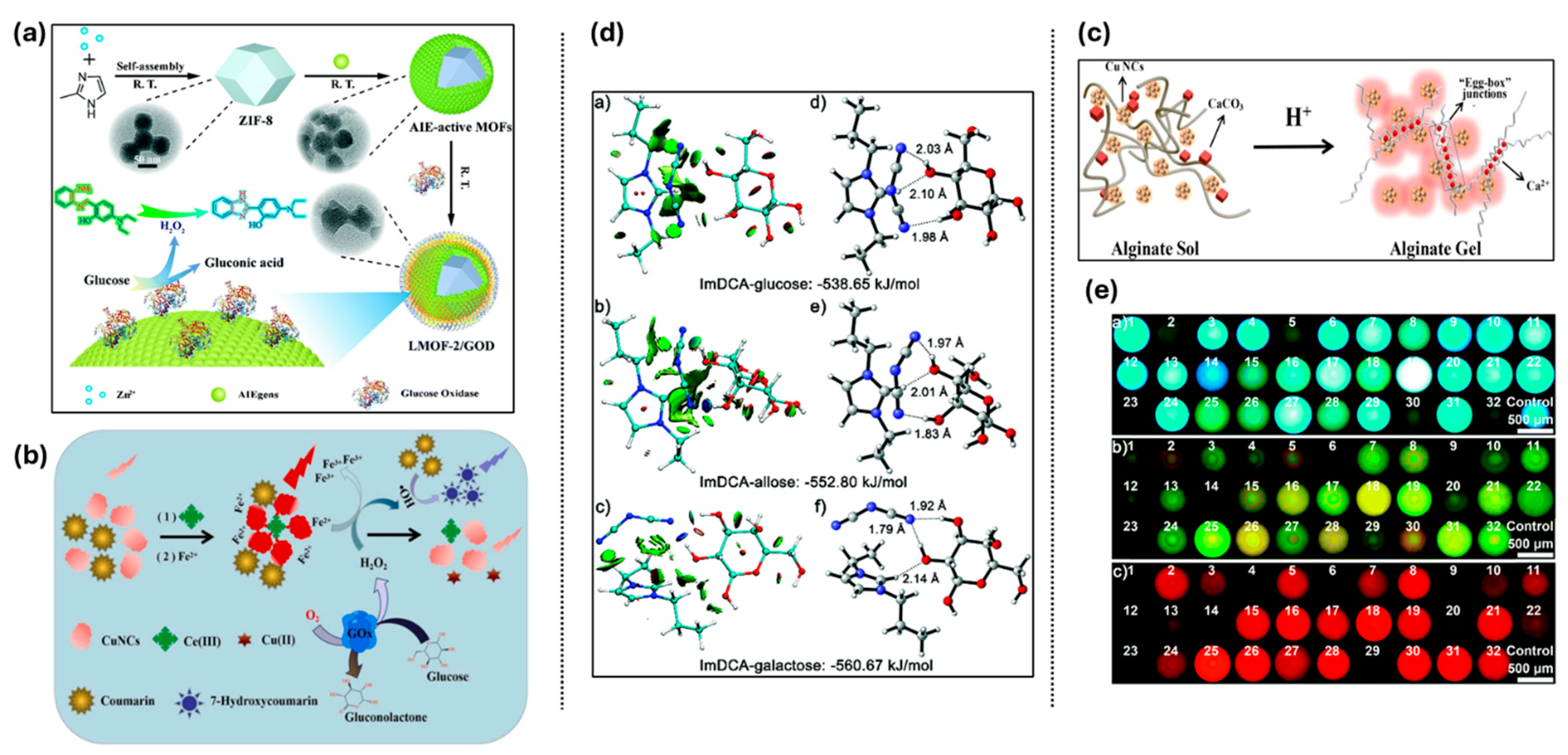
GOx and AIE-type gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) were incorporated into glucose biosensors by Sun et al. using a proton-responsive, acid-sensitive zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) nanocrystal matrix. This nanocomposite improved analyte enrichment, maintained enzyme activity, and triggered the bright-yellow emission of AIE-type AuNCs, making glucose detection easier. The sensor’s practical usefulness was confirmed when it was successfully tested for glucose detection in human serum and showed a dual linear window of 0–1000 μM and 1–20 mM and LOD of 4.7 μM [150]. By adding aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) to nanoscale ZIF-8, Xie et al. created luminous metal–organic frameworks (LMOFs) as shown in Figure 10a. Important AIE characteristics like high solid-state luminescence, significant Stokes shifts (115–202 nm), and excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) were all preserved in these AIE-active MOFs. Interestingly, their fluorescence was enhanced by more than 16 times when compared to the original AIEgens. Additionally, by altering AIEgen substituents, their emission might be adjusted. With a dynamic range of 1–100 nM and a low detection limit of 550 pM, the sensor showed ultrasensitive detection. Additionally, the researchers created a fluorescent allochroic test strip for visual glucose detection in the fasting blood glucose range (3–8 mM) in human serum by utilizing a glucose oxidase (GOD)-catalyzed cascade redox reaction. This provides a promising tool for clinical applications [151].
Mei et al. used the complementary effects of Ce3+ and Fe2+ on copper nanoclusters (CuNCs) and coumarin to create a ratiometric fluorescent probe for the sensitive detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) and glucose. In the CuNCs-Ce3+/Fe2+-coumarin system, Fe2+ catalyzed the Fenton reaction, which produced hydroxyl radicals (•OH), while Ce3+ caused the AIE of CuNCs (Figure 10b). The oxidation to Cu(II) upon contact with H2O2 caused red fluorescence of CuNC at 625 nm, but 7-hydroxycoumarin displayed blue fluorescence at 460 nm, which drastically enhanced as a result of •OH-induced coumarin oxidation. A ratiometric H2O2 test with a detection limit (LOD) of 0.6 μM was made possible by this reversible fluorescence shift, which also caused a color shift from red to blue. For glucose detection, the probe exhibited a linear range of 3.2–160 μM with an LOD of 0.96 μM, based on H2O2 generation during glucose oxidation by glucose oxidase (GOx) and O2 [152]. Further, Gou et al. combined the AIE qualities of CuNCs with the gel-forming capacity of alginate (caused by Ca2+) to create a pH-responsive luminous material as shown in Figure 10c. A freestanding gel developed when the pH dropped, and CuNCs’ PL intensity increased as well, which could be seen both visually and spectroscopically. The two-stage amplification was ascribed to the effects of gelatin and Ca2+. Using GOx’s glucose recognition capability and H+ output, this device was used as a glucose sensor. It demonstrated its promise for ocular glucose monitoring by obtaining a linear detection range of 0.1–2.0 mM (R = 0.992) and a LOD of 3.2 × 10−5 M [153]. Furthermore, Liang et al. developed a non-GOx glucose sensor by employing a polyvinyl borate (PVB) hydrogel encapsulated in alkaline phosphatase (ALP), which exhibited stable physical characteristics and experienced particular degradation when glucose was present. The system achieved two distinct linear ranges (0.1–1.0 mM and 1.0–10.0 mM) in the fluorescence channel and a linear detection range of 0.1–10.0 mM in the colorimetric channel by utilizing the electrochromic characteristics of PB and the AIEE of AuNCs. High sensitivity for glucose monitoring was demonstrated by the corresponding limits of detection (LODs), which were 0.018 mM for fluorescence and 0.02 mM for colorimetric [154].
For the first time, Zhang and co-workers reported the development of a poly(ionic liquid) (PIL) as a flexible sensor that could identify 23 distinct saccharides, mostly by means of electrostatic, hydrophobic, and hydrogen bonding interactions (Figure 10d). Notably, this platform can effectively carry out a variety of sensing tasks on demand by utilizing basic ion-exchanges of PIL receptors or improving AIE signaling channels. The ion-exchange properties of PILs allow for dynamic detection, while altering the counter-anion enables selective binding to specific target molecules. Furthermore, it has been demonstrated that adding various AIEgens to PILs with unique fluorescence channels can efficiently alter AIE signaling pathways, expanding the range of saccharides that can be detected (Figure 10e) [155].
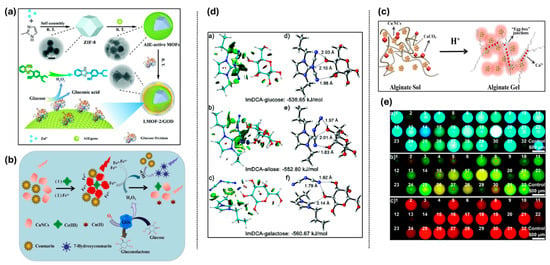
Figure 10.
(a) Schematic illustration of LMOF fabrication and cascade reaction for the detection of glucose. (b) Graphical representation of the ratiometric fluorescent assay of H2O2 and glucose based on CuNCs-Ce3+/Fe2+-coumarin platform. (c) Schematic illustration of the pH-responsive luminescent Cu NC–alginate materials. (d) Reduced density gradient isosurfaces and density functional theory (DFT) optimized structures illustrate the interactions between the ion pair (imidazolium cation and DCA anion) and three isomeric saccharides glucose, allose, and galactose. (e) FL responses of one quadruple channel PIL photonic sphere (doped with AIEgen-blue, AIEgen-yellow, and AIEgen-red; DCA as counteranion) to 32 saccharides. Reprinted with permission from refs. [151,152,153,155]. Copyright © 2020 Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC), Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc., Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society, Copyright © 2019 Royal Society of Chemistry.
Figure 10.
