Abstract
Herein, we propose a transparent high-performance extended-gate ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (EG-ISFET) using an electrospun indium-tin-oxide (ITO) nanofiber sensing membrane with a high specific surface area. Electrospinning is a simple and effective technique for forming nanofibers. Nevertheless, one-step calcination, such as conventional thermal annealing or microwave annealing, cannot sufficiently eliminate the inherent defects of nanofibers. In this study, we efficiently removed residual polymers and internal impurities from nanofibers via a two-step calcination process involving combustion and microwave annealing. Moreover, Ar plasma treatment was performed to improve the electrical characteristics of ITO nanofibers. Conformally coated thin-film sensing membranes were prepared as a comparative group and subjected to the same calcination conditions to verify the effect of the nanofiber sensing membrane. The characteristics of the ITO nanofiber and ITO thin-film sensing membranes were evaluated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), optical transmittance, and conductivity. Moreover, the sensor operation of the EG-ISFETs is evaluated in terms of sensitivity and non-ideal behaviors. The optimized process improves the sensor characteristics and sensing membrane quality. Therefore, the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane improves the sensitivity and stability of the EG-ISFET, suggesting its applicability as a high-performance biochemical sensor.
1. Introduction
With frequent outbreaks of pandemics threatening human life and the global economy, interest in healthcare has been increasing [1,2,3,4]. Rapid detection and point-of-care (POC) analysis of disease-causing pathogens poses challenges in establishing appropriate treatment strategies for the medical field. Among the various diagnostic techniques for detecting pathogens, electrochemical biosensor technology has led to the development of POC devices. Electrochemical biosensors have attracted considerable attention owing to their advantages, such as fast response, high sensitivity, selectivity, and ease of miniaturization capability. In particular, pH sensors based on ion-sensitive field-effect transistors (ISFETs) benefit from a smaller size, faster response time, and fabrication that is compatible with standard metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) technology [5,6,7,8]. In addition, the functions of pH ISFETs are diverse, particularly in biomedical applications [9,10,11]. In a typical ISFET, the sensing membrane and transducer FET constituting the sensor are placed on the same platform. Accordingly, when the sensing membrane is damaged from repetitive measurements, the transducer unit becomes inoperable, and the entire sensor platform needs to be replaced. Conversely, the extended-gate ion-sensitive field-effect transistor (EG-ISFET) has a structural feature that isolates the transducer FET from the chemical environment. Specifically, the chemically sensitive membrane is positioned at the end of the signal line, extending from the FET gate electrode, to separate the sensing and transducer units. As a result, the structure has many advantages, such as being insensitive to light, simple passivation and packaging, and shape flexibility of an extended gate area. Moreover, the EG-ISFET enables continuous detection by replacing only the EG sensing unit, which has a simple structure, is easy to prepare, and is inexpensive, without changing the entire platform [12,13]. The sensitivity of chemical sensors is significantly influenced by the surface conditions of the sensing materials. Since a higher specific surface area of a sensing material leads to higher sensitivity of the sensor, nanostructured materials that exploit the large specific surface area, such as nanoparticles, nanowires, nanofibers, and nanotubes, are beneficial for sensor sensitivity [14,15,16,17,18]. In particular, nanofibers prepared via electrospinning have a specific surface area that is approximately one to two orders of magnitude larger than that of flat films [19]. Therefore, electrospun nanofibers are promising candidates for sensor applications. Moreover, ion-sensitive metal oxides have unique electrical, electrochemical, and biocompatible characteristics, making them ideal candidates for water and food quality monitoring applications because of their fast response and long lifetime under various environmental conditions [20]. Therefore, metal oxide nanofiber sensing membranes with a high surface-to-volume ratio are expected to be key building blocks for electrochemical pH sensors with high sensitivity and selectivity. Nevertheless, impurities and defects included in electrospun metal oxide nanofibers deteriorate their physical and electrical characteristics. Therefore, calcination annealing is required at high temperatures to vaporize the polymer matrix constituting the nanofibers and improve the crystallinity of the metal oxide [21,22,23].
In this study, we propose a high-performance, high-transmittance EG-ISFET sensor platform that uses an electrospun indium-tin-oxide (ITO) nanofiber sensing membrane [24]. Conventionally, calcination using conventional thermal annealing (TA) or microwave annealing (MWA) has been performed; however, the residual polymers on the surface and impurities inside the nanofibers are not efficiently eliminated by the one-step calcination process. Therefore, we efficiently removed residual polymers and impurities from nanofibers via a novel two-step calcination process involving a combustion step and microwave annealing step [18,25,26,27,28]. Subsequently, the electrical characteristics of the ITO nanofibers are further improved by surface collisions with high-energy Ar plasma particles. To demonstrate the effectiveness of the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane and the improved calcination process, a spin-coated ITO thin-film sensing membrane with the same composition was also prepared for comparison [29]. Based on the calcination conditions, the characteristics of the ITO nanofibers and ITO thin-film sensing membranes were evaluated using scanning electron microscopy (SEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), optical transmittance, and conductivity. We fabricated EG-ISFETs using an EG unit equipped with an electrospun ITO nanofiber membrane, ITO thin-film membrane, and n-type MOSFET transducer unit. While the conventional EG unit comprises a Si substrate, conductive electrode, and a sensing membrane, the EG unit proposed in this study simplifies the process, making it cost-effective because ITO nanofibers spun on low-cost glass substrates simultaneously serve as a conductive electrode and a sensing membrane [11,30,31,32]. The differences between the EG-ISFET proposed in this study and conventional EG-ISFETs were compared in Table 1 [33,34,35,36,37,38]. The excellence of the electrospun ITO nanofiber-based EG-ISFET is verified through sensitivity and non-ideal effect evaluation. Moreover, the EG-ISFET performance improvement via two-step calcination and Ar plasma treatment of the electrospun ITO nanofiber [11,36,37,38] membrane is quantitatively evaluated.

