Enhanced NO2 Detection in ZnO-Based FET Sensor: Charge Carrier Confinement in a Quantum Well for Superior Sensitivity and Selectivity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Theoretical Details
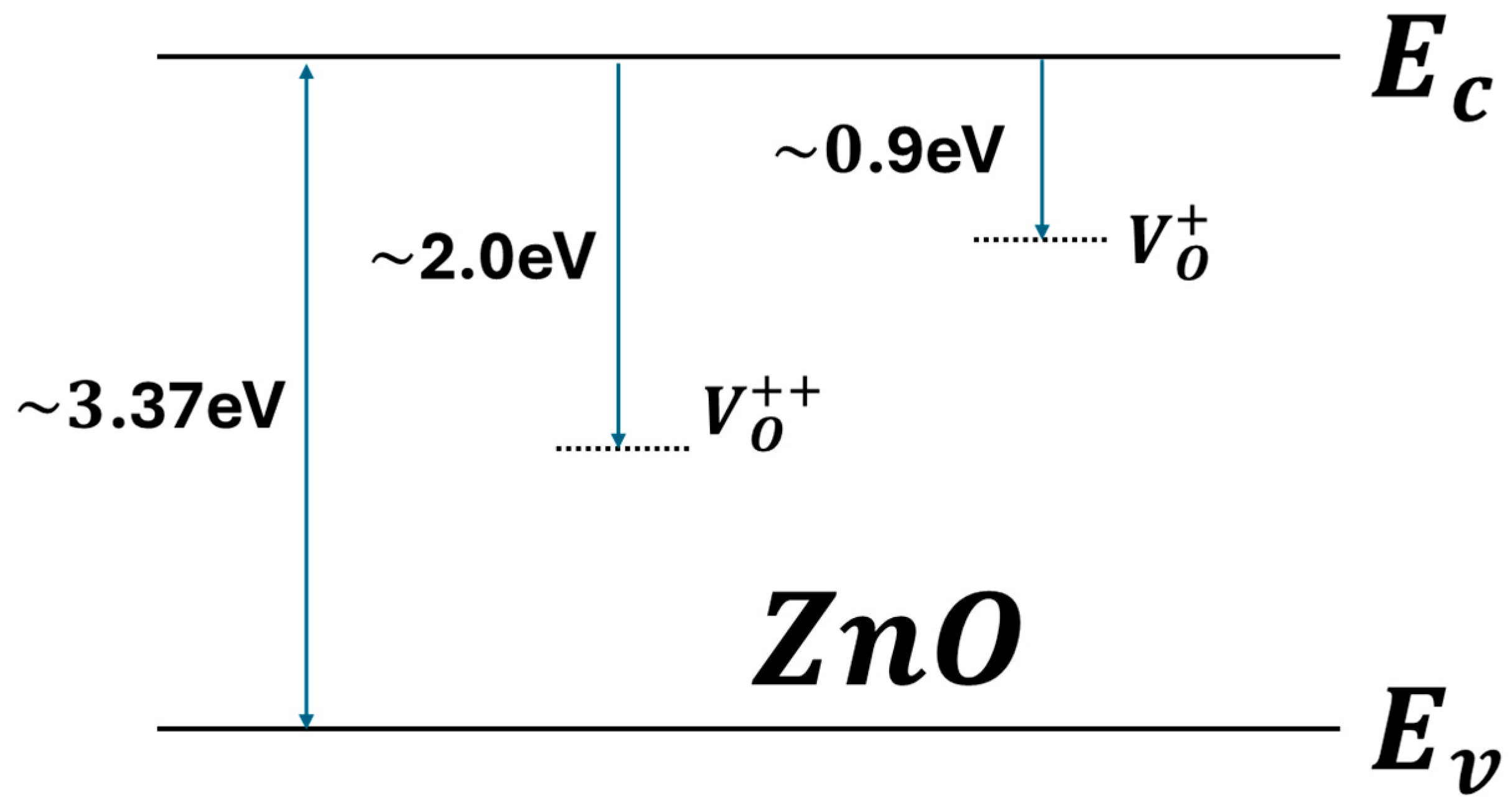
2.1. Working Principle of ZnO Sensor
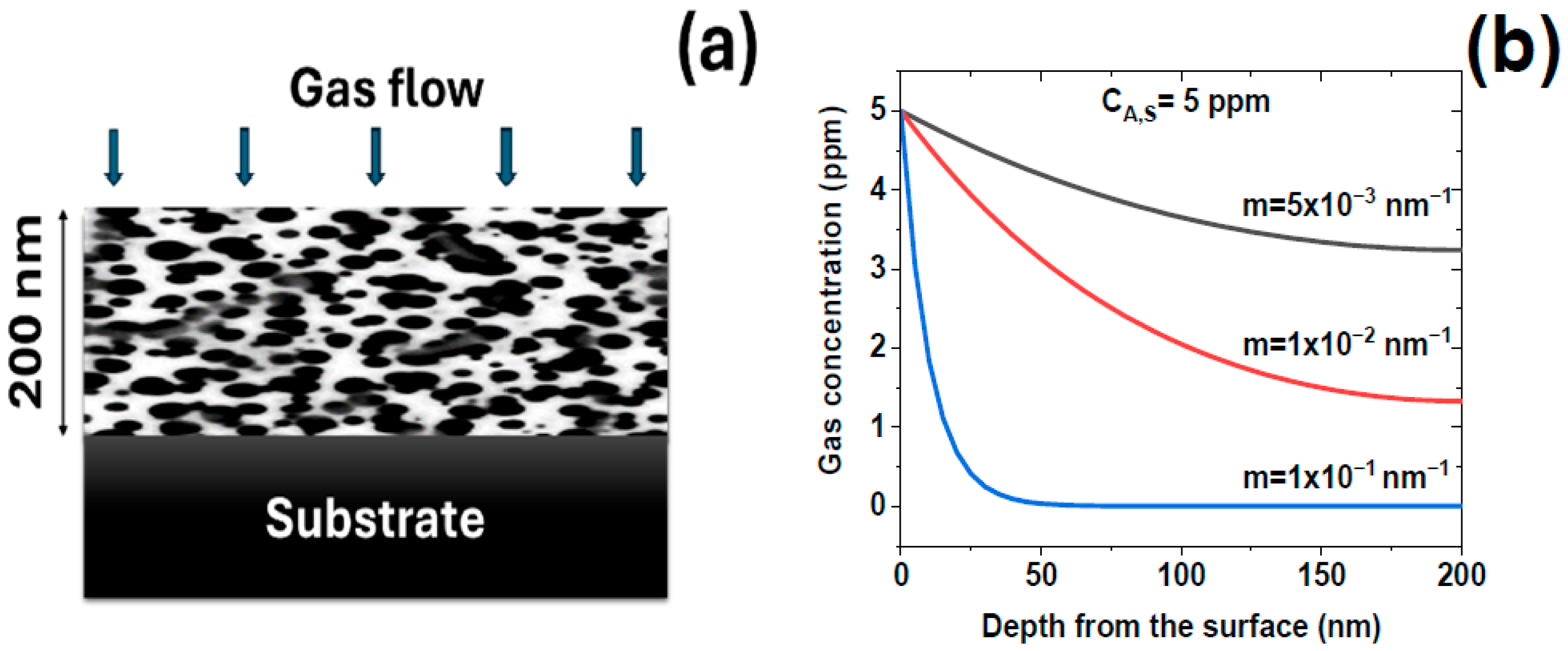
