Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules for Detection of Natural Free Amino Acid
Abstract
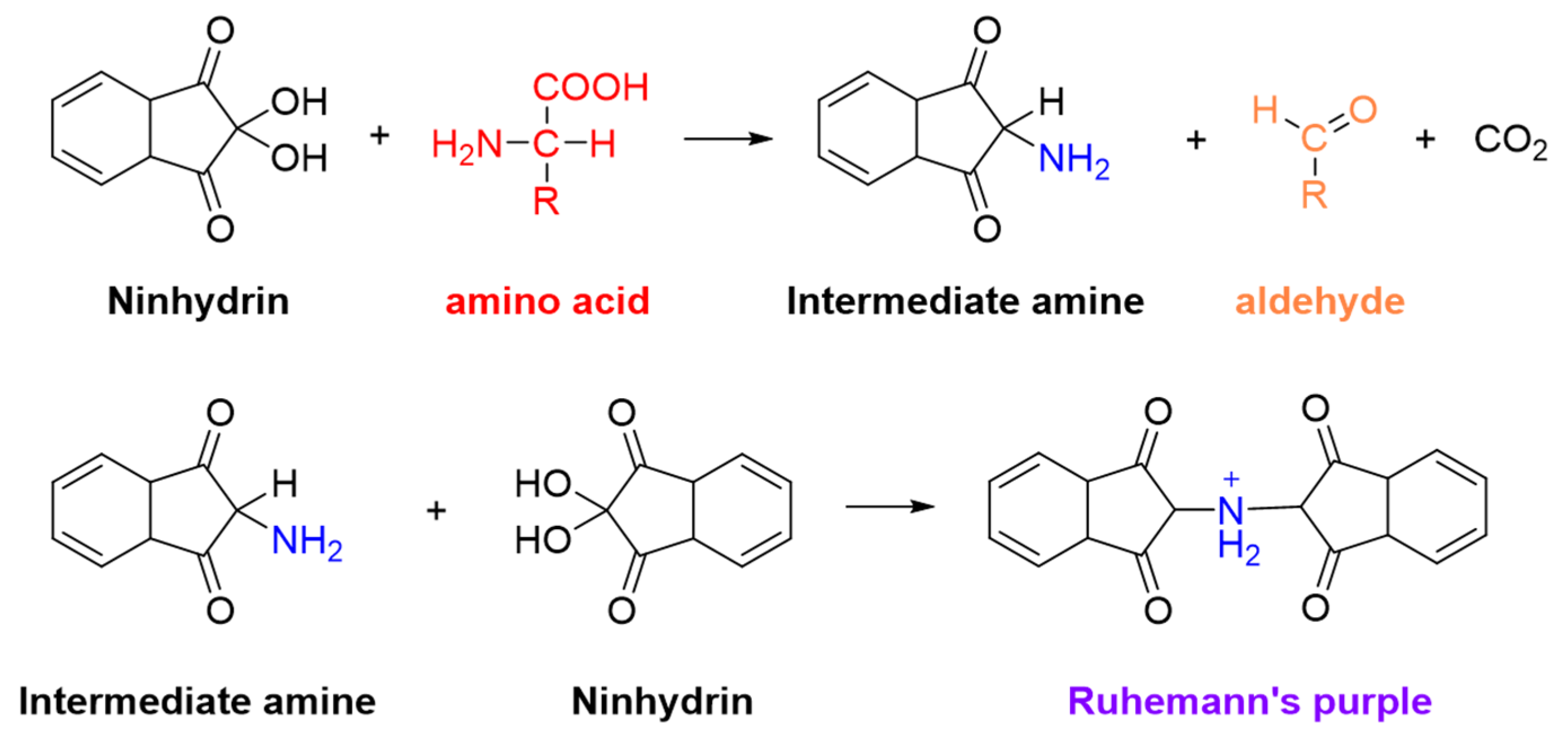
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
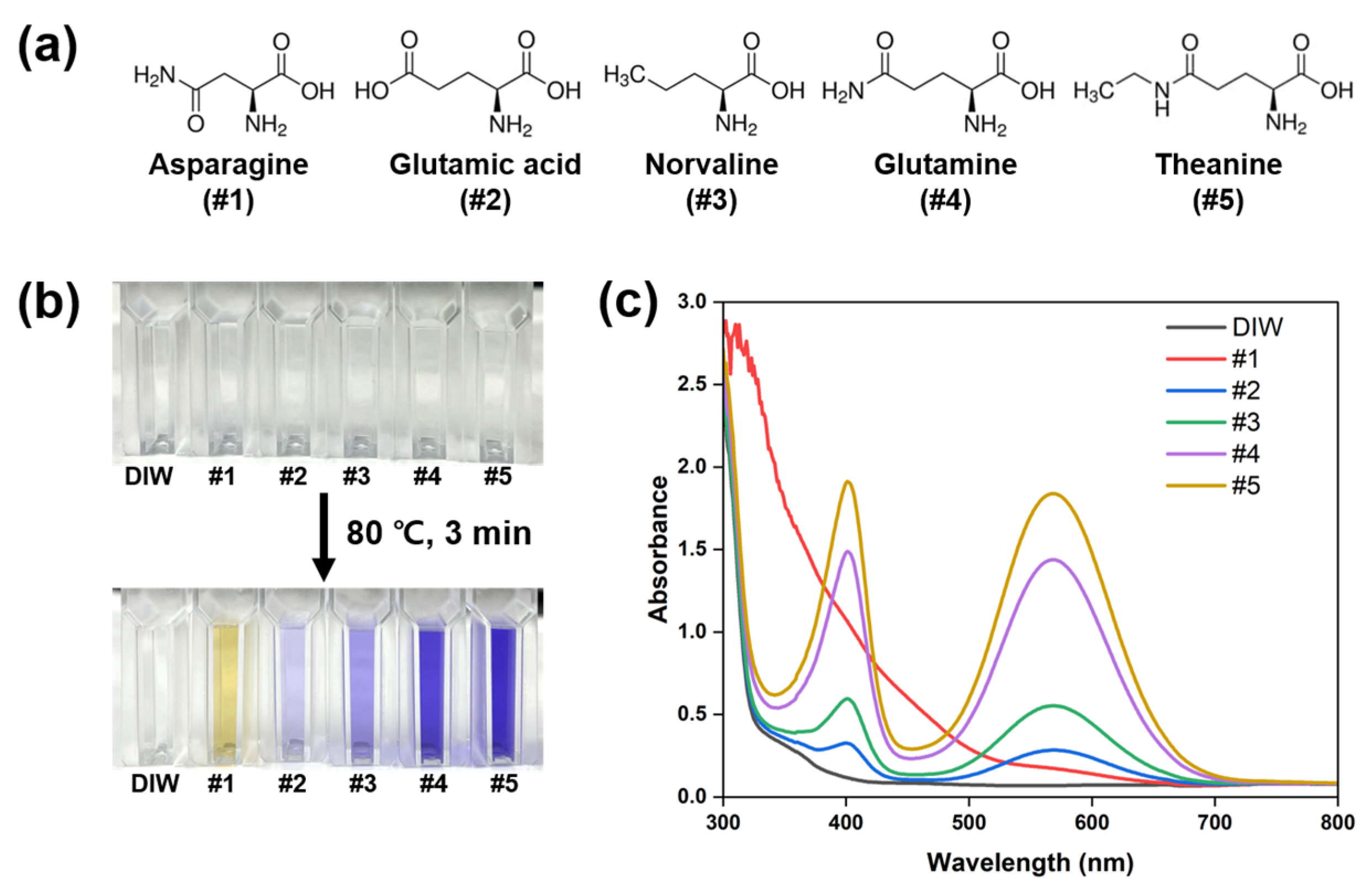
2.2. Ninhydrin Colorimetric Assay
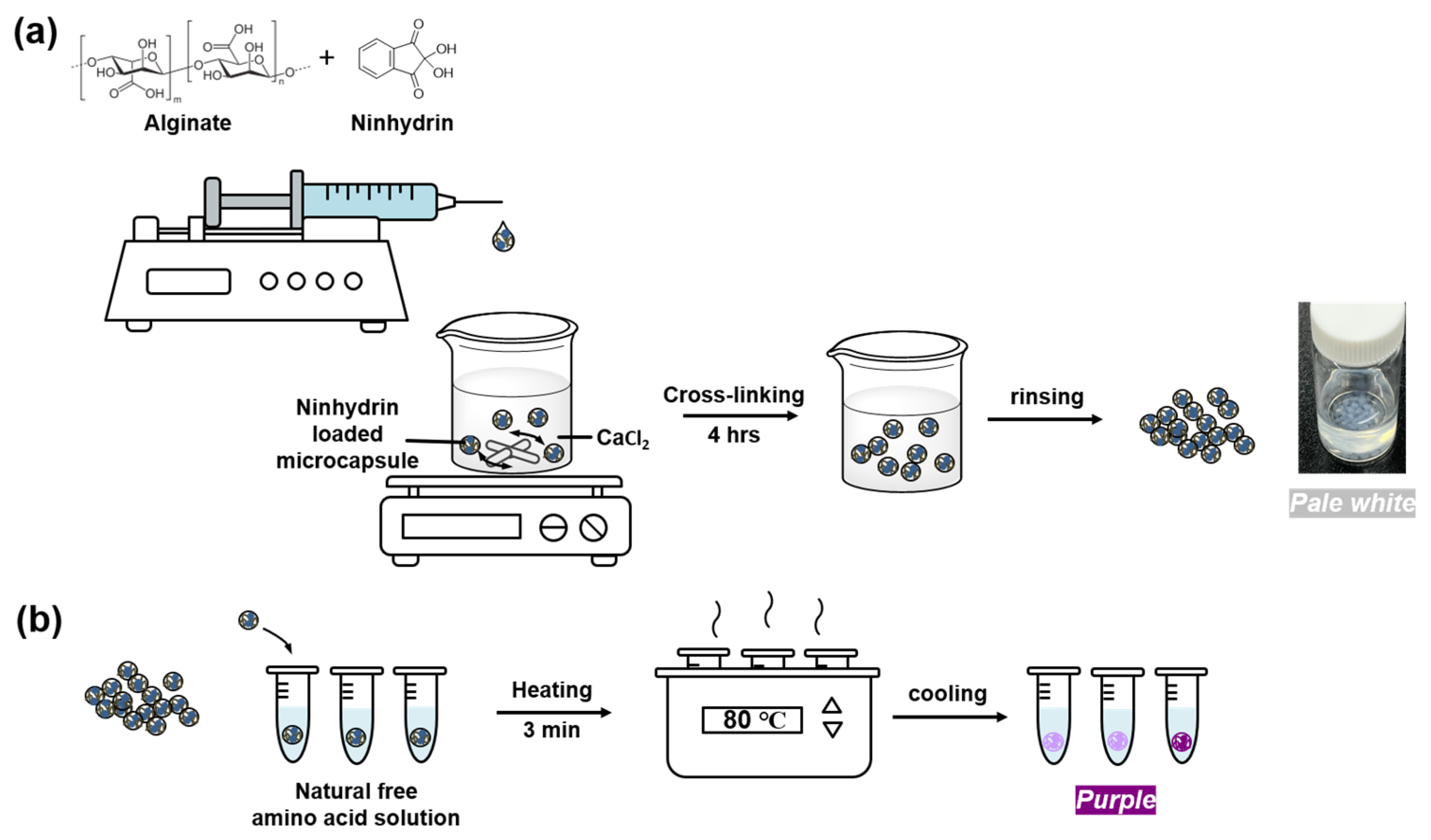
2.3. Preparation of Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules
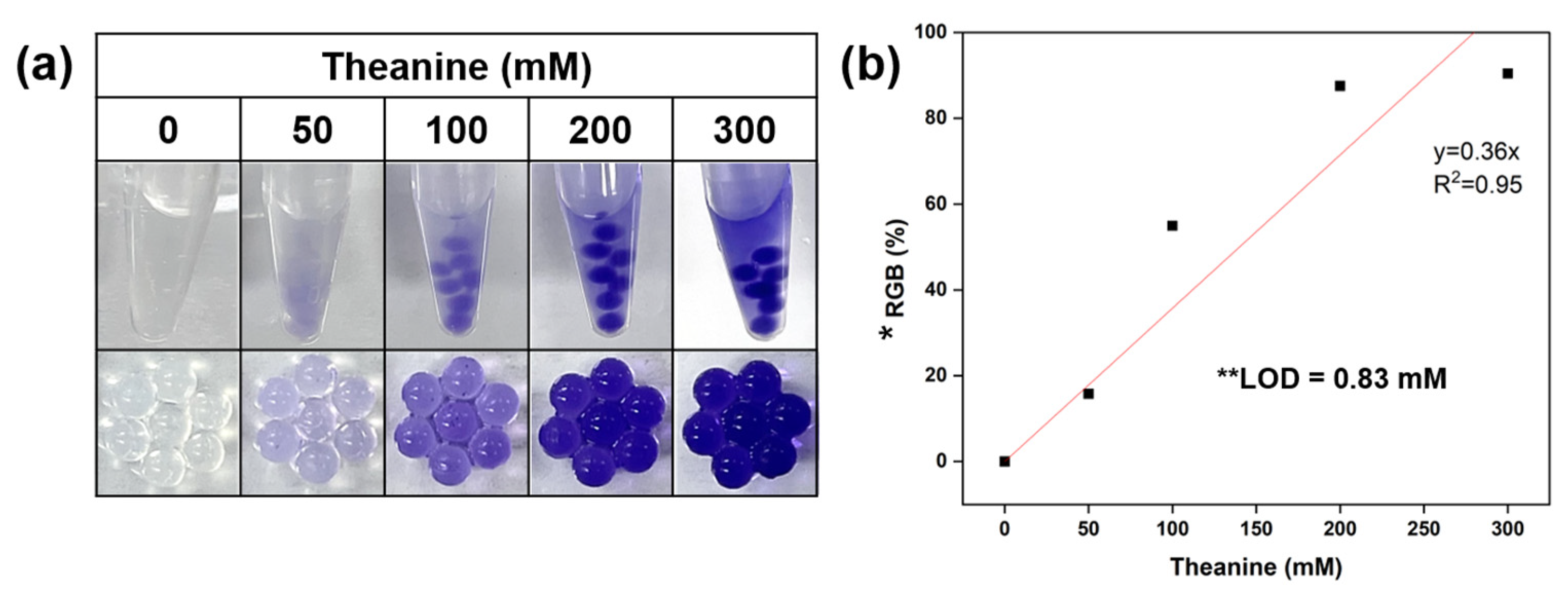
2.4. Detection Test Using Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scharbert, S.; Hofmann, T. Molecular definition of black tea taste by means of quantitative studies, taste reconstitution, and omission experiments. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 5377–5384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, C.; Özdemir, F.; Gökmen, V. Investigation of free amino acids, bioactive and neuroactive compounds in different types of tea and effect of black tea processing. Lwt 2020, 117, 108655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Chen, X.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; An, J.; Liu, X. Anti-Inflammatory Function of Plant-Derived Bioactive Peptides: A Review. Foods 2022, 11, 2361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keenan, E.K.; Finnie, M.D.A.; Jones, P.S.; Rogers, P.J.; Priestley, C.M. How much theanine in a cup of tea? Effects of tea type and method of preparation. Food Chem. 2011, 125, 588–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kimura, K.; Ozeki, M.; Juneja, L.R.; Ohira, H. l-Theanine reduces psychological and physiological stress responses. Biol. Psychol. 