UIO-66/Ag/TiO2 Nanocomposites as Highly Active SERS Substrates for Quantitative Detection of Hexavalent Chromium
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Materials
2.2. Apparatus and Measurements
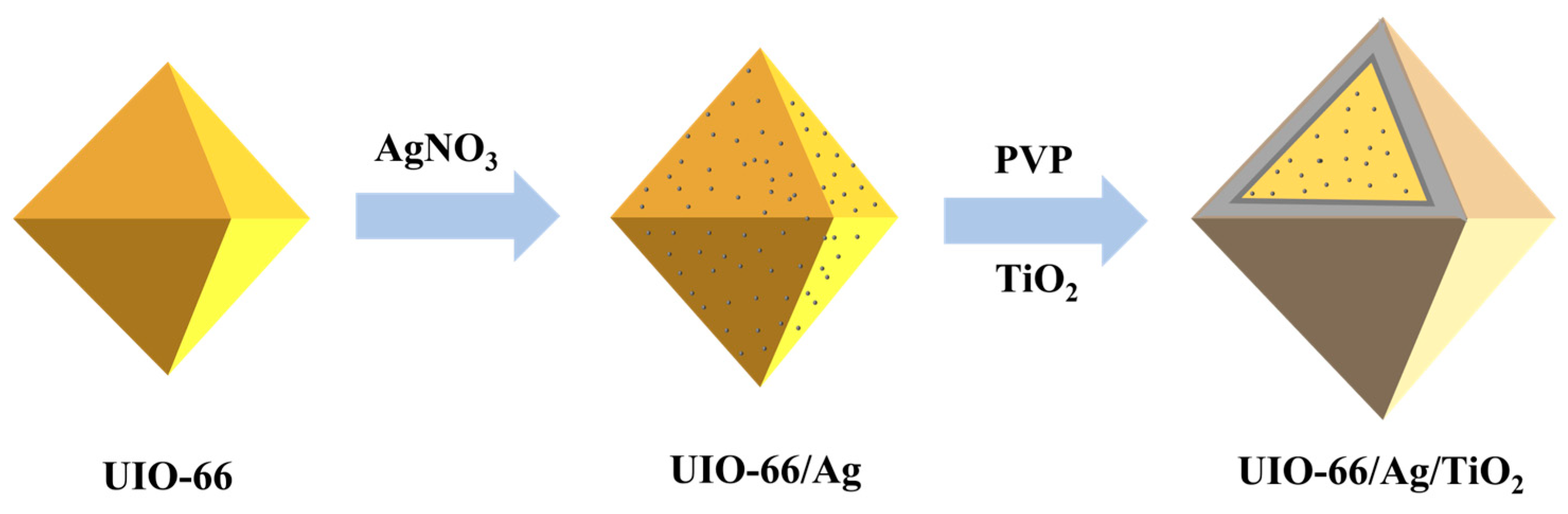
2.3. Preparation of UIO-66/Ag
2.4. Preparation of TiO2
2.5. Preparation of UIO-66/Ag/TiO2
2.6. Raman Spectroscopic Analysis
3. Results
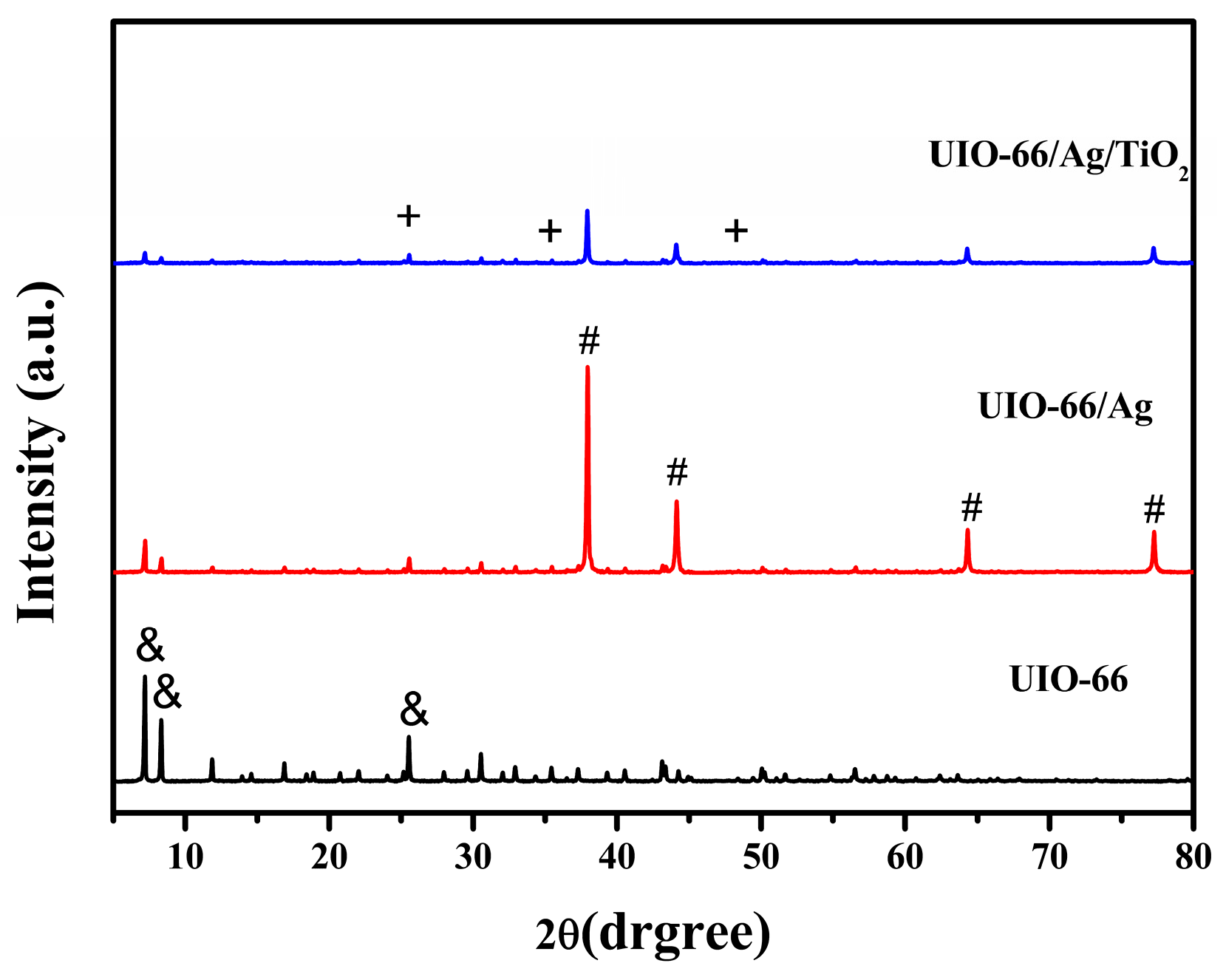
3.1. Fabrication and Characterization of UIO-66/Ag/TiO2 Nanocomposites
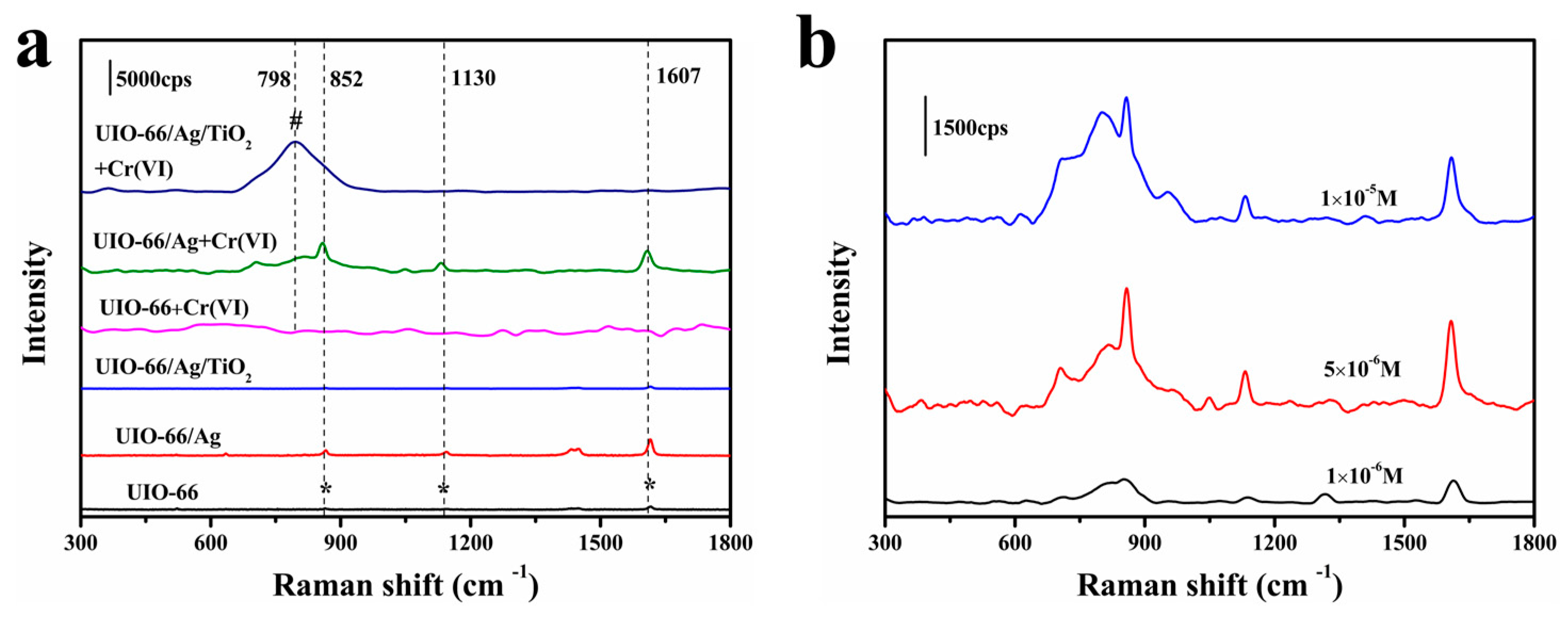
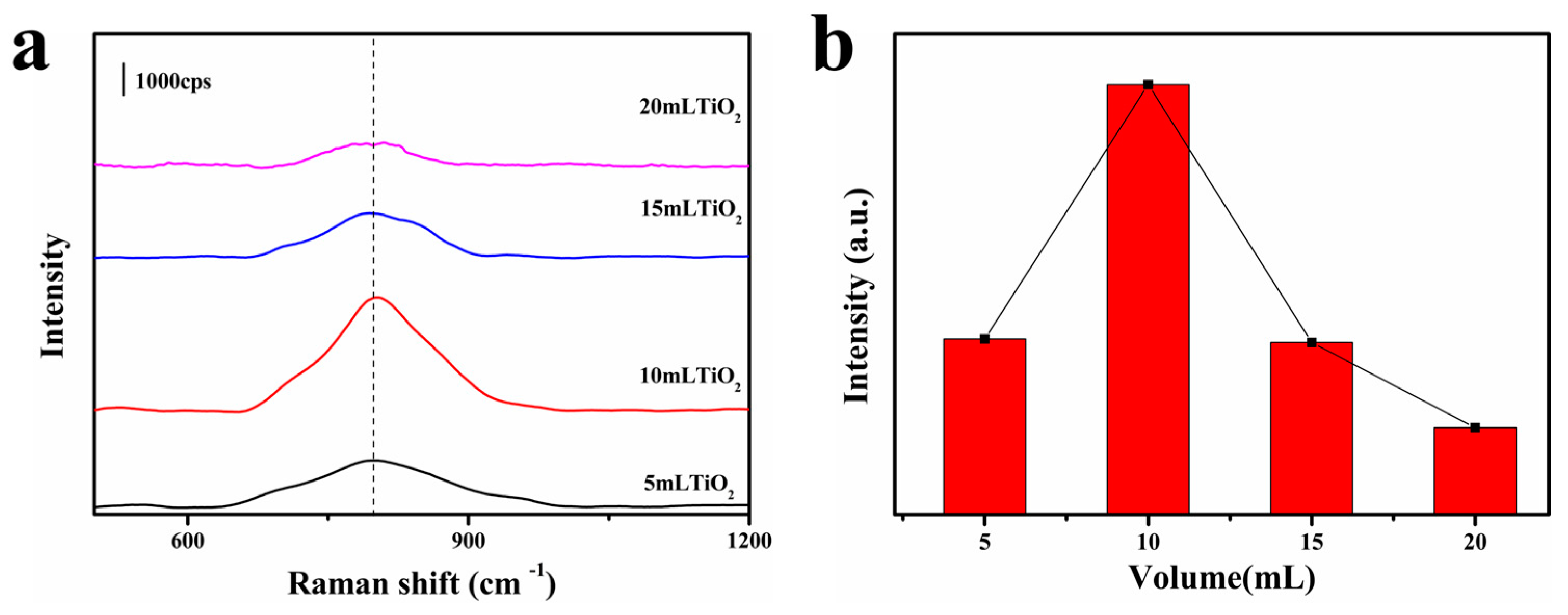
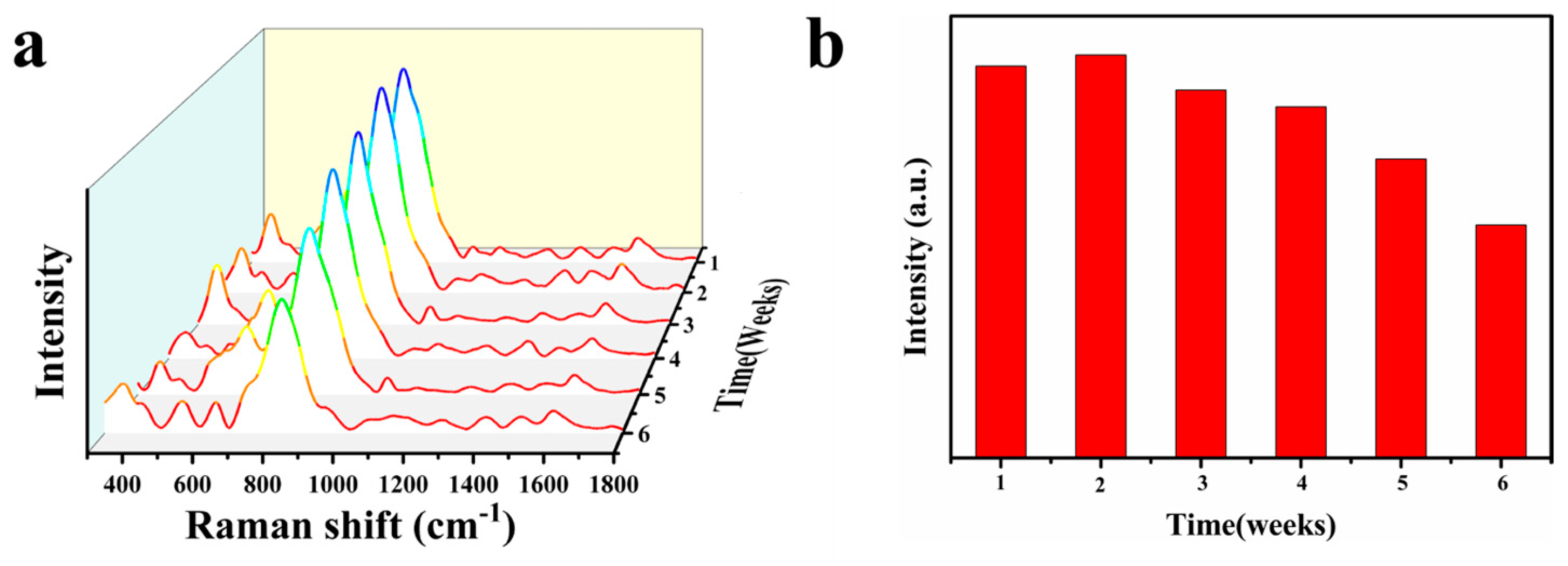
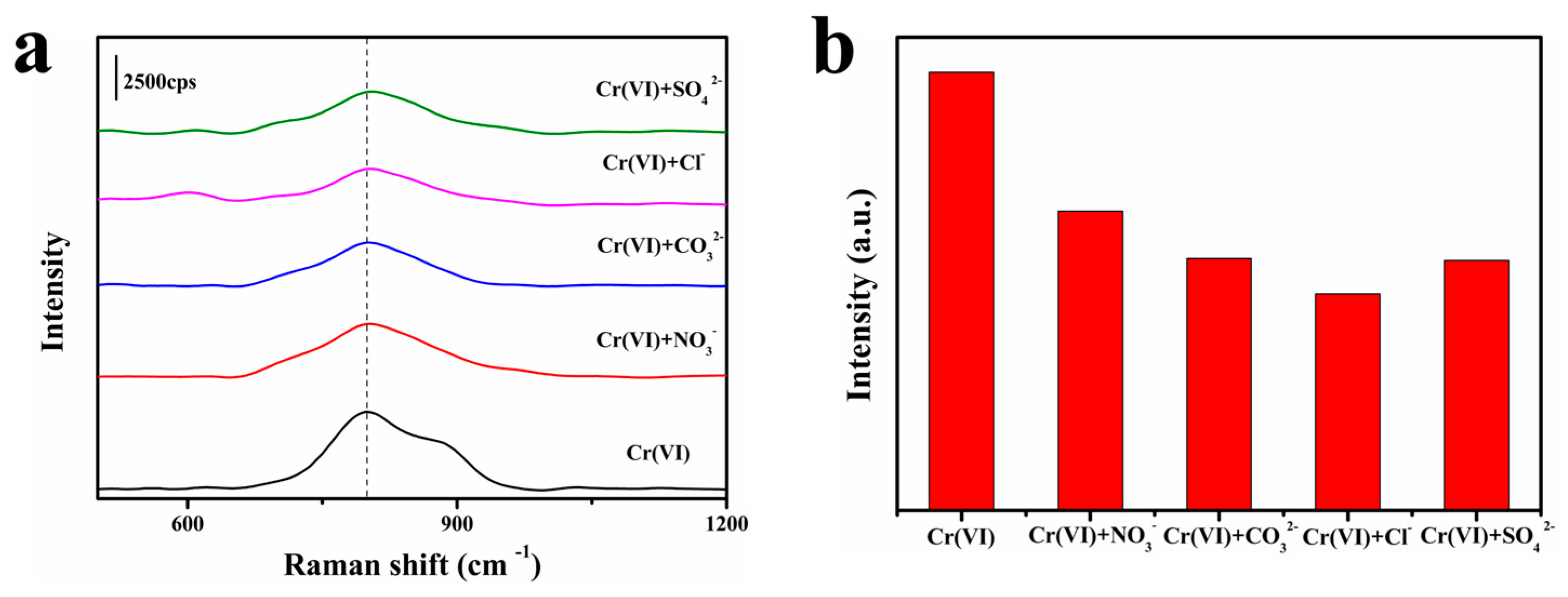
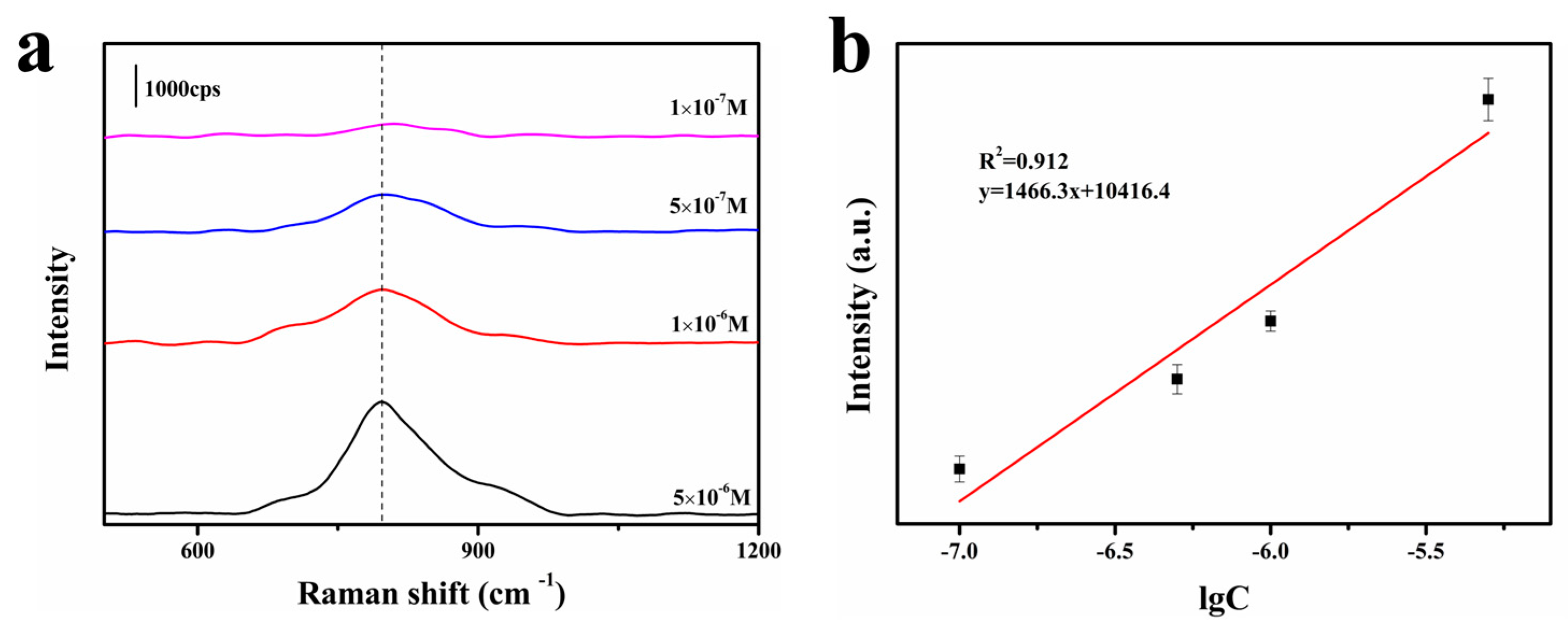
3.2. SERS Performance
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murali, A.; Sarswat, P.K.; Free, M.L. Adsorption-coupled reduction mechanism in ZnO-Functionalized MWCNTs nanocomposite for Cr (VI) removal and improved anti-photocorrosion for photocatalytic reduction. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 843, 155835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maitlo, H.A.; Kim, K.-H.; Kumar, V.; Kim, S.; Park, J.-W. Nanomaterials-based treatment options for chromium in aqueous environments. Environ. Int. 2019, 130, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dawodu, F.A.; Akpan, B.M.; Akpomie, K.G. Sequestered capture and desorption of hexavalent chromium from solution and textile wastewater onto low cost Heinsia crinita seed coat biomass. