Abstract
This review explores the application of chemometric techniques for the authentication, characterization, and adulteration detection of Cypriot agri-food products registered under European Union quality schemes, including Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) and Protected Geographical Indication (PGI). Given the increasing global demand for premium and geographically linked food products, ensuring their authenticity and integrity has become critical. Although Halloumi cheese, wines, and Zivania are the most researched Cypriot products, additional studies are still needed. Chemometrics, when coupled with spectroscopy, offers robust analytical tools for distinguishing genuine products from their imitations by characterizing them. This review provides an overview of certified Cypriot products and focuses on published applications where chemometric approaches have been used to assess product origin, composition, and adulteration. The paper concludes with current challenges, methodological limitations, and future directions for expanding the role of chemometrics in food integrity verification within the context of EU geographical indications.
1. Introduction
Geographical indications (GIs) and other EU quality schemes such as Protected Designation of Origin (PDO), Protected Geographical Indication (PGI), and Traditional Specialty Guaranteed (TSG) serve as intellectual property rights that legally protect the names of products linked to specific regions and traditional production methods [1,2]. These schemes not only safeguard against imitation and misuse but also preserve the integrity and reputation of regional products within the internal market and in international trade [3].
The legal recognition of EU quality schemes ensures that only products genuinely originating from a defined geographical area and meeting precise production criteria can bear the registered name. This protection enhances consumer trust, product traceability, and market differentiation, especially in premium segments where authenticity and provenance are valued [4,5]. Legal framework for the organization and management of agricultural markets in the EU, including provisions on marketing standards, production support, and protection of quality schemes such as PDO and PGI, is preserved by Regulation (EU) No 1308/2013 [6].
Commercially, quality-scheme products often command higher prices and enjoy greater market visibility, contributing significantly to rural development, job creation, and economic resilience in their regions [7,8]. Moreover, these products act as cultural ambassadors, reflecting local heritage, biodiversity, traditional knowledge, and culinary identity [9,10].
Food fraud is the deliberate substitution, addition, tampering, or misrepresentation of food, ingredients, or packaging for economic gain. Common forms include dilution, mislabeling of origin, counterfeit products, and replacing high-value ingredients with inferior or synthetic alternatives [3,11]. The primary motivation behind food fraud is economic, as producers may lower costs or inflate profit margins by compromising product integrity, often at the expense of consumer safety and brand reputation. Such practices can damage the competitiveness of legitimate producers, particularly those following strict standards under EU quality schemes.
Ensuring food authenticity and traceability is critical in maintaining consumer confidence and protecting the value of products under PDO and PGI labels. These certifications depend on a verifiable link between the product’s characteristics and its geographical origin or traditional production method [1,12]. Authenticity assures consumers that the product they purchase meets specific quality standards, while traceability enables tracking through the supply chain, which is vital for verifying origin, detecting fraud, and enforcing food safety regulations [4]. For quality-scheme products, where geographic and cultural identity are central to value, authenticity and traceability systems are not just quality control measures as they are fundamental tools for preserving heritage, fairness in trade, and the economic sustainability of rural communities [7,10].
The integration of analytical techniques with chemometrics has been extensively applied to trace the origin and verify the authenticity of cheese products. Two main analytical strategies are used: targeted approaches, which focus on identifying and quantifying specific pre-selected compounds, and untargeted approaches, which analyze the entire spectral or metabolomic fingerprint of a sample without prior assumptions.
The untargeted approach, often combined with chemometric tools, provides a holistic view of the sample, enhancing its discriminatory power. Several recent studies have demonstrated the effectiveness of this approach. For instance, NMR-based metabolomics successfully distinguished PDO Asiago cheese from pasture-fed versus hay-fed milk, though the model was more reliable for short-ripened varieties [13]. Parmigiano Reggiano was also accurately classified according to geographical origin using NMR and chemometrics, with further studies showing the potential of ATR-FTIR combined with LDA to differentiate grated PDO cheese. Also, an untargeted approach enabled detection across both aqueous and lipid fractions, while a parallel targeted analysis identified key discriminatory compounds, as presented by Maestrello et al. [14].
While the EU’s quality schemes offer valuable frameworks to safeguard the identity and authenticity of traditional agri-food products, their implementation presents distinct challenges in smaller Member States such as Cyprus. Cypriot products often originate from small-scale, family-run operations with fragmented production systems and limited access to advanced analytical infrastructure. Moreover, there is a noticeable gap in peer-reviewed scientific studies that focus specifically on Cypriot PDO/PGI products, which hampers the development of robust, evidence-based authentication methods. These factors underscore the need for targeted research and tailored chemometric approaches that can accommodate the variability and complexity of indigenous cultivars, traditional products, and practices. Addressing these gaps is crucial to enhancing traceability, maintaining consumer trust, and supporting the long-term sustainability of Cyprus’s agri-food sector within the competitive EU market [15].
The objective of this review is to critically examine and synthesize current research studies on the application of chemometric techniques for the authentication and characterization of Cypriot products bearing PDO or PGI status. The review focuses on how multivariate data analysis has been employed with analytical methods, such as spectroscopy, chromatography, and elemental profiling, to verify product authenticity, determine geographical origin, and detect adulteration. By mapping the methodological landscape, highlighting validated approaches, and identifying research gaps, this review aims to support future efforts in food authentication, regulatory compliance, and preserving Cyprus’s gastronomic heritage.
2. Overview of Certified Cypriot Products
As of 2025, Cyprus boasts 29 certified products under the European Union’s quality schemes, as shown in Table 1, in terms of PDO and PGI. These certifications serve to protect the authenticity, traditional methods, and regional identity of Cypriot agri-food products, while enhancing their value and competitiveness in both local and international markets. These belong to 3 categories, i.e., food products, wines, and spirit drinks, with 14, 13, and 2 representatives, respectively, in each category.

Table 1.
Cyprus’ 29 certified products under the European Union’s quality schemes, listed from the most recent to the oldest, as of May 2025.