Table 1.
Comparison of EG-ISFETs according to various materials and process conditions.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Material Specifications
The material specifications of the study are as follows: glass substrate (Corning 7059; Corning Inc., Corning, NY, USA), indium trichloride (InCl3; purity = 99.9%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), anhydrous tin chloride (SnCl4; purity = 99.995%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF; purity = 99.8%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP; average Mw ~1,300,000, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), 2-Methoxy ethanol (purity = 99.99%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA), mono-ethanolamine (C2H7NO; purity = 99.5%, Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. Fabrication of the EG Sensing Units
The EG sensing units, comprising a transparent substrate, sensing membrane, and a polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) reservoir, were fabricated in a 1.5 × 3 cm2 size using Corning 7059 glass substrates. An ITO precursor solution for electrospinning was prepared by mixing N,N-dimethylformamide (DMF) (1 mL), indium trichloride (InCl3) powder (66.92 mg), and anhydrous tin chloride (SnCl4) powder (9.38 mg), followed by stirring at 800 rpm for 3 h at room temperature [28]. A polyvinylpyrrolidone (PVP) solution was prepared by stirring PVP powder (600 mg) in ethanol (3 mL) at 800 rpm for 3 h at room temperature. The ITO nanofibers were electrospun using a syringe pump (NE-1000; New Era Pump Systems, New York, NY, USA). While maintaining the electrospinning environment at a temperature of 20 °C and humidity of 30%, the ITO nanofibers were spun for 20 min by setting the flow rate of the syringe pump to 0.4 mL/h. A copper plate was used as a grounded collector, and a voltage of 20 kV was applied between the pin head and copper plate. Under these process conditions, the ITO nanofiber precursor was electrospun from the pinhead flow 20 cm (working distance) to form nanofibers on the substrate. As a comparative group, for the spin coating of the ITO thin-film sensing membrane, an ITO precursor with the same composition (InCl3 66.92 mg, SnCl4 9.38 mg) was synthesized via a sol-gel reaction. These powders were dissolved in 2-methoxyethanol (4 mL), and mono-ethanolamine (C2H7NO) (0.5 mL) was added for stable coating, and the mixture was stirred at 50 °C for 2 h [29]. The prepared ITO precursor solution was spin-coated at 3000 rpm for 30 s and baked at 180 °C for 10 min to fabricate an EG unit with a 100-nm-thick ITO thin-film sensing membrane. The thickness of the ITO thin-film sensing membrane was measured to be ~100 nm using a stylus profilometer (DektakXT; Bruker, Billerica, MA, USA). Following the fabrication of ITO nanofibers or thin-film sensing membranes, calcination was performed to remove the residual polymers and impurities from the surface. We distinguished the heat treatment process into one-step calcination by MWA and two-step calcination by TA and MWA. Specifically, TA was performed at 180 °C for 30 min in a resistance-heating muffle furnace, and MWA was performed at 1800 W for 2 min in a 2.45 GHz microwave irradiation system. Both calcination processes were performed under an oxygen ambient. In the subsequent process of calcination, Ar plasma treatment was performed at 200 W for 2 min to improve the electrical characteristics of the ITO nanofibers [29,39,40,41,42]. The fabrication process flow of the electrospun ITO nanofiber sensing membrane and photographs of the ITO nanofibers fabricated on the glass substrate are depicted in Figure 1a,b, respectively.
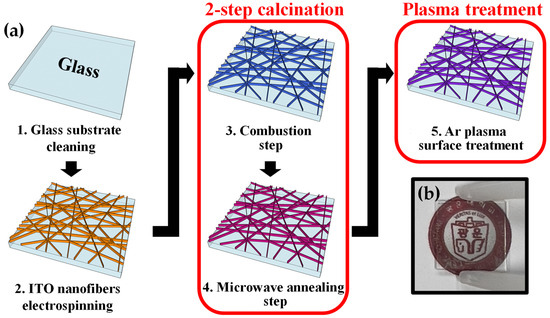
Figure 1.
(a) Fabrication process flow of the electrospun ITO nanofiber sensing membrane. (b) Photograph of ITO nanofibers prepared on a glass substrate.
2.3. Characterization of the Fabricated EG-ISFET Sensor Platform
In the proposed EG-ISFET, as shown in Figure 2, an ITO nanofiber sensing membrane was placed on the EG at the end of the signal line, extending from the FET gate electrode, to isolate the transducer FET from the chemical environment.
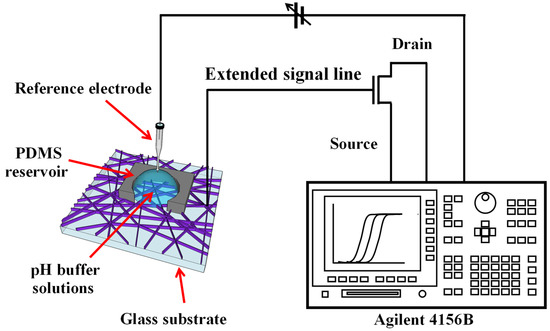
Figure 2.
Schematic diagram of the proposed EG-ISFET with electrospun ITO nanofibers sensing membrane.