(a) Schematic illustration of LMOF fabrication and cascade reaction for the detection of glucose. (b) Graphical representation of the ratiometric fluorescent assay of H2O2 and glucose based on CuNCs-Ce3+/Fe2+-coumarin platform. (c) Schematic illustration of the pH-responsive luminescent Cu NC–alginate materials. (d) Reduced density gradient isosurfaces and density functional theory (DFT) optimized structures illustrate the interactions between the ion pair (imidazolium cation and DCA anion) and three isomeric saccharides glucose, allose, and galactose. (e) FL responses of one quadruple channel PIL photonic sphere (doped with AIEgen-blue, AIEgen-yellow, and AIEgen-red; DCA as counteranion) to 32 saccharides. Reprinted with permission from refs. [151,152,153,155]. Copyright © 2020 Royal Society of Chemistry (RSC), Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Inc., Copyright © 2019 American Chemical Society, Copyright © 2019 Royal Society of Chemistry.
3.5.2. Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP)
One of the primary energy carriers in living cells is adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is hydrolyzed to produce adenosine diphosphate (ADP) and a free phosphate group. Protein synthesis, cell division, and muscle contraction are all fueled by this mechanism [156]. Since ATP is unique among phosphates in that it serves as an external signaling mediator in metabolism as well as an intracellular energy source, its sensitivity and selective detection are essential. Using a tetraphenylethylene derivative (TPE-COOH), Ren et al. fabricated fluorescent sensors to identify ATP and cupric ions (Cu2+) in aqueous solutions. ATP competitively bound Cu2+, causing TPE-COOH reassembly and a “turn-on” fluorescence response, whereas Cu2+ produced TPE-COOH deconstruction. Furthermore, TPE-COOH test strips offered a quick and affordable way to find traces of ATP and Cu2+ in biological systems [157]. Since adenosine 5′-triphosphate (ATP) and Cu2+ ions are essential for cellular metabolism, their detection is critical. Using a tetraphenylethylene (TPE) amphiphile (1) that generates AIE micelles in aqueous solution, Ding et al. created an interfacial system for sequential Cu2+ and ATP recognition (Figure 11a). Fluorescence was quenched by a 1:2 probe-Cu2+ complex formed by Cu2+ binding, but emission was restored when ATP broke the complex. Cu2+ had a detection limit of 1.0 × 10−7 M, while ATP had a detection limit of 1.5 × 10−6 M [158]. Li et al. used an aptamer conformational transition to create a label-free fluorometric sensor for ATP measurement. ATP caused a change from a random coil to a G-quadruplex, which stopped exonuclease I (Exo I) from digesting it. Fluorescence was increased by adding DSAI, a cationic anthracene derivative, which caused aggregation on the aptamer/ATP complex (Figure 11b). The sensor successfully measured ATP in human serum with a recovery rate of 93.2% to 107.6%, exhibiting great sensitivity (LOD: 32.8 nM) and excellent ATP specificity [159].
Using a Schiff-base reaction, Wang et al. created a red-emissive AIE fluorescent probe (CPD) from natural camphor for the sequential ratiometric detection of ATP and Ga3+ in aqueous solution. Upon detecting Ga3+, CPD’s rapid response, high selectivity, and sensitivity caused the fluorescence to change from red to bright green. Using test strips, it successfully measured trace Ga3+ in water samples and separated it from other metal ions. Additionally, the CPD-Ga3+ compound functioned as an ATP sensor with a quick response and a detection limit of 32.1 nM [160]. In order to detect ATP, Kim et al. developed a fluorescent nanoprobe (AAP-1) utilizing an AIEgen. In aqueous environments, the probe TPE-TA formed AAP-1 by combining mono-triamine (TA) as a sensing moiety with tetraphenylethylene (TPE) as a signaling unit. It demonstrated great selectivity, sensitivity (LOD: 0.275 ppb), and an ultrafast reaction (within 10 s) when interacting with ATP through electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions [161]. Using cationic polyelectrolyte PAH, Singh et al. created a self-assembled anionic AIE probe. Tetra-anionic Su-TPE showed enhanced fluorescence as a result of charge neutralization and aggregation on poly(allylamine) as shown in Figure 11c. Temperature and ionic strength caused photophysical changes in the Su-TPE-PAH assembly, emphasizing weak and electrostatic interactions. ATP competitively displaced Su-TPE from PAH, resulting in a spectrum shift, when this supramolecular aggregate was utilized for ATP detection. The sensor demonstrated its practicality by functioning well in human serum and exhibiting a linear fluorescence drop (0–35 μM range) with a LOD of 0.37 μM [162].
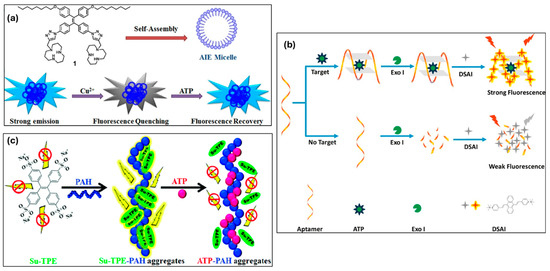
Figure 11.
(a) Graphical representation of the formation of AIE micelle and the sequential recognition of Cu2+ and ATP. (b) Schematic illustration of the label-free aptamer-based ATP assay. (c) Mechanism of the ATP-induced dissociation of Su-TPE-PAH aggregates. Reprinted with permission from refs. [158,159,162] Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. Copyright © 2020 Royal Society of Chemistry.
Figure 11.
(a) Graphical representation of the formation of AIE micelle and the sequential recognition of Cu2+ and ATP. (b) Schematic illustration of the label-free aptamer-based ATP assay. (c) Mechanism of the ATP-induced dissociation of Su-TPE-PAH aggregates. Reprinted with permission from refs. [158,159,162] Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. Copyright © 2020 Royal Society of Chemistry.
3.5.3. Vitamins