Moreover, it must be noted that Table 1 highlights the ongoing efforts to protect the authenticity and heritage of local produce through the registration of these products, ensuring that they are recognized for their geographical and cultural significance. The registrations are spread across various dates, the most recent being in 2024 for Agros Rosewater and Cyprus red soil potatoes. The mix of registered and published statuses reflects the ongoing process of securing these recognitions, which serve not only to preserve local traditions but also to provide economic benefits through the promotion of Cypriot specialties in both domestic and international markets.
3. Chemometric Approaches in Food Authentication
Chemometrics is the application of mathematical and statistical techniques to analyze complex data, which is particularly useful in food authentication. It allows for the effective analysis of large and multidimensional datasets, helping to ensure the quality, safety, and authenticity of food products. By employing advanced analytical techniques, chemometrics helps detect adulteration, verify product authenticity, and confirm compliance with regulatory standards [16,17].
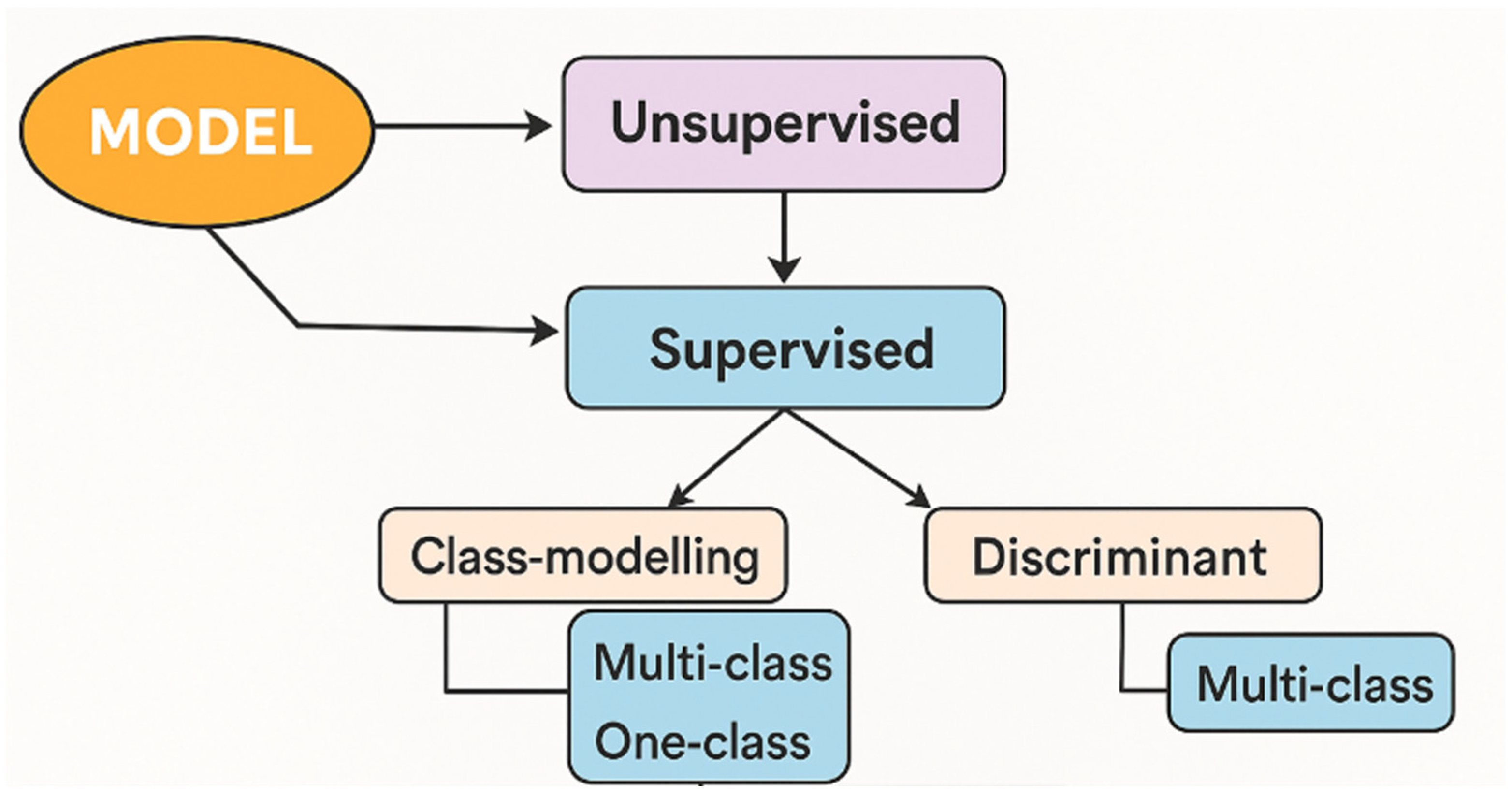
The pre-processed training dataset is subjected to a modeling procedure. Pattern recognition techniques are broadly classified into two main categories: unsupervised and supervised methods. Within supervised methods, a further distinction is made between discriminative and modeling approaches. Modeling techniques can target either a single class (one class) or multiple classes and may follow either a strict (rigorous) or flexible (compliant) strategy, as illustrated in Figure 1. The first category, unsupervised methods, acts like tools for preliminary or exploratory analysis, serving as an initial step before developing supervised models. The second category, supervised methods, encompasses very commonly used approaches in food analysis literature [16,18].
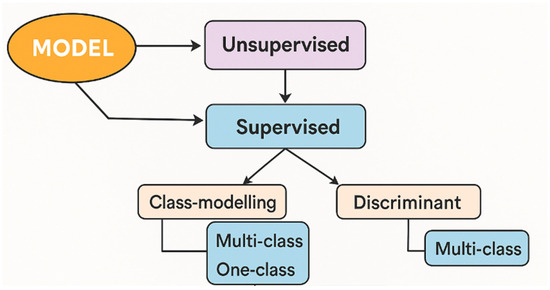
Figure 1.