ITO nanofibers obtained through electrospinning were used as pH-sensitive membranes for electrodes, which were connected to commercial NMOSFET devices (2N7000; ON Semiconductor, Phoenix, AZ, USA). In addition, an Ag/AgCl electrode (Horiba 2080-06T; Kyoto, Japan) was used as the reference electrode, and the distance between the reference electrode and ITO sensing membrane was fixed at approximately 3 mm. The reference electrode was dipped into the buffer solution in the PDMS reservoir on the EG unit and connected to the gate of the MOSFET. An Agilent 4156 B Semiconductor Parameter Analyzer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) was used to measure the threshold voltage (Vth) of the EG-ISFET at pH 3, 4, 6, 7, 9, and 10 buffer solutions. The sensitivity of the EG-ISFET was determined by measuring the change in the gate voltage at a drain current of 1 nA according to the pH of the buffer solution. For non-ideal behaviors, the hysteresis effect, which represents the stability during repeated operation, and the drift effect, which represents the stability during long-term operation, were evaluated. The hysteresis voltage was defined as the difference in the reference voltage (VREF) between the first pH 7 point and the final pH 7 point in the pH loop 7→10→7→4→7. The drift effect was evaluated by exposing the sensing membrane to a pH 7 buffer for 10 h and monitoring the change in the reference voltage.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Evaluation of Electrospun ITO Nanofiber Sensing Membrane
Figure 3 illustrates the SEM images of electrospun ITO nanofibers under different process conditions. The process conditions are classified into four categories: ‘MWA’, ‘TA+MWA’, ‘MWA→Ar plasma’, and ‘TA+MWA→Ar plasma’. It is evident that the surface morphology of ITO nanofiber sensing membranes is significantly influenced by calcination. The diameters of the nanofibers are approximately between 500–1000 nm after one-step calcination (MWA), as shown in (a) and (b), whereas it reduced to approximately 50–100 nm after two-step calcination (TA combustion + MWA), as shown in Figure 3c,d. Additionally, the shapes of the nanofibers are unclear after one-step calcination. In contrast, the shapes are clarified after two-step calcination. The result indicates that the two-step calcination process is more effective in removing the residual polymer and internal impurities from the electrospun ITO nanofibers.
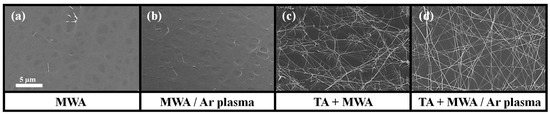
Figure 3.
SEM images of electrospun ITO nanofibers according to calcination conditions and plasma treatment.
Figure 4 shows the XRD pattern of the ITO sensing membrane according to calcination conditions and plasma treatment. In both nanofibers and thin-film sensing membranes, XRD peaks are observed at the same specific angle, with the peaks designated as (222), (400), (440), and (622). The X-ray diffraction pattern shows that both sensing membranes are cubic structures and preferentially grown along the (222) plane [28,29,43,44]. The effect of the process conditions on the crystallization of the ITO sensing membrane is similar to that of the SEM images shown in Figure 3. The ITO sensing membrane subjected to two-step calcination (TA combustion + MWA) has larger and sharper peaks than the sensing membrane with one-step calcination (MWA). Therefore, two-step calcination with an additional TA combustion step eliminates residual polymers and internal impurities, facilitating a sensing membrane with superior crystallinity. The crystallinity of the ITO sensing membrane was quantified by extracting the average grain size from the main peak (222) using the Scherrer equation [45]. The average particle sizes of the ITO thin-films for MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma were estimated to be approximately 11.5, 9.3, 9.8, and 7.8 nm, respectively. The average particle sizes of the ITO nanofibers were estimated to be 27.5, 19.1, 25, and 15.6 nm, respectively, which are better than those of the ITO thin-film in terms of crystallinity. It is worth mentioning that the TA combustion step significantly influences ITO crystallinity enhancement.
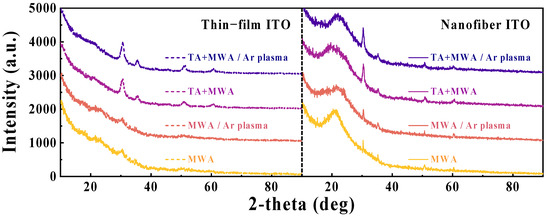
Figure 4.
XRD patterns of the ITO sensing membranes according to the calcination conditions and plasma treatment.
Figure 5 illustrates the XPS analysis performed to distinguish changes in the ITO sensing membrane according to the calcination conditions. The O1s spectrum is deconvolved by the M-O (530.5 eV) peak due to the In2O3 lattice, the M-Ovac (531.9 eV) peak due to the In2O3 lattice with oxygen vacancies, and the M-OH (532.8 eV) peak due to oxygen contamination [29,46,47,48]. In the case of nanofiber ITO spun on a glass substrate, an O-Si (533.4 eV) peak is also detected due to the glass substrate partially exposed through the gap between the ITO nanofibers [49,50]. The deconvoluted O1s spectra show that the M-Ovac peak increases after the two-step calcination. Since oxygen vacancies contribute to the conductivity of ITO by increasing the carrier concentration, the increase in the M-Ovac peak suggests that the conductive characteristics of the ITO sensing membrane are improved. Meanwhile, the C1s spectra, shown in the insets, compare the number of carbon-based impurities remaining in the sensing membrane and is divided into C-C (285 eV), C-O-C (286.5 eV), C=O (288 eV), and O=C-O (289 eV) peaks [48,51]. When two-step calcination was applied, the C1s spectra for thin-film ITO and nanofiber ITO decreased by 54.71% and 25.42%, respectively. Owing to the characteristics of the electrospinning process, it is essential to effectively remove impurities present in the ITO sensing membrane. The decreased C1s spectrum proves that the two-step calcination process can perform this role excellently.
