Abstract
In this paper, graphdiyne (GDY)−modified glassy carbon electrode was prepared and further used for the sensitive and simultaneous detection of three target heavy metal ions of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ by codeposition with Bi3+ in the mixture solution. GDY−modified electrodes exhibit a larger electrode area and abundant active sites, which is favorable for absorbing more metal ions. Bismuth has low toxicity and can form alloys with zinc, cadmium and mercury. Therefore, three kinds of heavy metal ions can be pre-concentrated with bismuth on the GDY−modified electrode surface, and the following stripping analysis results in high sensitivity and selectivity. By using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry, the detection ranges of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were from 2.0 to 100.0 μM with low detection limits of 0.255 μM, 0.367 μM and 0.796 μM, respectively. In addition, the sensor showed excellent repeatability, reproducibility, and stability, which was applied to sensitive analysis of river water samples with satisfactory results.
1. Introduction
Heavy metals pose a serious pollution threat to ecosystems and human health, which can be gradually accumulated through the food chain to the human body and cause serious poisoning [1]. For example, cadmium ion (Cd2+) and mercury ion (Hg2+) are harmful environmental pollutants with high toxicity, which can pollute the drinking water, accumulate in plant crops, and damage the human organs such as skin, bones, teeth, or the nervous system [2]. Although zinc ion (Zn2+) plays a key role in the life system, excessive Zn2+ amount can lead to impaired liver and kidney functions and immunity in the human body [3]. Therefore, sensitive methods for the simultaneous detection and monitoring of heavy metal ions are of great importance in different fields such as food and water safety, human health, and so on [4,5].
At present, various detection methods have been established for the analysis of heavy metal ions, including inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP−MS) [6], atomic absorption spectrometry (AAS) [7], X-ray fluorescence spectrometry (XRF) [8] and inductively coupled plasma optical emission spectrometry (ICP−OES) [9]. These methods are important and valid for the detection of heavy metals, which are costly and require professionals to operate the equipment. Electrochemical methods have been widely used for the monitoring of heavy metal ions with low cost, rapid−response, high sensitivity and portability [10,11]. Moreover, the electrochemical instruments are inexpensive and simple with different methods explored. Among them, differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) has gained much attention for its ability to significantly improve sensitivity due to the effective pre−deposition or pre−concentration step. DPASV is mainly based on the following two−stage process: pre−concentration and dissolution steps. First, the pre−concentration refers to heavy metal ions in the tested sample solution deposited on the surface of the working electrode by reduction at a constant potential. Secondly, the dissolution step is to dissolve the formed heavy metal from surface of working electrode with potential scan and record the current signal in the dissolution process [12]. For example, Kumar et al. detected trace Pb2+ and Cd2+ simultaneously by DPASV at a quercetin−reduced graphene oxide−modified electrode [13]. Shi et al. prepared a mercury film and reduced graphene oxide composites−modified electrode for the simultaneous detection Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ by DPASV [14]. Sherigara et al. fabricated mercury-film-modified carbon paste electrode for the sensitive detection of low−concentration heavy metal ions [15].
In traditional DPASV experiments, mercury is often used as the film material for the deposition of heavy metal ions, which are capable of forming alloys with heavy metals [14]. However, mercury is a liquid metal with strong toxicity and is difficult to handle. Therefore, environmentally friendly mercury−free electrodes have been the research focuses for investigations. Recently the “green metal” bismuth (Bi) has been used as sensing materials due to the property of bismuth to form “fused alloys” with heavy metals, which is analogous to the amalgams that mercury forms. In addition, Bi provides several advantages of partial insensitivity to dissolved oxygen, its ability to operate in high pH solutions, and the better separation between peaks in stripping analysis, which have attracted the attentions of the electroanalytical community [16]. Various bismuth-film-modified electrodes have been designed to replace the mercury electrodes [17,18,19] and applied to the metal ion analysis. For example, a disposable bismuth film electrode was prepared by the photolithographic method for the determination of trace Pb2+ and Cd2+ with the detection limits of 0.5 μg/L and 1.0 μg/L [20]. Finšgar et al. reported a bismuth–tin-film alloy-modified glassy carbon electrode (GCE), which exhibited a better selectivity for Zn2+, Cd2+ and Pb2+ determination with clearly separated stripping peaks when compared to the single metal film electrode [21]. Thanh et al. prepared a bismuth−film electrode by simultaneously depositing bismuth and the target metal ions on GCE for determination of Zn2+, Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ in the aqueous solution [22].
Nowadays, carbon−based nanomaterials have been widely applied to electrochemical sensors, which exhibit the advantages such as large surface area and strong electron transfer performance [23]. As a new carbon nanosheet, graphdiyne (GDY) has a flat network structure that composed of sp2 and sp hybridized carbon atoms [24]. The planar structure allows GDY to have a high π−conjugation, possess the large specific surface area with uniformly distributed pore structure, and tunable electronic structure properties [25]. Therefore, GDY−based composites have been used in the electrode modification, which exhibit the promoted surface area and charge transfer rate. Yan et al. used GDY and ionic liquid composite materials for the electrochemical reaction of rutin [26]. The acetyl−linked group of π−electron−rich GDY can transport electrons along the GDY network and makes the surface of GDY more electrically negative with more metal ions enriched on its surface [27]. Therefore, GDY−based electrodes have been proved to enhance the analytical performances of electrochemical sensors.
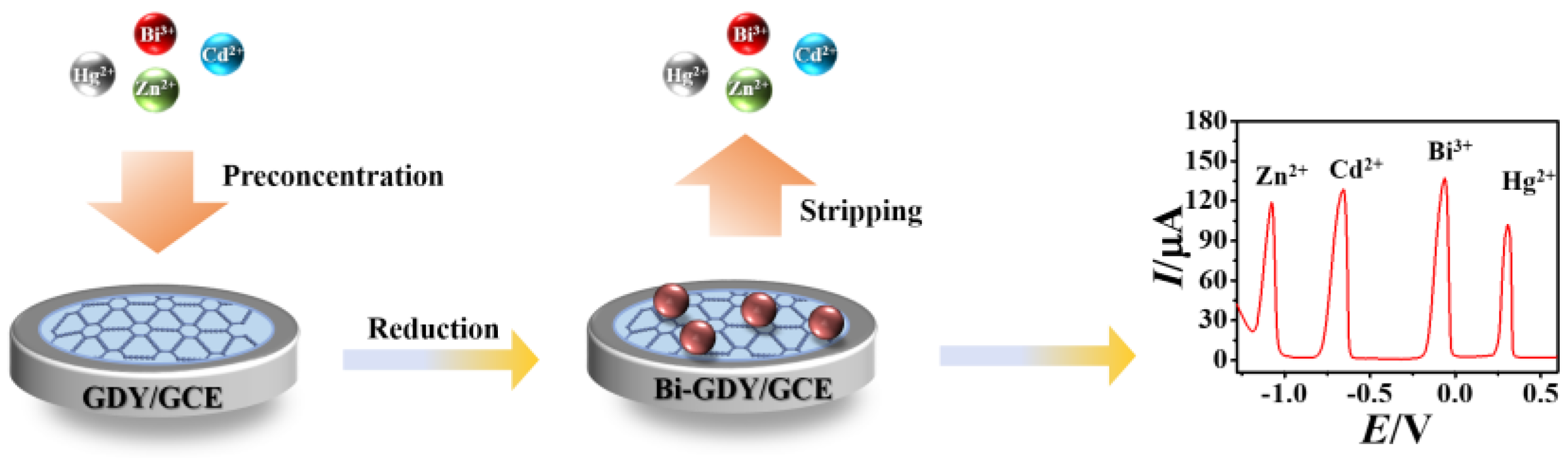
In this paper, GDY−modified GCE was prepared with the morphology and electrochemical performance characterized by SEM and cyclic voltammetry (CV). Furthermore, GDY/GCE was applied to the simultaneous detection of three heavy metal ions (Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+) by co-deposition with 0.1 mM Bi3+ solution using the sensitive DPASV method. The preparation procedure of Bi–GDY/GCE and electrochemical detection of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were illustrated in Figure 1.
