Sensitive Evanescence-Field Waveguide Interferometer for Aqueous Nitro-Explosive Sensing
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Instruments
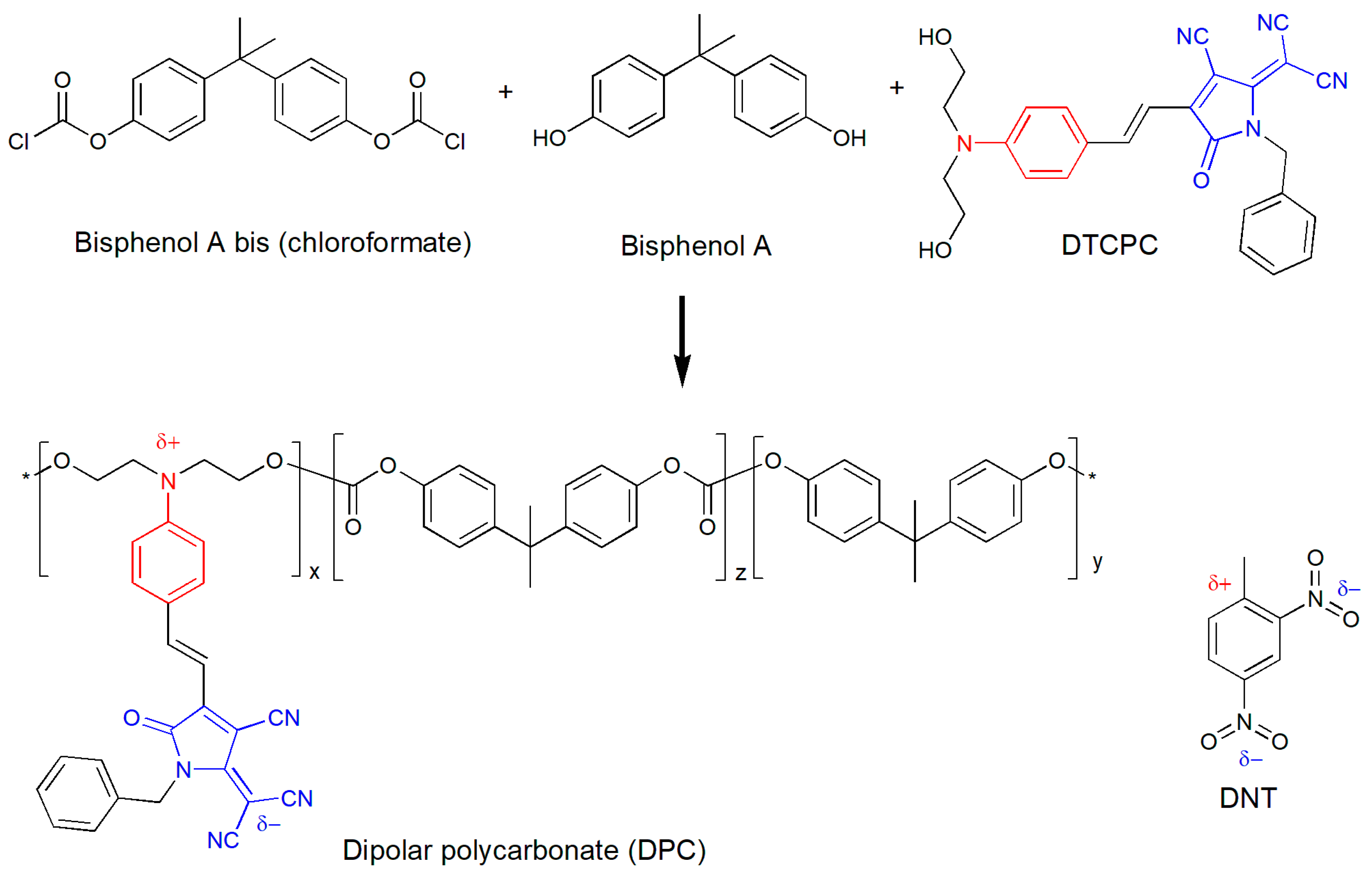
2.2. Synthesis of the Sensing Dipolar Polycarbonate
2.3. Refractive-Index-Sensing Principle of DNT Detection
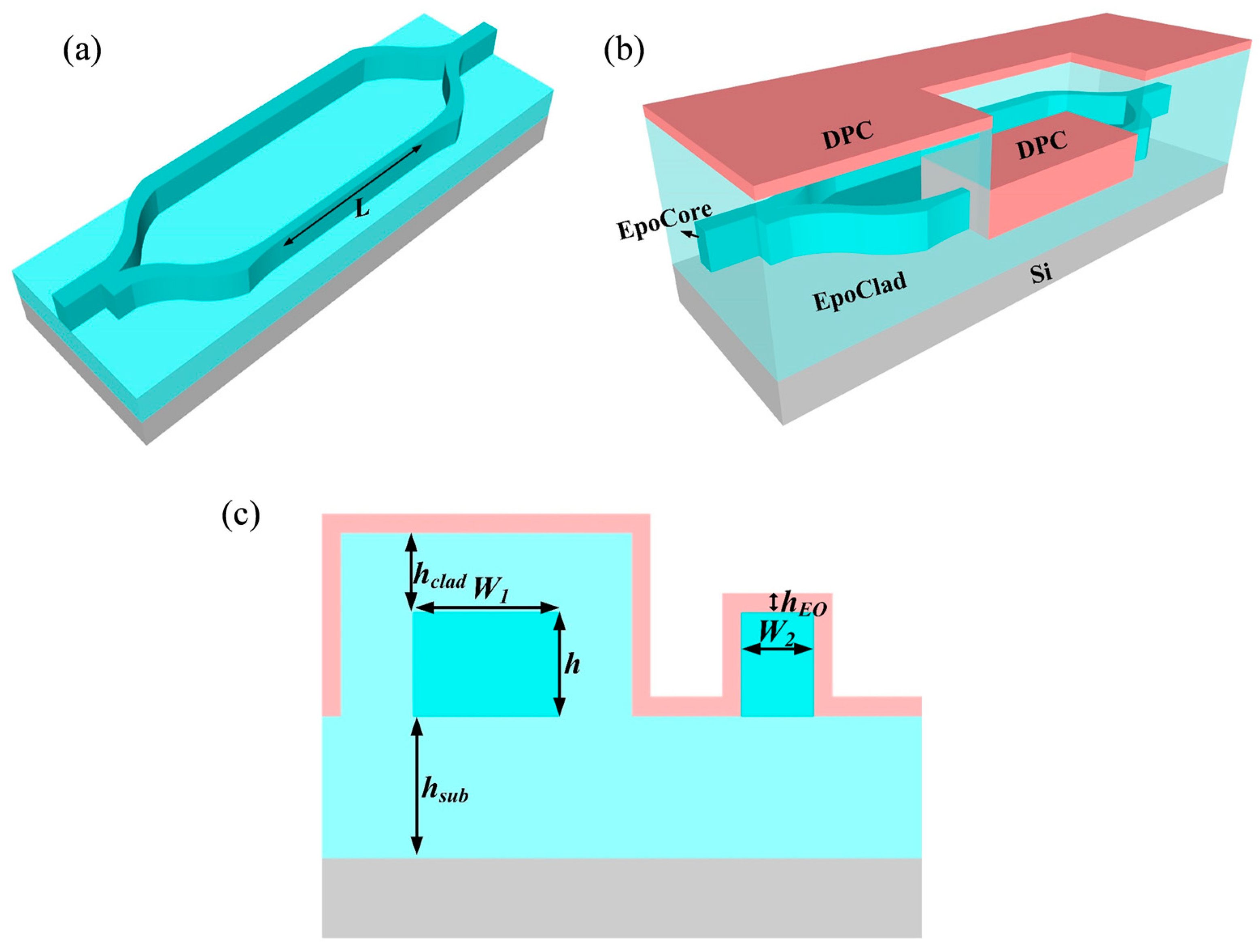
2.4. MZI Waveguide Design
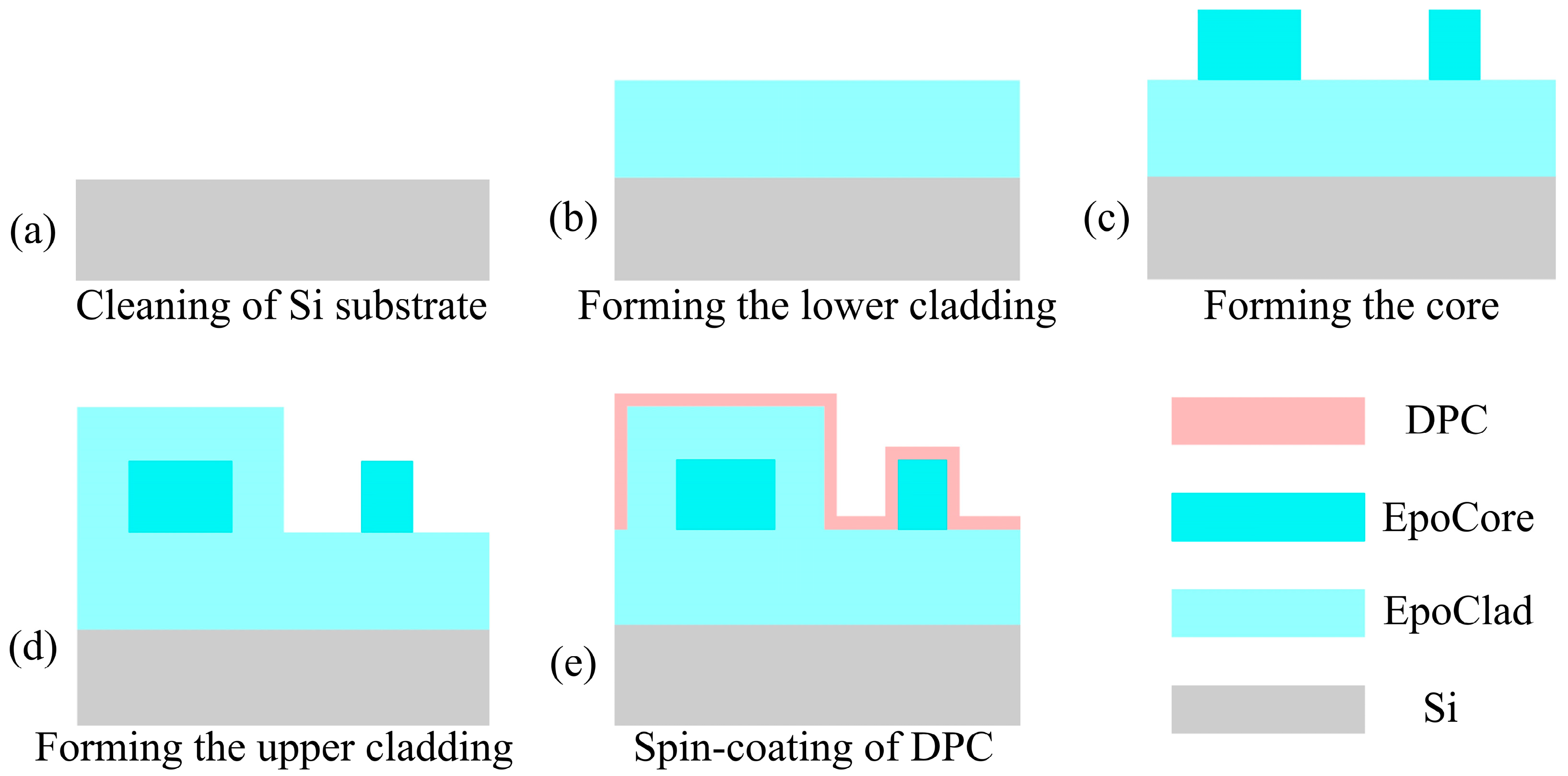
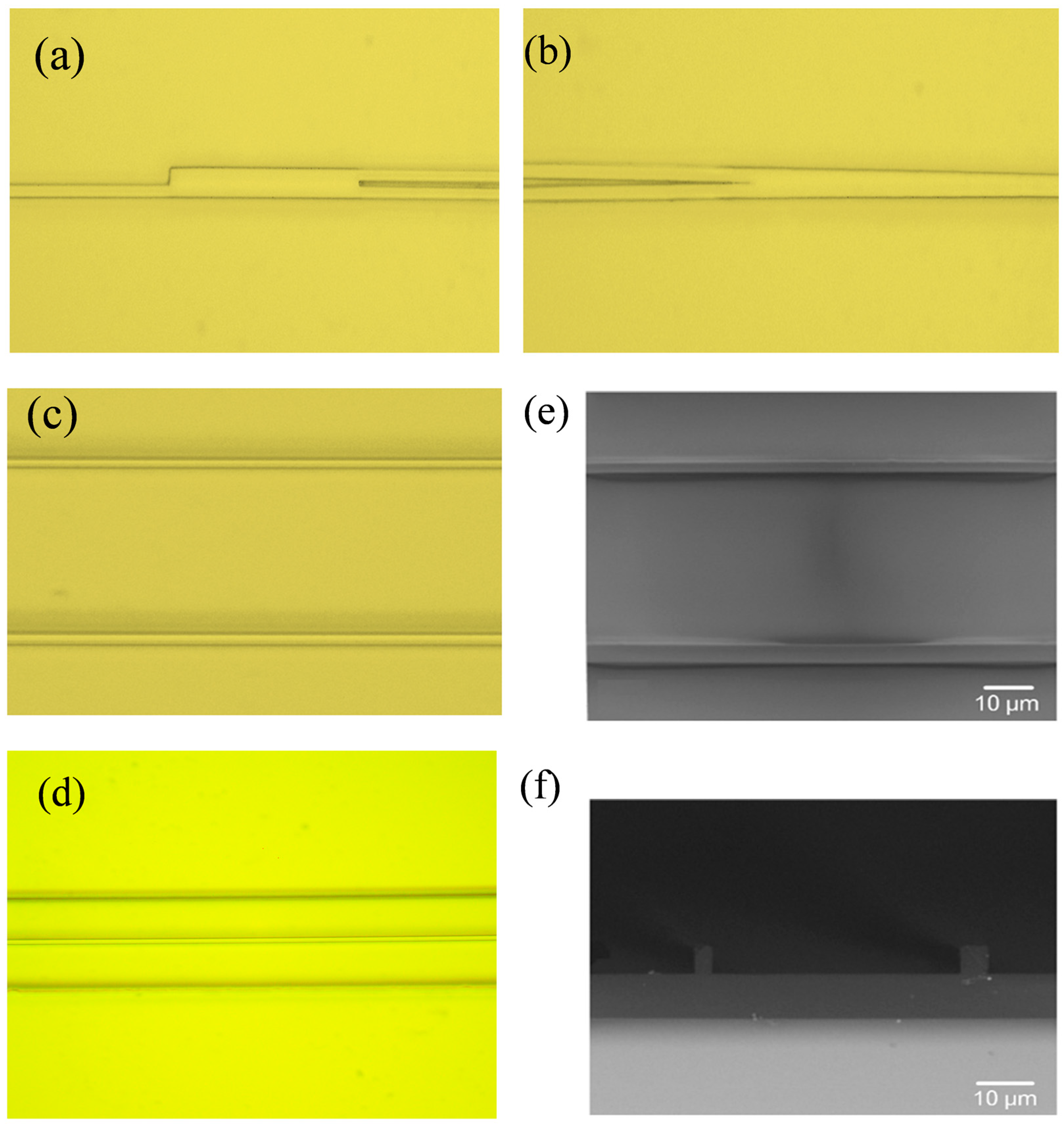
2.5. Device Fabrication
- An 8.0 μm thick EpoClad film was spin-coated on a O2-plasma-treated silicon substrate and then pre-baked at 50 °C for 10 min and 90 °C for 10 min. After cooling down to room temperature, the chip was exposed to UV light for 1 min to initiate the cross-linking of epoxy and then baked at 120 °C for 3 h.
- A 5.0 μm thick EpoCore film was spin-coated onto the Epoclad film and then pre-baked at 50 °C for 10 min and 90 °C for 10 min. Then, the pattern of the waveguide was transferred from mask to chip using UV photolithography, followed by heating at 50 °C for 10 min and 90 °C for 35 min, cooling and developing in a special developing solution to obtain the waveguide pattern. Finally, the waveguide was cured by baking at 140 °C for 3 h.
- An 8.0 μm thick EpoClad film was spin-coated on the EpoCore waveguide and then pre-baked at 50 °C for 10 min and 90 °C for 10 min. After cooling down to room temperature, the pattern of the cladding was transferred from another mask to chip by UV photolithography, followed by heating at 50 °C for 10 min and 90 °C for 35 min, cooling and developing in a special developing solution to obtain the cladding pattern. Then, the chip was baked at 120 °C for 3 h. In this state, the MZI waveguide was covered by EpoClad, leaving the narrower arm with air cladding.
- Finally, the DPC was spin-coated onto the sample to form a 500 nm thick sensing coating, and the chip was cured at 80 °C in vacuum for 12 h. After the device was cooled down to room temperature, the ends of the device were cut off and deconstructed using a diamond knife to obtain a flat waveguide end surface for edge coupling.
