A Comprehensive Review of Non-Destructive Monitoring of Food Freshness and Safety Using NIR Spectroscopy and Biosensors: Challenges and Opportunities
Abstract
1. Introduction
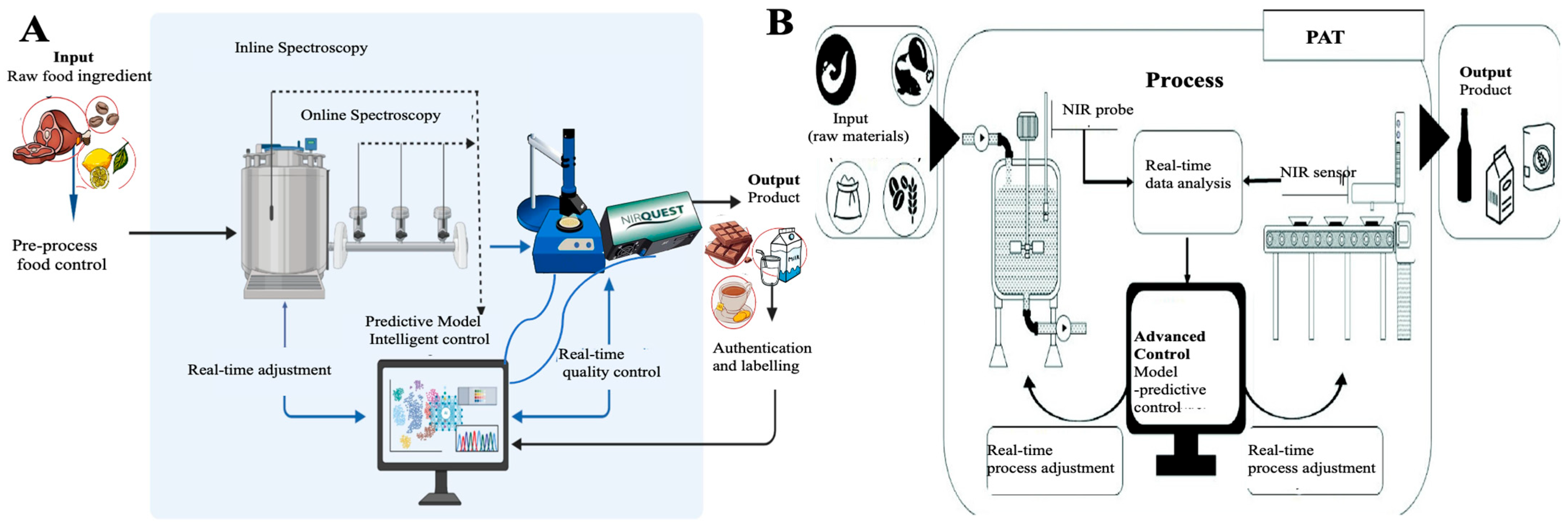
2. NIR Spectroscopy for Food Freshness and Quality
2.1. Principles of NIR Spectroscopy and Spectral Interpretation
2.2. Portable and Online NIR Systems
2.3. Chemometric Models and AI Integration
2.4. Applications Across Food Categories
| Food Product/Matrix | Analytical Target(s) | NIR System and Wavelength Range | Acquisition Mode | Sample Preparation | Chemometric/AI Model | Sample Size/Replicates | Performance Metrics | Key Findings/Notes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Eggs | Haugh Unit, (Regression) | Portable Vis-NIR (902–1810 nm) | Reflectance | Whole eggs, unwashed | PLS, PCA, PLS-DA | 180 | R2c = 0.986, Accuracy = 95% | Portable NIR devices can provide rapid, non-destructive estimation of egg freshness comparable to lab measurements. | [43] |
| Eggs | Freshness (Regression) | Smartphone-connected NIR | Reflectance | Whole egg shell intact | ANN + Savitzky–Golay | 120 | R2 = 0.83, RMSE = 1.97 days | Consumer-level smartphone-linked NIR systems can reliably predict freshness within ±2 days. | [44] |
| Pork | pH, TVB-N | Vis–NIR (400–1000 nm) | Reflectance | Fresh meat slabs | CNN–SVR, CNN–PLSR | 150 | R2 > 0.92, RPD > 3.6 | Hybrid CNN-based models improved prediction robustness, enabling inline industrial monitoring. | [35] |
| Mussels | Freshness Index, Viability (Regression) | Portable NIR (950–1650 nm) | Reflectance | Live mussels, shells intact | OPLSR | 90 | R2p = 0.91 | Detected subtle spectral changes linked to spoilage without removing shells, suitable for aquaculture logistics. | [45] |
| Preserved Eggs | TVB-N | Lab-based NIR (1000–2500 nm) | Transmittance | Sliced samples | PCA, SVR | 75 | R2p = 0.91, RMSEP = 0.38 | Adapted NIR to high-salt processed eggs for rapid spoilage screening. | [47] |
| Apples | Degradation Progress | Phase-based reflectance | Phase Reflectance (850–1700 nm) | Whole fruits | 60 | Low calibration requirement | Cost-efficient method requiring minimal calibration, ideal for field checks. | [49] | |
| Chicken Meat | Drip Loss, pH | Vis–NIR | Reflectance | Fresh chicken breasts | PLS-DA | 100 | Accuracy > 95% | Industrial applicability for real-time poultry grading. | [46] |
| Salmon | Lipid oxidation, TVB-N | Hyperspectral NIR (900–1700 nm) | Reflectance (400–1000 nm) | Whole filets, skin on | PLSR, SVM | 80 | R2p = 0.94 | Detected early spoilage and oxidation before visual signs. | [12] |
| Milk | Protein, fat content | FT-NIR (1000–2500 nm) | Transmittance | Homogenized | PLSR | 200 | R2 > 0.99 | Lab-level compositional analysis in under 1 min. | [54] |
| Cheddar Cheese | Ripening stage | Portable NIR (950–1650 nm) | Reflectance | Sliced cheese | PCA + PLS-DA | 50 | Accuracy 92% | Discriminated maturity stages for optimized flavor profiles. | [55] |
| Coffee Beans | Moisture, defects | NIR (1100–2500 nm) | Reflectance | Whole beans | ANN | 300 | R2p = 0.97 | Detected defects and optimized roasting profiles. | [56] |
| Wheat Flour | Moisture, protein | FT-NIR (1000–2500 nm) | Transmittance | Ground flour | PLSR | 250 | R2c = 0.98 | Rapid quality grading for milling operations. | [57] |
| Peanuts | Aflatoxin contamination | NIR (900–1700 nm) | Reflectance | Whole kernels | PLS-DA | 120 | Accuracy > 90% | Early detection of contaminated lots before processing. | [58] |
| Beer | Alcohol %, turbidity | FT-NIR (1000–2500 nm) | Transmittance | Degassed beer | PLSR | 60 | R2 = 0.99 | Accurate inline brewery QC. | [59] |
| Grapes | Sugar content (°Brix) | Portable NIR (900–1700 nm) | Reflectance | Intact grapes | PLSR | 150 | R2p = 0.97 | Enabled selective harvesting based on ripeness. | [60] |
| Rice | Moisture, amylose | NIR (900–1700 nm) | Reflectance | Milled grains | PLSR | 180 | R2c = 0.96 | Facilitated rapid classification for export quality compliance. | [52] |
| Honey | Adulteration detection | Portable NIR (950–1650 nm) | Transmittance | Liquid honey | PLS-DA | 100 | Accuracy = 96% | Detected multiple adulterants within 30 s. | [53] |
| Tomatoes | Lycopene, firmness | Hyperspectral NIR (900–1700 nm) | Reflectance | Intact fruits | PLSR, SVM | 90 | R2p = 0.95 | Predicted ripeness and post-harvest storage potential. | [61] |
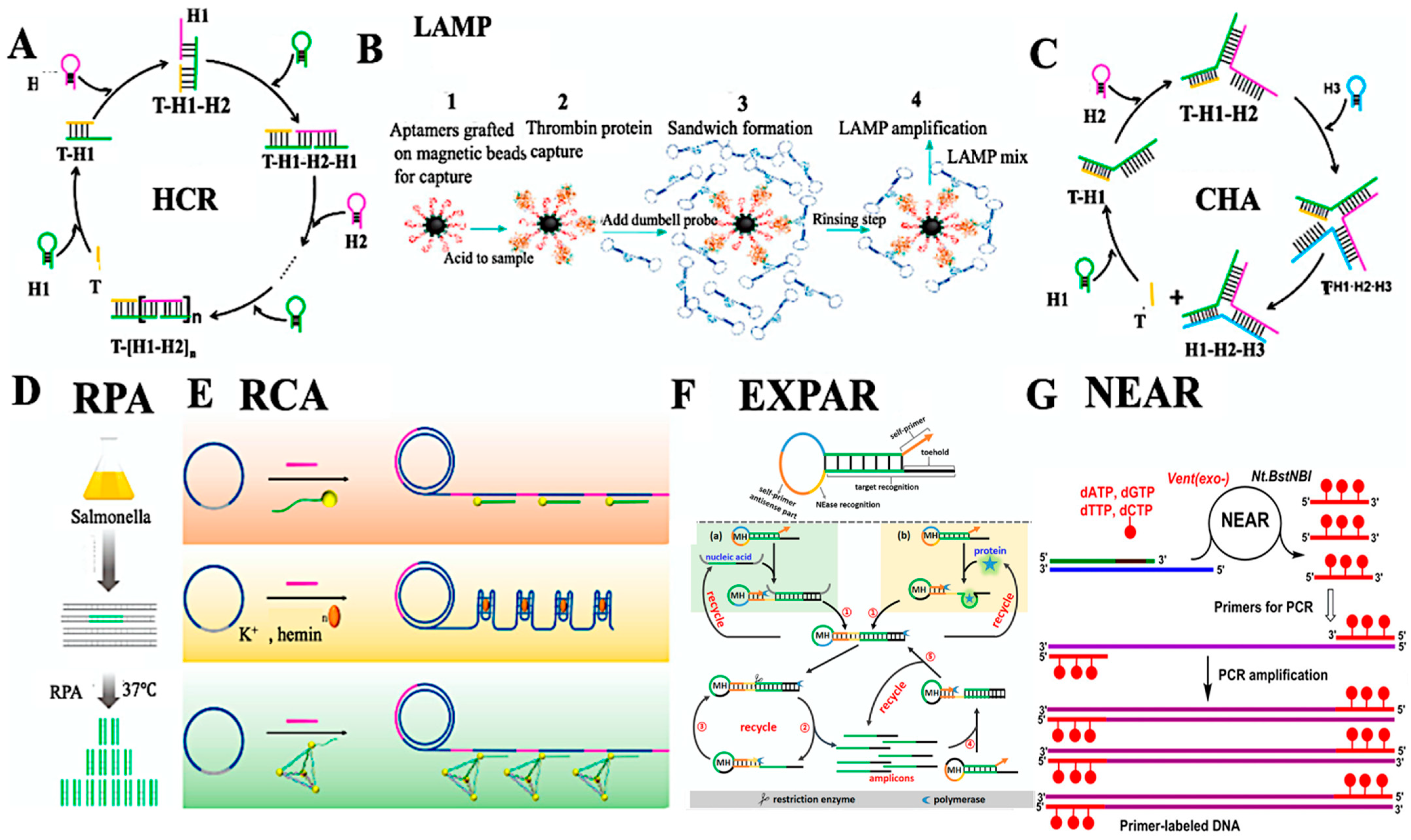
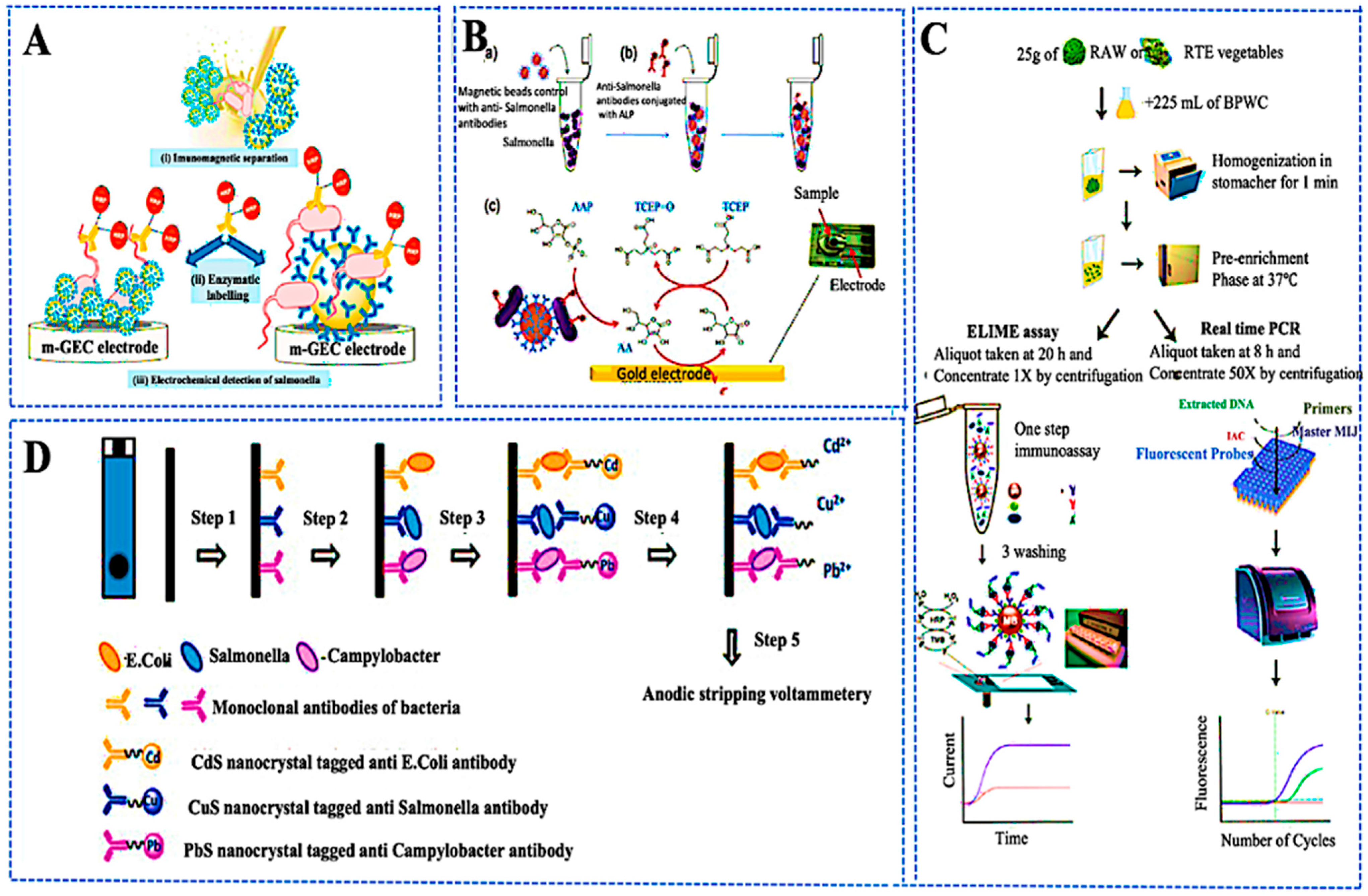
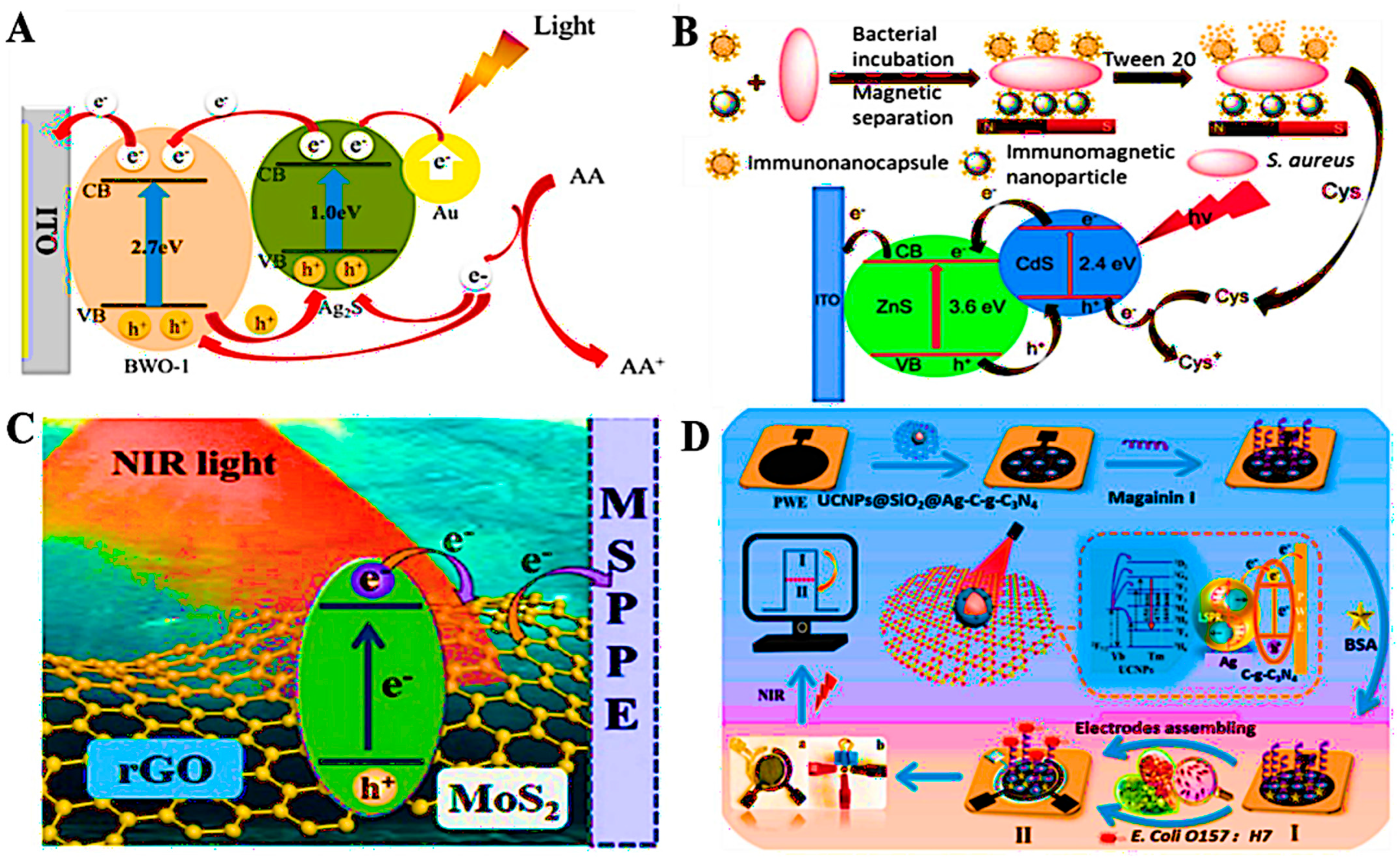
3. Biosensor Applications in Food Safety and Spoilage Detection
3.1. Overview of Biosensor Mechanisms
3.2. Detection of Pathogens, Pesticides, and Spoilage Metabolites
3.3. Optical and Electrochemical Transduction Strategies
3.4. Miniaturized and Integrated Biosensing Platforms
4. Synergistic Use of NIR Spectroscopy and Biosensors
4.1. Complementary Strengths and Integration Rationale
4.2. Hybrid Sensing Systems and Real-Time Monitoring
4.3. Real-World Applications and Hybrid Systems
4.4. Potential for Blockchain and IoT-Enabled Traceability
5. Challenges in Commercial Deployment
5.1. Calibration Transfer and Environmental Variability
5.2. Sensor Drift, Fouling, and Shelf-Life Issues
5.3. Economic and Manufacturing Constraints
5.4. Regulatory Hurdles and Market Acceptance
6. Future Directions and Innovation Potential
6.1. Advances in Wearables, Handhelds, and Wireless Platforms
6.2. AI and Cloud-Based Food Monitoring Systems
6.3. Green and Sustainable Sensing Materials
6.4. Research Needs and Industry–Policy Recommendations
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ha, Y. Advancements in gaseous sensor technology for ensuring food safety: A review. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2025, 60, vvae026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, X.; Xiao, X. Electrical impedance spectroscopy for non-destructive meat freshness assessment. Discov. Food 2024, 4, 177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, W.; Tian, Y.; Lu, D.; Chen, B. Research Progress of Applying Infrared Spectroscopy Technology for Detection of Toxic and Harmful Substances in Food. Foods 2022, 11, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, K.; Zhong, M.; Zhu, W.; Rashid, A.; Han, R.; Virk, M.S.; Duan, K.; Zhao, Y.; Ren, X. Advances in Computer Vision and Spectroscopy Techniques for Non-Destructive Quality Assessment of Citrus Fruits: A Comprehensive Review. Foods 2025, 14, 386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoriello, T.; Ciorba, R.; Ruggiero, G.; Masciola, F.; Scutaru, D.; Ciccoritti, R. Vis/NIR Spectroscopy and Vis/NIR Hyperspectral Imaging for Non-Destructive Monitoring of Apricot Fruit Internal Quality with Machine Learning. Foods 2025, 14, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hameed, I.N.S.; Badea, M.; Bano, N.; Andreescu, S.; Hayat, A.; Jubeen, F. Optical Fiber Mediated Biosensors for Multiplex and Onsite Food Safety Analysis: A Review. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2025, 172, 017522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Chen, J.; Xie, L. Optical biosensor array based on nanozyme for environmental monitoring and food safety detection: Principle, design, and application. Anal. Methods 2024, 17, 882–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y. Sensing technology empowering food safety: Research progress of SERS-assisted multimodal biosensing toward food hazard factors. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 3083–3110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Zhang, X.; Chu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Kong, F.; Ni, X.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, Q.; Zou, B. Research Progress on Nanotechnology-Driven Enzyme Biosensors for Electrochemical Detection of Biological Pollution and Food Contaminants. Foods 2025, 14, 1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhal, S.B.; Kar, D. Leveraging artificial intelligence and advanced food processing techniques for enhanced food safety, quality, and security: A comprehensive review. Discov. Appl. Sci. 2025, 7, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk, A.B.; Heathcote-Fumador, I.E.; McSey, I.A.; M’NKubitu, E.; Thomi, D.; Wainaina, S.; Taherzadeh, M.J. Food Waste Management through Machine Learning, IoT, and Blockchain, 1st ed.; Ranjna Sirohi, A.T., de Souza Vandenberghe, L.P., Taherzadeh, M.J., Pandey, A., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FA, USA, 2025; p. 30. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, C.; Zhong, Y.; Luo, Z. Applications of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy for Nondestructive Quality Analysis of Fish and Fishery Products. Foods 2024, 13, 3992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Huang, J.; Niu, Y.; Tong, H. Monitoring the Concentrations of Na, Mg, Ca, Cu, Fe, and K in Sargassum fusiforme at Different Growth Stages by NIR Spectroscopy Coupled with Chemometrics. Foods 2025, 14, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Gao, Y.; Song, J.; Ao, M. Using VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging and deep learning for non-destructive high-throughput quantification and visualization of nutrients in wheat grains. Food Chem. 2024, 461, 140651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Hieu, N.; Hien, N.L.H.; Toan, D.M.; Binh, P.; Nhat, P.M.; Anh, P.T.; Hung, L.V.; Tuong, N.H. NIRsViT: A novel deep learning model for manure identification using near-infrared-spectroscopy and imbalanced data handling. Cybern. Phys. 2024, 13, 323–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candeias, D.N.C.; de Barros, S.R.C.; Lyra, W.; Fernandes, D.D.; Diniz, P.H.G.D. Assessing the Quality of Wheat Flour Blended with Cassava Starch Using a Handheld NIR Spectrophotometer and Chemometrics. J. Braz. Chem. Soc. 2025, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamptey, F.P.; Teye, E.; Kaburi, S.A.; Flavio, O.-Y.; Amuah, C.L.Y.; Abano, E.E.; Otoo, G.S. Feasibility study on fingerprinting organic and conventional mango fruits, chips, and juice using portable near-infrared spectroscopy. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 1518–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Jiang, H.; Liu, G.; Mei, C.; Huang, Y. Identification of Radix puerariae starch from different geographical origins by FT-NIR spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Prop. 2017, 20 (Suppl. S2), 1567–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Sun, J.; Yao, K.; Dai, C. Generalized and hetero two-dimensional correlation analysis of hyperspectral imaging combined with three-dimensional convolutional neural network for evaluating lipid oxidation in pork. Food Control 2023, 153, 109940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wu, X.; Zheng, J.; Wu, B. Rapid identification of green tea varieties based on FT-NIR spectroscopy and LDA/QR. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e73022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Xu, X.; Huang, W. Monitoring of critical parameters in thermophilic solid-state fermentation process of soybean meal using NIR spectroscopy and chemometrics. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2022, 17, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Li, Z.; Bian, Z.; Jin, H. Overview of Deep Learning and Nondestructive Detection Technology for Quality Assessment of Tomatoes. Foods 2025, 14, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of mineral oil pollution in peanut oil by Fourier transform near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2024, 469, 142590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- León, L.; Ortiz, A.; Freire, M.; Mesías, F.J.; Tejerina, D. Effectiveness of handheld near infrared spectrometer for traceability of Angus steaks. Food Chem. 2024, 455, 139958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Sun, J.; Zhang, B.; Du, X.; Chen, C. On-line monitoring of egg freshness using a portable NIR spectrometer combined with deep learning algorithm. Infrared Phys. Technol. 2024, 138, 105207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilkova, D.D.; Novichenko, O.V.; Belova, M.; Kutuzov, M.N.; Nikitin, I.A. Infrared Spectroscopy as a Rapid Method the Assessment of the Shelf-Life and Freshness of Refrigerated Rainbow Trout. Storage Process. Farm Prod. 2024, 32, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Wu, X.; Yang, Y.; Wu, B.; Fu, H. Discrimination of the Red Jujube Varieties Using a Portable NIR Spectrometer and Fuzzy Improved Linear Discriminant Analysis. Foods 2022, 11, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Wu, X.; Wu, B.; Dai, C.; Fu, H. Rapid authentication of the geographical origin of milk using portable near-infrared spectrometer and fuzzy uncorrelated discriminant transformation. J. Food Process. Eng. 2022, 45, e14040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, G.; Kang, X.; Su, J.; Qiu, J. Rapid detection of fumonisin B(1) and B(2) in ground corn samples using smartphone-controlled portable near-infrared spectrometry and chemometrics. Food Chem. 2022, 384, 132487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, H.; Aru, V.; Sørensen, K.M.; Engelsen, S.B. Towards on-line cheese monitoring: Exploration of semi-hard cheeses using NIR and 1H NMR spectroscopy. Food Chem. 2024, 454, 139786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonazza, F.; Monti, L.; Povolo, M.; Gasparini, A.; Pelizzola, V.; Cabassi, G. Monitoring the Shelf Life of Hemp Seed Oil Stored at Two Temperatures in Different Materials via Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy. Molecules 2024, 29, 5577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.P.; Clément, A.; Erkinbaev, C. Miniaturized spectroscopy and AI-driven probes in food industry automation. Food Res. Int. 2025, 214, 116646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grassi, S.; Alamprese, C. Advances in NIR spectroscopy applied to process analytical technology in food industries. Curr. Opin. Food Sci. 2018, 22, 17–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fodor, M.; Matkovits, A.; Benes, E.L.; Jókai, Z. The Role of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy in Food Quality Assurance: A Review of the Past Two Decades. Foods 2024, 13, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Ning, W.; Chen, R.; Wang, H. Rapid non-destructive detection of pork freshness using visible-near infrared spectroscopy based on convolutional neural network hybrid models. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 140, 107199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C.; Chen, H.; Zeng, M.; Xue, Z. Characterization of the Freshness of Pork by Near-Infrared Spectroscopy (NIRS) and Ensemble Learning. Anal. Lett. 2024, 58, 2698–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjonaj, L.; Generalao, O.B.; Alguno, A.C.; Malaluan, R.M.; Lubguban, A.A.; Dumancas, G.G. Quantification of Argan Oil (Argania spinosa L.) Adulterated with Avocado, Flaxseed, Walnut, and Pumpkin Oils Using Fourier-Transform Infrared Spectroscopy and Advanced Chemometric and Machine Learning Techniques. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, M.; Li, X.; Liang, J.; Liao, M.; Han, Y. An effective deep learning fusion method for predicting the TVB-N and TVC contents of chicken breasts using dual hyperspectral imaging systems. Food Chem. 2024, 456, 139847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Deng, J.; Jiang, H. Markov Transition Field Combined with Convolutional Neural Network Improved the Predictive Performance of Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Models for Determination of Aflatoxin B(1) in Maize. Foods 2022, 11, 2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zou, Y.; Sun, C. Nondestructive determination of edible quality and watercore degree of apples by portable Vis/NIR transmittance system combined with CARS-CNN. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2024, 18, 4058–4073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Shi, Y.; Huang, X. Non-destructive discrimination of homochromatic foreign materials in cut tobacco based on VIS-NIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2023, 103, 4545–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yolandani; Liu, D.; Raynaldo, F.A.; Dabbour, M. Comparison of prediction models for soy protein isolate hydrolysates bitterness built using sensory, spectrofluorometric and chromatographic data from varying enzymes and degree of hydrolysis. Food Chem. 2024, 442, 138428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, P.P.; Patil, V.N. NIR Spectroscopy for Freshness Detection and Classification of Chicken Eggs. presented at the Business Data Analytics. In Proceedings of the 2024 11th International Conference on Computing for Sustainable Global Development, Piscataway, NJ, USA, 28 February–1 March 2025; pp. 23–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Shen, F.; Deng, H.; Cai, F.; Chen, S. Smartphone imaging spectrometer for egg/meat freshness monitoring. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidini, S.; Varrà, M.O.; Bersellini, D. Real-time and non-destructive control of the freshness and viability of live mussels through portable near-infrared spectroscopy. Food Control 2024, 160, 110353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, D. Mathematical modeling for freshness/spoilage of chicken breast using chemometric analysis. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2023, 7, 100590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Bao, Z.; Zhang, S.; Ran, Y. A Novel NIR-Based Strategy for Rapid Freshness Assessment of Preserved Eggs. Food Anal. Methods 2022, 15, 1457–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, J.; Jiang, H.; Chen, Q. Enhancing Fourier Transform Near-infrared Spectroscopy with Explainable Ensemble Learning Methods for Detecting Mineral Oil Contamination in Corn Oil. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2025, 143, 107594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaad, M. Non-destructive, non-invasive, in-line real-time phase-based reflectance for quality monitoring of fruit. Int. J. Smart Sens. Intell. Syst. 2020, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, S.; Sun, J.; Xin, Z.; Mao, H.; Wu, X.; Qinglin, L. Visualizing distribution of pesticide residues in mulberry leaves using NIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process. Eng. 2017, 40, e12510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zareef, M.; Chen, Q.; Hassan, M.M.; Arslan, M. An Overview on the Applications of Typical Non-linear Algorithms Coupled With NIR Spectroscopy in Food Analysis. Food Eng. Rev. 2020, 12, 173–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burestan, N.F.; Sayyah, A.H.A.; Safi, M. Prediction of amylose content, protein content, breakdown, and setback viscosity of Kadus rice and its flour by near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) analysis. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020, 45, e15069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caredda, M.; Ciulu, M.; Tilocca, F.; Langasco, I. Portable NIR Spectroscopy to Simultaneously Trace Honey Botanical and Geographical Origins and Detect Syrup Adulteration. Foods 2024, 13, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, C.; Li, W.; Wen, P.; Wang, D.; Ren, X.; Li, C.; Zhang, N.; Xu, G.; Liu, L.; Li, Y.; et al. Influence of milk storage time on mid-infrared spectroscopy and its predictions for amino acid content. J. Dairy Sci. 2025, 108, 9113–9128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seratlic, S.; Guha, B.; Moore, S. Advances in Spectroscopic Methods for Predicting Cheddar Cheese Maturity: A Review of FT-IR, NIR, and NMR Techniques. NDT 2024, 2, 392–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Sanchez, B.; Sandoval-Gonzalez, O.; Flores-Cuautle, J.D.J.A.; Landeta-Escamilla, O.; Portillo-Rodriguez, O.; Aguila-Rodriguez, G. A Study of the Physical Characteristics and Defects of Green Coffee Beans That Influence the Sensory Notes Using Machine Learning Models. Processes 2023, 12, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Guo, Z.; Ren, Z.; Wang, S.; Yue, M.; Zhang, S.; Yin, X.; Gong, K.; Ma, C. Rapid determination of protein, starch and moisture content in wheat flour by near-infrared hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 117, 105134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, M.; Xu, L.; Gao, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Jiang, S.; Cao, L.; Pang, M. Monitoring of the Physicochemical Properties and Aflatoxin of Aspergillus flavus-Contaminated Peanut Kernels Based on Near-Infrared Spectroscopy Combined with Machine Learning. Foods 2025, 14, 2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahle, E.-M.; Zarnkow, M.; Jacob, F. Beer Turbidity Part 1: A Review of Factors and Solutions. J. Am. Soc. Brew. Chem. 2021, 79, 99–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, S.; Shi, J. Advancing food safety and quality assessment: A comprehensive review of non-destructive analytical technologies. Anal. Methods 2025, 17, 4697–4717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Lu, L.-M.; Zhao, X.-H.; Hu, D.-Y.; Tang, T.-Y.; Tang, Y.-L. Nondestructive detection of tomato quality based on multiregion combination model. J. Food Process. Eng. 2022, 45, e14100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Liu, Y.; Du, X.; Gui, Y.; He, J.; Xie, F.; Cai, J. Recent Advances in Design and Application of Nanomaterials-Based Colorimetric Biosensors for Agri-food Safety Analysis. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 46346–46361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aubret, M.; Savonnet, M.; Laurent, P.; Roupioz, Y.; Cubizolles, M.; Buhot, A. Development of an Innovative Quantification Assay Based on Aptamer Sandwich and Isothermal Dumbbell Exponential Amplification. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 3376–3385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zheng, T.; Xie, Y.N.; Li, F.; Jiang, X.; Hou, X.; Wu, P. Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Coupled with a Photosensitization Colorimetric Assay for Fast Salmonella spp. Testing. Testing. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 6559–6566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Chen, M.; Peng, Y.; Bai, J.; Li, S.; Han, D.; Ren, S.; Qin, K.; et al. Dual Sensitization Smartphone Colorimetric Strategy Based on RCA Coils Gathering Au Tetrahedra and Its Application in the Detection of CK-MB. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 16922–16931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, D.; Huang, T.; Yang, Z.; Liu, B.; Sun, M.; Chen, J.-X.; Dai, Z.; Zou, X. Isothermal Self-Primer EXPonential Amplification Reaction (SPEXPAR) for Highly Sensitive Detection of Single-Stranded Nucleic Acids and Proteins. Anal. Chem. 2021, 93, 12707–12713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ménová, P.; Raindlová, V.; Hocek, M. Scope and Limitations of the Nicking Enzyme Amplification Reaction for the Synthesis of Base-Modified Oligonucleotides and Primers for PCR. Bioconjugate Chem. 2013, 24, 1081–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Wei, Z.; Zheng, X.; Zhu, J. Advancements in magnetic nanomaterial-assisted sensitive detection of foodborne bacteria: Dual-recognition strategies, functionalities, and multiplexing applications. Food Chem. 2025, 478, 143626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X. A DNA tetrahedral scaffolds-based electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of AFB1 and OTA. Food Chem. 2023, 442, 138312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Wu, X.; Jayan, H. Recent developments and applications of surface enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy in safety detection of fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2024, 434, 137469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Y.; Shi, Y.; Wang, T.; Ji, S. Quantum dots as advanced nanomaterials for food quality and safety applications: A comprehensive review and future perspectives. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e13339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Huang, A.; He, L.; Cai, C.; You, T. Recent advances in foodborne pathogen detection using photoelectrochemical biosensors: From photoactive material to sensing strategy. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2024, 8, 1432555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, S.; Zhou, R.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, X.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Chen, S.; Niu, L.; Li, X.; Guo, Z.; Zou, X. Magnetic nanoparticle-based immunosensors and aptasensors for mycotoxin detection in foodstuffs: An update. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2023, 23, e13266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, K.; Lin, J. Optical biosensors for the detection of foodborne pathogens: Recent development and future prospects. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 177, 117785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zhu, W.; Li, L.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, X.; Hao, N.; Guo, Y.; Wang, K. A colorimetric biosensor for simultaneous ochratoxin A and aflatoxins B1 detection in agricultural products. Food Chem. 2020, 319, 126544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandão, D.; Liébana, S.; Campoy, S.; Alegret, S.; Pividori, M.I. Immunomagnetic separation of Salmonella with tailored magnetic micro and nanocarriers. A comparative study. Talanta 2015, 143, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wang, Z.; Chen, J.; Kinchla, A.J.; Nugen, S.R. Rapid detection of Salmonella using a redox cycling-based electrochemical method. Food Control 2016, 62, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabiani, L.; Pucci, E.; Delibato, E.; Volpe, G.; Piermarini, S.; De Medici, D.; Capuano, F.; Palleschi, G. ELIME assay vs Real-Time PCR and conventional culture method for an effective detection of Salmonella in fresh leafy green vegetables. Talanta 2017, 166, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viswanathan, S.; Rani, C.; Ho, J.-A.A. Electrochemical immunosensor for multiplexed detection of food-borne pathogens using nanocrystal bioconjugates and MWCNT screen-printed electrode. Talanta 2012, 94, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhai, X.; Zou, X.; Shi, J.; Huang, X.; Li, Z.; Gong, Y.; Holmes, M.; Povey, M.; Xiao, J. Bilayer pH-sensitive colorimetric films with light-blocking ability and electrochemical writing property: Application in monitoring crucian spoilage in smart packaging. Food Chem. 2021, 336, 127634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Guo, C.; Sun, L.; Zuo, M.; Chen, Q.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X. Identification of the apple spoilage causative fungi and prediction of the spoilage degree using electronic nose. J. Food Process. Eng. 2021, 44, e13816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonah, E.; Huang, X.; Aheto, J.H.; Osae, R. Application of electronic nose as a non-invasive technique for odor fingerprinting and detection of bacterial foodborne pathogens: A review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 57, 1977–1990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Liu, D.; Li, Y.; Dong, N.; Chen, T.; You, T. Engineering the Signal Transduction between CdTe and CdSe Quantum Dots for in Situ Ratiometric Photoelectrochemical Immunoassay of Cry1Ab Protein. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 13583–13591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hao, H.; Zhang, Z.; Ding, C.; Zhang, G.; Bi, J.; Yan, S.; Liu, G.; Hou, H. A novel photoelectrochemical aptamer sensor based on rare-earth doped Bi2WO6 and Ag2S for the rapid detection of Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microchem. J. 2021, 165, 106132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, X.; Wang, H.; Deng, W.; Tan, Y.; Ma, M.; Xie, Q. Sensitive photoelectrochemical immunoassay of Staphylococcus aureus based on one-pot electrodeposited ZnS/CdS heterojunction nanoparticles. Analyst 2019, 145, 165–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, R.; Lin, X.; Dai, H.; Wei, J.; Jiao, T.; Chen, Q.; Oyama, M.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X. Photoelectrochemical Sensors with Near-Infrared-Responsive Reduced Graphene Oxide and MoS2 for Quantification of Escherichia Coli O157:H7. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2022, 14, 41649–41658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, M.; Liu, C.; Ge, R.; Fang, Y.; Wei, J.; Chen, X.; Chen, Q.; Chen, X. Paper-supported near-infrared-light-triggered photoelectrochemical platform for monitoring Escherichia coli O157:H7 based on silver nanoparticles-sensitized-upconversion nanophosphors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 203, 114022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.; He, Y.; Yuan, B.; Li, L.; Luo, L.; You, T. Simultaneous detection of multiple mycotoxins in agricultural products: Recent advances in optical and electrochemical sensing methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2024, 23, e70062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Huang, C.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Shen, J.; Han, E. Structure-Switching Electrochemical Aptasensor for Single-Step and Specific Detection of Trace Mercury in Dairy Products. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 10106–10112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, X.; Li, Z.; Zhang, J.; Shi, J.; Zou, X.; Huang, X.; Zhang, D.; Sun, Y.; Yang, Z.; Holmes, M.; et al. Natural Biomaterial-Based Edible and pH-Sensitive Films Combined with Electrochemical Writing for Intelligent Food Packaging. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018, 66, 12836–12846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Fan, L.; Chen, Y.; Zeng, Y.; Yu, Z.; Dong, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, C.; Ye, C. Application of visual intelligent labels in the assessment of meat freshness. Food Chem. 2024, 460, 140562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Haruna, S.A.; Ahmad, W.; Wu, J.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q. Tunable multiplexed fluorescence biosensing platform for simultaneous and selective detection of paraquat and carbendazim pesticides. Food Chem. 2022, 388, 132950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Xie, R.; Hao, Y.; Pang, J.; Gao, H.; Qu, F.; Tian, M.; Guo, C.; Mao, B.; Chai, F. Portable smartphone-integrated AuAg nanoclusters electrospun membranes for multivariate fluorescent sensing of Hg2+, Cu2+ and l-histidine in water and food samples. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, H.; Yin, L.; Xue, S.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Raman spectroscopy-based microfluidic platforms: A promising tool for detection of foodborne pathogens in food products. Food Res. Int. 2024, 180, 114052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Xu, P.; Sanchez, S.; Duran, P.; Andreazza, F.; Isaacs, R.; Dong, K. Behavioral and physiological responses of Drosophila melanogaster and D. suzukii to volatiles from plant essential oils. Pest Manag. Sci. 2021, 77, 3698–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naik, A.; Lee, H.S.; Herrington, J.; Barandun, G.; Flock, G.; Güder, F.; Gonzalez-Macia, L. Smart Packaging with Disposable NFC-enabled Wireless Gas Sensors for Monitoring Food Spoilage. ACS Sensors 2024, 9, 6789–6799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peddareddigari, S.; Vijayan, S.V.H.; Annamalai, M. IoT, Blockchain, Big Data and Artificial Intelligence (IBBA) Framework—For Real-Time Food Safety Monitoring. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Al, A.; Newaz, H. NANOTECHNOLOGY-ENABLED FOOD SAFETY: INNOVATIVE SOLUTIONS FOR AGRICULTURAL DEVELOPMENT, SMART PACKAGING, DELIVERY SYSTEMS, AND FOOD SECURITY. Nanotechnol. Percept. 