Tailoring Ruthenium(II) and Rhenium(I) Complexes for Turn-On Luminescent Sensing of Antimony(III)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Instruments and Devices
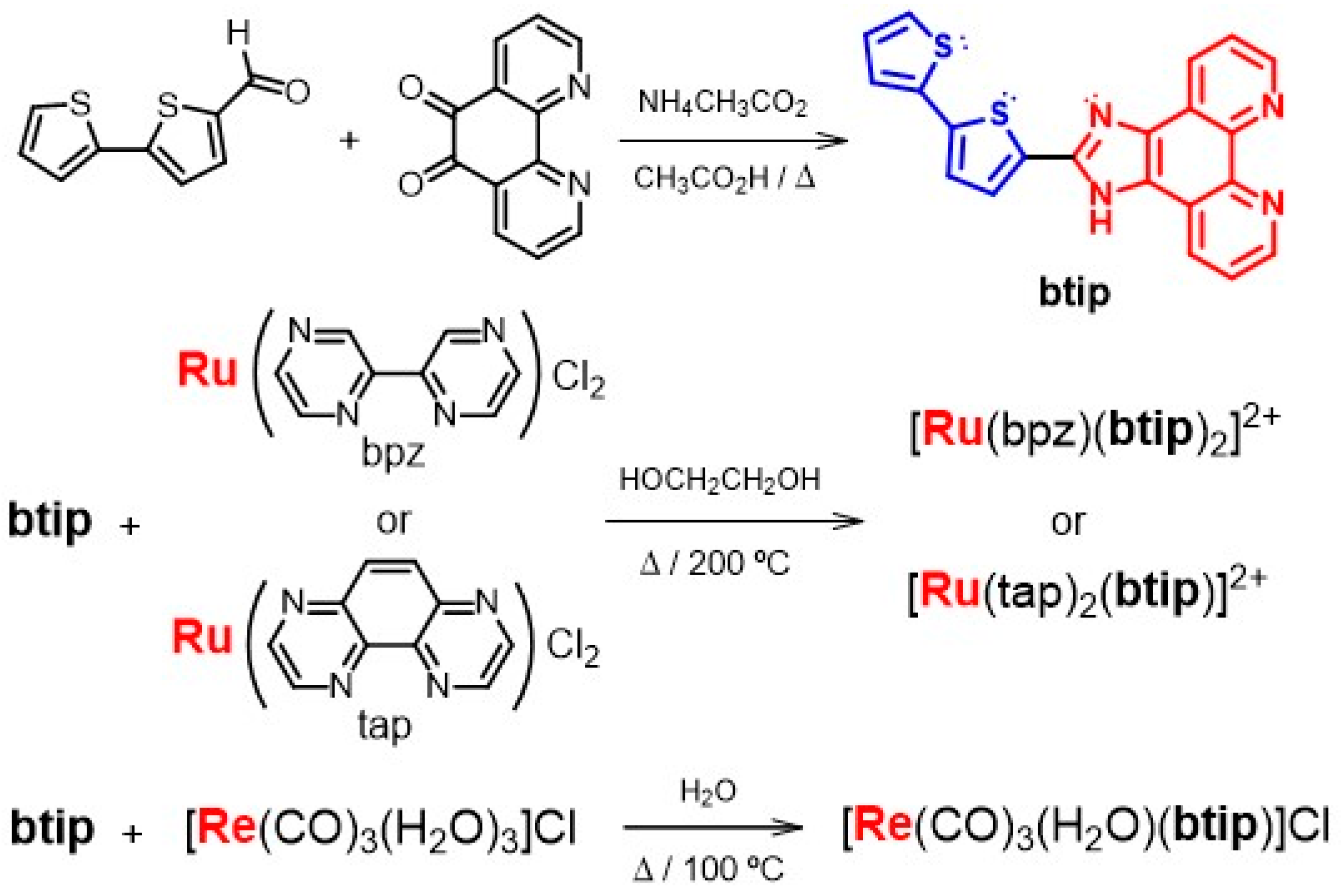
2.3. Synthesis of the Sb(III) Probes
2.3.1. Synthesis of 2,2′-Bipyrazine (bpz)
2.3.2. Synthesis of cis-bis(2,2′-Bipyrazine)(dichloro)ruthenium(II)
2.3.3. Synthesis of 1,10-phenanthroline-5,6-dione (PD)
2.3.4. Synthesis of 2-(2,2′-Bithien-5-yl)-1H-imidazo [4,5-f]-1,10-phenanthroline (btip)
2.3.5. Synthesis of [Ru(bpz)(btip)2]2+(CF3CO2−)2
2.3.6. Synthesis of [Ru(tap)2(btip)]2+(PF6−)2
2.3.7. Synthesis of fac-[Re(CO)3(H2O)(btip)]+Cl−
2.4. Determination of the UV-Vis Absorption Spectra
2.5. Luminescence Study of the Probes in the Presence of Antimony Salts
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Ligands and Ru(II) and Re(I) Polypyridyl Probes for Antimony
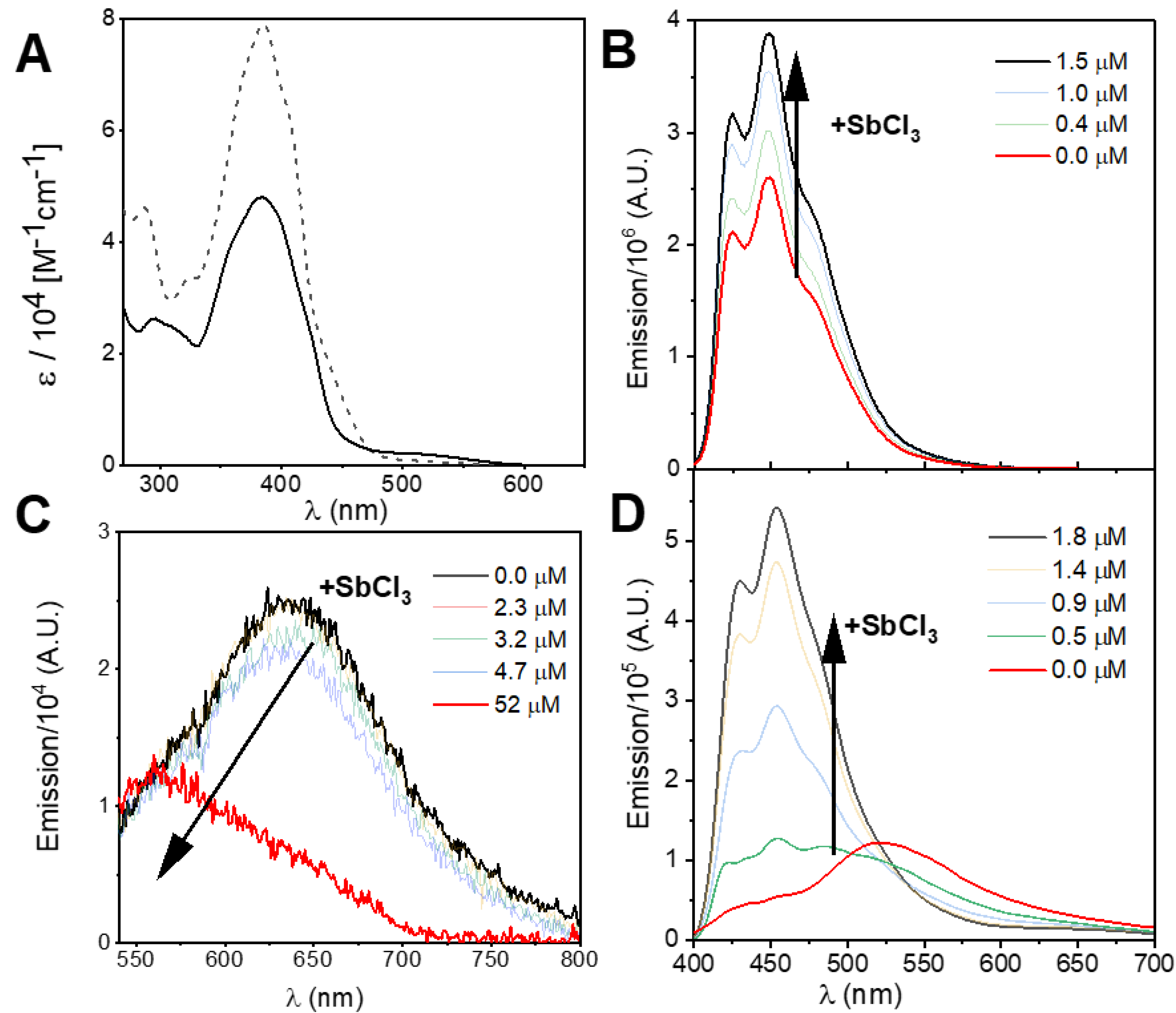
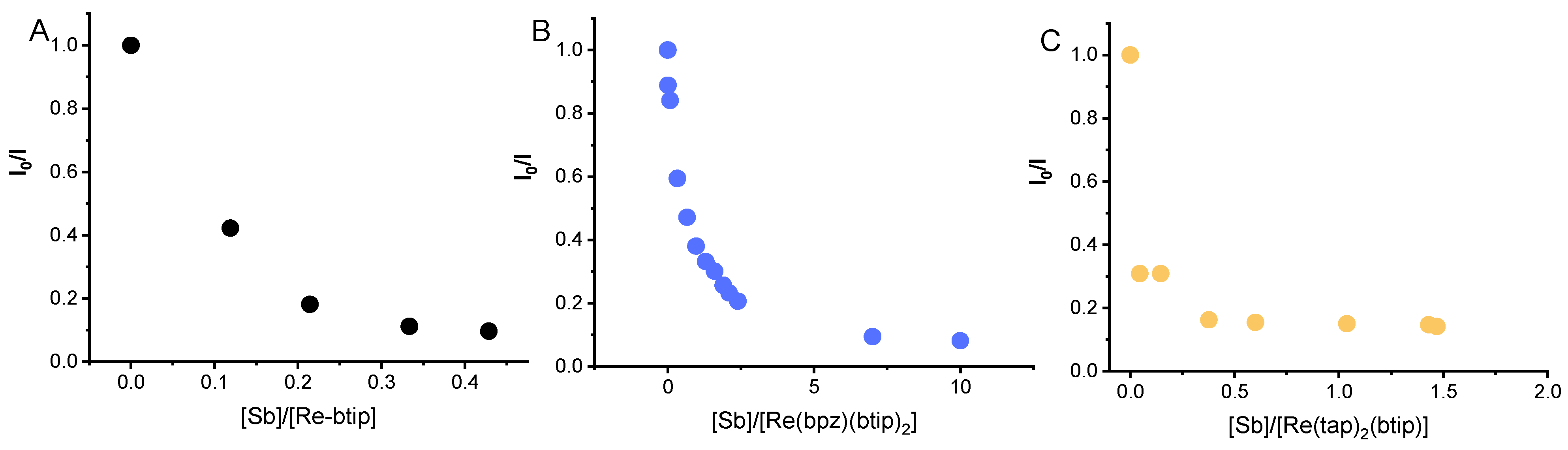
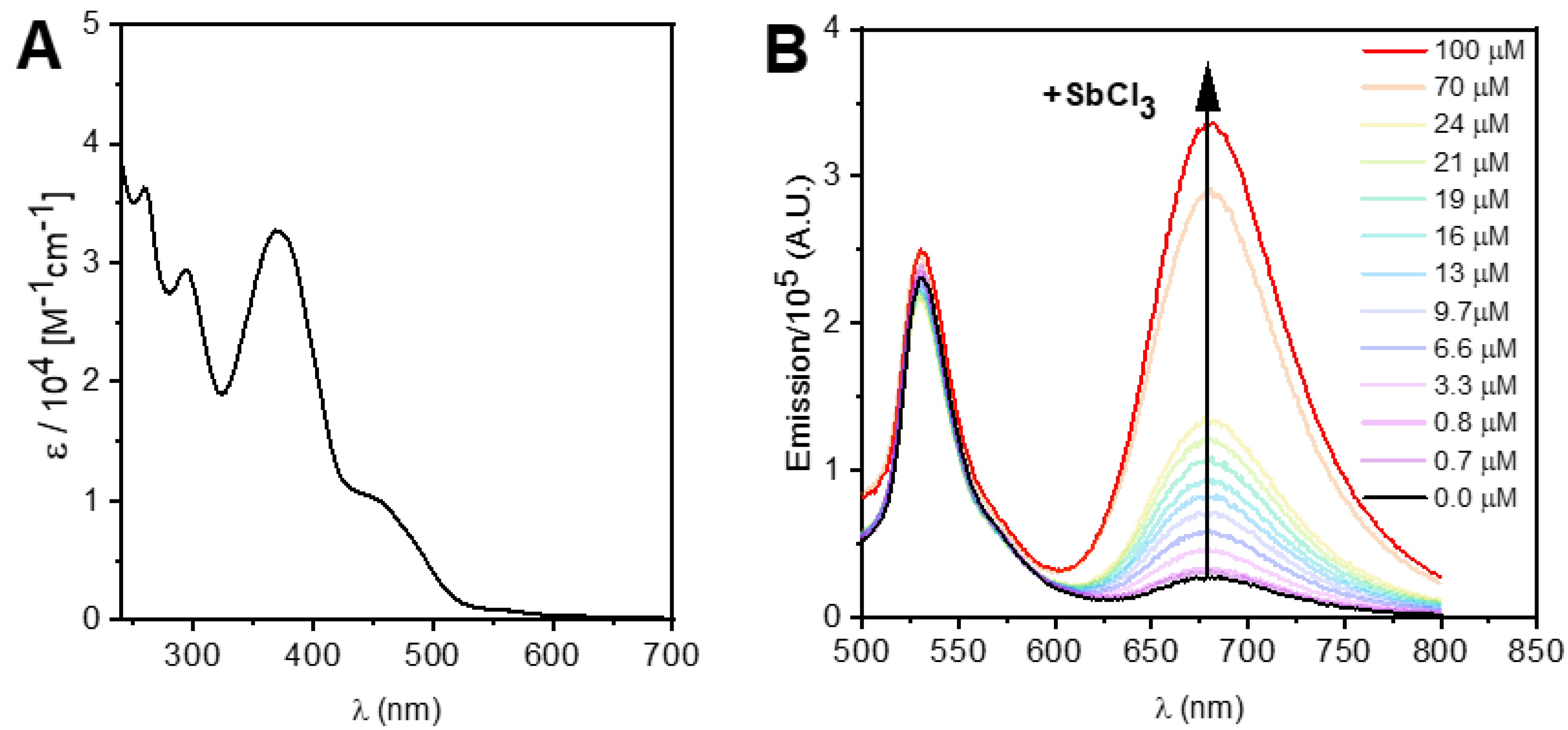
3.2. Spectroscopic and Photochemical Features of the Rhenium(I) Probe
3.3. Spectroscopic and Photochemical Features of the Ruthenium(II) Probes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dembele, S.; Akcil, A.; Panda, S. Technological trends, emerging applications and metallurgical strategies in antimony recovery from stibnite. Minerals Eng. 2022, 175, 107304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M. (Ed.) Antimony; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2021; ISBN 9783110665345. [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins, D.J. (Ed.) Properties and Uses of Antimony; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2022; ISBN 9798886970883. [Google Scholar]
- Blackmon, D. Antimony: The Most Important Mineral You Never Heard Of. Forbes, 2021, May 6. Available online: https://www.forbes.com/sites/davidblackmon/2021/05/06/antimony-the-most-important-mineral-you-never-heard-of/ (accessed on 9 August 2024).