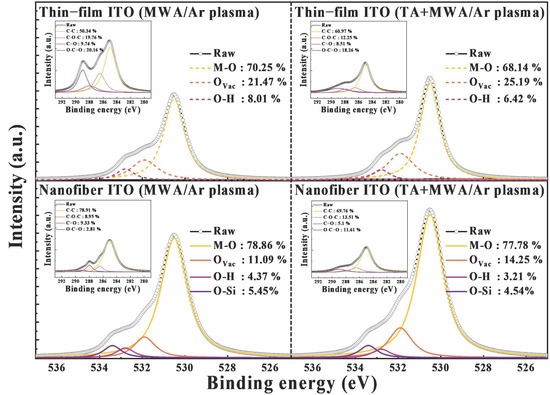
Figure 5.
XPS O1s spectra of ITO sensing membranes according to the calcination conditions. Inset shows the XPS C1s spectra of each condition.
Figure 6 shows the optical transmittance spectra of the ITO sensing membranes on a glass substrate. The average transmittance extracted in the visible light region (400–700 nm) is higher for the ITO nanofiber sensing membranes than for the ITO thin-film sensing membranes. For the conditions of MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma, the ITO thin-film sensing membranes are 77.79, 83.24, 89.79, 88.91%, and the ITO nanofiber sensing membranes are 83.15, 85.51, 87.61, and 91.21%, respectively. In particular, the optical transmittance of the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane optimized via two-step calcination (TA+MWA) and Ar plasma treatment exceeds 91% and is expected to be a sensing material that is applicable to various transparent sensors.
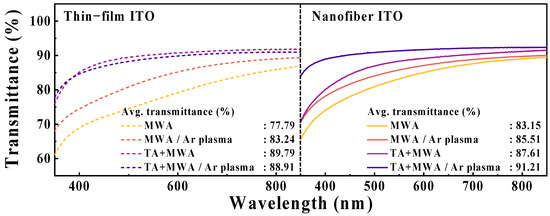
Figure 6.
Optical transmittance spectra of ITO sensing membranes on glass substrates under different calcination conditions and plasma.
Figure 7 illustrates a plot of the light absorption coefficient (α) versus photon energy for the ITO sensing membrane. The absorption coefficient (α) was calculated from the transmittance spectrum in the ultraviolet (UV) region using the following equation [52,53]:
where t denotes the sensing membrane thickness, and T denotes the transmittance. We extracted the optical bandgap (Eg) using the following relationship with the absorption coefficient [52]:
where h denotes the Planck constant, and ν denotes the frequency of the photon. For the conditions of MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma, the ITO thin-film sensing membranes are 4.51, 4.58, 4.55, and 4.60 eV, respectively, and the ITO nanofiber sensing membranes are 4.56, 4.59, 4.60, and 4.66 eV, respectively. The extracted Eg is higher for the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane than that for the ITO thin-film sensing membrane. In particular, the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane optimized via two-step calcination (TA+MWA) and Ar plasma treatment exhibits the widest optical bandgap. These results show the same tendencies as the optical transmission spectrum shown in Figure 5. Accordingly, the effectiveness of removing residual polymers and impurities via two-step calcination and Ar plasma treatment is successfully demonstrated.
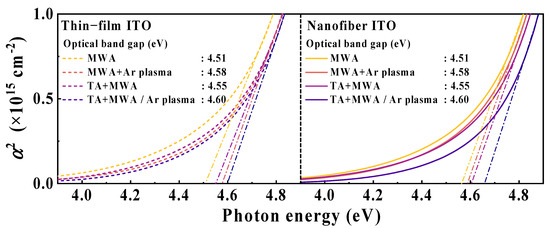
Figure 7.
Dependence of absorption coefficient on photon energy of ITO sensing membranes according to calcination conditions and plasma treatment.
Figure 8 illustrates the current-voltage (I-V) curves of the ITO sensing membranes according to the calcination conditions and plasma treatment. In the conduction characteristics, it can be observed that the effect of Ar plasma treatment is dominant. Following Ar plasma treatment, the current increased by ~13 times (MWA) and ~16 times (TA+MWA) in the ITO thin-film sensing membrane, and by ~33 times (MWA) and ~17 times (TA+MWA) in the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane. The results can be attributed to the improved conductance of the ITO sensing membrane layer due to the Ar plasma treatment, which is consistent with the results of a previous study [29]. In general, the conduction mechanism of oxide semiconductors, including ITO, is described as a function of free electrons owing to oxygen vacancies [54,55,56]. The ion bombardment effect of Ar plasma increases the number of oxygen vacancies in the ITO layer through the surface collisions of high-energy plasma particles. The conductivity of the ITO thin-film sensing membranes is 27.9, 254, 81.4, and 1286.1 S/cm, and the ITO nanofiber sensing membranes are 0.8, 27, 18.6, and 264.3 S/cm, respectively, for the conditions of MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma [57,58,59]. A significant increase in current and conductivity provides evidence of an improvement in the conduction characteristics of ITO sensing membranes due to the ion bombardment effect, demonstrating the validity of the Ar plasma treatment.
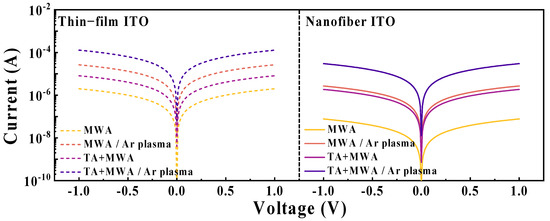
Figure 8.
Current-Voltage (I-V) curves of the ITO sensing membranes according to calcination conditions and plasma treatment.