A range of approaches to pattern recognition. Moreover, interpretability is an important consideration in food authentication, as it helps ensure that chemometric models are transparent and understandable. For non-experts, such as food producers or regulatory bodies, the models must be interpretable to facilitate trust and decision-making. Understanding which features are most influential in making predictions can provide valuable insights into why certain products are classified as authentic or adulterated. Additionally, interpretability allows better transparency in the decision-making process, which is essential for regulatory compliance [19,20].
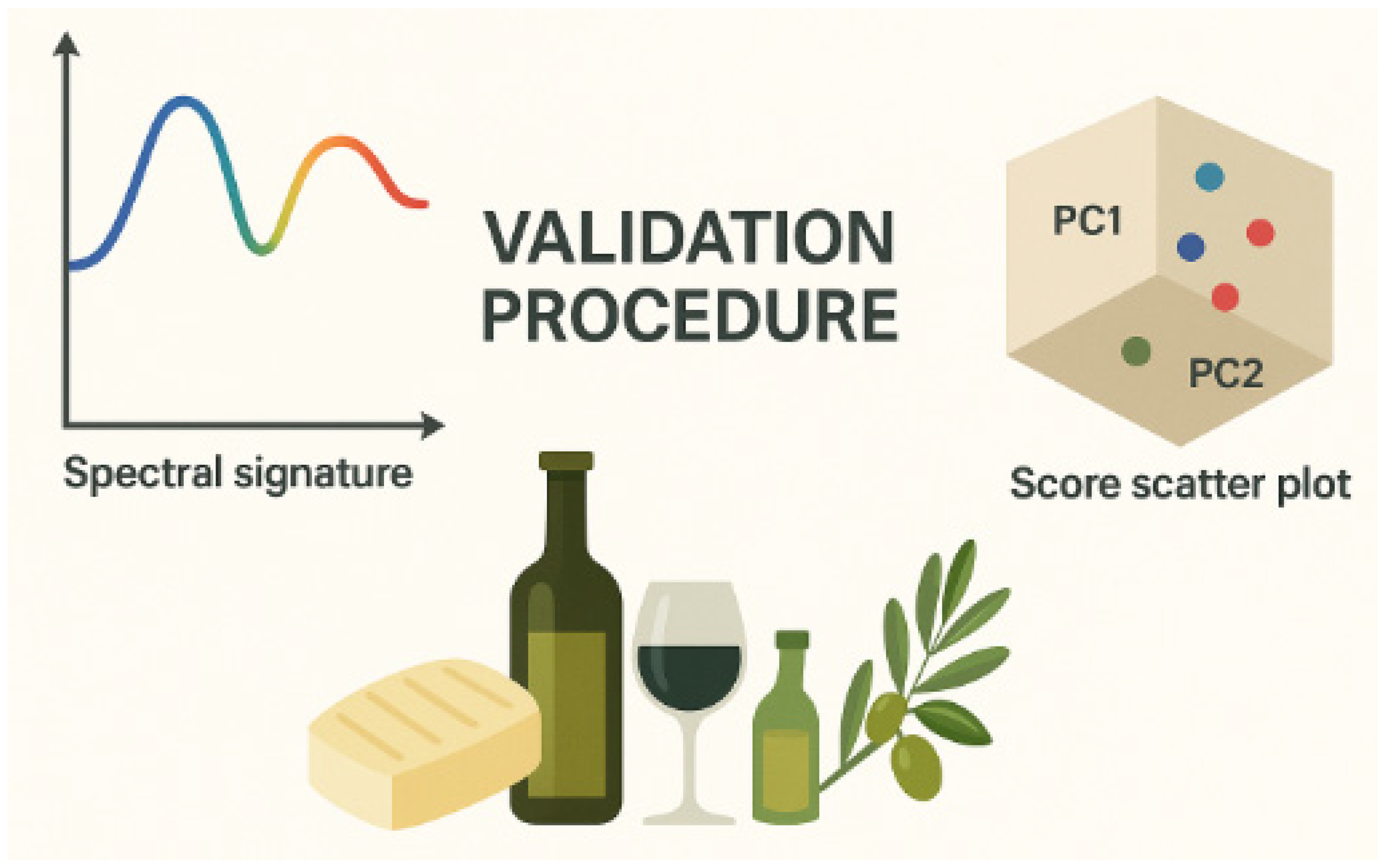
Robustness is another key factor in chemometric approaches, as presented in Figure 2. A robust model can handle variability in the data, such as differences in environmental conditions, measurement instruments, or sample composition. A model that is sensitive to small changes in the data may not perform reliably in real-world applications, so robustness ensures the model remains accurate and stable across a variety of conditions. Furthermore, a robust model should be generalizable, meaning that it performs well not only on the data it was trained on but also on new, unseen data. This ability to generalize is crucial for ensuring the model’s effectiveness in real-world food authentication scenarios, where data may vary over time or across different geographic regions [16,21,22].

Figure 2.
A proper validation strategy applied to analytical data (e.g., spectral signatures) can yield robust models.
By considering both the interpretability and robustness of chemometric models, food authentication can become more reliable, transparent, and applicable to real-world conditions. This integrated approach not only enhances the scientific credibility of the results but also builds trust among stakeholders, ultimately benefiting both producers and consumers by ensuring food safety, protecting product authenticity, and supporting regulatory compliance [16,22].
4. Applications of Chemometrics in Studies Related to Cypriot Food and Beverage Products with Quality Schemes
This section explores the studies that took place and combine chemometrics to study any GI-protected Cypriot products, which are summarized in Table 2. The small volume of this table shows that research on Cyprus’s GI foodstuffs and beverages is scarce and needs to be enriched in the future. The earliest study dates to 2003 and focused on Zivania. This was followed by research on Commandaria and other wines, then Halloumi cheese, and most recently, Cyprus potatoes.

Table 2.
Chronological overview of studies on Cypriot food and beverage products with geographical indications.
Despite the valuable insights provided by the studies summarized in Table 2, a few common limitations can be identified. These include the use of relatively small sample sizes, which may limit the statistical power and generalizability of the findings, and the frequent absence of external validation, which is essential to confirm the robustness of the developed models; however, some of them were preliminary studies. Additionally, there is limited standardization in chemometric workflows across studies, making it difficult to compare results or replicate methodologies. Addressing these issues in future research will be crucial to strengthening the reliability and applicability of chemometric tools for the authentication of Cypriot PDO/PGI products.
