Using Polyvinyl Chloride and Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Levofloxacin in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradants in River Water: A Comparative Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Instrumentation
2.2. Chemicals, Reagents, and Standard Solutions
2.3. Preparation of LEVO Ion Exchanger
2.4. Preparation of Electrodes
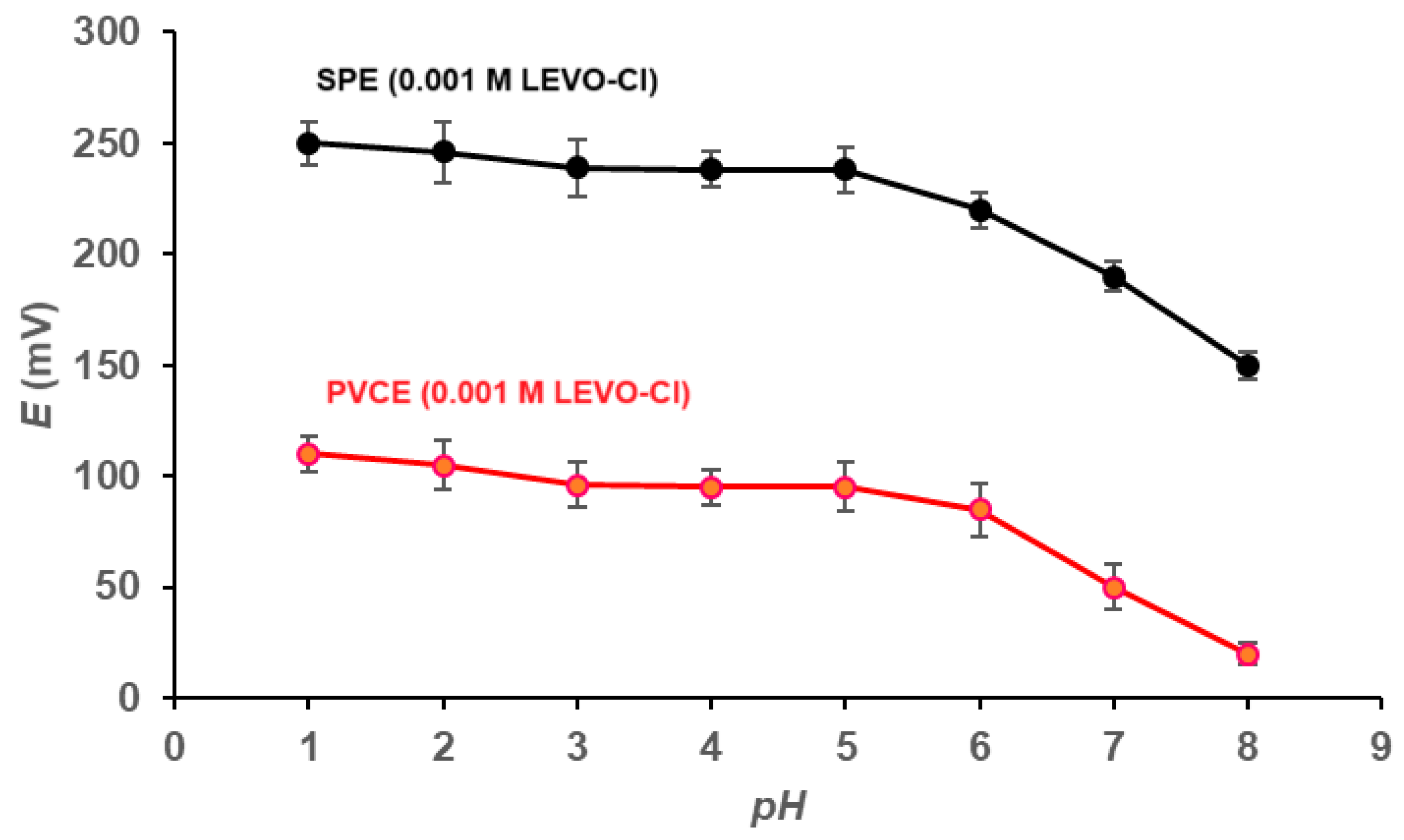
2.5. Sensors’ Calibration and Optimization
2.6. Application
2.6.1. Quantification of LEVO-Cl in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradants
2.6.2. Determination of LEVO-Cl in Different Water Samples
3. Results
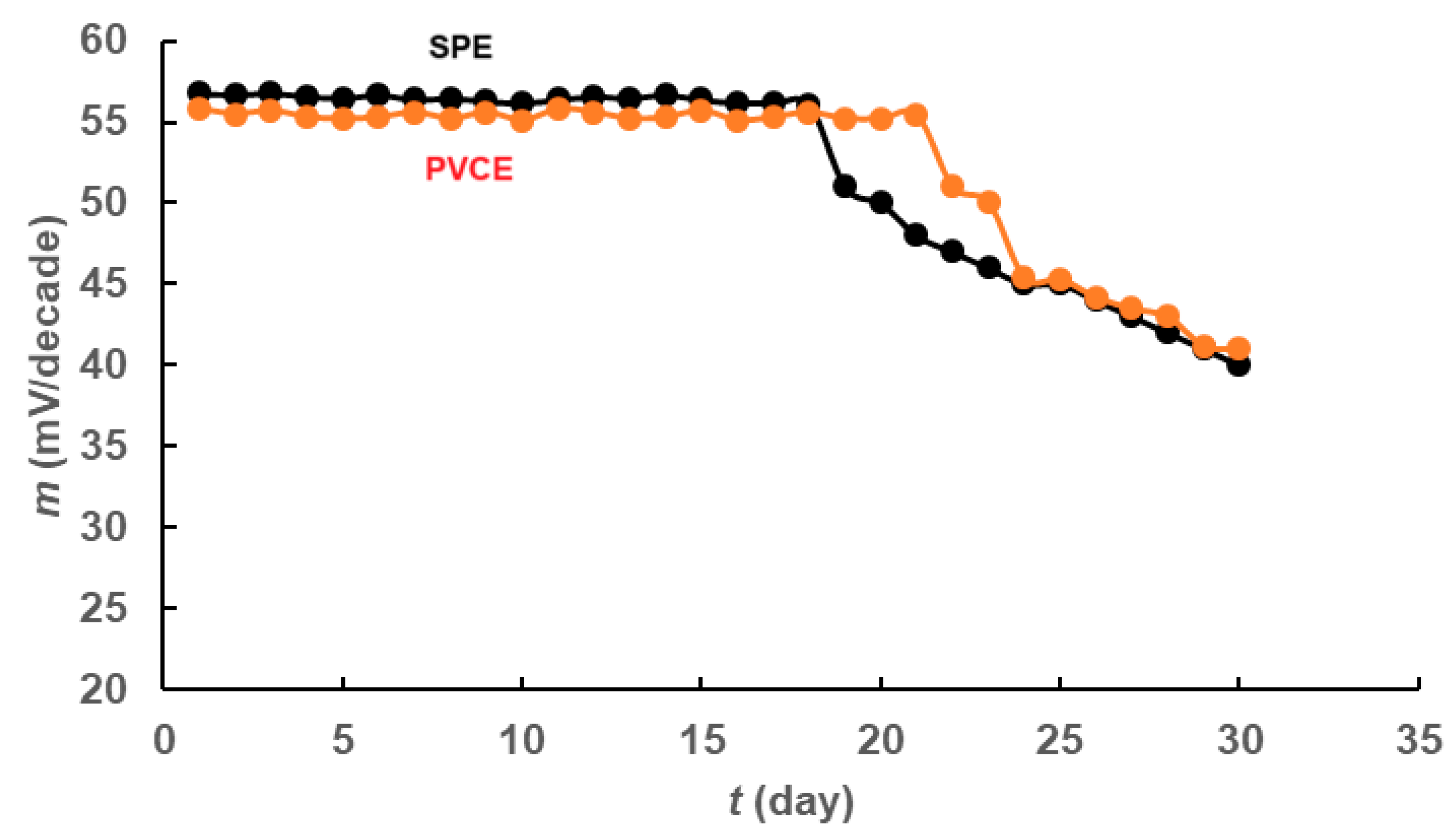
3.1. Evaluation and Validation of the Fabricated Sensors
3.2. Method Application
3.2.1. Determination of LEVO-Cl in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradation Products
3.2.2. Assay of LEVO-Cl in Different Water Samples
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, G.F.; Liu, X.; Zhang, S.; Pan, B.; Liu, M.L. Ciprofloxacin derivatives and their antibacterial activities. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018, 146, 599–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radi, A.; El-Sherif, Z. Determination of levofloxacin in human urine by adsorptive square-wave anodic stripping voltammetry on a glassy carbon electrode. Talanta 2002, 58, 319–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, C.; Fang, B. Current progress of fluoroquinolones-increased risk of aortic aneurysm and dissection. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redgrave, L.S.; Sutton, S.B.; Webber, M.A.; Piddock, L.J. Fluoroquinolone resistance: Mechanisms, impact on bacteria, and role in evolutionary success. Trends Microbiol. 2014, 22, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, N.; Nakata, Y.; Yazaki, A. New findings on the structure-phototoxicity relationship and photostability of fluoroquinolones with various substituents at position 1. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, Y.; Sato, E.; Moroi, R. Photodegradation products of levofloxacin in aqueous solution. Arzneimittelforschung 1993, 43, 601–606. [Google Scholar]