Both vitamin C (L-ascorbic acid, AA) and vitamin B9 (folic acid, FA) are vital nutrients with different functions. While vitamin C is a potent antioxidant that promotes immunity, wound healing, and connective tissue health, vitamin B9 aids in the production of red blood cells and DNA synthesis, particularly during pregnancy. Part of the B-complex, vitamin B9 comes in two forms: natural folate and synthetic folic acid, which are found in supplements and fortified foods. It aids in the conversion of food into energy and promotes the health of the liver, skin, hair, eyes, and nervous system. A water-soluble antioxidant found in a variety of meals, supplements, and fortified goods, vitamin C shields cells from harm caused by free radicals and promotes general health. A group of chemosensors for the detection of FA and AA will be discussed [163,164].
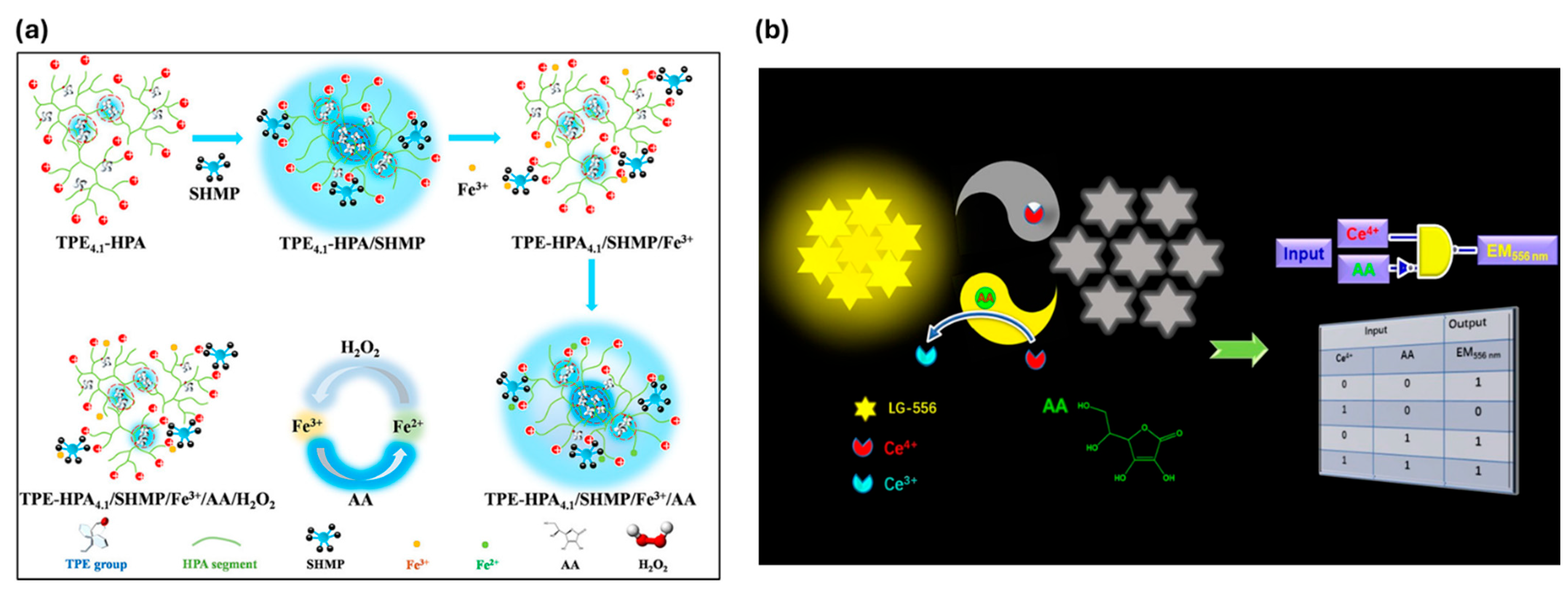
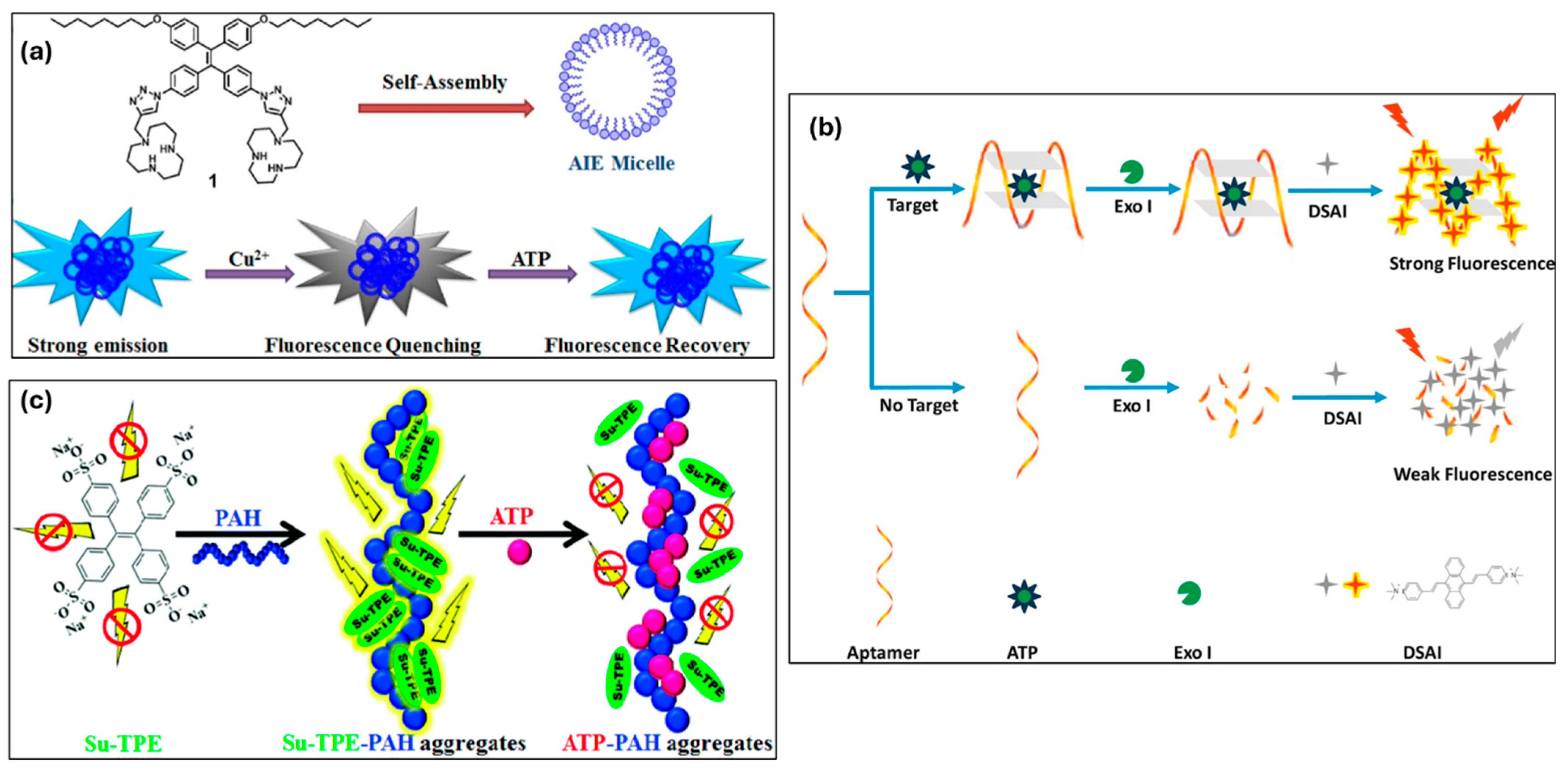
By incorporating a small quantity of tetraphenylethene (TPE) units into hyperbranched poly(amido amine) (TPE–HPA), Li et al. created a water-soluble quadruple-target fluorescence sensor while regulating the TPE content in HPA. The sequential “off–on–off–on–off” fluorescence response of the nonfluorescent TPE–HPA in water allowed for the sensitive and specific detection of sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP), Fe3+, ascorbic acid (AA), and H2O2, as shown in Figure 12a. The detection limits for SHMP, Fe3+, AA, and H2O2 were 29 nM, 20 nM, 0.66 μM, and 0.78 μM, respectively. The sensor’s practical usefulness was confirmed when it showed effective detection of these targets in actual samples [165]. Adenosine monophosphate-stabilized bimetallic gold/silver nanoclusters (AMP-Au/Ag NCs) were created by Ungor et al. using a one-pot synthesis technique. These yellow-emitting NCs (λem = 560 nm) demonstrated outstanding kinetic and photostability in addition to a 7.3% quantum yield. Their size, content, and pH-dependent aggregation-induced emission were all verified by thorough characterization. Both liquid phase and paper-based fast tests were used to investigate their potential as folic acid (FA) biosensors. According to thermodynamic studies, the quenching process was ascribed to an etching reaction of alloy clusters, and fluorescence quenching studies yielded a detection limit of 0.109 µM and a dynamic range of 0.15–2.5 µM [166].
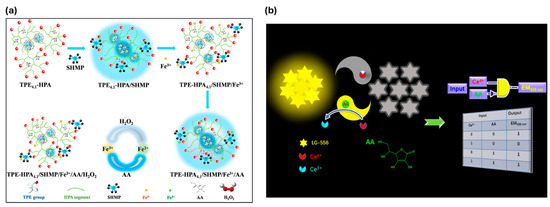
Figure 12.
(a) Mechanisms for TPE4.1–HPA to sequentially detect SHMP, Fe3+, AA, and H2O2. (b) graphical representation of the LG556-based fluorescence probe for sequential detection of Ce4+ and AA. Reprinted with permission from refs. [165,167]. Copyright © 2020 American Chemical Society, Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V.
Li et al. developed LG556 (4,4′,4″,4‴-(ethene-1,1,2,2-trayltetrakis (benzene-4,1-diyl))tetrakis(1-carboxymethyl-pyridin-1-ium)bromide), a fluorescent probe based on intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) between connected electron donor-acceptor units. Due to the inner filter effect (IFE) and nanoaggregate breakdown, LG556 fluorescence was suppressed in the presence of Ce4+ (Figure 12b). It showed a linear detection range of 1–150 μM with a limit of detection of 0.62 μM. The problem of aggregate formation was solved by utilizing AIE. Ce4+ was converted to Ce3+ upon the addition of ascorbic acid, causing LG556 re-assembly with a low detection limit of 39.2 nM, surpassing numerous documented techniques. A reversible implication logic gate was made possible by this “on-off-on” fluorescence conversion, which allowed for the highly accurate detection of ascorbic acid and Ce4+ in aqueous solutions [167]. Using a straightforward process, Jiang et al. produced a crown ether-bridged bis-tetraphenylethylene molecule (Bis-TPE-1) with a yield of 78–84%. In solid films and THF/H2O solutions, the molecule demonstrated strong AIE characteristics. High selectivity for folic acid was demonstrated by sensing investigations, which also showed a blue shift in emission from 380 nm to 365 nm and fluorescence amplification. With little interference from metal ions and other biomolecules, the sensor showed a low detection limit of 6.36 × 10−7 M [168].
3.5.4. HSA (Human Serum Albumin), BSA (Bovine Serum Albumin), and Collagen
Serum albumin, the most abundant protein in blood plasma, plays multiple biological roles in the circulatory system. Abnormal serum albumin levels can indicate various health conditions, including coronary artery disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, stroke, and venous thromboembolism. Extremely low or high albumin levels are also linked to an increased risk of chronic kidney disease, particularly in hypertensive patients [169]. Therefore, developing effective clinical methods for serum albumin detection is significant. Human serum albumin (HSA) is the most abundant protein in human serum, playing critical roles in physiological processes such as biomolecule transport and the regulation of blood osmotic pressure. Gao et al. developed a fluorescent probe, TPE-IL, by functionalizing the AIE dye E-1,2-bis(4-hydroxyphenyl)-1,2-diphenylethylene (TPE-OH) with the ionic liquid HOOCMIMBr (Figure 13a) [170]. Hydrophobic and hydrogen-bonding interactions between HSA amino acid residues and TPE-IL facilitated spontaneous and energetically favorable binding within HSA’s hydrophobic subdomain, resulting in significant fluorescence enhancement. This sensor achieved highly sensitive and selective HSA detection with a linear range of 0.02–10 μg/mL and a detection limit of 0.007 μg/mL. Additionally, Li et al. designed a TPE-sodium dodecyl sulfonate (TPE-SDS) dye with a long hydrophobic chain. Through hydrophobic interactions with proteins during polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE), TPE-SDS aggregates and forms fluorescent complexes, with fluorescence intensity correlating to protein concentration. This biosensor serves as an effective protein prestaining reagent for PAGE analysis, offering advantages such as rapid staining, stability, and ease of use [171].