Other studies, related to chemometrics and focused on Cyprus’ fruits like prickly pears [33,34], carobs [35,36,37,38], anari cheese [29], kefalotyri cheese [30,39], honey [40,41], olive oil [42,43] and olives [44] are also important, but their Cyprus foodstuffs have not yet been registered as PDO/PGI. In addition, another study by Kastanos et al. [45] related to milk species’ origin in Halloumi cheese took place through triplex-PCR, but without using chemometrics.
5. Challenges, Limitations, and Future Perspectives
Chemometric techniques, when coupled with spectroscopic and chromatographic analyses, have shown significant potential in verifying the authenticity and quality of GI food products and beverages [46,47]. This section discusses the key limitations and emerging perspectives critical for advancing the application of chemometrics in Cypriot GI product authentication.
One of the most significant scientific challenges in applying chemometric techniques is the inherent variability in food matrices. Cypriot quality-scheme products, often produced using traditional and region-specific methods, exhibit high intra-class variability due to differences in raw material composition, seasonal fluctuations, terroir effects, microflora, and artisanal production techniques. For instance, milk composition in Halloumi varies depending on whether it is made from sheep, goat, or a mixture of milks (as well as the animals’ feeding regimes), and this variation directly affects fat, protein, and moisture levels, parameters critical in spectral signatures [30,31]. Such complexity complicates the development of robust and generalizable chemometric models. Matrix effects can mask or distort the signals of interest, leading to poor model performance or overfitting. Traditional multivariate statistical approaches like PCA, PLS-DA, or LDA may not sufficiently account for this heterogeneity without careful data pre-treatment and model optimization. To overcome these challenges, it is necessary to adopt comprehensive experimental designs that capture a wide range of natural variability during model training. Advanced signal processing and variable selection techniques can help isolate the most informative features in complex datasets [48,49,50].
Moreover, the absence of harmonized analytical and computational protocols represents a major bottleneck in translating chemometric research into standardized quality control workflows. Currently, methodologies vary widely across research groups and laboratories regarding sample preparation, instrumental settings (e.g., resolution, scanning range), spectral pre-processing (e.g., baseline correction, normalization), and chemometric modeling strategies. These inconsistencies hinder the reproducibility and comparability of results, impeding cross-validation and technology transfer [51,52,53].
For Cypriot PDO products, where authentication must often comply with both local and EU regulatory frameworks, standardized protocols are essential to ensure legal robustness and acceptance. Developing harmonized protocols requires interdisciplinary collaboration among chemists, data scientists, food technologists, and regulatory agencies. Such protocols should include standardized sample collection procedures, minimum data quality requirements, recommended spectral pre-processing pipelines, and criteria for model validation and performance assessment. Initiatives like the METROFOOD-RI project offer useful templates for establishing such protocols [54,55].
Despite their scientific merit, chemometric methods still face limited acceptance in official control laboratories and regulatory contexts. This is primarily due to the perception of these models as “black boxes” lacking transparency and legal defensibility. Regulators typically require analytical methods to meet stringent validation criteria such as accuracy, repeatability, reproducibility, specificity, and robustness. However, chemometric models, especially those based on non-targeted analysis, often struggle to meet these parameters in a legally defensible way when model outputs are probabilistic rather than deterministic [54,56]. The development of decision-support tools that integrate chemometrics with conventional targeted analysis (e.g., GC-MS, HPLC) may provide a more balanced solution, where chemometrics serves as a rapid screening tool that flags suspicious samples for further confirmatory testing [54].
Furthermore, robust chemometric models rely heavily on comprehensive reference datasets that encompass the full range of variability in authentic and fraudulent samples. Datasets collected with different instruments, under varied conditions, or using different protocols are often incompatible, limiting model portability and scalability. Another related challenge is model transferability. A model developed on one spectroscopic device may not perform well on another, even if both are nominally the same model. This instrument-to-instrument variability, often caused by differences in optics, light sources, or calibration routines, can lead to significant degradation in model accuracy. Techniques such as calibration transfer, domain adaptation, and standardization methods (e.g., piecewise direct standardization) can help mitigate these issues, but they are not yet routinely implemented. Establishing shared, open access spectral databases, supported by consistent metadata, is essential for enhancing the robustness, transparency, and scalability of chemometric authentication models [47,53].
The evolution of machine learning (ML) and deep learning (DL) algorithms offers exciting possibilities for enhancing the analytical power of chemometric models [50,57]. Unlike traditional linear models, these advanced methods can capture complex, non-linear relationships in high-dimensional datasets, enabling improved discrimination between authentic and adulterated samples [15,52]. However, the application of ML/DL also introduces new challenges, including the need for large, well-annotated training datasets and high computational resources. Overfitting remains a significant risk, especially when the number of samples is small relative to the number of variables. Furthermore, interpretability continues to be a concern in regulatory contexts, where explainable AI (XAI) tools will be crucial for model acceptance. Despite these limitations, ML/DL approaches are likely to play a pivotal role in the future of food authentication, particularly when combined with portable or online sensing systems [58,59].