3. Results
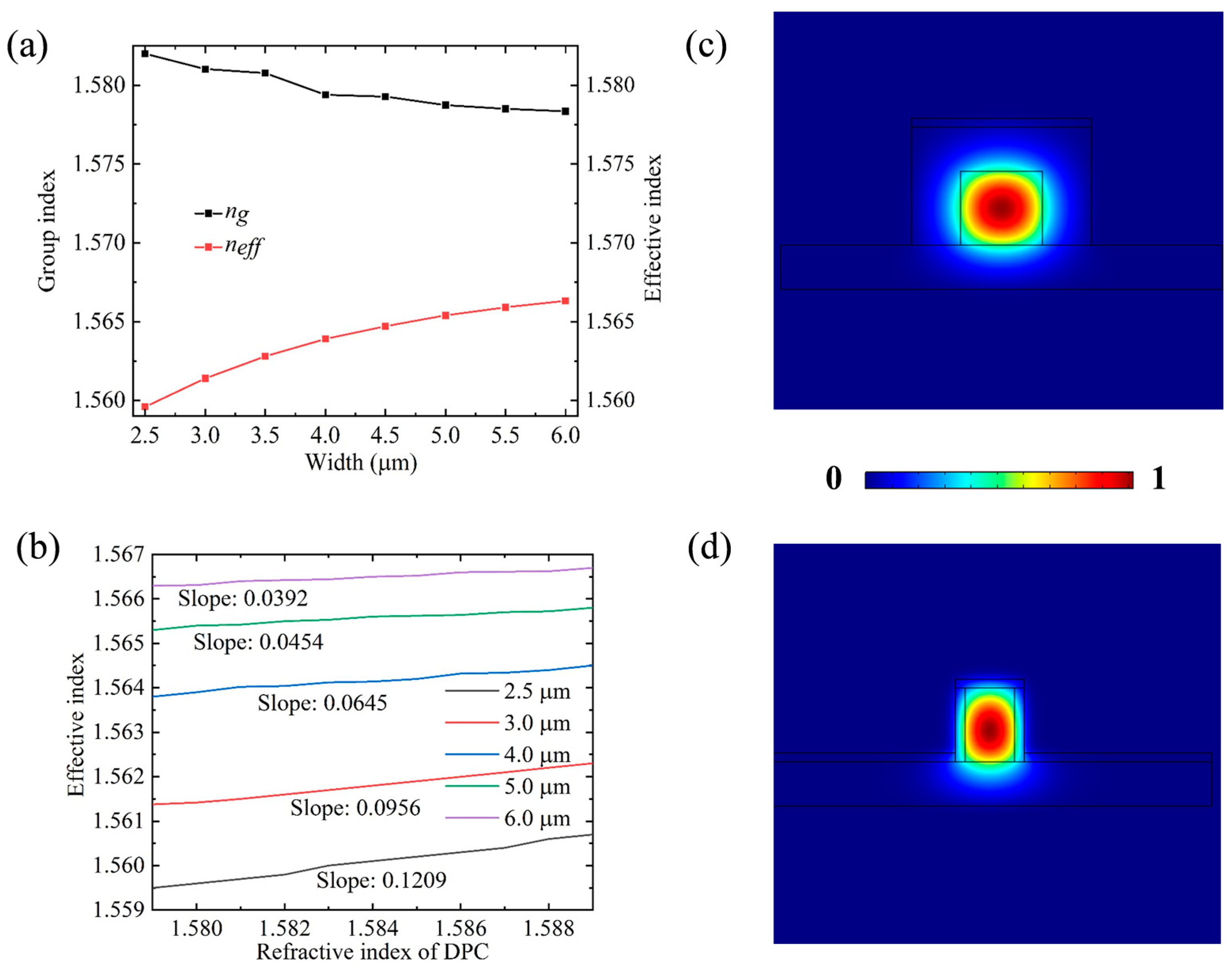
3.1. Waveguide Characterization
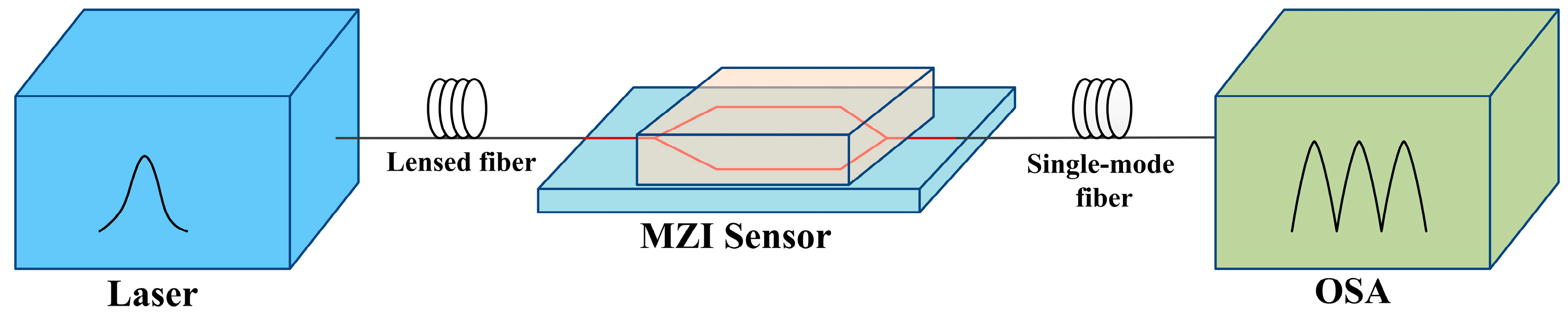
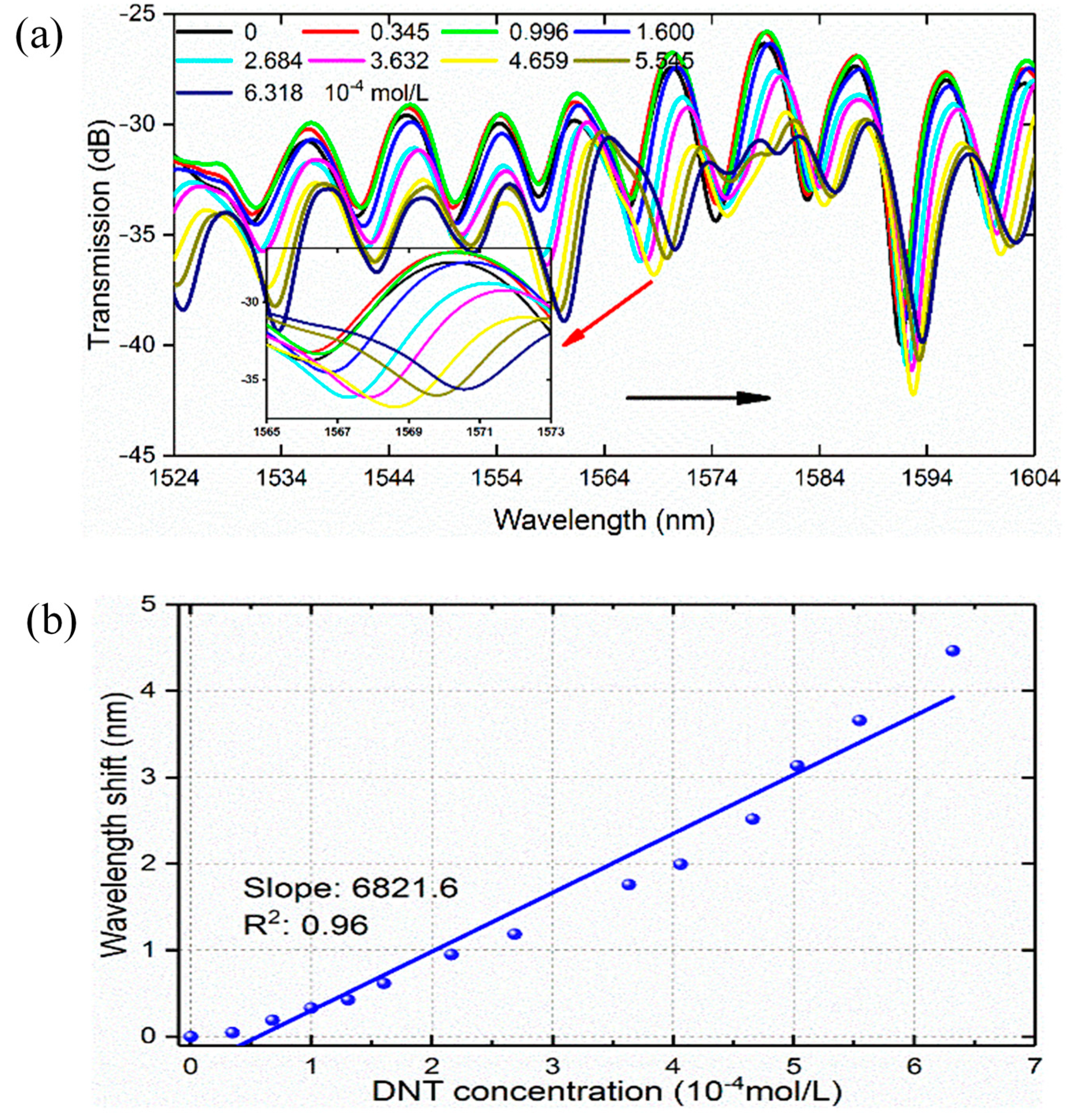
3.2. DNT Detection
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shanmugaraju, S.; Mukherjee, P.S. Pi-Electron rich small molecule sensors for the recognition of nitroaromatics. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 16014–16032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simić, M.; Gillanders, R.; Avramović, A.; Gajić, S.; Jovanović, V.; Stojnić, V.; Risojević, V.; Glackin, J.; Turnbull, G.; Filipi, J.; et al. Honeybee Activity Monitoring in a Biohybrid System for Explosives Detection. IFMBE Proc. 2020, 73, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazarowski, L.; Waggoner, L.P.; Krichbaum, S.; Singletary, M.; Haney, P.S.; Rogers, B.; Angle, C. Selecting Dogs for Explosives Detection: Behavioral Characteristics. Front. Veter- Sci. 2020, 7, 597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, M.; Sharma, B.; Gupta, A.K.; Pandey, D. Recent developments of image processing to improve explosive detection methodologies and spectroscopic imaging techniques for explosive and drug detection. Multimedia Tools Appl. 2022, 82, 6849–6865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, E.G.; Dentinger, C.; Robotham, C. Detection of homemade explosives using Raman excitation at 1064 nm. In Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets Xx; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2015; Volume 9454, pp. 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayhew, C.; Sulzer, P.; Petersson, F.; Haidacher, S.; Jordan, A.; Märk, L.; Watts, P.; Märk, T. Applications of proton transfer reaction time-of-flight mass spectrometry for the sensitive and rapid real-time detection of solid high explosives. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 289, 58–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, K.; Bradley, D. A review of X-ray explosives detection techniques for checked baggage. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2012, 70, 1729–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McFee, J.E.; Faust, A.A.; Andrews, H.R.; Kovaltchouk, V.; Clifford, E.T.; Ing, H. A Comparison of Fast Inorganic Scintillators for Thermal Neutron Analysis Landmine Detection. IEEE Trans. Nucl. Sci. 2009, 56, 1584–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qin, T.; Qin, Y.; Abdelrahman, A.H.; Witte, R.S.; Xin, H. Microwave-Induced Thermoacoustic Imaging for Embedded Explosives Detection in High-Water Content Medium. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 2019, 67, 4803–4810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallowell, S.F. Screening people for illicit substances: A survey of current portal technology. Talanta 2001, 54, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caygill, J.S.; Davis, F.; Higson, S.P. Current trends in explosive detection techniques. Talanta 2012, 88, 14–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhgari, F.; Fattahi, H.; Oskoei, Y.M. Recent advances in nanomaterial-based sensors for detection of trace nitroaromatic explosives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 221, 867–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodka, M.D.; Shpil, J.C.; Schnee, V.P.; Polcha, J.M.P. Sensor array and preconcentrator for the detection of explosives in water. In Detection and Sensing of Mines, Explosive Objects, and Obscured Targets XVII; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2012; Volume 8357, pp. 594–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moscoso, F.G.; Almeida, J.; Sousaraei, A.; Lopes-Costa, T.; Silva, A.M.G.; Cabanillas-Gonzalez, J.; Cunha-Silva, L.; Pedrosa, J.M. A lanthanide MOF immobilized in PMMA transparent films as a selective fluorescence sensor for nitroaromatic explosive vapours. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 3626–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firtat, B.; Moldovan, C.; Brasoveanu, C.; Muscalu, G.; Gartner, M.; Zaharescu, M.; Chesler, P.; Hornoiu, C.; Mihaiu, S.; Vladut, C.; et al. Miniaturised MOX based sensors for pollutant and explosive gases detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 249, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singha, D.K.; Majee, P.; Mondal, S.K.; Mahata, P. A Eu-Doped Y-Based Luminescent Metal–Organic Framework as a Highly Efficient Sensor for Nitroaromatic Explosives. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 8, 1390–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, D.; Hu, Z.; Li, J. Luminescent metal–organic frameworks as explosive sensors. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 10668–10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Shi, N.; Zhang, J.; Wu, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, L.; Yang, R.; Ou, C.; Xue, W.; Feng, X.; et al. Electrospun fluorescent sensors for the selective detection of nitro explosive vapors and trace water. J. Mater. Chem. A 2018, 6, 18543–18550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campos, B.B.; Contreras-Cáceres, R.; Bandosz, T.J.; Jiménez-Jiménez, J.; Rodríguez-Castellón, E.; da Silva, J.C.E.; Algarra, M. Carbon dots as fluorescent sensor for detection of explosive nitrocompounds. Carbon 2016, 106, 171–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Li, X.; Qin, C.; Shao, K.-Z.; Su, Z.-M. A fluorescent sensor for highly selective sensing of nitro explosives and Hg(ii) ions based on a 3D porous layer metal–organic framework. Crystengcomm 2016, 18, 4765–4771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitzer, D.; Cottineau, T.; Piazzon, N.; Josset, S.; Schnell, F.; Pronkin, S.N.; Savinova, E.R.; Keller, V. Bio-Inspired Nanostructured Sensor for the Detection of Ultralow Concentrations of Explosives. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2012, 51, 5334–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procek, M.; Stolarczyk, A.; Pustelny, T.; Maciak, E. A Study of a QCM Sensor Based on TiO2 Nanostructures for the Detection of NO2 and Explosives Vapours in Air. Sensors 2015, 15, 9563–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, P.; Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Chen, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.; Shi, J.; Yao, Z.; et al. Single-Molecule Tunneling Sensors for Nitrobenzene Explosives. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 12042–12050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekar, S.; Gawas, P.; Bhat, S.V.; Nutalapati, V. Highly fluorescent 2D-BCNO sheets based chemical sensor for selective detection of the explosive Dunnite and 4-nitrophenol in aqueous medium. Environ. Sci. Nano 2021, 8, 2908–2919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barata, P.D.; Prata, J.V. Fluorescent Calix[4]arene-Carbazole-Containing Polymers as Sensors for Nitroaromatic Explosives. Chemosensors 2020, 8, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Fan, M.; Deng, G.; Gong, C.; Chen, K.; Luo, J.; Chiang, K.S.; Rao, Y.-J.; Gong, Y. Optofluidic laser explosive sensor with ultralow detection limit and large dynamic range using donor-acceptor-donor organic dye. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 298, 126830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Q.; Wang, B.; Li, D.; Yu, J. Fluorescent sensors based on AIEgen-functionalised mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the detection of explosives and antibiotics. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2018, 5, 2183–2188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodkhomkhum, R.; Masik, M.; Watchasit, S.; Suksai, C.; Boonmak, J.; Youngme, S.; Wanichacheva, N.; Ervithayasuporn, V. Imidazolylmethylpyrene sensor for dual optical detection of explosive chemical: 2,4,6-Trinitrophenol. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 245, 665–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Joshi, S.; Cordova-Sintjago, T.C.; Pant, D.D.; Sakhuja, R. Highly sensitive fluorescent imidazolium-based sensors for nanomolar detection of explosive picric acid in aqueous medium. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2016, 229, 599–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toal, S.J.; Trogler, W.C. Polymer sensors for nitroaromatic explosives detection. J. Mater. Chem. 2006, 16, 2871–2883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Fu, Y.-Y.; Zhu, D.-F.; Xu, J.-Q.; He, Q.-G.; Cheng, J.-G. Recent advances in fluorescence sensor for the detection of peroxide explosives. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2016, 27, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salinas, Y.; Martínez-Máñez, R.; Marcos, M.D.; Sancenón, F.; Costero, A.M.; Parra, M.; Gil, S. Optical chemosensors and reagents to detect explosives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1261–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, M.T.; Thomas, R.C.; Berton, M.E. Fiber waveguide chemical sensors for detection of explosive related vapors. In Detection and Remediation Technologies for Mines and Minelike Targets Vii; Society of Photo Optical: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2002; Volume 4742, pp. 509–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Lv, L.; Zou, G.; Zhang, Q. Fluorescent Porous Film Modified Polymer Optical Fiber via “Click” Chemistry: Stable Dye Dispersion and Trace Explosive Detection. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, F.; Cui, M.; Ma, J.; Zou, G.; Zhang, Q. An optical fiber taper fluorescent probe for detection of nitro-explosives based on tetraphenylethylene with aggregation-induced emission. Opt. Fiber Technol. 