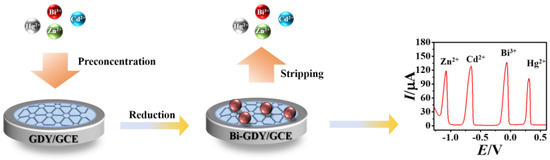
Figure 1.
The preparation procedure of Bi–GDY/GCE and the application for simultaneous DPASV detection of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ with co-deposition of Bi3+.
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Apparatus
Graphdiyne (GDY) powder was purchased from Nanjing XF Nano Material Technology Co. Ltd. (Nanjing, China), which was stacked of GDY flakes with the thickness of 3–4 nm and lateral size of 40–100 nm. Bi(NO3)3·5H2O was obtained from Tianjin Yongda Chemical Reagent Co. Ltd. (Tianjin, China). Potassium ferricyanide (K3[Fe(CN)6]), potassium ferrocyanide (K4Fe(CN)6), Zn(NO3)2·6H2O, CdCl2, HgCl2, FeCl3, FeCl2·4H2O, MgCl2·6H2O, Co(NO3)2·6H2O, and Ni(NO3)2·6H2O were purchased from Shanghai Aladdin Reagent Co. Ltd. (Shanghai, China). CuCl2·2H2O, MnSO4 and KCl were provided by Xilong Science Co. Ltd. (Guangzhou, China). Acetate buffer (HAc–NaAc, 0.1 M, pH 4.5) was served as the supporting electrolyte. All the reagents used were analytically pure, and the ultra−pure water with specific resistance of 18.2 MΩ cm (Milli−Q IQ7000, Merck Millipore, Darmstadt, Germany) was used throughout experiments.
Scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and transmission electron microscopy (TEM) were performed using JSM−7100F field emission scanning electron microscope and JEM−2010F transmission electron microscope (Japan Electronics Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), respectively. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) was performed on an ESCALAB 250Xi instrument (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) with an Al−Kα X-ray source (hν = 1486.6 eV) and a pass energy of 30.0 eV. Raman spectrum was recorded by the LabRAM HR system using 532 nm laser (Horiba, Japan). Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry (DPASV) were measured on a CHI 1040C electrochemical workstation with electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) on a CHI 660E electrochemical workstation (Shanghai Chenhua Instrument Company, Shanghai, China) using a standard three−electrode system. A bare or modified GCE (Φ = 3 mm), Ag/AgCl (3 M KCl) electrode, and a platinum wire were adopted as the working electrode, the reference electrode and the counter electrode, respectively.
2.2. Fabrication of GDY/GCE
The bare GCE was polished with 1.0 μm, 0.3 μm and 0.05 μm Al2O3 powder successively, ultrasonic washed with water and ethanol, and dried in a stream of N2. GDY powder was dispersed in 1.0 mL water and sonicated for 30 min to obtain a homogeneous 1.0 mg/mL GDY suspension. Then, a certain volume of 1.0 mg/mL GDY suspension was dripped on the newly treated GCE by several times, and then dried under infrared light to prepare the GDY/GCE.
2.3. Electrochemical Procedure
The simultaneous analysis of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ was performed by co-depositing bismuth ion, zinc ion, cadmium ion and mercury ion on GDY/GCE (named Bi–GDY/GCE) and then stripping out. The three−electrode system was immersed into a 10.0 mL electrochemical cell containing appropriate amounts of Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ and 0.1 mM Bi3+ with 0.1 M HAc–NaAc (pH 4.5) as the electrolyte. DPASV was performed at the deposition potential of −1.5 V for 150 s with stirring, then the stripping analysis was further recorded in scanning potential range from −1.5 V to 0.6 V with the following parameters: pulse amplitude of 50 mV, pulse width of 50 ms, potential step of 4 mV and pulse period of 0.5 s. Prior to the next usage, the electrode was cleaned at the potential of 0.5 V for 200 s in 0.1 M HAc–NaAc (pH 4.5) to assure the completely elimination of the deposited Zn, Cd and Hg. The above processes were carried out at room temperature during the electrochemical experiments.
3. Discussion
3.1. Characterization of GDY and Modified Electrodes
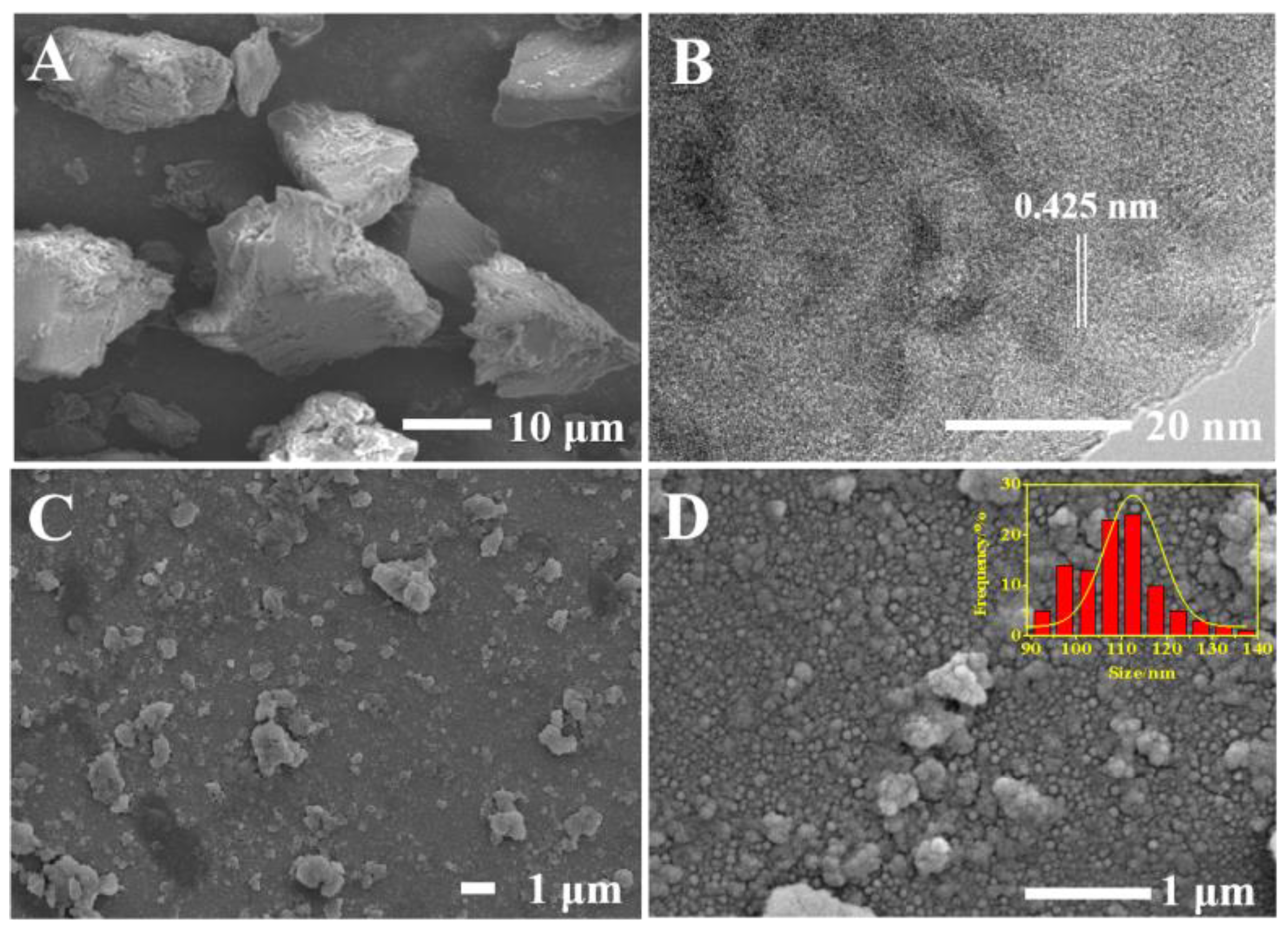
The morphology of GDY powder, GDY suspension, GDY/GCE and GDY/GCE co-deposited with Bi3+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were recorded (Figure 2). SEM image of GDY power exhibited a large block, which indicated that flaky GDY are stacked together and not scattered. After ultrasonically dispersing GDY power into a suspension, a two−dimensional layered structure could be observed in the TEM image (Figure 2B) with a layer distance of 0.425 nm, which was in agreement with previous reports [28,29]. After being dropped on the GCE surface, the SEM of GDY/GCE (Figure 2C) showed some granular structure with partly aggregation of GDY nanosheet, which was beneficial to expose the active sites of GDY as well as provide excellent support for alloy nanoparticles. After co-deposition of Bi3+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ on the GDY/GCE surface, metal ions were reduced and formed alloy together. As shown in Figure 2D, the diameters of alloy microspheres were 112.5 ± 2.5 nm, which proved that target metal and Bi were successfully formed on the modified electrode, and bismuth−based electrodes could be served as a favorable replacement for mercury film electrodes.