2.2. Modeling Gas Diffusion and Surface Kinetics in Porous ZnO
3. Experimental Details
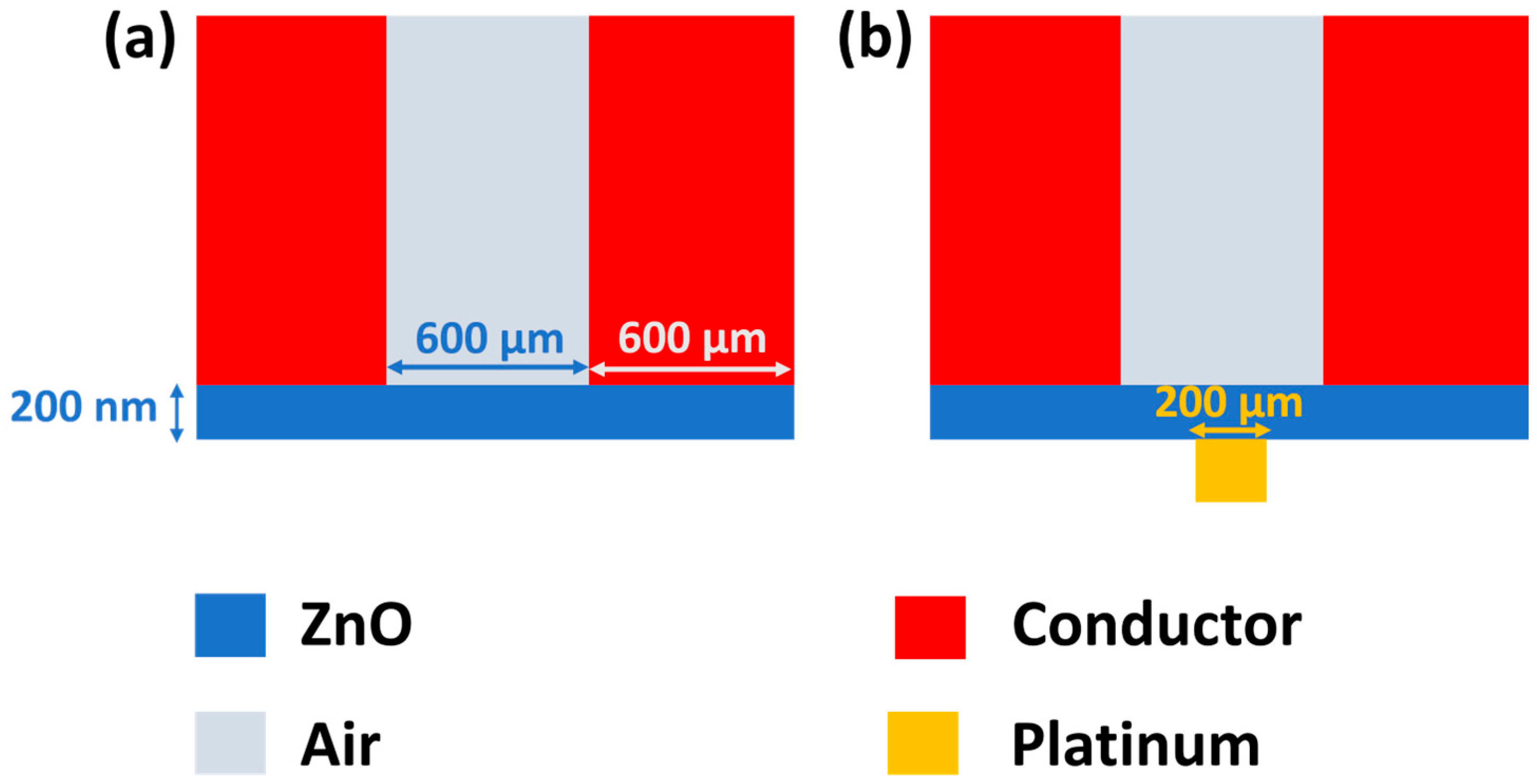
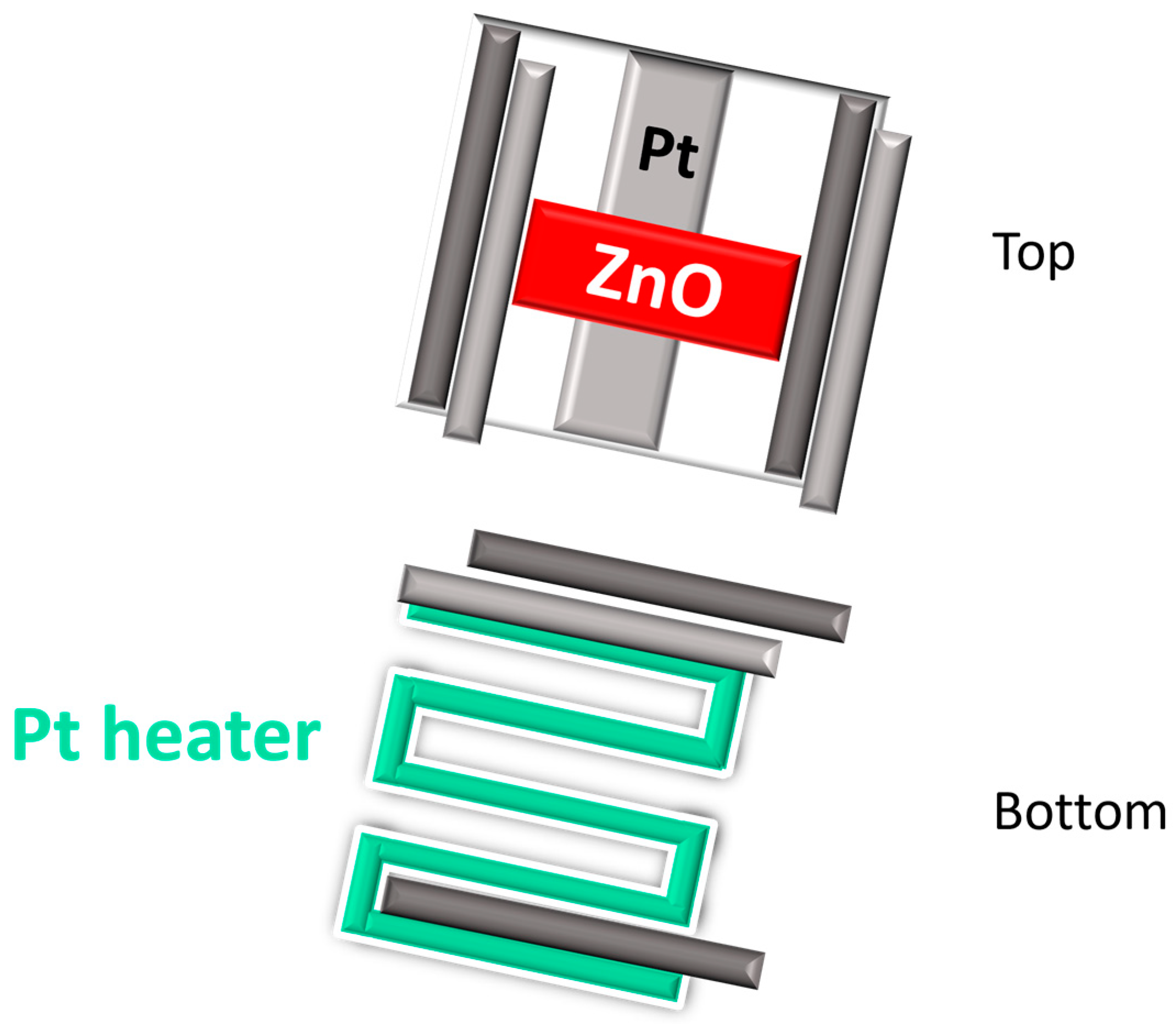
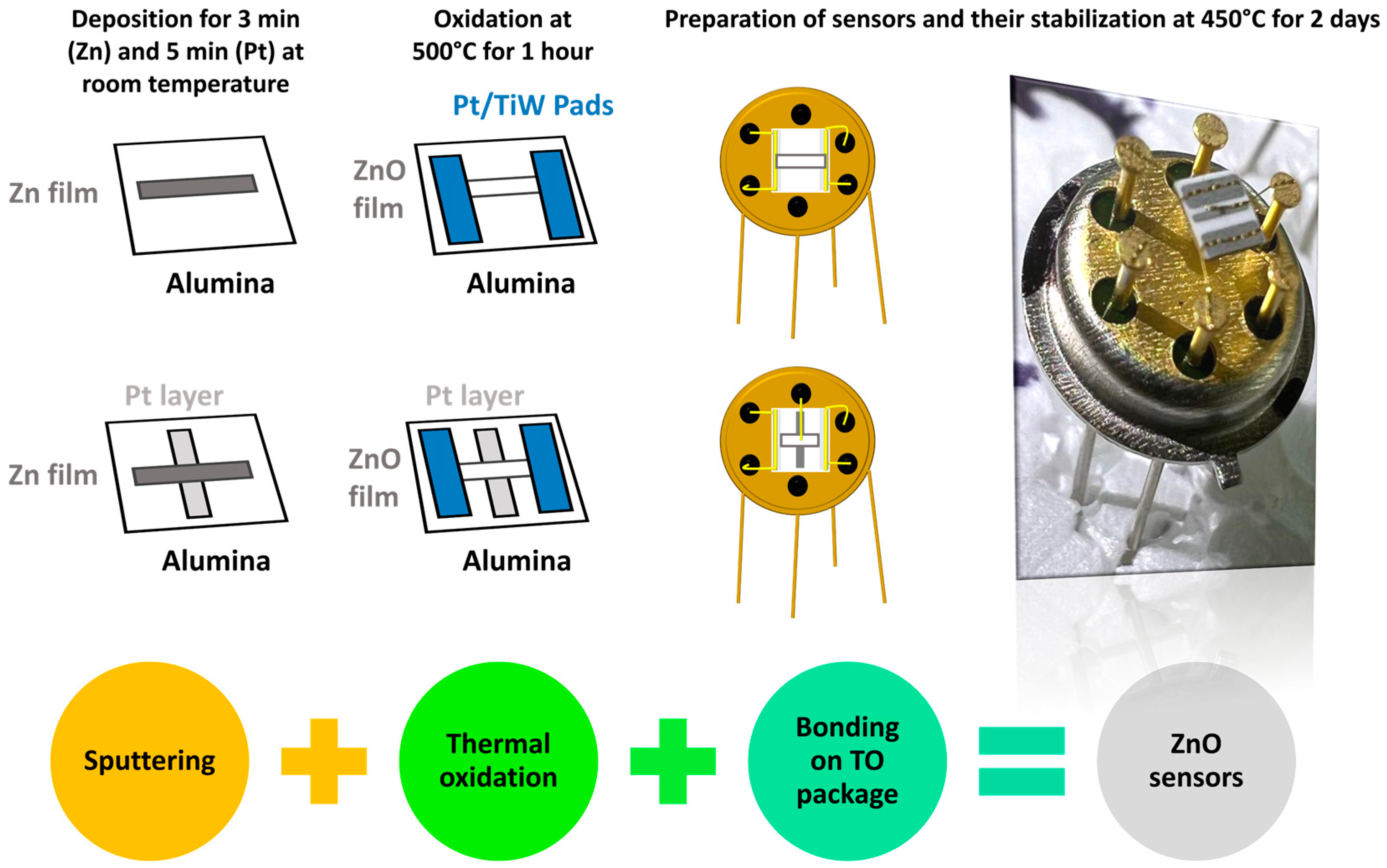
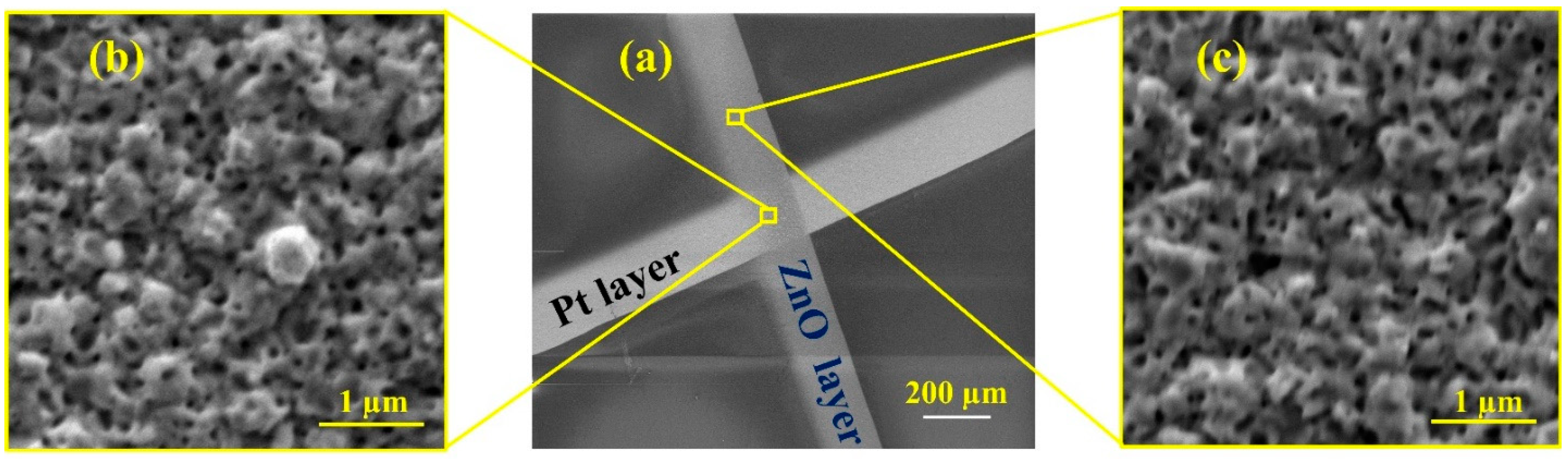
3.1. Fabrication Process
3.2. Characterizations
- Two pins were connected to the platinum heater on the backside of the alumina