2007, 74, 39–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, P.J.; Smith, J.E.; Heatherley, S.V.; Pleydell-Pearce, C.W. Time for tea: Mood, blood pressure and cognitive performance effects of caffeine and theanine administered alone and together. Psychopharmacology 2008, 195, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Liu, H.Y.; Wu, D.T.; Kenaan, A.; Geng, F.; Li, H.B.; Gunaratne, A.; Li, H.; Gan, R.Y. L-Theanine: A Unique Functional Amino Acid in Tea (Camellia sinensis L.) With Multiple Health Benefits and Food Applications. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 853846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anas Sohail, A.; Ortiz, F.; Varghese, T.; Fabara, S.P.; Batth, A.S.; Sandesara, D.P.; Sabir, A.; Khurana, M.; Datta, S.; Patel, U.K. The Cognitive-Enhancing Outcomes of Caffeine and L-theanine: A Systematic Review. Cureus 2021, 13, e20828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ma, J.; Li, Q.; Fan, S.; Fan, L.; Ma, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L. Determination of 35 Free Amino Acids in Tea Using Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled With Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 767801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, W.; He, C.; Ma, Y.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.H.; Peng, Y.; Xiao, P. Investigation of free amino acid, total phenolics, antioxidant activity and purine alkaloids to assess the health properties of non-Camellia tea. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2016, 6, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazan, R.M.; Seddik, H.A.; Marstani, Z.M.; Elsutohy, M.M.; Yasri, N.G. Determination of amino acids content in tea species using liquid chromatography via pre-column fluorescence derivatization. Microchem. J. 2019, 150, 104103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, P.; Zhao, F.; Chen, M.; Ye, N.; Lin, Q.; Ouyang, L.; Cai, X.; Meng, P.; Gong, X.; Wang, Y. Determination of 21 free amino acids in 5 types of tea by ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry (UHPLC–MS/MS) using a modified 6-aminoquinolyl-N-hydroxysuccinimidyl carbamate (AQC) method. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2019, 81, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- How, Z.T.; Busetti, F.; Linge, K.L.; Kristiana, I.; Joll, C.A.; Charrois, J.W.A. Analysis of free amino acids in natural waters by liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1370, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, K.H.; Lee, J.H. Quantitative analysis of metabolites in Korean green tea using NMR. J. Korean Magn. Reson. Soc. 2018, 22, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M. Applications of the Ninhydrin Reaction for Analysis of Amino Acids, Peptides, and Proteins to Agricultural and Biomedical Sciences. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 385–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S. Recent applications of ninhydrin in multicomponent reactions. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 18875–18906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pilicer, S.L.; Wolf, C. Ninhydrin Revisited: Quantitative Chirality Recognition of Amines and Amino Alcohols Based on Nondestructive Dynamic Covalent Chemistry. J. Org. Chem. 2020, 85, 11560–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad Raus, R.; Wan Nawawi, W.M.F.; Nasaruddin, R.R. Alginate and alginate composites for biomedical applications. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 16, 280–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, S.; Son, S.U.; Kim, J.; Kim, H.; Lim, J.; Seo, S.B.; Kang, B.; Kang, T.; Jung, J.; Seo, S.; et al. Polydiacetylene-based hydrogel beads as colorimetric sensors for the detection of biogenic amines in spoiled meat. Food Chem. 2023, 403, 134317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raji, M.A.; Chinnappan, R.; Shibl, A.; Suaifan, G.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J.; El Shorbagy, E.; Al-Kattan, K.; Zourob, M. Low-cost colorimetric diagnostic screening assay for methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Talanta 2021, 225, 121946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottom, C.B.; Hanna, S.S.; Siehr, D.J. Mechanism of the ninhydrin reaction. Biochem. Educ. 1978, 6, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.J.; Kraft, J.J.; Schuster, S.M. Schuster A specific quantitative colorimetric assay for L-asparagine. Anal. Biochem. 