- Szerkus, O.; Jacyna, J.; Wiczling, P.; Gibas, A.; Sieczkowski, M.; Siluk, D.; Matuszewskib, M.; Kaliszan, R.; Markuszewski, M.J. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatographic determination of levofloxacin in human plasma and prostate tissue with use of experimental design optimization procedures. J. Chromatogr. B 2016, 1029, 48–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebrahim, H.; Sonbol, H.; Malak, M.; Ali, A.; Aboulella, Y.; Hadad, G.; Zarad, W.; Emara, S.; Bazan, L. Green automated solid phase extraction to measure levofloxacin in human serum via liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection for pharmacokinetic study. Separations 2023, 10, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.; Bair, M.; Hu, C. Determination of levofloxacin in human urine with capillary electrophoresis and fluorescence detector. J. Chin. Chem. Soc. 2007, 54, 991–995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.M.; Cao, J.T.; Wang, H. Capillary electrophoresis with electrochemiluminescence detection for the analysis of quinolone drugs and pharmacokinetics study. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2008, 19, 962–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elgendy, K.H.; Zaky, M.; Altorky, A.M.M.; Fadel, S. Determination of levofloxacin, norfloxacin, and moxifloxacin in pharmaceutical dosage form or individually using derivative UV spectrophotometry. BMC Chem. 2024, 18, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domes, C.; Popo, J.; Hagel, S.; Pletz, M.W.; Frosch, T. Towards therapeutic drug monitoring of antibiotic levels—Analyzing the pharmacokinetics of levofloxacin using DUV-resonance Raman spectroscopy. Analyst 2023, 148, 3057–3064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dabhi, B.; Parmar, B.; Patel, N.; Jadeja, Y.; Patel, M.; Jebaliya, H.; Karia, D.; Shah, A.K. A stability indicating UPLC method for the determination of levofloxacin hemihydrate in pharmaceutical dosage form: Application to pharmaceutical analysis. Chromatogr. Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 432753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, M.L.; Chandrasekhar, K.B. A validated stability-indicating RP-HPLC method for levofloxacin in the presence of degradation products, its process related impurities and identification of oxidative degradant. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2009, 50, 710–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaber, M.; Abu Shawish Hazem, M.; Khedr, A.M.; Abed-Almonem, K.I. Determination of benzalkonium chloride preservative in pharmaceutical formulation of eye and ear drops using new potentiometric sensors. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2012, 32, 2299–2305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizk, M.S.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M. Plastic membrane electrodes for the determination of flavoxate hydrochloride and cyclopentolate hydrochloride. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 5592–5597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, S.F.; Al-bayati, Y.K. Determination of levofloxacin in pure forms and pharmaceutical preparations used molecularly imprinted polymers membrane. Int. J. Pharm. Res. 2010, 4, 09752366. [Google Scholar]
- Abdel-Haleem, F.M.; Mahmoud, S.; Abdel-Ghani, N.E.T.; El Nashar, R.M.; Bechelany, M.; Barhoum, A. Polyvinyl chloride modified carbon paste electrodes for sensitive determination of levofloxacin drug in serum, urine, and pharmaceutical formulations. Sensors 2021, 21, 3150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel Ghani, N.E.T.; Abdel-Haleem, F.M.; Mahmoud, S.; El Nashar, R.M. Electrochemical detection of the different species of levofloxacin using PVC, carbon paste and screen-printed electrodes: Effect of pH. J. Anal. Test. 2018, 2, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffery, G.; Bassett, J.; Mendham, J.; Deny, R. Vogel’s Textbook of Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 5th ed.; Elbs with Longman Ltd.: London, UK, 1989. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, G.G.; Ali, T.A.; El-Shahat, M.F.; Al-Sabagh, A.M.; Migahed, M.A.; Elmorsy, K. Potentiometric determination of cetylpyridinium chloride using a new type of screen-printed ion selective electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2010, 673, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindner, E.; Umezawa, Y. Performance evaluation criteria for preparation and measurement of macro-and microfabricated ion-selective electrodes (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2008, 80, 85–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Othman, A.M.; Rizk, N.M.H.; El-Shahawi, M.S. Polymer membrane sensors for sildenafil citrate (Viagra) determination in pharmaceutical preparations. Anal. Chim. Acta 2004, 515, 303–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, E.; Buhlmann, P.; Pretsch, E. Carrier-based ion-selective electrodes and bulk optodes. 