Figure 2.
SEM of (A) GDY power, (C) GDY/GCE, (D) GDY/GCE enriched with Bi3+, Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ (inset was size distribution histogram), and (B) TEM of GDY suspension.
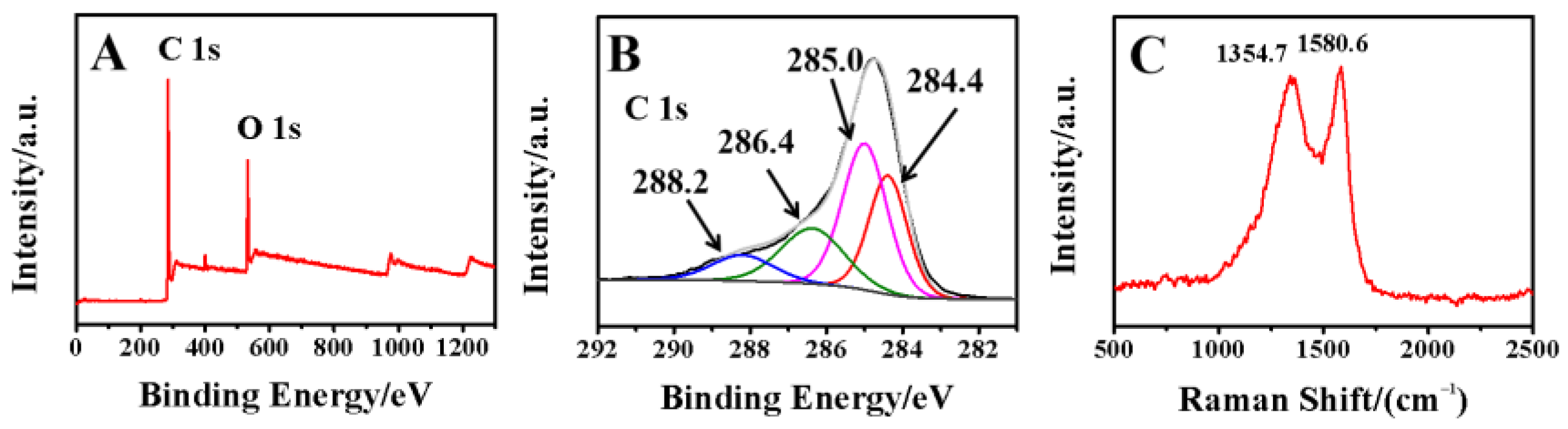
XPS survey spectrum of GDY was recorded (Figure 3A), which verified that only carbon and oxygen elements appeared. The O 1s peak located at 531.6 eV could be attributed to the absorption of oxygen and slightly oxidization of terminal alkenyl group of GDY. The high-resolution asymmetric C 1s spectrum (Figure 3B) could be deconvoluted into four sub-peaks, including the sp2 (C=C in benzene rings) at 284.4 eV, sp (C≡C) at 285.0 eV, C–O at 286.4 eV and C=O at 288.2 eV, respectively. The binding energy of these sub-peaks are consistent with the reported results [30]. In addition, the largest peak area of C≡C indicated that GDY contained a large number of acetylenic bonds, which might provide more active sites for preconcentration of heavy metal ions.
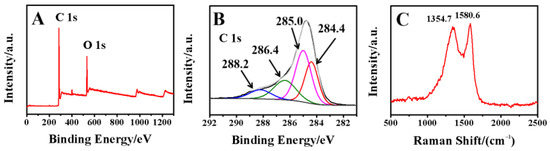
Figure 3.
(A) XPS survey spectrum and (B) high-−resolution C 1s spectrum of GDY, (C) Raman spectrum of GDY.
Raman spectroscopy is also a powerful tool to characterize carbon materials. Figure 3C showed the typical Raman spectrum of GDY with two main peaks at 1354.7 cm−1 (D–band) and 1580.6 cm−1 (G–band), which were consistent with the previous literature [31]. The D–band and G–band correspond to the breathing vibration of benzene rings and the first-order scattering of the E2g mode for in-phase stretching vibration of the sp2 carbon lattice in aromatic rings, respectively.
3.2. Electrochemical Characterizations
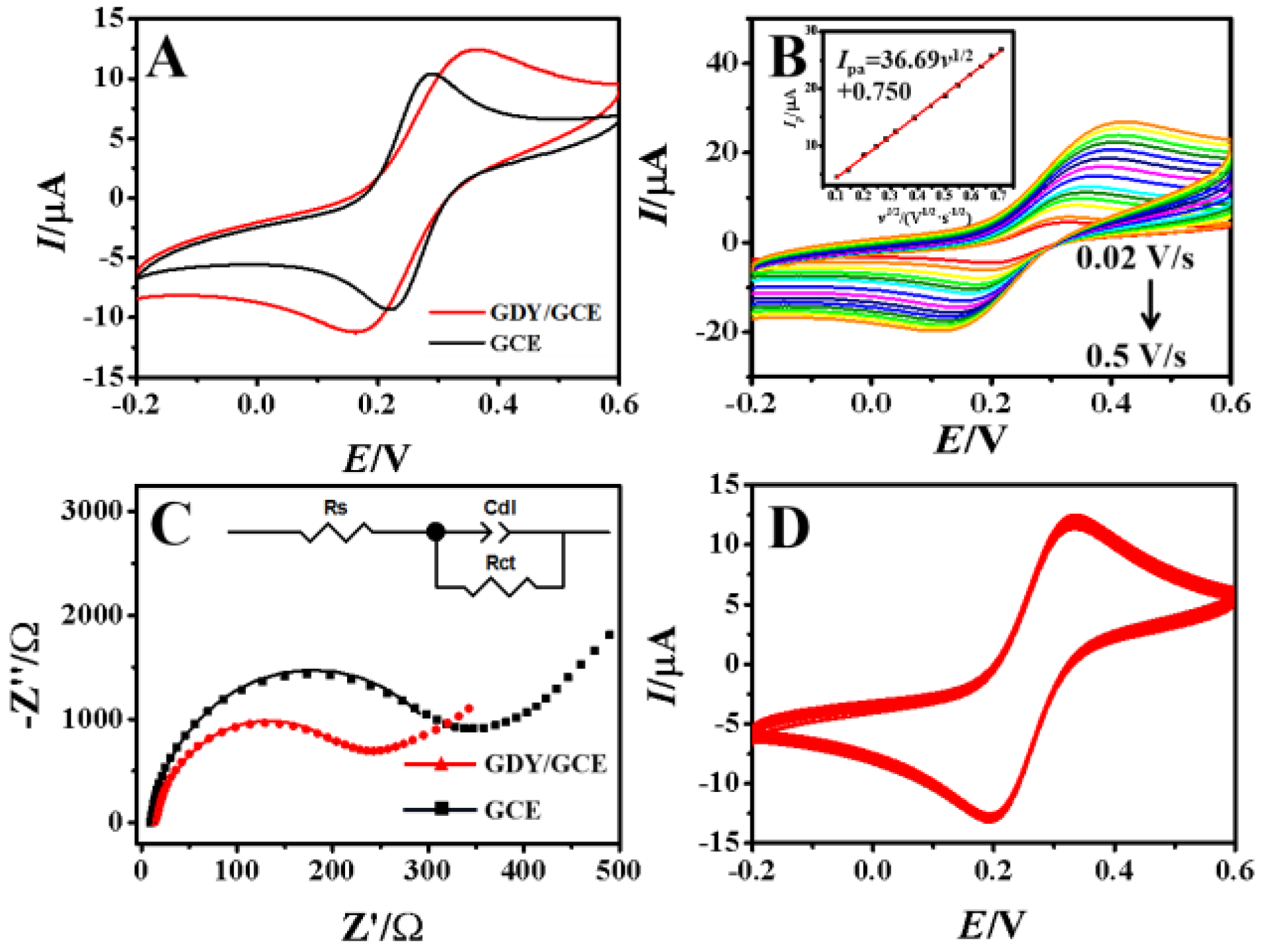
The bare GCE and GDY/GCE were characterized electrochemically using CV techniques in 1.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− solution containing 1.0 M KCl (Figure 4A). The results indicated that an enhanced peak current of 20.74% appeared on GDY/GCE, which could be attributed to the increase in the electroactive surface area with the acceleration of the electron transfer rate.