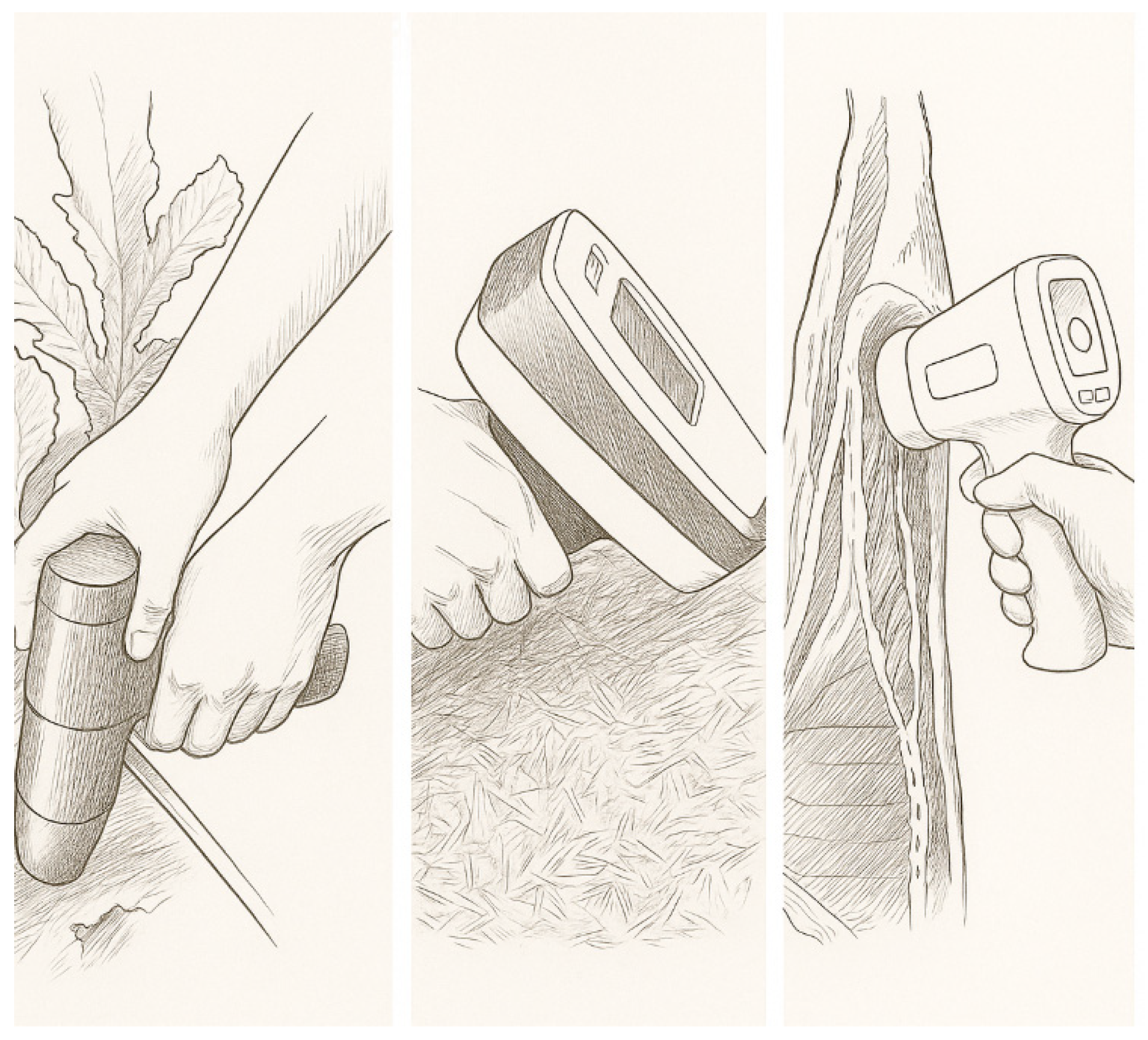
The emergence of portable and miniaturized spectrometers, such as handheld NIR, Raman, and FTIR devices, has opened up new possibilities for in situ food authentication. These tools can bring chemometric screening capabilities directly to farms, factories, markets, and border control points, allowing real-time decision-making without the need for sophisticated lab infrastructure [60,61,62,63], as shown in Figure 3 For Cypriot quality-scheme products, especially those exported to international markets, field-based screening could offer an effective first line of defense against fraud and lower quality. On the other hand, the practical deployment of portable devices faces limitations, including lower spectral resolution, reduced signal-to-noise ratios, and sensitivity to environmental conditions such as temperature, humidity, and light exposure. The chemometric models used on portable devices must be highly optimized and validated under real-world conditions. Model updates and cloud-based connectivity may help address these issues by enabling continuous learning and remote support. Future developments should focus on integrating portable sensors with mobile apps and cloud analytics to ensure user-friendliness, traceability, and scalability [61,64,65,66].
Figure 3.
Portable and miniaturized spectrometers, such as handheld NIR devices, have opened up new possibilities for in situ food authentication.
The integration of chemometric data with blockchain technology offers a powerful approach to strengthening food integrity and supply chain transparency. In a blockchain-based system, analytical results from chemometric authentication tests can be securely recorded and linked to specific product batches via QR codes or digital certificates. This creates a tamper-proof audit trail that can be accessed by stakeholders across the supply chain, including producers, certifiers, retailers, and consumers. For Cypriot quality-scheme products, which often rely on traditional and decentralized production systems, blockchain could help ensure compliance with geographical origin and production specifications. However, challenges include the cost and complexity of blockchain implementation, the need for digital literacy among producers, and the development of interfaces that integrate seamlessly with existing laboratory information management systems (LIMS). Future research should explore hybrid solutions that combine blockchain with other digital traceability tools, including Internet of Things (IoT) sensors and geolocation data [67,68,69,70].
Finally, the successful implementation of chemometric approaches in food authentication depends on collaborative efforts across disciplines and sectors. Policymakers, researchers, regulatory authorities, producer cooperatives, and technology providers must work together to establish clear frameworks for method validation, data sharing, training, and policy development. In Cyprus, national and regional authorities can play a critical role in promoting chemometric applications and AI by funding pilot studies, creating certification pathways, and facilitating stakeholder engagement [15].
European initiatives such as the EU Food Fraud Network, the Joint Research Centre (JRC), and several COST Actions provide ideal platforms for building such collaborations. Capacity-building programs, especially those targeting SMEs and artisanal producers, will be essential for ensuring inclusive adoption [71,72,73]. Looking ahead, the creation of an EU-recognized roadmap for chemometric-based food authentication, incorporating Cypriot products as case studies, could significantly advance both scientific understanding and practical implementation.
