Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Electrochemical Biosensors
Abstract
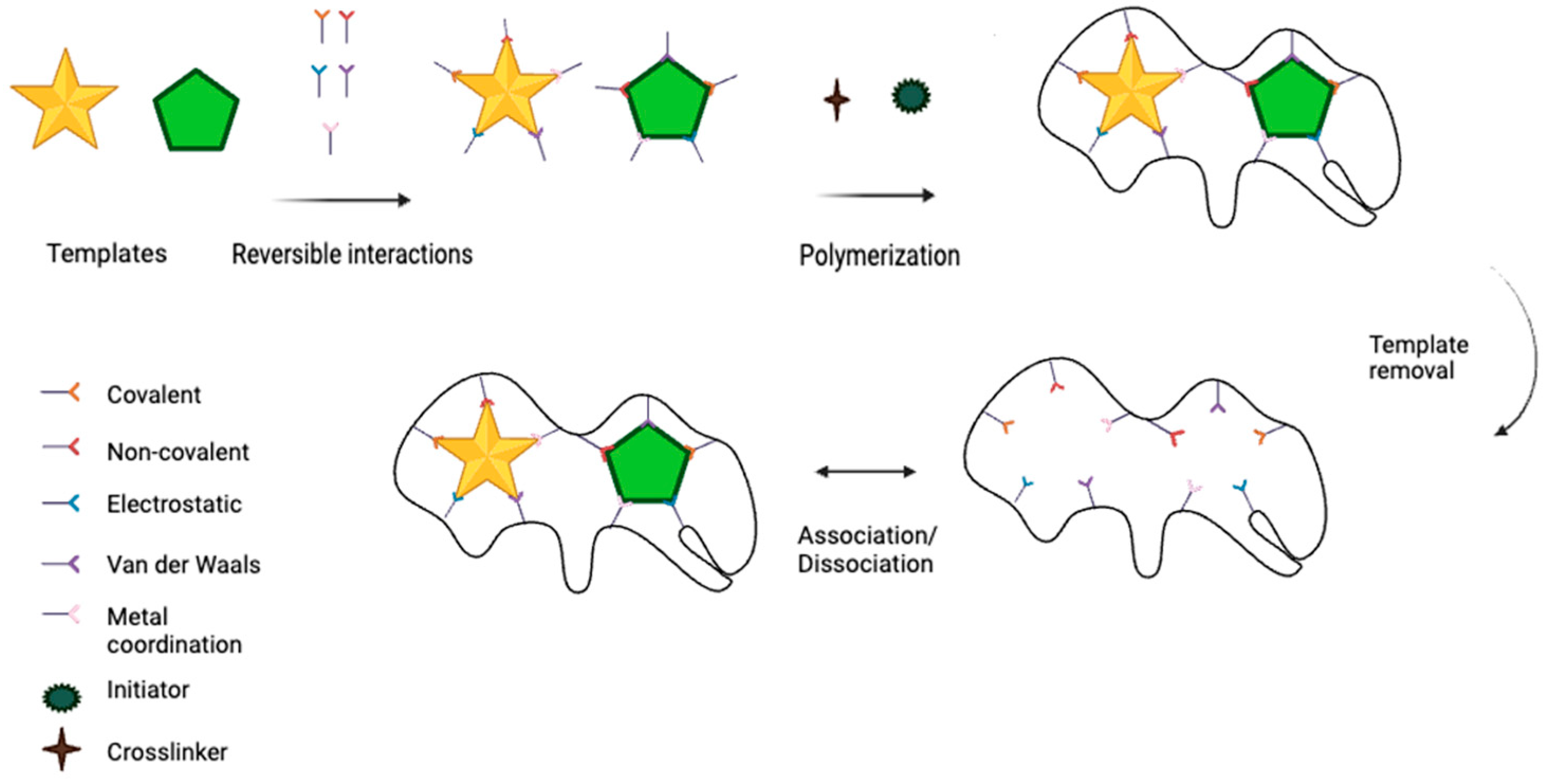
1. Introduction
2. Detection of Targets by MT-MIP
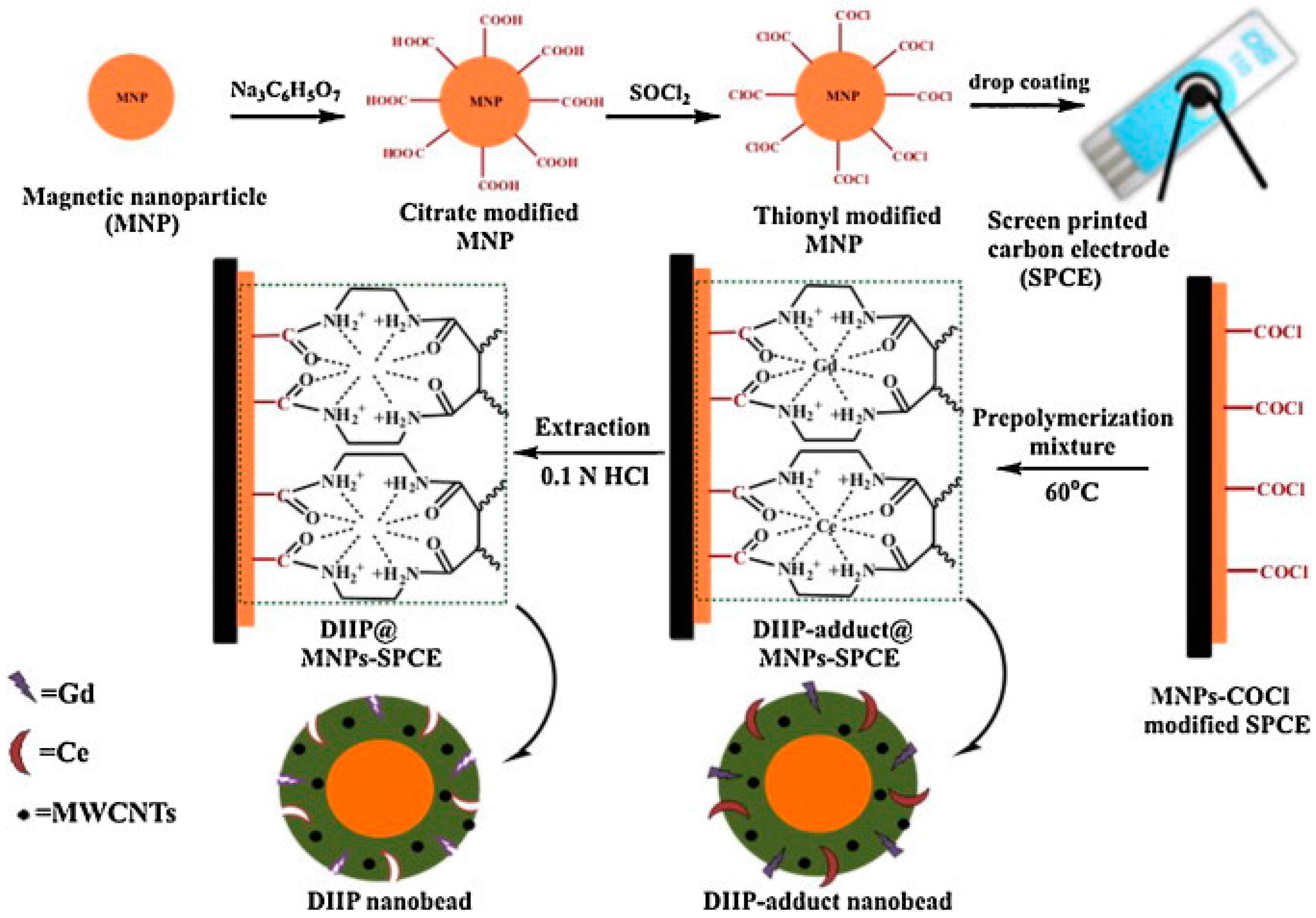
2.1. Detection of Ions
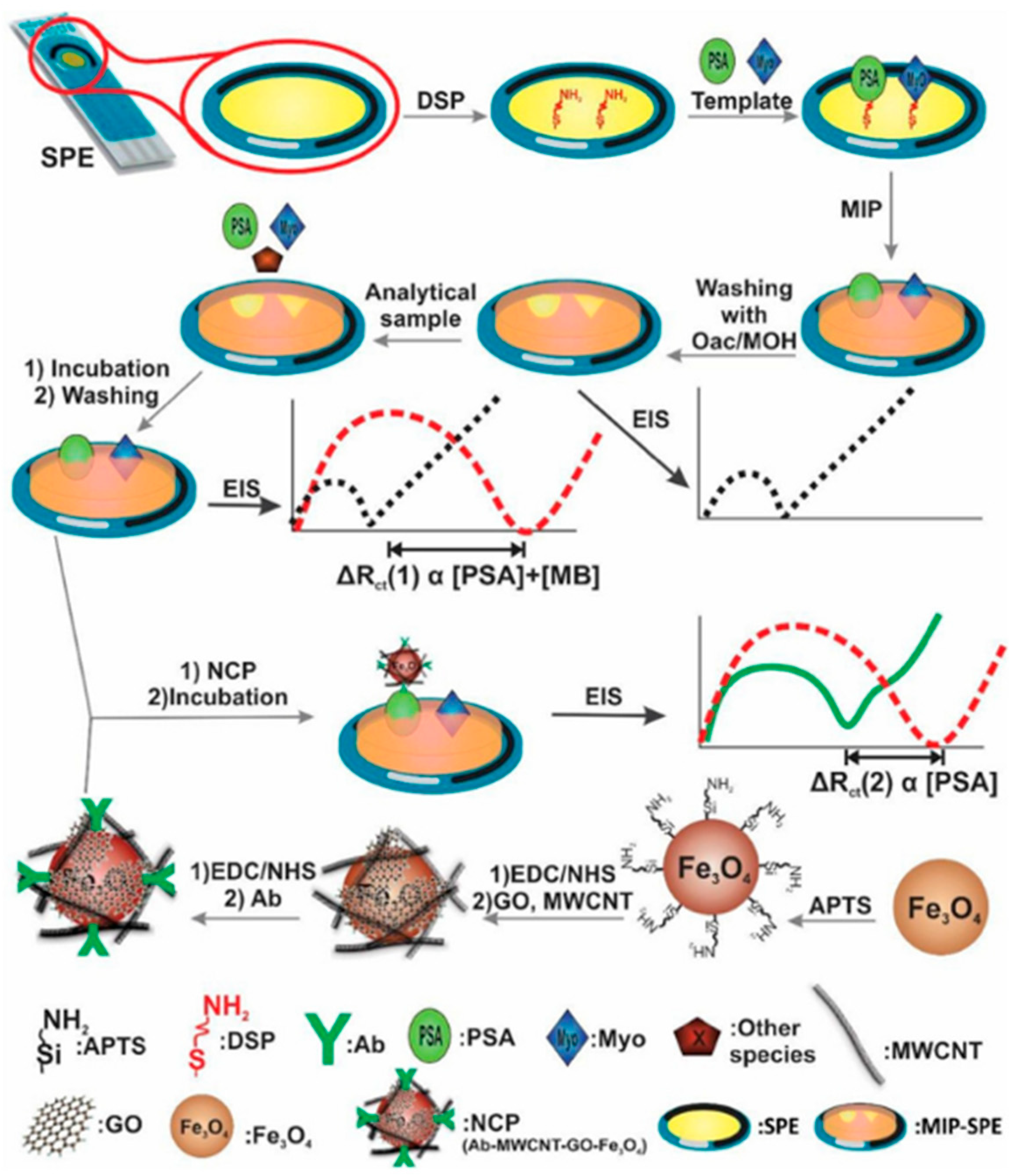
2.2. Detection of Biomarkers
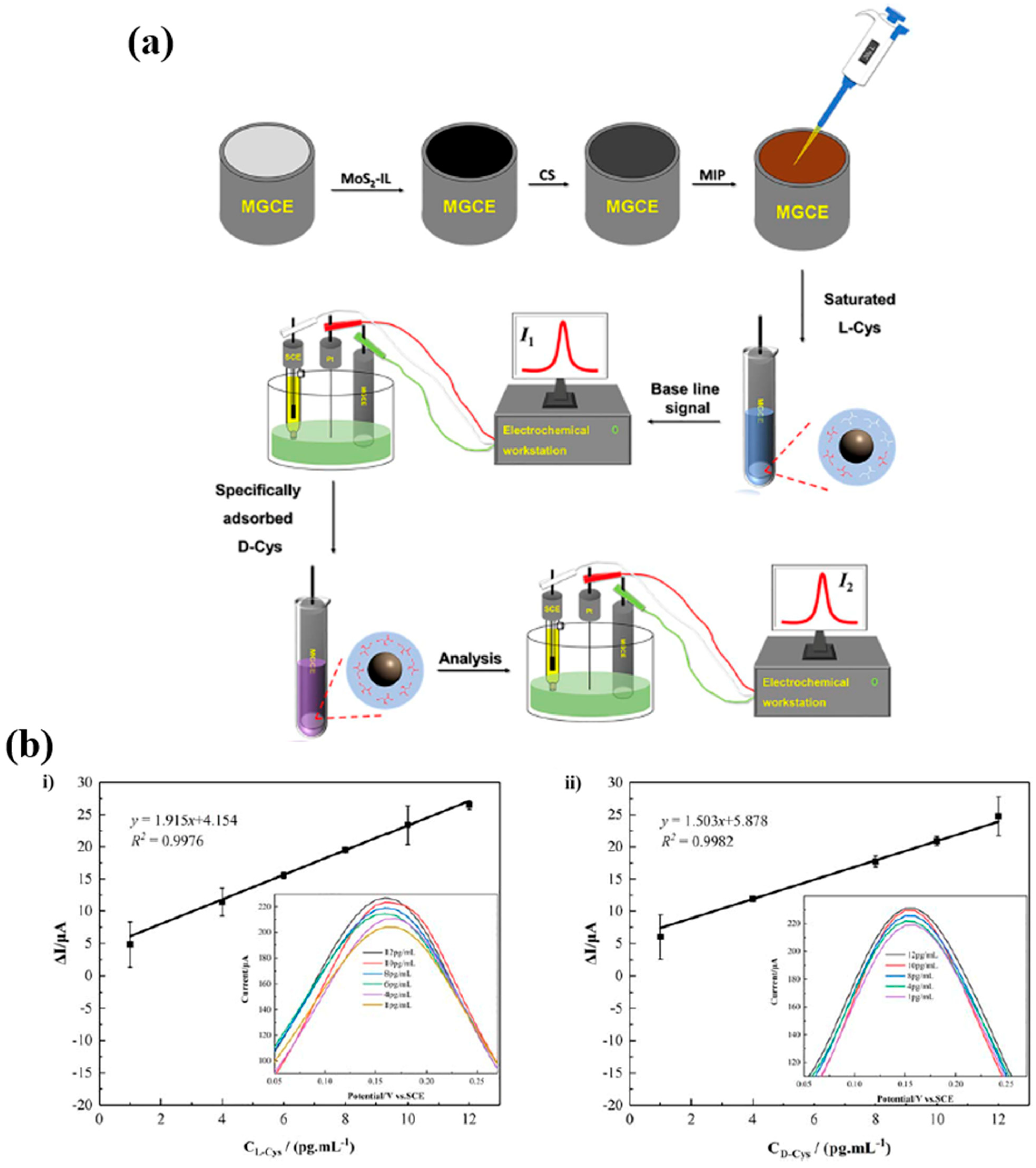
2.3. Detection of Amino Acids
2.4. Detection of Pharmaceutical Compounds
2.5. Detection of Neurotransmitters
2.6. Detection of Environmental Pollutants
2.7. Detection of Cells and Viruses
3. Integration of Microfluidics and Commercialization
4. Future Perspectives
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aydin, E.B.; Aydin, M.; Sezginturk, M.K. Biosensors in Drug Discovery and Drug Analysis. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2019, 15, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu, H.; Hossain, M.A.M.; Marlinda, A.; Al Mamun, M.; Simarani, K.; Johan, M.R. Nanomaterials Based Electrochemical Nucleic Acid Biosensors for Environmental Monitoring: A Review. Appl. Surf. Sci. Adv. 2021, 4, 100064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, G.E.S.; Akim, A.M.; Safdar, N.; Yasmin, A.; Begum, S.; Sung, Y.Y.; Sifzizul, T.; Muhammad, T. Cancer and Disease Diagnosis-Biosensor as Potential Diagnostic Tool for Biomarker Detection. J. Adv. Pharm. Technol. Res. 2022, 13, 243–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mi, F.; Hu, C.M.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Peng, F.; Geng, P.F.; Guan, M. Recent Advancements in Microfluidic Chip Biosensor Detection of Foodborne Pathogenic Bacteria: A Review. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 2883–2902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.L.; Xie, M.J.; Zhao, F.G.; Han, S.Y. Application of Nanomaterial Modified Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Sensor in Detection of Heavy Metal Ions. Foods 2022, 11, 1404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naresh, V.; Lee, N. A Review on Biosensors and Recent Development of Nanostructured Materials-Enabled Biosensors. Sensors 2021, 21, 1109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajini, T.; Mathew, B. A Brief Overview of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Highlighting Computational Design, Nano and Photo-Responsive Imprinting. Talanta Open 2021, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Refaat, D.; Aggour, M.; Farghali, A.; Mahajan, R.; Wiklander, J.; Nicholls, I.; Piletsky, S. Strategies for Molecular Imprinting and the Evolution of MIP Nanoparticles as Plastic Antibodies-Synthesis and Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wackerlig, J.; Lieberzeit, P.A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Nanoparticles in Chemical Sensing—Synthesis, Characterisation and Application. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2015, 207, 144–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasanah, A.N.; Safitri, N.; Zulfa, A.; Neli, N.; Rahayu, D. Factors Affecting Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Methods on Finding Template-Monomer Interaction as the Key of Selective Properties of the Materials. Molecules 2021, 26, 5612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.X.; Wang, X.Y.; Lu, W.H.; Wu, X.Q.; Li, J.H. Molecular Imprinting: Perspectives and Applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2137–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodakat, K.; Kumar, K.G. Fabrication of a Selective and Sensitive Electro-synthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-based Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of Xanthine. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2023, 53, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, N.; Shah, K.; Singh, M. An Epitope-Imprinted Piezoelectric Diagnostic Tool for Neisseria meningitidis detection. J. Mol. Recognit. 2016, 29, 572–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.L.; Gao, Y.L.; Wang, P.P.; Shang, H.; Pan, S.Y.; Li, X.J. Sol-gel Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Selective Solid Phase Microextraction of Organophosphorous Pesticides. Talanta 2013, 115, 920–927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lah, N.F.C.; Ahmad, A.L.; Low, S.C.; Zaulkiflee, N.D. Isotherm and Electrochemical Properties of Atrazine Sensing Using PVC/MIP: Effect of Porogenic Solvent Concentration Ratio. Membranes 2021, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Zhang, L.; Zeng, J.; Hu, X.; Wang, X.; Yu, L.; Wang, D.; Cheng, L.; Ahmed, R.; Romanovski, V.; et al. Multi-templates Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Recognition of Multiple Targets: From Academy to Application. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 166, 117173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, K.; Okamura, N.; Kimachi, T.; Haginaka, J. Evaluation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Chlorpromazine and Bromopromazine Prepared by Multi-step Swelling and Polymerization Method-The Application for the Determination of Chlorpromazine and Its Metabolites in Rat Plasma by Column-switching LC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2019, 174, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Yao, D.; Wang, C.; Zhang, L.; Hou, S.; Chen, L.; Yuan, C. The Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on SBA-15 for Selective Separation and Determination of Panax notoginseng Saponins Simultaneously in Biological Samples. Polymers 2017, 9, 653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Xie, H.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Huang, L. Water-compatible Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Solid Phase Extraction of Dencichine from the Aqueous Extract of Panax notoginseng. J. Chromatogr. B-Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2016, 1008, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nkosi, S.; Mahlambi, P.; Chimuka, L. Synthesis, Characterisation and Optimisation of Bulk Molecularly Imprinted Polymers from Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs. S. Afr. J. Chem.-Suid-Afr. Tydskr. Vir Chem. 2022, 76, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miura, C.; Funaya, N.; Matsunaga, H.; Haginaka, J. Monodisperse, Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Creatinine by Modified Precipitation Polymerization and Their Applications to Creatinine Assays for Human Serum and Urine. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2013, 85, 288–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Shimizu, K. Development of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers as Tailored Templates for the Solid-state [2+2] photodimerization. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 640–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurrokhimah, M.; Nurerk, P.; Kanatharana, P.; Bunkoed, O. A Nanosorbent Consisting of a Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Graphene Oxide for Multi-residue Analysis of Cephalosporins. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratama, K.F.; Manik, M.E.R.; Rahayu, D.; Hasanah, A.N. Effect of the Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Component Ratio on Analytical Performance. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 1013–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murdaya, N.; Triadenda, A.L.; Rahayu, D.; Hasanah, A.N. A Review: Using Multiple Templates for Molecular Imprinted Polymer: Is It Good? Polymers 2022, 14, 4441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, R.; Tian, J.; Guan, Y.; Zhang, Y. Peptide-Cross-Linked Protein-Imprinted Polymers: Easy Template Removal and Excellent Imprinting Effect. CCS Chem. 2019, 1, 544–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, Y.; Turner, A. Too Large to Fit? Recent Developments in Macromolecular Imprinting. Trends Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 218–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, S.; Prasad, B.B.; Singh, K.; Singh, R.; Jaiswal, S. A Reduced Graphene Oxide Ceramic Electrode Modified with One MoNomer Doubly Imprinted Acryloylated Tetraamine Cobalt Phthalocyanine Polymer for the Simultaneous Analysis of Anticancerous Drugs. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2019, 281, 139–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali Prasad, B.; Jauhari, D.; Prasad Tiwari, M. A Dual-template Imprinted Polymer-modified Carbon Ceramic Electrode for Ultra Trace Simultaneous Analysis of Ascorbic Acid and Dopamine. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 50, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jauhari, D.; Tiwari, M.P. Doubly Imprinted Polymer Nanofilm-modified Electrochemical Sensor for Ultra-trace Simultaneous Analysis of Glyphosate and Glufosinate. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 59, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.; Pathak, P. Development of Surface Imprinted Nanospheres Using the Inverse Suspension Polymerization Method for Electrochemical Ultra Sensing of Dacarbazine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2017, 974, 75–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, K.L.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X.N.; Zhou, Q.; Lei, H.B.; Yang, Z.X.; Zhang, Z.H. Smartphone-integrated Tri-color Fluorescence Sensing Platform Based on Acid-sensitive Fluorescence Imprinted Polymers for Dual-mode Visual Intelligent Detection of Ibuprofen, Chloramphenicol and Florfenicol. Anal. Chim. Acta 2023, 1260, 341174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Mei, X.C.; Peng, Z.C.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.C. A Paper-based Microfluidic Sensor Array Combining Molecular Imprinting Technology and Carbon Quantum Dots for the Discrimination of Nitrophenol Isomers. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.Y.; Li, B.W.; Wang, J.A.; Qi, J.; Li, J.H.; Ma, J.P.; Chen, L.X. A Rotary Multi-positioned Cloth/Paper Hybrid Microfluidic Device for Simultaneous Fuorescence Sensing of Mercury and Lead Ions by Using Ion Imprinted Technologies. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, F.; Zheng, J.W.; Qin, P.; Han, T.; Zhao, D.Y. A Novel Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor Array Based on Molecular Imprinted Polymers for Simultaneous Detection of Clenbuterol and Its Metabolites. Talanta 2017, 167, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Li, X.L.; Ma, X.H.; Ou, G.R.; Gao, Z.X. Rapid and Multiple Detections of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins by Two-dimensional Molecularly Imprinted Film-coated QCM Sensor. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2014, 191, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; He, X.; Cui, P.L.; Liu, J.; Li, Z.B.; Jia, B.J.; Zhang, T.; Wang, J.P.; Yuan, W.Z. Preparation of a Chemiluminescence Sensor for Multi-detection of Benzimidazoles in Meat Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Food Chem. 2019, 280, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.P. Preparation of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Chemiluminescence Sensor for the Determination of Amantadine and Rimantadine in Meat. Anal. Methods 2018, 10, 5025–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haginaka, J.; Tabo, H.; Matsunaga, H. Preparation of Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Organophosphates and Their Application to the Recognition of Organophosphorus Compounds and Phosphopeptides. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 748, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, M.M.; She, Y.X.; Cao, X.L.; Ma, J.; Chen, G.; Hong, S.H.; Shao, Y.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Wang, M.; Wang, J. A Molecularly Imprinted Polymer with Integrated Gold Nanoparticles for Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering Based Detection of the Triazine Herbicides, Prometryn and Simetryn. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Z.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, G.; Sun, M.; Jiang, Y.; He, H.; Wang, Y.; Zou, P.; Wang, X.; et al. A Dual-Template Imprinted Polymer Electrochemical Sensor Based on AuNPs and Nitrogen-doped Graphene Oxide Quantum Dots Coated on NiS2/Biomass Carbon for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Chlorpromazine. Chem. Eng. J. 2020, 389, 124417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siavash Moakhar, R.; del Real Mata, C.; Jalali, M.; Shafique, H.; Sanati, A.; Vries, J.; Strauss, J.; AbdElFatah, T.; Ghasemi, F.; McLean, M.; et al. A Versatile Biomimic Nanotemplating Fluidic Assay for Multiplex Quantitative Monitoring of Viral Respiratory Infections and Immune Responses in Saliva and Blood. Adv. Sci. 2022, 9, 2204246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer (MIP) Based Electrochemical Sensors and Their Recent Advances in Health Applications. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2023, 5, 100153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostojic, J.; Herenda, S.; Besic, Z.; Milos, M.; Galic, B. Advantages of an Electrochemical Method Compared to the Spectrophotometric Kinetic Study of Peroxidase Inhibition by Boroxine Derivative. Molecules 2017, 22, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusumkar, V.V.; Galambos, M.; Viglasova, E.; Dano, M.; Smelkova, J. Ion-Imprinted Polymers: Synthesis, Characterization, and Adsorption of Radionuclides. Materials 2021, 14, 1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, J.Q.; Chen, L.X.; Li, J.H.; Zhang, Z. Current Status and Challenges of Ion Imprinting. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 13598–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bali Prasad, B.; Jauhari, D.; Verma, A. A Dual-Ion Imprinted Polymer Embedded in Sol–Gel Matrix for the Ultra Trace Simultaneous Analysis of Cadmium and Copper. Talanta 2014, 120, 398–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behbahani, M.; Barati, M.; Bojdi, M.K.; Pourali, A.R.; Bagheri, A.; Tapeh, N.A.G. A Nanosized Cadmium(II)-Imprinted Polymer for Use in Selective Trace Determination of Cadmium in Complex Matrices. Microchim. Acta 2013, 180, 1117–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsipur, M.; Fasihi, J.; Khanchi, A.; Hassani, R.; Alizadeh, K.; Shamsipur, H. A Stoichiometric Imprinted Chelating Resin for Selective Recognition of Copper(II) Ions in Aqueous Media. Anal. Chim. Acta 2007, 599, 294–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birlik, E.; Ersöz, A.; Denizli, A.; Say, R. Preconcentration of Copper Using Double-Imprinted Polymer via Solid Phase Extraction. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 565, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jauhari, D. Double-ion Imprinted Polymer @Magnetic Nanoparticles Modified Screen Printed Carbon Electrode for Simultaneous Analysis of Cerium and Gadolinium Ions. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 875, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, M.M.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.S.; Bae, H.S.; Hong, S.B. Fluorimetric Determination of Cerium(IV) with Ascorbic Acid. J. Fluoresc. 2006, 16, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Focarelli, F.; Giachino, A.; Waldron, K.J. Copper Microenvironments in the Human Body Define Patterns of Copper Adaptation in Pathogenic Bacteria. PLoS Pathog. 2022, 18, e1010617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chasapis, C.T.; Loutsidou, A.C.; Spiliopoulou, C.A.; Stefanidou, M.E. Zinc and Human Health: An Update. Arch. Toxicol. 2012, 86, 521–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilschefski, S.C.; Baxter, M.R. Inductively Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometry: Introduction to Analytical Aspects. Clin. Biochem. Rev. 2019, 40, 115–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Madhuri, R.; Prasad Tiwari, M.; Sinha, P.; Bali Prasad, B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Modified Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Determination of Copper and Zinc. Adv. Mater. Lett. 2011, 2, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.Q.; Tan, T.W.; Svec, F. Molecular Imprinting of Proteins in Polymers Attached to The Surface of Nanomaterials for Selective Recognition of Biomacromolecules. Biotechnol. Adv. 2013, 31, 1172–1186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinc, M.; Esen, C.; Mizaikoff, B. Recent Advances on Core-Shell Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Biomacromolecules. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 114, 202–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzotta, E.; Di Giulio, T.; Malitesta, C. Electrochemical Sensing of Macromolecules Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Challenges, Successful Strategies, and Opportunities. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 5165–5200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Schich, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Feith, M.; Beyer, S.; Sternbæk, L.; Ohlsson, L.; Stollenwerk, M.; Wingren, A.G. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers in Biological Applications. Biotechniques 2020, 69, 406–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Q.M.; Wang, B.W.; Lv, Y.Q. Molecularly imprinted monoliths: Recent Advances in the Selective Recognition of Biomacromolecules Related Biomarkers. J. Sep. Sci. 2022, 45, 1469–1481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nontawong, N.; Ngaosri, P.; Chunta, S.; Jarujamrus, P.; Nacapricha, D.; Lieberzeit, P.A.; Amatatongchai, M. Smart Sensor for Assessment of Oxidative/Nitrative Stress Biomarkers Using A Dual-Imprinted Electrochemical Paper-Based Analytical Device. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1191, 339363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, G.V.; Tavares, A.P.M.; Fortunato, E.; Sales, M.G.F. Paper-Based Sensing Device for Electrochemical Detection of Oxidative Stress Biomarker 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) in Point-of-Care. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 14558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.Q.; Sun, G.H.; Chen, Z.G.; Liang, Y.W.; Zhou, Q.; Pan, Y.F.; Zhai, H.Y. Constructing a Novel Composite of Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Coated AuNPs Electrochemical Sensor for the Determination of 3-Nitrotyrosine. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 259, 893–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.P.; Wang, H.S. Electrochemical Reduction Synthesis of Graphene/Nafion Nanocomposite Film and Its Performance on the Detection of 8-Hydroxy-2′-Deoxyguanosine in the Presence of Uric Acid. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2013, 705, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, K.; Zhao, C.; Luo, Y.; Pan, C.; Li, J. Electrochemical Sensor for the Simultaneous Detection of CA72-4 And CA19-9 Tumor Markers Using Dual Recognition via Glycosyl Imprinting and Lectin-Specific Binding for Accurate Diagnosis of Gastric Cancer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 216, 114672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, G.L.; Chen, R.T.; Xu, L.Y.; Lu, X.; Yang, Z.Q.; Zhou, G.B.; Li, L.; Chen, W.; Peng, H.P. One-pot Ultrasonic Synthesis of Multifunctional Au Nanoparticle-Ferrocene-WS2 Nanosheet Composite for the Construction of an Electrochemical Biosensing Platform. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1099, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Feng, J.J.; Liu, W.D.; Jiang, L.Y.; Wang, A.J. A Novel Label-Free Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on the Enhanced Catalytic Currents of Oxygen Reduction by AuAg Hollow Nanocrystals for Detecting Carbohydrate Antigen 199. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 96, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Gan, N.; Zhang, H.; Li, T.; Qiao, L.; Cao, Y.; Su, X.; Jiang, S. Simultaneous Electrochemical Immunoassay Using Graphene–Au Grafted Recombinant Apoferritin-Encoded Metallic Labels As Signal Tags and Dual-Template Magnetic Molecular Imprinted Polymer As Capture Probes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 65, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, F.Y.; Xu, B.Y.; Xu, J.J.; Chen, H.Y. Simultaneous Electrochemical Immunoassay Using Cds/DNA and Pbs/DNA Nanochains As Labels. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2013, 39, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taheri, N.; Khoshsafar, H.; Ghanei, M.; Ghazvini, A.; Bagheri, H. Dual-template Rectangular Nanotube Molecularly Imprinted Polypyrrole for Label-Free Impedimetric Sensing of AFP and CEA As Lung Cancer Biomarkers. Talanta 2022, 239, 123146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Xu, H.; Bai, L.J.; Wang, W.X.; Yang, H.W.; Wei, D.L.; Yuan, B.Q. A Multiple Signal Amplification Based on PEI and rGO Nanocomposite for Simultaneous Multiple Electrochemical Immunoassay. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2019, 301, 127071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, S.P.; Chen, X.S.; Shao, T.L.; Feng, D.X. Electrochemical Immunosensor Based on Metal Ions Functionalized CNSs@Au NPs Nanocomposites As Signal Amplifier for Simultaneous Detection of Triple Tumor Markers. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2021, 880, 114882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, P.; Bagheri, H.; Johari-Ahar, M.; Khoshsafar, H.; Arduini, F.; Afkhami, A. Dual-modality Impedimetric Immunosensor for Early Detection of Prostate-Specific Antigen and Myoglobin Markers Based on Antibody-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer. Talanta 2019, 202, 111–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merriel, S.W.D.; Pocock, L.; Gilbert, E.; Creavin, S.; Walter, F.M.; Spencer, A.; Hamilton, W. Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) for the Detection of Prostate Cancer in Symptomatic Patients. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johari-Ahar, M.; Karami, P.; Ghanei, M.; Afkhami, A.; Bagheri, H. Development of a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Tailored on Disposable Screen-Printed Electrodes for Dual Detection of EGFR and VEGF Using Nano-Liposomal Amplification Strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 107, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.B.; Huang, H.M.; Huang, L.Z.; Lin, Z.Y.; Guo, L.H.; Qiu, B.; Chen, G.N. Electrochemical Biosensor for Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Detection with Peptide Ligand. Electrochim. Acta 2013, 109, 233–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omidfar, K.; Darzianiazizi, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Daneshpour, M.; Shirazi, H. A High Sensitive Electrochemical Nanoimmunosensor Based on Fe3O4/TMC/Au Nanocomposite and PT-Modified Electrode for the Detection of Cancer Biomarker Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2015, 220, 1311–1319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, Y.; Abe, K.; Ikebukuro, K. Electrochemical Detection of Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor with Aptamer Sandwich. Electrochemistry 2012, 80, 363–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pandey, I.; Tiwari, J.D. A Novel Dual Imprinted Conducting Nanocubes Based Flexible Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of Hemoglobin and Glycated Haemoglobin in Gestational Diabetes Mellitus Patients. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2019, 285, 470–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Yin, Z.-Z.; Zheng, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, M.; Li, S.; Kong, Y. Dual-template Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Biosensor for IgG-IgM Combined Assay Based on a Dual-Signal Strategy. Bioelectrochemistry 2022, 148, 108267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.B.; Jaiswal, S.; Singh, K. Ultra-trace Analysis of D-And L-Aspartic Acid Applying One-By-One Approach on a Dual Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2017, 240, 631–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, H.; Tang, S.; Wang, W.; Liu, M.; Liang, A.; Sun, L.; Luo, A. Electrochemical Enantioanalysis of D-and L-Cysteine with a Dual-Template Molecularly Imprinted Sensor. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2022, 169, 037506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaidi, S.A. Facile and Efficient Electrochemical Enantiomer Recognition of Phenylalanine Using Β-Cyclodextrin Immobilized on Reduced Graphene Oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 94, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Niu, X.H.; Mo, Z.L.; Wang, J.; Shuai, C.; Pan, Z.; Liu, Z.Y.; Liu, N.J.; Guo, R.B. 3D Nitrogen and Sulfur Co -Doped Graphene/Integrated Polysaccharides for Electrochemical Recognition Tryptophan Enantiomers. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, B1053–B1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afsharara, H.; Asadian, E.; Mosta, B.; Banan, K.; Bigdeli, S.A.; Hatamabadi, D.; Keshavarz, A.; Hussain, C.M.; Kecili, R.; Ghorbani-Bidkorpeh, F. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Modified Carbon Paste Electrodes (MIP-CPE): A Review on Sensitive Electrochemical Sensors for Pharmaceutical Determinations. Trac-Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 160, 116949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Samukaite-Bubniene, U.; Ratautaite, V.; Bechelany, M.; Ramanavicius, A. Electrochemical Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Sensors for Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Applications (Review). J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2022, 215, 114739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Singh, M. Design of Imprinting Matrix for Dual Template Sensing via Electropolymerized Polythiophene Films. J. Mol. Recognit. 2022, 35, e2962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulik, B.B.; Dhumal, S.T.; Sapner, V.S.; Rehman, N.; Dixit, P.P.; Sathe, B.R. Graphene Oxide-Based Electrochemical Activation of Ethionamide Towards Enhanced Biological Activity. Rsc Adv. 2019, 9, 35463–35472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kushwaha, A.; Singh, S.; Gupta, N.; Singh, A.K.; Singh, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Antipyrine-Imprinted Polymers and Their Application for Sustained Release. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 5235–5252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; He, J.; Waterhouse, G.I.N.; Xu, L.; Zhang, H.; Qiao, X.; Xu, Z. A Selective Molecularly Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor With GO@COF Signal Amplification for the Simultaneous Determination of Sulfadiazine and Acetaminophen. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2019, 300, 126993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teleanu, R.I.; Niculescu, A.G.; Roza, E.; Vladâcenco, O.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Teleanu, D.M. Neurotransmitters-Key Factors in Neurological and Neurodegenerative Disorders of the Central Nervous System. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si, B.; Song, E. Recent Advances in the Detection of Neurotransmitters. Chemosensors 2018, 6, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, B.; Song, E. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Selective Detection of Multi-Analyte Neurotransmitters. Microelectron. Eng. 2018, 187–188, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Cui, F.; Li, H.; Wang, S.; Zhuo, B. Three-dimensional Hybrid Networks of Molecularly Imprinted Poly(9-Carbazoleacetic Acid) and MWCNTs for Simultaneous Voltammetric Determination of Dopamine and Epinephrine in Plasma Sample. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2020, 323, 128669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fatma, S.; Prasad, B.B.; Jaiswal, S.; Singh, R.; Singh, K. Electrochemical Simultaneous Analysis of Dopamine and Epinephrine Using Double Imprinted One Monomer Acryloylated Graphene Oxide-Carbon Black Composite Polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 135, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.; Singh, M. Highly Selective and Specific Monitoring of Pollutants Using Dual Template Imprinted MIP Sensor. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2022, 926, 116939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thimoonnee, S.; Somnet, K.; Ngaosri, P.; Chairam, S.; Karuwan, C.; Kamsong, W.; Tuantranont, A.; Amatatongchai, M. Fast, Sensitive and Selective Simultaneous Determination of Paraquat and Glyphosate Herbicides in Water Samples Using a Compact Electrochemical Sensor. Anal. Methods 2022, 14, 820–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Núñez, O.; Moyano, E.; Puignou, L.; Galceran, M.T. Sample Stacking with Matrix Removal for the Determination of Paraquat, Diquat and Difenzoquat in Water by Capillary Electrophoresis. J. Chromatogr. A 2001, 912, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.J.; Zhang, Y.; Luo, Y.L.; Shen, F.; Sun, C.Y. Efficient Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Between Oppositely Charged CdTe Quantum Dots and Gold Nanoparticles for Turn-on Fluorescence Detection of Glyphosate. Talanta 2014, 125, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, H.; Liu, X.; Ding, F.; Wan, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, R.; Zou, P.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhao, Q. Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanosheet Frameworks Decorated with Fe and Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Simultaneous Detection of Mebendazole and Catechol. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 338, 478–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, J.; Ahamad, T.; AlShehri, S.M. Iron-Nickel Nanoparticles as Bifunctional Catalysts in Water Electrolysis. Chemelectrochem 2017, 4, 1222–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Denno, M.E.; Pyakurel, P.; Venton, B.J. Recent Trends in Carbon Nanomaterial-Based Electrochemical Sensors for Biomolecules: A Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2015, 887, 17–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golabi, M.; Kuralay, F.; Jager, E.W.H.; Beni, V.; Turner, A.P.F. Electrochemical Bacterial Detection Using Poly(3-Aminophenylboronic Acid)-Based Imprinted Polymer. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 93, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tokonami, S.; Nakadoi, Y.; Takahashi, M.; Ikemizu, M.; Kadoma, T.; Saimatsu, K.; Dung, L.Q.; Shiigi, H.; Nagaoka, T. Label-Free and Selective Bacteria Detection Using a Film with Transferred Bacterial Configuration. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 4925–4929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayankojo, A.G.; Boroznjak, R.; Reut, J.; Öpik, A.; Syritski, V. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based Electrochemical Sensor for Quantitative Detection of SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2022, 353, 131160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancharoen, C.; Sukjee, W.; Thepparit, C.; Jaimipuk, T.; Auewarakul, P.; Thitithanyanont, A.; Sangma, C. Electrochemical Biosensor Based on Surface Imprinting for Zika Virus Detection in Serum. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amorim, M.S.; Sales, M.G.F.; Frasco, M.F. Recent Advances in Virus Imprinted Polymers. Biosens. Bioelectron. X 2022, 10, 100131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, K.K.; Shao, S.; Tan, T.; Lv, Y. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for the Selective Recognition of Microorganisms. Biotechnol. Adv. 2020, 45, 107640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crapnell, R.D.; Hudson, A.; Foster, C.W.; Eersels, K.; van Grinsven, B.; Cleij, T.J.; Banks, C.E.; Peeters, M. Recent Advances in Electrosynthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensing Platforms for Bioanalyte Detection. Sensors 2019, 19, 1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, X.; Zhang, L.; Gao, J.; Ma, Q. Electrochemiluminescence Detection of Escherichia coli O157: H7 Based on a Novel Polydopamine Surface Imprinted Polymer Biosensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 5430–5436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasmeen, N.; Etienne, M.; Sharma, P.S.; El-Kirat-Chatel, S.; Helú, M.B.; Kutner, W. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer As a Synthetic Receptor Mimic for Capacitive Impedimetric Selective Recognition of Escherichia coli K-12. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1188, 339177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, X.L.; Yamauchi, T.; Shiigi, H.; Nagaoka, T. Binding Constant of the Cell-shaped Cavity Formed on a Polymer for Escherichia Coli O157. Anal. Sci. 2018, 34, 483–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.K.; Wang, R.N.; Lu, Y.F.; Jia, M.; Yan, J.; Bian, X.J. Facile Preparation of a Bacteria Imprinted Artificial Receptor for Highly Selective Bacterial Recognition and Label-Free Impedimetric Detection. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 1027–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezdekova, J.; Hutarova, J.; Tomeckova, K.; Vaculovicova, M. Isolation and Detection of Bacteria Using Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers. In Proceedings of the 25th International Phd Students Conference (Mendelnet 2018), Brno, Czechia, 7–8 November 2018; pp. 484–488. [Google Scholar]
- Yasmeen, N.; Etienne, M.; Sharma, P.S.; Kutner, W. Artificial Receptors for Electrochemical Sensing of Bacteria. Curr. Opin. Electrochem. 2023, 39, 101291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roushani, M.; Sarabaegi, M.; Rostamzad, A. Novel Electrochemical Sensor Based on Polydopamine Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Sensitive and Selective Detection of Acinetobacter baumannii. J. Iran. Chem. Soc. 2020, 17, 2407–2413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buensuceso, C.E.; Tiu, B.D.B.; Lee, L.P.; Sabido, P.M.G.; Nuesca, G.M.; Caldona, E.B.; del Mundo, F.R.; Advincula, R.C. Electropolymerized-molecularly Imprinted Polymers (E-MIPS) As Sensing Elements for the Detection of Dengue Infection. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 1347–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idil, N.; Mattiasson, B. Imprinting of Microorganisms for Biosensor Applications. Sensors 2017, 17, 708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, H.H.T.; Dalsgaard, A.; Andersen, P.S.; Nguyen, H.M.; Ta, Y.T.; Nguyen, T.T. Large-Scale Staphylococcus aureus Foodborne Disease Poisoning Outbreak among Primary School Children. Microbiol. Res. 2021, 12, 43–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samadpour, M.; Stewart, J.; Steingart, K.; Addy, C.; Louderback, J.; McGinn, M.; Ellington, J.; Newman, T. Laboratory Investigation of an E. coli O157:H7 Outbreak Associated with Swimming in Battle Ground Lake, Vancouver, Washington. J. Environ. Health 2002, 64, 16–20, 25, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Osborn, B.; Hatfield, J.; Lanier, W.; Wagner, J.; Oakeson, K.; Casey, R.; Bullough, J.; Kache, P.; Miko, S.; Kunz, J.; et al. Shiga Toxin-Producing Escherichia coli O157:H7 Illness Outbreak Associated with Untreated, Pressurized, Municipal Irrigation Water—Utah, 2023. MMWR Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2024, 73, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.L.; Lin, X.H.; Wang, L.L.; Ma, Y.X.; Sun, T.; Bian, X.J. A Novel Dual Bacteria-Imprinted Polymer Sensor for Highly Selective and Rapid Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria. Biosensors 2023, 13, 868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prasad, B.B.; Fatma, S. One MoNomer Doubly Imprinted Dendrimer Nanofilm Modified Pencil Graphite Electrode for Simultaneous Electrochemical Determination of Norepinephrine and Uric Acid. Electrochim. Acta 2017, 232, 474–483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Huang, H.; Sun, H.; Yan, Y.; Xu, F.; Liao, J. Simultaneous Analysis of Catechol and Hydroquinone by Polymelamine/CNT with Dual-Template Molecular Imprinting Technology. Polymer 2022, 242, 124593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Du, X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Wang, Y.; Du, H.; Yin, H.; Rao, H. Novel Dual-Template Molecular Imprinted Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Detection of CA And TPH Based on Peanut Twin-Like NiFe2O4/CoFe2O4/NCDs Nanospheres: Fabrication, Application and DFT Theoretical Study. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 190, 113408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, W.; Zhao, M.; Liu, W.; Yu, S.; Niu, L.; Li, G.; Li, H.; Liu, W. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Polymer/Reduced Graphene Oxide Composite for Simultaneous Determination of Uric Acid and Tyrosine. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2018, 813, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karazan, Z.M.; Roushani, M. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Molecularly Imprinted Copolymer for Selective and Simultaneous Determination of Ascorbic Acid and Tyrosine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. Res. 2023, 10, 269–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Yu, P.; Tong, Y.; Ye, B.-C. A High Sensitivity Electrochemical Sensor Based on a Dual-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Simultaneous Determination of Clenbuterol Hydrochloride and Ractopamine. Analyst 2021, 146, 6323–6332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vahidifar, M.; Es’haghi, Z. Magnetic Nanoparticle-Reinforced Dual-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for the Simultaneous Determination of Oxazepam and Diazepam Using an Electrochemical Approach. J. Anal. Chem. 2022, 77, 625–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, P.; Zhu, R.; Tao, Y.; Jiang, W.; Liu, X.; Tan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, D. Dual-Analyte Sensing with a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Based on Enhancement-Mode Organic Electrochemical Transistors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2023, 15, 30567–30579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, J.; Qu, J.; Huang, J.; Tan, R.; Yu, Y.; Wu, J.; Yang, J.; Li, Y.; et al. A Bifunctional Electrochemical Sensor for Simultaneous Determination of Electroactive and Non-Electroactive Analytes: A Universal Yet Very Effective Platform Serving Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 208, 114233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawool, C.R.; Srivastava, A.K. A Dual Template Imprinted Polymer Modified Electrochemical Sensor Based on Cu Metal Organic Framework/Mesoporous Carbon for Highly Sensitive and Selective Recognition of Rifampicin and Isoniazid. Sens. Actuators. B Chem. 2019, 288, 493–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Nan, C.; Mei, X.; Sun, Y.; Feng, H.; Li, Y. Electrochemical Sensor Based on Dual-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer and Nanoporous Gold Leaf Modified Electrode for Simultaneous Determination of Dopamine and Uric Acid. Mikrochim. Acta 2020, 187, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, T.; Xuan, X.; Li, M.; Li, C.; Li, P.; Li, H. Molecularly Imprinted Ni-Polyacrylamide-Based Electrochemical Sensor for the Simultaneous Detection of Dopamine and Adenine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1202, 339689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vahidifar, M.; Es’haghi, Z.; Oghaz, N.M.; Mohammadi, A.A.; Kazemi, M.S. Multi-template Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Hybrid Nanoparticles for Selective Analysis of Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs and Analgesics in Biological and Pharmaceutical Samples. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2022, 29, 47416–47435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitesides, G.M. The Origins and the Future of Microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regmi, S.; Poudel, C.; Adhikari, R.; Luo, K.Q. Applications of Microfluidics and Organ-on-a-Chip in Cancer Research. Biosensors 2022, 12, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, J.; Li, B.W.; Zhou, N.; Wang, X.Y.; Deng, D.M.; Luo, L.Q.; Chen, L.X. The Strategy of Antibody-Free Biomarker Analysis by In-Situ Synthesized Molecularly Imprinted Polymers on Movable Valve Paper-Based Device. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 142, 111533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, P.S.; Iskierko, Z.; Noworyta, K.; Cieplak, M.; Borowicz, P.; Lisowski, W.; D’Souza, F.; Kutner, W. Synthesis and Application of a “Plastic Antibody” in Electrochemical Microfluidic Platform for Oxytocin Determination. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 100, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.K.; Wang, Y.H.; Zhang, L.N.; Xu, C.X.; Yu, J.H. Highly Sensitive Microfluidic Paper-based Photoelectrochemical Sensing Platform Based on Reversible Photo-Oxidation Products and Morphology Preferable Multi-plate ZnO Nanoflowers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 110, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, L.; Wang, S.M.; Yu, J.H.; Li, N.Q.; Ge, S.G.; Yan, M. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Grafted Porous Au-Paper Electrode for an Microfluidic Electro-Analytical Origami Device. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 3115–3123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellens, E.; Bove, H.; Vandenryt, T.; Lambrichts, J.; Dekens, J.; Drijkoningen, S.; D’Haen, J.; De Ceuninck, W.; Thoelen, R.; Junkers, T.; et al. Micro-patterned Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Structures on Functionalized Diamond-coated Substrates for Testosterone Detection. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2018, 118, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, Y.; Jiang, M.; Tian, L.P.; Sun, S.G.; Zhao, N.; Zhao, F.L.; Li, Y.C. Electrochemical Microfluidic Chip Based on Molecular Imprinting Technique Applied for Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 91, 714–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, C.H.; Yeh, W.M.; Ho, K.C.; Lee, G.B. A Microfluidic System Utilizing Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Films for Amperometric Detection of Morphine. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2007, 121, 576–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dincer, C.; Bruch, R.; Kling, A.; Dittrich, P.S.; Urban, G.A. Multiplexed Point-of-Care Testing—xPOCT. Trends Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 728–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fava, E.L.; Silva, T.A.; do Prado, T.M.; de Moraes, F.C.; Faria, R.C.; Fatibello, O. Electrochemical Paper-based Microfluidic Device for High Throughput Multiplexed Analysis. Talanta 2019, 203, 280–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Somvanshi, S.B.; Ulloa, A.M.; Zhao, M.; Liang, Q.Y.; Barui, A.K.; Lucas, A.; Jadhav, K.M.; Allebach, J.P.; Stanciu, L.A. Microfluidic Paper-based Aptasensor Devices for Multiplexed Detection of Pathogenic Bacteria. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2022, 207, 114214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glatz, R.T.; Ates, H.C.; Mohsenin, H.; Weber, W.; Dincer, C. Designing Electrochemical Microfluidic Multiplexed Biosensors for On-Site Applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2022, 414, 6531–6540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volpetti, F.; Garcia-Cordero, J.; Maerkl, S.J. A Microfluidic Platform for High-Throughput Multiplexed Protein Quantitation. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Alvarez, M.; Arroyo-Manzanares, N.; Campillo, N.; Viñas, P. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymers for Selective Extraction of Aflatoxins from Feeds. Toxins 2024, 16, 120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orbay, S.; Sanyal, A. Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Particles Created Using Droplet-Based Microfluidics: Preparation and Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowdon, J.W.; Diliën, H.; Singla, P.; Peeters, M.; Cleij, T.J.; van Grinsven, B.; Eersels, K. MIPs for Commercial Application in Low-Cost Sensors and Assays—An Overview of the Current Status Quo. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 325, 128973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.W.; Jeans, C.W.; Brain, K.R.; Allender, C.J.; Hlady, V.; Britt, D.W. From 3D to 2D: A Review of the Molecular Imprinting of Proteins. Biotechnol. Prog. 2006, 22, 1474–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixit, C.K.; Bhakta, S.; Reza, K.K.; Kaushik, A. Exploring Molecularly Imprinted Polymers As Artificial Antibodies for Efficient Diagnostics and Commercialization: A Critical Overview. Hybrid Adv. 2022, 1, 100001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldoneschi, V.; Palladino, P.; Banchini, M.; Minunni, M.; Scarano, S. Norepinephrine as New Functional Monomer for Molecular Imprinting: An Applicative Study for the Optical Sensing of Cardiac Biomarkers. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 157, 112161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Mutio, D.; Gómez-Caballero, A.; Gotiandia, A.; Larrauri, I.; Goicolea, M.; Barrio, R. Controlled Grafting of Molecularly Imprinted Films on Gold Microelectrodes Using a Self-Assembled Thiol Iniferter. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 279, 57–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Puyana, V.; Wieringa, P.; Guerrero, A.; Romero, A.; Moroni, L. (Macro)Molecular Imprinting of Proteins on PCL Electrospun Scaffolds. ACS Appl. Mater. InterfacES 2021, 13, 29293–29302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, G.K.; Omer, K.M. Molecular Imprinted Polymer Combined with Aptamer (MIP-Aptamer) As a Hybrid Dual Recognition Element for Bio(Chemical) Sensing Applications. Review. Talanta 2022, 236, 122878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.X.; Dykstra, G. Recent Progress on Electrochemical (Bio)Sensors Based on Aptamer-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Dual Recognition. Sens. Actuators Rep. 2022, 4, 100112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phonklam, K.; Wannapob, R.; Sriwimol, W.; Thavarungkul, P.; Phairatana, T. A Novel Molecularly Imprinted Polymer PMB/MWCNTs Sensor for Highly-Sensitive Cardiac Troponin T Detection. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2020, 308, 127630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rad, A.O.; Azadbakht, A. An Aptamer Embedded in a Molecularly Imprinted Polymer for Impedimetric Determination of Tetracycline. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, A.M.; Alkahtani, S.A.; Alyami, B.A.; El-Wekil, M.M. Dual-recognition Molecularly Imprinted Aptasensor Based on Gold Nanoparticles Decorated Carboxylated Carbon Nanotubes for Highly Selective and Sensitive Determination of Histamine in Different Matrices. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1133, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.H.; Ma, X.H.; Pang, C.H.; Tian, H.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Y.; Lv, D.Z.; Ge, H.L. Fluorometric Aptasensor for Cadmium(II) by Using an Aptamer-Imprinted Polymer As the Recognition Element. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.M.; Kan, X.W. Aptamer and Molecularly Imprinted Polymer: Synergistic Recognition and Sensing of Dopamine. Electrochim. Acta 2021, 367, 137433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Yuan, Y.; Gao, X.; Xiong, Z.; Zhao, L. Magnetic Dummy-template Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Based on Multi-Walled Carbon Nanotubes for Simultaneous Selective Extraction and Analysis of Phenoxy Carboxylic Acid Herbicides in Cereals. Food Chem. 2020, 333, 127540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Luo, J.; Yi, C.; Liu, X. Paracetamol Sensor Based on Molecular Imprinting by Photosensitive Polymers. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 1907–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tadi, K.; Motghare, R.; Ganesh, V. Electrochemical Detection of Epinephrine Using a Biomimic Made Up of Hemin Modified Molecularly Imprinted Microspheres. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 99115–99124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Alsoud, G.; Bottaro, C. Porous Thin-film Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Device for Simultaneous Determination of Phenol, Alkylphenol and Chlorophenol Compounds in Water. Talanta 2021, 223, 121727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tamboli, V.; Bhalla, N.; Jolly, P.; Bowen, C.; Taylor, J.; Bowen, J.; Allender, C.; Estrela, P. Hybrid Synthetic Receptors on MOSFET Devices for Detection of Prostate Specific Antigen in Human Plasma. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 11486–11490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agar, M.; Laabei, M.; Leese, H.S.; Estrela, P. Aptamer-Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Sensors for the Detection of Bacteria in Water. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2024, in press. [CrossRef]
- Gros, M.; Pizzolato, T.; Petrovic, M.; de Alda, M.; Barceló, D. Trace Level Determination of Β-Blockers in Waste Waters by Highly Selective Molecularly Imprinted Polymers Extraction Followed by Liquid Chromatography-Quadrupole-Linear Ion Trap Mass Spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2008, 1189, 374–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zhou, W.; Guo, X.; Chen, F.; Zhao, H.; Lin, L.; Wang, X. Molecularly Imprinted Polymer As SPE Sorbent for Selective Extraction of Melamine in Dairy Products. Talanta 2009, 80, 821–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Template | MIP Components | Elution Solution | Electrochemical Method | Linear Range | LOD | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cd(II) Cu(II) | AEDP, L-histidine, EGDMA, AIBN | EDTA | DPASV | 0.124–2.989 ng/mL 0.124–0.725 ng/mL | 0.053 ng/mL 0.035 ng/mL | Human blood serum Cow’s milk Lake water | [47] |