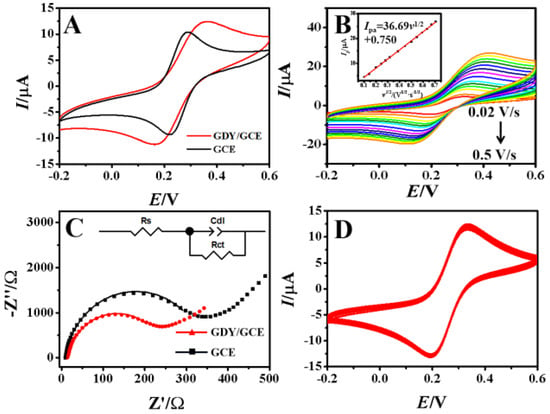
Figure 4.
CV curves of (A) GCE and GDY/GCE at the scan rate of 0.1 V/s, (B) GDY/GCE at different scan rate (inset the linear relationship of Ipa versus square root of scan rate) in 1.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− solution containing 1.0 M KCl, (C) Nyquist plots of GCE and GDY/GCE in 5.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− solution containing 0.1 M KCl in the frequency range from 10 kHz to 0.1 Hz with the amplitude of 0.005 V and the potential of 0.3 V. Inset shows the Randle equivalent circuit that consists of the electrolyte resistance (Rs), charge transfer resistance (Rct) and double layer capacitance (Cdl), (D) Multi−scan CV curves of GDY/GCE in 1.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− containing 1.0 M KCl solution at the scan rate of 0.1 V/s.
In order to further calculate the electroactive surface area (A) of different electrodes, the CV curves at different scan rates were recorded (Figure 4B). It could be seen that the redox peak current increased linearly with the square root of the scan rate. According to Randles−Sevcik equation [32]:
where Ipa is the anodic peak current (μA), n is the number of electrons transferred (n = 1 in the [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox system), A is electroactive surface area (cm2), C is concentration of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− (1.0 × 10−6 mol/cm3), ν is the scan rate (V/s) and D is the diffusion coefficient of [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− (6.7 × 10−6 cm2/s). Thus, from the slope of the Ipa vs. ν1/2 the electroactive surface area (A) was recorded as 0.0527 cm2 for GDY/GCE, which was bigger than that of 0.0435 cm2 for bare GCE. Therefore, the presence of GDY on GCE can increase the electroactive surface area, and provide more active sites for the following enrichment of heavy metal ions [33].
Ipa = 2.69 × 105 n3/2 ACD1/2 ν1/2
EIS is a commonly used method for characterizing the charge transfer reaction and the interfacial properties of modified electrodes. By using [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− redox couple as a probe, the conductive behavior of the GDY−modified electrode surface and the kinetic barrier of the electrode/solution interface were investigated with the curves shown in Figure 4C. The values of charge transfer resistance (Rct) fitted by Randle equivalent circuit for GCE and GDY/GCE are 339 Ω and 258 Ω, respectively. The decrease in the Rct value indicated the presence of GDY on GCE surface could reduce the interface resistance due to the high conductivity and fast electron transfer efficiency of GDY. Subsequently, the long−term stability of GDY/GCE was investigated by the multi−scan CV in 1.0 mM [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− and 1.0 M KCl mixture solution with a scan rate of 0.1 V/s. As shown in Figure 4D, the redox peak currents remained 96.89% of the original current after 100 circles CV scan, which also indicated that the GDY/GCE had good stability.
3.3. Electrochemical Behaviors of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+
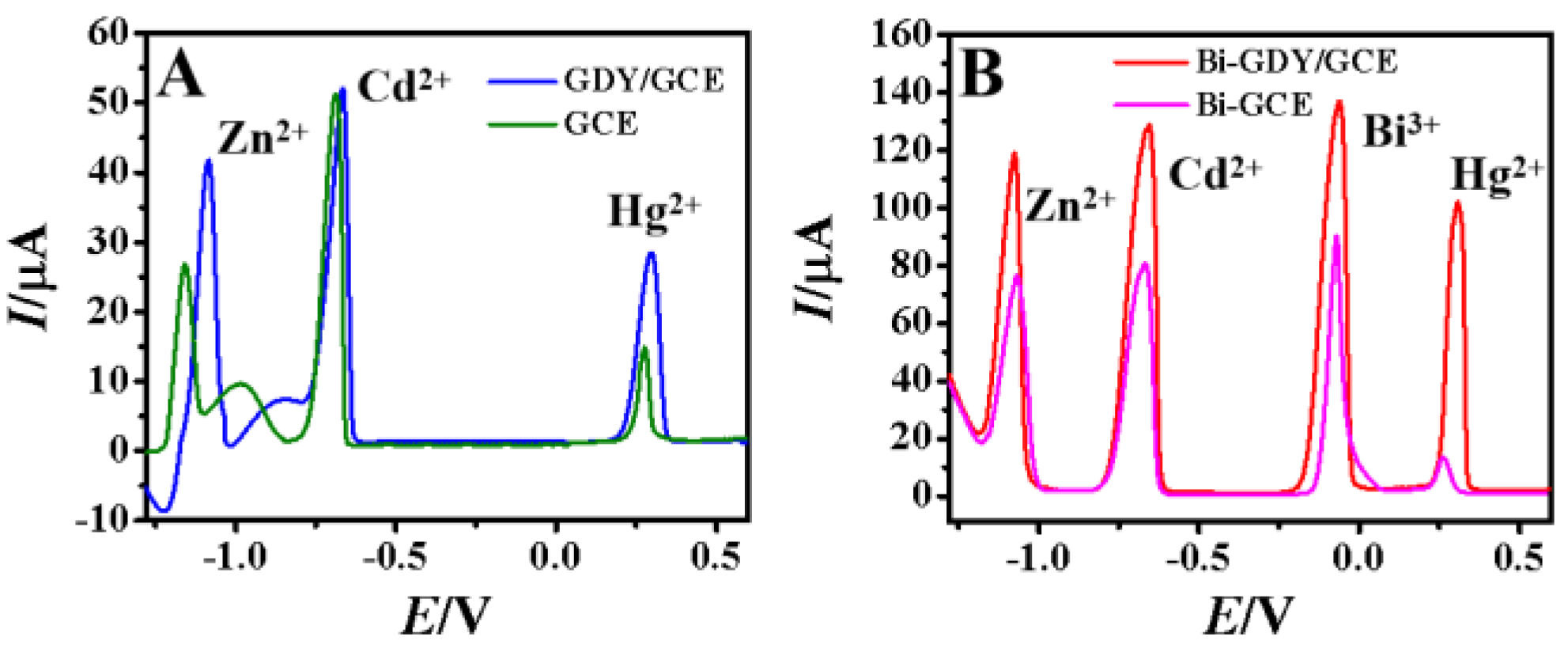
Figure 5 showed the DPASV curves of 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ on different modified electrodes with the current values listed in Table 1. As for the bare GCE (Figure 5A), three small stripping peaks appeared at −1.16 V, −0.71 V and 0.32 V, which could be ascribed to the responses of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+. In the DPASV process, metal ions are reduced and preconcentrated on the electrode surface to form metal, which are reoxidized to metal ions at the following stripping procedure. After GDY was modified on GCE (Figure 5A), both the stripping currents of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ increased, proving the positive effect of GDY on metal ions accumulation including large electroactive surface area and reactive sites. However, the increase ratios are different, indicating that molecular GDY has different effects on different ions. GDY has sp−hybrid carbon and acetylenic bond in its structure, which can provide electrons to bind with heavy metal ions [27]. As for the Bi–GCE (Figure 5B), the stripping currents of Zn2+ and Cd2+ were about 2.64 times and 1.58 times that of bare GCE, proving the coexistence of Bi3+ was benefit for the Zn2+ and Cd2+ analysis due to the formation of alloys. The stripping current of Hg2+ changed less, which may be due to the stripping of metal Bi before Hg, and the current was similar to that of GCE without the presence of Bi. The DPASV curves recorded on Bi–GDY/GCE exhibited a well–defined, high, and undistorted stripping peaks for Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ with peak potentials located at −1.06, −0.66 and 0.24 V, which were consistent with those in the literature [11,34]. In addition, the stripping currents of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ on Bi–GCY/GCE were 4.29 times, 2.55 times and 7.85 times of bare GCE (Table 1). All the results demonstrated that the synergistic positive effects of GDY and Bi in the electrochemical analysis of metal ions, including the large electrode interface and the formation of alloys of Bi with other metals.