Table 2 summarizes the experimental results of the physical property tests performed on ITO nanofibers and thin-film sensing membranes.

Table 2.
Summary of experimental results on the ITO sensing membranes.
3.2. pH Sensing Operation of EG-ISFET with Electrospun ITO Nanofiber Sensing Membrane
Figure 9 shows the pH sensing characteristics of the EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film sensing membranes or ITO nanofiber sensing membranes according to the calcination conditions and plasma treatment. The sensitivity was extracted as the amount of voltage change at a reference current (IREF) of 1 nA from the transfer characteristic curves of the FET for a buffer solution of pH 3–10.
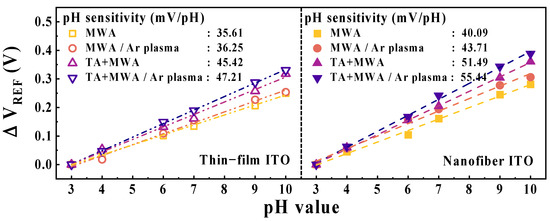
Figure 9.
pH sensitivity of EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film sensing membrane or ITO nanofiber sensing membrane according to calcination conditions and plasma treatment.
The pH sensitivities of EG-ISFETs with ITO nanofiber sensing membranes are 40.09, 43.71, 51.49, and 55.44 mV/pH for MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma conditions, respectively. Meanwhile, the EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film sensing membranes exhibit sensitivities of 35.61, 36.25, 45.42, and 47.21 mV/pH, respectively. Evidently, the ITO nanofiber membranes implemented a higher sensitivity of the EG-ISFET than the ITO thin-film membranes under the same calcination process and plasma treatment.
It is essential for electrochemical pH sensors to maintain high stability and reliability, along with sensitivity, for repeated and continuous operation. Non-ideal behaviors, which are crucial performance indicators of the stability and reliability of electrochemical pH sensors, include hysteresis and drift effects [60,61]. Figure 10 illustrates the hysteresis effect of EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film membranes or ITO nanofiber sensing membranes, according to the calcination conditions and plasma treatment. Repeated exposure of the sensing membrane to different pH buffer solutions causes a hysteresis effect owing to the reaction between electrolyte ions (H+ or OH−) and the surface or slow transport of ionic species in the membrane bulk, resulting in reliability deterioration [61]. The hysteresis experiments were performed under a loop cycle of pH 7−10−7−4–7 at room temperature. The hysteresis voltage (VH) is defined as the difference in voltage values between the start and end points of the pH loop. The VH of EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film sensing membranes are 22.69, 31.61, 21.01, and 22.71 mV for MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma conditions, respectively. Meanwhile, the EG-ISFETs with ITO nanofiber sensing membranes have VH values of 27.69, 17.97, 13.11, and 15.63 mV, respectively.
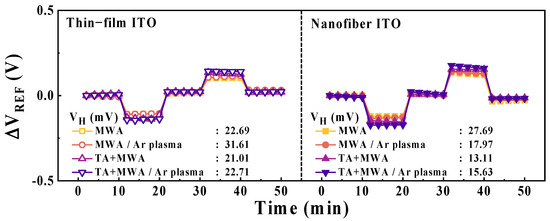
Figure 10.
Hysteresis effect of EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film or ITO nanofiber sensing membranes according to the calcination conditions and plasma treatment.
Figure 11 illustrates the drift effect of EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film membranes or ITO nanofiber sensing membranes, depending on the calcination conditions and plasma treatment. During long-term continuous operation of the pH sensor, a hydration layer is formed on the surface of the sensing membrane, causing a drift effect that hinders an accurate sensing operation [60,62]. The drift rate (Rdrift) was measured by exposing the sensing membrane to a pH 7 buffer solution at room temperature for 10 h. For MWA, TA+MWA, MWA/Ar plasma, and TA+MWA/Ar plasma conditions, the Rdrift values of EG-ISFET with ITO thin-film membranes are 8.82, 9.56, 5.59, and 6.05 mV/h, respectively, whereas those of the EG-ISFET with ITO nanofiber membranes are 5.14, 4.06, 3.42, and 3.75 mV/h, respectively. Therefore, the non-ideal behaviors derived from the hysteresis voltage and drift rate were suppressed in the nanofiber sensing membrane and effectively improved by the two-step calcination and plasma treatment. These results suggest that the proposed two-step calcined, and plasma-treated ITO nanofiber sensing membranes have stable operational capabilities in repeated and continuous measurement environments. The experimental results of the pH sensitivity, hysteresis voltage, and drift rate performed on the ITO nanofiber and thin-film sensing membranes are summarized in Table 3.
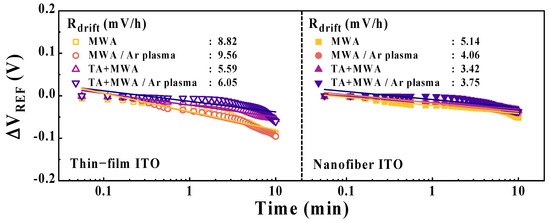
Figure 11.
Drift effect EG-ISFETs with ITO thin-film or ITO nanofiber sensing membranes depending on calcination conditions and plasma treatment.

Table 3.
pH sensing characteristics of EG-ISFETs with ITO sensing membranes.