substrate, ensuring precise thermal control of the device;
- The remaining two pins were connected to the Pt pads on the top ZnO surface for electrical signal measurement.
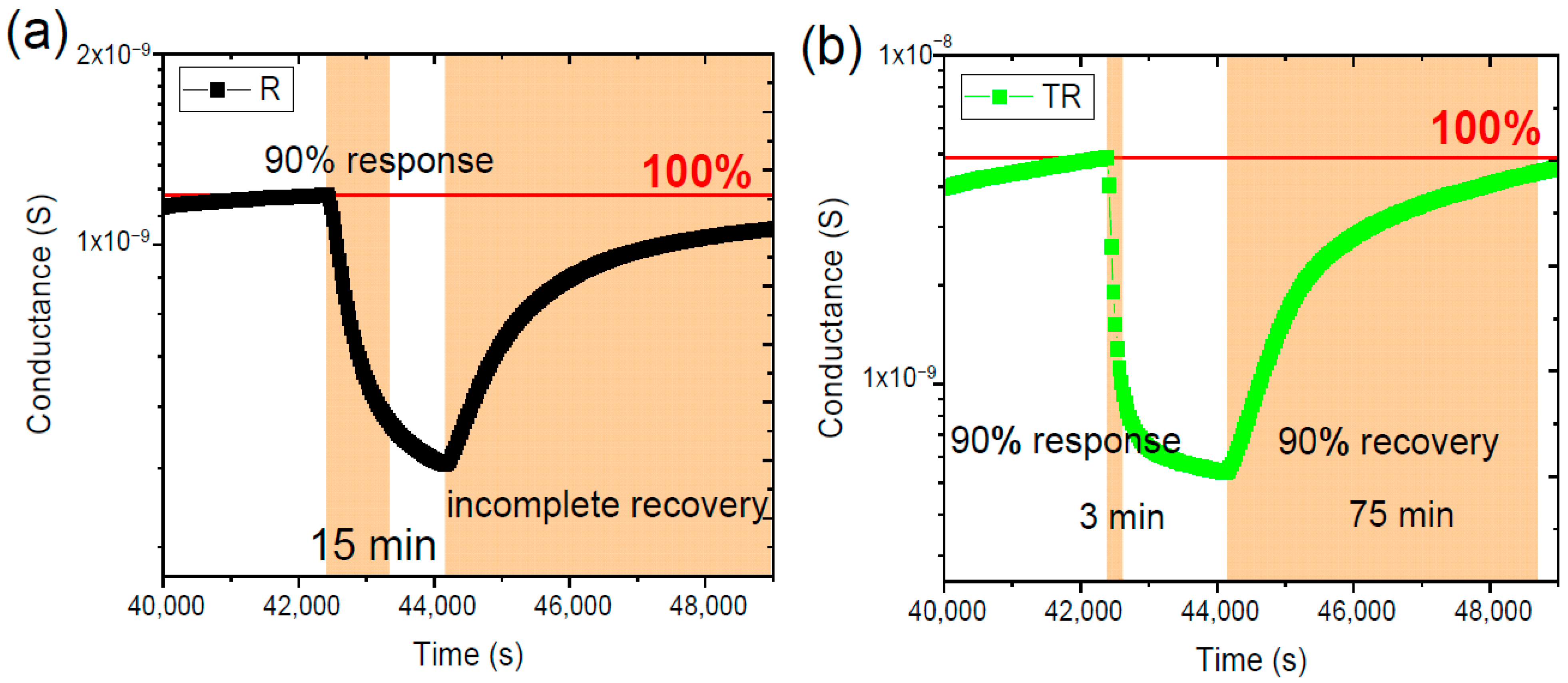
- 30 min of exposure to the target analyte,
- followed by 90 min of synthetic air flow to allow the sensor to return to its baseline conductance.