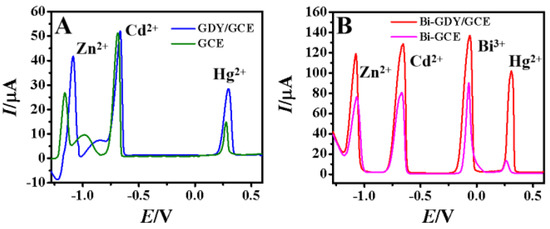
Figure 5.
DPASV curves of (A) GCE and GDY/GCE in 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ without Bi3+ and (B) GCE and GDY/GCE in 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ solution containing 0.1 mM Bi3+.

Table 1.
The stripping currents of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ on different working electrodes.
In detail, GDY can provide a larger electroactive surface area and more active sites for the interaction with metal ions [27]. Bi can form alloys with zinc, cadmium and mercury, and further enhance the stripping signals of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ [35]. Therefore, compared with other modified electrodes and sensing strategies, the using of GDY/GCE and Bi3+ solution in the electrochemical procedure exhibit higher sensitivity and better detection performance.
3.4. Optimization of Experimental Conditions
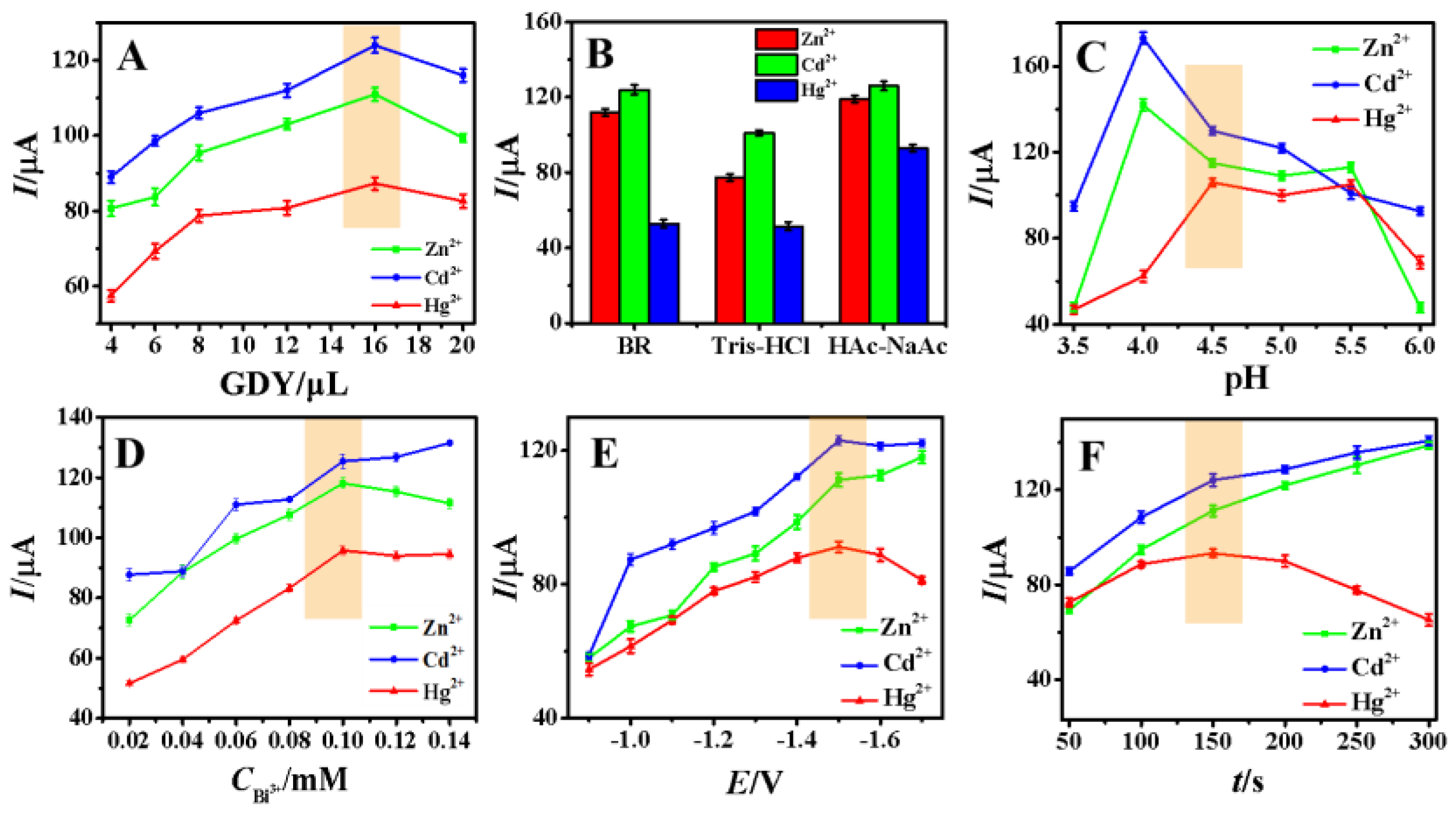
To obtain the optimum working conditions for the quantitative analysis of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+, various parameters such as GDY suspension volume, buffer system, buffer pH, Bi3+ concentration, deposition potential and time were optimized to obtain the largest responses.
The influence of the amount of 1.0 mg/mL GDY suspension was firstly investigated and the experimental results were shown in Figure 6A. The stripping currents of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were obviously dependent on the amount of GDY suspension modified on the electrode surface, which increased gradually with the amount from 4 μL to 16 μL and then decreased. This phenomenon suggests that the thick mass of GDY film have great effect on the adsorption of heavy metal ions. Therefore, the optimal GDY (1.0 mg/mL) modification volume on the electrode surface was chosen as 16 μL in this paper.
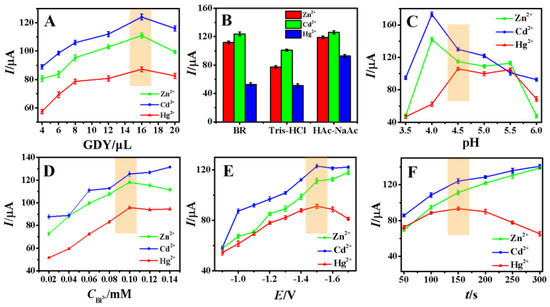
Figure 6.
The effect of (A) different volumes of 1.0 mg/mL GDY suspension, (B) the types of 0.1 M supporting electrolytes (HAc–NaAc, Tris–HCl, BR), (C) pH of HAc–NaAc, (D) the concentration of Bi3+, (E) deposition potentials and (F) deposition time on the stripping currents of Zn2+, Cd2+, and Hg2+ (n = 3). The orange area is the selected experimental condition.
The effects of different buffer systems such as HAc–NaAc, Tris–HCl and BR on the stripping currents of target heavy metal ions were further investigated with results shown in Figure 6B. It can be seen that all the DPASV signals reached the maximum responses in HAc–NaAc buffer, so 0.1 M HAc–NaAc buffer solution was selected as the best buffer system for the sensor operation.
The optimal pH of HAc–NaAc buffer solution was further optimized and the peak currents of target heavy metal ions in the pH range of 3.0–6.0 were investigated with the results shown in Figure 6C. When the pH was fixed at 4.0, the stripping signals of Cd2+ and Zn2+ were larger, but the Hg2+ dissolution signal was weak. When the pH was 4.5, the stripping signals of Cd2+ and Zn2+ were decreased a little but the stripping peak current of Hg2+ reached the maximum. When the pH was higher than 4.5, Bi3+ was very easy to form hydroxide complexes and interfered with the experimental results. Therefore, HAc–NaAc at pH 4.5 was used as the best buffer pH for the following experiments.