Sun et al. reported a new 1,8-naphthalimide-based fluorescent probe, NapTpa-bs, constructed from a 4-triphenylamine-N-(3-hydroxyphenyl)-1,8-naphthalimide moiety modified with 1,2-oxathiane 2,2-dioxide. NapTpa-bs was designed for bovine serum albumin (BSA) detection, where the flexible long chains of NapTpa-bs penetrate the cavities of BSA, resulting in a sixfold fluorescence enhancement at 629 nm at a BSA concentration of 11 μM, exhibiting a light-up AIE characteristic [172]. Additionally, Wang et al. synthesized a cationic poly(diketopyrrolopyrrole-co-ethynylfluorene)-based biosensor for fluorescence turn-on detection of BSA. A neutral polymer composed of AIE-active diketopyrrolopyrrole (DPP) and ACQ-active fluorene units connected through flexible alkyl spacers in the main chain was synthesized and subsequently converted into its polyelectrolyte form (P1) via ionization using CH3I (Figure 13b) [173]. The probe features ammonium groups in its side chains, improving water solubility and biocompatibility, and providing positively charged binding sites for electrostatic interaction with negatively charged BSA. Upon interaction with BSA, the probe’s fluorescence intensity increases by approximately two- to threefold, making it a promising tool for BSA detection and bioimaging applications.
Further, collagen is the most prevalent protein found in the human body, and its breakdown products are implicated in a variety of diseases, including tumors, arthritis, and chronic wounds. Despite widespread research devoted to generating efficacious assays for detecting collagen fragments, there remain challenges due to the repetitive amino acid sequences and uniform triple-helical structure, which render it troublesome to generate highly specific antibodies. Well-known fluorescent probes, polymethine dyes, especially cyanines, are known to form J-aggregates when they interact with biomacromolecules like collagen and gelatin. Narrow, red-shifted absorption bands and noticeably increased fluorescence are characteristics of these J-aggregates. On biomolecular surfaces, cyanine dyes self-assemble into highly ordered J-aggregates via a mix of hydrophobic and electrostatic interactions. Because J-aggregate formation offers a potent readout of conformational chirality and secondary structure, this property has been successfully used for the sensitive detection of structurally organized biomolecules, particularly collagen [174]. To diagnose collagen-related pathologies like connective tissue disorders, chronic wounds, and cancer-associated extracellular matrix remodeling, Tatikolov et al. reported that certain anionic cyanine dyes bind to collagen fibers preferentially, allowing for the differentiation of native and denatured states. Polymethine dyes are useful in both structural and diagnostic biosensing applications because of the spectral and fluorescence changes linked to J-aggregates, which enable them to act as conformational reporters in addition to molecular presence indicators [175]. On the other hand, AIE fluorophores function through a radically distinct mechanism. Unlike conventional dyes that often fluoresce due to π–π stacking in ordered aggregates, AIE luminogens remain non-emissive in solution and only emit upon restriction of intramolecular motion, typically triggered by aggregation or binding events.
Xiao et al. reported for the first time the construction of a graphene-based AIE biosensor for the detection of charged collagen peptides. In their work, an AIE fluorophore, tetraphenylethene (TPE), was conjugated to a triple-helical peptide (TPE-PRG), which emitted strong fluorescence due to intramolecular rotation restriction in the trimeric conformation [176]. Adsorption of TPE-PRG onto the GO surface quenched fluorescence, while the presence of the target collagen peptide EOG released the probe from GO, restoring the fluorescence. The TPE-PRG/GO complex thus displayed a highly specific “turn-on” sensing platform for charged collagen peptides and showed minimal interference from other biomolecules, and separated the target peptide effectively from its single amino acid mutant. This strong assay is of enormous promise for advancing the pathological analysis and molecular diagnosis of collagen-related diseases.
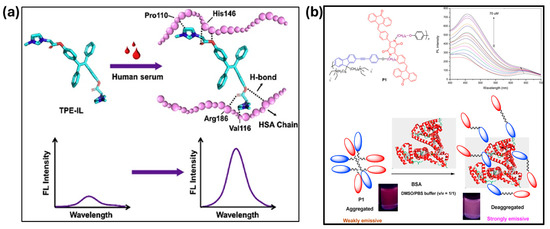
Figure 13.
(a) Schematic illustration of the interaction between TPE-IL and HSA leading to fluorescence enhancement through hydrogen bonding. (b) Proposed mechanism for the interaction of P1 and BSA and emission spectra of P1 with various fractions of DMSO and water. Reprinted with permission from refs. [170,173]. Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V., Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V.
Figure 13.
(a) Schematic illustration of the interaction between TPE-IL and HSA leading to fluorescence enhancement through hydrogen bonding. (b) Proposed mechanism for the interaction of P1 and BSA and emission spectra of P1 with various fractions of DMSO and water. Reprinted with permission from refs. [170,173]. Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V., Copyright © 2016 Elsevier B.V.
4. Conclusions and Perspectives
The concept of AIE-based fluorescent biosensors possesses distinct advantages in the detection of biomolecules, especially in the area of biomedicine, forensics, environmental monitoring, food safety, and national security. To create AIE sensors with high sensitivity, selectivity, and quick response times, a variety of detection mechanisms have been investigated, such as chemical reactions, supramolecular interactions, physical adsorption, and photophysical processes. This review highlights recent advancements in AIE-based fluorescent sensors for detecting a wide range of biomolecules, including amino acids, biogenic amines, enzymes, nucleic acids, saccharides, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), vitamins, albumin, and collagen (refer to Table 2 for a detailed summary). Despite significant progress, challenges remain in achieving ultrahigh sensitivity comparable to instrumental analysis, particularly for trace bio-analyte detection. In addition, it is still a great challenge to design precisely calibrated ratiometric fluorescence responses for the quantitative assay of analytes. Additional efforts should be required to incorporate AIEgens into low-cost and portable diagnostic devices like fluorescence sensor arrays and microfluidic chips for practical applications. Future studies need to aim at increasing the selectivity of AIE sensors for targeted biomolecules and investigating the incorporation of artificial intelligence (AI) and the Internet of Things (IoT) to increase overall sensing performance. The ongoing growth of high-performance AIE-based sensing technologies will continue to open up broader applications. In conclusion, AIE sensors represent a promising and versatile platform for diverse sensing applications. We hope this review sparks innovative ideas and drives further advancements in this rapidly evolving field.

Table 2.
Recent examples of AIE-based fluorescent sensors for biomolecule detection.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Acknowledgments
K.S.K. acknowledges support from the EMS Sustainability Fund for Research and Innovation, Pennsylvania State University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, W.; Xue, Y.; Zhang, J. Fluorescent Sensors for Detecting and Imaging Metal Ions in Biological Systems: Recent Advances and Future Perspectives. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manna, A.S.; Ghosh, S.; Ghosh, T.; Karchaudhuri, N.; Das, S.; Roy, A.; Maiti, D.K. Smart Luminescent Materials for Emerging Sensors: Fundamentals and Advances. Chem. Asian J. 2025, 2, e202401328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, R.; Fang, B.; Lai, Y.; Peng, B.; Bai, H.; Liu, X.; Li, L.; Huang, W. Small-Molecule Fluorogenic Probes for Mitochondrial Nanoscale Imaging. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 52, 942–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, F.Y.; Mei, L.J.; Tian, R.; Li, C.; Wang, Y.L.; Xiang, S.L.; Zhu, M.Q.; Tang, B.Z. Recent Advances in Super-Resolution Optical Imaging Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2024, 53, 3350–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yin, J.; Yoon, J. Recent Advances in Development of Chiral Fluorescent and Colorimetric Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4918–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrin, A.; Jayaraj, A.; Gayathri, M.S.; Chinna Ayya Swamy, P. An Overview of Schiff Base-Based Fluorescent Turn-on Probes: A Potential Candidate for Tracking Live Cell Imaging of Biologically Active Metal Ions. Sens. Diagn. 2023, 2, 988–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Zheng, Y.; Duan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhong, W. Recent Advances in Design of Fluorescence-Based Assays for High-Throughput Screening. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 482–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadananda, D.; Mallikarjunaswamy, A.M.M.; Prashantha, C.N.; Mala, R.; Gouthami, K.; Lakshminarayana, L.; Ferreira, L.F.R.; Bilal, M.; Rahdar, A.; Mulla, S.I. Recent Development in Chemosensor Probes for the Detection and Imaging of Zinc Ions: A Systematic Review. Chem. Pap. 2022, 76, 5997–6015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritu; Narang, U.; Kumar, V. Heavy Metal Detection with Organic Moiety-Based Sensors: Recent Advances and Future Directions. ChemBioChem 2024, 25, e202400191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargazi, S.; Fatima, I.; Hassan Kiani, M.; Mohammadzadeh, V.; Arshad, R.; Bilal, M.; Rahdar, A.; Díez-Pascual, A.M.; Behzadmehr, R. Fluorescent-Based Nanosensors for Selective Detection of a Wide Range of Biological Macromolecules: A Comprehensive Review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 206, 115–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakayode, S.O.; Lisse, C.; Medawala, W.; Brady, P.N.; Bwambok, D.K.; Anum, D.; Alonge, T.; Taylor, M.E.; Baker, G.A.; Mehari, T.F.; et al. Fluorescent Chemical Sensors: Applications in Analytical, Environmental, Forensic, Pharmaceutical, Biological, and Biomedical Sample Measurement, and Clinical Diagnosis. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2024, 59, 1–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immanuel David, C.; Lee, H. Cutting-Edge Advances in Colorimetric and Fluorescent Chemosensors for Detecting Lethal Cyanide Ion: A Comprehensive Review. Microchem. J. 2024, 200, 110359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbhijnaKrishna, R.; Velmathi, S. Exploring Fluorescent and Colorimetric Probes for Analyte Detection: Utilizing It in Live Cell Imaging and Real-Time Sample Analysis. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2024, 567, 122039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.-J.; Xin, Z.-Y.; Su, X.; Hao, L.; Qiu, Z.; Li, K.; Luo, Y.; Cai, X.-M.; Zhang, J.; Alam, P.