2017, 36, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eisner, L.; Flachenecker, G.; Schade, W. Doped silica sol layer coatings on evanescent field fiber Bragg gratings for optical detection of nitroaromate based explosives. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2022, 343, 113687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, F.; Tsiminis, G.; Spooner, N.A.; Monro, T.M. Explosives detection by fluorescence quenching of conjugated polymers in suspended core optical fibers. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2014, 199, 22–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, P.; Li, X.; Zhao, Z.; Qin, J.; Li, X. Optical fiber bundle fluorescence sensor for a triacetone triperoxide vapor detection of trace explosives. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2022, 371, 132536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhaduri, A.; Singh, S.; Thapa, K.B.; Yadav, B. Visible light-induced, highly responsive, below lower explosive limit (LEL) LPG sensor based on hydrothermally synthesized barium hexaferrite nanorods. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Wu, J.; Qu, S.; Deng, G.; Li, Z.; Sun, K.; Jiang, L.; Chen, K.; Luo, J. Photo-bleaching of optical waveguide polymers with dipolar chromophores to improve their sensitivity for explosive vapor detection. J. Mater. Chem. C 2020, 8, 13010–13018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.; Sun, H.; Pyayt, A.; Zhang, X.; Luo, J.; Jen, A.; Sullivan, P.A.; Elangovan, S.; Dalton, L.R.; Dinu, R.; et al. Chromophore-Containing Polymers for Trace Explosive Sensors. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 8072–8078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Wu, J.; Chen, K.