- Ruiz-Postigo, J.A.; Jain, S. Pentavalent Antimonials in the Treatment of Human Leishmaniasis. In Antimony; Filella, M., Ed.; De Gruyter: Berlin, Germany, 2021; pp. 303–317. ISBN 9783110665345. [Google Scholar]
- Periferakis, A.; Caruntu, A.; Periferakis, A.-T.; Scheau, A.-E.; Badarau, I.A.; Caruntu, C.; Scheau, C. Availability, Toxicology and Medical Significance of Antimony. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Zhang, D.; Pan, X.; Lee, D.J. Complexation of HSA with different forms of antimony (Sb): An application of fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Lumin. 2013, 136, 80–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagas, M.R.; Wang, A.; Dorman, D.C.; Hall, A.L.; Pi, J.B.; Sergi, C.M.; Symanski, E.; Ward, E.M.; Arrandale, V.H.; Azuma, K.; et al. Carcinogenicity of cobalt, antimony compounds, and weapons-grade tungsten alloy. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, P577–P578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolan, N.; Kumar, M.; Singh, E.; Kumar, A.; Singh, L.; Kumar, S.; Keerthanan, S.; Hoang, S.A.; El-Naggar, A.; Vithanage, M.; et al. Antimony contamination and its risk management in complex environmental settings: A review. Environ. Internat. 2022, 158, 106908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filella, M. Antimony and PET bottles: Checking facts. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 127732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ding, C.; Gong, D.; Deng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Xiong, S.; Tang, R.; Wang, Y.; Su, L. A review of the environmental chemical behavior, detection and treatment of antimony. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2021, 24, 102026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matulis, R.M.; Guyon, J.C. Spectrophotometric Determination of Antimony. Anal. Chem. 1965, 37, 1391–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Hilal, A.H.; Riley, J.P. The spectrophotometric determination of antimony in water, effluents, marine plants and silicates. Anal. Chim. Acta 1981, 131, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, S.; Jardim, W.; Dórea, J. A simple spectrophotometric procedure for the determination of antimony(III) and (V) in antileishmanial drugs. Fresenius J. Anal. Chem. 1997, 358, 548–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matusiewicz, H.; Krawczyk, M. Determination of total antimony and inorganic antimony species by hydride generation in situ trapping flame atomic absorption spectrometry: A new way to (ultra)trace speciation analysis. J. Anal. Atomic Spectrom. 2008, 23, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correia, F.O.; Almeida, T.S.; Garcia, R.L.; Queiroz, A.F.S.; Smichowski, P.; da Rocha, G.O.; Araujo, R.G.O. Sequential determination and chemical speciation analysis of inorganic as and sb in airborne particulate matter collected in outdoor and indoor environments using slurry sampling and detection by HG-AAS. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2019, 26, 21416–21424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, S.L.C.; Pereira dos Anjos, J.; Felix, C.S.A.; Marques da Silva Junior, M.; Palacio, E.; Cerdá, V. Speciation analysis of antimony in environmental samples employing atomic fluorescence spectrometry—Review. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2019, 110, 335–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toghill, K.E.; Lu, M.; Compton, R.G. Electroanalytical Determination of Antimony. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2011, 6, 3057–3076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa Bosch, M.; Ruiz Sanchez, A.J.; Sanchez Rojas, F.; Bosch Ojeda, C. Arsenic and antimony speciation analysis in the environment using hyphenated techniques to inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry: A review. Int. J. Environ. Waste Manag. 