ZnS Nanomaterials with Hexagon and Pentagon Structures: Effect of Surfactants on Surface Morphology and Biosensing Application
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Synthesis Procedure
2.2. Materials Characterization
2.3. Antibacterial Activity Assay
2.4. Statistical Analysis Method
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Surface Morphological Study
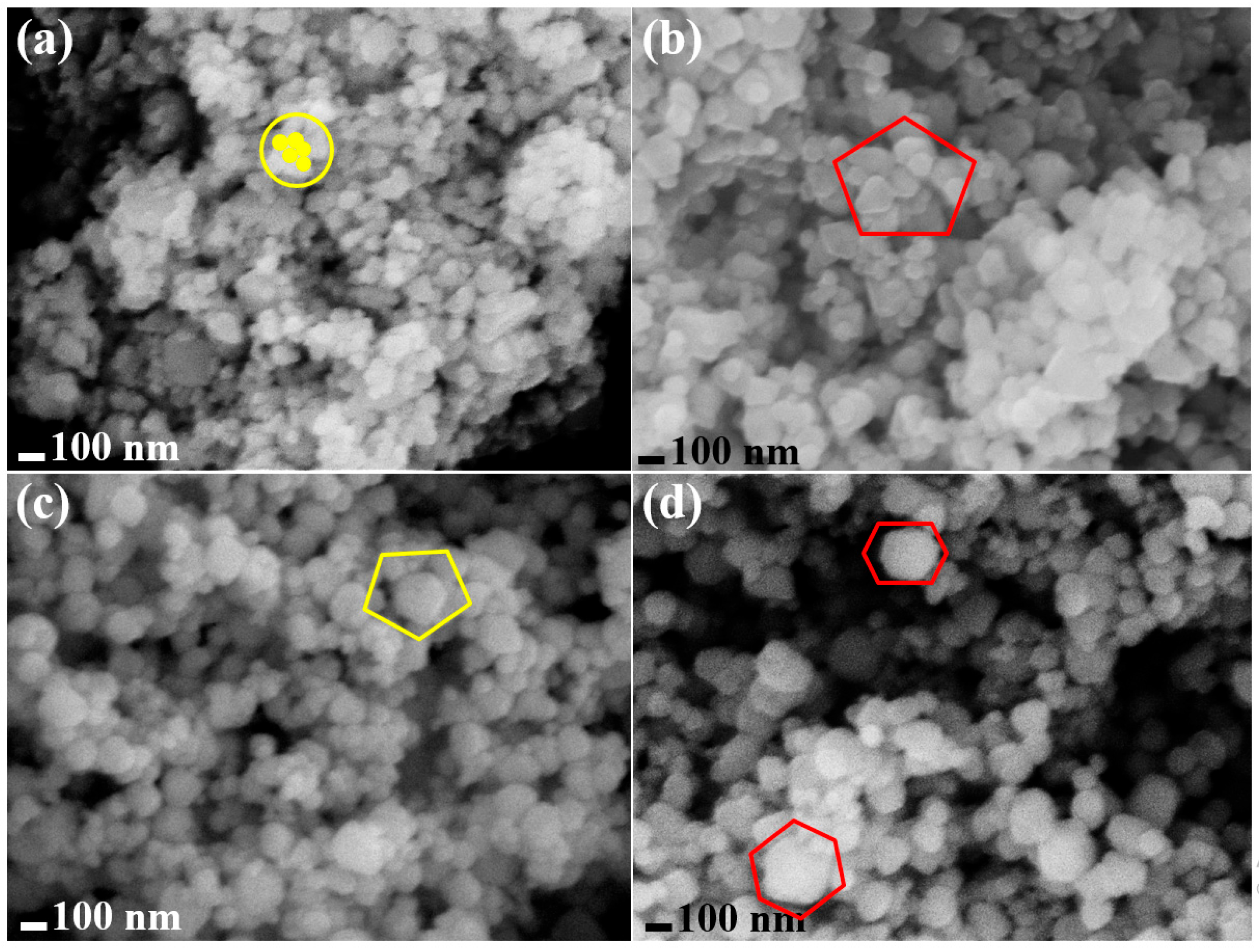
3.1.1. The Surface Morphological Analysis Using FESEM
3.1.2. The ZnS NMs Growth Mechanism in Hydrothermal Method
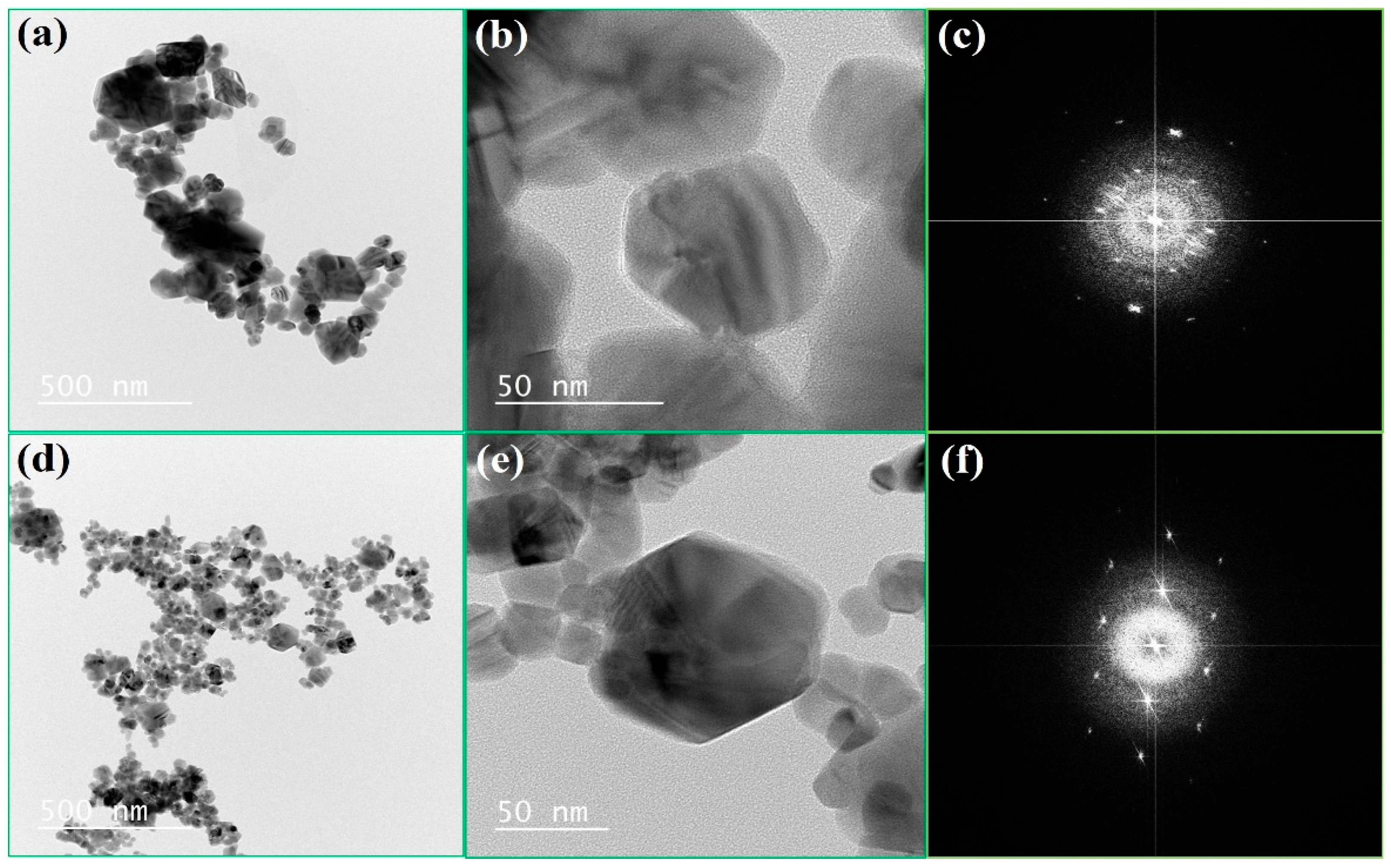
3.1.3. The Surface Morphological Analysis Using TEM
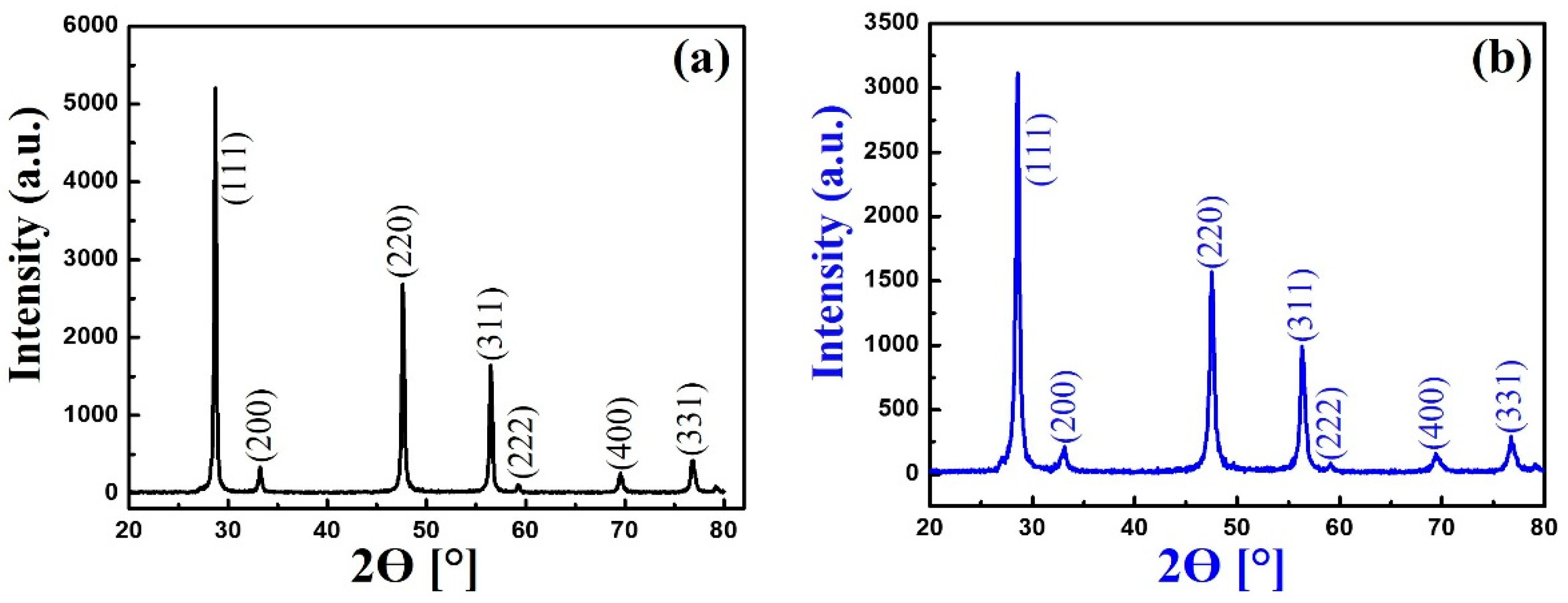
3.2. The X-Ray Diffraction Analysis
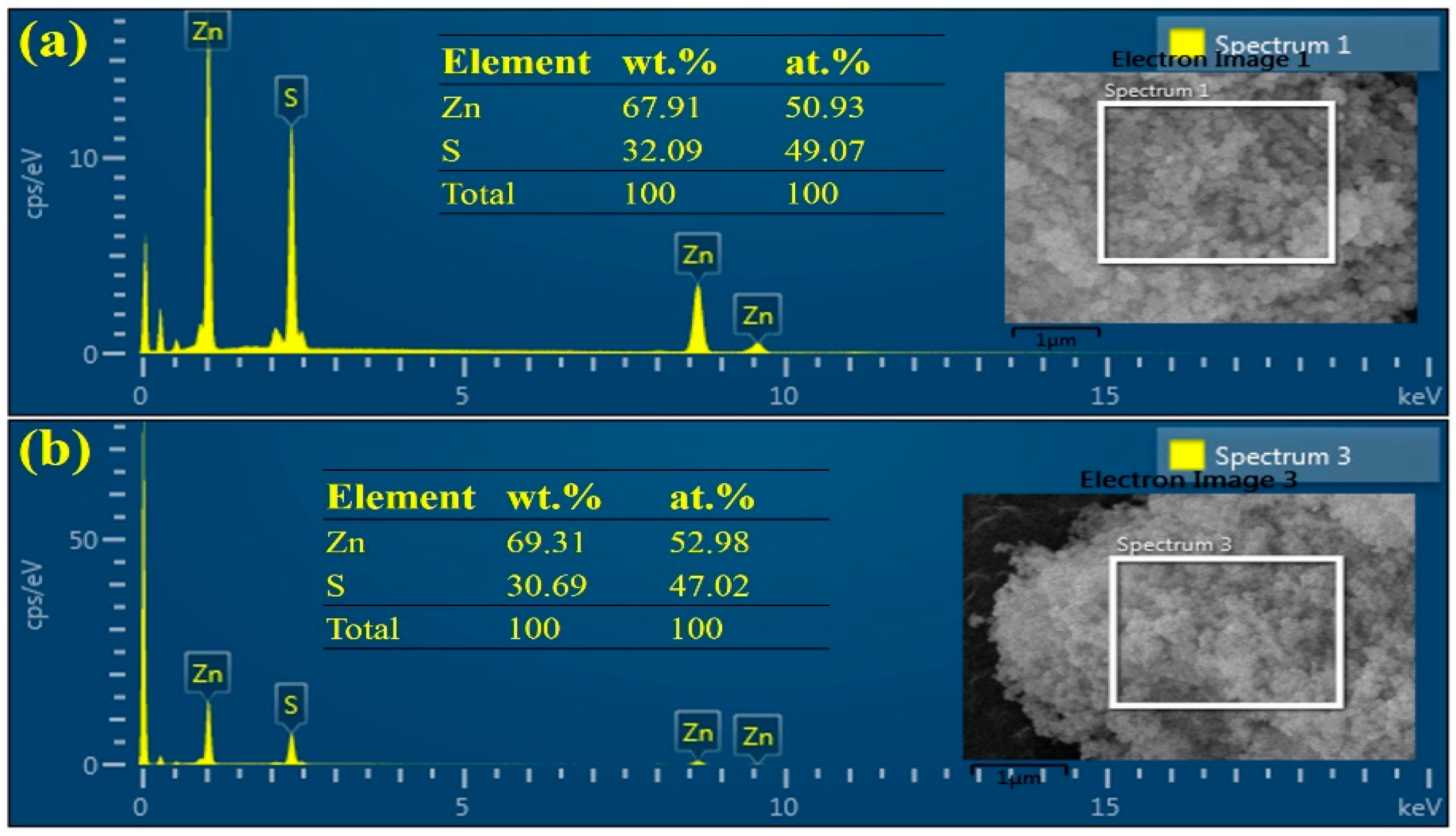
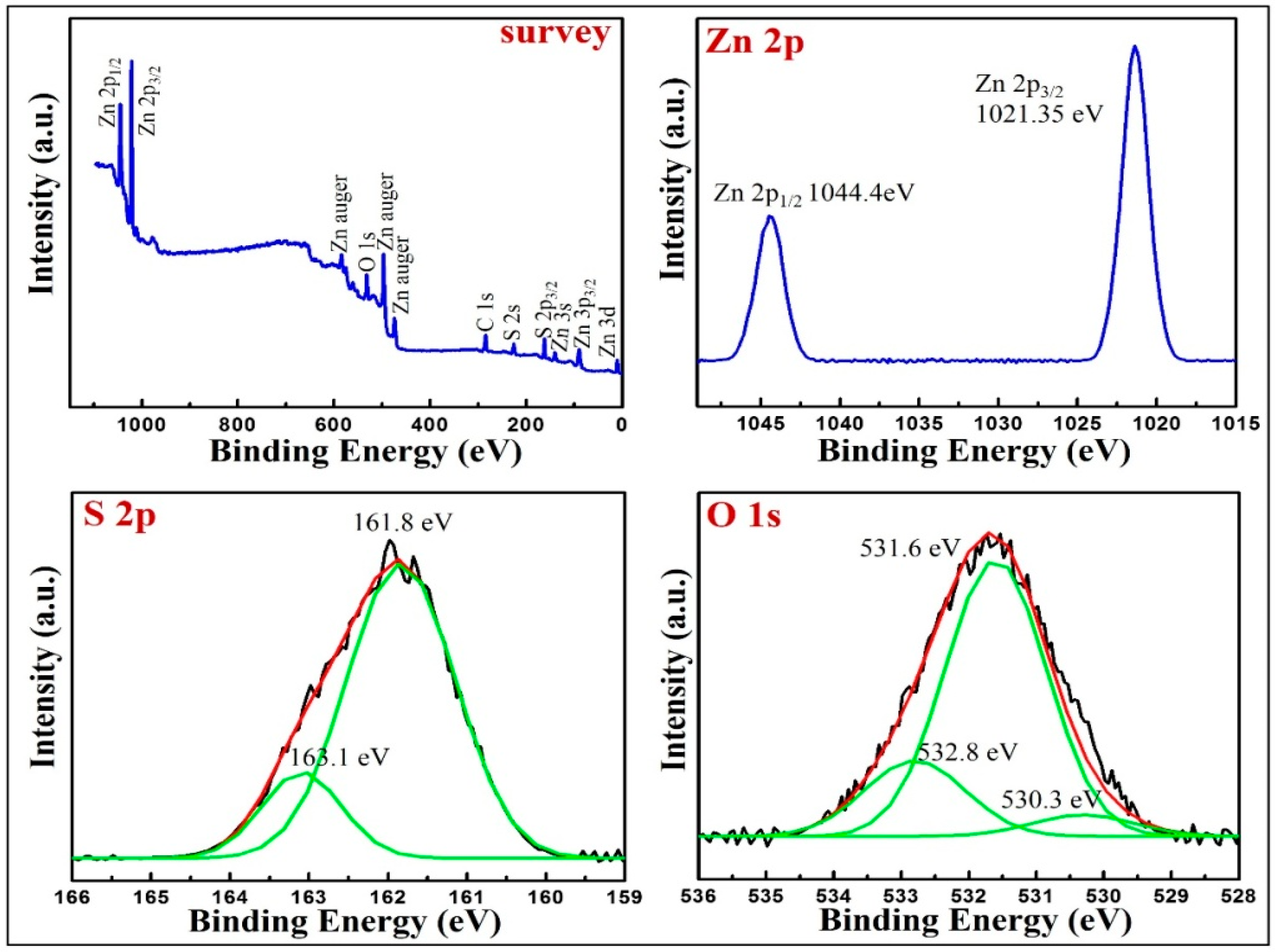
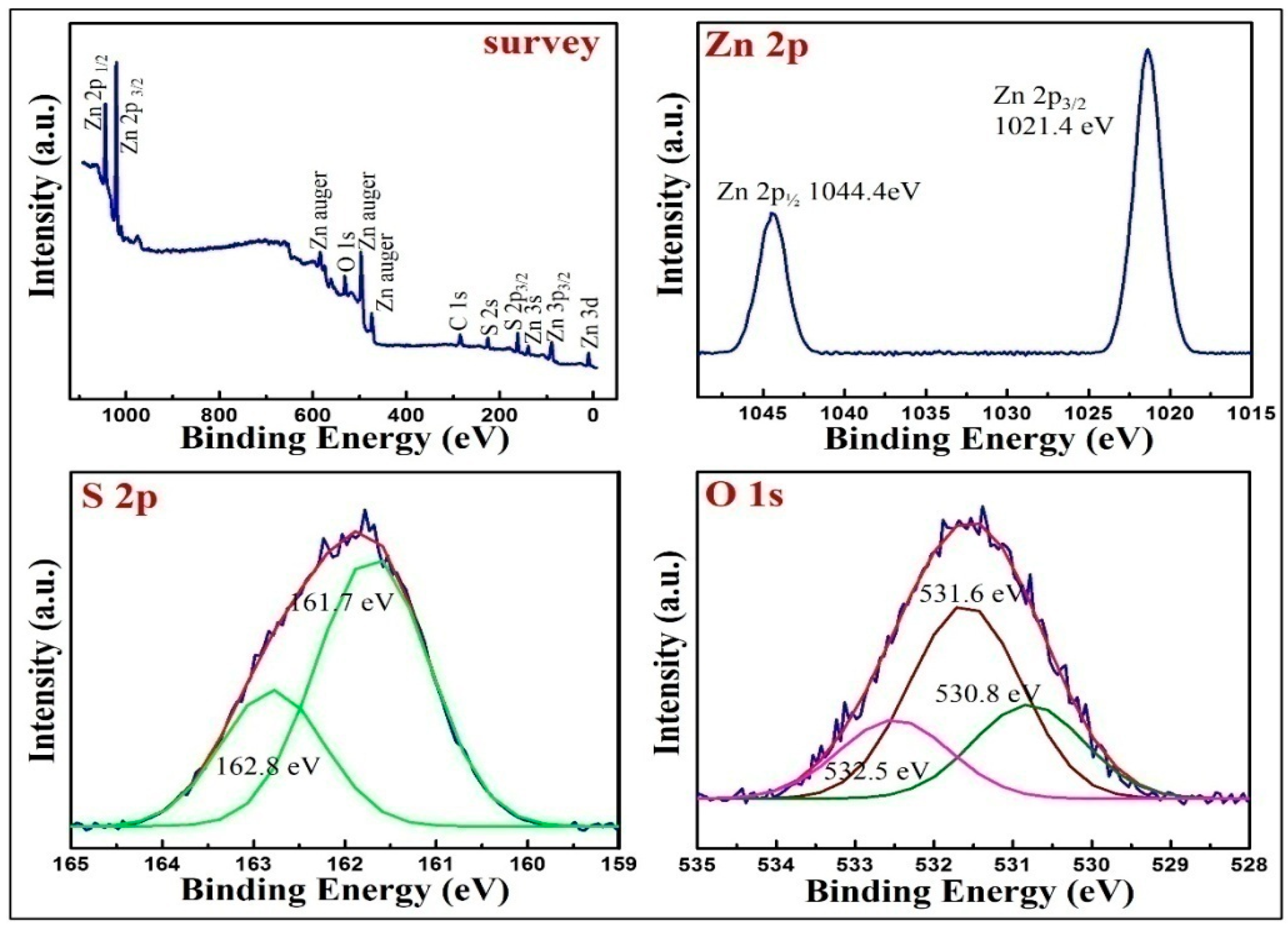
3.3. The Surface Chemical Analysis
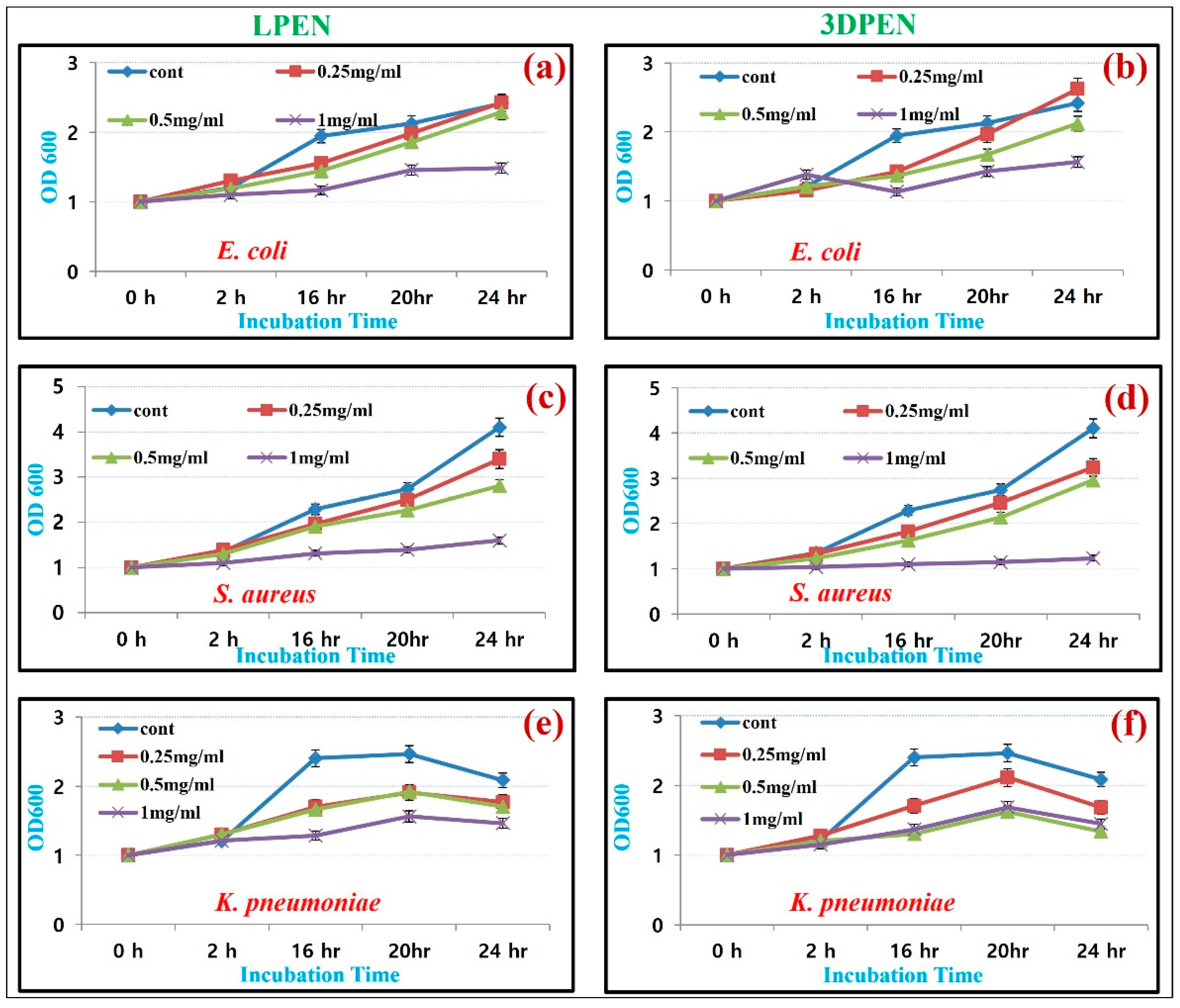
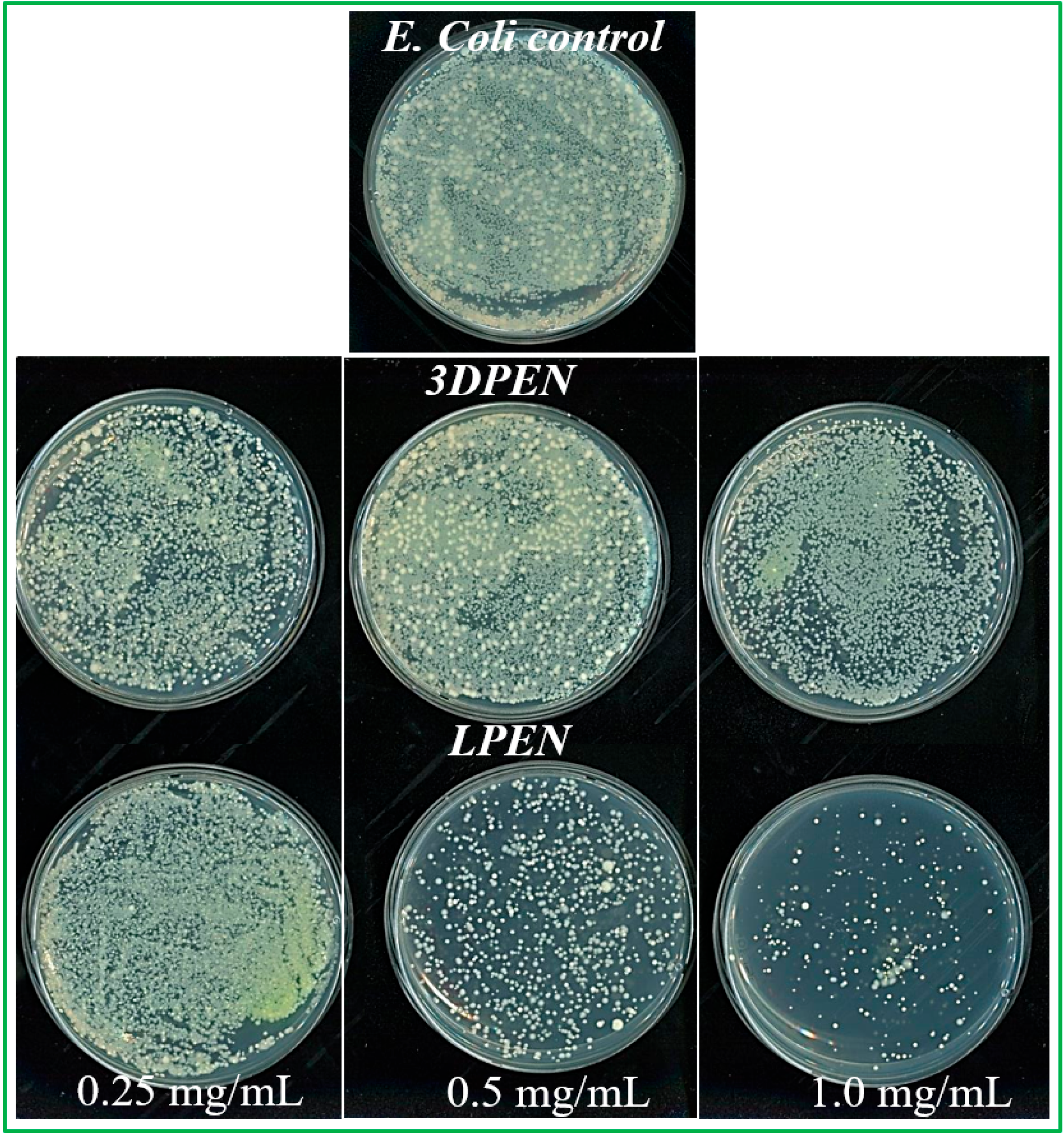
3.4. Antibacterial Biosensing Studies of the ZnS NMs
The MIC Determination
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Suyver, J.F.; Wuister, S.F.; Kelly, J.J.; Meijerink, A. Synthesis and Photoluminescence of Nanocrystalline ZnS: Mn2+. Nano Lett. 2001, 1, 429–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.; Saleem, S.; Salman, M.; Khan, M. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of ZnS–ZnO nanocomposites. Chem. Phys. 2020, 248, 122900–122908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Huang, F.; Ren, G.; Li, D.; Zheng, M.; Wang, Y.; Lin, Z. ZnS nano-architectures: Photocatalysis, deactivation and regeneration. Nanoscale 2010, 2, 2062–2064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Q.; Yin, M.; Yao, Y. Synthesis of sphere-like ZnS architectures via a solvothermal method and their visible-light catalytic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2017, 28, 17827–17832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Hamidy, S.M. The optical behavior of multi-emission quantum dots based on Tb-doped ZnS developed via solvothermalroute for bio imaging applications. Optik-Inter. J. Light Elect. Optics 2020, 207, 163868–163873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Khan, S.; Cho, S.-H.; Kim, J. ZnS nanoparticles as new additive for polyethersulfone membrane in humic acid filtration. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2019, 79, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Porta, F.A.; Ferrer, M.M.; de Santana, Y.V.B.; Raubach, C.W.; Longo, V.M.; Sambrano, J.R.; Longo, E.; Andres, J.; Li, M.S.; Varela, J.A. Synthesis of wurtzite ZnS nanoparticles using the microwave assisted solvothermal method. J. Alloys. Compd. 2013, 556, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabaghi, V.; Davar, F.; Fereshteh, Z. ZnS nanoparticles prepared via simple reflux and hydrothermal method: Optical and photocatalytic properties. Ceram. Inter. 2018, 44, 7545–7556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yin, R.-H.; Wu, Q.-S. Solvothermal Synthesis of Well-Disperse ZnS Nanorods with Efficient Photocatalytic Properties. J. Nanomater. 2012, 2012, 560310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Du, J.; Xiong, S.; Li, H.; Zhu, Y.; Qian, Y. Synthesis of Wurtzite ZnS Nanowire Bundles Using a Solvothermal Technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 12658–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, A.; Gregory, D.H.; Mok, Y.S. Synthesis, Characterization and Shape-Dependent Catalytic CO Oxidation Performance of Ruthenium Oxide Nanomaterials: Influence of Polymer Surfactant. Appl. Sci. 2015, 5, 344–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, G.; Sun, Y.; Gao, D.; Sun, Y. Uniform hematite α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles: Morphology, size-controlled hydrothermal synthesis and formation mechanism. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 1911–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.-J.; Wu, J.J. Recent developments in ZnS photocatalysts from synthesis to photocatalytic applications—A review. Powder Technol. 2017, 318, 8–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayati, F.A. Synergistic antibacterial activity between Thymus vulgaris and Pimpinellaanisum essential oils and methanol extracts. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2008, 116, 403–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Wu, Q.; Wu, J. Synthesis of Nanoparticles via Solvothermal and Hydrothermal Methods. In Handbook of Nanoparticles; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 295–328. [Google Scholar]
- Rak, Z.; Brenner, D.W. Negative Surface Energies of Nickel Ferrite Nanoparticles under Hydrothermal Conditions. J. Nanomater. 2019, 2019, 5268415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibupoto, Z.H.; Khun, K.; Liu, X.; Willander, M. Hydrothermal Synthesis of Nanoclusters of ZnS Comprised on Nanowires. Nanomaterials 2013, 3, 564–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, S.; Xu, Z.; Ma, J.; Shen, X. Ultrathin ZnS Single Crystal Nanowires: Controlled Synthesis and Room-Temperature Ferromagnetism Properties. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 15605–15612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, G.H.; Yan, P.X.; Yan, D.; Fan, X.Y.; Wang, M.X.; Qu, D.X.; Liu, J.Z. Hydrothermal synthesis of single-crystal ZnS nanowires. Appl. Phys. A 2006, 84, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Fang, P.; Wang, S. Synthesis of ZnS nanorod arrays by an aqua-solution hydrothermal process on pulse-plating Zn nanocrystallines. J. Mater. Res. 2009, 24, 2821–2827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solatani, N.; Saion, E.; Hussein, M.Z.; Erfani, M.; Abedini, A.; Bahmanrokh, G.; Navasery, M.; Vaziri, P. Visible Light-Induced Degradation of Methylene Blue in the Presence of Photocatalytic ZnS and CdS Nanoparticles. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 12242–12258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Huang, B.; Li, Z.; Lou, Z.; Wang, Z.; Dai, Y.; Whangbo, M.-H. Synthesis and characterization of ZnS with controlled amount of S vacancies for photocatalytic H2 production under visible light. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 8544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhu, B.; Wang, J.; Lan, H.; Chen, X. Synthesis of porous ZnS, ZnO and ZnS/ZnO nanosheets and their photocatalytic properties. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 30956–30962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, M.; Jiang, L.; Wu, L.; Zhang, M.; Wang, T. The structure control of ZnS/graphene composites and their excellent properties for lithium-ion batteries. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13384–13389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, J.C.; Ngo, C.; Prikhodko, S.; Kodambaka, S.; Li, J.L.; Richards, R. Gram-scale wet chemical synthesis of wurtzite-8H nanoporous ZnS spheres with high photocatalytic activity. Appl. Catal. B 2011, 106, 212–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyiriuka, E.C. Zinc phosphate glass surfaces studied by XPS. J. Non Cryst. Solid 1993, 163, 268–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hertl, W. Surface Chemical Properties of Zinc Sulfide. Langmuir 1988, 4, 594–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mofokeng, T.P.; Moloto, M.J.; Shumbula, P.M.; Nyamukamba, P.K.; Takaidza, S.; Marais, L. Antimicrobial Activity of Amino Acid-Capped Zinc and Copper Sulphide Nanoparticles. J. Nanotechnol. 2018, 2018, 4902675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaliha, C.; Nath, B.K.; Verma, P.K.; Kalita, E. Synthesis of functionalized Cu:ZnS nano systems and its antibacterial potential. Arab. J. Chem. 2019, 12, 515–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, A.; Han, I.; Akter, M.; Boo, J.-H.; Choi, E.H. Handy Soft Jet Plasma as an Effective Technique for Tailored Preparation of ZnS Nanomaterials and Shape Dependent Antibacterial Performance of ZnS. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2020, 90, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ananth, A.; Dharaneedharan, S.; Heo, M.-S.; Mok, Y.S. Copper oxide nanomaterials: Synthesis, characterization and structure-specific antibacterial performance. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 262, 179–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sample Name | Zn Precursor Conc. (M) | Na2S Conc. (M) | Surfactant Conc. (mM) | Surface Morphology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPA | Nitrate, 0.1 | 0.2 | - | Spherical aggregates |
| LPEN | Nitrate, 0.1 | 0.2 | PEG, 1.0 | Layered pentagon |
| 3DPEN | Chloride, 0.1 | 0.2 | - | 3D pentagon |
| NHEX | Sulfate, 0.1 | 0.2 | PVP, 1.0 | Nano-hexagon |
| Bacteria Name | Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (µg/mL) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SPA | LPEN | 3DPEN | NHEX | |
| E. coli | 125.0 | 125.0~250.0 | 125.0~250.0 | 62.5 |
| S. aureus | 62.5 | 62.5~125.0 | 62.5~125.0 | 62.5 |
| K. pneumoniae | 15.6~62.5 | 62.5 | 62.5 | 31.25 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ananth, A.; Han, I.; Choi, E.H.; Boo, J.-H. ZnS Nanomaterials with Hexagon and Pentagon Structures: Effect of Surfactants on Surface Morphology and Biosensing Application. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120419
Ananth A, Han I, Choi EH, Boo J-H. ZnS Nanomaterials with Hexagon and Pentagon Structures: Effect of Surfactants on Surface Morphology and Biosensing Application. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(12):419. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120419
Chicago/Turabian StyleAnanth, Antony, Ihn Han, Eun Ha Choi, and Jin-Hyo Boo. 2025. "ZnS Nanomaterials with Hexagon and Pentagon Structures: Effect of Surfactants on Surface Morphology and Biosensing Application" Chemosensors 13, no. 12: 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120419
APA StyleAnanth, A., Han, I., Choi, E. H., & Boo, J.-H. (2025). ZnS Nanomaterials with Hexagon and Pentagon Structures: Effect of Surfactants on Surface Morphology and Biosensing Application. Chemosensors, 13(12), 419. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13120419