4. Results and Discussions
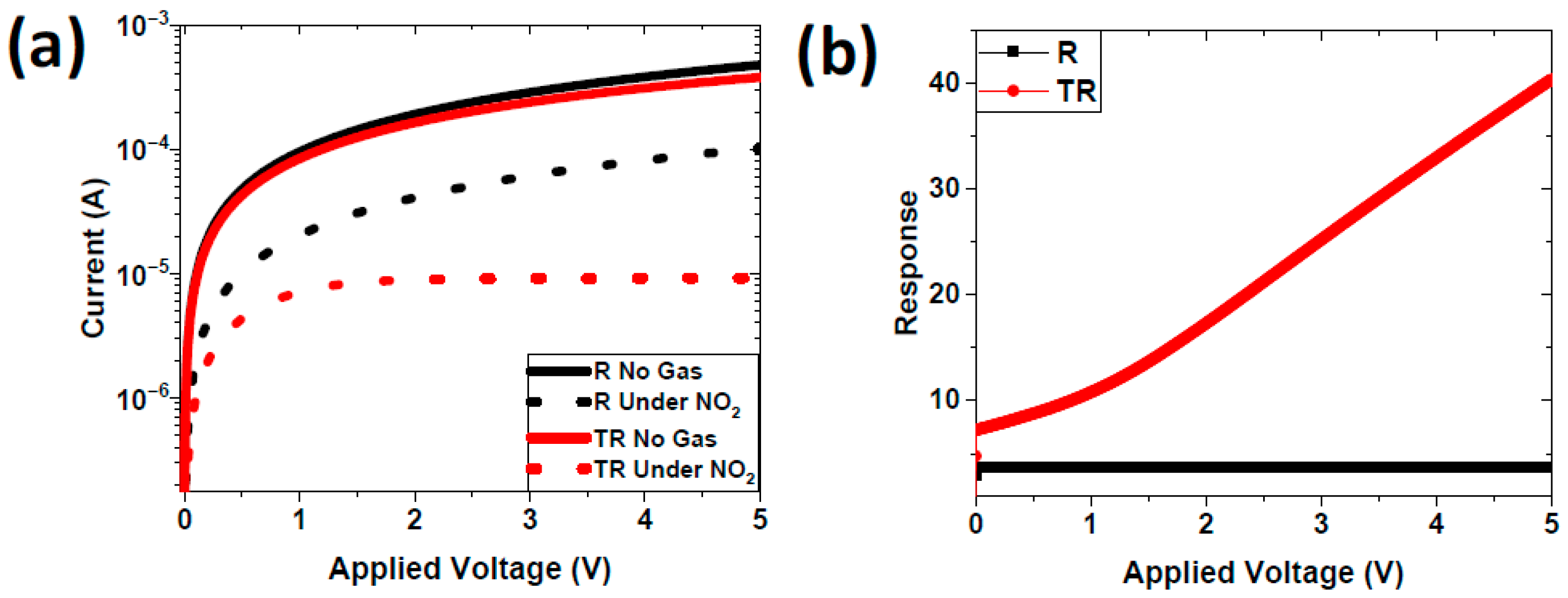
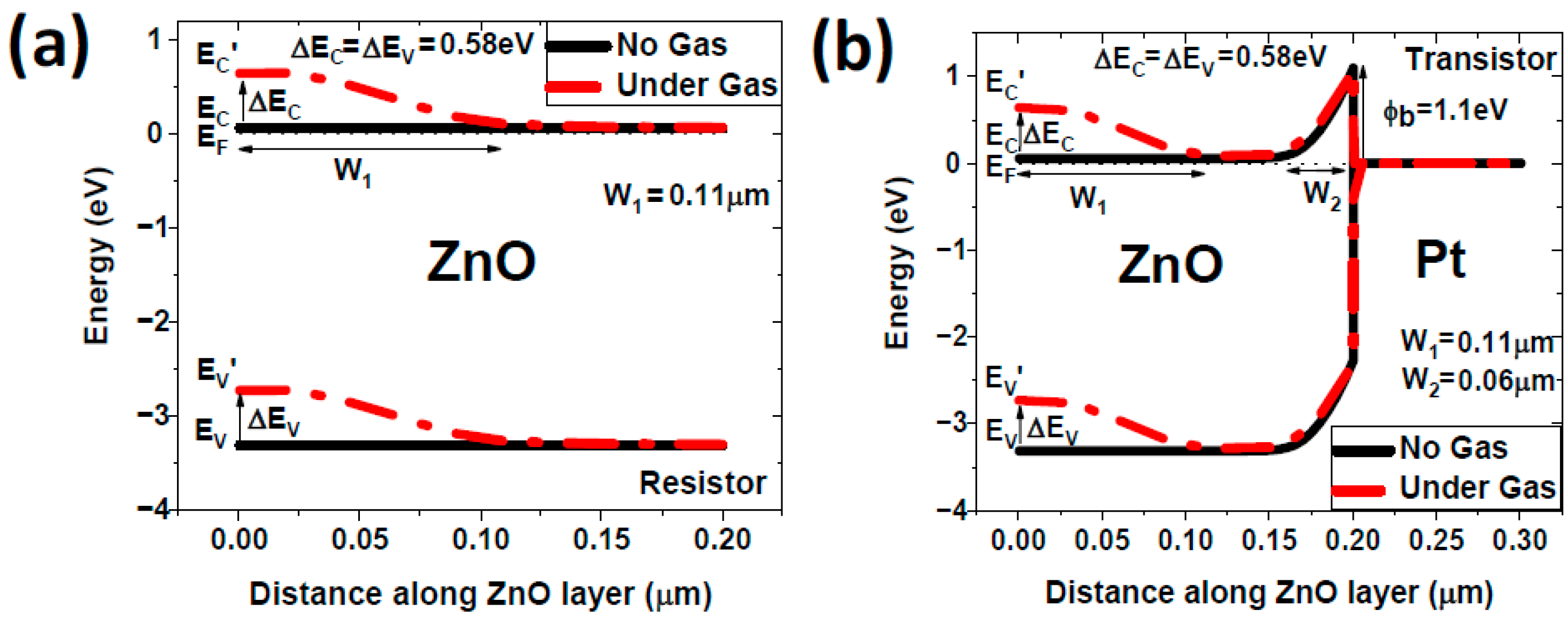
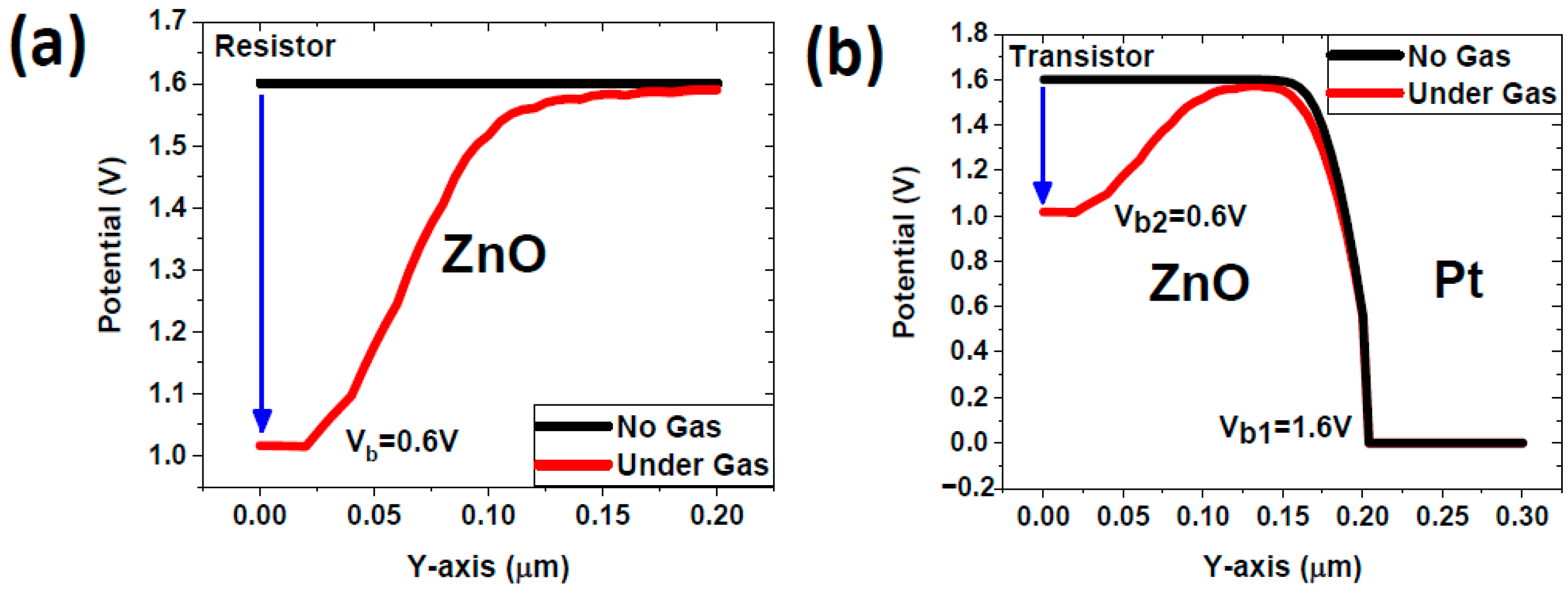
4.1. Modelling Results
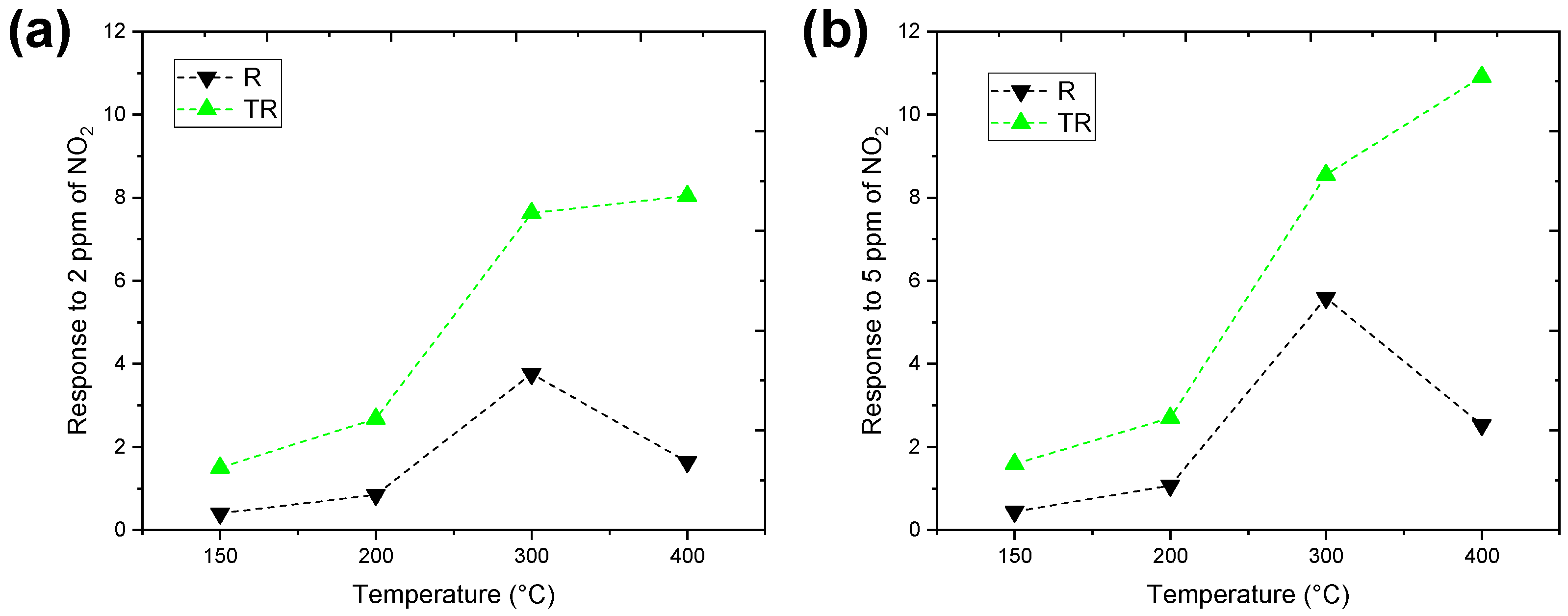
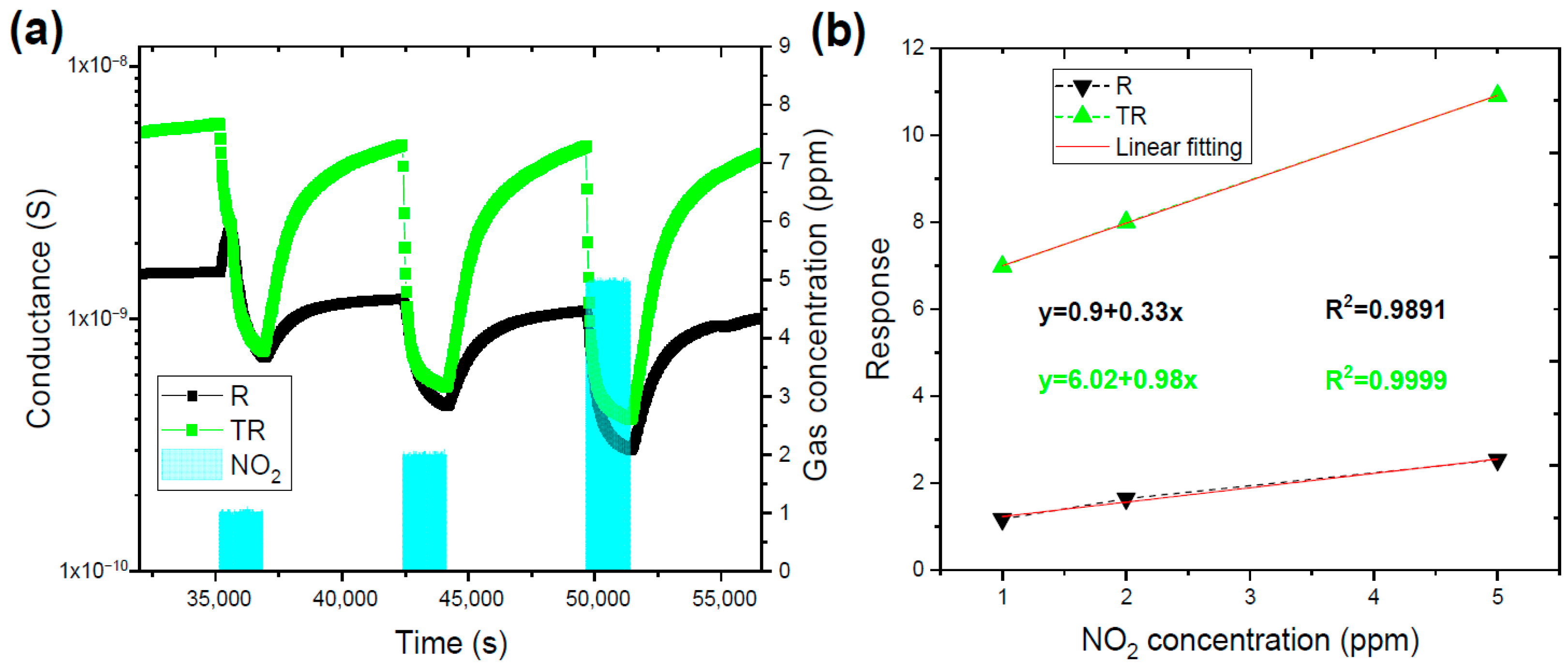
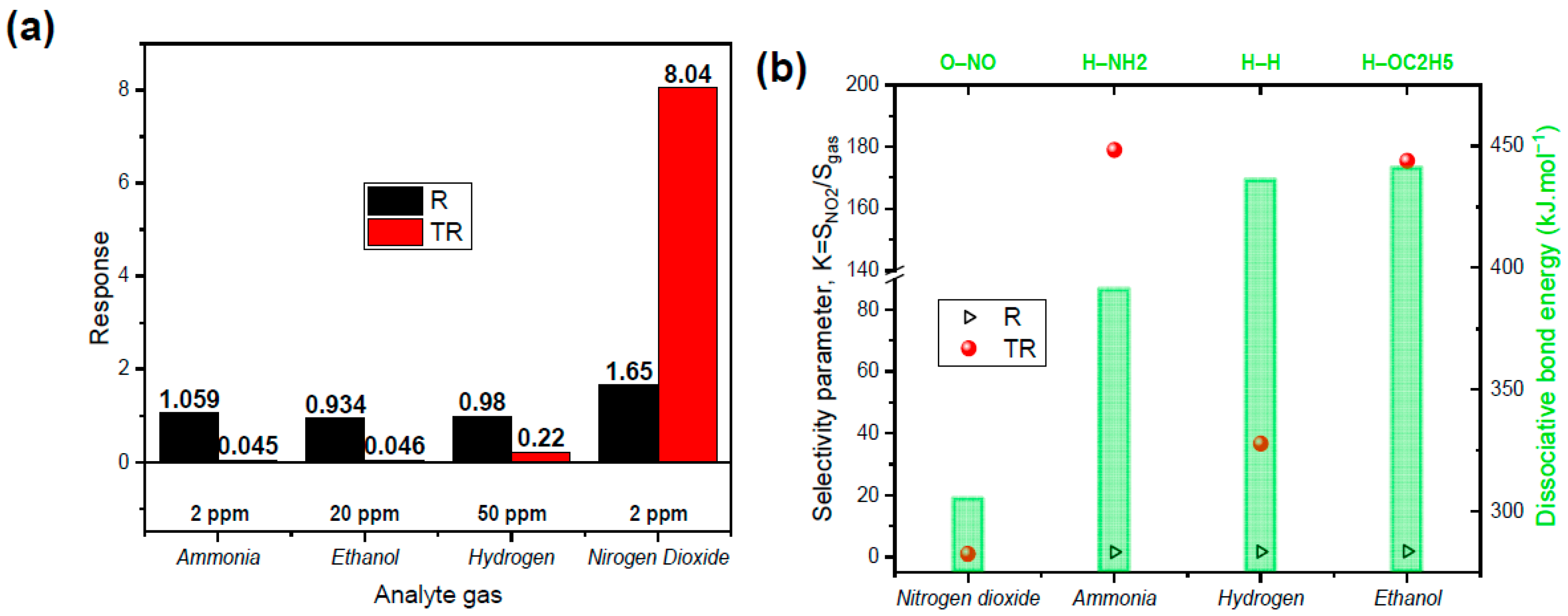
4.2. Experimental Results
- Schottky barrier at the ZnO/Pt interface: This barrier arises due to the difference in work function between ZnO and Pt [29]. The Schottky barrier establishes a potential difference that influences charge carrier dynamics within the FGFET structure.