2010, 5, 4–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Chen, Y.-J.; Hu, X.; Lian, H.-Z. Magnetic solid phase extraction for the determination of trace antimony species in water by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Talanta 2015, 134, 292–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-A.; Jiang, S.-J.; Sahayam, A.C. Determination of antimony compounds in waters and juices using ion chromatography-inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Food Chem. 2017, 230, 76–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G. Fluorescence-Based Sensors. In Optical Chemical Sensors; Baldini, F., Chester, A.N., Homola, J., Martellucci, S., Eds.; NATO Sci Ser II; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherland, 2006; Volume 224, pp. 99–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demchenko, A.P. Introduction to Fluorescence Sensing, 3rd ed.; Springer Nature: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G.; Darder, M.M.; Quílez-Alburquerque, J. Luminescence-Based Sensors for Water Quality Analysis. In Encyclopedia of Sensors and Biosensors; Narayan, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2023; Volume 4, pp. 599–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filer, T.D. Fluorometric determination of submicrogram quantities of antimony. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 725–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, N.; Ehtisham-ul-Haque, S.; Abbas, M.; Yameen, M.; Azhar, M.F.; Mahmoudi, G.; Nazir, A.; Iqbal, M. Synthesis of fluorescent di-dansyl substituted ethoxy compound: A selective sensor for antimony and thallium metals detection. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 1576–1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhang, W.-J.; Zeng, X.; Mu, L.; Xue, S.-F.; Tao, Z.; Yamato, T. New fluorescent sensor for antimony and transition metal cations based on rhodamine amide-arm homotrioxacalix[3]arene. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2010, 66, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orellana, G.; García-Fresnadillo, D. Environmental and industrial optosensing with tailored luminescent Ru(II) polypyridyl complexes. In Optical Sensors: Industrial, Environmental and Diagnostic Applications; Narayanaswamy, R., Wolfbeis, O.S., Eds.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 309–357. ISBN 978-3-540-40886-4. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.; Zhang, Z.; Yong, J.; Schenk, P.M.; Tian, D.; Xu, Z.P.; Zhang, R. Determination and Imaging of Small Biomolecules and Ions Using Ruthenium(II) Complex-Based Chemosensors. Topics Curr. Chem. 2022, 380, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashid, A.; Mondal, S.; Ghosh, P. Development and Application of Ruthenium(II) and Iridium(III) Based Complexes for Anion Sensing. Molecules 2023, 28, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, L.C.-C.; Lo, K.K.-W. Strategic Design of Luminescent Rhenium(I), Ruthenium(II), and Iridium(III) Complexes as Activity-Based Probes for Bioimaging and Biosensing. Chem. Asian J. 2022, 17, e202200840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Urriza-Arsuaga, I.; Ielasi, G.; Bedoya, M.; Orellana, G. Luminescence-Based Sensors for Bioprocess Applications. In Fluorescence in Industry; Pedras, B., Ed.; Springer Nature: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2019; pp. 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrin, D.D.; Armarego, W.L.F.; Perrin, D.R. Purification of Laboratory Chemicals, 2nd ed.; Pergamon: Oxford, UK, 1980; ISBN 0-08-022961-1. [Google Scholar]
- Crutchley, R.J.; Lever, A.B.P. Comparative Chemistry of Bipyrazyl and Bipyridyl Metal Complexes: Spectroscopy, Electrochemistry, and Photoanation. Inorg. Chem. 1982, 21, 2276–2282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickerson, J.E.; Summers, L.A. Derivatives of 