The Bi3+ concentration plays an important role in the preconcentrated process of heavy metals ions, which was further optimized with curves shown in Figure 6D. The peak currents of three metals increased with the increasing Bi3+ concentration, which could be explained by the increase in alloy amount formed with Bi3+ from 0.02 mM to 0.1 mM. When Bi3+ concentration was higher than 0.10 mM, no obvious change in the peak current was observed, so 0.10 mM Bi3+ was chosen as the optimal concentration for the subsequent assay.
The deposition potential was an important factor that affects the analytical sensitivity and detection performance of DPASV, which was optimized with the experimental results shown in Figure 6E. In the potential range of −1.7 to −0.9 V, the stripping peak currents of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ showed the biggest response at −1.5 V. When the deposition potential was in the range of −1.7 to −1.5 V, hydrogen evolution at the electrode surface was easily occurred, which would perhaps decrease the deposition efficiency and hence reduce the stripping signal. Therefore, the optimum deposition potential was set as −1.5 V in this experiment.
The effect of deposition time on the electrochemical signals of three target heavy metal ions was further investigated with the results shown in Figure 6F. In the time from 50 s to 150 s, the peak currents of Zn, Cd and Hg increased gradually, suggesting more and more heavy metal deposited on the electrode surface with increasing deposition time. When the time was longer than 150 s, the peak current of Hg2+ began to decrease, and the slope of the peak current curves of Zn2+ and Cd2+ began to level off. The reason may be due to the saturation of the available electrode surface for Zn, Cd and Hg deposition. In view both of sensitivity and determination efficiency, 150 s was selected as the deposition time for the subsequent experiment.
3.5. Electroanalysis Performance
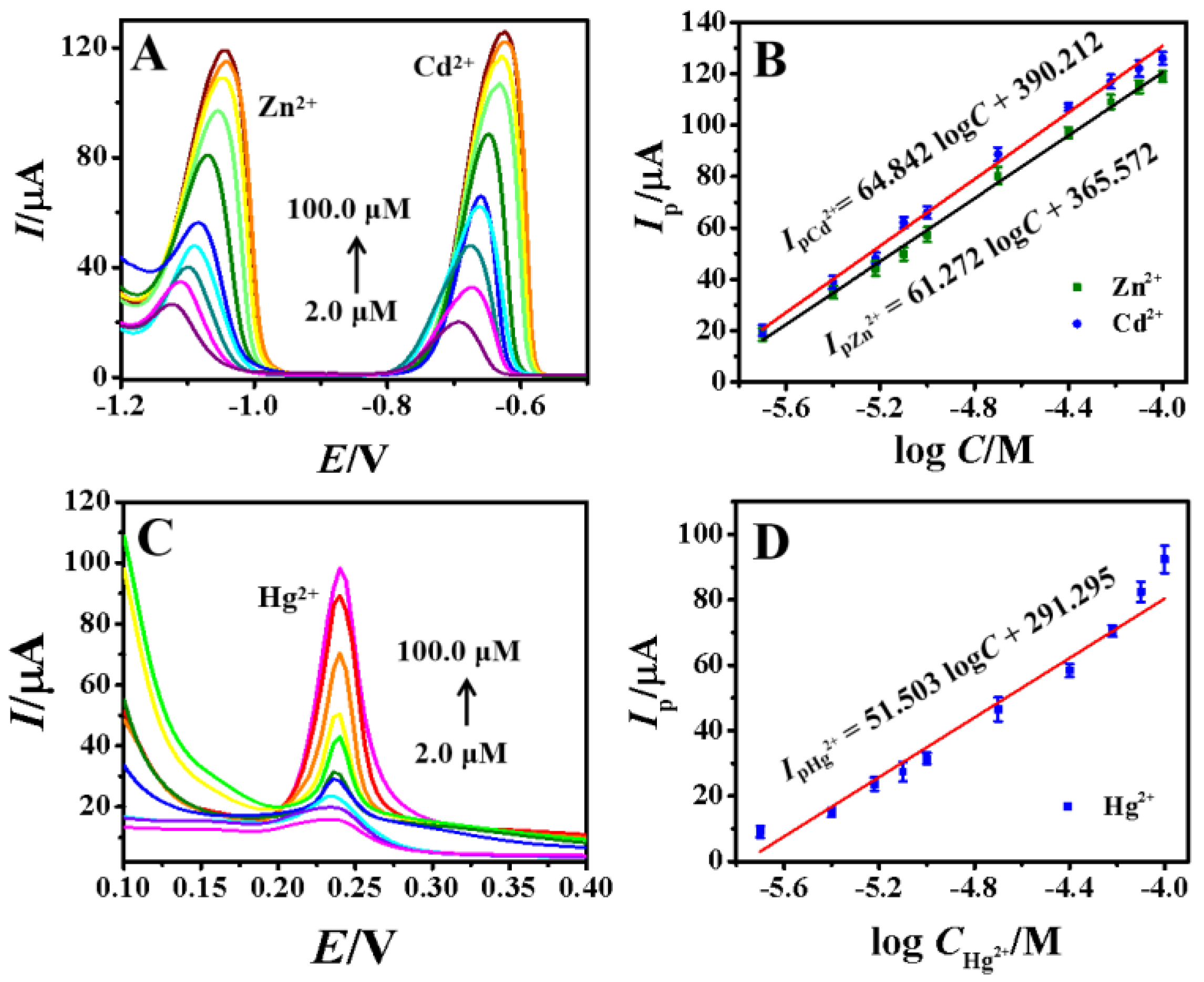
Under the optimized conditions, the DPASV curves for simultaneously detecting different concentrations of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were investigated under the optimal experimental conditions with the results shown in Figure 7. It can be seen that the peak currents (Ip) increased linearly with the concentrations in the range from 2.0 μM to 100.0 μM with the linear regression equations plotted as follows.
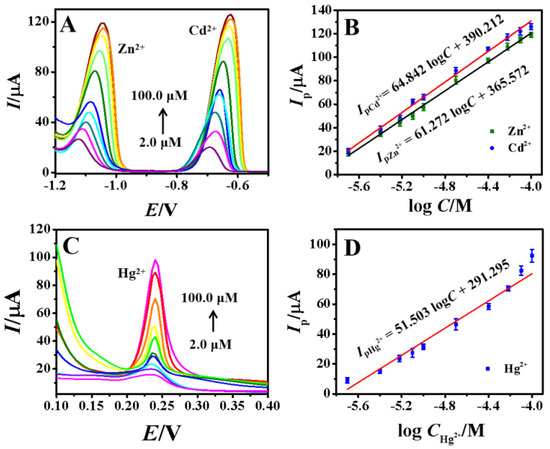
Figure 7.
DPASV curves of different concentrations of (A) Zn2+, Cd2+, and (C) Hg2+ (2.0, 4.0, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0, 20.0, 40.0, 60.0, 80.0, 100.0 μM); the linear plots of Ip versus the logarithm of concentration (B) Zn2+ and Cd2+, and (D) Hg2+.
Based on the signal−to−noise ratio (S/N = 3), the detection limits of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were calculated to be 0.255 μM, 0.367 μM and 0.796 μM, respectively. Moreover, the detection performance of the proposed sensor was compared with previously reported and the results were listed in Table 2. It could be found that sensing strategy in this work offered relative lower detection limits or wider detection ranges for three metal ions.

Table 2.
Comparison of different modified electrodes for determination of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+.