4. Conclusions
We propose a transparent and high-performance EG-ISFET using an ITO nanofiber sensing membrane with excellent electrical, electrochemical, and biocompatibility characteristics. ITO, a metal oxide material, has excellent optical properties and has a wide range of electrical applications. In addition, electrospun nanofibers can realize a higher specific surface area than thin-films, so using ITO nanofibers as a sensing membrane is advantageous for high-sensitivity electrochemical pH sensors. The ITO nanofibers spun on the glass substrate simultaneously serve as a conductive electrode and a sensing membrane, making the fabrication process simple and cost-effective compared to conventional EG units. A two-step calcination process involving the combustion step and microwave annealing step was developed to efficiently remove residual polymers and impurities that deteriorate the sensing characteristics of electrospun ITO nanofibers. As a subsequent process to boost pH sensitivity, Ar plasma treatment was applied to improve the conductivity of the electrospun nanofiber sensing membrane. The characteristics of the ITO nanofibers and ITO thin-film membranes according to the calcination conditions and plasma treatment were evaluated by SEM, XRD, XPS, optical transmittance, and conductivity. The combustion step was found to be the most effective in improving crystallinity, optical transmittance, and conductivity. Meanwhile, Ar plasma treatment significantly improved the optical transmittance and conductivity of the sensing membranes. The effectiveness of the ITO nanofiber was verified by evaluating the sensitivity and non-ideal behavior of EG-ISFETs comprising an n-type MOSFET transducer unit and an EG unit with an ITO nanofiber or an ITO thin-film sensing membrane. The ITO nanofiber-based EG-ISFET has a sensitivity of 55.44 mV/pH, hysteresis of 15.63 mV, and a drift rate of 3.75 mV/h, while the ITO thin-film-based EG-ISFET has a sensitivity of 47.21 mV/pH, hysteresis of 22.71 mV, and a drift rate of 6.05 mV/h. Under the same calcination and plasma treatment conditions, the ITO nanofiber sensing membrane exhibited 1.1 to 1.2 times better sensitivity than the ITO thin-film sensing membrane. Two-step calcination and Ar plasma treatment enhanced the sensitivity of the same sensing membrane material by 1.3 to 1.4 times. In particular, in the non-ideal behaviors, the hysteresis voltage and drift rate of the nanofibers decreased to 56% and 73%, respectively, after the two-step calcination and Ar plasma treatment. The results indicate that the electrospun ITO nanofiber sensing membrane is more transparent and sensitive than the ITO thin-film and provides higher stability and reliability as well as high sensitivity via the proposed two-step calcination process and Ar plasma treatment. Therefore, we expect that the proposed electrospun ITO nanofiber sensing membrane-based EG-ISFETs can be utilized as multifunctional and high-performance biochemical sensors.
Author Contributions
Y.-U.K.: conceptualization, formal analysis, methodology, investigation, data curation, visualization, software, resources, and writing the original draft. W.-J.C.: conceptualization, methodology, investigation, resources, formal analysis, funding acquisition, supervision, validation, writing, review, and editing. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korean government (MSIT) (No. 2020R1A2C1007586). This research was supported by Korea Institute for Advancement of Technology (KIAT) grant funded by the Korea Government (MOTIE). (P0002397, The Competency Development Program for Industry Specialist).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The present Research has been conducted by the Research Grant of Kwangwoon University in 2023 and the Excellent research support project of Kwangwoon University in 2023.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Ding, X.; Clifton, D.; Ji, N.; Lovell, N.H.; Bonato, P.; Chen, W.; Yu, X.; Xue, Z.; Xiang, T.; Long, X. Wearable Sensing and Telehealth Technology with Potential Applications in the Coronavirus Pandemic. IEEE Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 14, 48–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.; Rogers, J.A.; Xu, S. Continuous On-Body Sensing for the COVID-19 Pandemic: Gaps and Opportunities. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eabd4794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, A.P.; Pimm, S.L.; Hannah, L.; Kaufman, L.; Ahumada, J.A.; Ando, A.W.; Bernstein, A.; Busch, J.; Daszak, P.; Engelmann, J. Ecology and Economics for Pandemic Prevention. Science 2020, 369, 379–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awotunde, J.B.; Jimoh, R.G.; AbdulRaheem, M.; Oladipo, I.D.; Folorunso, S.O.; Ajamu, G.J. IoT-Based Wearable Body Sensor Network for COVID-19 Pandemic. In Advances in Data Science and Intelligent Data Communication Technologies for COVID-19; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2022; pp. 253–275. [Google Scholar]
- Bergveld, P. Development, Operation, and Application of the Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor as a Tool for Electrophysiology. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1972, BME-19, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, A.; Miyahara, Y. Current and Emerging Challenges of Field Effect Transistor Based Bio-Sensing. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 10702–10718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, D.; Liu, W.; Xie, X.; Anselmo, A.C.; Mitragotri, S.; Banerjee, K. MoS2 Field-Effect Transistor for next-Generation Label-Free Biosensors. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 3992–4003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Sun, P.; Xiao, G.; Tang, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhao, H.; Zhao, S.; Lu, H.; Yue, Z. ISFET-based Sensors for (Bio) Chemical Applications: A Review. Electrochem. Sci. Adv. 2022, e2100207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Jiang, Y.; Yan, M.; Wu, D. A Dual-Mode Large-Arrayed CMOS ISFET Sensor for Accurate and High-Throughput PH Sensing in Biomedical Diagnosis. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2015, 62, 2224–2233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pijanowska, D.G.; Torbicz, W. PH-ISFET Based Urea Biosensor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1997, 44, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chodavarapu, V.P.; Titus, A.H.; Cartwright, A.N. CMOS ISFET Microsystem for Biomedical Applications. In Proceedings of the SENSORS, 2005 IEEE, Irvine, CA, USA, 30 October–3 November 2005; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2005; p. 4. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, L.-T.; Chou, J.-C.; Chung, W.-Y.; Sun, T.-P.; Hsiung, S.-K. Study of Indium Tin Oxide Thin Film for Separative Extended Gate ISFET. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2001, 70, 12–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, L.-T.; Chou, J.-C.; Chung, W.-Y.; Sun, T.-P.; Hsiung, S.-K. Separate Structure Extended Gate H+-Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistor on a Glass Substrate. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2000, 71, 106–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Cui, T. Ion-Sensitive Field-Effect Transistor Based PH Sensors Using Nano Self-Assembled Polyelectrolyte/Nanoparticle Multilayer Films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 123, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajmirzaheydarali, M.; Sadeghipari, M.; Akbari, M.; Shahsafi, A.; Mohajerzadeh, S. Nano-Textured High Sensitivity Ion Sensitive Field Effect Transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2016, 119, 054303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrady, A.L. Nanofiber-Based Chemical Sensors. In Applications of Polymer Nanofibers; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 100–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, K.; Rim, T.; Park, C.; Kim, D.; Meyyappan, M.; Lee, J.-S. Suspended Honeycomb Nanowire ISFETs for Improved Stiction-Free Performance. Nanotechnology 2014, 25, 345501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.-K.; Cho, W.-J. High Sensitivity In-Ga-Zn-O Nanofiber-Based Double Gate Field Effect Transistors for Chemical Sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 326, 128827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, B.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Sun, G. Gas Sensors Based on Electrospun Nanofibers. Sensors 2009, 9, 1609–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manjakkal, L.; Szwagierczak, D.; Dahiya, R. Metal Oxides Based Electrochemical PH Sensors: Current Progress and Future Perspectives. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2020, 109, 100635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Zheng, B.; Jiang, Y.; Cai, Y.; Du, J.; Yuan, H.; Xiao, D. Improvement of Sensitive CuO NFs–ITO Nonenzymatic Glucose Sensor Based on in Situ Electrospun Fiber. Talanta 2012, 101, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keereeta, Y.; Thongtem, T.; Thongtem, S. Characterization of ZnMoO4 Nanofibers Synthesized by Electrospinning–Calcination Combinations. Mater Lett. 2012, 68, 265–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascariu, P.; Homocianu, M.; Cojocaru, C.; Samoila, P.; Airinei, A.; Suchea, M. Preparation of La Doped ZnO Ceramic Nanostructures by Electrospinning–Calcination Method: Effect of La3+ Doping on Optical and Photocatalytic Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 476, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.M.; Iskandar, F.; Yun, K.M.; Okuyama, K.; Abdullah, M. Optical and Electrical Properties of Indium Tin Oxide Nanofibers Prepared by Electrospinning. Nanotechnology 2008, 19, 145603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppa, B.J.; Fulton, C.C.; Hartlieb, P.J.; Davis, R.F.; Rodriguez, B.J.; Shields, B.J.; Nemanich, R.J. In Situ Cleaning and Characterization of Oxygen-and Zinc-Terminated, n-Type, ZnO {0001} Surfaces. J. Appl. Phys. 2004, 95, 5856–5864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-K.; Cho, W.-J. Performance Improvement in Electrospun InGaZnO Nanofibres Field-Effect-Transistors Using Low Thermal Budget Microwave Calcination and Ar/O2 Mixed-Plasma Surface Treatment. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 3645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, S.-K.; Cho, W.-J. Microwave-Assisted Calcination of Electrospun Indium–Gallium–Zinc Oxide Nanofibers for High-Performance Field-Effect Transistors. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 38351–38356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, E.-K.; Cho, W.-J. Microwave Calcination of Electrospun ITO Nanofibers and Improvement of Transparent Electrode Characteristics through Vacuum Rapid Thermal Annealing. Mater. Res. Express 2020, 7, 075013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-H.; Cho, W.-J. Enhancement of Electrical Properties of Sol–Gel Indium–Tin–Oxide Films by Microwave Irradiation and Plasma Treatment. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajji, B.; Temple-Boyer, P.; Launay, J.; do Conto, T.; Martinez, A. PH, PK and PNa Detection Properties of SiO2/Si3N4 ISFET Chemical Sensors. Microelectron. Reliab. 2000, 40, 783–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poghossian, A.S. The Super-Nernstian PH Sensitivity of Ta2O5-Gate ISFETs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 1992, 7, 367–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, Y.-L.; Chou, J.-C.; Sun, T.-P.; Liao, H.-K.; Chung, W.-Y.; Hsiung, S.-K. A Novel SnO2/Al Discrete Gate ISFET PH Sensor with CMOS Standard Process. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2001, 75, 36–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed Ali, A.M.; Ahmed, N.M.; Mohammad, S.M.; Sabah, F.A.; Kabaa, E.; Alsadig, A.; Sulieman, A. Effect of Gamma Irradiation Dose on the Structure and PH Sensitivity of ITO Thin Films in Extended Gate Field Effect Transistor. Results Phys. 2019, 12, 615–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.C.; Lee, M.C.; Chiang, J.L. Annealing Effect of Sol-Gel TiO2 Thin Film on PH-EGFET Sensor. In Proceedings of the Proceedings—2014 International Symposium on Computer, Consumer and Control, IS3C 2014, Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 June 2014; pp. 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Singh, R.; Sharma, R.; Mukhiya, R.; Awasthi, K.; Kumar, M. Bismuth Oxide Extended-Gate Field-Effect Transistor as PH Sensor. J. Electron. Mater. 