- Additional barrier due to NO2 interaction: Upon the introduction of NO2 gas, the molecules adsorb onto the ZnO surface, leading to an increase in electron depletion and the formation of an additional potential barrier.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khorramifar, A.; Karami, H.; Lvova, L.; Kolouri, A.; Łazuka, E.; Piłat-Rożek, M.; Łagód, G.; Ramos, J.; Lozano, J.; Kaveh, M.; et al. Environmental Engineering Applications of Electronic Nose Systems Based on MOX Gas Sensors. Sensors 2023, 23, 5716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Hu, J.; Wang, J.; Ong, C.; Zhu, F. Nano-crystalline Cu-doped ZnO thin film gas sensor for CO. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 115, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, B.; Abaab, M.; Rezig, B. Structural and electrical properties of ZnO films prepared by screen printing technique. Thin Solid Film. 2001, 383, 92–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, H.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Choi, K.; Park, M.-K.; Hwang, J.; Lee, S.; Joo, Y.-C.; Jung, G.; Lee, J.-H. Optimization of co-sputtered zinc indium tin oxide-based MOSFET-type sensor for effective NO2 gas detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2025, 428, 137262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andringa, A.-M.; Piliego, C.; Katsouras, I.; Blom, P.W.M.; Leeuw, D.M.D. NO2 Detection and Real-Time Sensing with Field-Effect Transistors. Chem. Mater. 2014, 26, 773–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Hong, S.; Jeong, Y.; Jung, G.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, C.; Park, B.-G.; Lee, J.-H. Effect of charge storage engineering on the NO2 gas sensing properties of a WO3 FET-type gas sensor with a horizontal floating-gate. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9009–9017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-H. Gas sensors using hierarchical and hollow oxide nanostructures: Overview. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 140, 319–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazoe, N.; Shimanoe, K. Roles of shape and size of component crystals in semiconductor gas sensors: I. Response to oxygen. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2008, 155, J85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagarjuna, Y.; Hsiao, Y.-J.; Wang, S.-C.; Shao, C.-Y.; Huang, Y.-C. Nanoporous ZnO structure prepared by HiPIMS sputtering for enhanced ozone gas detection. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pleshek, D.; Tran, J.; Li, Y.; Shirani, A.; Shevchenko, E.V.; Berman, D. Swelling-assisted sequential infiltration synthesis of nanoporous ZnO films with highly accessible pores and their sensing potential for ethanol. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 35941–35948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, S.; Huang, W.; Shi, W.; Yu, J. Performance improvement of organic field-effect transistor ammonia gas sensor using ZnO/PMMA hybrid as dielectric layer. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 203, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, M.B.; Kim, S.-H.; Yoon, J.-B.; Comini, E. Preparation of NiO NWs by Thermal Oxidation for Highly Selective Gas-Sensing Applications. Sensors 2025, 25, 2075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Li, B.; Meng, F.; Liu, J.; Yuan, Z.; Wang, C.; Liu, J. Highly sensitive and selective butanol sensors using the intermediate state nanocomposites converted from β-FeOOH to α-Fe2O3. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 273, 543–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Qin, S.; Tang, P.; Feng, Y.; Li, D. Ultra-sensitive ethanol gas sensors based on nanosheet-assembled hierarchical ZnO-In2O3 heterostructures. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 391, 122191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wang, Z.; Han, D.; Gu, F.; Guo, G. High-sensitivity NO2 gas sensors based on flower-like and tube-like ZnO nanomaterials. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 157, 565–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, W.; Yuan, Z.; Gao, H.; Zhang, R.; Meng, F. Perovskite-structured LaCoO3 modified ZnO gas sensor and investigation on its gas sensing mechanism by first principle. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 341, 130015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurylev, V.; Perng, T.P. Defect engineering of ZnO: Review on oxygen and zinc vacancies. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2021, 41, 4977–4996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonker, R.K.; Sabhajeet, S.; Singh, S.; Yadav, B. Synthesis of ZnO nanopetals and its application as NO2 gas sensor. Mater. Lett. 2015, 152, 189–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.R.; Murugesan, T.; Dash, A.; Hsu, C.-H.; Gupta, S.; Manikandan, A.; Kumar Anbalagan, A.; Lee, C.-H.; Tai, N.-H.; Chueh, Y.-L. Ultrasensitive and light-activated NO2 gas sensor based on networked MoS2/ZnO nanohybrid with adsorption/desorption kinetics study. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 536, 147933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Jiang, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, F.; He, J.; Liu, A.; Lv, S.; You, R.; Yan, X.; Sun, P. Flexible resistive NO2 gas sensor of three-dimensional crumpled MXene Ti3C2Tx/ZnO spheres for room temperature application. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cai, C.; Li, Z.-H. Knudsen diffusion differs from Fickian diffusion. Phys. Fluids 2021, 33, 042009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Gao, J.; Fu, H.; Liu, S.; Hua, Z. A selective methane gas sensor based on SnO2 utilizing a reactive and porous substrate. Chin. J. Anal. Chem. 2025, 53, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakai, G.; Matsunaga, N.; Shimanoe, K.; Yamazoe, N. Theory of gas-diffusion controlled sensitivity for thin film semiconductor gas sensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 80, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbia, M.B.; Helal, H.; Saidi, F.; Maaref, H. Investigation of 1.9 μm GINA Simulated as Intrinsic Layer in a GaAs Homojunction: From 25% Towards 32.4% Conversion Yield. J. Electron. Mater. 