3.6. Selectivity, Repeatability, and Stability Study
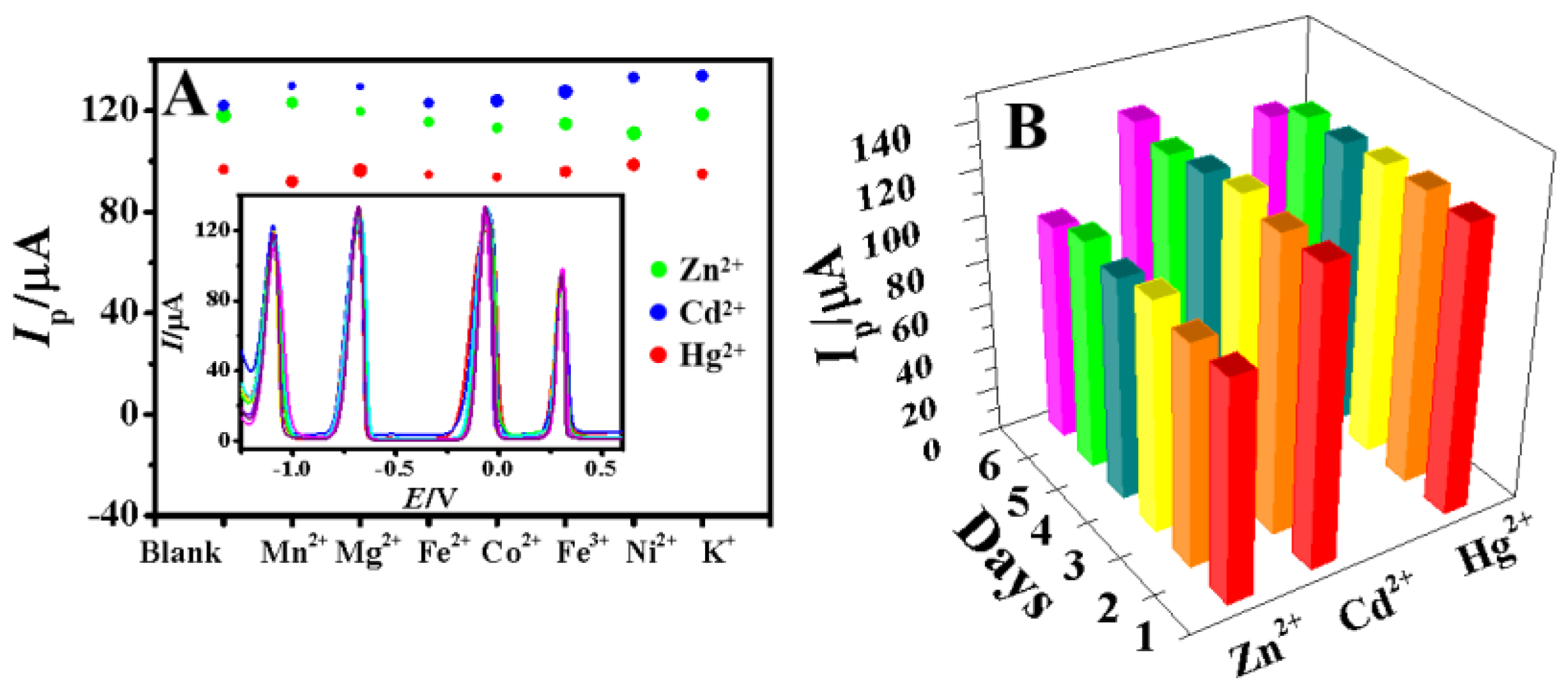
Various interfering ions (Mn2+, Mg2+, Fe2+, Co2+, Fe3+, Ni2+, K+) with 10−fold concentrations were added to HAc–NaAc containing 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ to investigate the selectivity of Bi–GDY/GCE. As shown in Figure 8A, these interfering metal ions had little effects on the detection signal with the relative error less than 2.87%. Therefore, the proposed method has excellent selectivity for the detection of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+, which is due to the fact that the presence of GDY on the electrode with alkynyl group and electron rich sp−hybrid carbon can easily chelate with Cd2+ and Zn2+ [27], and the in situ codeposition of Bi can form alloy with three metal ions [41].
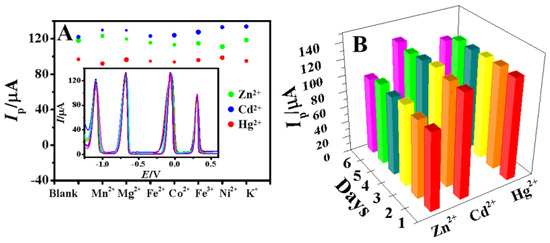
Figure 8.
(A) The stripping peak currents of 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ on Bi–GDY/GCE with 10−fold interfering ions (n = 3), the size of dots represents the peak current deviations (inset the overlay of corresponding DPASV curves), (B) Histogram of the peak currents of 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+, Hg2+ and 0.1 mM Bi3+ for six consecutive days.
The repeatability of the electrochemical sensor was further investigated. A GDY/GCE was used to successively measure in 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ solution containing 0.1 mM Bi3+ for six times (the electrode was electrochemically cleaned in the same solution after each measurement), and the relative standard deviations (RSDs) were 2.24% for zinc ion, 1.33% for cadmium ion and 3.12% for mercury ion, respectively. To check the stability of the sensor, GDY/GCE was stored in a refrigerator and tested for 100.0 μM Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ for six consecutive days with the results shown in Figure 8B. The RSDs were less than 5.5%, indicating that the sensor had good stability.
3.7. Analytical Applications
River water sample was collected from Meishe River in Haikou city of Hainan province, which was filtered by 0.22 μm syringe filter and diluted 10 times with 0.1 M HAc–NaAc (pH 4.5). Then the contents of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ were determined on Bi–GDY/GCE by the standard calibration curve, and the recovery was checked by spiking standard solution into the real water sample solution. As shown in Table 3, the concentrations of Zn2+ and Cd2+ in river samples were calculated as 1.566 μM and 1.012 μM, and the recoveries were 93.36–102.7%, 98.08–105.2% and 95.37–102.4%, respectively. The results indicate that this electrochemical sensor can be effectively applied to the detection of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ in real river water sample.

Table 3.
Analytical results of real river water samples using this method (n = 3).
4. Conclusions
In this paper, an electrochemical procedure based on GDY−modified GCE was constructed for the quantitative analysis of Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ with the co-deposition of Bi3+ in the test solution. Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ can be simultaneously determined in the concentration range from 2.0 to 100.0 μM with the detection limits of Zn2+ (0.255 μM), Cd2+ (0.367 μM) and Hg2+ (0.796 μM), respectively. In addition, the sensor was applied to detect Zn2+, Cd2+ and Hg2+ concentration in real river water samples. By combining novel carbon nanomaterial GDY as the modifier on the working electrode with the Bi3+ co-deposition in the solution, the target ions can be easily detected with the analytical performances improved by using the DAPSV method. The synergistic effects of GDY and Bi–alloy with the pre−concentration procedure allows the higher sensitivity for the target heavy metal ions with wider linear range and lower detection limit, which extends the application of GDY−modified electrode for metal analysis. In addition, the electrochemical sensor for heavy metal ions designed in this experiment provides certain application prospects.