2022, 51, 2673–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Wei, W.; Li, B.; Gao, M.; Chim, W.K.; Zhu, C. Low Drift Reference-Less ISFET Comprising Two Graphene Films with Different Engineered Sensitivities. ACS Appl. Electron. Mater. 2022, 4, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsaee, S.K.; Ahmed, N.M.; Mzwd, E.; Omar, A.F.; Aljameel, A.I.; Afzal, N.; Razak, I.A.; Arshad, S. PH Sensor Based on AuNPs/ ITO Membrane as Extended Gate Field-Effect Transistor. Appl. Phys. B 2022, 128, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.J.; Savagatrup, S.; Kim, Y.; Lang, J.H.; Swager, T.M. Precision PH Sensor Based on WO3 Nanofiber-Polymer Composites and Differential Amplification. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 2593–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liston, E.M. Plasma Treatment for Improved Bonding: A Review. J. Adhes. 1989, 30, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.D.; Song, J.Q.; Lai, P.T. Improved Performance of Scaled-Down α-InGaZnO Thin-Film Transistor by Ar Plasma Treatment. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2016, 37, 1574–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, R.; Ray, S.; Basu, N.; Batabyal, A.K.; Barua, A.K. Degradation of Tin-doped Indium-oxide Film in Hydrogen and Argon Plasma. J. Appl. Phys. 1987, 62, 912–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, F.; Lin, L.; Gai, R.; Lin, Y.; Huang, Z. Determination of Optical Constants and Thicknesses of In2O3: Sn Films from Transmittance Data. Thin Solid Film. 2007, 515, 7387–7392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thirumoorthi, M.; Thomas Joseph Prakash, J. Structure, Optical and Electrical Properties of Indium Tin Oxide Ultra Thin Films Prepared by Jet Nebulizer Spray Pyrolysis Technique. J. Asian Ceram. Soc. 2016, 4, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.C.; Kim, J.Y.; Lee, D.D.; Lim, J.O.; Huh, J.S. Effects of Crystal Structures on Gas Sensing Properties of Nanocrystalline ITO Thick Films. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2003, 89, 180–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monshi, A.; Foroughi, M.R.; Monshi, M.R. Modified Scherrer Equation to Estimate More Accurately Nano-Crystallite Size Using XRD. World J. Nano Sci. Eng. 2012, 02, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, V.M.; Berry, A.D.; Kim, H.; Piqué, A. Functionalization of Indium Tin Oxide. Langmuir 2006, 22, 11113–11125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekargoftar, M.; Krumpolec, R.; Homola, T. Enhancement of Electrical Properties of Flexible ITO/PET by Atmospheric Pressure Roll-to-Roll Plasma. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2018, 75, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voros, J.; Tang, C.S.; Antoni, M.; Schönbächler, I.; Keller, B.; Textor, M. Electrically-Assisted Formation and Desorption of Dodecyl Phosphate Self-Assembled Monolayers on Indium Tin Oxide Surfaces. ECS Trans. 2006, 1, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Görlich, E.; Haber, J.; Stoch, A.; Stoch, J. XPS Study of α-Quartz Surface. J. Solid. State Chem. 1980, 33, 121–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.-P.; Yang, J.-H.; Yang, J.-G.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Huang, W.; Yuan, G.-J.; Feng, J.-J.; Jen, T.-C.; Lu, H.-L. Systematic Study of the SiOx Film with Different Stoichiometry by Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition and Its Application in SiOx/SiO2 Super-Lattice. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C. Accessing the Robustness of Adventitious Carbon for Charge Referencing (Correction) Purposes in XPS Analysis: Insights from a Multi-User Facility Data Review. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 597, 153681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenny, N.; Kannewurf, C.R.; Whitmore, D.H. Optical Absorption Coefficients of Vanadium Pentoxide Single Crystals. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 1966, 27, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarey, R.D.; Raju, T.A. A Method for the Deposition of Transparent Conducting Thin Films of Tin Oxide. Thin Solid Film. 1985, 128, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nigo, S.; Kubota, M.; Harada, Y.; Hirayama, T.; Kato, S.; Kitazawa, H.; Kido, G. Conduction Band Caused by Oxygen Vacancies in Aluminum Oxide for Resistance Random Access Memory. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 033711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kevane, C.J. Oxygen Vacancies and Electrical Conduction in Metal Oxides. Phys. Rev. 1964, 133, A1431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Mei, Z.; Tang, A.; Azarov, A.; Kuznetsov, A.; Xue, Q.-K.; Du, X. Oxygen Vacancies: The Origin of n-Type Conductivity in ZnO. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 93, 235305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, H.; Shin, E.-S.; Huh, J.N.; Noh, Y.-Y.; Park, B.; Hwang, I. Toward High Conductivity of Electrospun Indium Tin Oxide Nanofibers with Fiber Morphology Dependent Surface Coverage: Postannealing and Polymer Ratio Effects. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 34305–34313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Hu, L.; Carney, T.; Ruan, Z.; Kong, D.; Yu, Z.; Yao, Y.; Cha, J.J.; Zhu, J.; Fan, S. Low Reflectivity and High Flexibility of Tin-Doped Indium Oxide Nanofiber Transparent Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 27–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arlindo, E.P.S.; Lucindo, J.A.; Bastos, C.M.O.; Emmel, P.D.; Orlandi, M.O. Electrical and Optical Properties of Conductive and Transparent ITO@ PMMA Nanocomposites. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 12946–12952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, J.C.; Wang, Y.F. Preparation and Study on the Drift and Hysteresis Properties of the Tin Oxide Gate ISFET by the Sol-Gel Method. Sens Actuators B Chem 2002, 86, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, C.N.; Chou, J.C.; Sun, T.P.; Hsiung, S.K. Study on the Sensing Characteristics and Hysteresis Effect of the Tin Oxide PH Electrode. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 108, 877–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahdal, A.; Toumazou, C. ISFET-Based Chemical Switch. IEEE Sens. J. 2012, 12, 1140–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).