2024, 20, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meliana, C.; Liu, J.; Show, P.L.; Low, S.S. Biosensor in smart food traceability system for food safety and security. Bioengineered 2024, 15, 2310908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Lin, H.; Xu, P.; Bi, X.; Sun, L. Egg Freshness Evaluation Using Transmission and Reflection of NIR Spectroscopy Coupled Multivariate Analysis. Foods 2021, 10, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, S.; Pan, T.; Li, G. Evaluation of the physicochemical content and solid-state fermentation stage of Zhenjiang aromatic vinegar using near-infrared spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Eng. 2020, 16, 20200127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Zou, X.B.; Xiao, J.B.; Mahunu, G.K.; Shi, J.Y.; Jun-Li Xu, J.-L.; Sun, D.-W. Recent Progress in Rapid Analyses of Vitamins, Phenolic, and Volatile Compounds in Foods Using Vibrational Spectroscopy Combined with Chemometrics: A Review. Food Anal. Methods 2019, 12, 2361–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Huang, W.; Peng, Y.; Chen, Q.; Ouyang, Q.; Zhao, J. Color compensation and comparison of shortwave near infrared and long wave near infrared spectroscopy for determination of soluble solids content of ‘Fuji’ apple. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2016, 115, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingting, S.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y.; Li, Z.H.; Huang, X.W.; Xu, Y.W.; Chen, W. Determination Geographical Origin and Flavonoids Content of Goji Berry Using Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Chemometrics. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 68–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Zhou, J.; Fu, R.; Cui, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Jiao, B.; He, Y. Multicolor colorimetric detection of ochratoxin A via structure-switching aptamer and enzyme-induced metallization of gold nanorods. Food Chem. 2020, 320, 126607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Lv, Y.; Qi, S.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Z. Sensitive colorimetric aptasensor based on stimuli-responsive metal-organic framework nano-container and trivalent DNAzyme for zearalenone determination in food samples. Food Chem. 2022, 371, 131145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerdsri, J.; Thunkhamrak, C.; Jakmunee, J. Development of a colorimetric aptasensor for aflatoxin B1 detection based on silver nanoparticle aggregation induced by positively charged perylene diimide. Food Control 2021, 130, 108323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.; Foda, M.F.; He, J.; Zhou, J.; Cai, J. Robust and facile label-free colorimetric aptasensor for ochratoxin A detection using aptamer-enhanced oxidase-like activity of MnO2 nanoflowers. Food Chem. 2023, 401, 134144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.J.; Hu, X.T.; Huang, X.W.; Zhang, X.N.; Zou, X.B.; Shi, J.Y. A visible colorimetric sensor array based on chemo-responsive dyes and chemometric algorithms for real-time potato quality monitoring systems. Food Chem. 2023, 405, 134717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Xiao, H.D.; Jayan, H.; Majeed, U.; Ashiagbor, K.; Jiang, S.Q.; Zou, X.B. Multi-sensor fusion and deep learning for batch monitoring and real-time warning of apple spoilage. Food Control 2025, 172, 111174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Gómez, P.L.; Alzamora, S.M.; Zou, X.; Guo, Z. Enhanced composite Co-MOF-derived sodium carboxymethyl cellulose visual films for real-time and in situ monitoring fresh-cut apple freshness. Food Hydrocoll. 2024, 157, 110475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Chen, X.; Dai, J.; Cui, H.; Lin, L. A pH indicator film based on dragon fruit peel pectin/cassava starch and cyanidin/alizarin for monitoring the freshness of pork. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2023, 40, 101215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Huang, C.; Lu, F.; Ye, X.; Ma, H. In-situ and real-time monitoring of two-stage enzymatic preparation of ACE inhibitory peptides from Cordyceps militaris medium residues by ultrasonic-assisted pretreatment. Food Chemistry 2023, 418, 135886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Ding, Y.; Hu, F.; Liu, Z.; Lin, X.; Fu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, Z.-H.; Ma, H.; Gao, X. Constructing in-situ and real-time monitoring methods during soy sauce production by miniature fiber NIR spectrometers. Food Chem. 2023, 418, 135886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Liu, C.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Q.; Lu, M.; Bi, S.; Jing, Z.; Yu, Q.; Peng, W. Label-Free Near-Infrared Plasmonic Sensing Technique for DNA Detection at Ultralow Concentrations. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhai, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, C.; Zou, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Huang, X. Facile fabrication of three-dimensional gold nanodendrites decorated by silver nanoparticles as hybrid SERS-active substrate for the detection of food contaminants. Food Control 2021, 122, 107772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, Z.; Zhang, W.; Arslan, M.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Shi, J.; Zou, X. Ratiometric Fluorescent Metal–Organic Framework Biosensor for Ultrasensitive Detection of Acrylamide. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2022, 70, 10065–10074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anzevino, M.; Marra, D.; Fulgione, A.; Giarra, A.; Nava, D.; Biondi, L.; Capuano, F.; Iannotti, V.; Della Ventura, B.; Velotta, R. Antibody-Functionalized Gold Nanoparticles as a Highly Sensitive Two-Step Colorimetric Biosensor for Detecting Salmonella Typhimurium in Food. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2024, 7, 21048–21056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konstantinou, L.; Varda, E.; Apostolou, T.; Loizou, K.; Dougiakis, L.; Inglezakis, A.; Hadjilouka, A. A Novel Application of B.EL.D™ Technology: Biosensor-Based Detection of Salmonella spp. in Food. Biosensors 2024, 14, 582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.-H.; Wang, S.; Cheng, L.; Ma, H.; Gao, X.; Brennan, C.S.; Yan, J.-K. Micro-nano-bubble technology and its applications in food industry: A critical review. Food Rev. Int. 2023, 39, 4213–4235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farka, Z.; Juřík, T.; Pastucha, M.; Kovář, D.; Lacina, K.; Skládal, P. Rapid Immunosensing of Salmonella Typhimurium Using Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy: The Effect of Sample Treatment. Electroanalysis 2016, 28, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wang, R.; Li, Y. Rapid detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7 and Salmonella Typhimurium in foods using an electrochemical immunosensor based on screen-printed interdigitated microelectrode and immunomagnetic separation. Talanta 2016, 148, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Punbusayakul, N.; Talapatra, S.; Ajayan, P.M.; Surareungchai, W. Label-free as-grown double wall carbon nanotubes bundles for Salmonella typhimuriumimmunoassay. Chem. Central J. 2013, 7, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhao, H.; Xu, M.; Ma, Q.; Ai, S. A label-free electrochemical impedance immunosensor based on AuNPs/PAMAM-MWCNT-Chi nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode for detection of Salmonella typhimurium in milk. Food Chem. 2013, 141, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Hao, X.; Mi, J.; Cao, Y.; Shi, J. A highly sensitive AgNPs/Ni3(HHTP)2 SERS substrate for the detection of food additives and pesticide residues. Phys. Scr. 2024, 99, 105604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Macadaeg, F.; Armstrong, P.R.; Maghirang, E.B.; Scully, E.D.; Brabec, D.L.; Arthur, F.H.; Adviento-Borbe, A.D.; Yaptenco, K.F.; Suministrado, D.C. Developing a Multi-Spectral NIR LED-Based Instrument for the Detection of Pesticide Residues Containing Chlorpyrifos-Methyl in Rough, Brown, and Milled Rice. Sensors 2024, 24, 4055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Yuan, J.; Khan, I.M.; Zhang, L.; Ma, P.; Wang, Z. Research progress of aptasensor technology in the detection of foodborne pathogens. Food Control 2023, 153, 109891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, L.; Sharanagat, V.S. Application of biosensors against food-borne pathogens. Nutr. Food Sci. 2023, 54, 207–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giussani, B.; Riu, J. Biosensors and Smart Analytical Systems in Food Quality and Safety: Status and Perspectives. Foods 2023, 12, 2292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, R.; Rathore, N.; Parihar, K.; Chauhan, M.S.; Binani, S.; Kumar, N. Unveiling the Nano World: Expanding Food Safety Monitoring Through Nano-biosensor Technology. J. Food Chem. Nanotechnol. 