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, G.; Zhang, X.; Li, Z.; Chiang, K.S. Polymer waveguide Mach-Zehnder interferometer coated with dipolar polycarbonate for on-chip nitroaromatics detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2019, 305, 127406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostenko, K.V.; Kryukov, Y.S. Technique for detecting a direct signal pulse from an underwater explosive source in a waveguide. Acoust. Phys. 2016, 62, 112–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Yadav, C.S.; Sharma, G.; Kumar, S.; Singh, V. Common path interferometeric analysis of a planar polymer optical waveguide having adlayer of 2D materials for biosensing applications. Opt. Quantum Electron. 2021, 53, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, A.; Yadav, C.S.; Maurya, R.; Sharma, G.; Singh, T.S.; Kumar, S.; Singh, V. Experimental detection of chlorpyrifos by MoS2 coated planar polymer waveguide sensor utilizing common path interferometric principle. Optik 2023, 276, 170668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, W.; Deng, G.; Hu, Z.; Chen, K.; Wu, J. Sensitive Evanescence-Field Waveguide Interferometer for Aqueous Nitro-Explosive Sensing. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040246
Wang W, Deng G, Hu Z, Chen K, Wu J. Sensitive Evanescence-Field Waveguide Interferometer for Aqueous Nitro-Explosive Sensing. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(4):246. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040246
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Wen, Guowei Deng, Zhanwei Hu, Kaixin Chen, and Jieyun Wu. 2023. "Sensitive Evanescence-Field Waveguide Interferometer for Aqueous Nitro-Explosive Sensing" Chemosensors 11, no. 4: 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040246
APA StyleWang, W., Deng, G., Hu, Z., Chen, K., & Wu, J. (2023). Sensitive Evanescence-Field Waveguide Interferometer for Aqueous Nitro-Explosive Sensing. Chemosensors, 11(4), 246. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11040246