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens Realizing High-Contrast Bioimaging. ACS Nano 2025, 19, 281–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gawade, V.K.; Jadhav, R.W.; Bhosale, S.V. AIE-Based & Organic Luminescent Materials: Nanoarchitectonics and Advanced Applications. Chem. Asian J. 2024, 19, e202400682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, F.; Pal, A.; Sk, M.P. Review—Aggregation-Induced Emission in Carbon Dots for Potential Applications. ECS J. Solid. State Sci. Technol. 2021, 10, 021001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joseph, E.; Ciocca, M.; Wu, H.; Keremane, K.; Poudel, B.; Priya, S.; Brown, T.M. Photovoltaic bioelectronics merging biology with new generation semiconductors and light in biophotovoltaics photobiomodulation and biosensing. Npj Biosensing 2024, 1, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, S.; Mohanty, A.; Naik, P.; Dasgupta, J.; Patil, S. Deciphering intramolecular charge transfer in fluoranthene derivatives. J. Mater. Chem. C 2024, 12, 9200–9209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.H.; Chin, K.L.O.; Loh, X.J.; Zhu, Q.; Xu, J. Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Nanostructures: Beyond Biomedical Applications. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 1845–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, A.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Luminogenic Polymers with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2012, 37, 182–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Qin, A.; Tang, B.Z. AIE Polymers: Synthesis and Applications. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2020, 100, 101176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Leung, N.L.C.; Tang, B.Z. AIE Macromolecules: Syntheses, Structures and Functionalities. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 4494–4562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhu, B.; Luo, J.; Liu, B. Design and Property Modulation of Metal–Organic Frameworks with Aggregation-Induced Emission. ACS Mater. Lett. 2021, 3, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shustova, N.B.; Ong, T.-C.; Cozzolino, A.F.; Michaelis, V.K.; Griffin, R.G.; Dincă, M. Phenyl Ring Dynamics in a Tetraphenylethylene-Bridged Metal–Organic Framework: Implications for the Mechanism of Aggregation-Induced Emission. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 15061–15070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Cui, Z.; Shen, W. Mechanism, Structural Design, Modulation and Applications of Aggregation-Induced Emission-Based Metal-Organic Framework. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2022, 146, 110038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalapati, S.; Jin, E.; Addicoat, M.; Heine, T.; Jiang, D. Highly Emissive Covalent Organic Frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 5797–5800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Ding, D.; Liu, J.; Yuan, W.Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Biocompatible Nanoparticles with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics as Far-Red/near-Infrared Fluorescent Bioprobes for in Vitro and in Vivo Imaging Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, B.; Tian, W. Fluorescent Nanoparticles Based on AIE Fluorogens for Bioimaging. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 2471–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Huang, Q.; Liu, M.; Xu, D.; Huang, H.; Zhang, X.; Wei, Y. Aggregation-Induced Emission Active Luminescent Polymeric Nanoparticles: Non-Covalent Fabrication Methodologies and Biomedical Applications. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 9, 145–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, C.K.; Kant, K.; Naik, P.; Sharma, V.; Keremane, K.; Singh, V.; Malakar, C.C. Reductive C−N Bond Formation of Nitroarenes Using Pd@rGO-CuFe2O4 Magnetic Nanoparticles in Water towards the Synthesis of N-Aryl Formamide and Azole Derivatives. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2024, 13, e202400255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, J.; Qin, F.; He, P.; Wu, S.; Zhu, Y.; Yuan, G.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.; Ren, L. Carbon Dots-Based Luminescent Materials with Aggregation-Induced Emission and Solvent Crystallization-Induced Emission Behaviors. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2023, 151, 110614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ru, Y.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Lu, S. Aggregation in Carbon Dots: Special Issue: Emerging Investigators. Aggregate 2022, 3, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Z.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, D.; Zhang, X.; Zhuang, J.; Lei, B.; Liu, Y.; Hu, C. High-Efficiency Solid-State Luminescence from Hydrophilic Carbon Dots with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2023, 33, 2207296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.E.; Ma, J.; Feng, A.; Wang, Z.; Rogach, A.L. Aggregation-Induced Emission of Copper Nanoclusters. Aggregate 2021, 2, e112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Lin, X.; Shu, T.; Su, L.; Liang, F.; Zhang, X. Self-Assembly of Metal Nanoclusters for Aggregation-Induced Emission. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goswami, N.; Yao, Q.; Luo, Z.; Li, J.; Chen, T.; Xie, J. Luminescent Metal Nanoclusters with Aggregation-Induced Emission. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2016, 7, 962–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Yang, X.; Li, J.; Li, D.; Wang, E. Stable Cu Nanoclusters: From an Aggregation-Induced Emission Mechanism to Biosensing and Catalytic Applications. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 237–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Ji, X.; Xie, H.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Gels: Fabrications, Functions, and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wang, J.; Li, H.; Song, N.; Wang, D.; Tang, B.Z. Supramolecular Materials Based on AIE Luminogens (AIEgens): Construction and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 1144–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liow, S.S.; Zhou, H.; Sugiarto, S.; Guo, S.; Chalasani, M.L.S.; Verma, N.K.; Xu, J.; Loh, X.J. Highly Efficient Supramolecular Aggregation-Induced Emission-Active Pseudorotaxane Luminogen for Functional Bioimaging. Biomacromolecules 2017, 18, 886–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, P.; Ji, X.; Gong, J.; Hu, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Peng, H.Q.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; et al. Bioinspired Simultaneous Changes in Fluorescence Color, Brightness, and Shape of Hydrogels Enabled by AIEgens. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, H.; Hong, Y.; Dong, Y.; Häußler, M.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Li, Z.; Guo, Z.; Guo, Z.; Tang, B.Z. Fluorescent “Light-up” Bioprobes Based on Tetraphenylethylene Derivatives with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Chem. Commun. 2006, 35, 3705–3707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Law, C.C.W.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Dong, Y.; Lo, S.M.F.; Williams, I.D.; Zhu, D.; Tang, B.Z. Synthesis, Light Emission, Nanoaggregation, and Restricted Intramolecular Rotation of 1,1-Substituted 2,3,4,5-Tetraphenylsiloles. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 1535–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Miao, Y.; Ou, Q.; Niu, R.-X.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, C. Full-Color-Tunable Nanohydrogels as High-Stability Intracellular Nanothermometers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 55423–55430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duangkamol, C.; Wangngae, S.; Wet-osot, S.; Khaikate, O.; Chansaenpak, K.; Lai, R.Y.; Kamkaew, A. Quinoline-Malononitrile-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Probe for Monoamine Oxidase Detection in Living Cells. Molecules 2023, 28, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Li, L.; Nie, H.; Tong, J.; Yan, L.; Xu, B.; Sun, J.Z.; Tian, W.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, A.; et al. Tetraphenylpyrazine-Based AIEgens: Facile Preparation and Tunable Light Emission. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 1932–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, W.; He, W.; Feng, X.; Liu, G.; Shi, Q.; Tan, J.; Hu, J.; Yang, S.; Liu, G.; Yang, R. Cationic Single-Unit Monomer Insertion (CSUMI): From Discrete Oligomers to the α-/ω-End and In-Chain Sequence-Regulated Polymers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2023, 145, 3636–3646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, L.; Mao, X.; Wang, Q.; Mu, Z.; An, L.; Zhang, W.; Feng, X.; Redshaw, C.; Cao, C.; et al. Pyrene-Based Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogens (AIEgens) with Less Colour Migration for Anti-Counterfeiting Applications. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2021, 9, 12828–12838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, H.; Liu, W.; Li, H.; Sun, W.; Du, J.; Fan, J.; Peng, X. 2,1,3-Benzothiadiazole Derivative AIEgens for Smart Phototheranostics. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 473, 214803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Zhang, W.; Guo, H.; Liang, J.; Huang, D.; Xiao, H. Two Spirobifluorene-Based Fluorescent Probes with Aggregation-Induced Emission Properties: Synthesis and Application in the Detection of Zn2+ and Cell Imaging. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2019, 7, 2240–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fowler, W.C. Intrinsic Fluorescence in Peptide Amphiphile Micelles with Protein-Inspired Phosphate Sensing. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4804–4813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Phenomenon, Mechanism and Applications. Chem. Commun. 2009, 29, 4332–4353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dou, L.; Li, Q.; Wang, Z.; Shen, J.; Yu, W. AIEgens: Next Generation Signaling Source for Immunoassays? ACS Sens. 2022, 7, 3243–3257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, G.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.; Bouffard, J.; Kim, Y. Excimers Beyond Pyrene: A Far-Red Optical Proximity Reporter and Its Application to the Label-Free Detection of DNA. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 3984–3988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Bu, L.; Li, J.; Yang, C.; Li, X.; Tao, Y.; Yang, W. Aqueous Nanoaggregation-Enhanced One- and Two-Photon Fluorescence, Crystalline J-Aggregation-Induced Red Shift, and Amplified Spontaneous Emission of 9,10-Bis(p-Dimethylaminostyryl)anthracene. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 15576–15583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, B.-K.; Kwon, S.-K.; Jung, S.-D.; Park, S.Y. Enhanced Emission and Its Switching in Fluorescent Organic Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 14410–14415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Lager, E.; Aguilar-Aguilar, A.; Liu, J.