2024, 10, S94–S100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Zuo, J.; Yang, C.; Jiang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Ping, J.; Li, P. Current trends in biosensors for biotoxins (mycotoxins, marine toxins, and bacterial food toxins):principles, application, and perspective. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 165, 117144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadak, S.; Silah, H.; Uslu, B. Detection of Toxins in Food by Biosensors. In Biosensing Technology for Human Health: Eco-Friendly Materials and Real-World Applications; Manjunatha, J.G., Ed.; Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2024; Volume 27. [Google Scholar]
- D’Almeida, A.P.; de Albuquerque, T.L. Innovations in Food Packaging: From Bio-Based Materials to Smart Packaging Systems. Processes 2024, 12, 2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussa, L.; Hassan, H.F.; Savvaidis, I.N.; Karam, L. Impact of source, packaging and presence of food safety management system on heavy metals levels in spices and herbs. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0307884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, K.P.N.; Kumar, D.; Sharma, S.K. Aptasensors for Food Safety Fundamentals and Applications. In Aptasensors for Food Safety Fundamentals and Applications; Raju Khan, A.S., Sharma, R., Rajput, Y.S., Eds.; CRC Press; Boca Raton, FA, USA, 2024; Volmue 25.
- Nsanzabera, F.; Mwiseneza, A.; Irakoze, E.; Nsengiyumva, J.B.; Nduwayezu, B.; Manishimwe, A.; Nkurikiyimana, F. Emerging Trends of Immunosensors Development for Detection of Food Toxins. Turk. J. Agric.-Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 12, 1046–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guruprasath, N.; Sankarganesh, P.; Adeyeye, S.A.O.; Babu, A.S.; Parthasarathy, V. Review on emerging applications of nanobiosensor in food safety. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 3950–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Ramírez, A.Y.; González-Estrada, R.R.; Chacón-López, M.A.; García-Magaña, M.d.L.; Montalvo-González, E.; Álvarez-López, A.; Rodríguez-López, A.; López-García, U.M. Detection of foodborne pathogens in contaminated food using nanomaterial-based electrochemical biosensors. Anal. Biochem. 2024, 693, 115600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, M.; Lv, X.; Wang, K.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, X. Advancements in Chemical and Biosensors for Point-of-Care Detection of Acrylamide. Sensors 2024, 24, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Kaur, S.; Kayabasi, A.; Ranjbaran, M.; Rath, I.; Benschikovski, I.; Raut, B.; Ra, K.; Rafiq, N.; Verma, M.S. A portable, easy-to-use paper-based biosensor for rapid in-field detection of fecal contamination on fresh produce farms. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, 259, 116374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popoola, O.; Finny, A.; Dong, I.; Andreescu, S. Smart and Sustainable 3D-Printed Nanocellulose-Based Sensors for Food Freshness Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 60920–60932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trinh, T.N.D.; Nguyen, H.A.; Thi, N.P.A.; Nam, N.N.; Tran, N.K.S.; Trinh, K.T.L. Biosensors for Seafood Safety Control—A Review. Micromachines 2024, 15, 1509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Wang, H.; Li, G.; Li, J.; Zhang, F.; Wu, Y.; Weng, Z. Multiplex detection methods for mycotoxins in agricultural products: A systematic review. Food Control 2023, 158, 110207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szelenberger, R.; Cichoń, N.; Zajaczkowski, W.; Bijak, M. Application of Biosensors for the Detection of Mycotoxins for the Improvement of Food Safety. Toxins 2024, 16, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, W.; Lim, S. A Review on Gas Indicators and Sensors for Smart Food Packaging. Foods 2024, 13, 3047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, L.; Battino, M.; Farag, M.A.; Xiao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Gao, H.; Jiang, W. Blockchain: An emerging novel technology to upgrade the current fresh fruit supply chain. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 124, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mu, R.; Hong, X.; Ni, Y.; Li, Y.; Pang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xiao, J.; Zheng, Y. Recent trends and applications of cellulose nanocrystals in food industry. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 93, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, S.; Li, J.; Xia, Y.; Tian, X.; Guo, Z.; Huang, W. Long-term evaluation of soluble solids content of apples with biological variability by using near-infrared spectroscopy and calibration transfer method. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2019, 151, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.; Hou, X.; Tang, Y.; He, R.; Mintah, B.K.; Dabbour, M.; Ma, H. Monitoring of polypeptide content in the solid-state fermentation process of rapeseed meal using NIRS and chemometrics. J. Food Process. Eng. 2018, 41, e12853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.-Y.; Aheto, J.H.; Bai, J.-W.; Dai, C.; Ren, Y.; Chang, X. Quantitative analysis and visualization of moisture and anthocyanins content in purple sweet potato by Vis–NIR hyperspectral imaging. J. Food Process. Preserv. 2021, 45, e15128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, H.E.; Xiaobo, Z.; Tinting, S.; Jiyong, S.; Mariod, A.A. Near-Infrared (NIR) Spectroscopy for Rapid Measurement of Antioxidant Properties and Discrimination of Sudanese Honeys from Different Botanical Origin. Food Anal. Methods 2016, 9, 2631–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Chen, N.; Yang, J.; Yang, B.; Ouyang, Z.; Wu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, W.; Chen, M. An integrated approach combining HPLC, GC/MS, NIRS, and chemometrics for the geographical discrimination and commercial categorization of saffron. Food Chem. 2018, 253, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahir, H.E.; Arslan, M.; Mahunu, G.K.; Mariod, A.A.; Wen, Z.; Xiaobo, Z.; Xiaowei, H.; Jiyong, S.; El-Seedi, H. Authentication of the geographical origin of Roselle (Hibiscus sabdariffa L) using various spectroscopies: NIR, low-field NMR and fluorescence. Food Control 2020, 114, 107231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoaib, M.; Li, H.; Zareef, M.; Khan, I.M.; Iqbal, M.W.; Niazi, S.; Raza, H.; Yan, Y.; Chen, Q. Recent Advances in Food Safety Detection: Split Aptamer-Based Biosensors Development and Potential Applications. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 4397–4424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Huang, X.; Zou, X.; Tan, W.; Zhang, X.