Future studies should adopt rigorous validation protocols, including cross-validation, external validation, and independent test sets, to ensure model robustness. Collaboration with producers and regulatory bodies is also essential to translate analytical findings into traceability tools and certification support. Finally, integrating chemometrics with other emerging technologies (e.g., sensor networks, portable devices, and AI-based classification) could enhance real-time quality control and strengthen the global competitiveness of Cypriot products. Future studies should focus on developing shared spectral libraries and benchmarking datasets to support cross-laboratory reproducibility.
6. Conclusions
Authentication, characterization, and adulteration detection of Cypriot agri-food products protected under EU quality schemes were the primary focus of this review. Since 2003, significant progress has been made, particularly in studies on Halloumi cheese, Commandaria wine, and Zivania. However, there remains a clear need for broader research encompassing a wider range of products and the application of more advanced analytical approaches. Addressing current challenges, such as limited sample availability, complex food matrices, and the need for methodological standardization, will be essential to developing robust and reliable chemometric models.
Halloumi cheese has recently become the subject of some analytical studies aimed at verifying its authenticity. Chemometric workflows have been applied to spectroscopic data to classify Halloumi samples based on milk composition (cow vs. goat/sheep), production practices, and compliance with PDO specifications. Principal component analysis (PCA) has been used for initial data exploration, followed by discriminant analysis. These models achieved high sensitivity and specificity; however, there is a need for larger sample sets and further validation.
Future efforts should prioritize the integration of emerging technologies, expansion of comprehensive databases, and enhanced collaboration among researchers, producers, and regulatory bodies to effectively safeguard the authenticity and reputation of Cypriot quality-scheme products in local as well as global markets. To realize the full potential of chemometric tools in GI product authentication, Cyprus must invest in interdisciplinary research hubs, international collaborations, and digital infrastructure supporting traceability and consumer transparency.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, C.R.T.; resources, C.R.T.; writing—original draft preparation, M.T.; writing—review and editing, I.P. and C.R.T.; supervision, I.P. and C.R.T.; project administration, C.R.T. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Albuquerque, T.G.; Oliveira, M.B.P.; Costa, H.S. 25 years of European Union (EU) quality schemes for agricultural products and foodstuffs across EU Member States. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 2475–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Commission. First Turkish Cypriot ‘Halloumi’/‘Hellim’ Cheese Certified Protected Designation of Origin. 2023. Available online: https://agriculture.ec.europa.eu/media/news/first-turkish-cypriot-halloumihellim-cheese-certified-protected-designation-origin-2023-03-28_en (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Cassago, A.L.L.; Artêncio, M.M.; de Moura Engracia Giraldi, J.; Da Costa, F.B. Metabolomics as a marketing tool for geographical indication products: A literature review. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2021, 247, 2143–2159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katerinopoulou, K.; Kontogeorgos, A.; Salmas, C.E.; Patakas, A.; Ladavos, A. Geographical origin authentication of agri-food products: A review. Foods 2020, 9, 489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadílek, T. Utilization of food quality labels included in the european union quality schemes. Int. J. Food Syst. Dyn. 2020, 11, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regulation (EU) No 1308/2013 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 17 December 2013 Establishing a Common Organisation of the Markets in Agricultural Products and Repealing Council Regulations (EEC) No 922/72, (EEC) No 234/79, (EC) No 1037/2001 and (EC) No 1234/2007. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2013/1308/oj/eng (accessed on 28 August 2025).
- Sgroi, F.; Modica, F. Localized agri-food systems: The case of Pecorino Siciliano PDO a food product of the tradition of Mediterranean gastronomy. Int. J. Gastron. Food Sci. 2022, 27, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cei, L.; Defrancesco, E.; Stefani, G. From geographical indications to rural development: A review of the economic effects of european union policy. Sustainability 2018, 10, 3745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, V.A.; Lourenzani, A.E.B.S.; Caldas, M.M.; Bernardo, C.H.C.; Bernardo, R. The benefits and barriers of geographical indications to producers: A review. Renew. Agric. Food Syst. 2022, 37, 707–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandecandelaere, E.; Teyssier, C.; Barjolle, D.; Fournier, S.; Beucherie, O.; Jeanneaux, P. Strengthening sustainable food systems through geographical indications: Evidence from 9 worldwide case studies. J. Sustain. Res. 2020, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parastar, H.; Tauler, R. Big (bio) chemical data mining using chemometric methods: A need for chemists. Angew. Chem. 2022, 134, e201801134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibbert, D.B. Vocabulary of concepts and terms in chemometrics (IUPAC Recommendations 2016). Pure Appl. Chem. 2016, 88, 407–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segato, S.; Caligiani, A.; Contiero, B.; Galaverna, G.; Bisutti, V.; Cozzi, G. 1H NMR metabolic profile to discriminate pasture based alpine asiago PDO cheeses. Animals 2019, 9, 722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maestrello, V.; Solovyev, P.; Franceschi, P.; Stroppa, A.; Bontempo, L. 1H-NMR approach for the discrimination of PDO Grana Padano cheese from non-PDO cheeses. Foods 2024, 13, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Agriopoulou, S.; Artemi, A. Quality Schemes and Geographical Indicators in the Cheese Agribusiness and the Case of the Cypriot Traditional Cheese Halloumi. In Agribusiness Innovation and Contextual Evolution, Volume I: Strategic, Managerial and Marketing Advancements; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 155–182. [Google Scholar]