1,10-Phenanthroline-5,6-quinone. Aust. J. Chem. 1970, 23, 1023–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masschelein, A.; Jacquet, L.; Kirsch-De Mesmaeker, A.; Nasielski, J. Ruthenium complexes with 1,4,5,8-tetraazaphenanthrene. Unusual photophysical behavior of the tris-homoleptic compound. Inorg. Chem. 1990, 29, 855–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ragone, F.; Saavedra, H.H.M.; García, P.F.; Wolcan, E.; Argüello, G.A.; Ruiz, G.T. Association studies to transporting proteins of fac-ReI(CO)3(pterin)(H2O) complex. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 22, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, N.N.; Earnshaw, A. Chemistry of the Elements, 2nd ed.; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 1997; pp. 578–583. ISBN 0750633654. [Google Scholar]
- Aghazada, S.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics 2018, 6, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naithani, S.; Goswami, T.; Thetiot, F.; Kumar, S. Imidazo [4,5-f][1, 10] phenanthroline based luminescent probes for anion recognition: Recent achievements and challenges. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2023, 475, 214894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedras, B.; Batista, R.M.F.; Tormo, L.; Costa, S.P.G.; Raposo, M.M.M.; Orellana, G.; Capelo, J.L.; Lodeiro, C. Synthesis, characterization, photophysical studies and interaction with DNA of a new family of Ru(II) furyl- and thienyl-imidazo-phenanthroline polypyridyl complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2012, 381, 95–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, G.; Monro, S.; Hennigar, R.; Colpitts, J.; Fong, J.; Kasimova, K.; Yin, H.; DeCoste, R.; Spencer, C.; Chamberlain, L.; et al. Ru(II) Dyads Derived from α-Oligothiophenes: A New Class of Potent and Versatile Photosensitizers for PDT. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 282−283, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batista, R.M.F.; Costa, S.P.G.; Belsey, M.; Lodeiro, C.; Raposo, M.M.M. Synthesis and characterization of novel (oligo)thienyl-imidazo-phenanthrolines as versatile p-conjugated systems for several optical applications. Tetrahedron 2008, 64, 9230–9238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Kuroda, S.; Shimao, I. Synthesis and Properties of Diamino-Substituted Dipyrido (3, 2-a: 2‘, 3‘-c) phenazine. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1992, 65, 1006–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choroba, K.; Penkala, M.; Palion-Gazda, J.; Malicka, E.; Machura, B. Pyrenyl-Substituted Imidazo[4,5-f][1,10]phenanthroline Rhenium(I) Complexes with Record-High Triplet Excited-State Lifetimes at Room Temperature: Steric Control of Photoinduced Processes in Bichromophoric Systems. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62, 19256–19269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korte, L.; Lipka, A.; Mootz, D. Addukte schwefelhaltiger Heteroaromaten mit SbCl3 Untersuchungen zur Bildung und Kristallstruktur von 2,2′-Dithienyl· 2 SbCl3 und Benzo-[b]-thiophen· 2 SbCl3. Z. Anorg. Chem. 1985, 524, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouchi, A.; Takeuchi, T.; Taminaga, I. The syntheses and properties of the benzothiazole or benzimidazole derivative adduct of Tin(II, IV) and antimony(III) halides. Bull. Chem. Soc. Japan 1970, 43, 2840–2844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortmans, I.; Moucheron, C.; Kirsch-De Mesmaeker, A. Ru(II) polypyridine complexes with a high oxidation power. Comparison between their photoelectrochemistry with transparent SnO2 and their photochemistry with desoxyribonucleic acids. Coord. Chem. Rev. 1998, 168, 233–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urriza-Arsuaga, I.; Bedoya, M.; Orellana, G. Unprecedented reversible real-time luminescent sensing of H2S in the gas phase. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2231–2238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majewski, M.B.; Tacconi, N.R.D.; MacDonnell, F.M.; Wolf, M.O. Ligand-Triplet-Fueled Long-Lived Charge Separation in Ruthenium(II) Complexes with Bithienyl-Functionalized Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 9939–9941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

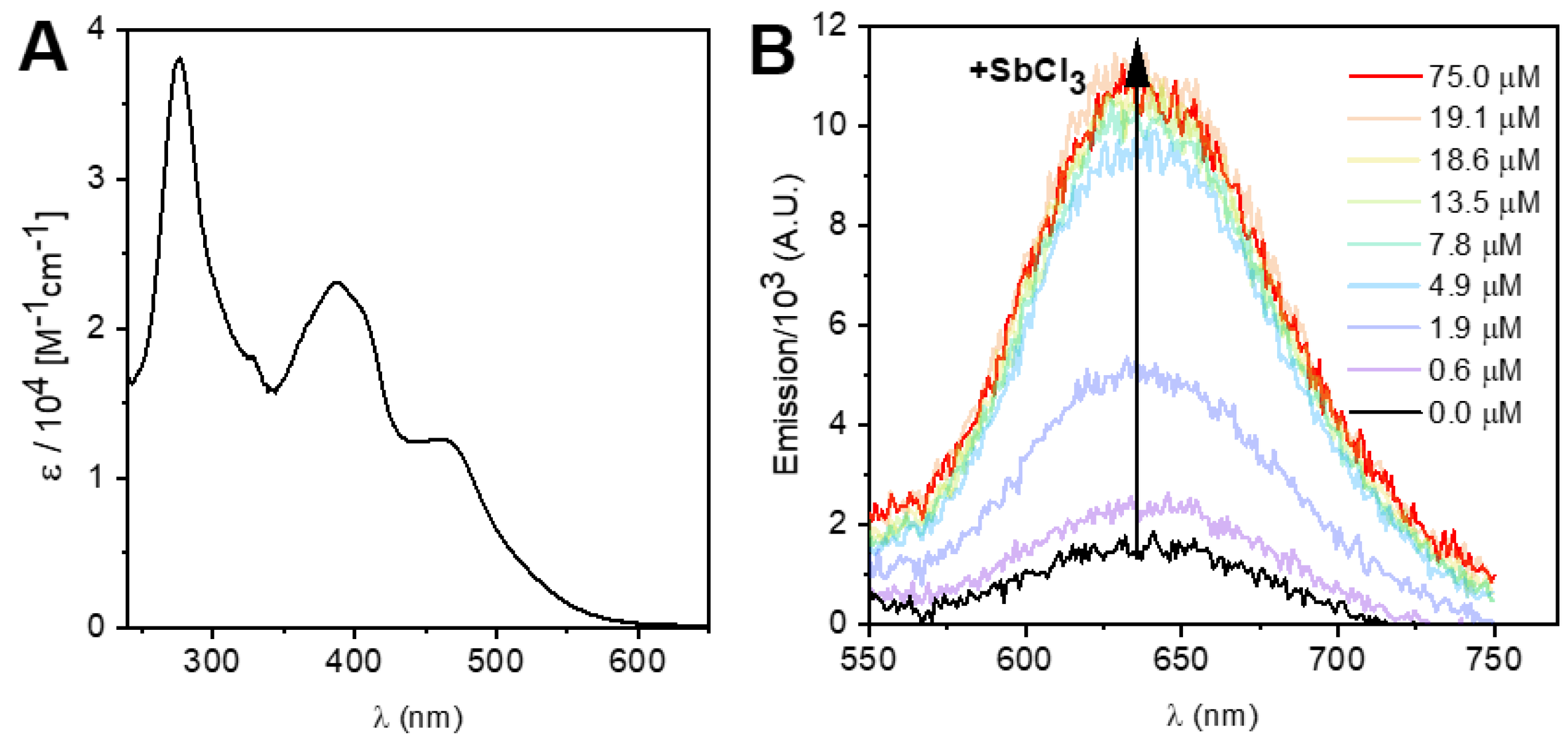
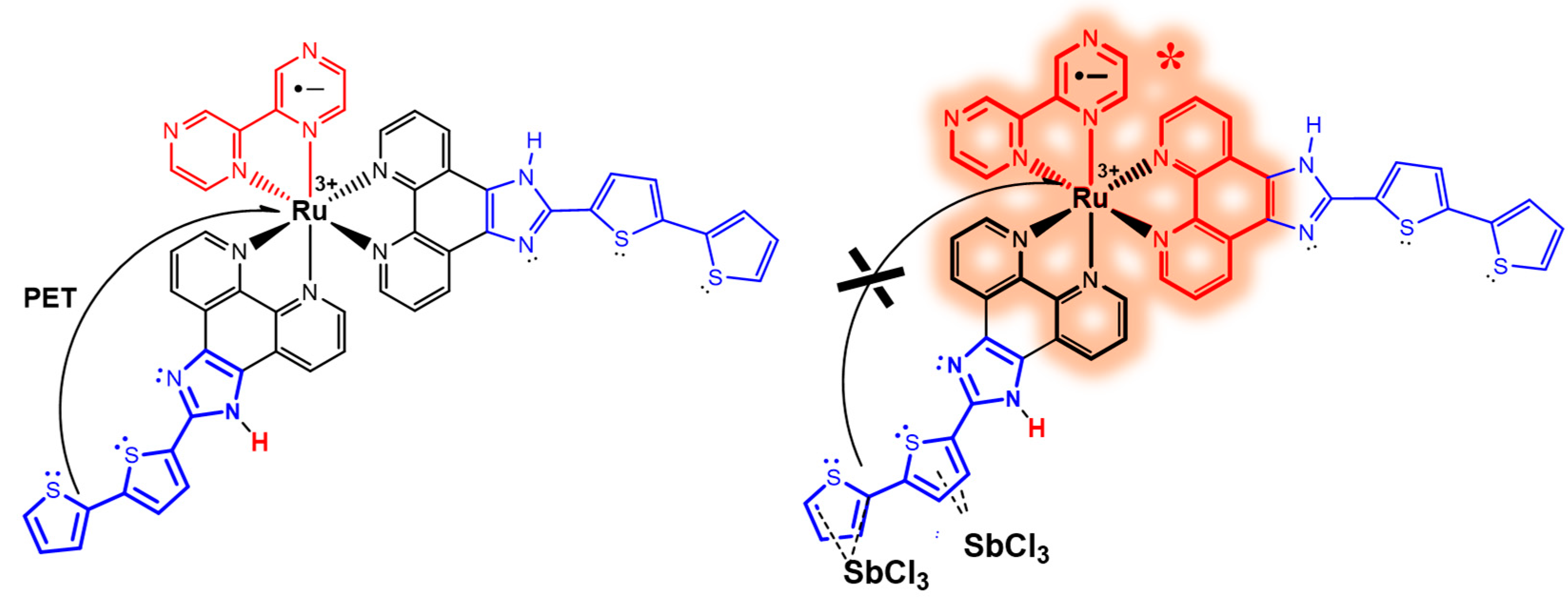
| [SbCl3]/μmol L−1 | τ1/ns (%) a | τ2/ns (%) a | τ3/ns (%) a | τM/ns b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.00 | 12 (47) | 40 (30) | 268 (22) | 21.5 |
| 0.68 | 14 (35) | 65 (22) | 326 (43) | 34 |
| 1.36 | 17 (32) | 79 (23) | 336 (46) | 43 |
| 2.00 | 18 (18) | 115 (22) | 351 (60) | 76 |
| 10.0 | 19 (7) | 140 (25) | 359 (68) | 139 |
| 14.0 | 27 (6) | 162 (29) | 362 (65) | 178 |
| 47.0 | 41 (2) | 186 (34) | 386 (63) | 247 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Silva, A.V.; Ragone, F.; Ruiz, G.T.; Orellana, G. Tailoring Ruthenium(II) and Rhenium(I) Complexes for Turn-On Luminescent Sensing of Antimony(III). Chemosensors 2024, 12, 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100217
Silva AV, Ragone F, Ruiz GT, Orellana G. Tailoring Ruthenium(II) and Rhenium(I) Complexes for Turn-On Luminescent Sensing of Antimony(III). Chemosensors. 2024; 12(10):217. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100217
Chicago/Turabian StyleSilva, Alexandre Vieira, Fabricio Ragone, Gustavo Teodosio Ruiz, and Guillermo Orellana. 2024. "Tailoring Ruthenium(II) and Rhenium(I) Complexes for Turn-On Luminescent Sensing of Antimony(III)" Chemosensors 12, no. 10: 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100217
APA StyleSilva, A. V., Ragone, F., Ruiz, G. T., & Orellana, G. (2024). Tailoring Ruthenium(II) and Rhenium(I) Complexes for Turn-On Luminescent Sensing of Antimony(III). Chemosensors, 12(10), 217. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12100217