1. General characteristics. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 3083–3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşofre, V.V.; Buck, R.P. Recent advances in pharmaceutical analysis with potentiometric membrane sensors. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 1993, 24, 1–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
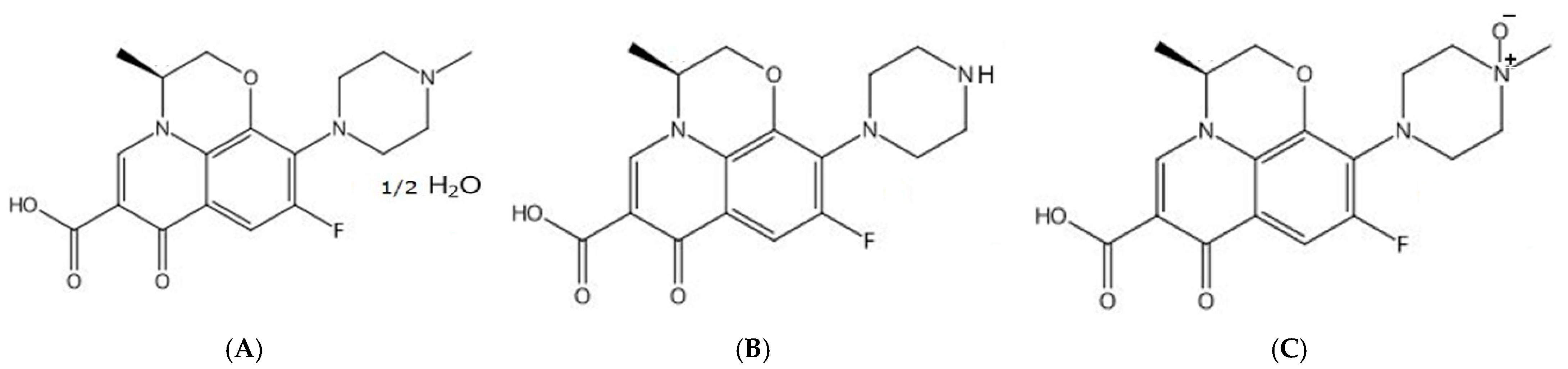


| Parameter | PVCE | SPE |
|---|---|---|
| Slope (mV/decade) * | 55.80 ± 0.70 | 56.90 ± 0.50 |
| Response time (s) | 20 | 15 |
| Working pH range | 3.0–5.0 | 3.0–5.0 |
| Concentration range (M) | 1 × 10−6–1 × 10−2 | 1 × 10−6–1 × 10−2 |
| Stability (days) | 21 | 18 |
| Accuracy (Mean * ± SD) | 100.20 ± 0.81 | 100.42 ± 0.93 |
| Detection limit (M) | 5 × 10−7 | 5 × 10−7 |
| Ruggedness † | 101.41 * ± 1.32 | 100.27 * ± 1.11 |
| Robustness Ψ | 100.28 * ± 0.56 | 100.98 * ± 0.49 |
| Item | PVCE | SPE | Reference Method [14] * |
|---|---|---|---|
| (Mean ± SD) | 100.20 ± 0.81 | 100.42 ± 0.93 | 99.81 ± 0.59 |
| RSD | 0.81 | 0.93 | 0.59 |
| Variance | 0.65 | 0.86 | 0.35 |
| n | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| F-value (6.39) | 1.90 | 2.50 | - |
| Student’s t-test (2.306) | 0.920 | 1.242 | - |
| Interferent | PVCE (Mean * ± S.D.) | SPE (Mean * ± S.D.) |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | 2.3 × 10−3 ± 0.54 | 2.2 × 10−3 ± 0.62 |
| K+ | 3.6 × 10−4 ± 0.55 | 3.5 × 10−4 ± 0.55 |
| NH4+ | 3.4 × 10−4 ± 0.67 | 3.3 × 10−4 ± 0.74 |
| Norfloxacin hydrochloride | 2.8 × 10−4 ± 0.89 | 2.9 × 10−4 ± 0.59 |
| Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride | 3.5 × 10−4 ± 0.64 | 3.6 × 10−4 ± 0.78 |
| Added Intact LEVO-Cl | Added LEVO-DES | Added LEVO-OXD | PVCE (Intact Drug Recovery% * ± S.D.) | SPE (Intact Drug Recovery% * ± S.D.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 90% (9 × 10−4 M) | 5% | 5% | 100.23 ± 0.67 | 101.33 ± 0.45 |
| 70% (7 × 10−4 M) | 15% | 15% | 100.13 ± 0.45 | 99.43 ± 0.35 |