- Grassi, S.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; D’Alessandro, A.; Agriopoulou, S.; Strani, L.; Varzakas, T. How chemometrics can fight milk adulteration. Foods 2022, 12, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriopoulou, S.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; Varzakas, T. (Eds.) Chemometrics and Authenticity of Foods of Plant Origin; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- de Araújo Gomes, A.; Azcarate, S.M.; Špánik, I.; Khvalbota, L.; Goicoechea, H.C. Pattern recognition techniques in food quality and authenticity: A guide on how to process multivariate data in food analysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 164, 117105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smaoui, S.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; Agriopoulou, S.; D’Amore, T.; Varzakas, T. Current state of milk, dairy products, meat and meat products, eggs, fish and fishery products authentication and chemometrics. Foods 2023, 12, 4254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Domínguez, R.; Sayago, A.; Fernández-Recamales, Á. An overview on the application of chemometrics tools in food authenticity and traceability. Foods 2022, 11, 3940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Yang, J. Advanced chemometrics toward robust spectral analysis for fruit quality evaluation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 150, 104612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riedl, J.; Esslinger, S.; Fauhl-Hassek, C. Review of validation and reporting of non-targeted fingerprinting approaches for food authentication. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 885, 17–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinofta, R.; Petrakis, P.V.; Mavromoustakos, T.; Theocharis, C.R. Authenticity of the traditional cypriot spirit “Zivania” on the basis of metal content using a combination of coupled plasma spectroscopy and statistical analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 6233–6239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kokkinofta, R.I.; Theocharis, C.R. Chemometric characterization of the Cypriot spirit “Zivania”. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5067–5073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrakis, P.; Touris, I.; Liouni, M.; Zervou, M.; Kyrikou, I.; Kokkinofta, R.; Theocharis, C.R.; Mavromoustakos, T.M. Authenticity of the traditional cypriot spirit “zivania” on the basis of 1H NMR spectroscopy diagnostic parameters and statistical analysis. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5293–5303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou-Papayianni, E.; Kokkinofta, R.I.; Theocharis, C.R. Authenticity of Cypriot sweet wine commandaria using FT-IR and chemometrics. J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, C420–C427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinofta, R.; Economidou, N.; Tzioni, E.; Damianou, K.; Poulli, K.; Savvidou, C.; Louka, C.; Kanari, P. Studies on the authenticity of local wines by spectroscopic and chemometric analysis. J. Chem. Chem. Eng. 2014, 8, 101. [Google Scholar]
- Kamilari, E.; Mina, M.; Karallis, C.; Tsaltas, D. Metataxonomic analysis of grape microbiota during wine fermentation reveals the distinction of cyprus regional terroirs. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12, 726483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Theocharis, C.R. Discrimination of Anari cheese samples in comparison with Halloumi cheese samples regarding the origin of the species by FTIR measurements and chemometrics. Analytica 2023, 4, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Pashalidis, I.; Theocharis, C.R. Discrimination of Cheese Products Regarding Milk Species’ Origin Using FTIR, 1H-NMR, and Chemometrics. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Logan, N.; Hardy, M.; Montgomery, H.; Haughey, S.A.; Elliott, C.T.; Theocharis, C.R. A Pre-Trial Study to Identify Species of Origin in Halloumi Cheese Utilising Chemometrics with Near-Infrared and Hyperspectral Imaging Technologies. Analytica 2024, 5, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannou-Papayianni, E.; Damaskinos, C.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; Louka, C.; Savvidou, C.; Tzioni, E.; Kokkinofta, R. Utilizing isotopic and elemental markers to enhance the authenticity of potatoes. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2025, 251, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppis, A.P.; Constantinou, M.S.; Kosma, I.S.; Badeka, A.V.; Kontominas, M.G.; Blando, F.; Stamatakos, G. Identification of quality markers for the geographical and botanical differentiation of Mediterranean prickly pears based on conventional physicochemical parameters, volatile compounds, sugars and colour. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 123, 105579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppis, A.P.; Constantinou, M.S.; Kontominas, M.G.; Blando, F.; Stamatakos, G. Geographical and botanical differentiation of Mediterranean prickly pear using specific chemical markers. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2023, 119, 105219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinofta, R.; Yiannopoulos, S.; Stylianou, M.A.; Agapiou, A. Use of chemometrics for correlating carobs nutritional compositional values with geographic origin. Metabolites 2020, 10, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krokou, A.; Kokkinofta, R.; Stylianou, M.; Agapiou, A. Decoding carob flavor aroma using HS–SPME–GC–MS and chemometrics. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2020, 246, 1419–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaefstathiou, E.; Agapiou, A.; Giannopoulos, S.; Kokkinofta, R. Nutritional characterization of carobs and traditional carob products. Food Sci. Nutr. 2018, 6, 2151–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christou, C.; Agapiou, A.; Kokkinofta, R. Use of FTIR spectroscopy and chemometrics for the classification of carobs origin. J. Adv. Res. 2018, 10, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Theocharis, C.R. Discrimination of Cheddar, Kefalotyri, and Halloumi cheese samples by the chemometric analysis of Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and proton nuclear magnetic resonance spectra. J. Food Process Eng. 2022, 45, e13933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Louppis, A.P.; Kontakos, S.; Drouza, C.; Papastephanou, C. Characterization and botanical differentiation of monofloral and multifloral honeys produced in Cyprus, Greece, and Egypt using physicochemical parameter analysis and mineral content in conjunction with supervised statistical techniques. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 7698251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karabagias, I.K.; Papastephanou, C.; Karabagias, V.K. Geographical differentiation of Cypriot multifloral honeys through specific volatile compounds and the use of DFA. AIMS Agric. Food 2019, 4, 149–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Salces, R.M.; Moreno-Rojas, J.M.; Holland, M.V.; Reniero, F.; Guillou, C.; Héberger, K. Virgin olive oil authentication by multivariate analyses of 1H NMR fingerprints and δ13C and δ2H data. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 5586–5596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araghipour, N.; Colineau, J.; Koot, A.; Akkermans, W.; Rojas, J.M.M.; Beauchamp, J.; Wisthaler, A.; Märk, T.D.; Downey, G.; Guillou, C.; et al. Geographical origin classification of olive oils by PTR-MS. Food Chem. 2008, 108, 374–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kritioti, A.; Menexes, G.; Drouza, C. Chemometric characterization of virgin olive oils of the two major Cypriot cultivars based on their fatty acid composition. Food Res. Int. 2018, 103, 426–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kastanos, E.; Papaneophytou, C.; Georgiou, T.; Demoliou, C. A simple and fast triplex-PCR for the identification of milk’s animal origin in Halloumi cheese and yoghurt. J. Dairy Res. 2022, 89, 323–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karabagias, I.K. Advances of spectrometric techniques in food analysis and food authentication implemented with chemometrics. Foods 2020, 9, 1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodionova, O.Y.; Oliveri, P.; Malegori, C.; Pomerantsev, A.L. Chemometrics as an efficient tool for food authentication: Golden pillars for building reliable models. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 147, 104429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consonni, V.; Todeschini, R.; Gosetti, F.; Ballabio, D. Authenticity and chemometrics basics. In Chemometrics and Authenticity of Foods of Plant Origin; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2022; pp. 9–35. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, X.; Bouzembrak, Y.; Lansink, A.O.; Van Der Fels-Klerx, H.J. Application of machine learning to the monitoring and prediction of food safety: A review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2022, 21, 416–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Deng, L.; Zhu, H.; Wang, W.; Ren, Z.; Zhou, Q.; Lu, S.; Sun, S.; Zhu, Z.; Gorriz, J.M.; et al. Deep learning in food category recognition. Inf. Fusion 2023, 98, 101859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dayananda, B.; Owen, S.; Kolobaric, A.; Chapman, J.; Cozzolino, D. Pre-processing applied to instrumental data in analytical chemistry: A brief review of the methods and examples. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 2745–2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharbach, M.; Alaoui Mansouri, M.; Taabouz, M.; Yu, H. Current application of advancing spectroscopy techniques in food analysis: Data handling with chemometric approaches. Foods 2023, 12, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulberth, F.; Koeber, R. Reference materials for food authentication. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2025, 417, 2427–2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agriopoulou, S.; D’Amore, T.; Tarapoulouzi, M.; Varzakas, T.; Smaoui, S. Chemometrics in Mycotoxin Detection by Mass Spectrometry. In Mass Spectrometry in Food Analysis: Principles and Applications; World Scientific Publishing: Singapore, 2025; pp. 277–303. [Google Scholar]
- Tsimidou, M.Z.; Ordoudi, S.A.; Mantzouridou, F.T.; Nenadis, N.; Stelzl, T.; Rychlik, M.; Belc, N.; Zoani, C. Strategic priorities of the scientific plan of the European Research Infrastructure METROFOOD-RI for promoting metrology in food and nutrition. Foods 2022, 11, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castañeda, F.N.; Vidal, R.B.P.; Aspromonte, J. Untargeted chromatographic methods coupled with chemometric strategies for the analysis of food and related samples. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 173, 117650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, H.; Pu, D.; Yan, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zuo, M.; Zhang, Y. Recent advances and application of machine learning in food flavor prediction and regulation. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2023, 138, 738–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassija, V.; Chamola, V.; Mahapatra, A.; Singal, A.; Goel, D.; Huang, K.; Scardapane, S.; Spinelli, I.; Mahmud, M.; Hussain, A. Interpreting black-box models: A review on explainable artificial intelligence. Cogn. Comput. 2024, 16, 45–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyuktepe, O.; Catal, C.; Kar, G.; Bouzembrak, Y.; Marvin, H.; Gavai, A. Food fraud detection using explainable artificial intelligence. Expert Syst. 2025, 42, e13387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuya, D.E.G.; Bolfe, É.L.; Parreiras, T.C.; Barbedo, J.G.A.; Santos, T.T.; Gebler, L. Combination of Remote Sensing and Artificial Intelligence in Fruit Growing: Progress, Challenges, and Potential Applications. Remote Sens. 2024, 16, 4805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Marín, D.; Fearn, T. Non-destructive/Non-invasive Method Development, Evaluation, and Transfer. In Non-Invasive and Non-Destructive Methods for Food Integrity; Springer Nature Switzerland: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 17–38. [Google Scholar]
- Yazgan, N.N.; Hummel, D.; Hinrichs, J.; Hitzmann, B. Raman Spectroscopy as a Tool for In-Line Quality Management in Food Processing. In Raman Spectroscopy in the Food Industry; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2025; pp. 205–229. [Google Scholar]
- Tarapoulouzi, M.; Ioannidis, I.; Pashalidis, I. Applications, trends, and challenges in the non-destructive assessment of microplastics in fish. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2025, 341, 126462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pal, A.; Dubey, S.K.; Goel, S.; Kalita, P.K. Portable sensors in precision agriculture: Assessing advances and challenges in soil nutrient determination. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2024, 180, 117981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beć, K.B.; Grabska, J.; Huck, C.W. Principles and applications of miniaturized near-infrared (NIR) spectrometers. Chem.—A Eur. J. 2021, 27, 1514–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albu, C.; Chira, A.; Radu, G.L.; Eremia, S.A. Advances in Cost-Effective Chemosensors for Sustainable Monitoring in Food Safety and Processing. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.; Zhang, M.; Mujumdar, A.S. Blockchain-based fresh food quality traceability and dynamic monitoring: Research progress and application perspectives. Comput. Electron. Agric. 2024, 224, 109191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, M.A.; Rather, M.Y.; Singh, P.; Hassan, S.; Hussain, N. Advances in smart food authentication for enhanced safety and quality. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2024, 155, 104800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukacs, M.; Toth, F.; Horvath, R.; Solymos, G.; Alpár, B.; Varga, P.; Kertesz, I.; Gillay, Z.; Baranyai, L.; Felfoldi, J.; et al. Advanced digital solutions for food traceability: Enhancing origin, quality, and safety through NIRS, RFID, Blockchain, and IoT. J. Sens. Actuator Netw. 2025, 14, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayikci, Y.; Durak Usar, D.; Aylak, B.L. Using blockchain technology to drive operational excellence in perishable food supply chains during outbreaks. Int. J. Logist. Manag. 2022, 33, 836–876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Angelis, D.; Summo, C.; Pasqualone, A.; Faccia, M.; Squeo, G. Advancements in food authentication using soft independent modelling of class analogy (SIMCA): A review. Food Qual. Saf. 2024, 8, fyae032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos, R.R.; Guarnieri, P. Social gains for artisanal agroindustrial producers induced by cooperation and collaboration in agri-food supply chain. Soc. Responsib. J. 2021, 17, 1131–1149. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Global Strategy for Food Safety 2022–2030: Towards Stronger Food Safety Systems and Global Cooperation; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).