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arellano-Sánchez, M.G.; Devouge-Boyer, C.; Hubert-Roux, M.; Afonso, C.; Mignot, M. Quantitative extraction of chromium VI and III from tanned leather: A comparative study of pretreatment methods. J. Leather Sci. Eng. 2021, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazi, F.K.M.; Cooper, P.A. Method to recover and reuse chromated copper arsenate wood preservative from spent treated wood. Waste Manag. 2006, 26, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-G.; Lee, S.; Park, J.-A.; Park, C.; Lee, S.J.; Kim, S.-B.; An, B.; Yun, S.-T.; Lee, S.-H.; Choi, J.-W. Removal of copper, nickel and chromium mixtures from metal plating wastewater by adsorption with modified carbon foam. Chemosphere 2017, 166, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motora, K.G.; Wu, C.-M. Magnetically separable highly efficient full-spectrum light-driven WO2.72/Fe3O4 nanocomposites for photocatalytic reduction of carcinogenic chromium (VI) and organic dye degradation. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2020, 117, 123–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakya, A.; Agarwal, T. Removal of Cr(VI) from water using pineapple peel derived biochars: Adsorption potential and re-usability assessment. J. Mol. Liq. 2019, 293, 111497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Yang, J.; Wang, X.; Song, G.; Lu, F.; You, L.; Li, J. Ag nanoparticles decorated Ag@ZrO2 composite nanospheres as highly active SERS substrates for quantitative detection of hexavalent chromium in waste water. J. Mol. Liq. 2020, 319, 114158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Qiao, J.; Guan, X. Multi-wavelength spectrophotometric determination of Cr(VI) in water with ABTS. Chemosphere 2017, 171, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohira, S.