2020, 49, 6308–6316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvaco International. ATLAS User’s Manual a 2D Numerical Device Simulator, 2004; Silvaco Int.: Santa Clara, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, G.W.; Seo, S.G.; Choi, S.; Kim, D.H.; Jin, S.H. Unscrambling for subgap density-of-states in multilayered MoS2 field effect transistors under DC bias stress via optical charge-pumping capacitance-voltage spectroscopy. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 73090–73102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, A.; Karmakar, A.; Ghosh, R.; Saha, P. (Eds.) Investigation of MoS2 based dual gate MOSFET as a H2 sensor considering catalytic metal gate approach. In 2022 IEEE VLSI Device Circuit and System (VLSI DCS); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, S.; Seo, S.G.; Yu, H.R.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Jin, S.H. Hydrophobic Polymer Encapsulation Effects on Subgap Density of States in Multilayered Molybdenum Disulfide Field—Effect Transistors. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL)-Rapid Res. Lett. 2020, 14, 1900492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chirakkara, S.; Choudhury, P.R.; Nanda, K.K.; Krupanidhi, S.B. Understanding Pt–ZnO:In Schottky nanocontacts by conductive atomic force microscopy. Mater. Res. Express 2016, 3, 045023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.A.; Conti, P.P.; Andre, R.S.; Correa, D.S. A review on chemiresistive ZnO gas sensors. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modak, M.; Mahajan, S.; Shinde, M.; Rane, S.; Jagtap, S. Sensitive, selective and low detection limit of NO2 gas sensor based on Cu/ZnO/rGO nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2022, 33, 26205–26224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, S.; Karmakar, N.; Shah, A.; Shimpi, N.G. Development of Ni doped ZnO/polyaniline nanocomposites as high response room temperature NO2 sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2019, 247, 114381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; Alkaoud, A.; Neri, G. Low operating temperature of UV photo-activated In-doped ZnO NO2 sensors. Appl. Phys. A 2023, 129, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaballah, S.; Hjiri, M.; Zahmouli, N.; Albargi, H.B.; Dhahri, R.; Dahman, H.; Mir, L.E.; Neri, G. Room temperature UV-Vis activated NO2 gas sensor-based Mg-doped zinc oxide nanopowders. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 2023, 34, 137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjiri, M.; Neri, G. Photo-Activated Ga-ZnO Gas Sensor for NO2 Detection at Near Ambient Temperature. J. Inorg. Organomet. Polym. Mater. 2023, 34, 3374–3383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, T.-H.; Bak, S.-Y.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.H.; Han, Y.-J.; Yi, M. Decoration of CuO NWs Gas Sensor with ZnO NPs for Improving NO2 Sensing Characteristics. Sensors 2021, 21, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mun, Y.; Park, S.; An, S.; Lee, C.; Kim, H.W. NO2 gas sensing properties of Au-functionalized porous ZnO nanosheets enhanced by UV irradiation. Ceram. Int. 2013, 39, 8615–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Chavarri, J.; Parellada-Monreal, L.; Castro-Hurtado, I.; Castaño, E.; Mandayo, G.G. ZnO nanoneedles grown on chip for selective NO2 detection indoors. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 255, 1244–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, J.; Wei, D.; Lu, R.; Zhu, L.; Li, H.; Shen, Y. In-situ growth of ZnO nanowire arrays on the sensing electrode via a facile hydrothermal route for high-performance NO2 sensor. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 435, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijjapu, M.T.; Surya, S.G.; Yuvaraja, S.; Zhang, X.; Alshareef, H.N.; Salama, K.N. Fully Integrated Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide NO2 Gas Detector. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 984–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobelspies, S.; Bierer, B.; Daus, A.; Takabayashi, A.; Salvatore, G.A.; Cantarella, G.; Ortiz Perez, A.; Wöllenstein, J.; Palzer, S.; Tröster, G. Photo-Induced Room-Temperature Gas Sensing with a-IGZO Based Thin-Film Transistors Fabricated on Flexible Plastic Foil. Sensors 2018, 18, 358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.S.; Ahn, C.H.; Jung, S.H.; Cho, S.W.; Cho, H.K. Toward Adequate Operation of Amorphous Oxide Thin-Film Transistors for Low-Concentration Gas Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 10185–10193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, X.; Zhao, X.; Chen, J.; Bermak, A.; Fan, Z. A fast-response/recovery ZnO hierarchical nanostructure based gas sensor with ultra-high room-temperature output response. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 206, 764–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Jha, P.; Singh, A.; Chauhan, A.K.; Gupta, S.K.; Aswal, D.K.; Muthe, K.P.; Gadkari, S.C. Modeling of gate bias controlled NO2 response of the PCDTBT based organic field effect transistor. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2018, 698, 7–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sik Choi, M.; Young Kim, M.; Mirzaei, A.; Kim, H.-S.; Kim, S.-i.; Baek, S.