1993, 211, 242–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, M.; David Williams, L. Stoichiometry of formation of Ruhemann’s purple in the ninhydrin reaction. Bioorganic Chem. 1974, 3, 267–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jeong, S.; Jeon, Y.; Mun, J.; Jeong, S.M.; Liang, H.; Chung, K.; Yi, P.-I.; An, B.-S.; Seo, S. Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules for Detection of Natural Free Amino Acid. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010049
Jeong S, Jeon Y, Mun J, Jeong SM, Liang H, Chung K, Yi P-I, An B-S, Seo S. Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules for Detection of Natural Free Amino Acid. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(1):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010049
Chicago/Turabian StyleJeong, Suhui, Yeji Jeon, Jaehun Mun, Se Min Jeong, Huiling Liang, Kyeongwoon Chung, Pyong-In Yi, Beum-Soo An, and Sungbaek Seo. 2023. "Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules for Detection of Natural Free Amino Acid" Chemosensors 11, no. 1: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010049
APA StyleJeong, S., Jeon, Y., Mun, J., Jeong, S. M., Liang, H., Chung, K., Yi, P.-I., An, B.-S., & Seo, S. (2023). Ninhydrin Loaded Microcapsules for Detection of Natural Free Amino Acid. Chemosensors, 11(1), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010049