Author Contributions
Y.A. writing—original draft preparation; Y.A., L.W., W.F. and X.Y. carried out the experimental and theoretical investigations; J.Z. analyzed the data; X.Z. and S.H. writing—review and editing; W.S. conceived the study and supervision. All authors contributed equally to writing, editing and reviewing the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21964007, 22102043), the Key Research and Development Program of Hainan Province (ZDYF2020204), the Specific Research Fund of the Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province (YSPTZX202126), the Innovation Platform for Academicians of Hainan Province, the Postgraduate Innovation Research Project of Hainan Province (Qhyb2021-42).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data sharing not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Mukherjee, S.; Bhattacharyya, S.; Ghosh, K.; Souvik, P.; Halder, A.; Naseri, M.; Mohammadniaei, M.; Sarkar, S.; Ghosh, A.; Sun, Y.; et al. Sensory development for heavy metal detection: A review on translation from conventional analysis to field-portable sensor. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 109, 674–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, G.; Nguyen, T.D.; Piro, B. Modified electrodes used for electrochemical detection of metal ions in environmental analysis. Biosensors 2015, 5, 241–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fosmire, G.J. Zinc toxicity. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1990, 51, 225–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alloway, B.J. Sources of Heavy Metals and Metalloids in Soils. In Heavy Metals in Soils: Trace Metals and Metalloids in Soils and Their Bioavailability; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.Q.; Hu, J.M.; Yang, J.G.; Zheng, B.; Ha, Y.Q. Multi-component analysis by flow injection-diode array detection-spectrophotometry using partial least squares calibration model for simultaneous determination of zinc, cadmium and lead. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 461, 181–188. [Google Scholar]
- Schramel, P.; Wendler, I.; Angerer, J. The determination of metals (antimony, bismuth, lead, cadmium, mercury, palladium, platinum, tellurium, thallium, tin and tungsten) in urine samples by inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Int. Arch. Occup. Environ. Health 1997, 69, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.B. Determination of lead and other heavy metals in urine by atomic absorption spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 1962, 34, 614–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyle, S.M.; Nocerino, J.M.; Deming, S.N.; Palasota, J.A.; Palasota, J.M.; Miller, E.L.; Hillman, D.C.; Kuharic, C.A.; Cole, W.H.; Fitzpatrick, P.M. Comparison of AAS, ICPAES, PSA, and XRF in determining lead and cadmium in soil. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 30, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becka, N.G.; Franks, R.P.; Bruland, K.W. Analysis for Cd, Cu, Ni, Zn, and Mn in estuarine water by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry coupled with an automated flow injection system. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 455, 11–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, R.; Zhu, Z.; Tatum, C.E.; Chambers, J.Q.; Xue, Z.L. Simultaneous stripping detection of Zn(II), Cd(II) and Pb(II) using a bimetallic Hg–Bi/single-walled carbon nanotubes composite electrode. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2011, 656, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mettakoonpitak, J.; Mehaffy, J.; Volckens, J.; Henry, C.S. AgNP/Bi/Nafion-modified disposable electrodes for sensitive Zn(II), Cd(II), and Pb(II) detection in aerosol samples. Electroanalysis 2016, 29, 880–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odobasic, A.; Voudouris, K.; Voutsa, D. Determination and speciation of trace heavy metals in natural water by DPASV. Water Qual. Monit. Assess. 2012, 4, 429–456. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, K.K.; Devendiran, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Narayanan, S.S. Quercetin-rGO based mercury-free electrode for the determination of toxic Cd (II) and Pb (II) ions using DPASV technique. Environ. Res. 2021, 202, 111707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, D.; Wu, W.; Li, X. Multiplexed detection of aqueous Cd2+, Pb2+ and Cu2+ ions at mercury-on-graphene film modified electrode by DPASV. Sens. Bio-Sens. Res. 2021, 34, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherigara, B.S.; Shivaraj, Y.; Mascarenhas, R.J.; Satpatic, A.K. Simultaneous determination of lead, copper and cadmium onto mercury film supported on wax impregnated carbon paste electrode: Assessment of quantification procedures by anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2007, 52, 3137–3142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Economou, A. Bismuth-film electrodes: Recent developments and potentialities for electroanalysis. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2005, 24, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, S.; Cui, G. Simultaneous determination of trace Pb(II), Cd(II), and Zn(II) using an integrated three-electrode modified with bismuth film. Microchem. J. 2021, 168, 106390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.J.; Lee, H.M.; Uhm, Y.R.; Lee, M.K.; Rhee, C.K. Square-wave voltammetric determination of thallium using surface modified thick-film graphite electrode with Bi nanopowder. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 1920–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Hu, L.Z.; Han, S.; Yuan, Y.L.; Wang, J.G.; Xu, G.B. Electrodes with extremely high hydrogen overvoltages as substrate electrodes for stripping analysis based on bismuth-coated electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 738, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokkinos, C.; Economou, A.; Raptis, I.; Efstathioua, C.E. Lithographically fabricated disposable bismuth-film electrodes for the trace determination of Pb (II) and Cd (II) by anodic stripping voltammetry. Electrochim. Acta 2008, 53, 5294–5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finšgar, M.; Petovar, B.; Vodopivec, K. Bismuth-tin-film electrodes for Zn (II), Cd (II), and Pb (II) trace analysis. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 676–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, N.M.; Van Hop, N.; Luyen, N.D.; Hai Phong, N.; Toan, T.T.T. Simultaneous determination of Zn (II), Cd (II), Pb (II), and Cu (II) using differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry at a bismuth film-modified electrode. Adv. Mater Sci. Eng. 2019, 1826148, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilge, S.; Karadurmus, L.; Sınağ, A.; Ozkan, S.A. Green synthesis and characterization of carbon-based materials for sensitive detection of heavy metal ions, TrAC-Trend Anal. Chem. 2021, 145, 116473. [Google Scholar]
- Du, Y.; Zhou, W.; Gao, J.; Pan, X.; Li, Y. Fundament and application of graphdiyne in electrochemical energy, Acc. Chem. Res. 2020, 53, 459–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Li, Y.; Wang, N.; Xue, Y.; Zuo, Z.; Liu, H.; Li, Y. Progress in research into 2D graphdiyne-based materials. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 7744–7803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Hu, T.; Li, X.; Ding, F.; Wang, B.; Wang, B.; Zhang, B.; Shi, F.; Sun, W. Graphdiyne and ionic liquid composite modified gold electrode for sensitive voltammetric analysis of rutin. Electroanalysis 2022, 34, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Huang, H.; Cui, R.; Wang, D.; Yin, Z.; Wang, D.; Zheng, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, Y.; Yuan, H.; et al. Electrochemical sensor based on graphdiyne is effectively used to determine Cd2+ and Pb2+ in water. Sens. Actuat. B-Chem. 2021, 332, 129519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Zuo, Z.; Li, L.; Li, K.; He, F.; Jiang, Z.; Li, Y. Large-Area Aminated-Graphdiyne Thin Films for Direct Methanol Fuel Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 15010–15015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Si, H.; Fan, W.; Shi, M.; Li, M.; Xu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liao, Q.; Sattar, A.; Kang, Z.; et al. Graphdiyne omnibearingly bridges the collocation between SnO2 and perovskite in planar solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 132, 2–12. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.X.; Wang, F.H.; Qi, G.C.; Cheng, J.L.; Chen, L.; Liu, H.B.; Wang, B. Rechargeable Li-CO2 batteries with graphdiyne as efficient metal-free cathode catalysts. Adv. Funct. Mater 2021, 31, 2101423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Li, Y.; Liu, H.; Guo, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, D. Architecture of graphdiyne nanoscale films. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 3256–3258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R.; White, H.S. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, X.; Duan, M.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Bai, Q.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Yang, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Sui, N. Ultrathin graphdiyne/graphene heterostructure as a robust electrochemical sensing platform. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 13598–13606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mafa, P.J.; Idris, A.O.; Mabuba, N.; Arotiba, O.A. Electrochemical co-detection of As (III), Hg (II) and Pb (II) on a bismuth modified exfoliated graphite electrode. Talanta 2016, 153, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Wang, L.; Chen, Z.; Megharaj, M.; Naidu, R. Voltammetric determination of lead (II) and cadmium (II) using a bismuth film electrode modified with mesoporous silica nanoparticles, Electrochim. Acta 2014, 132, 223–229. [Google Scholar]
- Lei, P.; Zhou, Y.; Zhao, S.; Dong, C.; Shuang, S.M. Carbon-supported X-manganate (X = Ni, Zn, and Cu) nanocomposites for sensitive electrochemical detection of trace heavy metal ions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 435, 129036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devnani, H.; Rajawat, D.S.; Satsangee, S.P. Black rice modified carbon paste electrode for the voltammetric determination of Pb(II), Cd(II), Cu(II) and Zn(II). Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. India A 2014, 84, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finšgar, M.; Kovačec, L. Copper-bismuth-film in situ electrodes for heavy metal detection, Microchem. J. 2020, 154, 104635. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Dong, S.; Gu, G.; Huang, T. Simultaneous determination of Cd2+, Pb2+, Cu2+, and Hg2+ at a carbon paste electrode modified with ionic liquidfunctionalized ordered mesoporous silica, Bull. Korean Chem. Soc. 2010, 31, 2949–2954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meenakshi, S.; Devi, S.; Pandian, K.; Chitra, K.; Tharmaraj, P. Aniline-mediated synthesis of carboxymethyl cellulose protected silver nanoparticles modified electrode for the differential pulse anodic stripping voltammetry detection of mercury at trace level. Ionics 2019, 25, 3431–3441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Li, X.; Yu, J.; Ye, J. Facile and simultaneous stripping determination of zinc, cadmium and lead on disposable multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified screen-printed electrode. Electroanalysis 2013, 25, 567–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).