-H.; Won Chun, D.; Jin, C.; Hyoung Lee, K. Selective, sensitive, and stable NO2 gas sensor based on porous ZnO nanosheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 568, 150910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amna, B.; Ozturk, T. Organic field-effect transistor-based sensors: Recent progress, challenges and future outlook. J. Mater. Chem. C 2025, 13, 8354–8424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, N.D. An Investigation of the Performance and Stability of Zinc Oxide Thin-Film Transistors and the Role of High-k Dielectrics. Ph.D. Thesis, De Montfort University, Leicester, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Bai, Z.; Xie, C.; Hu, M.; Zhang, S.; Zeng, D. Effect of humidity on the gas sensing property of the tetrapod-shaped ZnO nanopowder sensor. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2008, 149, 12–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.; Jung, G.; Hong, S.; Jeong, Y.; Park, J.; Kim, D.; Jang, D.; Kwon, D.; Bae, J.-H.; Park, B.-G.; et al. Proposition of deposition and bias conditions for optimal signal-to-noise-ratio in resistor- and FET-type gas sensors. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 19768–19775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.-W.; Cho, S.; Wang, M.-S.; Dung, D.D. Co-contribution of hydrogen impurities and native defects might be the answer for the n-type conductivity in ZnO. Phys. Lett. A 2016, 380, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Li, X.; Xia, Y.; Yang, C. Synergistic effects of UV activation and surface oxygen vacancies on the room-temperature NO2 gas sensing performance of ZnO nanowires. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Arbia, M.; Helal, H.; Comini, E. Recent Advances in Low-Dimensional Metal Oxides via Sol-Gel Method for Gas Detection. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaneti, Y.V.; Yue, J.; Jiang, X.; Yu, A. Controllable synthesis of ZnO nanoflakes with exposed (1010) for enhanced gas sensing performance. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 13153–13162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, G.; Kwon, D.; Shin, W.; Park, M.-K.; Kim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-H. Fast-response/recovery In2O3 thin-film transistor-type NO2 gas sensor with floating-gate at low temperature. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2023, 394, 134477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marikutsa, A.; Rumyantseva, M.; Konstantinova, E.A.; Gaskov, A. The Key Role of Active Sites in the Development of Selective Metal Oxide Sensor Materials. Sensors 2021, 21, 2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pakdel, H.; Borsi, M.; Ponzoni, M.; Comini, E. Enhanced Gas Sensing Performance of CuO-ZnO Composite Nanostructures for Low-Concentration NO2 Detection. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
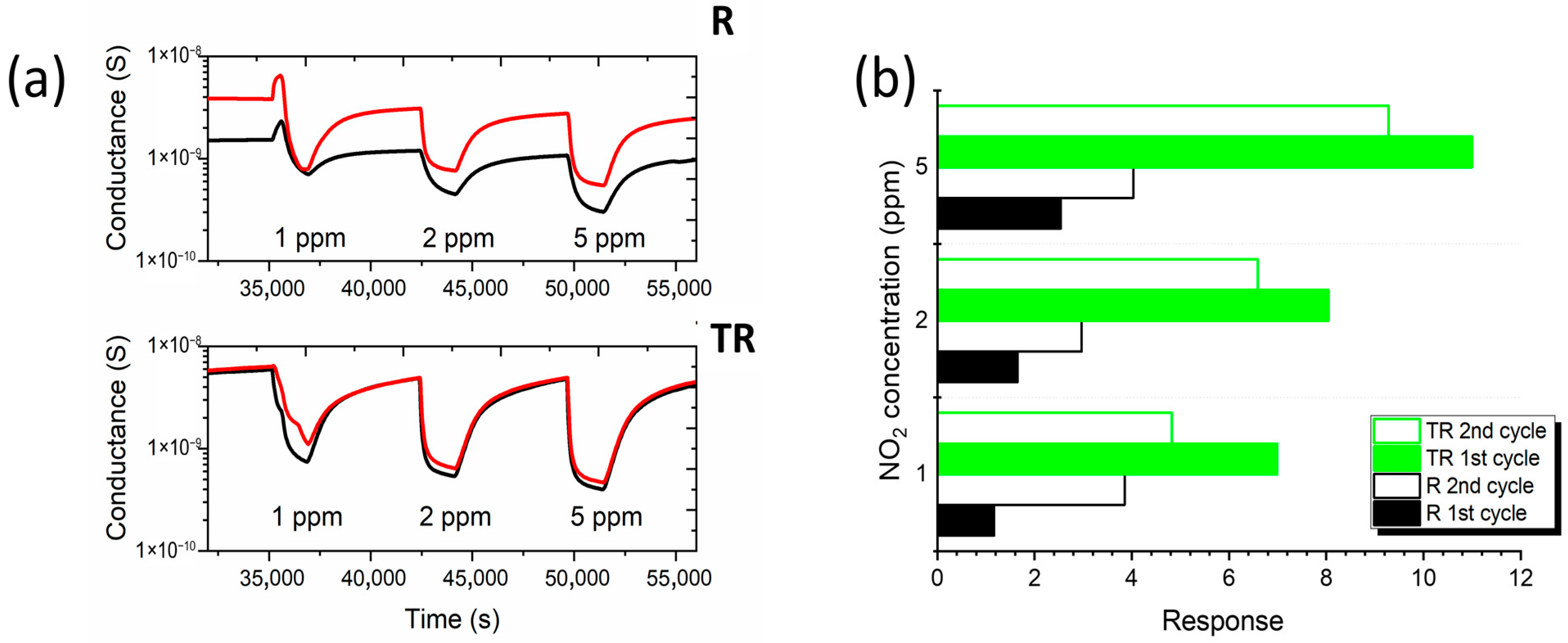
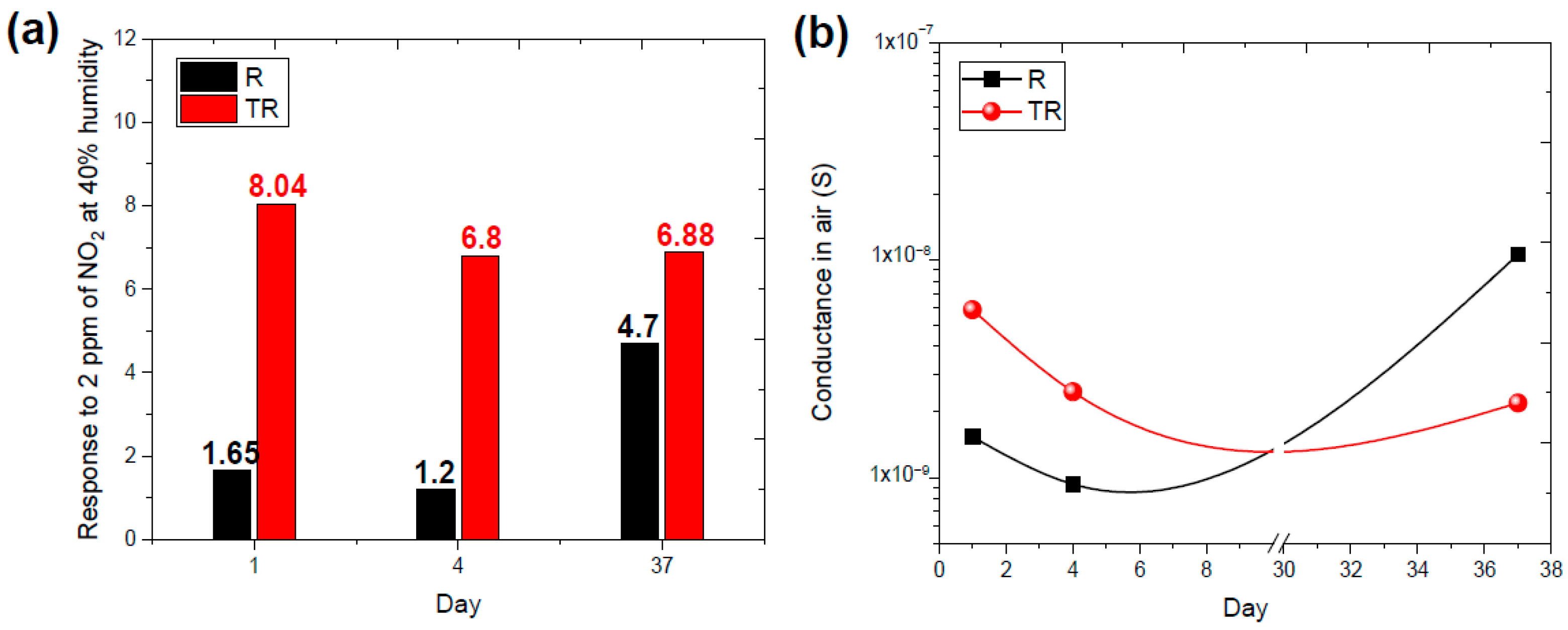
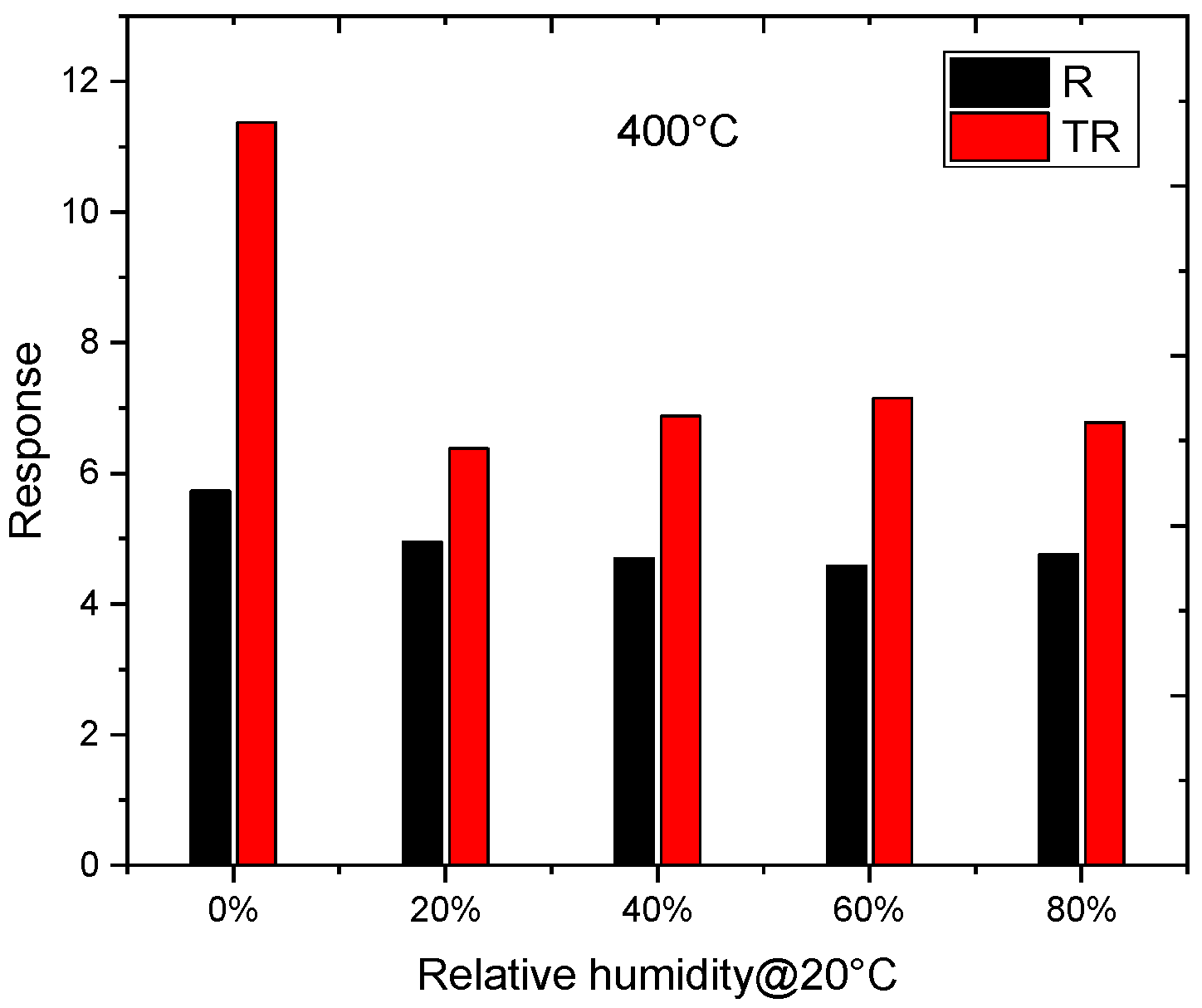
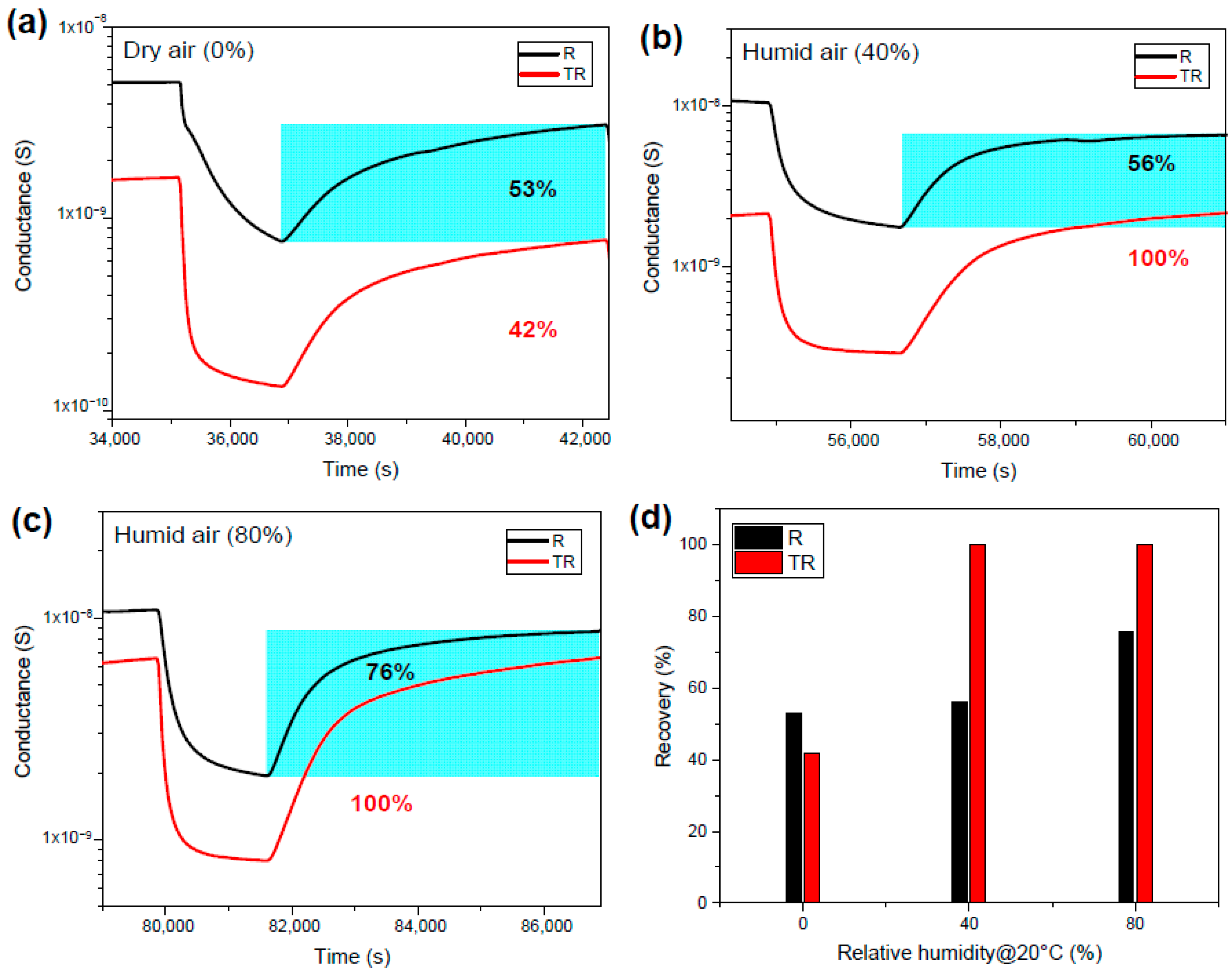
| Device Type | Substrate | Sensing Layer | Sensing Condition | Response | LOD (ppb) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Conductometric sensor | Alumina | ZnO thin film | 400 °C | 2.54 (1) | 927 | Present work |
| Resistive sensor | Alumina | ZnO film | 250 °C | 1.42 (2) | NA * | [31] |
| Resistive sensor | Glass | Ni-doped ZnO/PANi nanocomposite | RT ** | 0.14 (3) | NA | [32] |
| Resistive sensor | Alumina | ZnO | 100 °C, under UV exposure | <1.5 (2) | NA | [33] |
| Resistive sensor | Alumina | Mg-doped ZnO | 400 °C 30 °C, under UV exposure | 1.01 (2) ≈1.5 (2) | NA NA | [34] |
| Resistive sensor | Alumina | ZnO | 300 °C, under UV exposure | 1.5 (2) | NA | [35] |
| Resistive sensor | NA | ZnO NPs decorated on CuO NWs | 250 °C | 1.17 (4) | NA | [36] |
| Resistive sensor | Oxidized Si substrate | ZnO nanosheets | RT, under UV exposure (1.2 mW/cm2) | ≈1.37 (2) | NA | [37] |
| Resistive sensor | Oxidized Si substrate | Au-functionalized ZnO nanosheets | RT, under UV exposure (0.35 mW/cm2) RT, under UV exposure (1.2 mW/cm2) | ≈1.33 (2) ≈4.55 (2) | NA NA | [37] |
| Resistive sensor | Alumina | ZnO nanoneedles | 195 °C | 1.04 (5) | 80 | [38] |
| Resistive sensor | Alumina | ZnO Nanowires | 250 °C | 3.3 (2) | NA | [39] |
| Thin Film Transistor | Pt/Alumina | ZnO thin film | 400 °C | 11 (1) | 89 | Present work |
| Thin Film Transistor | SiO2/Si | Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide thin film | RT | −0.998 (6) | 100 | [40] |
| Thin Film Transistor | Flexible Plastic Foil | Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide thin film | RT | <1.5 (7) | NA | [41] |
| Thin Film Transistor | SiO2/Si | Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide thin film | 100 °C | <4 (8) | NA | [42] |
| Thin Film Transistor | Silicon chip | ZnO nanowires | RT | 1.088 (2) | NA | [43] |
| Organic Field Effect Transistor | BOPET | PCDTBT polymer | RT | ≈0.5 (6) | 1000 | [44] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Helal, H.; Ben Arbia, M.; Pakdel, H.; Zappa, D.; Benamara, Z.; Comini, E. Enhanced NO2 Detection in ZnO-Based FET Sensor: Charge Carrier Confinement in a Quantum Well for Superior Sensitivity and Selectivity. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13100358
Helal H, Ben Arbia M, Pakdel H, Zappa D, Benamara Z, Comini E. Enhanced NO2 Detection in ZnO-Based FET Sensor: Charge Carrier Confinement in a Quantum Well for Superior Sensitivity and Selectivity. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(10):358. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13100358
Chicago/Turabian StyleHelal, Hicham, Marwa Ben Arbia, Hakimeh Pakdel, Dario Zappa, Zineb Benamara, and Elisabetta Comini. 2025. "Enhanced NO2 Detection in ZnO-Based FET Sensor: Charge Carrier Confinement in a Quantum Well for Superior Sensitivity and Selectivity" Chemosensors 13, no. 10: 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13100358
APA StyleHelal, H., Ben Arbia, M., Pakdel, H., Zappa, D., Benamara, Z., & Comini, E. (2025). Enhanced NO2 Detection in ZnO-Based FET Sensor: Charge Carrier Confinement in a Quantum Well for Superior Sensitivity and Selectivity. Chemosensors, 13(10), 358. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13100358