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Sung, H.H.Y.; Williams, I.D.; Zhong, Y.; Wong, K.S.; Peña-Cabrera, E.; et al. Twisted Intramolecular Charge Transfer and Aggregation-Induced Emission of BODIPY Derivatives. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 15845–15853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Li, S.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, J.; Wang, S.; Li, Y.; Yang, G. Understanding the Aggregation Induced Emission Enhancement for a Compound with Excited State Intramolecular Proton Transfer Character. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 2044–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Fundamental Understanding and Future Developments. Mater. Horiz. 2019, 6, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Xie, Z.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Cheng, L.; Chen, H.; Qiu, C.; Kwok, H.S.; Zhan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, D.; et al. Aggregation-Induced Emission of 1-Methyl-1,2,3,4,5-Pentaphenylsilole. Chem. Commun. 2001, 18, 1740–1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Ma, H.; Niu, Y.; Li, W.; Wang, D.; Peng, Q.; Shuai, Z.; Liang, W. Spectroscopic Signature of the Aggregation-Induced Emission Phenomena Caused by Restricted Nonradiative Decay: A Theoretical Proposal. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 5040–5047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keremane, K.; Pellegrin, Y.; Planchat, A.; Odobel, F.; Adhikari, A.V. New carbazole-based sensitizers for p-type DSSCs: Impact of the position of acceptor units on device performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2022, 126, 12383–12390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Qin, A.; Tang, Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: The Whole Is More Brilliant than the Parts. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 5429–5479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 5361–5388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, D.; Li, K.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. Bioprobes Based on AIE Fluorogens. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2441–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, J.; Leung, N.L.C.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Aggregation-Induced Emission: Together We Shine, United We Soar! Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11718–11940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Xu, Z. Fluorescence Imaging of Metal Ions Implicated in Diseases. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4487–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Tang, B.Z.; Liu, B. Specific Light-up Bioprobes Based on AIEgen Conjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 2798–2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, R.T.K.; Leung, C.W.T.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Biosensing by Luminogens with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 4228–4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, C.; Ryu, J.-H. Array-Based Protein Sensing Using an Aggregation-Induced Emission (AIE) Light-Up Probe. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 9276–9281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.Q.; Soenksen, L.R.; Donghia, N.M.; Angenent-Mari, N.M.; de Puig, H.; Huang, A.; Lee, R.; Slomovic, S.; Galbersanini, T.; Lansberry, G.; et al. Wearable Materials with Embedded Synthetic Biology Sensors for Biomolecule Detection. Nat. Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 1366–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Kim, H.; Han, J.; Nguyen, V.N.; Peng, X.; Yoon, J. Activity-Based Smart AIEgens for Detection, Bioimaging, and Therapeutics: Recent Progress and Outlook. Aggregate 2021, 2, e51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, D.K.; Badon, I.W.; Lim, J.M.; Vales, T.P.; Lee, J.; Kim, H.J. Triphenylphosphonium-functionalized BODIPY derivatives for mitochondria-targeted cell imaging and fluorescence turn-on sensing with protein selectivity. Dyes Pigm. 2023, 208, 110856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, I.M.; Niazi, S.; Iqbal Khan, M.K.; Pasha, I.; Mohsin, A.; Haider, J.; Iqbal, M.W.; Rehman, A.; Yue, L.; Wang, Z. Recent Advances and Perspectives of Aggregation-Induced Emission as an Emerging Platform for Detection and Bioimaging. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 119, 115637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.H.; Shah, K.W.; Zhou, H.; Xu, J. Recent Advances in Aggregation-Induced Emission Chemosensors for Anion Sensing. Molecules 2019, 24, 2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-F.; Aldred, M.P.; Gong, W.-L.; Li, C.; Zhu, M.-Q. Utilising Tetraphenylethene as a Dual Activator for Intramolecular Charge Transfer and Aggregation Induced Emission. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7711–7713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Guo, Y.; Ye, H.; Huang, K.; Lv, Z.; Ke, Y. Different Effects of Titanium Dioxide Nanoparticles Instillation in Young and Adult Mice on DNA Methylation Related with Lung Inflammation and Fibrosis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2019, 176, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.; Hou, H.; Li, K. Fast and Highly Selective Detection of Acetaldehyde in Liquor and Spirits by Forming Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 285, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Yang, C.; Lu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Y. Construction of Salicylaldehyde Analogues as Turn-on Fluorescence Probes and Their Electronic Effect on Sensitive and Selective Detection of As(v) in Groundwater. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.; Sun, T.; Li, T.; Guo, Z.; Pang, H. Highly Sensitive and Selective Colorimetric/Fluorescent Probe with Aggregation Induced Emission Characteristics for Multiple Targets of Copper, Zinc and Cyanide Ions Sensing and Its Practical Application in Water and Food Samples. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 266, 730–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, L.; Cao, H.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Han, M.; Wang, H.; Li, J. Photodynamic Therapy with Liposomes Encapsulating Photosensitizers with Aggregation-Induced Emission. Nano Lett. 2019, 19, 1821–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalili, R.; Khataee, A. Aluminum(III) Triggered Aggregation-Induced Emission of Glutathione-Capped Copper Nanoclusters as a Fluorescent Probe for Creatinine. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Nie, J.; Niu, J.; Wang, W.; Lin, W. An AIE + ESIPT Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Sulfur Dioxide with Distinct Ratiometric Fluorescence Signals in Mammalian Cells, Mouse Embryonic Fibroblast and Zebrafish. J. Mater. Chem. B 2018, 6, 1973–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, Y.; Duan, Q.; Zheng, G.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, H.; He, J.; Sun, H.; Ho, D. An Ultra-Sensitive and Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe Based on the DTBET Process for Hg2+ Detection and Imaging Applications. Analyst 2019, 144, 1353–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathan, S.; Jalal, M.; Prasad, S.; Bose, S. Aggregation-Induced Enhanced Photoluminescence in Magnetic Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots as a Fluorescence Probe for As(Iii) Sensing. J. Mater. Chem. A Mater. 2019, 7, 8510–8520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Xu, K.; Xiao, K.; Xu, Q.; Wang, L.; Li, P.; Zhou, J.; Zhao, D.; Bai, L.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Biomolecule Sensors Based on Organic Electrochemical Transistors. npj Flex. Electron. 2025, 9, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Li, Z. AIE Probes towards Biomolecules: The Improved Selectivity with the Aid of Graphene Oxide. Sci. China Chem. 2015, 58, 1800–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, P.; Leung, N.L.C.; Zhang, J.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. AIE-Based Luminescence Probes for Metal Ion Detection. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2021, 429, 213693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V. Advances in Synthetic Biology; Springer: Singapore, 2020; ISBN 9789811500817. [Google Scholar]
- Christensen, T.M.; Jama, M.; Ponek, V.; Lyon, E.; Wilson, J.A.; Hoffmann, M.L.; Bejjani, B.A. Design, Development, Validation, and Use of Synthetic Nucleic Acid Controls for Diagnostic Purposes and Application to Cystic Fibrosis Testing. J. Mol. Diagn. 2007, 9, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erickson, R.P. Somatic Gene Mutation and Human Disease Other than Cancer: An Update. Mutat. Res./Rev. Mutat. Res. 2010, 705, 96–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.; Jin, L.; Duan, J.; Lu, Y. New conjugated poly(pyridinium salt) derivative: AIE characteristics, the interaction with DNA and selective fluorescence enhancement induced by dsDNA. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 103358–103364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurya, R.; Bhattacharjee, G.; Gohil, N.; Alzahrani, K.J.; Singh, V. Chapter Nine—Aggregation Induced Emission Molecules for Detection of Nucleic Acids. In Progress in Molecular Biology and Translational Science; Bhosale, R.S., Singh, V., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2021; Volume 184, pp. 219–227. ISSN 1877-1173. [Google Scholar]
- Ligasová, A.; Koberna, K. Dna Dyes—Highly Sensitive Reporters of Cell Quantification: Comparison with Other Cell Quantification Methods. Molecules 2021, 26, 5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragan, A.I.; Pavlovic, R.; McGivney, J.B.; Casas-Finet, J.R.; Bishop, E.S.; Strouse, R.J.; Schenerman, M.A.; Geddes, C.D. SYBR Green I: Fluorescence Properties and Interaction with DNA. J. Fluoresc. 2012, 22, 1189–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuma, R.S.; Beaudet, M.P.; Jin, X.; Jones, L.J.; Cheung, C.-Y.; Yue, S.; Singer, V.L. Characterization of SYBR Gold Nucleic Acid Gel Stain: A Dye Optimized for Use with 300-Nm Ultraviolet Transilluminators. Anal. Biochem. 1999, 268, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragan, A.I.; Casas-Finet, J.R.; Bishop, E.S.; Strouse, R.J.; Schenerman, M.A.; Geddes, C.D. Characterization of PicoGreen Interaction with DsDNA and the Origin of Its Fluorescence Enhancement upon Binding. Biophys. J. 2010, 99, 3010–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Yan, S.; Zhou, Y.; Huang, R.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J.; Weng, X.; Zhou, X. A Novel Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorescent Probe for Nucleic Acid Detection and Its Applications in Cell Imaging. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2014, 24, 1654–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Tang, B.Z.; Liu, B. Specific Nucleic Acid Detection Based on Fluorescent Light-up Probe from Fluorogens with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 10135–10138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.-P.; Song, Z.