-I.; Nakamura, K.; Chiba, M.; Dasgupta, P.K.; Toda, K. Matrix isolation with an ion transfer device for interference-free simultaneous spectrophotometric determinations of hexavalent and trivalent chromium in a flow-based system. Talanta 2017, 164, 445–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Li, T.; Wu, Q.; Yan, X.; Wu, C.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G. Carbon nanodots as a fluorescence sensor for rapid and sensitive detection of Cr(VI) and their multifunctional applications. Talanta 2017, 165, 216–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spanu, D.; Monticelli, D.; Binda, G.; Dossi, C.; Rampazzi, L.; Recchia, S. One-minute highly selective Cr(VI) determination at ultra-trace levels: An ICP-MS method based on the on-line trapping of Cr(III). J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 412, 125280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhriyan, G.; Mousavi, H.Z.; Sajjadi, S.M. Speciation and determination of Cr(iii) and Cr(vi) by directly suspended droplet microextraction coupled with flame atomic absorption spectrometry: An application of central composite design strategy as an experimental design tool. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 5070–5078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Hou, L.; Han, Z. Polyoxometalate-based crystalline catalytic materials for efficient electrochemical detection of Cr(VI). Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 305, 127469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Tang, H.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhu, C. Nanoporous Ag-Decorated Ag7O8NO3 Micro-Pyramids for Sensitive Surface-Enhanced Raman Scattering Detection. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Xiao, K.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Chen, W.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, D.; Ni, D.; Liang, P. Fabrication of GO/Fe3O4@Au MNPs for Magnetically Enriched and Adsorptive SERS Detection of Bifenthrin. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Hui, B.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, J.; Gong, Z.; Fan, M. Facile Preparation of Ag-NP-Deposited HRGB-SERS Substrate for Detection of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons in Water. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wang, B.; Yang, P.; Li, J.; Xiao, G.; Yao, J.; Gong, X.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H. The Functional Fe3O4@SiO2@AuNPs SERS Nanomaterials for Rapid Enrichment and Detection of Mercury Ions in Licorice. Chemosensors 2022, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, Y.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Liu, Z. Ultrasensitive detection of Cr(VI) using a novel SERS optical fiber probe modified by dual-functional methimazole. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 910, 164916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Guo, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, T.; Song, P.; Xia, L. A sensitive surface-enhanced resonance Raman scattering sensor with bifunctional negatively charged gold nanoparticles for the determination of Cr(VI). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 830, 154598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, H.; Min, Y.; Li, X.; You, L.; Li, J. Fe3O4@m-ZrO2@Ag ternary magnetic nanocomposites for sensitive SERS sensing and photocatalytic removal of Cr(VI) and organic dyes. Compos. Part B Eng. 2022, 239, 109959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Shang, M.; Wei, H.; Zhang, M.; Zou, W.; Meng, X.; Chen, W.; Shao, H.; Lai, Y. Specific and sensitive on-site detection of Cr(VI) by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 346, 130594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Zhao, Y.; Bu, T.; Wang, X.; Xu, Z.; Zhangsun, H.; Wang, L. Semi-sacrificial template growth-assisted self-supporting MOF chip: A versatile and high-performance SERS sensor for food contaminants monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 352, 131025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Yu, X.; Hu, J.; Zhuang, X.; Wang, J.; Qiu, H.; Ren, H.; Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y. Constructing a Highly Sensitivity SERS Sensor Based on a Magnetic Metal–Organic Framework (MOF) to Detect the Trace of Thiabendazole in Fruit Juice. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2022, 10, 8400–8410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Xiong, Y.; Wu, H.; Feng, X.; Li, J.; Feng Luo, F. MOF + Technique Showing Significant Synergic Effect and thus Enabling Super-Performance in the Chromate Removal. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2017, 51, 16376–16379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ye, Y.; Sun, X.; Liu, B.; Li, G.; Liang, Z.; Liu, Y. A multifunctional Zr(iv)-based metal–organic framework for highly efficient elimination of Cr(vi) from the aqueous phase. J. Mater. Chem. A 2019, 7, 16833–16841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, W.; Wang, Y.; Tanabe, I.; Han, X.; Zhao, B.; Ozaki, Y. Semiconductor-driven “turn-off” surface-enhanced Raman scattering spectroscopy: Application in selective determination of chromium(vi) in water. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 342–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, B.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jing, C. Multifunctional satellite Fe3O4-Au@TiO2 nano-structure for SERS detection and photo-reduction of Cr(VI). Colloids Surf. Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2017, 513, 234–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhu, J.; Cheng, Y.; Cai, D. Functionalized UIO-66@Ag nanoparticles substrate for rapid and ultrasensitive SERS detection of di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate in plastics. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 349, 130793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhang, L.; Yao, T.; Liu, W.; Lin, Y.; Ju, H.; Dong, J.; Zheng, L.; Yan, W.; et al. Uncoordinated Amine Groups of Metal–Organic Frameworks to Anchor Single Ru Sites as Chemoselective Catalysts toward the Hydrogenation of Quinoline. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 9419–9422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prathapani, S.; More, V.; Bohm, S.; Bhargava, P.; Yella, A.; Mallick, S. TiO2 colloid-based compact layers for hybrid lead halide perovskite solar cells. Appl. Mater. Today 2017, 7, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Yang, Z.; Xiong, W.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Xu, R.; Zhang, Y. One-step synthesis of Co-doped UiO-66 nanoparticle with enhanced removal efficiency of tetracycline: Simultaneous adsorption and photocatalysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 353, 126–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, H.; Zhang, M.; Duan, W.; Liu, B. A dual-functional UiO-66/TiO2 composite for water treatment and CO2 capture. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 16232–16237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Du, B.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.; Feng, G.; Wang, X. α-Fe2O3 nanoclusters confined into UiO-66 for efficient visible-light photodegradation performance. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 956–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Shi, X.; Ma, H.; Lv, Y.; Zhang, L.; Mao, Z. The preparation and antibacterial effects of dopa-cotton/AgNPs. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2011, 257, 6799–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Tang, Q.; Sun, W.-Y.; Yao, Z.-Y.; Zhu, W.; Li, T.; Wang, J. Assembling ultrafine TiO2 nanoparticles on UiO-66 octahedrons to promote selective photocatalytic conversion of CO2 to CH4 at a low concentration. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2020, 270, 118856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athira, T.; Roshith, M.; Babu, T.S.; Kumar, D.V.R. Fibrous red phosphorus as a non-metallic photocatalyst for the effective reduction of Cr(VI) under direct sunlight. Mater. Lett. 2020, 283, 128750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Jing, C. Preparation of Fe3O4@Ag SERS substrate and its application in environmental Cr(VI) analysis. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 358, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben, Z.; Ma, G.; Xu, F. UIO-66/Ag/TiO2 Nanocomposites as Highly Active SERS Substrates for Quantitative Detection of Hexavalent Chromium. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060315
Ben Z, Ma G, Xu F. UIO-66/Ag/TiO2 Nanocomposites as Highly Active SERS Substrates for Quantitative Detection of Hexavalent Chromium. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(6):315. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060315
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen, Zixiang, Guangran Ma, and Fugang Xu. 2023. "UIO-66/Ag/TiO2 Nanocomposites as Highly Active SERS Substrates for Quantitative Detection of Hexavalent Chromium" Chemosensors 11, no. 6: 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060315
APA StyleBen, Z., Ma, G., & Xu, F. (2023). UIO-66/Ag/TiO2 Nanocomposites as Highly Active SERS Substrates for Quantitative Detection of Hexavalent Chromium. Chemosensors, 11(6), 315. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11060315