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; et al. Impedimetric aptasensor based on highly porous gold for sensitive detection of acetamiprid in fruits and vegetables. Food Chem. 2020, 322, 126762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Tahir, H.E.; Zou, X.; Wang, P. Rapid and wide-range determination of Cd(II), Pb(II), Cu(II) and Hg(II) in fish tissues using light addressable potentiometric sensor. Food Chem. 2017, 221, 541–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhao, C.; Zhao, Q.; Yang, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, K.; Qian, J.; Long, L. Construction of a Colorimetric and Near-Infrared Ratiometric Fluorescent Sensor and Portable Sensing System for On-Site Quantitative Measurement of Sulfite in Food. Foods 2024, 13, 1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.M.; He, P.; Xu, Y.; Zareef, M.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Rapid detection and prediction of chloramphenicol in food employing label-free HAu/Ag NFs-SERS sensor coupled multivariate calibration. Food Chem. 2022, 374, 131765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Jiang, H.; Lin, J.; Chen, Q.; Ali, S.; Teng, S.W.; Zuo, M. Rice Freshness Identification Based on Visible Near-Infrared Spectroscopy and Colorimetric Sensor Array. Food Anal. Methods 2021, 14, 1305–1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golly, M.K.; Ma, H.; Sarpong, F.; Dotse, B.P.; Oteng-Darko, P.; Dong, Y. Shelf-life extension of grape (Pinot noir) by xanthan gum enriched with ascorbic and citric acid during cold temperature storage. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 4867–4878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anandkumar, A.; Li, J.; Prabakaran, K.; Jia, Z.X.; Leng, Z.; Nagarajan, R.; Du, D. Accumulation of toxic elements in an invasive crayfish species (Procambarus clarkii) and its health risk assessment to humans. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2020, 88, 103449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
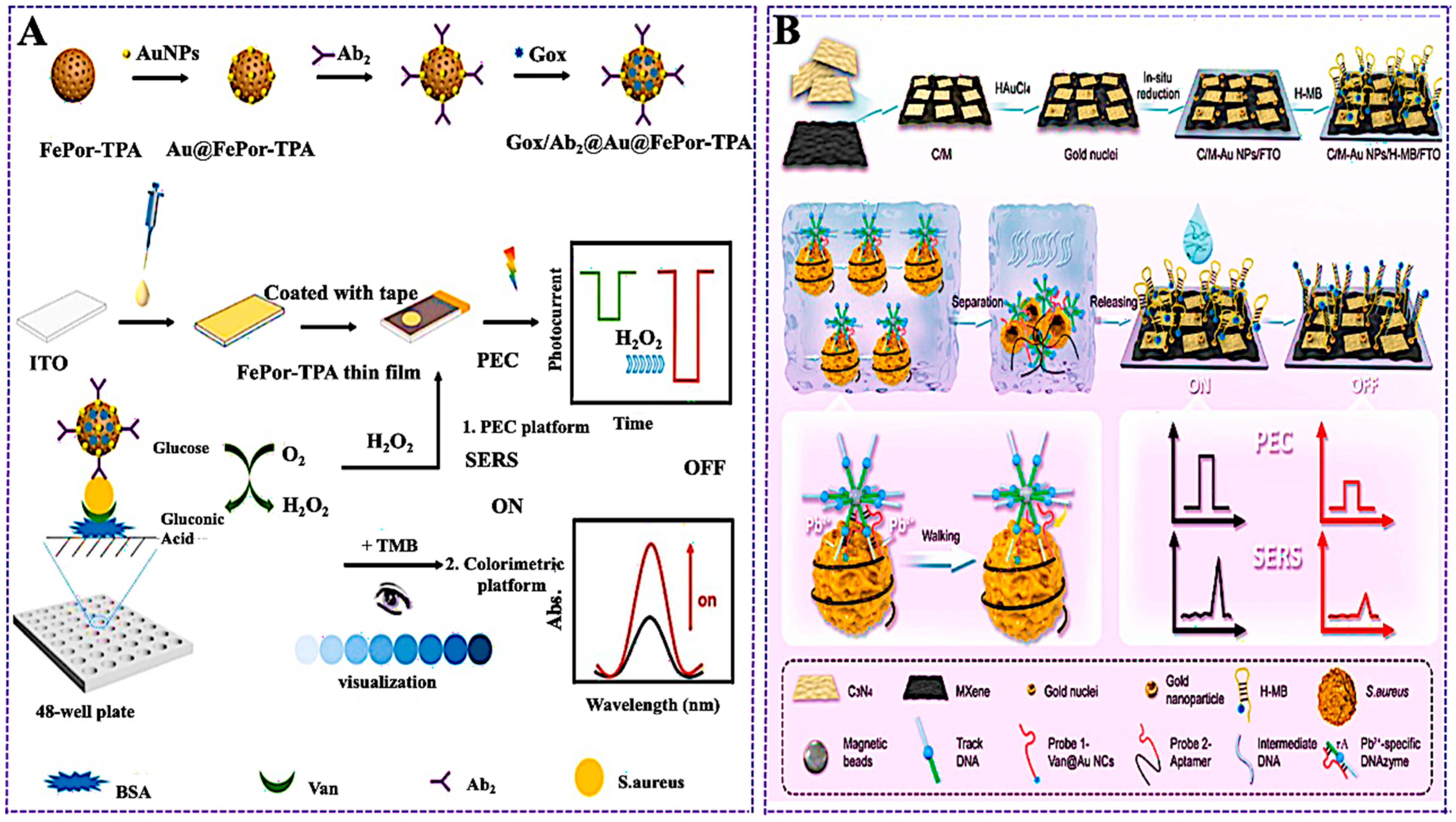
- Zheng, Z.; Ma, L.; Li, B.; Zhang, X. Dual-Modal Biosensor for Staphylococcus aureus Detection Based on a Porphyrin-Based Porous Organic Polymer FePor-TPA with Excellent Peroxidase-like, Catalase-like, and Photoelectrochemical Properties. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 13855–13863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhao, J.; Liu, X.; Zhen, X.; Feng, Q.; Gu, Y.; Yang, G.; Qu, L.; Zhu, J.-J. PEC-SERS Dual-Mode Detection of Foodborne Pathogens Based on Binding-Induced DNA Walker and C3N4/MXene-Au NPs Accelerator. Anal. Chem. 2023, 95, 14297–14307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Barimah, A.O.; Shujat, A.; Zhang, Z.; Ouyang, Q.; Shi, J.; El-Seedi, H.R.; Zou, X.; Chen, Q. Simultaneous quantification of active constituents and antioxidant capability of green tea using NIR spectroscopy coupled with swarm intelligence algorithm. Lwt-Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 129, 109510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Yuan, H.; Zhao, J.; Chen, Q. Prediction of black tea fermentation quality indices using NIRS and nonlinear tools. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 26, 853–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zabed, H.M.; Zhao, M.; Qi, X. Biosensor-Assisted Evolution of a β-Glucosidase for Enzymatic Robustness and In Vivo Cellobiose Metabolism in Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2025, 73, 12392–12402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Du, X.; Li, D.; Wang, X.; Xu, C.; Zhang, C.; Sun, A.; Schmidt, S.; Liu, X. Seasonal occurrence and abundance of norovirus in pre- and postharvest lettuce samples in Nanjing, China. LWT 2021, 152, 112226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.-S.; Li, L.; Wang, H.; Rui, J.; Cui, D. Synthesis and cholesterol-reducing potential of water-soluble phytosterol derivative. J. Funct. Foods 2019, 60, 103428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Venkitasamy, C.; Wu, B.; Pan, Z.; Ma, H. Effect of pulsed light on activity and structural changes of horseradish peroxidase. Food Chem. 2017, 234, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raynaldo, F.A.; Ackah, M.; Ngea, G.L.N.; Yolandani; Rehman, S.A.; Yang, Q.; Wang, K.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H. The potentiality of Wickerhamomyces anomalus against postharvest black spot disease in cherry tomatoes and insights into the defense mechanisms involved. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2024, 209, 112699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Mao, X.; Sun, Y.; Rajivgandhi, G.; Cui, H. Antibacterial properties of nanofibers containing chrysanthemum essential oil and their application as beef packaging. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 292, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Hortal, M.D.; Romero-Márquez, J.M.; Jiménez-Trigo, V.; Xiao, J.; Giampieri, F.; Forbes-Hernández, T.Y.; Grosso, G.; Battino, M.; Sánchez-González, C.; Quiles, J.L. Molecular bases for the use of functional foods in the management of healthy aging: Berries, curcumin, virgin olive oil and honey; three realities and a promise. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 11967–11986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Padalkar, G.; Mandlik, R.; Sudhakaran, S.; Vats, S.; Kumawat, S.; Kumar, V.; Kumar, V.; Rani, A.; Ratnaparkhe, M.B.; Jadhav, P.; et al. Necessity and challenges for exploration of nutritional potential of staple-food grade soybean. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2022, 117, 105093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngea, G.L.N.; Yang, Q.; Castoria, R.; Zhang, X.; Routledge, M.N.; Zhang, H. Recent trends in detecting, controlling, and detoxifying of patulin mycotoxin using biotechnology methods. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2020, 19, 2447–2472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, Y.; Ponpandian, L.N.; Zhang, G.; Yun, J.; Qi, X. Harnessing l-arabinose isomerase for biological production of d-tagatose: Recent advances and its applications. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 107, 16–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, L.; Wen, S.; Ye, Q.; Lou, H.; Gao, Y.; Bajpai, V.K.; Carpena, M.; Prieto, M.-A.; Simal-Gandara, J.; Xiao, J.; et al. Advances on delta 5-unsaturated-polymethylene-interrupted fatty acids: Resources, biosynthesis, and benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2022, 63, 767–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, K.; Sun, J.; Cheng, J.; Xu, M.; Chen, C.; Zhou, X. Nondestructive detection of S-ovalbumin content in eggs using portable NIR spectrometer and MPA-CARS. J. Food Process. Eng. 2023, 46, e14186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Xu, Y.; Sayada, J.; Zareef, M.; Shoaib, M.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Chen, Q. Progress of machine learning-based biosensors for the monitoring of food safety: A review. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2025, 267, 116782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimitrakopoulou, M.-E.; Garre, A. AI’s Intelligence for Improving Food Safety: Only as Strong as the Data that Feeds It. Curr. Food Sci. Technol. Rep. 2025, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayan, H.; Min, W.; Guo, Z. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Food Industry. Foods 2025, 14, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, S.; Zhang, X.; El-Mesery, H.S.; Lu, W.; Dai, X.; Xu, R. Electrochemical Biosensors Driving Model Transformation for Food Testing. Foods 2025, 14, 2669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, B.; Tan, G.; Muhammad, R.; Liu, J.; Bi, J. AI-Powered Innovations in Food Safety from Farm to Fork. Foods 2025, 14, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teixeira, S.C.; Gomes, N.O.; Oliveira, T.V.D.; Fortes-Da-Silva, P.; Soares, N.D.F.F.; Raymundo-Pereira, P.A. Review and Perspectives of sustainable, biodegradable, eco-friendly and flexible electronic devices and (Bio)sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2023, 14, 100371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Maiti, P.; Advances, M. Paper-based sustainable biosensors. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 3563–3586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, A.; Aguilar, M.R.; Arachchillage, K.G.G.P.; Chandra, S.; Rangan, S.; Gupta, S.G.; Vivancos, J.M.A. Biosensors for Public Health and Environmental Monitoring: The Case for Sustainable Biosensing. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2024, 12, 10296–10312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Bhardwaj, S.; Tiwari, P.; Dev, K.; Ghosh, K.; Maji, P.K. Recent advances in cellulose nanocrystals-based sensors: A review. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 2622–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otero, P.; Garcia-Oliveira, P.; Carpena, M.; Barral-Martinez, M.; Chamorro, F.; Echave, J.; Garcia-Perez, P.; Cao, H.; Xiao, J.; Simal-Gandara, J.; et al. Applications of by-products from the olive oil processing: Revalorization strategies based on target molecules and green extraction technologies. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 116, 1084–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Adeyanju, A.A.; Nwonuma, C.O.; Inyinbor, A.A.; Alejolowo, O.O.; Al-Hamayda, A.; Akinsemolu, A.; Onyeaka, H.; Olaniran, A.F. Physical field-assisted deep eutectic solvent processing: A green and water-saving extraction and separation technology. J. Food Sci. 2024, 89, 8248–8275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Ding, J.; Zhang, T.; Yang, D.; Qiu, F.; Chen, Q.; Xu, J. Flexible, versatility and superhydrophobic biomass carbon aerogels derived from corn bracts for efficient oil/water separation. Food Bioprod. Process. 2019, 115, 134–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araiza-Calahorra, A.; Wang, Y.; Boesch, C.; Zhao, Y.; Sarkar, A. Pickering emulsions stabilized by colloidal gel particles complexed or conjugated with biopolymers to enhance bioaccessibility and cellular uptake of curcumin. Curr. Res. Food Sci. 2020, 3, 178–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiruvengadam, M.; Chi, H.-Y.; Choi, H.-J.; Jung, B.-S.; Lee, S.-B.; Park, Y.; Jeon, D.; Ciftci, F.; Shariati, M.A.; Kim, S.-H. Sustainable and smart nano-biosensors: Integrated solutions for healthcare, environmental monitoring, agriculture, and food safety. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2025, 233, 121337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czaja, T.P.; Engelsen, S.B. Why nothing beats NIRS technology: The green analytical choice for the future sustainable food production. Spectrochimica Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 325, 125028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Guo, H.; Zong, B.; He, P.; Fan, F.; Gong, S. Rapid and non-destructive discrimination of special-grade flat green tea using Near-infrared spectroscopy. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 206, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


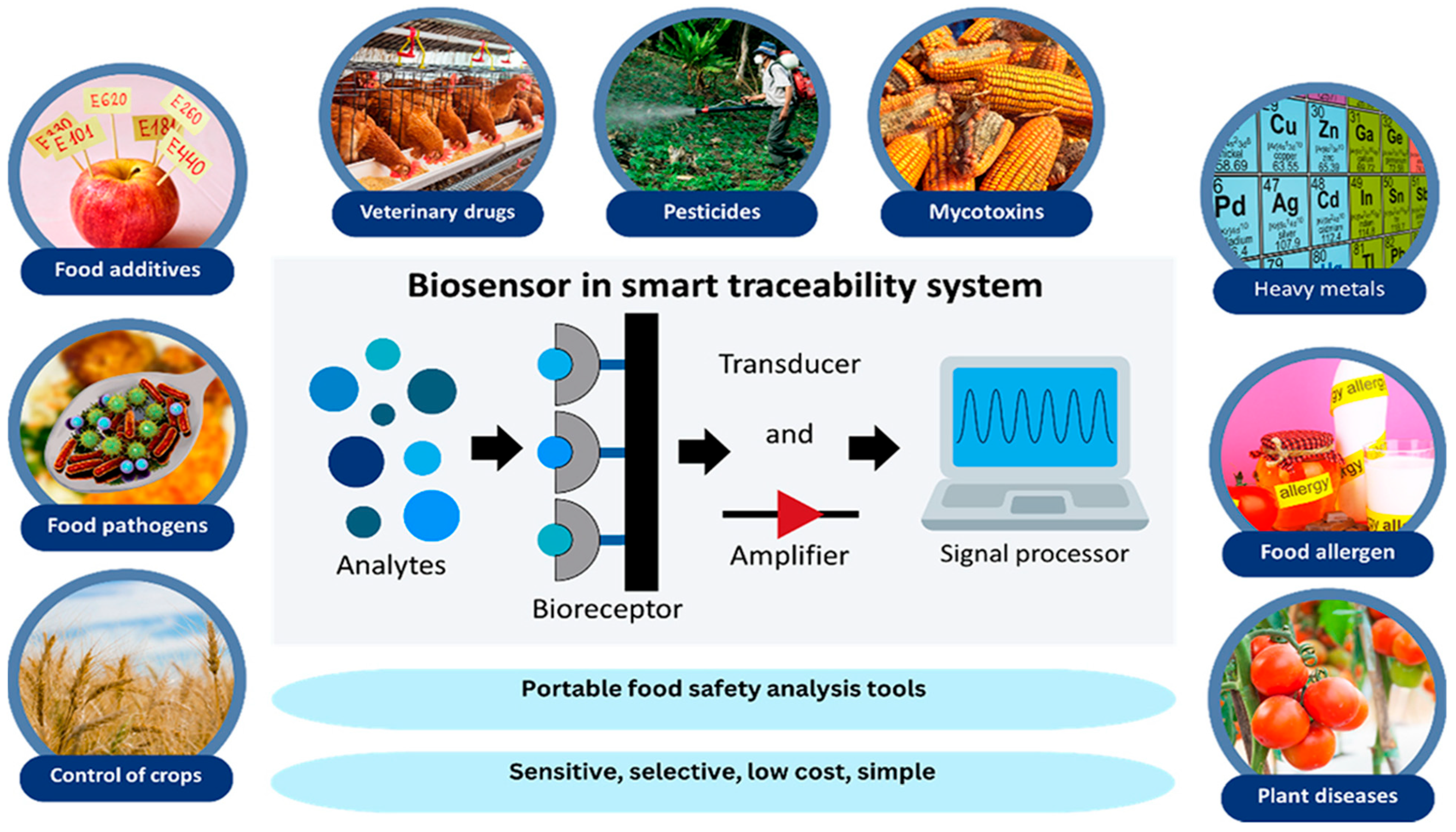
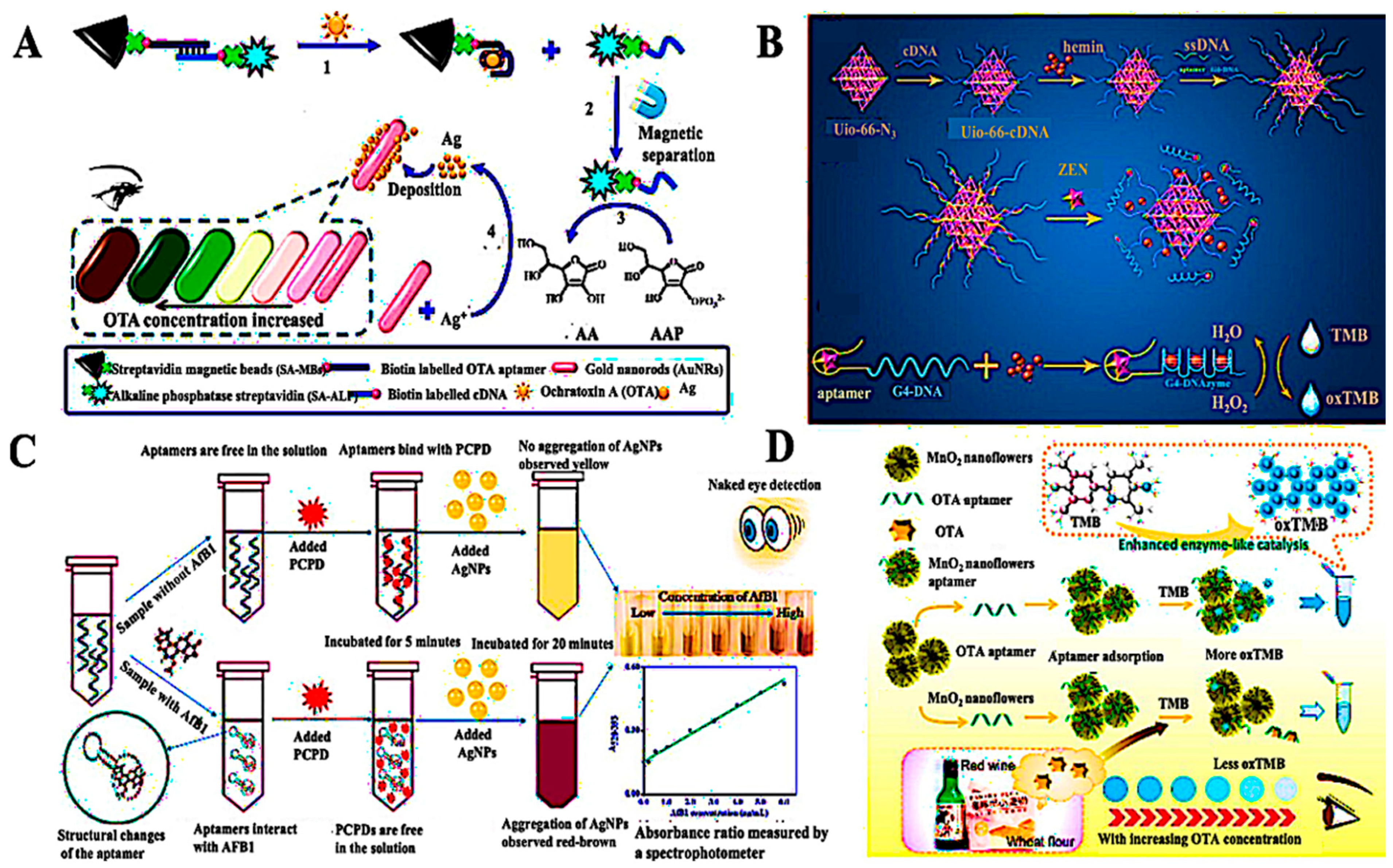
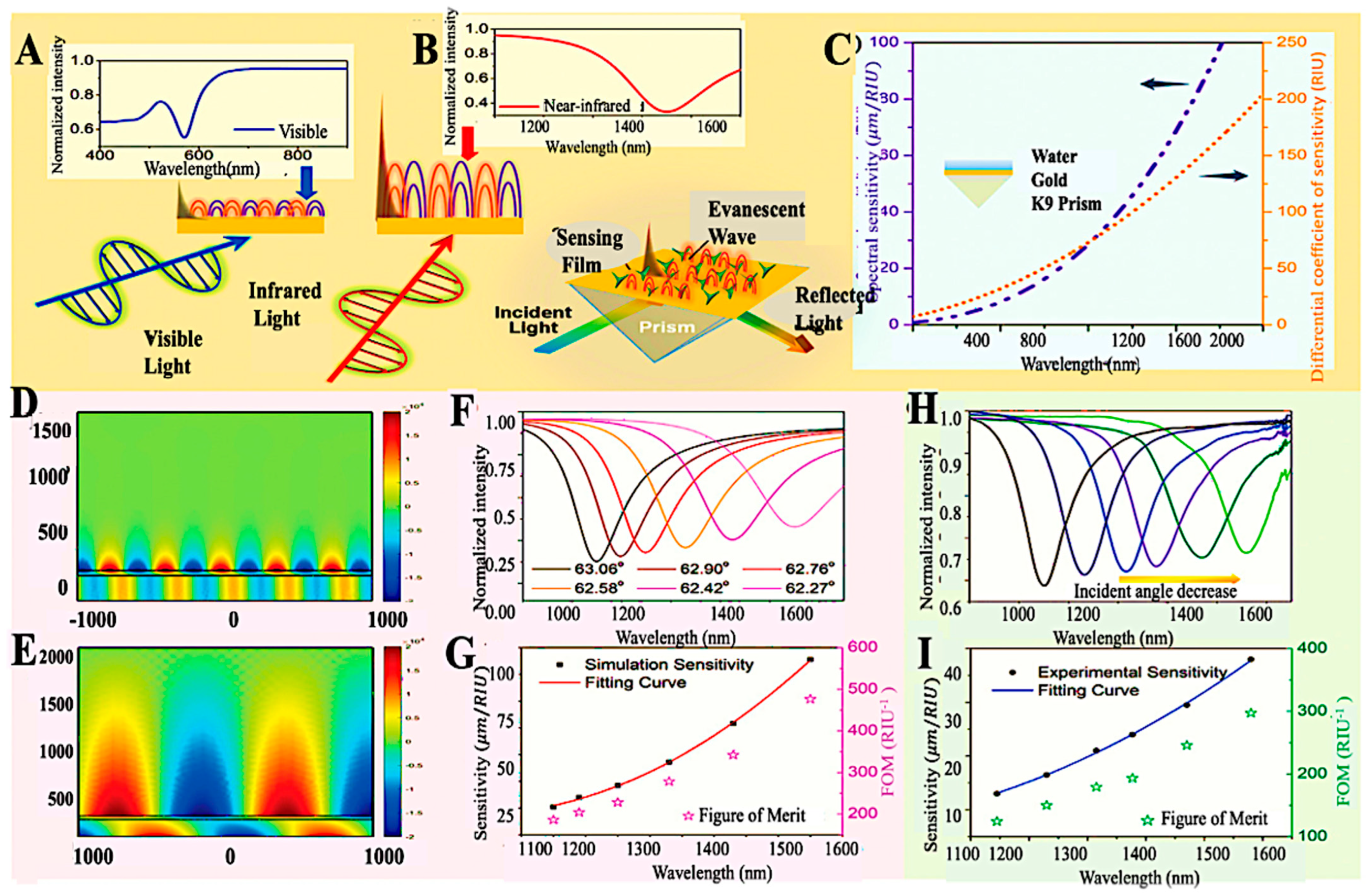
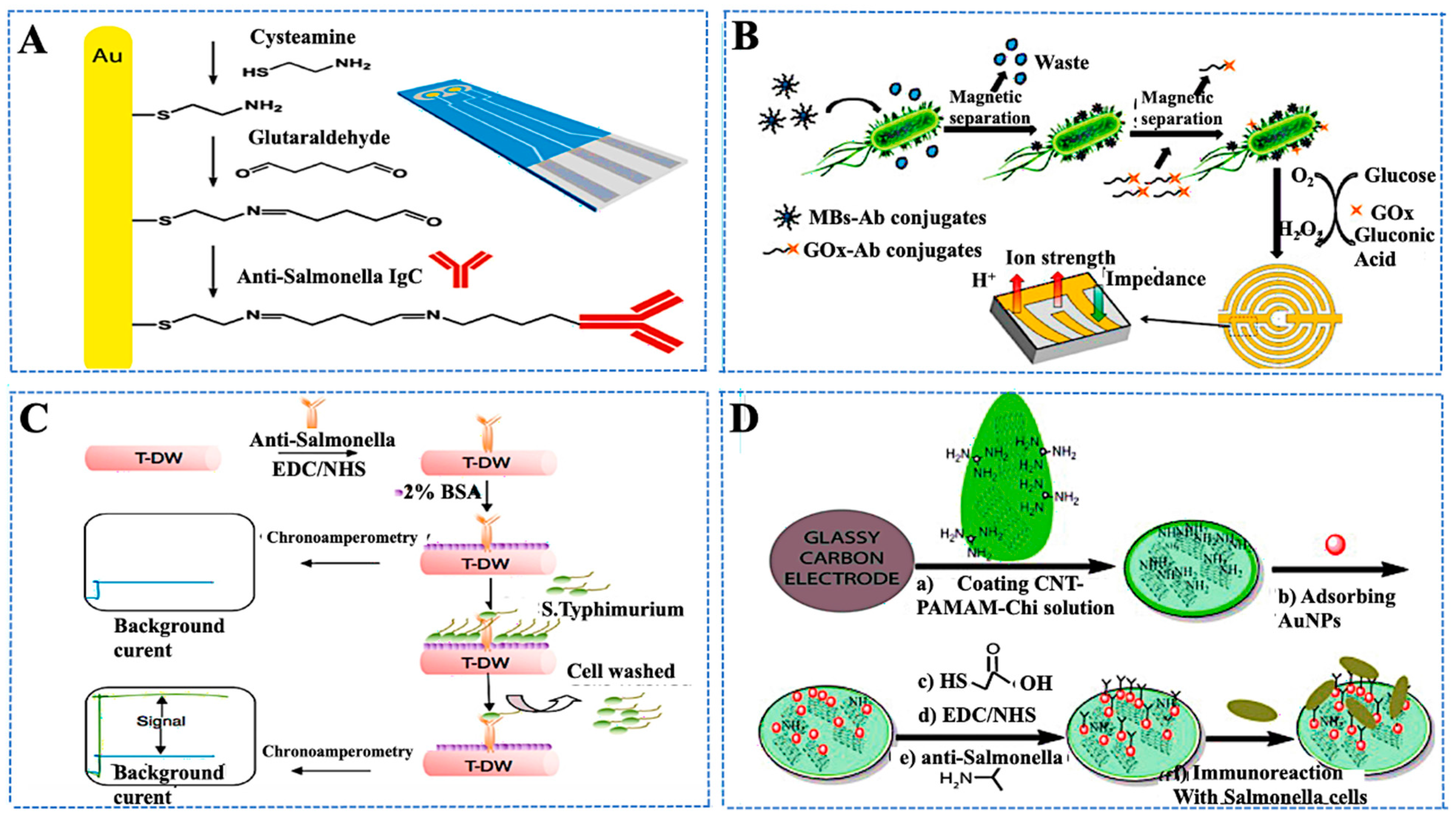
| Target/Analyte | Biosensor Type | Recognition Element | Signal Transduction | Sensitivity/LOD | Application Example | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Salmonella spp., allergens (peanut protein), bacterial toxins | Electrochemical | Enzymes, antibodies, aptamers | Amperometric, impedimetric, potentiometric | Varies; 1–10 CFU/mL for pathogens, ng/mL for allergens | Rapid (<30 min) screening across multiple contaminants in dairy, meat, and produce | [118,119] |
| Pesticide residues (organophosphates, carbamates) | Optical/Electrochemical | Enzymes (AChE), aptamers | Fluorescence quenching, electrochemical inhibition | ppt levels for chlorpyrifos, malathion | Real-time produce safety checks at farms and markets | [125,126] |
| Foodborne pathogens (E. coli, Listeria, Salmonella) | Flexible electrochemical biosensors | Antibodies, aptamers, phage proteins | Electrochemical impedance, voltammetry | Sub-femtomolar; <10 CFU/mL | On-site testing using flexible substrates. Spiked milk and chicken samples were validated | [127,128] |
| Food safety monitoring (multi-target) | Microfluidic biosensors | Antibodies, aptamers, MIPs | Electrochemical + optical | fM to nM; <5 μL volume | Dairy, cereal food matrices, real-time field monitoring, multiplexed detection | [129,130] |
| Pathogens, toxins, heavy metals | Optical biosensors | Antibodies, aptamers, enzymes, DNA probes | SPR, FRET, colorimetry | pM–nM | Multi-target screening in processed foods, beverages, produce | [131,132] |
| Ochratoxin A (mycotoxin) | Graphene FET aptasensor | ssDNA aptamer | Field-effect modulation | LOD ≈ 1.4 pM, 10 s response | Wine safety monitoring with reusable channels | [132] |
| Smart traceability systems | Integrated NIR + IoT + Blockchain | Optical NIR + digital ledger | Real-time traceability of food origin, freshness, handling history | [133] | ||
| Heavy metals (Pb2+, Hg2+, Cd2+) | Portable paper-based electrochemical | DNAzyme/aptamer | Electrochemical stripping voltammetry | Low ppb | Seafood and rice screening with smartphone readout | [134,135] |
| Food allergens (gluten, peanut, shellfish) | Lateral flow optical biosensor | Antibody or aptamer | Colorimetric (AuNP) | ng/mL | Consumer self-testing and restaurant verification. | [136,137] |
| Antimicrobial residues (β-lactams, tetracyclines) | Multiplex electrochemical biosensor | Enzyme inhibition assays | Differential pulse voltammetry | ng/mL–pg/mL | Dairy industry compliance monitoring | [138] |
| Microplastics in seafood | Optical biosensor | MIP | Fluorescence quenching | 0.5 μg/L | Rapid detection in fish and shellfish | [134] |
| Acrylamide in baked products | Electrochemical | Enzyme (asparaginase) | Amperometric | 0.02 μg/g | Monitoring contaminants in bread, biscuits | [139] |
| Norovirus in fresh produce | Microfluidic optical biosensor | DNA aptamer | SPR | 20 genome copies/mL | Detection in lettuce wash water | [140] |
| Biogenic amines in fish | Wearable electrochemical patch | Enzyme (DAO) | Potentiometric | 0.1 mg/L | Real-time freshness monitoring in packaging | [141] |
| Cyanotoxins in freshwater fish | Electrochemical aptasensor | DNA aptamer | Square wave voltammetry | 0.8 ng/L | On-site aquaculture monitoring | [142] |
| Mycotoxins in cereals (multi-class) | Multiplex optical biosensor | Aptamers | FRET | 0.2–1 ng/g | Simultaneous maize/wheat mycotoxin screening | [143,144] |
| pH and spoilage gases in packaged foods | Hybrid NIR–electrochemical smart label | pH-sensitive dye, conductive polymer | Optical + electrochemical | Smart packaging shelf-life tracking for meat/dairy | [145] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prempeh, N.Y.A.; Nunekpeku, X.; Kutsanedzie, F.Y.H.; Murugesan, A.; Li, H. A Comprehensive Review of Non-Destructive Monitoring of Food Freshness and Safety Using NIR Spectroscopy and Biosensors: Challenges and Opportunities. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110393
Prempeh NYA, Nunekpeku X, Kutsanedzie FYH, Murugesan A, Li H. A Comprehensive Review of Non-Destructive Monitoring of Food Freshness and Safety Using NIR Spectroscopy and Biosensors: Challenges and Opportunities. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(11):393. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110393
Chicago/Turabian StylePrempeh, Nama Yaa Akyea, Xorlali Nunekpeku, Felix Y. H. Kutsanedzie, Arul Murugesan, and Huanhuan Li. 2025. "A Comprehensive Review of Non-Destructive Monitoring of Food Freshness and Safety Using NIR Spectroscopy and Biosensors: Challenges and Opportunities" Chemosensors 13, no. 11: 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110393
APA StylePrempeh, N. Y. A., Nunekpeku, X., Kutsanedzie, F. Y. H., Murugesan, A., & Li, H. (2025). A Comprehensive Review of Non-Destructive Monitoring of Food Freshness and Safety Using NIR Spectroscopy and Biosensors: Challenges and Opportunities. Chemosensors, 13(11), 393. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13110393