-G.; Fang, Y.; Mei, J.; Jia, L.; Qin, A.J.; Sun, J.Z.; Ji, J.; Tang, B.Z. Label-Free Fluorescence Detection of Mercury(Ii) and Glutathione Based on Hg2+-DNA Complexes Stimulating Aggregation-Induced Emission of a Tetraphenylethene Derivative. Analyst 2010, 135, 3002–3007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, Y.; Chen, S.; Leung, C.W.T.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Tang, B.Z. Water-Soluble Tetraphenylethene Derivatives as Fluorescent “Light-up” Probes for Nucleic Acid Detection and Their Applications in Cell Imaging. Chemistry 2013, 8, 1806–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Cao, X.; Guo, Y.; Zheng, X.; Li, D.; Chen, S.K.; Chen, G.; You, J. An Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorogen/DNA Probe Carrying an Endosome Escaping Pass for Tracking Reduced Thiol Compounds in Cells. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 7811–7817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawamura, K.; Matsumoto, A.; Murashima, T. Facile DNA Detection Based on Fluorescence Switching of A Hydrophobic AIE Dye-Labeled Peptide Nucleic Acid Probe by Aggregation/Disaggregation. Int. J. Med. Nano Res. 2015, 2, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; He, Z.; He, X.; Zhang, H.; Weng, J.; Yang, X.; Meng, F.; Luo, L.; Tang, B.Z. Dual-Color Emissive AIEgen for Specific and Label-Free Double-Stranded DNA Recognition and Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms Detection. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 20097–20106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Wang, Y.; Sun, X.; Bai, J.; Peng, Y.; Ning, B.; Gao, Z.; Liu, B. Ultrasensitive Competitive Detection of Patulin Toxin by Using Strand Displacement Amplification and DNA G-Quadruplex with Aggregation-Induced Emission. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1106, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, S.; Bi, C.; Song, W. Detection of DNA Methyltransferase Activity Using Template-Free DNA Polymerization Amplification Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission. Anal. Biochem. 2020, 590, 113532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Yin, B.; Huang, Y.; Gu, Y.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wong, S.H.D.; Yang, M. A Dual “Turn-on” Biosensor Based on AIE Effect and FRET for in Situ Detection of MiR-125b Biomarker in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 230, 115270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duo, Y.; Xiang, Z.; Gao, G.; Luo, G.; Tang, B.Z. Biomedical Application of Aggregation-Induced Emission Luminogen-Based Fluorescent Sensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 167, 117252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Min, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Lu, S.; Xu, L.P.; Lou, X.; Xia, F.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. AIE-Based Superwettable Microchips for Evaporation and Aggregation Induced Fluorescence Enhancement Biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 111, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, E.; Lai, P.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Chen, S. Fluorescent Materials with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for Array-Based Sensing Assay. Front. Chem. 2020, 8, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chai, X.; He, X.-P.; Kim, H.-J.; Yoon, J.; Tian, H. Fluorogenic Probes for Disease-Relevant Enzymes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2019, 48, 683–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, J.E.; Channon, R.B.; Henry, C.S.; Geiss, B.J. A Nuclease Protection ELISA Assay for Colorimetric and Electrochemical Detection of Nucleic Acids. Anal. Methods 2019, 11, 1027–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Poulpiquet, A.; Diez-Buitrago, B.; Dumont Milutinovic, M.; Sentic, M.; Arbault, S.; Bouffier, L.; Kuhn, A.; Sojic, N. Dual Enzymatic Detection by Bulk Electrogenerated Chemiluminescence. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6585–6592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Pan, W.; Li, N.; Tang, B. Fluorescent Probes for Organelle-Targeted Bioactive Species Imaging. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6035–6071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keremane, K.; Rao, R.; Adhikari, A.V. Simple 3, 6-disubstituted Carbazoles as Potential Hole Transport Materials: Photophysical, Electrochemical and Theoretical Studies. Photochem. Photobiol. 2021, 97, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, M.; Tang, B.Z. Fluorescent Sensors Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission: Recent Advances and Perspectives. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Wen, J.; Chen, S.; Han, Y.; Ogaji, O.D.; Biu, A.M.; Cui, H.; Meng, X.; Li, J.; Du, K.; et al. Review of Advancement in Aggregation-Induced Emission-Based Fluorescent Biosensors for Enzyme Detection: Mechanisms and Biomedical Applications. Anal. Chim. Acta 2025, 1346, 343716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Shi, H.; Tang, B.Z.; Liu, B. Fluorescent Light-up Probe with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics for Alkaline Phosphatase Sensing and Activity Study. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 8784–8789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, R.; Pang, X.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, H.; Gu, B.; Wu, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y. Aggregation-Induced Emission Fluorescent Probe for Monitoring Endogenous Alkaline Phosphatase in Living Cells. Talanta 2019, 205, 120143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Z.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Zhao, E.; He, Z.; Hong, Y.; Lam, J.W.Y.; Liu, B.; Tang, B.Z. A Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe Based on ESIPT and AIE Processes for Alkaline Phosphatase Activity Assay and Visualization in Living Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 17245–17254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Meng, L.; Zi, Y.; You, J. Ratiometric Detection of Alkaline Phosphatase Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission Enhancement. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 7431–7440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, R.; Cheng, X.; Xu, S.; Liu, B. A FRET Probe with AIEgen as the Energy Quencher: Dual Signal Turn-on for Self-Validated Caspase Detection. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 4245–4250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, A.; Wang, H.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Ji, S.; Li, J.; Kong, D.; Tang, B.Z.; Liu, B.; Yang, Z.; Ding, D. Peptide-Induced AIEgen Self-Assembly: A New Strategy to Realize Highly Sensitive Fluorescent Light-Up Probes. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 3872–3878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Z.N.; Jiang, Y.F.; Ru, J.N.; Lu, J.H.; Ding, B.; Wu, J. Amino Acid Metabolism in Health and Disease. Signal Transduct. Target Ther. 2023, 8, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, Z.-H.; Han, X.; Shao, Y.; Fang, J.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, Y.-W.; Peng, Y. Fluorescein-Based Chromogenic and Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe for Highly Selective Detection of Cysteine and Its Application in Bioimaging. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 1937–1944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Xue, X.; Zhang, F.; Zhang, B.; Li, T.; Peng, L.; Cho, D.-H.; Chen, H.; Fang, J.; Chen, X. A Novel AIEgen-Based Probe for Detecting Cysteine in Lipid Droplets. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1127, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Saha, M.L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Song, B.; Lu, C.; Yan, X.; Li, X.; Huang, F.; Yin, S.; et al. Multicomponent Platinum(II) Cages with Tunable Emission and Amino Acid Sensing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5067–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Zhou, Y.; Qu, H.; Xu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Peng, X. A Novel AIE Plus ESIPT Fluorescent Probe with a Large Stokes Shift for Cysteine and Homocysteine: Application in Cell Imaging and Portable Kit. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2018, 57, 15216–15223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, M.H.; Zhou, H.; Lin, T.T.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Triphenylethylene- and Tetraphenylethylene-Functionalized 1,3-Bis(Pyrrol-2-Yl)Squaraine Dyes: Synthesis, Aggregation-Caused Quenching to Aggregation-Induced Emission, and Thiol Detection. ACS Omega 2018, 3, 16424–16435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Liu, N.; Li, F.; Fu, W.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, Y. Novel PSMA-Coated on-off-On Fluorescent Chemosensor Based on Organic Dots with AIEgens for Detection of Copper (II), Iron (III) and Cysteine. Polymers 2018, 10, 786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S. A Novel Ratiometric Fluorescence Nanoprobe Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission of Silver Nanoclusters for the Label-Free Detection of Biothiols. Talanta 2018, 188, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.-N.; Shi, N.-N.; Yang, D.; Wu, R.-X.; Xu, C.-G.; Zhu, B.; Shao, F.; Zhang, X.; Bi, S.-Y.; Fan, Y.-H. Solid-State Fluorescent Switch Based on the Intercoversion of J-Aggregation and Dimer and Aggregation Pattern-Dependent Fluorescence Colorimetric Sensing of GSH/Zn2+/Cd2+. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 342, 116946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Fan, S.; Cao, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, W. A Hydroxyphenylquinazolinone-Based Fluorescent Probe for Turn-on Detection of Cysteine with a Large Stokes Shift and Its Application in Living Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2018, 364, 750–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shu, T.; Lin, X.; Zhou, Z.; Zhao, D.; Xue, F.; Zeng, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, C.; Su, L.; Zhang, X. Understanding Stimuli-Responsive Oligomer Shell of Silver Nanoclusters with Aggregation-Induced Emission via Chemical Etching and Their Use as Sensors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 286, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Kong, R.; Tan, Q.; Qu, F.; Qu, F. A Label-Free Fluorescence Turn-on Assay for Glutathione Detection by Using MnO2 Nanosheets Assisted Aggregation-Induced Emission-Silica Nanospheres. Talanta 2017, 169, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.; Peng, Z.; Ji, M.; Chen, J.; Wang, P. Highly Selective Fluorescent Probe Based on AIE for Identifying Cysteine/Homocysteine. Bioorg Chem. 2022, 126, 105902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantini, A.; Vaudano, E.; Pulcini, L.; Carafa, T.; Garcia-Moruno, E. An Overview on Biogenic Amines in Wine. Beverages 2019, 5, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wójcik, W.; Łukasiewicz, M.; Puppel, K. Biogenic Amines: Formation, Action and Toxicity—A Review. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2021, 101, 2634–2640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, K.; You, J.; Ye, S.; Gu, D.; Wang, T.; Teng, Y.; Shen, Z.; Pan, Z. Gold Nanoclusters-Poly(9,9-Dioctylfluorenyl-2,7-Diyl) Dots@zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) Nanohybrid Based Probe for Ratiometric Analysis of Dopamine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1098, 102–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, F.; Fa, Q.; Yin, T.; Jiang, D.; Zhao, X. Aggregation-Induced Emission of Lead Halide Perovskites Modulated by Dispersed/Aggregated Gold Nanoparticles for Application in the Detection of Dopamine. Mater. Res. Bull. 2021, 142, 111405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhang, X.Y.; Wang, X.H.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Ratiometric Fluorescence Detection of Dopamine Based on Effect of Ligand on the Emission of Ag Nanoclusters and Aggregation-Induced Emission Enhancement. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 310, 127858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.; Zhu, W.; Chen, Q.; Li, X.; Zhang, G.; Li, Y.; Fan, X.; Wang, J. Selective Fluorescent Probes for Spermine and 1-Adamantanamine Based on the Supramolecular Structure Formed between AIE-Active Molecule and Cucurbit[n]Urils. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 261, 602–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, V.G.; Kumar, V.; Bhasikuttan, A.C.; Kadu, K.; Ramanan, S.R.; Bhosle, A.A.; Banerjee, M.; Chatterjee, A. Solid-Supported Amplification of Aggregation Emission: A Tetraphenylethylene–Cucurbit[6]Uril@Hydroxyapatite-Based Supramolecular Sensing Assembly for the Detection of Spermine and Spermidine in Human Urine and Blood. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2021, 4, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tejpal, R.; Kumar, M.; Bhalla, V. Spermidine Induced Aggregation of Terphenyl Derivative: An Efficient Probe for Detection of Spermidine in Living Cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 258, 841–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sha, Q.; Sun, B.; Yi, C.; Guan, R.; Fei, J.; Hu, Z.; Liu, B.; Liu, X. A Fluorescence Turn-on Biosensor Based on Transferrin Encapsulated Gold Nanoclusters for 5-Hydroxytryptamine Detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 294, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, T.; Xie, Y.; Su, S.; Liu, F.; Chen, Q.; Jing, J.; Zhang, R.; Niu, G.; Zhang, X. In Vitro Light-Up Visualization of a Subunit-Specific Enzyme by an AIE Probe via Restriction of Single Molecular Motion. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 10003–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Raj, P.; Yao, W.; Ying, H. Glucose Metabolism in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 1460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, I.; Jiang, N.; Shao, X.; Elsherif, M.; Alam, F.; Salih, A.; Butta, H.; Yetisen, A.K. Recent Advances in Optical Sensors for Continuous Glucose Monitoring. Sens. Diagn. 2022, 1, 1098–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Wu, P.; Gu, M.; Xue, J. Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe Based on AuNCs Induced AIE for Quantification and Visual Sensing of Glucose. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1104, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Shu, T.; Ma, J.; Dai, Q.; Peng, P.; Zhou, Z.; Zhou, X.; Su, L.; Zhang, X. Rational Design of ZIF-8 for Constructing Luminescent Biosensors with Glucose Oxidase and AIE-Type Gold Nanoclusters. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3408–3417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, S.; Liu, Q.; Zhu, F.; Chen, M.; Wang, L.; Xiong, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, X. AIE-Active Metal–Organic Frameworks: Facile Preparation, Tunable Light Emission, Ultrasensitive Sensing of Copper(Ii) and Visual Fluorescence Detection of Glucose. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2020, 8, 10408–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, H.; Wang, J.; Zhu, X.; Sun, J.; Shi, W.; Wang, H.; Qu, S.; Wang, X. Ce3+ and Fe2+ Co-Enhanced Ratiometric Fluorescence Probe Utilizing Copper Nanoclusters and Coumarin for Sensitive Assay of Hydrogen Peroxide and Glucose. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2022, 245, 114117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gou, S.; Shi, Y.; Li, P.; Wang, H.; Li, T.; Zhuang, X.; Li, W.; Wang, Z. Stimuli-Responsive Luminescent Copper Nanoclusters in Alginate and Their Sensing Ability for Glucose. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 6561–6567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, H.; Wang, J.; Qileng, A.; Chen, S.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y. “Two-in-One” Portable Strategy for Non-GOx Glucose Monitoring: Electrochromic and Fluorescent Assay Using Reversible Hydrogel. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 349, 130744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Liang, Y.; Gao, N.; Liu, C.; Wang, S.; Yin, X.; Li, G. Poly(Ionic Liquid)s as a Distinct Receptor Material to Create a Highly-Integrated Sensing Platform for Efficiently Identifying Numerous Saccharides. Chem. Sci. 2019, 10, 6617–6623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Walther, A. ATP-Responsive and ATP-Fueled Self-Assembling Systems and Materials. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 2002629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, L.-Y.; Zhao, Y.; Kamya, E.; Guo, J.-T.; Sun, B.; Feng, Y.-K.; Zhu, M.-F.; Ren, X.-K. Turn-off/on Fluorescent Sensors for Cu2+ and ATP in Aqueous Solution Based on a Tetraphenylethylene Derivative. J. Mater. Chem. C Mater. 2019, 7, 2640–2645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, A.-X.; Shi, Y.-D.; Zhang, K.-X.; Sun, W.; Tan, Z.-L.; Lu, Z.-L.; He, L. Self-Assembled Aggregation-Induced Emission Micelle (AIE Micelle) as Interfacial Fluorescence Probe for Sequential Recognition of Cu2+ and ATP in Water. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 440–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, Z.; Xie, W.; Sun, W.; Ji, S.; Tian, J.; Lv, L. A Label-Free Fluorometric Aptasensor for Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) Detection Based on Aggregation-Induced Emission Probe. Anal. Biochem. 2019, 578, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Li, M.; Luo, H.; Yang, Y.; Xu, X.; Yong, Q.; Wang, S. An Easily Available Camphor-Derived Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe with AIE Feature for Sequential Ga3+ and ATP Sensing in a near-Perfect Aqueous Media and Its Bio-Imaging in Living Cells and Mice. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 320, 128249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, N.H.; Kim, B.W.; Moon, H.; Yoo, H.; Kang, R.H.; Hur, J.K.; Oh, Y.; Kim, B.M.; Kim, D. AIEgen-Based Nanoprobe for the ATP Sensing and Imaging in Cancer Cells and Embryonic Stem Cells. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1152, 338269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.R.; Malegaonkar, J.N.; Bhosale, S.V.; Singh, P.K. An ATP Responsive Fluorescent Supramolecular Assembly Based on a Polyelectrolyte and an AIE Active Tetraphenylethylene Derivative. Org. Biomol. Chem. 2020, 18, 8414–8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.E.; Yan, J.Q.; Liu, M.; Zhou, Y.; Shen, X.; Ma, Y.L.; Feng, X.S.; Yang, J.; Li, G.H. A Review of the Extraction and Determination Methods of Thirteen Essential Vitamins to the Human Body: An Update from 2010. Molecules 2018, 23, 1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, C.N.; Seabrook, L.J.; Nguyen, S.T.; Leonard, J.T.; Albrecht, L.V. Simplifying the B Complex: How Vitamins B6 and B9 Modulate One Carbon Metabolism in Cancer and Beyond. Metabolites 2022, 12, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Wang, Y.-T.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. Hyperbranched Poly(Amido Amine) Entrapped Tetraphenylethene as a Fluorescence Probe for Sequential Quadruple-Target Detection and Its Potential as a Chemical Logic Gate. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 9755–9763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungor, D.; Szilágyi, I.; Csapó, E. Yellow-Emitting Au/Ag Bimetallic Nanoclusters with High Photostability for Detection of Folic Acid. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 338, 116695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Lai, Z.; Gu, J.; Liu, W.; Gao, J.; Wang, Q. Sequential Determination of Cerium (IV) Ion and Ascorbic Acid via a Novel Organic Framework: A Subtle Interplay between Intramolecular Charge Transfer (ICT) and Aggregated-Induced-Emission (AIE). J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 304, 112705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Hu, X.; Qiu, J.; Guo, H.; Yang, F. A Fluorescent Sensor for Folic Acid Based on Crown Ether-Bridged Bis-Tetraphenylethylene. Analyst 2019, 144, 2662–2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghibi, S.; Chen, T.; Jamshidi Ghahfarokhi, A.; Tang, Y. AIEgen-Enhanced Protein Imaging: Probe Design and Sensing Mechanisms. Aggregate 2021, 2, e41. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, L.; Lin, X.; Chen, X. Ionic Liquid Decorated AIE Luminogen for Selective Detection of HSA in Biofluids and Early Disease Screening. Talanta 2020, 212, 120763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Guan, W.; Lu, C.; Zhou, X.-R.; Luo, S.-Z.; You, Y.; Ouyang, J. Hydrophobicity-Induced Prestaining for Protein Detection in Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 2807–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Cao, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Wang, S. Selective and Sensitive Fluorescent Enhancement Detection of Keratin in Aqueous Media with Aggregation-Induced Emission Characteristics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 293, 159–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, L.; Zhu, L.; Cao, D.; Li, L. Synthesis, Characterization and Fluorescence “Turn-on” Detection of BSA Based on the Cationic Poly(Diketopyrrolopyrrole-Co-Ethynylfluorene) through Deaggregating Process. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 231, 733–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panova, I.G.; Sharova, N.P.; Dmitrieva, S.B.; Poltavtseva, R.A.; Sukhikh, G.T.; Tatikolov, A.S. Use of a Cyanine Dye as a Probe for Albumin and Collagen in the Extracellular Matrix. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 361, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tatikolov, A.S. Polymethine Dyes as Spectral-Fluorescent Probes for Biomacromolecules. J. Photochem. Photobiol. C Photochem. Rev. 2012, 13, 55–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Qiao, Y.; Li, W.; Sui, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Xiao, J. A Graphene Oxide-Aided Triple Helical Aggregation-Induced Emission Biosensor for Highly Specific Detection of Charged Collagen Peptides. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6027–6033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).