| 50% (5 × 10−4 M) | 25% | 25% | 102.43 ± 0.45 | 99.98 ± 0.56 |
| 30% (3 × 10−4 M) | 35% | 35% | 100.31 ± 0.57 | 101.56 ± 0.65 |
| 10% (1 × 10−4 M) | 45% | 45% | 101.16 ± 0.45 | 101.14 ± 0.45 |
| Specimen | PVCE (Rec.% * ± S.D.) | SPE (Rec.% * ± S.D.) |
|---|---|---|
| Distilled water | 100.89 ± 0.45 | 102.03 ± 0.82 |
| Tap water | 100.45 ± 0.78 | 100.45 ± 0.67 |
| River water sample 1 | 99.46 ± 0.68 | 100.01 ± 0.87 |
| River water sample 2 | 102.34 ± 1.56 | 101.31 ± 0.54 |
| River water sample 3 | 100.76 ± 0.97 | 101.56 ± 0.54 |
| Sample Number | PVCE Conc. β (M) ± S.D. | SPE Conc. β (M) ± S.D. | Reference Method [14] * Conc. β (M) ± S.D. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sample 1 | 2.10 × 10−4 ± 0.65 | 2.12 × 10−4 ± 0.78 | 2.11 × 10−4 ± 0.45 |
| Sample 2 | 3.32 × 10−5 ± 0.45 | 3.30 × 10−5 ± 0.86 | 3.29 × 10−5 ± 0.89 |
| Sample 3 | 5.47 × 10−4 ± 0.72 | 5.45 × 10−4 ± 0.59 | 5.48 × 10−4 ± 0.42 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alabbas, A.B.; Abdel-Gawad, S.A. Using Polyvinyl Chloride and Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Levofloxacin in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradants in River Water: A Comparative Study. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13020028
Alabbas AB, Abdel-Gawad SA. Using Polyvinyl Chloride and Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Levofloxacin in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradants in River Water: A Comparative Study. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(2):28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13020028
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlabbas, Alhumaidi B., and Sherif A. Abdel-Gawad. 2025. "Using Polyvinyl Chloride and Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Levofloxacin in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradants in River Water: A Comparative Study" Chemosensors 13, no. 2: 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13020028
APA StyleAlabbas, A. B., & Abdel-Gawad, S. A. (2025). Using Polyvinyl Chloride and Screen-Printed Electrodes for the Determination of Levofloxacin in the Presence of Its Main Photo-Degradants in River Water: A Comparative Study. Chemosensors, 13(2), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13020028