| Ce(IV) Gd(III) | But-2-enedioic acid bis-[(2-amino-ethyl)-amide], EGDMA AIBN | HCl | DPASV | 0.27–5.35 ng/mL 0.75–9.45 ng/mL | 0.063 ng/mL 0.182 ng/mL | Water Human serum | [51] |
| Cu(II) Zn(II) | BAAP, EGDMA, AIBN | EDTA | DPASV | 0.098–23.80 µg/L | 0.0159 µg/L 0.0275 µg/L | - | [56] |
| Template | MIP Components | Elution Solution | Electrochemical Method | Linear Range | LOD | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 8-OHdG 3-NT | NIPAM, DHEBA, AIBN | Methanol/acetic acid | SWV | 0.05–500 µM 0.01–500 µM | 0.0138 µM 0.0027 µM | Urine Serum | [62] |
| CA72-4 CA19-9 | 2-aminophenylboronic acid | Methanol/acetic acid | DPV | 0.005–100.0 U/mL | 0.0041 U/mL 0.0032 U/mL | Serum | [66] |
| AFP CEA | Dopamine | SDS | SWV | 0.001–5 ng/mL | 0.3 pg/mL 0.35 pg/mL | Human serum | [69] |
| AFP CEA | Pyrrole | NaOH | EIS | 10–104 pg/mL 5–104 pg/mL | 3.3 pg/mL 1.6 pg/mL | Human serum | [71] |
| PSA Myo | AM, NNMBA, | Oac | EIS | 0.01–100 ng/mL 1–20,000 ng/mL | 5.4 pg/mL 0.83 ng/mL | Serum Urine | [74] |
| EGFR VEGF | AM, NNMBA | Oac | PSA | 0.05–50,000 pg/mL 0.01–7000 pg/mL | 0.01 pg/mL 0.005 pg/mL | Serum | [76] |
| Hb HbA1c | APBA | PBS (overoxidation) | DPV | 0.1–250 ng/mL 0.5–235 ng/mL | 0.084 ng/mL 0.095 ng/mL | Blood | [80] |
| IgG IgM | Pyrrole | Acetic acid/SDS | DPV | 0.05–500 ng/mL 0.001–100 ng/mL | 0.0288 ng/mL 0.00058 ng/mL | Serum | [81] |
| Template | MIP Components | Elution Solution | Electrochemical Method | Linear Range | LOD | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| D-aspartic acid L-aspartic acid | NAPD, EGDMA, AIBN | NaOH/Phosphate buffer | DPASV | 3.89–66.23 ng/mL 3.99–66.12 ng/mL | 1.11 ng/mL 1.14 ng/mL | CSF Blood serum Pharmaceutical samples | [82] |
| D-Cys L-Cys | MAA, AM, NIPAM, MBA | Acetic acid/Acetonitrile | DPV | 1–12 pg/mL | 0.6136 pg/mL 0.7402 pg/mL | Fetal bovine serum | [83] |
| Chb Dac | aTACoPC, AIBN | Acetonitrile/Methanol | DPASV | 0.159–28.524 ng/mL 0.069–35.278 ng/mL | 0.037 ng/mL 0.016 ng/mL | Blood serum Urine Pharmaceutical samples | [28] |
| AnP ETH | 3-TAA | Methanol/Acetic acid | DPV | 0.05–0.6 µM 0.03–1.2 µM | 0.117 µM 0.15 µM | Human blood serum | [88] |
| SDZ AP | Pyrrole, TBAP | NaOH (Overoxidation) | DPV | 0.5–200 µM 0.05–20 µM | 0.16 µM 0.032 µM | Pork Chicken | [91] |
| DA EP | 9-carbazoleacetic acid | NaOH/Ethanol | DPSV | 0.04–70 µM | 0.015 µM 0.023 µM | Rat plasma | [95] |
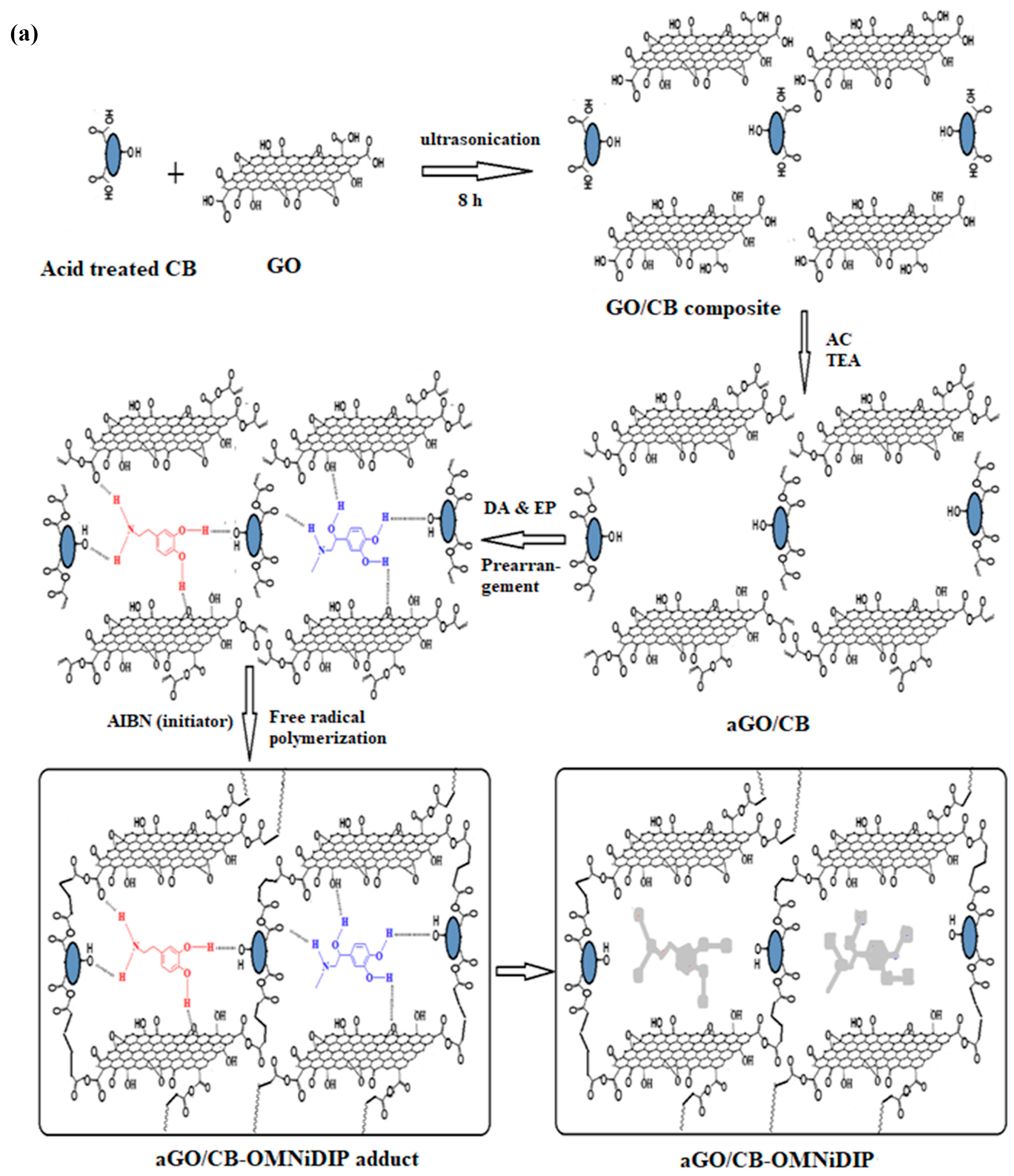
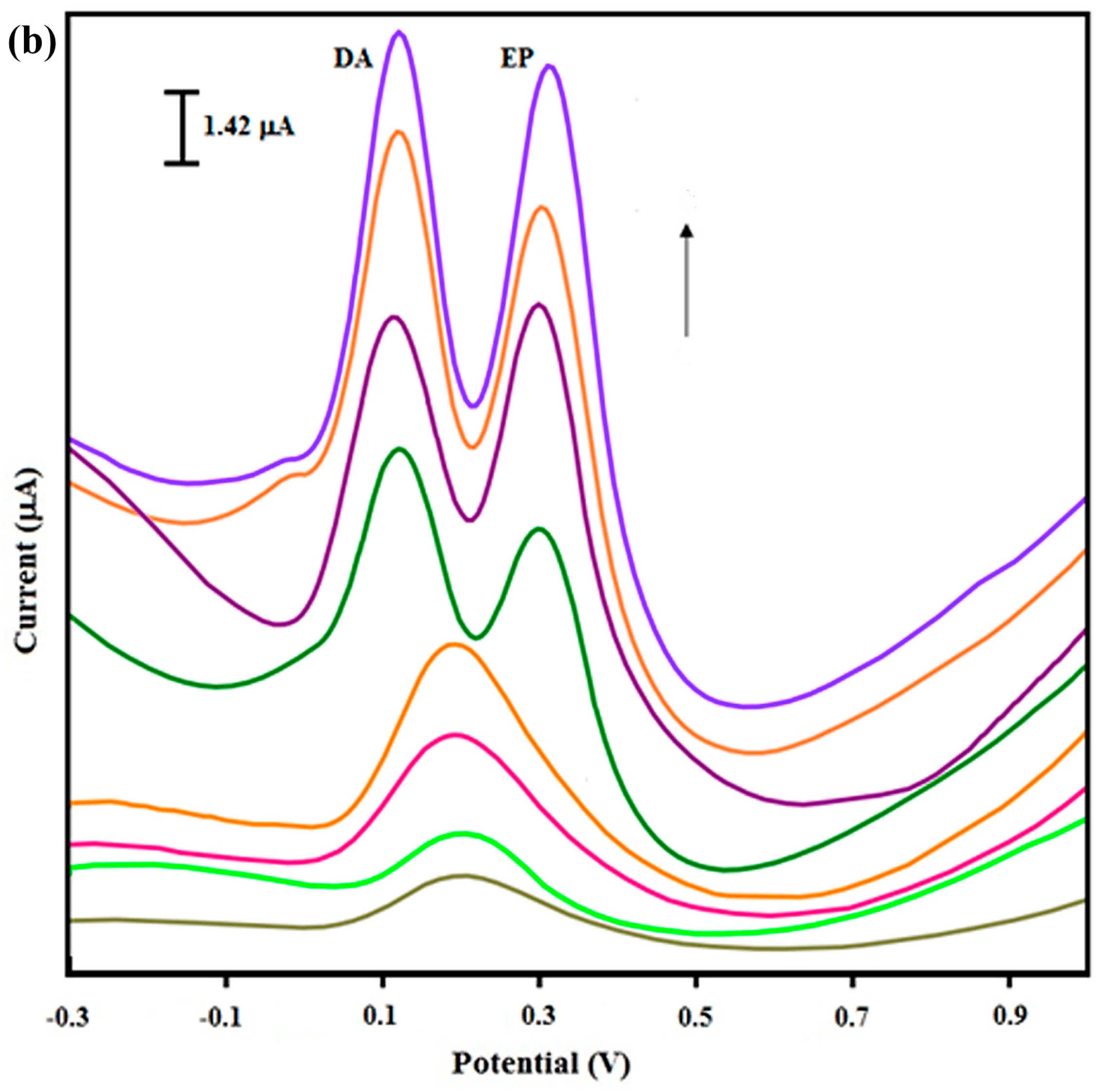
| DA EP | aGO/CB, AIBN | TEA/Methanol | DPASV | 0.12–4.578 ng/mL 0.075–1.188 ng/mL | 0.028 ng/mL 0.017 ng/mL | Blood serum Urine Pharmaceutical samples | [96] |
| 4-NP HQ | 4-ATP, p-PD | Methanol/Water | DPV | 0.8–200 µM | 0.37 µM 0.14 µM | Water (distilled, packaged, tap, river) | [97] |
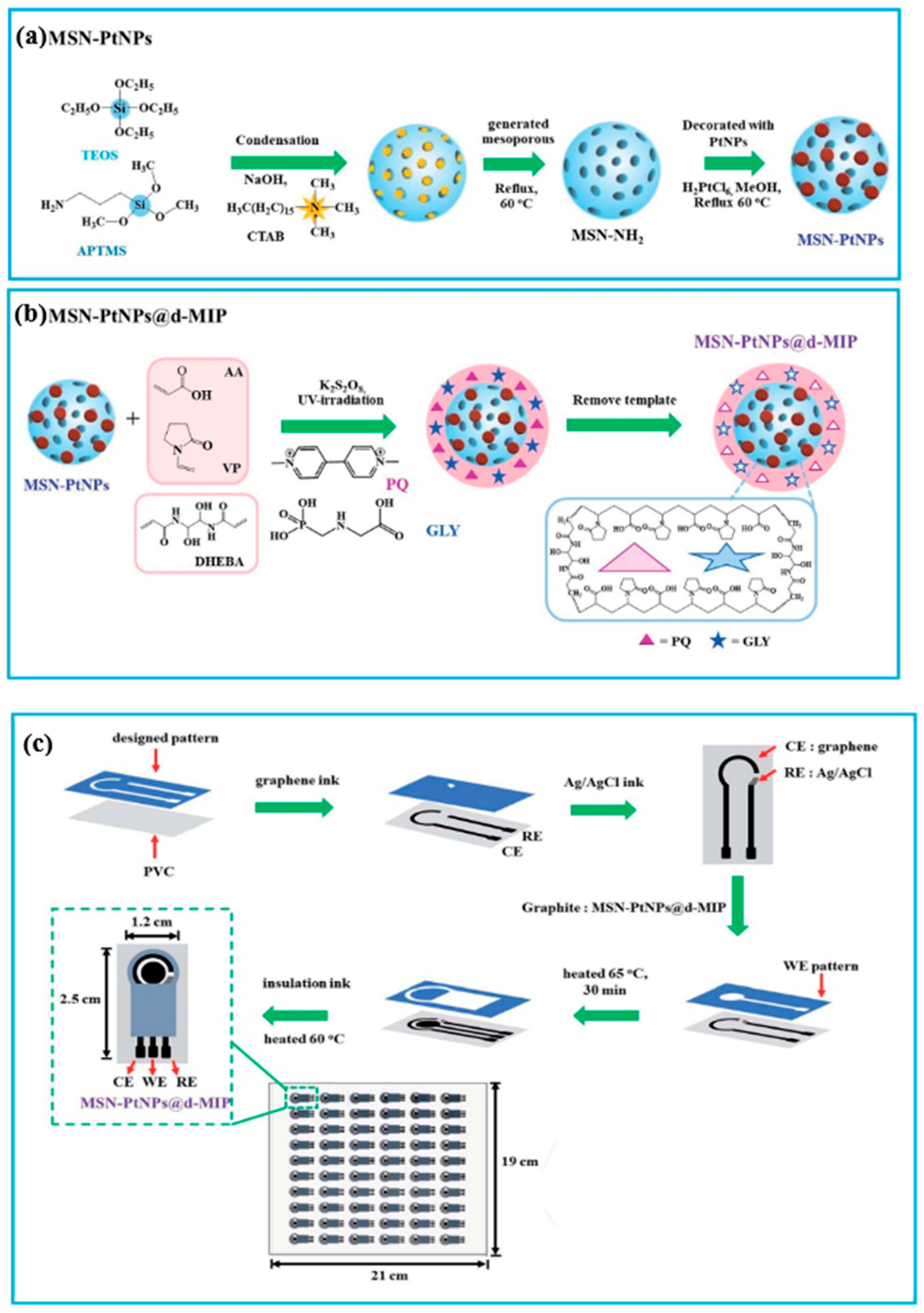
| PQ GLY | AA, VP, DHEBA, K2S2O8 | Sonication in water | DPV | 0.025–500 µM | 0.0031 µM 0.004 µM | Water (reservoir, pond, wastewater) | [98] |
| Meb CC | MAA, LiClO4 | Methanol/Acetic acid | DPV | 0.01–1.5 µM 0.5–25 µM | 0.004 µM 0.06 µM | Water (tap, river) | [101] |
| Template | MIP Components | Elution Solution | Electrochemical Method | Linear Range | LOD | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
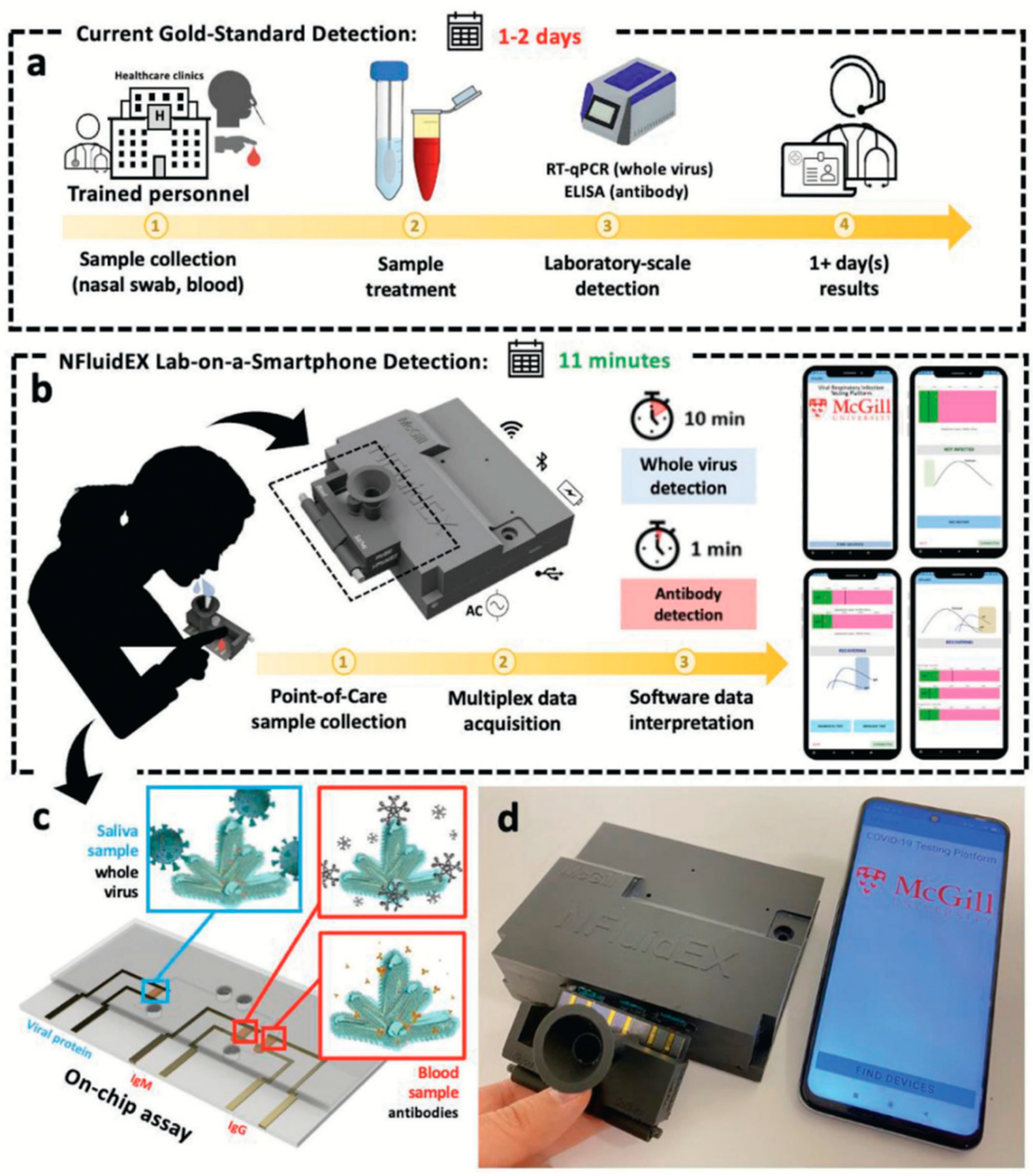
| Viral particles IgG IgM | o-PD | NaOH | EIS | 9.60 × 103–3.84 × 108 particles/mL 101–104 pg/µL 101–104 pg/µL | 2091.6 particles/mL 3.63 pg/µL 2.79 pg/µL | Saliva Plasma Blood | [42] |
| E. coli O157:H7 S. aureus | o-PD | CTAB/HAc | EIS | - | 9.4 CFU/mL 9.5 CFU/mL | Apple juice | [123] |
| Template | MIP Components | Elution Solution | Electrochemical Method | Linear Range | LOD | Application | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NE UA | TAT, AIBN | TEA/Methanol | DPASV | 2.98–40.69 ng/mL 1.94–43.59 ng/mL | 0.66 ng/mL 0.44 ng/mL | Blood serum Urine Pharmaceutical samples | [124] |
| HQ CC | Melamine | Ethanol/Water | DPV | 10–100 µM (for both) | 3.1 µM 3.5 µM | River water | [125] |
| AA DA | TAT, EGDMA | ACN/TEA | DPASV | 8.28–77.92 ng/mL 0.10–5.24 ng/mL | 2.21 ng/mL 0.22 ng/mL | CSF Blood serum Pharmaceutical samples | [29] |
| CA TPH | L-arginine | NaOH | DPV | 0.01–1.0 µM 0.1–100.0 µM | 1.3 nM 20.0 nM | Green tea Urine | [126] |
| UA Tyr | AMT | Ethanol | DPV | 0.01 µM–100 µM 0.1 µM–400 µM | 0.0032 µM 0.046 µM | Serum Urine | [127] |
| AA Tyr | m-DB, o-AP | Nitric acid | DPV | 0.1–300 µM 0.01–180 µM | 0.03 µM 0.003 µM | Human serum | [128] |
| CLB RAC | o-PD | NaOH (overoxidation) | CV | 1 pM–8 nM (for both) | 0.303 pM (for both) | Urine Raw pork CLB tablets | [129] |
| OX DZ | MAA, EGDMA, AIBN | Methanol/Acetic acid | DPV | 0.01–200 µM 0.05–150 µM | 59 nM 21 nM | Urine Tablet | [130] |
| GLY GLU | EGDMA, TEA | Acetonitrile/TEA | DPASV | 3.98–176.23 ng/mL 0.54–3.96 ng/mL | 0.35 ng/mL 0.19 ng/mL | Soil Human serum | [30] |
| Adrenaline UA | Dopamine, PBS | Methanol/Acetic acid | OECTs | 0.5 pM–10 µM 1 pM–1 mM | 1 pM (for both) | Urine | [131] |
| CFZ AVI | o-PD, PBS | NaOH (overoxidation) | SWV | 50–1000 µM 1–1000 µM | 35 µM 0.5 µM | Human serum Rabbit | [132] |
| RIF INZ | Pyrrole | Methanol/Water | AdSDPV | 0.08–85 µM (for both) | 0.287 nM 0.371 nM | Pharmaceutical samples Blood serum Urine | [133] |
| DA Chlorpromazine | Nicotinamide | Methanol/Acetic acid | DPV | 0.05–8 µM/8–40 µM 0.005–2 µM | 2.8 nM 0.25 nM | Human serum Urine Pharmaceutical sample | [41] |
| DA UA | o-PD, PBS | H2SO4 (overoxidation) | DPV | 2.0–180 µM 5.0–160 µM | 0.3 µM 0.4 µM | Bovine serum | [134] |
| DA Ade | AM | PBS (overoxidation) | DPV | 0.6–200 µM 0.4–300 µM | 0.12–0.37 µM 0.15–0.36 µM | Human serum | [135] |
| NPX MTH OMZ | MAA, EGDMA, AIBN | Acetic acid/Ethanol | DPV | 5.0 nM–100 µM 1.0 nM–130 µM 5.0 nM–100 µM | 1.0 nM 0.7 nM 1.5 nM | Human plasma Urine Tap water Tablet | [136] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Agar, M.; Laabei, M.; Leese, H.S.; Estrela, P. Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Electrochemical Biosensors. Chemosensors 2025, 13, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13010011
Agar M, Laabei M, Leese HS, Estrela P. Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Electrochemical Biosensors. Chemosensors. 2025; 13(1):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13010011
Chicago/Turabian StyleAgar, Meltem, Maisem Laabei, Hannah S. Leese, and Pedro Estrela. 2025. "Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Electrochemical Biosensors" Chemosensors 13, no. 1: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13010011
APA StyleAgar, M., Laabei, M., Leese, H. S., & Estrela, P. (2025). Multi-Template Molecularly Imprinted Polymeric Electrochemical Biosensors. Chemosensors, 13(1), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors13010011






